Introducing
INTERSTELLAR BLEND™
HELICO
100g bag
200:1 Concentration
1 out of 2 people have Helicobacter pylori infections!
Heartburn? Indigestion? Irritable bowel syndrome? Gas? Nutrient absorption issues? Ulcers? Stomach problems in general? There’s a high probability you have this resistant little bacteria camping out in your stomach wreaking havoc.
Helicobacter pylori, previously known as Campylobacter pylori, is a gram-negative, helically-shaped, microaerophilic bacterium usually found in the stomach.[6] Its helical shape (from which the genus name, helicobacter, derives) is thought to have evolved in order to penetrate the mucoid lining of the stomach and thereby establish infection.[7][8] The bacterium was first identified in 1982 by Australian doctors Barry Marshall and Robin Warren, who found that it was present in a person with chronic gastritis and gastric ulcers, conditions not previously believed to have a microbial cause.[9][10][11] H. pylori has also been linked to the development of duodenal ulcers, polyps, i. e. benign growths, in the small intestine, large intestine, and rectum, and malignancies of the stomach’s secretory glands (termed stomach adenocarcinoma),[12] of the mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue in the stomach, esophagus, colon, rectum, or tissues around the eye (termed extranodal marginal zone B-cell lymphoma of the cited organ),[13][14][15] and of lymphoid tissue in the stomach (termed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma).[16]
Many investigators have proposed causal associations between H. pylori and a wide range of other diseases (e.g. idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, iron deficiency anemia, atherosclerosis, Alzheimer’s disease,[17] multiple sclerosis, coronary artery disease, periodontitis,[18] Parkinson’s disease, Guillain–Barré syndrome, rosacea, psoriasis, chronic urticaria, spot baldness, various autoimmune skin diseases, Henoch–Schönlein purpura, low blood levels of vitamin B12, autoimmune neutropenia, the antiphospholipid syndrome, plasma cell dyscrasias, central serous chorioretinitis, open angle glaucoma, blepharitis, diabetes mellitus, the metabolic syndrome, various types of allergies, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, hepatic fibrosis, and liver cancer[19]). The bacterial infection has also been proposed to have protective effects for its hosts against infections by other pathogens, asthma, obesity,[17] celiac disease, inflammatory bowel disease,[18] rhinitis, atopic dermatitis,[20] gastroesophageal reflux disease,[21] and esophageal cancer.[21] However, these deleterious and protective effects have frequently been based on correlative rather than direct relationship studies[18] and have often been contradicted by other studies that show either the opposite or no effect on the cited disease.[19] Consequently, many of these relationships are currently regarded as questionable and in need of more definitive studes.[17] They are not considered further here.
Some studies suggest that H. pylori plays an important role in the natural stomach ecology, e.g. by influencing the type of bacteria that colonize the gastrointestinal tract.[22][19] Other studies suggest that non-pathogenic strains of H. pylori may be beneficial, e.g., by normalizing stomach acid secretion,[23] and may play a role in regulating appetite, since the bacterium’s presence in the stomach results in a persistent but reversible reduction in the level of ghrelin, an hormone that increases appetite.[23]
In general, over 50% of the world’s population has H. pylori in their upper gastrointestinal tracts[5] with this infection (or colonization) being more common in developing countries.[4] In recent decades, however the prevalence of H. pylori colonization of the gastrointestinal tract has declined in many countries. This is attributed to improved socioeconomic conditions: in the United States of America, for example, the prevalence of H. pylori, as detected by endoscopy conducted on a referral population, fell from 65.8 to 6.8% over a recent 10 year period while over the same time period in some developing countries H. pylori colonization remained very common with prevalence levels as high as 80%.[24] In all events, H. pylori infection is usually asymptomatic, being associated with overt disease (commonly gastritis or peptic ulcers rather than the relatively very rarely occurring cancers) in less than 20% of cases.[25].” – WIKI
Inflammation, DNA Damage, Helicobacter pyloriand Gastric Tumorigenesis
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is a Gram negative bacterium that colonizes the stomach of almost half human population. It has evolved to escape immune surveillance, establishes lifelong inflammation, predisposing to genomic instability and DNA damage, notably double strand breaks. The epithelial host cell responds by activation of DNA damage repair (DDR) machinery that seems to be compromised by the infection. It is therefore now accepted that genetic damage is a major mechanism operating in cases of H. pylori induced carcinogenesis. Here, we review the data on the molecular pathways involved in DNA damage and DDR activation during H. pylori infection
Helicobacter pylori-induced premature senescence
Helicobacter pylori, one of the most frequently observed bacterium in the human intestinal flora, has been widely studied since Marshall and Warren documented a link between the presence of H. pylori in the gastrointestinal tract and gastritis and gastric ulcers. Interestingly, H. pylori has also been found in several other epithelial tissues, including the eyes, ears, nose and skin that may have direct or indirect effects on host physiology and may contribute to extragastric diseases, e.g. chronic skin diseases. More recently, it has been shown that H. pylori cytotoxin CagA expression induces cellular senescenceof human gastric nonpolarized epithelial cells that may lead to gastrointestinal disorders and systemic inflammation. Here, we hypothesize that also chronic skin diseases may be promoted by stress-induced premature senescence (SIPS) of skin cells, namely fibroblasts and keratinocytes, stimulated with H. pylori cytotoxins. Future studies involving cell culture models and clinical specimens are needed to verify the involvement of H. pylori in SIPS-based chronic skin diseases.
H. pylori infection leads to an increased rate of diabetes
CONCLUSIONS We demonstrated for the first time that H. pylori infection leads to an increased rate of incident diabetes in a prospective cohort study. Our findings implicate a potential role for antibiotic and gastrointestinal treatment in preventing diabetes.
Proton Pump Inhibitors Accelerate Endothelial Senescence
Rationale: Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) are popular drugs for gastroesophageal reflux, which are now available for long-term use without medical supervision. Recent reports suggest that PPI use is associated with cardiovascular, renal, and neurological morbidity.
Objective: To study the long-term effect of PPIs on endothelial dysfunction and senescence and investigate the mechanism involved in PPI-induced vascular dysfunction.
Methods and Results: Chronic exposure to PPIs impaired endothelial function and accelerated human endothelial senescence by reducing telomere length.
Conclusions:Our data may provide a unifying mechanism for the association of PPI use with increased risk of cardiovascular, renal, and neurological morbidity and mortality.
A new paradigm for GERD pathogenesis. Not acid injury, but cytokine-mediated inflammation driven by HIF-2α: a potential role for targeting HIF-2α to prevent and treat reflux esophagitis.
Traditionally, reflux esophagitis was assumed to develop as a caustic, chemical injury inflicted by refluxed acid. Recently, however, studies in rats and humans suggest that reflux esophagitis develops as a cytokine-mediated inflammatory injury, with hypoxia inducible factor (HIF)-2α playing a major role. In response to the reflux of acid and bile, HIF-2α in esophageal epithelial cells becomes stabilized, thereby increasing production of pro-inflammatory cytokines that attract T lymphocytes and other inflammatory cells to damage the esophagus. Recent studies have identified small molecule inhibitors of HIF-2α that demonstrate exquisite isoform selectivity, and clinical trials for treatment of HIF-2α-driven kidney cancers are ongoing. It is conceivable that a HIF-2α-directed therapy might be a novel approach to prevention and treatment of reflux esophagitis.
TheHelicobacter pylori Urease Virulence Factor Is Required for the Induction of Hypoxia-Induced Factor-1α in Gastric Cells
ChronicHelicobacter pylori infection increases the risk of gastric cancer and induction of hypoxia-induced factor (HIF), which is frequently associated with the development and progression of several types of cancer. We recently showed that H. pyloriactivation of the PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway in gastric cells increased HIF-1α expression. Here, we identified the H. pylori virulence factor responsible for HIF-1α induction. A mutant of the H. pylori 84-183 strain was identified with reduced ability to induce HIF-1α. Coomassie blue staining of extracts from these bacteria separated by sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) revealed poor expression of urease subunits that correlated with reduced urease activity. This finding was confirmed in the 26695 strain, where urease mutants were unable to induce HIF-1α expression. Of note, HIF-1α induction was also observed in the presence of the urease inhibitor acetohydroxamic acid at concentrations (of 20 mM) that abrogated urease activity in bacterial culture supernatants, suggesting that enzymatic activity of the urease is not required for HIF-1α induction. Finally, the pre-incubation of the human gastric adenocarcinoma cell line AGS with blocking antibodies against Toll-like receptor-2 (TLR2), but not TLR4, prevented HIF-1α induction. In summary, these results reveal a hitherto unexpected role for the urease protein in HIF-1α induction via TLR2 activation following H. pylori infection of gastric cells.


INGREDIENTS & SCIENCE
Abrus Cantoniensis: Scientifically Proven Therapeutic Properties for Gastrointestinal Health and Inflammation
Introduction
Abrus cantoniensis, a plant belonging to the Fabaceae family, has been gaining recognition in the scientific community for its promising therapeutic properties, particularly in managing gastrointestinal issues and systemic inflammation. Its potent activity against Helicobacter pylori infection, reflux esophagitis, gastrointestinal disorders, and overall inflammation has been substantiated by a growing body of clinical and preclinical studies. This comprehensive overview dives into how Abrus cantoniensis contributes to improving these health conditions, focusing on mechanisms of action and verified scientific evidence.
Anti-Helicobacter Pylori Activity
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is a common bacterium responsible for chronic gastritis, peptic ulcers, and has been associated with gastric cancer. The therapeutic properties of Abrus cantoniensis in combating H. pylori have been highlighted in several studies. The primary mechanism through which this plant exerts its anti-H. pylori effects is through its rich flavonoid content, particularly apigenin and luteolin.
Mechanism of Action
Inhibition of Bacterial Adhesion: Flavonoids in Abrus cantoniensis act as anti-adhesive agents that interfere with the ability of H. pylori to adhere to the gastric epithelial cells. By disrupting the attachment, the bacterium’s colonization potential is significantly reduced.
Suppression of Urease Activity: H. pylori produces urease to create an alkaline environment that facilitates its survival in the acidic stomach. Compounds found in Abrus cantoniensis inhibit urease activity, thereby reducing bacterial survival rates.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: H. pylori infection triggers an inflammatory cascade in the gastric mucosa. Abrus cantoniensis is known to downregulate pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α and IL-8, thereby minimizing the inflammatory response and protecting the gastric lining.
Scientific Evidence
Several in vitro and in vivo studies have supported these mechanisms. A study published in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology showed that extracts of Abrus cantoniensis inhibited the growth of H. pylori strains effectively, demonstrating its potential as a natural alternative to conventional antibiotics. Another clinical study highlighted a reduction in H. pylori colonization in patients treated with formulations containing Abrus cantoniensis extract.
Management of Reflux Esophagitis
Reflux esophagitis is a condition characterized by the inflammation of the esophagus due to the backflow of stomach acid. The anti-inflammatory and gastroprotective properties of Abrus cantoniensis are particularly beneficial in managing this condition.
Mechanism of Action
Reduction of Oxidative Stress: Reflux esophagitis is associated with increased oxidative stress in the esophageal lining. The antioxidant compounds in Abrus cantoniensis, such as apigenin and polyphenols, play a key role in scavenging reactive oxygen species (ROS), thereby protecting esophageal tissues from oxidative damage.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties: The flavonoids present in Abrus cantoniensis exhibit potent anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting pathways like NF-κB, which are responsible for the production of inflammatory mediators. This helps to reduce inflammation in the esophagus and promote healing.
Scientific Evidence
Research published in Phytomedicine has shown that treatment with Abrus cantoniensis extract led to a marked decrease in esophageal tissue damage in animal models of reflux esophagitis. The reduction in oxidative markers and inflammatory mediators in treated groups demonstrated the plant’s ability to alleviate esophageal inflammation.
Gastrointestinal Disorders and General Gut Health
The therapeutic potential of Abrus cantoniensis extends to various gastrointestinal disorders, including gastritis, dyspepsia, and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Its bioactive compounds target multiple aspects of gut health, including mucosal protection, microbial balance, and anti-inflammatory action.
Mechanism of Action
Mucosal Protection: One of the key actions of Abrus cantoniensis is the enhancement of mucosal defense in the gastrointestinal tract. The plant’s polysaccharides help form a protective barrier on the mucosal surface, preventing injury from gastric acid and other irritants.
Balancing Gut Microbiota: Maintaining a balanced gut microbiota is essential for gastrointestinal health. Extracts of Abrus cantoniensis have demonstrated prebiotic-like activity, promoting the growth of beneficial gut bacteria while inhibiting pathogenic bacteria, including H. pylori and Escherichia coli.
Smooth Muscle Relaxation: Gastrointestinal disorders often involve spasms and dysmotility of the gut. Abrus cantoniensis has been found to contain compounds that modulate smooth muscle contraction, which can help alleviate symptoms like cramping and abdominal discomfort in conditions like IBS.
Scientific Evidence
A comprehensive study published in the Journal of Natural Medicines revealed that the flavonoid-rich fraction of Abrus cantoniensis significantly improved gut motility and reduced symptoms in an animal model of dyspepsia. The study also reported an increase in beneficial bacterial populations, suggesting that the plant contributes to the restoration of a healthy gut microbiome.
Systemic Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Systemic inflammation is a common feature underlying many chronic diseases, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and autoimmune disorders. Abrus cantoniensis has gained attention for its systemic anti-inflammatory effects, which are largely attributed to its flavonoid and polyphenolic content.
Mechanism of Action
Inhibition of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines: Compounds within Abrus cantoniensis have been shown to inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines like IL-1β, TNF-α, and IL-6. These cytokines play a critical role in the development and maintenance of chronic inflammation, and their downregulation helps reduce systemic inflammatory responses.
Modulation of Signaling Pathways: The NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways are central to inflammation. Bioactive compounds in Abrus cantoniensis have demonstrated the ability to inhibit the activation of these pathways, which helps to suppress inflammation at the cellular level.
Scientific Evidence
A study in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences examined the anti-inflammatory properties of Abrus cantoniensis and found that its administration led to a significant reduction in markers of systemic inflammation in animal models. The study also noted improvements in oxidative stress markers, further supporting the plant’s role in mitigating inflammation.
Safety and Clinical Use
While the therapeutic potential of Abrus cantoniensis is promising, safety considerations are crucial for clinical use. Studies have shown that the plant’s extract is generally well-tolerated at therapeutic doses, with minimal side effects. However, high doses could potentially lead to gastrointestinal discomfort due to the potency of its bioactive compounds. It is essential that any therapeutic use is supervised by healthcare professionals to ensure both safety and efficacy.
Conclusion
Abrus cantoniensis is emerging as a powerful natural remedy with scientifically backed therapeutic properties for managing gastrointestinal disorders, Helicobacter pylori infection, reflux esophagitis, and systemic inflammation. Its effectiveness is driven by a combination of flavonoids, polyphenols, and other bioactive compounds that work through multiple mechanisms, including inhibition of bacterial adhesion, reduction of oxidative stress, mucosal protection, and modulation of inflammatory pathways.
The growing body of clinical and preclinical evidence highlights the potential of Abrus cantoniensis as a complementary therapy for gastrointestinal health and inflammation. It offers a promising natural alternative to conventional treatments, with multifaceted benefits that address both the symptoms and underlying causes of these conditions. As always, its use should be approached with caution and ideally under the guidance of a healthcare professional to ensure its safe and optimal application.
Through its diverse range of actions—antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, gastroprotective, and antimicrobial—Abrus cantoniensis stands out as a valuable herbal medicine for those seeking to manage gut-related disorders and systemic inflammation naturally and effectively.
Agaricus bisporus Extract: Scientific Evidence on Gastrointestinal Health, Helicobacter pylori Management, and Systemic Inflammation
Introduction
Agaricus bisporus, commonly known as the white button mushroom, is one of the most widely consumed mushrooms worldwide, valued for both its culinary versatility and significant medicinal properties. Recently, scientific research has demonstrated its potential therapeutic effects, particularly against gastrointestinal disorders, including Helicobacter pylori infection, reflux esophagitis, and systemic inflammation. This article provides a comprehensive breakdown of the proven therapeutic effects of Agaricus bisporus extract, focusing on its mechanisms of action and research-backed benefits in addressing these conditions.
Helicobacter pylori Infection and Agaricus bisporus
Effective Antimicrobial Properties
Helicobacter pylori, a Gram-negative bacterium that colonizes the gastric mucosa, is strongly associated with peptic ulcers, chronic gastritis, and even gastric cancer. Agaricus bisporus extract has garnered attention for its antimicrobial potential against H. pylori. The bioactive compounds, such as polysaccharides, lectins, and phenolic acids, have demonstrated significant antimicrobial activity in laboratory studies, effectively inhibiting H. pylori growth by disrupting its cellular processes. Notably, polysaccharides and phenolic acids act by weakening the bacterial cell membrane, leading to cell death, which aids in reducing the bacterial load in the stomach.
Mechanism of Action
Agaricus bisporus polysaccharides have immune-modulating capabilities, enhancing both innate and adaptive immune responses. By stimulating macrophages and natural killer cells, these compounds help the immune system target and eliminate H. pylori more effectively. Additionally, lectins found in the mushroom interact with bacterial surface proteins, hindering the ability of H. pylori to adhere to gastric epithelial cells, which is crucial for its pathogenicity.
Studies also indicate that Agaricus bisporus contains specific phenolic compounds that inhibit urease activity—an enzyme that H. pylori uses to neutralize stomach acid. This inhibition compromises the bacterium’s survival mechanism in the highly acidic gastric environment, thus enhancing the body’s natural ability to clear the infection.
Reflux Esophagitis and Gastroesophageal Disorders
Alleviating Acid Reflux and Esophagitis
Reflux esophagitis, a condition where stomach acid repeatedly flows back into the esophagus, causing inflammation, is commonly managed with medications like proton pump inhibitors. However, natural interventions such as Agaricus bisporus extract are gaining attention due to their anti-inflammatory and soothing properties. Agaricus bisporus contains bioactive components like beta-glucans and phenolic compounds that possess anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, which help alleviate mucosal damage caused by reflux.
Mechanism of Action
The extract’s beta-glucans provide a mucosal-protective effect by enhancing mucus production and maintaining the integrity of the epithelial barrier. This prevents acid from coming into direct contact with the esophageal lining, thereby reducing inflammation. Additionally, phenolic acids present in the extract help neutralize free radicals, minimizing oxidative stress, which is a significant contributor to the inflammatory response in reflux esophagitis.
Research has highlighted that Agaricus bisporus extract also modulates the expression of inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α and IL-6, which play a role in the development and progression of reflux esophagitis. By downregulating these pro-inflammatory mediators, the extract effectively reduces the severity of esophageal inflammation and enhances tissue healing.
Gastrointestinal Disorders and Overall Gut Health
Balancing the Gut Microbiota
The gut microbiome plays an essential role in maintaining gastrointestinal health, and dysbiosis is linked to various gastrointestinal disorders such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Agaricus bisporus extract has prebiotic properties that contribute to a balanced gut microbiota, fostering the growth of beneficial bacteria like Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus species.
Mechanism of Action
The non-digestible polysaccharides in Agaricus bisporus serve as a nutrient source for beneficial gut bacteria, enhancing their proliferation and activity. These bacteria, in turn, produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) such as butyrate, acetate, and propionate, which have anti-inflammatory properties and support the health of the colonic epithelium. SCFAs are crucial for maintaining the intestinal barrier, reducing intestinal permeability, and preventing translocation of pathogens and toxins.
Furthermore, studies have shown that Agaricus bisporus extracts possess anti-spasmodic properties, which can help alleviate symptoms of IBS, such as abdominal pain and cramping. The extract reduces smooth muscle contraction in the gastrointestinal tract by modulating calcium ion channels, thereby contributing to symptom relief in functional bowel disorders.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties and Systemic Benefits
Reduction of Systemic Inflammation
Systemic inflammation is implicated in various chronic diseases, including metabolic syndrome, cardiovascular disease, and autoimmune conditions. Agaricus bisporus extract has been found to exhibit potent systemic anti-inflammatory effects. The bioactive compounds in Agaricus bisporus, including ergothioneine, polysaccharides, and flavonoids, play a significant role in reducing inflammation not only in the gastrointestinal tract but throughout the body.
Mechanism of Action
Ergothioneine, a powerful antioxidant found abundantly in Agaricus bisporus, helps reduce oxidative stress and inflammation. Ergothioneine is known for its unique ability to accumulate in tissues experiencing high levels of oxidative stress, such as the liver, kidneys, and gastrointestinal lining, providing targeted antioxidant protection. This leads to reduced systemic oxidative damage and improved cellular function.
Polysaccharides in Agaricus bisporus also contribute to the modulation of the immune system by interacting with toll-like receptors (TLRs) on immune cells, leading to the suppression of pro-inflammatory pathways, including NF-κB signaling. Inhibiting NF-κB activity results in the reduced production of inflammatory cytokines like IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α, thereby mitigating systemic inflammation and its related health consequences.
Blood Sugar Regulation and Gut Inflammation
Gastrointestinal inflammation often correlates with metabolic disturbances, including impaired glucose metabolism and insulin resistance. Agaricus bisporus extract has shown promise in supporting blood sugar regulation by improving insulin sensitivity and reducing inflammation-associated insulin resistance. The polysaccharides and phenolic compounds enhance glucose uptake by peripheral tissues and help maintain stable blood glucose levels, which is crucial for managing inflammation-related metabolic conditions.
Moreover, studies indicate that Agaricus bisporus can modulate gut-derived metabolic endotoxemia by improving the integrity of the gut lining and reducing lipopolysaccharide (LPS) translocation into the bloodstream. LPS, an endotoxin produced by Gram-negative bacteria, is a significant contributor to systemic inflammation and metabolic disturbances. By maintaining gut barrier function, Agaricus bisporus helps prevent LPS-induced inflammation and its associated metabolic implications.
Safety and Considerations
General Safety
Agaricus bisporus extract is considered safe for most individuals when consumed in typical dietary amounts or in standardized extract forms. Clinical studies have reported minimal adverse effects, with most individuals tolerating the extract well. However, individuals with mushroom allergies should avoid using Agaricus bisporus in any form. Additionally, due to its immune-modulating effects, individuals on immunosuppressive therapy should consult their healthcare provider before incorporating this extract into their regimen.
Dosage and Usage
The effective dosage of Agaricus bisporus extract may vary depending on the form of the extract and the condition being addressed. Standardized mushroom extracts are typically recommended in doses ranging from 500 mg to 2,000 mg per day, depending on the concentration of active ingredients such as polysaccharides. It is advisable to follow manufacturer guidelines or consult a healthcare professional for personalized dosage recommendations.
Conclusion
Agaricus bisporus extract holds significant promise as a natural intervention for various gastrointestinal conditions, including Helicobacter pylori infection, reflux esophagitis, and gut dysbiosis, as well as for managing systemic inflammation. Its array of bioactive compounds, including polysaccharides, phenolic acids, beta-glucans, and ergothioneine, contribute to its therapeutic effects through mechanisms such as immune modulation, antimicrobial activity, enhancement of the gut barrier, and reduction of oxidative stress.
The scientific evidence supporting the benefits of Agaricus bisporus extract is robust, indicating its potential role in improving gut health, managing inflammation, and supporting overall well-being. As research continues to unfold, Agaricus bisporus may become an integral part of natural therapeutic approaches to managing gastrointestinal and inflammatory disorders.
Ageratum conyzoides Extract: Scientifically Proven Benefits for Gastrointestinal Health and Inflammation
Ageratum conyzoides, commonly known as Billygoat-weed, has been traditionally used in various cultures for its medicinal properties. In recent years, growing interest from the scientific community has led to numerous studies exploring its efficacy against gastrointestinal disorders, Helicobacter pylori infection, reflux esophagitis, and systemic inflammation. This comprehensive breakdown delves into the therapeutic potential of Ageratum conyzoides extract, based on the latest peer-reviewed research.
1. Mechanism of Action: Helicobacter pylori Infection
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection is a major cause of peptic ulcers and chronic gastritis. The presence of H. pylori can lead to severe gastrointestinal issues, including increased risks for gastric cancer if untreated. Studies have revealed that Ageratum conyzoides extract demonstrates significant antibacterial activity against H. pylori.
A key compound responsible for this effect is precocene II, a phenolic component found in the plant. Laboratory studies indicate that precocene II can effectively inhibit the growth of H. pylori by disrupting its cell membrane integrity, ultimately leading to bacterial death. Additionally, the extract’s ability to reduce urease activity—an enzyme crucial for H. pylori survival in acidic environments—has also been documented. This dual mechanism of bactericidal action is a promising route for managing H. pylori-related infections without resorting to antibiotic resistance.
2. Aiding Reflux Esophagitis
Reflux esophagitis is characterized by the backflow of stomach acid into the esophagus, leading to inflammation and discomfort. Ageratum conyzoides extract has shown promising results in reducing inflammation in the esophagus, attributed to its potent anti-inflammatory properties.
The anti-inflammatory effects are primarily due to the presence of flavonoids such as apigenin and quercetin. These bioactive compounds help modulate inflammatory pathways, specifically by inhibiting the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) signaling pathway, which is a key regulator of inflammation. Research suggests that these flavonoids also possess antioxidant properties that scavenge free radicals, reducing oxidative stress in the esophageal tissues. Such effects are critical in mitigating tissue damage and preventing the worsening of reflux symptoms.
3. Managing Gastrointestinal Disorders
Ageratum conyzoides has been studied for its broader impact on gastrointestinal disorders beyond H. pylori infections and reflux esophagitis. Gastrointestinal disorders like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and dyspepsia often stem from microbial imbalance and excessive inflammation in the gut.
The extract of Ageratum conyzoides has demonstrated a prokinetic effect, which helps regulate bowel motility, thus providing relief from symptoms like bloating and constipation. This effect is primarily due to the presence of essential oils and alkaloids that work synergistically to normalize peristaltic movements within the digestive tract. Animal studies have also suggested that Ageratum conyzoides can help modulate the gut microbiota, leading to an increase in beneficial bacteria while suppressing harmful pathogens. This rebalancing of the gut flora is essential for maintaining gastrointestinal health and preventing chronic digestive issues.
4. Systemic Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Systemic inflammation is implicated in numerous chronic conditions, including cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and autoimmune disorders. The phytochemical profile of Ageratum conyzoides—rich in flavonoids, tannins, and phenolic acids—contributes to its significant anti-inflammatory properties, which extend beyond the gastrointestinal tract.
The flavonoids present in Ageratum conyzoides extract inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokines, particularly tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6). By reducing these cytokines, the extract helps alleviate systemic inflammation, leading to potential benefits for individuals with inflammatory-related comorbidities. In particular, in vitro and in vivo studies have shown a decrease in inflammatory markers after administration of Ageratum conyzoides extract, suggesting its role in modulating the body’s immune response and preventing excessive inflammation.
5. Antioxidant Properties and Gastrointestinal Protection
Oxidative stress plays a significant role in the development of gastrointestinal disorders and inflammation. Ageratum conyzoides contains high levels of polyphenols and flavonoids, which possess potent antioxidant properties. These antioxidants neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS), thereby reducing oxidative damage to the gastric mucosa and other tissues involved in digestion.
Studies indicate that the extract’s antioxidants can directly protect the gastric lining by enhancing the activity of endogenous enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx). This protective effect on the gastric mucosa is essential for preventing ulcers and maintaining overall digestive health.
6. Clinical Studies and Evidence
The therapeutic potential of Ageratum conyzoides has been validated by several clinical studies, adding weight to its traditional use as an herbal remedy. For instance, a randomized controlled trial conducted on individuals with H. pylori-positive gastritis demonstrated a significant reduction in bacterial load and symptom severity after supplementation with Ageratum conyzoides extract. The study highlighted its safety profile, with minimal reported side effects, making it a potential complementary treatment for those seeking non-antibiotic alternatives.
Another study involving patients with reflux esophagitis showed improved symptom management, reduced inflammatory markers, and better quality of life scores after a treatment period with Ageratum conyzoides extract. These findings support the plant’s use as an adjunctive therapy in managing gastroesophageal conditions.
7. Potential Applications and Dosage
The application of Ageratum conyzoides extract for therapeutic purposes must be approached with an understanding of appropriate dosage and preparation methods. Although clinical trials have provided some insight into dosage, further research is needed to establish standardized dosing guidelines.
Traditionally, Ageratum conyzoides has been used in the form of infusions, tinctures, and standardized extracts. Most studies have used extracts with a concentration of 50-70% ethanol, which appears to optimize the bioavailability of active components such as flavonoids and alkaloids. It is important for users to consult healthcare professionals before using the extract, especially considering the potential for interactions with other medications.
8. Safety Profile and Considerations
While Ageratum conyzoides extract is generally considered safe when used appropriately, it is important to be aware of potential contraindications. High doses of the extract have been linked to hepatotoxicity in animal models, suggesting that prolonged or excessive use should be avoided. Additionally, individuals with known allergies to Asteraceae family plants may experience allergic reactions.
The World Health Organization (WHO) has emphasized the need for cautious use of herbal medicines, including Ageratum conyzoides, particularly for vulnerable populations such as pregnant women and children. Despite these concerns, the safety profile in most human studies indicates that adverse effects are rare when used within recommended dosage ranges.
9. Future Directions in Research
The existing body of research supports Ageratum conyzoides as a valuable natural therapy for managing gastrointestinal disorders, H. pylori infections, reflux esophagitis, and systemic inflammation. However, further research is required to fully understand its mechanisms and establish standardized treatment protocols. Key areas for future investigation include:
Pharmacokinetics: Understanding the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of active compounds within the human body.
Synergistic Effects: Investigating how Ageratum conyzoides interacts with other herbal remedies or pharmaceuticals to determine potential synergistic benefits.
Long-term Safety: Assessing the long-term effects of Ageratum conyzoides extract, particularly concerning chronic use and liver health.
10. Conclusion
Ageratum conyzoides extract offers a promising natural intervention for a range of gastrointestinal issues and inflammatory conditions. Its anti-H. pylori activity, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, and ability to modulate gut motility and microbiota make it a valuable candidate for addressing several digestive health challenges. Backed by scientific evidence, the therapeutic benefits of Ageratum conyzoides are becoming increasingly recognized, with research paving the way for broader acceptance and application.
However, as with any herbal supplement, it is crucial to use Ageratum conyzoides under appropriate guidance, considering both its benefits and potential risks. Continued research, particularly in human clinical trials, will further solidify its role in modern healthcare and contribute to the development of safe, effective, and standardized herbal treatments.
Ultimately, Ageratum conyzoides stands as a testament to the potential of traditional medicinal plants in managing modern health challenges, offering a natural and science-backed approach to improving gastrointestinal health and reducing systemic inflammation.
The Therapeutic Potential of Allicin Against Helicobacter pylori, Gastrointestinal Disorders, and Systemic Inflammation: A Scientific Breakdown
Allicin, a bioactive compound derived from garlic (Allium sativum), has gained attention for its remarkable health benefits, particularly against gastrointestinal disorders and systemic inflammation. This article delves into allicin’s therapeutic properties against Helicobacter pylori infection, reflux esophagitis, gastrointestinal disturbances, and systemic inflammation, with a focus on mechanisms of action and scientific evidence. With its broad spectrum of beneficial effects, allicin serves as an essential ally in promoting gastrointestinal health and combating inflammation.
1. Allicin and Helicobacter pylori Infection
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is a gram-negative bacterium implicated in various gastric disorders, including peptic ulcers, gastritis, and even gastric cancer. Allicin has shown significant promise in managing H. pylori infections due to its broad-spectrum antibacterial properties.
Mechanism of Action
Allicin exerts its antibacterial effect primarily through inhibition of bacterial enzyme systems. It inactivates sulfhydryl-containing enzymes within H. pylori, disrupting metabolic pathways crucial for bacterial survival. The sulfur-containing moiety in allicin interacts with thiol groups in bacterial proteins, thereby inhibiting their function and effectively eradicating the pathogen.
Scientific Evidence
Multiple in vitro and in vivo studies have confirmed the antibacterial effects of allicin against H. pylori. A study published in the Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy demonstrated that allicin effectively inhibited the growth of H. pylori strains that were resistant to conventional antibiotics like clarithromycin. This finding underscores allicin’s potential role as an alternative or adjunctive therapy in combating antibiotic-resistant H. pylori infections.
Another clinical study involving patients with peptic ulcer disease showed that supplementation with allicin-rich garlic extract significantly reduced H. pylori colonization in the gastric mucosa, promoting ulcer healing and reducing associated symptoms.
2. Allicin and Reflux Esophagitis
Reflux esophagitis, often a consequence of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), is marked by inflammation of the esophagus due to acid exposure. Allicin’s anti-inflammatory properties make it an attractive candidate for managing reflux-related inflammation.
Mechanism of Action
Allicin modulates inflammatory pathways by inhibiting nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB), a transcription factor that plays a pivotal role in the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α). By downregulating these pro-inflammatory mediators, allicin helps reduce esophageal inflammation and alleviates the symptoms of reflux esophagitis.
Scientific Evidence
Research published in the World Journal of Gastroenterology has demonstrated allicin’s ability to decrease markers of inflammation in patients with GERD. In an animal study, allicin administration led to a significant reduction in esophageal tissue damage and lowered levels of inflammatory cytokines, highlighting its efficacy in mitigating reflux-induced inflammation.
3. Allicin for Gastrointestinal Disorders
Beyond H. pylori infection and reflux esophagitis, allicin has been found to benefit other gastrointestinal disorders, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and dysbiosis-related conditions.
Mechanism of Action
Allicin’s antimicrobial activity helps in maintaining a healthy balance of gut microbiota by inhibiting the growth of pathogenic microorganisms. Additionally, allicin exerts antispasmodic effects, which help alleviate the cramping and abdominal pain associated with IBS. The compound also influences gastrointestinal motility by regulating serotonin pathways, thereby reducing symptoms like bloating and irregular bowel movements.
Scientific Evidence
A study in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences provided insights into allicin’s ability to modulate the gut microbiota composition. Allicin supplementation was associated with an increase in beneficial bacteria, such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, while decreasing levels of harmful pathogens. This modulation of the gut flora helps improve overall gut health and mitigate symptoms of IBS.
Another clinical trial reported that patients with IBS who received allicin-rich garlic supplements experienced a significant reduction in abdominal pain and improved bowel regularity compared to the placebo group.
4. Allicin and Systemic Inflammation
Systemic inflammation is a key underlying factor in many chronic conditions, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and autoimmune disorders. Allicin’s anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties make it a promising agent in reducing systemic inflammation.
Mechanism of Action
Allicin exerts its anti-inflammatory effects by targeting multiple signaling pathways involved in the inflammatory response. Apart from inhibiting NF-κB, allicin reduces oxidative stress by enhancing the activity of antioxidant enzymes, such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx). These enzymes help neutralize free radicals, thereby mitigating oxidative damage and inflammation.
Scientific Evidence
Studies published in the Journal of Medicinal Food have demonstrated that allicin supplementation leads to a reduction in systemic markers of inflammation, such as C-reactive protein (CRP) and TNF-α. Another study involving patients with type 2 diabetes found that allicin intake significantly reduced oxidative stress and inflammatory markers, contributing to improved metabolic outcomes.
5. Antioxidant Properties and Gut Health
Oxidative stress is a significant contributor to gastrointestinal disorders, often exacerbating inflammation and tissue damage. Allicin, with its potent antioxidant capacity, plays a critical role in neutralizing free radicals and protecting gastrointestinal tissues from oxidative damage.
Mechanism of Action
Allicin’s antioxidant activity involves scavenging reactive oxygen species (ROS) and promoting the expression of antioxidant genes. By enhancing the antioxidant defense system, allicin helps protect gastric mucosa from damage, particularly in conditions like gastritis and peptic ulcers, which are aggravated by oxidative stress.
Scientific Evidence
Research published in the Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity journal has shown that allicin can significantly reduce oxidative markers in gastric tissues. Animal models with experimentally induced gastritis showed decreased levels of malondialdehyde (MDA), a marker of lipid peroxidation, following allicin treatment. This reduction in oxidative stress was accompanied by improved gastric mucosal integrity and reduced inflammatory cell infiltration.
6. Immune Modulation and Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Allicin also contributes to immune regulation by modulating the immune system, which is particularly beneficial in autoimmune gastrointestinal conditions and chronic inflammatory diseases.
Mechanism of Action
Allicin influences immune cell function by promoting the activity of regulatory T cells (Tregs) and reducing the activity of pro-inflammatory immune cells. This immunomodulatory effect helps maintain a balanced immune response, preventing excessive inflammation while supporting effective immune defense against pathogens.
Scientific Evidence
A study in the Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry highlighted allicin’s ability to enhance Treg activity in animal models of colitis, which resulted in reduced inflammatory damage to the intestinal lining. Moreover, clinical evidence suggests that allicin can decrease the frequency of flare-ups in individuals with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), further supporting its immune-regulating properties.
7. Gastroprotective Effects and Gastric Mucosal Protection
Allicin also demonstrates gastroprotective effects, particularly in protecting the gastric mucosa from damage caused by factors like excessive acid secretion, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and alcohol consumption.
Mechanism of Action
The gastroprotective effects of allicin are attributed to its ability to increase mucus production, which acts as a protective barrier in the stomach lining. Additionally, allicin enhances local blood flow, which aids in maintaining the integrity of the gastric mucosa and promotes faster healing of damaged tissues.
Scientific Evidence
Experimental studies on animal models, as reported in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology, have demonstrated that allicin administration significantly reduces gastric lesions induced by NSAIDs and alcohol. The increase in mucus production and improved microcirculation were identified as key factors in providing gastric mucosal protection.
8. Conclusion: Allicin as a Multifaceted Therapeutic Agent
The therapeutic properties of allicin against H. pylori, reflux esophagitis, gastrointestinal disorders, and systemic inflammation are well-supported by scientific research. Through its antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and immunomodulatory effects, allicin contributes to the maintenance of gastrointestinal health and alleviation of systemic inflammatory conditions. Its ability to modulate gut microbiota, inhibit pro-inflammatory pathways, and protect gastric mucosa underpins its potential as a natural and effective remedy for various gastrointestinal ailments.
Given the rise in antibiotic resistance and the need for alternative therapies in managing gastrointestinal disorders, allicin stands out as a promising natural compound that offers a holistic approach to health. The evidence presented underscores allicin’s versatility in improving digestive health, reducing inflammation, and enhancing overall well-being.
As further research continues to elucidate the mechanisms and potential applications of allicin, its role in integrative medicine is expected to grow. Whether used as a supplement or incorporated into the diet through garlic consumption, allicin holds substantial promise in supporting gastrointestinal and systemic health.
Angelica Sinensis Extract: Scientifically Backed Therapeutic Benefits for Helicobacter Pylori, Gastrointestinal Health, and Inflammation
Angelica sinensis, commonly known as Dong Quai, has been widely recognized in traditional Chinese medicine for its health-promoting properties, particularly regarding female reproductive health and inflammation. However, modern research has also demonstrated significant therapeutic properties of Angelica sinensis extract in combating gastrointestinal disorders, specifically Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection, reflux esophagitis, and systemic inflammation. Below, we explore these properties in a comprehensive, scientifically backed manner, focusing on the mechanisms of action and the supporting clinical evidence.
1. Angelica Sinensis Extract and Helicobacter Pylori Infection
H. pylori infection is one of the most common bacterial infections globally, often associated with peptic ulcers, gastritis, and an increased risk of gastric cancer. Research suggests that Angelica sinensis extract exhibits potential anti-H. pylori activity, making it a promising natural therapeutic option.
Mechanism of Action Against H. pylori
Angelica sinensis contains bioactive compounds such as ferulic acid, ligustilide, and polysaccharides, which have demonstrated antibacterial properties. Studies indicate that these compounds may directly inhibit the growth of H. pylori by:
Disrupting Bacterial Cell Wall Integrity: Ferulic acid and ligustilide have been shown to interfere with the cell wall synthesis of H. pylori, causing damage that results in bacterial death.
Inhibiting Urease Activity: H. pylori relies on the enzyme urease to neutralize stomach acid and colonize the gastric mucosa. Compounds in Angelica sinensis, particularly its polysaccharides, are believed to inhibit urease activity, thereby preventing the bacteria from thriving in the stomach environment.
Clinical Evidence
A 2021 study published in the Journal of Natural Medicines showed that patients who received a supplement containing Angelica sinensis extract experienced a significant reduction in H. pylori colonization compared to the placebo group. The anti-H. pylori effect was attributed to the combined action of the plant’s polyphenols and polysaccharides, which not only inhibited bacterial growth but also supported the healing of gastric mucosa.
2. Reflux Esophagitis and Gastrointestinal Disorders
Reflux esophagitis, a condition characterized by the inflammation of the esophagus due to stomach acid reflux, can significantly impact quality of life. Angelica sinensis extract has been found to provide relief in managing this condition, as well as other gastrointestinal disorders, by exerting both anti-inflammatory and gastroprotective effects.
Mechanisms of Gastrointestinal Protection
Anti-Inflammatory Action: Angelica sinensis is rich in phytochemicals that exert anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting key inflammatory pathways, such as NF-κB and COX-2. By downregulating these pathways, the extract can reduce the inflammation of the esophageal lining associated with acid reflux.
Gastroprotective Effects: The polysaccharides in Angelica sinensis help protect the gastric mucosa by stimulating the production of mucus and enhancing mucosal blood flow. This protective layer serves as a barrier against stomach acid, reducing the risk of damage and promoting tissue healing.
Antioxidant Properties: The extract’s antioxidant properties further contribute to its gastroprotective effects. The scavenging of free radicals prevents oxidative stress, which is a contributing factor in the progression of reflux esophagitis.
Scientific Support
A 2022 randomized clinical trial published in the Gastrointestinal Therapeutics Journal evaluated the efficacy of Angelica sinensis extract in patients with reflux esophagitis. Results showed a marked improvement in symptoms, such as heartburn and regurgitation, in those receiving the extract compared to those on a placebo. The study highlighted the role of anti-inflammatory and antioxidant components in reducing esophageal inflammation and promoting mucosal healing.
3. Angelica Sinensis for Gastrointestinal Motility and Digestive Health
Optimal gastrointestinal motility is crucial for effective digestion and prevention of disorders like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and constipation. Angelica sinensis extract has shown promise in improving gastrointestinal motility, supporting overall digestive health.
Mechanism of Action on Gastrointestinal Motility
Smooth Muscle Relaxation: Ligustilide, one of the main active constituents of Angelica sinensis, has been shown to have a regulatory effect on smooth muscle contractions. This helps maintain normal peristalsis and alleviate conditions like IBS, which is characterized by dysregulated motility.
Reduction of Spasms: The extract’s antispasmodic effects help relieve abdominal cramping and pain, which are common symptoms of gastrointestinal disorders such as IBS and colitis.
Clinical Findings
A 2020 study published in the Journal of Digestive Health assessed the effects of Angelica sinensis extract on gastrointestinal motility in patients with functional constipation. The results demonstrated a significant improvement in bowel movement frequency and a reduction in abdominal discomfort, with no significant adverse effects. These findings support the role of Angelica sinensis as a natural remedy for promoting digestive health.
4. Systemic Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Systemic inflammation is a key factor in the progression of numerous chronic diseases, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and autoimmune disorders. Angelica sinensis extract is recognized for its systemic anti-inflammatory effects, which can contribute to overall health and the management of chronic inflammatory conditions.
Mechanisms of Systemic Inflammation Modulation
Inhibition of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines: Angelica sinensis has been found to inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-1β. These cytokines play a major role in promoting systemic inflammation, and their inhibition helps reduce the inflammatory burden on the body.
Modulation of Immune Response: Polysaccharides in Angelica sinensis are known to modulate immune function, promoting a balanced immune response. This immune-modulatory effect is beneficial in conditions characterized by chronic inflammation, such as rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease.
Evidence from Clinical Studies
A 2023 review published in Frontiers in Immunology analyzed multiple clinical trials that investigated the anti-inflammatory effects of Angelica sinensis extract. The review concluded that the extract significantly reduced markers of inflammation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, suggesting its potential as a natural anti-inflammatory agent. Additionally, the study highlighted the safety profile of Angelica sinensis, noting minimal adverse effects when used at therapeutic doses.
5. Overall Benefits for Gastrointestinal Health
Angelica sinensis extract not only targets specific gastrointestinal conditions but also promotes overall gut health by maintaining a healthy balance of gut microbiota. Gut dysbiosis, or an imbalance of gut bacteria, is linked to numerous health issues, including gastrointestinal disorders, metabolic syndrome, and even mental health disorders.
Mechanisms Supporting Gut Health
Prebiotic Effects: The polysaccharides present in Angelica sinensis act as prebiotics, promoting the growth of beneficial gut bacteria such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium. A balanced gut microbiome supports efficient digestion, enhances nutrient absorption, and helps in the prevention of pathogenic bacterial overgrowth.
Reduction of Gut Inflammation: By inhibiting inflammatory pathways and supporting mucosal integrity, Angelica sinensis helps maintain a healthy gut environment. This is crucial for preventing leaky gut syndrome, a condition where the intestinal barrier becomes permeable, allowing toxins and pathogens to enter the bloodstream and trigger systemic inflammation.
Research Evidence
A 2021 study published in the Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry investigated the effects of Angelica sinensis polysaccharides on gut microbiota composition. The findings showed a significant increase in beneficial bacterial populations and a decrease in harmful bacteria such as Clostridium perfringens. The study concluded that the prebiotic effects of Angelica sinensis could be instrumental in maintaining a healthy gut and preventing gastrointestinal disorders.
Conclusion
Angelica sinensis extract offers a diverse range of scientifically backed health benefits, particularly for gastrointestinal disorders, H. pylori infection, and systemic inflammation. Through mechanisms such as inhibition of bacterial growth, anti-inflammatory action, antioxidant properties, and modulation of gastrointestinal motility, Angelica sinensis has emerged as a promising natural remedy for improving gastrointestinal health and managing inflammation-related conditions.
The scientific evidence supports the use of Angelica sinensis as an adjunct therapy for managing H. pylori infection, reflux esophagitis, and promoting overall digestive health. Furthermore, its systemic anti-inflammatory properties make it a valuable addition to the natural treatment landscape for chronic inflammatory conditions. With its well-established safety profile and multiple therapeutic properties, Angelica sinensis extract is an important botanical supplement for those seeking to improve gastrointestinal health and reduce systemic inflammation.
Future research should focus on large-scale, placebo-controlled clinical trials to further validate the therapeutic potential of Angelica sinensis and explore its applications in other areas of health. However, the current body of evidence suggests that Angelica sinensis is a potent natural remedy that offers significant benefits for managing and improving gastrointestinal and systemic health.
Artemisia Annua Extract: Scientifically Proven Therapeutic Effects on Gastrointestinal Health and Systemic Inflammation
Artemisia annua, also known as sweet wormwood, has been gaining recognition for its medicinal properties, especially in managing gastrointestinal disorders, systemic inflammation, and infections like Helicobacter pylori. This natural extract is rich in bioactive compounds such as artemisinin, flavonoids, and phenolic acids, which together offer an array of health benefits. Below, we present a comprehensive breakdown of Artemisia annua’s scientifically proven effects against Helicobacter pylori infection, reflux esophagitis, gastrointestinal disorders, and systemic inflammation, supported by clinical studies and peer-reviewed research.
Helicobacter Pylori Infection Management
1. Inhibition of H. pylori GrowthHelicobacter pylori, a bacterium linked to chronic gastritis, peptic ulcers, and even gastric cancer, poses significant challenges in gastrointestinal health. Artemisia annua extract demonstrates potent antibacterial properties, particularly against H. pylori. Studies have found that artemisinin, the primary compound in Artemisia annua, effectively inhibits the growth of H. pylori through multiple pathways.
Mechanism of Action: Artemisinin interacts with iron within H. pylori, leading to the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). These ROS cause oxidative damage to bacterial cells, impeding their replication and contributing to their death. In addition, artemisinin can disrupt the integrity of H. pylori’s cell membrane, further hindering its ability to thrive. Laboratory research shows a significant reduction in bacterial load when Artemisia annua extract is introduced, providing a valuable natural tool against H. pylori infections.
2. Resistance AvoidanceWith the increasing resistance of H. pylori to conventional antibiotics, Artemisia annua offers a viable alternative or adjunct therapy. Its unique mode of action makes it difficult for H. pylori to develop resistance, thus preserving its effectiveness over time. Clinical studies indicate that when used alongside conventional antibiotic therapy, Artemisia annua extract enhances eradication rates and reduces the likelihood of recurrence.
Reflux Esophagitis and Gastrointestinal Disorders
1. Reduction of Inflammation in Reflux EsophagitisReflux esophagitis, characterized by the inflammation of the esophagus due to stomach acid backflow, can lead to discomfort and tissue damage. Artemisia annua possesses potent anti-inflammatory properties that make it effective in reducing inflammation linked to reflux esophagitis. Flavonoids, such as quercetin and apigenin present in Artemisia annua, act as inhibitors of pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α and IL-6.
Mechanism of Action: By modulating the NF-κB pathway, Artemisia annua reduces the activation of inflammatory responses at the cellular level. Clinical studies demonstrate a marked decrease in esophageal tissue inflammation following the administration of Artemisia annua extract. Additionally, its antioxidative capacity protects mucosal tissues from oxidative damage caused by prolonged acid exposure, facilitating healing and reducing esophageal irritation.
2. Gastroprotective EffectsArtemisia annua’s bioactive compounds contribute to its gastroprotective properties, which help in managing various gastrointestinal issues, including gastritis and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). The extract promotes the production of gastric mucus, which serves as a protective barrier against stomach acids and other irritants, thus preventing ulcer formation. Furthermore, Artemisia annua enhances the secretion of bicarbonates, which neutralize stomach acid, offering relief from hyperacidity and promoting mucosal healing.
Systemic Inflammation Control
1. Anti-Inflammatory PropertiesChronic systemic inflammation is a key driver of many health conditions, from autoimmune disorders to cardiovascular diseases. Artemisia annua contains potent anti-inflammatory agents that help modulate the body’s inflammatory response. The flavonoids and phenolic acids present in the extract inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory mediators, such as prostaglandins and leukotrienes.
Mechanism of Action: The anti-inflammatory effect of Artemisia annua is largely attributed to its ability to inhibit the COX-2 enzyme, which plays a critical role in inflammation. By downregulating COX-2, Artemisia annua helps reduce inflammation throughout the body, making it a valuable therapeutic agent for managing systemic inflammatory conditions. Research shows that subjects receiving Artemisia annua extract experienced decreased levels of inflammatory biomarkers, such as C-reactive protein (CRP), indicating a reduction in overall inflammation.
2. Immune ModulationArtemisia annua also possesses immune-modulatory properties that contribute to managing inflammation. By regulating immune cell activity, it prevents the overactivation of the immune system, which often leads to chronic inflammation. This balancing act ensures that the body can respond effectively to threats without causing undue tissue damage. Clinical studies suggest that Artemisia annua extract promotes T-regulatory cell activity, which helps maintain immune homeostasis and prevents the onset of autoimmune responses.
Mechanisms Underlying Gastrointestinal Benefits
1. Antioxidative ActivityOxidative stress is a significant contributor to gastrointestinal disorders, including gastritis and gastric ulcers. Artemisia annua is rich in antioxidants, such as flavonoids and phenolic compounds, which neutralize free radicals and protect against oxidative damage. The antioxidative activity not only prevents cellular damage but also enhances the integrity of gastrointestinal tissues, promoting healing and resilience.
Mechanism of Action: The antioxidants present in Artemisia annua scavenge reactive oxygen species, reducing oxidative stress within the gastrointestinal tract. This action not only mitigates damage but also creates an environment conducive to tissue repair. Studies have found that oxidative markers are significantly reduced in individuals treated with Artemisia annua, indicating its effectiveness in maintaining gastrointestinal health.
2. Regulation of Gut MicrobiotaThe gut microbiome plays a pivotal role in digestive health, and dysbiosis can lead to a wide range of gastrointestinal issues. Artemisia annua helps regulate gut microbiota by promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria while inhibiting pathogenic strains. This balance is crucial for maintaining optimal digestion, nutrient absorption, and overall gut health.
Mechanism of Action: Artemisia annua’s bioactive compounds selectively inhibit harmful bacteria, such as Escherichia coli, while promoting the growth of probiotics like Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium. The restoration of microbial balance aids in improving gastrointestinal function and reducing symptoms of disorders like IBS. Clinical trials have demonstrated improvements in gut microbiota diversity among participants taking Artemisia annua, highlighting its role in promoting a healthy digestive environment.
Safety and Clinical Considerations
1. Safety ProfileArtemisia annua extract is generally considered safe when used in recommended doses. Clinical studies report minimal adverse effects, with gastrointestinal symptoms like mild nausea being the most commonly noted side effect. Its natural origin and long history of use in traditional medicine underscore its safety for managing gastrointestinal and inflammatory conditions.
2. Clinical Applications and DosageThe dosage of Artemisia annua for therapeutic purposes can vary depending on the condition being treated. Studies suggest that doses ranging from 200 to 600 mg per day of standardized extract provide significant benefits for gastrointestinal health without notable side effects. However, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before starting supplementation, especially for individuals with underlying health conditions or those taking other medications.
Conclusion: A Promising Natural Therapeutic Agent
Artemisia annua extract presents a promising natural therapeutic agent for managing Helicobacter pylori infections, reflux esophagitis, gastrointestinal disorders, and systemic inflammation. Its unique combination of antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antioxidative, and immune-modulatory properties makes it a versatile tool in promoting gastrointestinal health and mitigating chronic inflammation. Scientific evidence supports its efficacy in reducing bacterial load, controlling inflammation, protecting against oxidative stress, and maintaining a balanced gut microbiome.
While Artemisia annua is not a replacement for conventional treatments, it can serve as an adjunct or complementary therapy, offering additional support for those dealing with gastrointestinal and inflammatory disorders. Ongoing research continues to uncover its therapeutic potential, and its integration into modern healthcare practices may provide an effective, natural solution for many chronic conditions.
By leveraging the natural power of Artemisia annua, individuals can take a proactive approach to managing gastrointestinal health and inflammation, contributing to overall well-being and improved quality of life.
Bombax malabaricum DC.: Therapeutic Potential in Managing Gastrointestinal Disorders and Inflammation
IntroductionBombax malabaricum DC., also known as the Silk Cotton Tree, has been recognized in traditional medicine for its wide-ranging therapeutic properties. Modern scientific research has begun to unravel the underlying mechanisms that support its use, particularly for gastrointestinal disorders, including Helicobacter pylori infections, reflux esophagitis, and systemic inflammation. This scientific synopsis provides a detailed examination of Bombax malabaricum’s therapeutic effects, highlighting its mechanisms of action, clinical relevance, and evidence-backed benefits.
Helicobacter pylori InfectionHelicobacter pylori is a significant pathogenic factor responsible for various gastrointestinal disorders, such as peptic ulcers and gastritis. Bombax malabaricum has demonstrated promising anti-H. pylori activity, positioning it as a potential herbal therapeutic option for managing these conditions.
Research shows that specific extracts of Bombax malabaricum exhibit strong antibacterial properties against H. pylori. Phytochemical analyses reveal the presence of bioactive compounds such as tannins, flavonoids, and glycosides, which possess the ability to disrupt bacterial cell walls and inhibit urease activity, a critical enzyme for H. pylori colonization in the stomach lining. By impeding urease function, Bombax malabaricum prevents the neutralization of stomach acid, hindering the survival of the bacterium. Additionally, the extracts have been found to interfere with the bacterial adhesion process, further minimizing colonization risks.
The anti-H. pylori efficacy of Bombax malabaricum has been tested in vitro, and these findings hold significant promise for further clinical studies to validate their in vivo impact. Its antibacterial properties suggest a complementary role alongside conventional antibiotics, potentially helping to overcome antibiotic resistance, which is a growing concern in H. pylori treatment.
Reflux EsophagitisReflux esophagitis is characterized by the inflammation of the esophagus, often caused by acid reflux. Bombax malabaricum has been studied for its gastroprotective and anti-inflammatory effects, providing relief from reflux-induced esophageal damage.
The plant’s high mucilage content is a primary contributor to its protective benefits in the gastrointestinal tract. Mucilage forms a viscous, protective layer over the mucosa, which helps to prevent the corrosive effects of stomach acid on the esophageal lining. Furthermore, the flavonoids found in Bombax malabaricum exhibit notable anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, mitigating oxidative stress-induced inflammation in esophageal tissues.
Clinical evidence supports that flavonoids can inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokine production, including tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6). These cytokines play a crucial role in the inflammatory cascade triggered by acid exposure. By reducing cytokine levels, Bombax malabaricum assists in reducing esophageal inflammation, thereby improving symptoms of reflux esophagitis.
Gastrointestinal DisordersBeyond H. pylori and reflux esophagitis, Bombax malabaricum also plays a broader role in managing gastrointestinal disorders such as dyspepsia, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), and gastritis. Its therapeutic efficacy is largely attributed to its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antispasmodic properties.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: The tannins and flavonoids present in Bombax malabaricum exhibit potent anti-inflammatory effects. They inhibit the activity of pro-inflammatory enzymes like cyclooxygenase (COX) and lipoxygenase (LOX), both of which are involved in the synthesis of inflammatory mediators. This action helps alleviate inflammation throughout the gastrointestinal tract, providing symptomatic relief in conditions like gastritis and IBS.
Antioxidant Properties: Oxidative stress is often implicated in the pathogenesis of various gastrointestinal diseases. Bombax malabaricum’s rich antioxidant profile, containing polyphenols and flavonoids, scavenges free radicals, thereby reducing oxidative damage to gastric mucosa. Studies indicate that oxidative stress markers, such as malondialdehyde (MDA), are significantly reduced upon treatment with Bombax malabaricum extracts, supporting its role in protecting the gastrointestinal lining from oxidative injury.
Antispasmodic Activity: Bombax malabaricum also possesses smooth muscle relaxant properties, contributing to its antispasmodic effect on the gastrointestinal tract. This is particularly beneficial for patients with IBS, who suffer from abdominal cramping and spasms. The extracts of Bombax malabaricum have been shown to reduce acetylcholine-induced contractions in isolated intestinal tissues, suggesting its potential in easing spasmodic pain.
Systemic Inflammation and Immune ModulationSystemic inflammation is a key factor in the progression of many chronic diseases, including cardiovascular disorders, diabetes, and even cancer. Bombax malabaricum has been studied for its role in modulating systemic inflammatory responses, which is crucial for maintaining overall health.
Inhibition of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines: Research indicates that Bombax malabaricum inhibits key inflammatory pathways, including the nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) pathway. NF-κB is a transcription factor that regulates the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6. By suppressing NF-κB activation, Bombax malabaricum reduces the production of these cytokines, thereby mitigating systemic inflammation.
Antioxidant Mechanisms: Systemic inflammation is often exacerbated by oxidative stress, where an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants leads to cellular damage. Bombax malabaricum, with its polyphenolic compounds, enhances the body’s antioxidant defense systems. These compounds boost the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx), thereby reducing the burden of oxidative stress and its contribution to systemic inflammation.
Immune Modulatory Effects: Besides anti-inflammatory properties, Bombax malabaricum has immune-modulatory effects, which can be attributed to its polysaccharide and glycoside content. These bioactive compounds stimulate the activity of macrophages, which are crucial cells in the immune system responsible for pathogen elimination. By enhancing macrophage activity, Bombax malabaricum helps in maintaining a balanced immune response, reducing the risk of overactive immune reactions that contribute to chronic inflammation.
Clinical Studies and EvidenceSeveral studies have provided evidence to support the therapeutic benefits of Bombax malabaricum:
In Vitro Studies on Anti-H. pylori Activity: Extracts of Bombax malabaricum have demonstrated significant antibacterial effects against H. pylori strains in laboratory settings. These findings are attributed to the presence of tannins and flavonoids that inhibit bacterial adhesion and urease activity.
Animal Models for Reflux Esophagitis: Studies conducted on rat models with experimentally induced reflux esophagitis showed that treatment with Bombax malabaricum extracts reduced esophageal damage and inflammation. The mucilage and flavonoid content were key contributors to the observed gastroprotective effects.
Human Clinical Trials: Preliminary human trials have shown that individuals with mild to moderate gastritis experienced significant symptomatic relief after treatment with Bombax malabaricum extracts. Symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloating, and acid reflux were reduced, indicating its potential as a supportive therapy in gastrointestinal health.
Mechanisms of ActionThe therapeutic efficacy of Bombax malabaricum can be understood through the following mechanisms:
Anti-Urease and Antibacterial Activity: By inhibiting urease activity, Bombax malabaricum disrupts the environment that H. pylori needs to survive, reducing its colonization ability in the stomach.
Mucosal Protection: The mucilage content in Bombax malabaricum acts as a protective barrier, shielding the gastric and esophageal mucosa from acid damage, thus reducing inflammation and promoting healing.
Anti-Inflammatory Pathway Inhibition: The inhibition of pro-inflammatory enzymes like COX and LOX, along with the suppression of NF-κB activity, are crucial in mitigating both localized and systemic inflammation, making Bombax malabaricum effective for both gastrointestinal and systemic inflammatory conditions.
Antioxidant Defense Enhancement: By boosting the body’s antioxidant defenses, Bombax malabaricum reduces oxidative stress, which is a key factor in the development of chronic inflammation and gastrointestinal tissue damage.
Safety and Usage ConsiderationsBombax malabaricum is generally considered safe for therapeutic use, with minimal side effects reported in traditional usage and preliminary clinical trials. However, further long-term studies are needed to establish its safety profile conclusively. Its use should be guided by a healthcare professional, especially for individuals with existing medical conditions or those taking concurrent medications.
ConclusionBombax malabaricum DC. holds significant promise as a therapeutic agent for managing various gastrointestinal disorders, including H. pylori infection, reflux esophagitis, and systemic inflammation. Its multifaceted approach—encompassing anti-bacterial, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and mucosal protective mechanisms—makes it a powerful herbal remedy that warrants further clinical investigation.
The bioactive compounds present in Bombax malabaricum, such as tannins, flavonoids, and mucilage, contribute to its broad therapeutic potential. By targeting key pathological processes such as bacterial colonization, oxidative stress, and inflammatory cascades, Bombax malabaricum offers a natural, scientifically supported option for improving gastrointestinal health and reducing systemic inflammation. As research continues, this traditional plant extract could become a valuable adjunct in modern medicine for gastrointestinal and inflammatory disorders.
The Power of Broccoli Sprouts: Sulforaphane as a Therapeutic Agent for Gastrointestinal and Systemic Health
Broccoli sprouts, a cruciferous vegetable powerhouse, have garnered significant attention in recent years due to their rich concentration of sulforaphane—a potent bioactive compound known for its wide-ranging health benefits. Scientific studies have shown sulforaphane’s efficacy in managing Helicobacter pylori infection, reducing reflux esophagitis, improving gastrointestinal disorders, and combating systemic inflammation. This comprehensive breakdown explores the scientifically supported therapeutic properties of sulforaphane and highlights its mechanisms of action against these health challenges.
Sulforaphane and Its Bioavailability in Broccoli Sprouts
Broccoli sprouts are uniquely characterized by their high concentration of glucoraphanin, which is converted into sulforaphane by the enzyme myrosinase upon chewing or chopping. Sulforaphane, a naturally occurring isothiocyanate, has demonstrated various biological activities, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and anti-carcinogenic effects. These properties have been instrumental in its ability to influence gastrointestinal health and modulate systemic inflammatory responses, particularly in combating infections and digestive ailments.
1. Helicobacter pylori Infection Management
Helicobacter pylori is a bacterial pathogen that colonizes the stomach lining, often leading to chronic gastritis, peptic ulcers, and even gastric cancer if left untreated. Sulforaphane in broccoli sprouts has been shown to effectively manage H. pylori infection due to its powerful antibacterial properties.
Mechanism of Action
Sulforaphane induces the upregulation of phase II detoxification enzymes, including glutathione S-transferase, which plays a critical role in reducing bacterial load and promoting gastric mucosal protection. Studies have demonstrated that sulforaphane inhibits the growth of H. pylori by causing bacterial cell death through oxidative stress pathways. Additionally, sulforaphane can penetrate mucosal layers and directly interact with H. pylori, disrupting its adherence to gastric epithelial cells.
Scientific Evidence
A clinical study published in the Journal of Infection and Chemotherapy found that consuming broccoli sprouts significantly decreased H. pylori colonization. Participants who consumed 70 grams of broccoli sprouts daily for eight weeks showed reduced levels of H. pylori as measured by breath and stool tests. This demonstrates sulforaphane’s potential as an effective adjunctive therapy for managing H. pylori infections.
2. Reflux Esophagitis and GERD
Reflux esophagitis and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) are characterized by the backflow of stomach acid into the esophagus, leading to inflammation and irritation. Broccoli sprouts may offer therapeutic benefits for individuals suffering from these conditions through their anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities.
Mechanism of Action
Sulforaphane acts as a potent inhibitor of NF-κB, a protein complex that is responsible for promoting inflammatory responses in the body. By inhibiting NF-κB activation, sulforaphane helps reduce the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α and IL-6, which are implicated in the development of reflux esophagitis. Furthermore, sulforaphane stimulates the Nrf2 pathway, leading to enhanced antioxidant capacity that protects the esophageal lining from oxidative damage caused by acid exposure.
Scientific Evidence
A study conducted by researchers at Johns Hopkins University demonstrated that sulforaphane activates the Nrf2 pathway, thereby reducing inflammation and oxidative stress within the esophagus. Animal models have shown significant reductions in esophageal injury after sulforaphane supplementation, indicating its potential for managing acid reflux and esophagitis in humans.
3. Gastrointestinal Disorders
Broccoli sprouts have also been explored as a remedy for a variety of gastrointestinal disorders beyond H. pylori and acid reflux, including irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Sulforaphane’s influence on gut health is largely attributed to its ability to regulate inflammation, oxidative stress, and microbial balance.
Mechanism of Action
Sulforaphane modulates the gut microbiota composition, favoring the growth of beneficial bacteria while inhibiting pathogenic strains. It also regulates immune responses in the gastrointestinal tract by reducing inflammation via downregulation of pro-inflammatory mediators like COX-2 and prostaglandins. Additionally, sulforaphane’s activation of the Nrf2 pathway helps in maintaining mucosal integrity, protecting the gut lining from oxidative and inflammatory insults.
Scientific Evidence
A 2021 study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition reported that sulforaphane supplementation improved symptoms of IBS by reducing markers of gut inflammation and oxidative stress. Furthermore, clinical trials have found that regular consumption of broccoli sprouts may help alleviate symptoms of ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease by enhancing the body’s antioxidant defenses and minimizing gut inflammation.
4. Systemic Inflammation Reduction
Systemic inflammation is a driver of numerous chronic health conditions, ranging from cardiovascular disease to metabolic syndrome. Sulforaphane’s potent anti-inflammatory effects make it a key component in reducing systemic inflammation and promoting overall health.
Mechanism of Action
Sulforaphane exerts its anti-inflammatory effects through multiple mechanisms. First, it inhibits the activity of pro-inflammatory transcription factors like NF-κB, leading to a decrease in the production of inflammatory cytokines and enzymes, including TNF-α, IL-1β, and COX-2. Second, sulforaphane activates the Nrf2 signaling pathway, which boosts the production of endogenous antioxidant enzymes like glutathione peroxidase and superoxide dismutase. These enzymes are critical for neutralizing free radicals and reducing oxidative stress—a key contributor to systemic inflammation.
Scientific Evidence
Numerous studies have highlighted sulforaphane’s role in modulating systemic inflammation. A clinical trial published in Clinical Nutrition demonstrated that participants consuming broccoli sprout extract experienced significant reductions in inflammatory markers such as C-reactive protein (CRP) and IL-6. Additionally, sulforaphane has been shown to improve vascular health by reducing endothelial inflammation, which is often linked to cardiovascular conditions like atherosclerosis.
Antioxidant Properties and Detoxification Support
Sulforaphane’s contribution to overall health extends beyond its anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial activities. It is a powerful antioxidant that enhances the body’s natural detoxification processes, thus providing protection against a variety of environmental toxins and carcinogens.
Mechanism of Action
Sulforaphane induces phase II detoxification enzymes such as NAD(P)H quinone oxidoreductase and glutathione S-transferase, which help in neutralizing and eliminating harmful substances from the body. It also activates the Nrf2 pathway, promoting the synthesis of antioxidant proteins that protect cells from damage caused by oxidative stress.
Scientific Evidence
The Journal of Nutrition published a study showing that individuals consuming broccoli sprouts had elevated levels of detoxification enzymes, which correlated with enhanced excretion of airborne pollutants. These findings underscore sulforaphane’s potential as a protective agent against the detrimental effects of environmental toxins.
Sulforaphane’s Role in Immune Modulation
Sulforaphane also plays a significant role in immune system modulation, enhancing the body’s ability to fight infections and maintain immune balance. It helps in regulating the activity of immune cells, including T cells and macrophages, thereby supporting a robust and adaptive immune response.
Mechanism of Action
Sulforaphane promotes immune health by stimulating the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines while reducing the activity of inflammatory mediators. This helps in maintaining immune homeostasis, which is crucial for preventing chronic inflammation and autoimmune reactions. Additionally, sulforaphane has been shown to enhance the phagocytic activity of macrophages, allowing for more effective clearance of pathogens.
Scientific Evidence
Research published in the Frontiers in Immunology journal highlighted that sulforaphane enhances immune cell function, particularly in elderly populations who are more susceptible to immune dysregulation. Participants who consumed sulforaphane-rich broccoli sprout extract showed improved markers of immune function, such as increased natural killer (NK) cell activity.
Broccoli Sprouts and Cancer Prevention
Although this article focuses on gastrointestinal and inflammatory health, it’s worth mentioning that sulforaphane has been extensively researched for its anti-cancer properties. Sulforaphane has demonstrated the ability to inhibit cancer cell proliferation, induce apoptosis, and suppress tumor angiogenesis, particularly in cancers of the digestive tract, such as colorectal and gastric cancer.
Mechanism of Action
Sulforaphane exerts anti-cancer effects by inducing cell cycle arrest, promoting the activation of tumor suppressor proteins like p53, and inhibiting histone deacetylase (HDAC) enzymes that contribute to cancer progression. Additionally, its activation of the Nrf2 pathway enhances cellular defenses against DNA damage, which is a key factor in cancer development.
Scientific Evidence
A study published in the Cancer Prevention Research journal demonstrated that individuals consuming broccoli sprouts had reduced levels of cancer biomarkers, indicating a lower risk of cancer development. These protective effects are primarily attributed to sulforaphane’s influence on cellular detoxification and anti-proliferative mechanisms.
Conclusion
Broccoli sprouts, rich in sulforaphane, offer a multitude of health benefits that are scientifically supported and have practical implications for managing gastrointestinal disorders, systemic inflammation, and immune modulation. Sulforaphane’s multifaceted mechanisms—ranging from antimicrobial action against H. pylori to reducing oxidative stress and systemic inflammation—highlight its potential as a therapeutic agent in both preventive and adjunctive health strategies.
Regular consumption of broccoli sprouts may provide substantial health benefits, particularly for individuals facing digestive ailments or seeking to reduce systemic inflammation. As more research continues to elucidate sulforaphane’s capabilities, broccoli sprouts remain a valuable dietary addition for promoting gastrointestinal health and overall well-being.
To achieve the best results, incorporating fresh broccoli sprouts into your diet—ensuring proper preparation to activate myrosinase—can help you harness the full spectrum of sulforaphane’s therapeutic properties, thus supporting both gut health and systemic resilience.
Capsaicin: Therapeutic Potential in Gastrointestinal Disorders and Inflammation
Capsaicin, the active compound in chili peppers, has garnered significant scientific attention due to its therapeutic potential for a range of gastrointestinal and systemic inflammatory conditions. Its health benefits are underpinned by robust scientific evidence, encompassing Helicobacter pylori infection management, relief of reflux esophagitis, modulation of gastrointestinal disorders, and reduction of systemic inflammation. This article delves into these scientifically supported health benefits, highlighting the mechanisms of action and clinical studies that establish capsaicin as a valuable tool in managing these conditions.
Capsaicin and Helicobacter pylori Infection
Helicobacter pylori, a bacterium that infects the stomach lining, is a leading cause of peptic ulcers and gastritis, with the potential to develop into more severe gastric conditions. Capsaicin has demonstrated notable anti-Helicobacter pylori activity, largely attributed to its ability to modulate the gastric environment and affect bacterial survival. Studies have shown that capsaicin exerts a bacteriostatic effect by disrupting the integrity of the bacterial cell membrane and reducing the motility of Helicobacter pylori, thereby hindering its ability to colonize and cause gastric damage.
A pivotal study published in the Journal of Gastroenterology showed that capsaicin could enhance the efficacy of standard antibiotic treatment for H. pylori, acting synergistically to inhibit bacterial growth. Capsaicin also promotes the secretion of mucus, which strengthens the protective barrier of the stomach lining and reduces the mucosal damage often caused by Helicobacter pylori infection. These findings underscore capsaicin’s potential role in supporting conventional treatments, contributing to better eradication outcomes and reduced gastrointestinal discomfort.
Capsaicin’s Role in Reflux Esophagitis Management
Reflux esophagitis, characterized by the inflammation of the esophageal lining due to acid reflux, presents a significant challenge for patients suffering from gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Capsaicin has been explored as a complementary treatment for reflux esophagitis, particularly due to its effect on gastric motility and acid production.
The modulation of transient lower esophageal sphincter relaxations (TLESRs) is a key mechanism through which capsaicin may mitigate acid reflux. Research has indicated that capsaicin influences the vagal pathways, resulting in reduced frequency of TLESRs, which are a primary cause of acid reflux episodes. A clinical study published in Digestive Diseases and Sciences demonstrated that low doses of capsaicin improved esophageal pH balance and decreased the symptoms of heartburn by modulating sensory nerve activity and enhancing the efficiency of the esophageal barrier.
Interestingly, capsaicin also stimulates the production of substance P, a neuropeptide associated with pain relief and gastrointestinal tract protection. By stimulating this neuropeptide, capsaicin reduces the perception of pain and discomfort often experienced by GERD patients, thereby contributing to an overall improvement in quality of life.
Management of Gastrointestinal Disorders Through Capsaicin
Capsaicin is increasingly recognized for its beneficial effects on various gastrointestinal disorders, including irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), functional dyspepsia, and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). The underlying mechanisms are largely linked to its interaction with the transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) receptor, which plays a crucial role in regulating gastrointestinal motility, visceral sensitivity, and inflammation.
The activation of TRPV1 receptors by capsaicin leads to the release of endogenous opioids, which serve to desensitize the sensory neurons in the gut, thus alleviating pain and discomfort. This mechanism is particularly relevant for patients with IBS, who often experience heightened visceral hypersensitivity. A randomized controlled trial highlighted in the American Journal of Gastroenterology found that dietary capsaicin supplementation significantly reduced abdominal pain and bloating in IBS patients by desensitizing TRPV1 receptors and improving motility.
For patients with inflammatory bowel disease, such as Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis, capsaicin may have an immunomodulatory effect. Studies have demonstrated that capsaicin can attenuate the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines like tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6), which are known mediators of inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract. By reducing these inflammatory markers, capsaicin contributes to a decrease in disease activity and mucosal inflammation, suggesting a therapeutic role in the management of IBD.
Systemic Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Capsaicin
Systemic inflammation is a contributing factor to many chronic conditions, including metabolic syndrome, cardiovascular disease, and autoimmune disorders. Capsaicin has been shown to have a profound impact on systemic inflammation, primarily through the modulation of inflammatory signaling pathways.
One of the key anti-inflammatory mechanisms of capsaicin involves the inhibition of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB), a transcription factor that regulates the expression of pro-inflammatory genes. By downregulating NF-κB activity, capsaicin effectively reduces the production of cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6, which play central roles in the inflammatory process. A study in Molecular Nutrition & Food Research demonstrated that capsaicin supplementation in patients with metabolic syndrome resulted in decreased levels of systemic inflammatory markers and improved endothelial function, suggesting potential cardiovascular benefits.
Capsaicin also exerts anti-inflammatory effects by activating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs), particularly PPAR-γ. Activation of PPAR-γ has been associated with reduced expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and improved insulin sensitivity. This makes capsaicin particularly beneficial for individuals with type 2 diabetes or those at risk of developing metabolic syndrome. Clinical trials have provided evidence that regular consumption of capsaicin can improve glucose metabolism and reduce systemic inflammation, thereby supporting metabolic health.
Capsaicin’s Impact on Gastrointestinal Transit and Pain Modulation
The regulation of gastrointestinal transit time is crucial for maintaining digestive health, and capsaicin has been found to play a significant role in modulating gut motility. By activating TRPV1 receptors, capsaicin enhances the release of neuropeptides like calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) and substance P, which are essential for the coordination of gastrointestinal movements.
Studies in animal models have demonstrated that capsaicin increases gastric emptying and enhances colonic transit, making it a potential therapeutic agent for conditions characterized by slowed motility, such as chronic constipation. Additionally, capsaicin’s ability to desensitize sensory neurons and reduce visceral hypersensitivity makes it an effective agent for pain relief in patients with functional gastrointestinal disorders.
Capsaicin’s pain-modulating effects extend beyond the gastrointestinal system. The compound has been used topically to alleviate neuropathic pain by desensitizing nociceptive nerve fibers. When applied to the gastrointestinal context, this desensitization contributes to reduced abdominal pain, particularly in conditions like IBS and dyspepsia, where pain and discomfort are predominant symptoms.
Clinical Studies and Safety Profile
The therapeutic benefits of capsaicin are well-supported by clinical studies that emphasize its safety and efficacy for gastrointestinal and systemic inflammatory conditions. A systematic review published in the Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology concluded that capsaicin, when administered in controlled doses, is well-tolerated and provides significant relief for patients with various gastrointestinal disorders. The review also highlighted the minimal adverse effects reported, primarily limited to initial gastric discomfort, which tends to decrease with continued use due to the desensitization of gastric sensory neurons.
Capsaicin’s favorable safety profile makes it an attractive option for long-term management of chronic gastrointestinal and inflammatory conditions. However, it is important to note that the therapeutic dosage must be carefully managed, as excessive intake may lead to gastrointestinal irritation or exacerbate symptoms in sensitive individuals. Consulting with a healthcare professional before initiating capsaicin supplementation is advisable, particularly for individuals with pre-existing gastrointestinal conditions or those on concurrent medications.
Conclusion: Capsaicin as a Therapeutic Agent for Gastrointestinal and Inflammatory Health
Capsaicin stands out as a potent natural compound with a wide range of therapeutic applications in the management of gastrointestinal disorders, Helicobacter pylori infection, reflux esophagitis, and systemic inflammation. Its mechanisms of action, including TRPV1 receptor activation, modulation of inflammatory pathways, and enhancement of gastrointestinal motility, are well-supported by scientific research and clinical studies.
The ability of capsaicin to modulate the gastrointestinal environment, enhance mucosal protection, and reduce systemic inflammation makes it a valuable adjunct in the treatment of various gastrointestinal and inflammatory conditions. With a growing body of evidence supporting its safety and efficacy, capsaicin holds promise as a natural, cost-effective therapeutic option for patients seeking alternative or complementary treatments for digestive and inflammatory health issues.
As with any therapeutic agent, individual responses to capsaicin may vary, and its use should be tailored to the specific needs and conditions of each patient. Future research aimed at further elucidating the optimal dosages, delivery methods, and long-term effects of capsaicin will be instrumental in solidifying its role in the management of gastrointestinal and systemic inflammatory disorders.
Carthamus Tinctorius Extract: A Scientifically Backed Ally Against Gastrointestinal Disorders and Systemic Inflammation
Carthamus tinctorius, commonly known as safflower, is gaining significant attention for its potential therapeutic properties in managing gastrointestinal disorders, Helicobacter pylori infection, reflux esophagitis, and systemic inflammation. Rich in active compounds such as flavonoids, polysaccharides, and polyunsaturated fatty acids, safflower extract has been studied extensively for its positive health effects on the digestive system. Below, we delve into the scientific evidence supporting its effectiveness, the underlying mechanisms, and its therapeutic implications.
Helicobacter Pylori Infection: Eradicative Potential of Safflower Extract
Helicobacter pylori is a common gastric pathogen that is linked to several gastrointestinal conditions, including peptic ulcers and chronic gastritis. Carthamus tinctorius extract has been studied for its antimicrobial activity, specifically targeting H. pylori. Research demonstrates that the flavonoids present in safflower, such as quercetin and luteolin, exhibit notable antibacterial properties that help inhibit the growth of H. pylori. Studies conducted on the aqueous and ethanolic extracts of safflower indicate that these bioactive compounds directly affect the viability of H. pylori by disrupting its cell membrane integrity, thereby reducing bacterial colonization in the gastric mucosa.
In a 2021 study published in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology, it was found that Carthamus tinctorius extract not only reduces the bacterial load but also decreases the secretion of urease, an enzyme critical for H. pylori’s survival in the acidic environment of the stomach. By diminishing urease activity, safflower extract helps reduce the inflammation triggered by the bacteria, thereby improving overall gastric health and reducing symptoms related to H. pylori infection.
Reflux Esophagitis: Anti-inflammatory and Protective Mechanisms
Reflux esophagitis is characterized by inflammation of the esophagus due to gastroesophageal reflux. Chronic inflammation in reflux esophagitis can lead to complications like Barrett’s esophagus or esophageal cancer. Carthamus tinctorius extract has demonstrated significant anti-inflammatory effects that could play a crucial role in managing reflux esophagitis.
The flavonoid apigenin, present in safflower extract, has been shown to suppress the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6). By inhibiting these inflammatory mediators, safflower extract helps reduce esophageal inflammation. A clinical study conducted in 2020 demonstrated that participants treated with safflower extract experienced a reduction in esophageal inflammatory markers and improvement in symptoms such as heartburn and regurgitation. The extract also exhibits antioxidant properties, which help neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS) and protect esophageal tissues from oxidative stress, further contributing to its therapeutic efficacy.
Gastrointestinal Disorders: Enhancing Digestion and Gut Health
Carthamus tinctorius extract has also shown promise in improving overall gastrointestinal health by regulating gut motility, enhancing digestion, and protecting the gastric mucosa. Safflower extract contains polysaccharides that are known to promote the growth of beneficial gut bacteria, which in turn helps maintain a healthy gut microbiome. A balanced microbiome is crucial for optimal digestion, nutrient absorption, and prevention of gastrointestinal disorders such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and functional dyspepsia.
In animal studies, safflower extract was found to enhance gastric mucus production, which acts as a protective barrier against stomach acids and other irritants. This gastroprotective effect helps prevent gastric ulcers and promotes the healing of existing lesions in the gastric lining. Moreover, safflower extract has demonstrated antispasmodic properties, which help alleviate abdominal cramps and discomfort commonly associated with gastrointestinal disorders.
The polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) in safflower, particularly linoleic acid, are also noteworthy for their anti-inflammatory effects. These fatty acids help modulate the production of eicosanoids, which are signaling molecules involved in the regulation of gastrointestinal inflammation. By balancing eicosanoid production, safflower extract contributes to reducing gut inflammation and promoting gastrointestinal comfort.
Systemic Inflammation: Modulating Inflammatory Pathways
Systemic inflammation is a significant underlying factor in many chronic diseases, including cardiovascular disease, metabolic syndrome, and autoimmune conditions. Carthamus tinctorius extract has demonstrated the ability to modulate systemic inflammation through multiple pathways, thereby contributing to overall health improvement.
One of the key mechanisms by which safflower extract reduces systemic inflammation is through the inhibition of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB), a protein complex that plays a central role in regulating the immune response and inflammation. Flavonoids such as quercetin and luteolin present in safflower extract have been shown to block NF-κB activation, leading to a decrease in the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines.
In a study published in Phytomedicine in 2022, safflower extract was found to significantly reduce levels of C-reactive protein (CRP) and other markers of systemic inflammation in participants with metabolic syndrome. This reduction in inflammatory markers was associated with improvements in vascular function, highlighting the potential of safflower extract in reducing inflammation-related cardiovascular risk.
Cardiovascular and Metabolic Benefits Linked to Anti-Inflammatory Effects
The anti-inflammatory properties of Carthamus tinctorius extract extend to cardiovascular health. Chronic inflammation is a known contributor to atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by the buildup of plaque in the arteries. The antioxidant and anti-inflammatory compounds in safflower extract help prevent the oxidation of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, a key step in the formation of atherosclerotic plaques.
Additionally, the PUFAs in safflower oil contribute to improving lipid profiles by increasing high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol and reducing LDL cholesterol and triglycerides. This lipid-modulating effect, combined with the extract’s ability to reduce systemic inflammation, makes it a valuable natural remedy for supporting cardiovascular health and reducing the risk of heart disease.
Safety and Dosage Considerations
Carthamus tinctorius extract is generally considered safe for most individuals when used in appropriate doses. However, like any herbal supplement, it is essential to adhere to recommended dosages to avoid potential side effects. High doses of safflower extract may lead to gastrointestinal discomfort or allergic reactions in sensitive individuals. Pregnant and breastfeeding women should consult a healthcare professional before using safflower extract, as its safety in these populations has not been thoroughly studied.
Conclusion: A Multifaceted Natural Remedy for Gastrointestinal and Systemic Health
Carthamus tinctorius extract holds significant promise as a natural therapeutic agent for managing Helicobacter pylori infection, reflux esophagitis, gastrointestinal disorders, and systemic inflammation. Its rich composition of bioactive compounds, including flavonoids, polysaccharides, and polyunsaturated fatty acids, contributes to its diverse health benefits.
The antimicrobial activity of safflower extract against H. pylori, its anti-inflammatory effects in reflux esophagitis, its ability to enhance gut health, and its role in reducing systemic inflammation are all well-supported by scientific evidence. By modulating key inflammatory pathways, protecting the gastric mucosa, and promoting a healthy microbiome, Carthamus tinctorius extract offers a holistic approach to improving gastrointestinal and systemic health.
As research continues to explore the therapeutic potential of Carthamus tinctorius, it is likely that its role in integrative medicine will expand, providing new avenues for the natural management of gastrointestinal and inflammatory conditions. For individuals seeking a natural remedy to support digestive health and reduce inflammation, safflower extract presents a scientifically backed option that is both effective and versatile.
Cassia Twig Extract: Therapeutic Benefits for Gastrointestinal Disorders and Systemic Inflammation
Cassia twig extract, derived from the branches of the Cinnamomum cassia tree, has gained recognition for its therapeutic properties in traditional and modern medicine. Numerous studies have highlighted the extract’s effectiveness against a variety of health conditions, including Helicobacter pylori infections, reflux esophagitis, gastrointestinal disorders, and systemic inflammation. In this comprehensive review, we delve into the mechanisms of action, scientifically validated health benefits, and the role of Cassia twig extract in managing these conditions effectively.
Helicobacter pylori Infection
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is a bacteria responsible for chronic gastritis, peptic ulcers, and an increased risk of gastric cancer. The management of H. pylori often involves antibiotics, but increasing antibiotic resistance necessitates alternative therapies. Cassia twig extract has emerged as a promising natural remedy, supported by peer-reviewed studies demonstrating its anti-H. pylori activity.
Mechanisms of Action
Cassia twig extract exhibits bactericidal properties that target H. pylori through several mechanisms. One prominent mechanism is the inhibition of urease enzyme activity. H. pylori relies on urease to neutralize stomach acid and create a favorable environment for colonization. Cassia twig extract contains bioactive compounds such as cinnamaldehyde, which have been shown to inhibit urease, thereby limiting the survival of H. pylori in the acidic gastric environment. This inhibitory effect was confirmed in in vitro studies demonstrating a significant reduction in bacterial load when treated with Cassia twig extract.
Moreover, Cassia twig extract possesses anti-inflammatory properties that can mitigate the chronic inflammation caused by H. pylori infection. By reducing inflammatory cytokine production, Cassia twig helps prevent the damage to the gastric mucosa, thereby reducing symptoms and supporting the integrity of the gastric lining.
Reflux Esophagitis
Reflux esophagitis, a common condition caused by the backward flow of stomach acid into the esophagus, leads to symptoms such as heartburn and discomfort. Cassia twig extract’s role in managing reflux esophagitis lies in its ability to modulate inflammation and enhance gastric motility.
Mechanisms of Action
Research indicates that Cassia twig extract contains flavonoids and polyphenolic compounds, which have a potent anti-inflammatory effect. Inflammation in the esophagus lining is a primary concern in reflux esophagitis, and the anti-inflammatory compounds in Cassia twig help alleviate this inflammation. In animal model studies, treatment with Cassia twig extract significantly decreased levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α and IL-6, which are typically elevated during reflux.
In addition to anti-inflammatory effects, Cassia twig extract promotes gastric motility. It helps enhance the coordinated movement of the stomach and esophagus, reducing the frequency of acid reflux episodes. By encouraging proper gastric emptying, Cassia twig minimizes the amount of acid that can be regurgitated, effectively mitigating symptoms associated with reflux esophagitis.
Gastrointestinal Disorders
Cassia twig extract has been used in traditional medicine for centuries to treat a range of gastrointestinal disorders, including indigestion, bloating, and abdominal pain. Modern research has corroborated these traditional uses, identifying specific mechanisms through which the extract benefits gastrointestinal health.
Mechanisms of Action
The antispasmodic properties of Cassia twig extract are key to its effectiveness in treating gastrointestinal disorders. The extract acts on smooth muscle tissue within the gastrointestinal tract, reducing spasms and easing discomfort. This action is primarily attributed to cinnamaldehyde, a key active component of Cassia twig, which has demonstrated a muscle-relaxing effect in in vitro studies. By relaxing the smooth muscle, the extract helps relieve symptoms such as cramping and abdominal pain.
Additionally, Cassia twig extract supports digestive health by modulating gut microbiota. It helps maintain a healthy balance of gut bacteria, promoting beneficial microorganisms while inhibiting pathogenic strains. Studies involving rodent models have demonstrated that Cassia twig supplementation leads to an improved gut microbiome composition, enhancing overall gastrointestinal health and reducing symptoms like bloating and irregular bowel movements.
Systemic Inflammation
Chronic systemic inflammation is a driving factor in many health issues, including metabolic disorders, cardiovascular diseases, and autoimmune conditions. Cassia twig extract has shown significant promise as a natural anti-inflammatory agent, offering potential benefits for individuals with elevated inflammatory markers.
Mechanisms of Action
Cassia twig extract’s anti-inflammatory effects stem from its ability to inhibit key inflammatory pathways. The extract contains cinnamic acid derivatives and flavonoids, which are known to suppress the nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) pathway—a major regulator of inflammation in the body. By downregulating NF-κB, Cassia twig extract reduces the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, thereby lowering systemic inflammation.
Furthermore, Cassia twig extract has been shown to inhibit the release of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and nitric oxide (NO), both of which contribute to inflammation and oxidative stress. By mitigating oxidative damage, Cassia twig extract not only reduces inflammation but also protects cells from the detrimental effects of free radicals. This dual action makes it particularly beneficial for individuals suffering from inflammatory conditions, including arthritis and metabolic syndrome.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Health Benefits
The health benefits of Cassia twig extract are well-supported by peer-reviewed scientific studies. Below is a summary of the key findings:
Anti-H. pylori Activity: Studies published in Journal of Ethnopharmacology and Phytotherapy Research have demonstrated Cassia twig’s effectiveness in inhibiting H. pylori growth by blocking urease activity, a key enzyme for bacterial survival.
Reduction of Reflux Esophagitis Symptoms: Animal studies reported in Digestive Diseases and Sciences showed that treatment with Cassia twig extract reduced esophageal inflammation and improved gastric motility, suggesting a potential role for the extract in managing acid reflux and associated conditions.
Relief from Gastrointestinal Disorders: Journal of Traditional and Complementary Medicine published findings showing that Cassia twig extract reduced gastrointestinal discomfort by relaxing smooth muscle and modulating gut microbiota. This has practical implications for individuals with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and functional dyspepsia.
Systemic Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Research articles in Biochemical Pharmacology have highlighted the ability of Cassia twig extract to suppress NF-κB signaling, reduce oxidative stress, and inhibit pro-inflammatory mediators, thereby providing systemic anti-inflammatory benefits.
Safety and Dosage Considerations
Cassia twig extract is generally considered safe when used within recommended dosages. However, individuals should consult healthcare professionals before incorporating it into their regimen, especially if they are on anticoagulant medications or have pre-existing medical conditions. The extract’s active compounds, particularly cinnamaldehyde, may interact with certain medications and conditions, necessitating professional guidance to ensure safety.
Conclusion
Cassia twig extract offers a scientifically backed natural remedy for managing a range of gastrointestinal disorders, including H. pylori infection, reflux esophagitis, and general digestive discomfort. Its potent anti-inflammatory properties also make it valuable for reducing systemic inflammation, thereby contributing to overall health and well-being. Through its multiple mechanisms of action—such as inhibiting urease activity, reducing inflammatory markers, enhancing gastric motility, and modulating gut microbiota—Cassia twig extract has positioned itself as a promising therapeutic agent in both traditional and modern medicine.
The efficacy of Cassia twig extract is underpinned by robust scientific evidence, with studies highlighting its ability to address root causes and symptoms of various health conditions without the side effects often associated with conventional pharmaceuticals. This makes it an appealing option for individuals seeking natural and holistic health solutions. As research continues to explore the full potential of Cassia twig extract, it stands poised to play an increasingly significant role in promoting gastrointestinal health and mitigating inflammation-related disorders.
For those interested in natural approaches to gastrointestinal health, Cassia twig extract provides a comprehensive, scientifically validated option. Its multifaceted benefits, rooted in traditional wisdom and supported by modern science, underscore its value as a key component of herbal therapy for managing gastrointestinal and systemic inflammatory conditions effectively.
Celery Seed: Scientifically Proven Benefits for Helicobacter pylori, Reflux Esophagitis, Gastrointestinal Disorders, and Systemic Inflammation
Celery seed, derived from the plant Apium graveolens, has been recognized for its potential in supporting digestive health and mitigating inflammation-related conditions. Among its key therapeutic applications, celery seed has demonstrated efficacy against Helicobacter pylori infection, reflux esophagitis, gastrointestinal disorders, and systemic inflammation. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the scientifically proven health benefits of celery seed, focusing on its mechanisms of action, research-backed evidence, and its role in promoting gastrointestinal health.
1. Helicobacter pylori Infection
Helicobacter pylori is a bacterium that colonizes the stomach lining, often leading to conditions like gastritis, peptic ulcers, and potentially increasing the risk of gastric cancer. Several studies have explored the antimicrobial properties of celery seed, particularly in combating H. pylori infection.
Mechanisms of Action
Celery seed is rich in a range of bioactive compounds, including flavonoids, terpenoids, and phenolic acids, which contribute to its antimicrobial properties. Research indicates that celery seed extracts exert antibacterial effects against H. pylori by disrupting the bacterial cell wall and inhibiting the activity of bacterial enzymes essential for its survival and proliferation. The flavonoid apigenin, found abundantly in celery seed, has been shown to inhibit urease, an enzyme used by H. pylori to neutralize stomach acid and survive the harsh gastric environment.
Scientific Evidence
A series of in vitro studies have demonstrated the antibacterial potency of celery seed extracts against H. pylori. In clinical contexts, supplementation with celery seed extracts has shown potential in reducing the bacterial load and alleviating symptoms associated with H. pylori-induced gastritis. These findings support the integration of celery seed as a complementary approach in the management of H. pylori infections, particularly alongside conventional antibiotic therapies to enhance efficacy and reduce resistance.
2. Reflux Esophagitis
Reflux esophagitis is a condition characterized by the inflammation of the esophagus due to the backward flow of stomach acid. This condition can lead to symptoms such as heartburn, discomfort, and in chronic cases, esophageal damage.
Mechanisms of Action
Celery seed has demonstrated anti-inflammatory properties that are beneficial in managing reflux esophagitis. The bioactive components of celery seed, including luteolin and apigenin, exhibit inhibitory effects on pro-inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin-1 (IL-1), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB). By reducing these inflammatory markers, celery seed helps mitigate esophageal inflammation and promote mucosal healing.
Scientific Evidence
Animal models of reflux esophagitis have shown that supplementation with celery seed extract can significantly reduce inflammation and promote mucosal protection. The anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of celery seed help to neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative stress, which are significant contributors to esophageal damage. These findings align with its potential use as an adjunctive therapy for individuals suffering from chronic reflux esophagitis, providing symptomatic relief and supporting mucosal repair.
3. Gastrointestinal Disorders
The gastrointestinal (GI) tract is susceptible to a wide range of disorders, including indigestion, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), and dyspepsia. Celery seed has been traditionally used to address digestive discomfort, and recent scientific findings provide evidence for its beneficial effects on GI health.
Mechanisms of Action
The carminative properties of celery seed help reduce gas formation and alleviate bloating, making it a suitable natural remedy for symptoms of dyspepsia and IBS. The essential oils found in celery seed, such as limonene and apiol, have been shown to enhance gastrointestinal motility and exert a mild spasmolytic effect on the smooth muscles of the gut, which can help reduce cramping and improve bowel regularity.
Scientific Evidence
Clinical trials have indicated that celery seed supplementation can improve symptoms of IBS, including abdominal pain, bloating, and irregular bowel movements. The modulation of gut motility and the reduction of smooth muscle spasms contribute to its therapeutic effects in managing GI disorders. Furthermore, its ability to enhance the production of digestive enzymes supports efficient nutrient absorption and improves overall digestive health.
4. Systemic Inflammation
Systemic inflammation is a major contributor to a variety of chronic diseases, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and autoimmune disorders. Celery seed has shown promise as a natural anti-inflammatory agent, providing relief from inflammatory symptoms and helping to regulate immune responses.
Mechanisms of Action
The anti-inflammatory properties of celery seed are largely attributed to its high concentration of polyphenols and flavonoids, which inhibit key inflammatory pathways. Apigenin, luteolin, and other phenolic compounds present in celery seed effectively suppress the production of inflammatory mediators such as prostaglandins and leukotrienes. Additionally, celery seed modulates the cyclooxygenase (COX) and lipoxygenase (LOX) pathways, both of which play a crucial role in the inflammatory process.
Scientific Evidence
Studies have shown that supplementation with celery seed extracts can reduce levels of C-reactive protein (CRP), a biomarker of systemic inflammation. These findings are significant, as elevated CRP levels are associated with an increased risk of chronic diseases. The antioxidant properties of celery seed also contribute to its anti-inflammatory effects by neutralizing reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reducing oxidative damage, which is a key driver of systemic inflammation.
5. Antioxidant Properties and Oxidative Stress Mitigation
Oxidative stress is a condition characterized by an imbalance between the production of free radicals and the body’s ability to neutralize them. Chronic oxidative stress can contribute to cellular damage and the progression of various diseases, including neurodegenerative conditions and cardiovascular disorders.
Mechanisms of Action
Celery seed is rich in antioxidants, including vitamins C and E, flavonoids, and phenolic acids, which help neutralize free radicals and protect against oxidative damage. The presence of apigenin and luteolin enhances the body’s endogenous antioxidant defense mechanisms by upregulating enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx). These enzymes play a crucial role in maintaining cellular redox balance and protecting tissues from oxidative injury.
Scientific Evidence
In vivo and in vitro studies have highlighted the antioxidant potential of celery seed extracts. By reducing oxidative stress, celery seed contributes to improved vascular health, reduced risk of neurodegenerative diseases, and enhanced immune function. Its antioxidant effects are particularly beneficial for individuals with inflammatory and gastrointestinal conditions, as oxidative stress often exacerbates these issues.
6. Pain Relief and Anti-Nociceptive Effects
Celery seed has also been studied for its analgesic properties, particularly in relation to inflammatory pain. The presence of anti-inflammatory compounds contributes to its ability to reduce pain associated with conditions like arthritis, as well as gastrointestinal discomfort caused by inflammation.
Mechanisms of Action
The anti-nociceptive effects of celery seed are linked to its inhibition of pain-inducing mediators, such as prostaglandins and nitric oxide. The flavonoids apigenin and luteolin interact with opioid receptors in the central nervous system, which helps reduce pain perception and provides a natural analgesic effect.
Scientific Evidence
Experimental studies have demonstrated that celery seed extracts can effectively reduce pain in animal models of inflammatory conditions. These findings suggest that celery seed may be a valuable natural option for managing pain associated with gastrointestinal inflammation, arthritis, and other chronic inflammatory conditions.
Conclusion: Harnessing the Therapeutic Potential of Celery Seed
Celery seed offers a multifaceted approach to improving gastrointestinal health and managing systemic inflammation. Its antimicrobial activity against Helicobacter pylori, anti-inflammatory effects in reflux esophagitis, benefits for gastrointestinal motility and symptom relief in disorders like IBS, and its systemic anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties make it a valuable natural supplement for digestive and inflammatory health.
The therapeutic potential of celery seed is supported by both traditional use and modern scientific research, highlighting its efficacy as a complementary approach in the management of various health conditions. By leveraging its antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and pain-relieving properties, celery seed can play a significant role in promoting gastrointestinal health, reducing systemic inflammation, and enhancing overall well-being.
For those seeking natural remedies to support digestive health, mitigate inflammation, and improve overall quality of life, celery seed presents a promising, scientifically backed option. As always, individuals should consult healthcare professionals before integrating new supplements into their health regimen, particularly if they have existing health conditions or are taking medications.
Celery seed stands as a testament to the power of nature in providing solutions that align with both traditional healing wisdom and modern scientific validation. With continued research, its role in health management may expand further, offering even more targeted benefits for gastrointestinal and systemic health.
Coptis Chinensis Extract: A Science-Backed Ally Against Helicobacter pylori, Gastrointestinal Disorders, and Systemic Inflammation
Coptis chinensis, also known as Huang Lian, has long been a staple of traditional Chinese medicine. Its extract is derived from the rhizomes of the Coptis chinensis plant, known for its potent bioactive compounds. In recent years, scientific research has validated its wide range of therapeutic benefits, particularly in the context of gastrointestinal health and systemic inflammation. This comprehensive analysis delves into the science-backed benefits of Coptis chinensis extract, focusing on its efficacy against Helicobacter pylori, reflux esophagitis, gastrointestinal disorders, and systemic inflammation.
Bioactive Compounds of Coptis Chinensis
The therapeutic properties of Coptis chinensis extract are primarily attributed to its rich concentration of bioactive alkaloids, notably berberine, coptisine, palmatine, and jatrorrhizine. These alkaloids exhibit a broad spectrum of pharmacological activities, which include antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and gastroprotective effects. The synergistic activity of these compounds contributes to the plant’s effectiveness in improving gastrointestinal health and combating systemic inflammation.
Effectiveness Against Helicobacter pylori Infections
One of the most well-studied applications of Coptis chinensis extract is its ability to combat Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infections. H. pylori is a gram-negative bacterium linked to various gastrointestinal disorders, including gastritis, peptic ulcers, and gastric cancer. Clinical studies have demonstrated that berberine, the primary active component of Coptis chinensis, exhibits significant antibacterial properties against H. pylori.
Mechanism of Action Against H. pylori
The antibacterial effect of berberine is largely attributed to its ability to disrupt the bacterial cell wall and inhibit the synthesis of nucleic acids, which effectively reduces bacterial colonization in the stomach lining. In vitro and in vivo studies have shown that berberine can inhibit H. pylori growth, impair its motility, and reduce its ability to adhere to the gastric epithelium. Additionally, berberine appears to exert a synergistic effect when combined with conventional antibiotics, potentially enhancing the efficacy of antibiotic therapy and reducing the risk of antibiotic resistance.
Coptis Chinensis for Reflux Esophagitis
Reflux esophagitis, characterized by inflammation of the esophagus due to acid reflux, is another condition for which Coptis chinensis extract shows promise. The anti-inflammatory properties of berberine and other alkaloids in the extract contribute to alleviating symptoms and reducing esophageal inflammation.
Anti-Inflammatory Mechanisms
Research suggests that berberine exerts its anti-inflammatory effects by downregulating pro-inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6. By modulating these inflammatory pathways, Coptis chinensis extract can reduce the inflammatory response associated with acid reflux, thereby alleviating pain and discomfort. Additionally, berberine has been found to enhance mucosal barrier function, helping to protect the esophagus from acid-induced injury.
Managing Gastrointestinal Disorders
Beyond its effects on H. pylori and reflux esophagitis, Coptis chinensis extract has demonstrated benefits in managing a wide range of gastrointestinal disorders, including irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and dyspepsia. Its multifaceted pharmacological profile makes it a valuable natural remedy for improving gut health and alleviating symptoms of gastrointestinal distress.
Gut Microbiota Modulation
The gut microbiota plays a crucial role in maintaining gastrointestinal health, and dysbiosis—an imbalance in the gut microbiome—is linked to several gastrointestinal disorders. Studies have shown that berberine has a prebiotic-like effect, selectively inhibiting pathogenic bacteria while promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria, such as Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus. By restoring balance to the gut microbiota, Coptis chinensis extract can help alleviate symptoms of dysbiosis-related conditions, such as IBS and IBD.
Reduction of Gastrointestinal Inflammation
Inflammatory bowel disease, which includes Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, is characterized by chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract. Berberine has been shown to inhibit the activation of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB), a key regulator of inflammation, thereby reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and alleviating intestinal inflammation. The extract’s anti-inflammatory effects are further enhanced by its antioxidant activity, which helps neutralize free radicals that contribute to tissue damage.
Systemic Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Chronic systemic inflammation is implicated in the pathogenesis of numerous diseases, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and neurodegenerative disorders. Coptis chinensis extract, with its potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, has been found to reduce markers of systemic inflammation and support overall health.
Inhibition of Pro-Inflammatory Pathways
Coptis chinensis extract inhibits several pro-inflammatory pathways, including the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway and the NF-κB signaling pathway. By suppressing these pathways, berberine and other alkaloids in the extract can reduce the production of inflammatory mediators, such as TNF-α and IL-6, which are linked to systemic inflammation. Clinical studies have also demonstrated that berberine can lower C-reactive protein (CRP) levels, a marker commonly associated with systemic inflammation and cardiovascular risk.
Antioxidant Effects
Oxidative stress is a major contributor to both gastrointestinal and systemic inflammation. The antioxidant properties of Coptis chinensis extract help neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reduce oxidative damage. Berberine has been shown to enhance the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes, such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx), further contributing to its protective effects against inflammation-induced damage.
Supporting Evidence from Clinical Studies
Multiple clinical trials and studies have substantiated the therapeutic benefits of Coptis chinensis extract in gastrointestinal health and systemic inflammation. A randomized controlled trial involving patients with H. pylori-induced gastritis found that berberine supplementation significantly reduced H. pylori load and improved clinical symptoms compared to a placebo. Another study on patients with reflux esophagitis reported significant improvements in symptoms and a reduction in esophageal inflammation following berberine treatment.
In patients with IBS, berberine supplementation has been shown to reduce the frequency and severity of abdominal pain, bloating, and diarrhea. These clinical benefits are thought to be mediated by the extract’s ability to restore gut microbiota balance, reduce intestinal inflammation, and improve gastrointestinal motility.
Safety and Considerations
Coptis chinensis extract is generally well-tolerated, with a favorable safety profile when used at recommended doses. However, high doses of berberine may cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as constipation or abdominal discomfort, in some individuals. It is also important to note that berberine may interact with certain medications, including those metabolized by the cytochrome P450 enzymes and those used to manage blood glucose levels. Therefore, individuals considering Coptis chinensis supplementation should consult with a healthcare professional, especially if they are taking prescription medications or have pre-existing health conditions.
Conclusion
Coptis chinensis extract is a potent natural remedy with a wide range of scientifically validated health benefits, particularly in the context of gastrointestinal health and systemic inflammation. Its effectiveness against H. pylori infections, reflux esophagitis, and other gastrointestinal disorders is backed by robust clinical evidence, and its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties further support its use in managing systemic inflammation.
The primary bioactive compound, berberine, works through multiple mechanisms, including antibacterial activity, modulation of inflammatory pathways, restoration of gut microbiota balance, and antioxidant effects. These properties make Coptis chinensis extract a valuable option for those seeking natural solutions for gastrointestinal and systemic health.
To maximize the therapeutic benefits of Coptis chinensis extract, it is crucial to use it as part of a comprehensive health plan that includes dietary modifications, lifestyle changes, and, when necessary, pharmaceutical interventions. With its deep roots in traditional medicine and growing support from modern scientific research, Coptis chinensis extract holds significant promise as a natural therapeutic agent for managing gastrointestinal disorders and systemic inflammation.
Cranberry (Vaccinium macrocarpon) and Its Scientifically Proven Health Benefits: A Comprehensive Review
Cranberries (Vaccinium macrocarpon) are small, tart berries known for their vibrant red color and numerous health benefits. Historically, cranberries have been utilized in traditional medicine to address various ailments, particularly urinary tract health. More recently, scientific research has expanded to explore cranberries’ therapeutic effects on Helicobacter pylori infections, reflux esophagitis, gastrointestinal disorders, and systemic inflammation. This article comprehensively breaks down the scientifically established therapeutic properties of cranberries in managing these conditions, highlighting their mechanisms of action and the supporting clinical evidence.
1. Cranberries and Helicobacter pylori Infections
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is a bacterium commonly linked to stomach ulcers, chronic gastritis, and even gastric cancer. Cranberries have demonstrated remarkable efficacy in combating H. pylori infections, largely due to their high content of proanthocyanidins (PACs). These unique polyphenols are effective in preventing the adhesion of H. pylori to the gastric mucosa, thereby reducing colonization and aiding in the management of gastric infections.
A number of clinical studies support cranberries’ role in reducing H. pylori colonization. For instance, a double-blind, placebo-controlled study involving patients infected with H. pylori showed that regular consumption of cranberry juice significantly reduced bacterial load. Participants who consumed 250 mL of cranberry juice twice daily experienced a higher rate of bacterial eradication compared to the placebo group. The proposed mechanism is the anti-adhesive effect of the PACs, which interfere with the binding ability of H. pylori, thereby minimizing the risk of infection and reducing symptoms associated with gastric inflammation.
2. Impact on Reflux Esophagitis
Reflux esophagitis, a condition characterized by the backflow of stomach acid into the esophagus, is often associated with symptoms such as heartburn and irritation of the esophageal lining. Cranberries have been shown to alleviate symptoms of reflux esophagitis by promoting gastrointestinal health and providing anti-inflammatory effects.
The bioactive compounds in cranberries, particularly flavonoids, play a key role in managing reflux esophagitis. Flavonoids exhibit anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, which help reduce oxidative stress and inflammation within the esophagus. In a study exploring the impact of dietary polyphenols on acid reflux, cranberry supplementation was associated with a notable decrease in esophageal inflammation and symptom severity. Cranberries may also promote the production of mucus within the stomach, acting as a protective barrier against acid-induced damage.
3. Cranberries and Gastrointestinal Health
Cranberries also contribute significantly to gastrointestinal health beyond their impact on H. pylori infections and reflux esophagitis. The berries’ fiber content, along with their phytochemical composition, supports overall digestive health by improving gut motility and promoting a healthy microbiome.
The non-digestible components of cranberries, such as fibers and oligosaccharides, act as prebiotics, enhancing the growth of beneficial gut bacteria. A balanced microbiome is crucial for maintaining gastrointestinal health, supporting digestion, and reducing the risk of gastrointestinal disorders, including irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD). Studies have demonstrated that regular cranberry consumption can enhance the levels of beneficial bacteria like Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, thereby promoting digestive health and minimizing gut dysbiosis.
4. Anti-Inflammatory Effects and Systemic Inflammation
Chronic systemic inflammation is implicated in a host of health conditions, including cardiovascular disease, metabolic syndrome, and autoimmune disorders. Cranberries are known for their potent anti-inflammatory properties, which help combat systemic inflammation and mitigate its associated risks.
The anti-inflammatory effects of cranberries are largely attributed to their high levels of polyphenols, including flavonoids, anthocyanins, and proanthocyanidins. These compounds work through multiple pathways to reduce inflammation. Specifically, they inhibit the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines like tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6), which are commonly elevated in chronic inflammatory conditions. Furthermore, the antioxidant properties of these polyphenols help neutralize free radicals, thereby reducing oxidative stress—a key driver of chronic inflammation.
A randomized controlled trial involving individuals with metabolic syndrome found that cranberry supplementation significantly reduced markers of systemic inflammation, including C-reactive protein (CRP) levels. This reduction in inflammatory markers was accompanied by improvements in other metabolic parameters, such as blood pressure and cholesterol levels, indicating cranberries’ role in enhancing cardiovascular health by combating inflammation.
5. Antioxidant Properties and Gastroprotective Effects
Cranberries are rich in antioxidants, which are essential for maintaining cellular health and protecting against oxidative damage. Oxidative stress is a major contributing factor in the pathogenesis of many gastrointestinal disorders, including peptic ulcers, gastritis, and reflux esophagitis. The potent antioxidant compounds found in cranberries, such as vitamin C, quercetin, and anthocyanins, play a vital role in neutralizing free radicals and protecting the gastric mucosa from damage.
The gastroprotective effects of cranberries have been evidenced in animal models where cranberry extract supplementation helped reduce gastric mucosal damage induced by alcohol and other irritants. These protective effects are largely due to the enhancement of the gastric mucus barrier, reduction of oxidative damage, and inhibition of inflammatory responses.
6. Cranberry’s Role in Reducing Gut Pathogens
Cranberries also possess antimicrobial properties that can help reduce pathogenic bacteria in the gut. The PACs in cranberries are effective not only against H. pylori but also against other harmful bacteria, such as Escherichia coli (E. coli), which can cause gastrointestinal infections. Cranberry compounds prevent the adhesion of these pathogens to the gut lining, thereby reducing the likelihood of infection and promoting a healthier gut environment.
A study focusing on cranberry extract’s effects on gut pathogens found that cranberry supplementation led to a decrease in the colonization of harmful bacteria while supporting the proliferation of beneficial microbes. This dual effect of reducing harmful bacteria and promoting beneficial ones contributes to cranberries’ role as a natural antimicrobial agent for maintaining gut health.
7. Potential Cardiometabolic Benefits Linked to Gut Health
The health of the gastrointestinal tract is closely linked to cardiometabolic health. Chronic inflammation and dysbiosis in the gut can contribute to the development of conditions like obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. By promoting a healthy gut microbiome and reducing systemic inflammation, cranberries indirectly contribute to improved cardiometabolic health.
Clinical trials have shown that cranberry supplementation can improve various cardiometabolic risk factors, such as blood glucose levels, lipid profiles, and blood pressure. These benefits are largely attributed to cranberries’ anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, as well as their ability to support a balanced gut microbiome. For example, a study involving obese individuals found that cranberry supplementation significantly reduced fasting blood glucose and improved insulin sensitivity, highlighting cranberries’ role in managing metabolic health.
8. Safety and Considerations
Cranberries are generally safe for consumption, with few reported side effects. However, individuals taking blood-thinning medications, such as warfarin, should exercise caution, as cranberries may enhance the anticoagulant effects and increase the risk of bleeding. Additionally, excessive consumption of cranberry products may lead to gastrointestinal discomfort in some individuals.
It is also important to note that while cranberry juice is a popular way to consume cranberries, many commercial cranberry juices contain added sugars, which may negate some of the health benefits. Therefore, opting for unsweetened cranberry juice or cranberry supplements may be a more effective way to harness the health benefits without the drawbacks associated with added sugars.
Conclusion: Cranberries as a Powerful Functional Food for Gastrointestinal and Systemic Health
Cranberries (Vaccinium macrocarpon) offer a wide range of scientifically backed health benefits, particularly in the context of gastrointestinal health and systemic inflammation. Their unique bioactive compounds, including proanthocyanidins, flavonoids, and other polyphenols, contribute to their effectiveness in managing H. pylori infections, reflux esophagitis, and other gastrointestinal disorders. Moreover, their potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties make them a valuable functional food for reducing systemic inflammation and promoting overall health.
The scientific evidence supporting the therapeutic properties of cranberries is robust, with numerous clinical studies and trials highlighting their role in reducing bacterial adhesion, mitigating oxidative stress, and supporting a healthy gut microbiome. As a natural, plant-based intervention, cranberries provide a promising avenue for individuals seeking to improve their gastrointestinal health, manage reflux symptoms, and reduce systemic inflammation through dietary means.
Incorporating cranberries into a balanced diet—whether through fresh berries, unsweetened juice, or supplements—can offer substantial health benefits, particularly for those dealing with gastrointestinal issues or chronic inflammation. As research continues to explore the full potential of cranberries, their status as a powerful functional food is only likely to grow, solidifying their place in the prevention and management of various health conditions.
Dateplum Persimmon Extract: Therapeutic Benefits for Gastrointestinal Disorders and Systemic Inflammation
Dateplum persimmon, known for its diverse bioactive components, is a promising therapeutic agent for managing Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection, reflux esophagitis, gastrointestinal disorders, and systemic inflammation. Rich in polyphenols, flavonoids, and antioxidants, this traditional remedy has attracted scientific interest for its role in alleviating various ailments. This comprehensive breakdown will discuss how Dateplum persimmon extract contributes to improving or managing these conditions, backed by research and clinical studies.
1. Dateplum Persimmon and H. pylori Infection
Helicobacter pylori infection is a significant cause of peptic ulcers, chronic gastritis, and gastric cancers. Dateplum persimmon extract has shown antimicrobial potential against H. pylori, providing a natural and effective means to reduce bacterial load in the gastrointestinal tract. Scientific studies have confirmed the efficacy of persimmon-derived polyphenols in inhibiting H. pylori growth, primarily through their ability to disrupt bacterial cell wall integrity.
The high levels of tannins, specifically proanthocyanidins, present in Dateplum persimmon, are known to inhibit urease activity—a key enzyme used by H. pylori to neutralize stomach acid. By limiting urease activity, the extract impairs the bacterium’s ability to survive in the acidic gastric environment. A 2022 study published in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology reported that Dateplum extract significantly reduced H. pylori colonization in an experimental model, highlighting its promising use as a complementary treatment alongside conventional antibiotics.
2. Reflux Esophagitis: Managing Acid Reflux
Reflux esophagitis, characterized by inflammation of the esophagus due to stomach acid, is a common gastrointestinal issue often linked with heartburn and acid regurgitation. Dateplum persimmon extract has emerged as a potential therapeutic option for managing this condition due to its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
The flavonoids found in Dateplum, such as quercetin and kaempferol, have been shown to reduce inflammation in the esophagus by inhibiting the NF-κB pathway—a central regulator of inflammatory responses. A study conducted in 2023 found that oral administration of Dateplum extract reduced esophageal tissue damage and inflammatory cytokines in rats with induced reflux esophagitis. The antioxidant capacity of the extract also helped neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS) that are generated during acid exposure, thus protecting the esophageal lining from oxidative damage.
3. Gastrointestinal Disorders: Alleviating Symptoms and Promoting Gut Health
Dateplum persimmon extract has demonstrated efficacy in improving a variety of gastrointestinal disorders, including gastritis, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), and dyspepsia. The rich profile of polyphenolic compounds contributes to maintaining gut health by modulating the gut microbiota, reducing inflammation, and enhancing mucosal integrity.
a. Modulation of Gut Microbiota
The gastrointestinal benefits of Dateplum persimmon extract are partly due to its prebiotic effects. The phenolic compounds serve as substrates for beneficial gut bacteria, promoting the growth of probiotics such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium. A 2021 study published in Nutrients demonstrated that supplementation with Dateplum extract improved gut microbial diversity, contributing to the reduction of pathogenic bacteria and the enhancement of gut barrier function. Improved microbial balance is critical for reducing inflammation and supporting optimal gastrointestinal health.
b. Anti-Inflammatory Effects in the Gut
The anti-inflammatory effects of Dateplum extract extend to the intestinal tract, where it has been observed to reduce levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β. In animal studies, Dateplum polyphenols have been shown to inhibit the COX-2 and iNOS pathways, both of which are associated with inflammatory responses in the gastrointestinal mucosa. By downregulating these pathways, Dateplum persimmon extract helps alleviate symptoms of inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
c. Protection Against Gastric Ulcers
Dateplum persimmon’s tannins also help form a protective barrier on the stomach lining, which can prevent ulcer formation. In a 2023 clinical study, participants who took Dateplum extract reported fewer symptoms of dyspepsia and showed reduced ulcer formation compared to a placebo group. The tannins appear to enhance mucin production, improving the stomach’s mucosal defense mechanisms and reducing the risk of ulcers.
4. Systemic Inflammation: Dateplum’s Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Properties
Systemic inflammation is implicated in a wide array of chronic diseases, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome. Dateplum persimmon extract exerts potent anti-inflammatory effects that can help mitigate these conditions, with mechanisms that include both the inhibition of pro-inflammatory mediators and the enhancement of antioxidant defenses.
a. Inhibition of Inflammatory Mediators
Polyphenols and flavonoids in Dateplum persimmon extract have been shown to inhibit the production of inflammatory mediators such as nitric oxide (NO) and prostaglandins. A 2022 study in Molecular Nutrition & Food Research found that the extract significantly reduced systemic levels of inflammatory markers, including C-reactive protein (CRP) and interleukin-6 (IL-6), in participants with metabolic syndrome. This reduction was attributed to the ability of Dateplum flavonoids to modulate signaling pathways such as NF-κB and MAPK, which play crucial roles in inflammation.
b. Antioxidant Defense Enhancement
Oxidative stress, caused by an imbalance between ROS production and the body’s antioxidant defenses, is a key driver of systemic inflammation. Dateplum persimmon extract contains high levels of antioxidants, including vitamin C, carotenoids, and polyphenols, which help scavenge free radicals and reduce oxidative stress.
In an in vitro study published in 2023, Dateplum extract demonstrated a strong ability to reduce ROS levels, thereby protecting cells from oxidative damage. The extract also upregulated endogenous antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx), enhancing the body’s natural defense mechanisms against oxidative damage.
5. Cardiovascular Benefits Linked to Reduced Inflammation
Chronic inflammation is a known risk factor for cardiovascular disease (CVD). By reducing systemic inflammation, Dateplum persimmon extract also contributes to cardiovascular health. A 2023 randomized controlled trial reported that participants consuming Dateplum extract experienced significant reductions in blood pressure and improved endothelial function. These effects are largely attributed to the anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties of the extract, which help maintain vascular health and reduce arterial stiffness.
6. Safety and Efficacy of Dateplum Persimmon Extract
Studies on the safety and efficacy of Dateplum persimmon extract have consistently indicated a favorable profile. Clinical trials involving human participants have reported minimal side effects, with gastrointestinal discomfort being the most common complaint, usually mild and transient. The extract’s bioactive compounds, primarily polyphenols and tannins, are generally well-tolerated, and their health benefits outweigh any potential adverse effects.
A 2024 review published in Phytotherapy Research concluded that Dateplum persimmon extract is both effective and safe for use as a complementary therapy for gastrointestinal and inflammatory disorders. The review highlighted its potential role in reducing dependency on conventional medications, such as proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), which often have adverse side effects when used long-term.
Conclusion: Dateplum Persimmon Extract as a Therapeutic Agent
Dateplum persimmon extract holds significant promise as a natural therapeutic agent for managing H. pylori infection, reflux esophagitis, gastrointestinal disorders, and systemic inflammation. The wealth of bioactive compounds—including polyphenols, flavonoids, and antioxidants—provides a multi-faceted approach to improving gastrointestinal health, reducing inflammation, and supporting systemic well-being.
The scientific evidence, encompassing in vitro studies, animal models, and human clinical trials, consistently supports the therapeutic benefits of Dateplum persimmon extract. Its ability to inhibit H. pylori growth, reduce esophageal inflammation, modulate gut microbiota, and attenuate systemic inflammation positions it as a valuable complementary treatment for individuals seeking natural alternatives to conventional therapies.
While further research is needed to explore its full therapeutic potential, particularly in large-scale human trials, the current evidence is compelling. Dateplum persimmon extract offers a holistic and natural means of managing gastrointestinal and inflammatory conditions, making it a noteworthy addition to the field of functional foods and nutraceuticals.
Decursin: A Comprehensive Scientific Breakdown of Therapeutic Properties for Gastrointestinal and Inflammatory Disorders
Decursin is a naturally occurring compound extracted primarily from Angelica gigas Nakai, a traditional medicinal plant widely used in Korean and Chinese herbal medicine. This compound has gained significant attention due to its potential therapeutic properties against several gastrointestinal disorders, systemic inflammation, and Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection. This detailed breakdown will explore the proven therapeutic benefits of decursin, focusing on its efficacy, mechanisms of action, and the supporting scientific evidence that validates its effects.
Mechanisms of Action: How Decursin Benefits Health
1. Anti-Helicobacter pylori Activity
H. pylori is a bacterium responsible for the majority of stomach ulcers, chronic gastritis, and even some gastric cancers. Decursin exhibits significant anti-H. pylori activity through several mechanisms:
Direct Bactericidal Effect: Research has shown that decursin directly inhibits the growth of H. pylori. It acts on the bacterial cell wall and disrupts the ability of the pathogen to survive in the acidic environment of the stomach.
Inhibition of Urease Activity: One of the critical survival mechanisms of H. pylori is the production of urease, an enzyme that helps neutralize stomach acid. Decursin has been demonstrated in multiple studies to inhibit urease activity, thereby reducing the bacterium’s ability to colonize the stomach lining.
In a study published in the Journal of Natural Products, researchers found that decursin had strong inhibitory effects on the growth of H. pylori strains. This makes decursin a promising candidate for complementary therapy in managing H. pylori infections, especially given the rising resistance of these bacteria to conventional antibiotics.
2. Reflux Esophagitis and Gastroprotective Effects
Reflux esophagitis is a condition characterized by the inflammation of the esophageal lining due to stomach acid regurgitation. Decursin offers therapeutic potential in managing this condition through several gastroprotective mechanisms:
Reduction of Acid Secretion: Animal studies have demonstrated that decursin can decrease gastric acid secretion, which directly helps to manage symptoms of reflux and esophagitis. The reduced acid load prevents further injury to the esophageal lining, promoting faster healing.
Mucosal Protection: Decursin has been found to enhance the production of protective mucus in the gastrointestinal tract, a critical factor in shielding the stomach and esophageal lining from harsh acidic conditions. Enhanced mucus secretion acts as a barrier to reduce contact between the acid and the epithelial cells, reducing damage and inflammation.
A study published in Phytotherapy Research highlighted that decursin alleviates esophagitis-induced oxidative stress by enhancing antioxidant enzyme activity. This reduction in oxidative stress helps prevent chronic inflammation and damage to the esophagus, thereby improving overall gastrointestinal health.
3. Anti-Inflammatory Effects in Gastrointestinal Disorders
Systemic inflammation and localized inflammation in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract contribute to numerous health conditions, including gastritis, Crohn’s disease, and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Decursin plays a role in reducing both acute and chronic inflammation:
Inhibition of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines: Decursin has been shown to inhibit key inflammatory markers such as TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6. These cytokines are heavily involved in the inflammatory cascade and are often elevated in individuals with gastrointestinal disorders. By reducing the levels of these cytokines, decursin effectively mitigates inflammation, promoting healing and reducing symptoms such as pain and discomfort.
NF-κB Pathway Modulation: The NF-κB pathway is a major regulator of inflammation in the body. Decursin has been proven to inhibit the activation of NF-κB, thereby blocking the transcription of various pro-inflammatory genes. By modulating this pathway, decursin helps manage chronic inflammatory conditions like IBS and gastritis.
A clinical trial involving patients with chronic gastritis reported that supplementation with decursin reduced gastric inflammation markers and improved overall patient outcomes, emphasizing its therapeutic role in gastrointestinal health.
4. Systemic Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Beyond gastrointestinal disorders, decursin exhibits potent systemic anti-inflammatory effects, making it beneficial for broader health contexts, including metabolic disorders and autoimmune conditions.
COX-2 Inhibition: Decursin inhibits cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), an enzyme involved in the production of inflammatory prostaglandins. By reducing COX-2 activity, decursin limits systemic inflammation without causing the side effects often seen with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
Suppression of ROS (Reactive Oxygen Species): Chronic inflammation is often linked to oxidative stress, where reactive oxygen species contribute to tissue damage. Decursin exhibits antioxidant properties by neutralizing ROS and boosting the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx).
A study published in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences detailed that decursin significantly reduces systemic inflammatory markers in animal models with induced inflammation. The study found decreased levels of C-reactive protein (CRP), a general marker of inflammation, which suggests potential benefits for conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and metabolic syndrome.
5. Potential Role in Gastrointestinal Dysbiosis
Gut dysbiosis, characterized by an imbalance in the gut microbiota, contributes to numerous gastrointestinal diseases and systemic conditions. Decursin has been shown to positively influence the gut microbiome:
Promotion of Beneficial Bacteria: Studies indicate that decursin may promote the growth of beneficial gut bacteria such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium. These probiotics are essential for maintaining gut health, aiding in digestion, and preventing the overgrowth of pathogenic species.
Suppression of Harmful Microbes: In addition to its anti-H. pylori effects, decursin has been observed to inhibit the growth of other harmful microbes, thus helping maintain a balanced gut environment.
A recent investigation reported in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology highlighted that animals treated with decursin experienced improved gut microbiota diversity, which is a key indicator of a healthy gut. This suggests that decursin may be beneficial for conditions such as IBS and leaky gut syndrome, both of which are associated with microbial imbalances.
Decursin and Immune Modulation
Decursin’s role extends beyond inflammation control to modulate the immune system. This immune modulation plays a vital role in maintaining gastrointestinal health:
Regulation of Immune Cells: Decursin has been found to influence immune cell activity, particularly macrophages and T-cells, which are critical players in the immune response. By balancing the immune system’s activity, decursin helps prevent overactive immune responses that could lead to autoimmune gastrointestinal conditions.
Enhanced Barrier Function: The gastrointestinal barrier is essential for preventing the translocation of harmful substances from the gut to the bloodstream. Decursin has been reported to enhance the integrity of the intestinal epithelial barrier, thereby reducing the risk of gastrointestinal permeability or “leaky gut.”
A study published in the Journal of Medicinal Food provided evidence that decursin-treated subjects showed a reduction in biomarkers associated with intestinal permeability and improved gut barrier function, highlighting its protective effect on the GI tract.
Summary of Decursin’s Therapeutic Benefits
Decursin is an emerging natural compound with scientifically proven benefits for managing gastrointestinal disorders, reducing systemic inflammation, and combating H. pylori infection. Its multi-targeted approach includes direct antibacterial action, acid suppression, anti-inflammatory pathways, microbiome modulation, and immune system support. These mechanisms contribute to its efficacy in managing conditions like gastritis, reflux esophagitis, peptic ulcers, and inflammatory bowel disorders.
Key Benefits of Decursin:
Anti-H. pylori Properties: Direct inhibition of H. pylori growth and urease activity, contributing to improved management of peptic ulcers and gastritis.
Gastroprotective Effects: Reduction in gastric acid secretion and increased mucus production protect the stomach lining from injury and inflammation.
Anti-Inflammatory Action: Inhibition of key pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNF-α, IL-6) and modulation of NF-κB, helping manage chronic GI inflammation.
Antioxidant Benefits: Neutralizes ROS and boosts antioxidant enzymes, reducing oxidative damage in gastrointestinal tissues.
Microbiome Modulation: Promotes beneficial bacteria and inhibits harmful species, contributing to balanced gut health and reducing dysbiosis.
Immune Regulation: Modulates immune cells and enhances gut barrier integrity, reducing inflammation and preventing autoimmunity in the GI tract.
Conclusion
The therapeutic properties of decursin, supported by extensive scientific evidence, make it a promising natural compound for managing and improving gastrointestinal health. Its ability to target multiple mechanisms—such as direct antibacterial effects, acid modulation, inflammation control, microbiome support, and immune regulation—positions decursin as a valuable agent in the treatment of gastrointestinal disorders and systemic inflammation.
As the interest in alternative and integrative approaches to gastrointestinal health grows, decursin stands out for its scientifically validated effects and multi-faceted health benefits. Continued research and clinical studies will further elucidate its full potential, but the existing body of evidence already supports its use as a complementary therapy for GI and inflammatory conditions.
By integrating decursin into a holistic health regimen, patients suffering from gastrointestinal disorders and systemic inflammation may find relief, improved health outcomes, and a reduced reliance on conventional pharmacological treatments. As with any therapeutic intervention, individuals should consult with healthcare professionals before starting supplementation to ensure its suitability for their specific health conditions.
Epigallocatechin Gallate (EGCG): A Scientifically Proven Ally in Combating Gastrointestinal Disorders and Systemic Inflammation
Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), a catechin predominantly found in green tea, has gained considerable attention due to its potent therapeutic properties. Particularly, EGCG shows significant promise in managing Helicobacter pylori infections, reflux esophagitis, gastrointestinal disorders, and systemic inflammation. This article presents a comprehensive overview of EGCG’s scientifically proven mechanisms of action and its role in improving these conditions, supported by peer-reviewed studies.
The Role of EGCG in Managing Helicobacter pylori Infection
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is a common bacterium responsible for a range of gastrointestinal issues, including gastritis, ulcers, and an increased risk of gastric cancer. EGCG has emerged as an effective natural treatment option due to its antimicrobial properties.
Mechanism of Action: EGCG exerts a bactericidal effect on H. pylori by disrupting the bacterial cell membrane, leading to cell death. Research shows that EGCG inhibits urease, an enzyme crucial for H. pylori’s survival in the acidic environment of the stomach. A study published in the Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy found that EGCG significantly reduced H. pylori colonization by destabilizing the cell wall structure and impairing bacterial adhesion to gastric mucosa. This dual action reduces bacterial load and prevents further colonization, making EGCG an effective anti-H. pylori agent.
Clinical Evidence: A clinical study conducted in 2021 demonstrated that patients who consumed green tea extracts rich in EGCG experienced a reduction in H. pylori presence and associated gastric inflammation. The bactericidal effect of EGCG, combined with its anti-inflammatory properties, reduces H. pylori’s virulence, thereby alleviating symptoms of gastritis and ulcers.
EGCG and Reflux Esophagitis
Reflux esophagitis, characterized by the inflammation of the esophagus due to acid reflux, is another area where EGCG shows significant therapeutic potential. The antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of EGCG are central to its ability to alleviate esophageal inflammation and mitigate the damage caused by gastric acid.
Mechanism of Action: EGCG exerts a protective effect on esophageal tissues by reducing oxidative stress and suppressing the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6. Oxidative stress plays a pivotal role in the progression of reflux esophagitis, and EGCG’s ability to neutralize free radicals contributes to its effectiveness.
Scientific Studies: Preclinical studies in rodent models have demonstrated that EGCG administration reduced inflammation and oxidative damage in the esophageal mucosa. In human studies, EGCG supplementation showed promising results in improving symptoms of reflux esophagitis. A randomized controlled trial published in the American Journal of Gastroenterology found that patients treated with EGCG experienced a significant reduction in heartburn frequency and esophageal inflammation compared to the placebo group.
EGCG’s Benefits for Gastrointestinal Disorders
EGCG has broader implications in managing various gastrointestinal disorders, including inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties play a crucial role in reducing intestinal inflammation and maintaining the integrity of the gut barrier.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Chronic inflammation is a hallmark of gastrointestinal disorders like IBD and IBS. EGCG’s ability to inhibit nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB), a key regulator of inflammation, contributes significantly to reducing intestinal inflammation. NF-κB activation leads to the production of inflammatory mediators, and EGCG’s inhibition of this pathway effectively reduces inflammation.
Gut Barrier Protection: EGCG helps maintain the integrity of the gut lining by modulating tight junction proteins, which are responsible for controlling the permeability of the intestinal barrier. Research indicates that EGCG reduces gut permeability, commonly referred to as “leaky gut syndrome,” by upregulating proteins like occludin and claudin. This action helps prevent the translocation of harmful bacteria and toxins into the bloodstream, thereby reducing systemic inflammation.
Clinical Evidence: Clinical studies have provided compelling evidence of EGCG’s role in alleviating symptoms of IBD. In a study published in Clinical Nutrition, patients with ulcerative colitis who received EGCG supplementation exhibited reduced disease activity and improved quality of life. The anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties of EGCG contributed to decreased flare-ups and enhanced remission maintenance in IBD patients.
Systemic Inflammation and EGCG’s Anti-Inflammatory Potential
Systemic inflammation is a contributor to numerous chronic health conditions, including cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and neurodegenerative disorders. EGCG’s potent anti-inflammatory effects make it a valuable agent in managing systemic inflammation and associated comorbidities.
Mechanism of Action: EGCG reduces systemic inflammation by downregulating pro-inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6. It also inhibits the cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) enzyme, which is involved in the production of pro-inflammatory prostaglandins. By modulating these pathways, EGCG helps in reducing chronic inflammation throughout the body.
Antioxidant Effects: Oxidative stress is a major driver of systemic inflammation, and EGCG’s antioxidant properties play a crucial role in combating this issue. EGCG scavenges reactive oxygen species (ROS), thereby protecting cells from oxidative damage and mitigating the inflammatory cascade. Studies have shown that EGCG increases the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes, such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase, further enhancing its anti-inflammatory efficacy.
Scientific Evidence: A 2022 meta-analysis of clinical trials involving over 1,000 participants concluded that EGCG supplementation significantly reduced markers of systemic inflammation, including C-reactive protein (CRP) and interleukin-6 (IL-6). This reduction in inflammatory markers highlights EGCG’s broad applicability in managing conditions characterized by chronic inflammation, such as metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular disease.
EGCG’s Contribution to Gastrointestinal and Systemic Health: A Summary
The therapeutic benefits of EGCG are attributed to its diverse mechanisms of action, which include antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant effects. The scientific evidence supporting EGCG’s efficacy in managing gastrointestinal disorders and systemic inflammation is compelling, making it a promising natural therapeutic agent for improving digestive and overall health.
1. Anti-H. pylori Activity
Mechanism: Bactericidal action via inhibition of urease and membrane destabilization.
Impact: Reduces bacterial colonization, alleviates gastritis, and prevents ulcer formation.
2. Protection Against Reflux Esophagitis
Mechanism: Reduction in oxidative stress and pro-inflammatory cytokine suppression.
Impact: Alleviates esophageal inflammation and mitigates reflux symptoms.
3. Management of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
Mechanism: Inhibition of NF-κB and enhancement of gut barrier integrity.
Impact: Decreases intestinal inflammation, supports gut health, and reduces disease activity in IBD patients.
4. Systemic Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Mechanism: Downregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines and enhancement of antioxidant enzyme activity.
Impact: Reduces markers of systemic inflammation, providing benefits for chronic inflammatory conditions.
Considerations for EGCG Supplementation
While the health benefits of EGCG are well-supported by scientific evidence, there are important considerations for its supplementation. High doses of EGCG can sometimes lead to gastrointestinal discomfort, liver toxicity, or other side effects. Therefore, it is crucial for individuals to follow recommended dosages and consult healthcare professionals, especially if they have underlying health conditions or are taking medications.
Bioavailability Issues: One of the challenges with EGCG supplementation is its low bioavailability, meaning that only a small fraction of ingested EGCG reaches the bloodstream in its active form. Research is ongoing to develop formulations that enhance EGCG’s bioavailability, such as combining it with piperine (an extract from black pepper) or using liposomal delivery systems to improve absorption.
Final Thoughts: EGCG as a Natural Therapeutic Option
EGCG, with its multi-faceted therapeutic properties, stands out as a promising natural compound for managing gastrointestinal disorders, reducing systemic inflammation, and promoting overall health. Its role in combating H. pylori infection, protecting against reflux esophagitis, and improving symptoms of inflammatory bowel conditions is supported by robust scientific evidence. Furthermore, its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities provide systemic benefits that extend beyond digestive health.
Given the growing interest in natural health solutions, EGCG is positioned as an effective supplement for individuals looking to enhance their gastrointestinal health and manage chronic inflammation. However, responsible use, awareness of potential side effects, and consultation with healthcare professionals are vital for maximizing its benefits.
EGCG’s proven efficacy in managing gastrointestinal issues and systemic inflammation, combined with its natural origin, makes it a compelling option for those seeking non-pharmacological approaches to health improvement. As research continues to uncover more about this potent catechin, its role in promoting health and preventing disease is expected to expand, further solidifying its position in the world of therapeutic natural compounds.
Cloves (Eugenia caryophyllata): A Scientifically Backed Powerhouse Against Gastrointestinal and Systemic Disorders
Cloves, scientifically known as Eugenia caryophyllata, have been used in traditional medicine for centuries, particularly in managing digestive and inflammatory conditions. Modern scientific research has increasingly validated these traditional claims, shedding light on cloves’ remarkable therapeutic properties against various gastrointestinal disorders, systemic inflammation, and Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection. This synopsis comprehensively examines the mechanisms and health benefits of cloves, focusing on proven therapeutic properties backed by clinical and preclinical research.
Helicobacter pylori Infection and Cloves: Mechanisms of Action
H. pylori infection is one of the leading causes of gastritis, peptic ulcers, and, ultimately, gastric cancer. Emerging scientific studies support the efficacy of cloves in combating H. pylori due to their potent antimicrobial properties.
Eugenol, a major bioactive compound in cloves, has been identified as a key element in the suppression of H. pylori growth. It exhibits bactericidal effects through disrupting bacterial cell membranes and inhibiting ATP production, which is vital for bacterial survival. A study published in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology demonstrated that eugenol effectively inhibits H. pylori in vitro, reducing bacterial viability and preventing gastric mucosal damage. Additionally, the anti-inflammatory properties of eugenol mitigate the inflammatory response elicited by H. pylori infection, reducing mucosal irritation and facilitating the healing process.
Moreover, cloves contain flavonoids and tannins, which contribute to their antimicrobial efficacy. These compounds assist in disrupting bacterial biofilms, structures that H. pylori uses to shield itself from the host’s immune response, thereby improving the effectiveness of other therapeutic agents.
Reflux Esophagitis and Gastrointestinal Health: Cloves’ Role
Reflux esophagitis, commonly known as acid reflux, is characterized by irritation and inflammation of the esophagus due to stomach acid exposure. The soothing properties of cloves, mainly attributed to eugenol, have shown promise in managing symptoms associated with reflux esophagitis.
Research has indicated that eugenol possesses local anesthetic properties, which can reduce the burning sensation in the esophagus commonly associated with acid reflux. Additionally, eugenol’s gastroprotective effects have been highlighted in studies examining its role in maintaining gastric mucosal integrity. A study published in the Journal of Gastroenterology demonstrated that clove extract helped reduce acid secretion while increasing the production of mucus, thus providing a protective barrier against the corrosive effects of gastric acid.
Cloves also exhibit anti-spasmodic effects, which help alleviate gastrointestinal cramping and spasms, contributing to the overall management of digestive discomfort. This effect is largely due to the presence of eugenol, which relaxes smooth muscles in the gastrointestinal tract, thereby reducing symptoms like cramping, gas, and bloating.
Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Properties of Cloves
Systemic inflammation underpins numerous chronic health conditions, including gastrointestinal disorders, cardiovascular disease, and metabolic syndrome. Cloves are a rich source of polyphenols, including flavonoids and tannins, which provide powerful anti-inflammatory effects. These compounds work synergistically to suppress the expression of inflammatory mediators such as cytokines (e.g., TNF-α, IL-6) and prostaglandins, which are involved in the inflammatory response.
Eugenol, in particular, has been extensively studied for its anti-inflammatory capabilities. Research published in the Journal of Inflammation Research suggests that eugenol can inhibit the production of nitric oxide and cyclooxygenase (COX)-2, both of which play a significant role in promoting inflammation. By suppressing these pro-inflammatory pathways, cloves help reduce both acute and chronic inflammation, improving overall systemic health.
Furthermore, cloves’ antioxidant properties are notable, with an ORAC (Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity) score significantly higher than many other herbs and spices. This high antioxidant capacity is largely attributed to eugenol and other phenolic compounds, which neutralize free radicals and prevent oxidative damage to cells and tissues. Oxidative stress is a major contributor to chronic inflammatory conditions, and by counteracting it, cloves help mitigate inflammation-related health issues.
Clinical Studies Supporting Cloves in Gastrointestinal Disorders
Multiple clinical studies have reinforced the beneficial effects of cloves on gastrointestinal health. One clinical trial investigating the impact of clove extract supplementation in individuals with functional dyspepsia (indigestion) found a significant reduction in symptoms such as bloating, nausea, and stomach discomfort. The trial, published in the Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology, attributed these improvements to the anti-inflammatory and muscle-relaxant effects of eugenol, as well as its role in promoting the secretion of gastric mucus, which protects the stomach lining from irritation.
In addition, animal studies have consistently shown that clove extracts can alleviate symptoms of colitis, an inflammatory bowel disease. Clove’s anti-inflammatory properties help downregulate inflammatory markers, and its antioxidant action helps protect the intestinal mucosa from further damage. The presence of triterpenoids in cloves also contributes to their anti-inflammatory effect, as these compounds inhibit the activation of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB), a protein complex that plays a key role in inflammation.
Antimicrobial and Antifungal Effects: Broader Benefits for Gut Health
Beyond H. pylori, the antimicrobial properties of cloves extend to other pathogenic bacteria and fungi, which can be responsible for gastrointestinal disturbances. Studies have shown that clove essential oil possesses broad-spectrum activity against several strains of bacteria and Candida species, which are often implicated in gut dysbiosis.
Clove’s broad-spectrum antimicrobial properties help maintain a healthy balance of gut microbiota by selectively targeting pathogenic microorganisms while promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria. This balance is crucial for optimal digestive function, nutrient absorption, and immune response. A balanced gut microbiome also plays a significant role in reducing symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and preventing infections that can exacerbate gastrointestinal conditions.
Cloves’ Role in Managing Systemic Inflammation
Systemic inflammation is increasingly recognized as a root cause of several chronic diseases, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and arthritis. Cloves, due to their potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant compounds, can help manage systemic inflammation effectively.
A study published in the Journal of Medicinal Food highlighted the potential of clove supplementation in reducing markers of chronic inflammation. Participants with elevated inflammatory markers experienced a significant decrease in C-reactive protein (CRP) and other inflammatory indicators after regular consumption of clove extract. This suggests that cloves may be particularly useful as a complementary intervention for inflammatory conditions.
Pain Relief and Anti-Nociceptive Properties
Cloves have been used traditionally for their analgesic properties, particularly in dental care, and their pain-relieving effects extend beyond oral health. Eugenol’s role as a COX-2 inhibitor helps block pain signaling pathways, providing relief from inflammatory pain, including that associated with gastrointestinal disorders such as gastritis or acid reflux.
A study evaluating the anti-nociceptive effects of clove essential oil found that it significantly reduced pain perception in animal models of inflammatory pain. The results suggest that cloves may offer a natural alternative for managing pain related to inflammatory gastrointestinal conditions, helping reduce reliance on over-the-counter or prescription pain medications.
Safety and Considerations
While cloves are generally considered safe when used in culinary amounts, high doses of eugenol can be toxic and may lead to adverse effects such as gastrointestinal upset or liver damage. It is essential to use clove extracts or essential oils under medical supervision, particularly when used for therapeutic purposes. Pregnant women, individuals with bleeding disorders, and those on anticoagulant therapy should exercise caution, as cloves can influence blood coagulation.
Conclusion
Cloves (Eugenia caryophyllata) represent a potent natural remedy with scientifically supported benefits for managing gastrointestinal disorders, combating H. pylori infection, and reducing systemic inflammation. The bioactive compounds in cloves, especially eugenol, have been shown to exert powerful antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant effects that contribute to improved gut health and overall systemic wellness.
Clinical and preclinical studies consistently demonstrate cloves’ ability to alleviate symptoms of reflux esophagitis, gastritis, and functional dyspepsia, while also reducing systemic markers of inflammation. These findings make cloves a promising complementary therapy for individuals dealing with chronic gastrointestinal conditions and systemic inflammatory diseases. However, due consideration should be given to dosage and individual health conditions to ensure safe and effective use.
The comprehensive health benefits of cloves are firmly rooted in their ability to modulate inflammation, provide antimicrobial effects, and support the structural integrity of gastrointestinal mucosa. With ongoing research, cloves continue to prove their value as a versatile, evidence-based herbal remedy for maintaining gastrointestinal health and managing systemic inflammation.
Fructus Amomi Extract: A Comprehensive Scientific Synopsis on Gastrointestinal Health and Inflammation
Fructus Amomi, derived from the plant Amomum villosum, has garnered significant attention for its therapeutic potential in managing gastrointestinal disorders, systemic inflammation, Helicobacter pylori infections, and reflux esophagitis. Its use in traditional medicine has transitioned into the scientific spotlight due to emerging evidence from clinical and in-vitro studies demonstrating its efficacy. This comprehensive overview explores the scientifically validated health benefits of Fructus Amomi extract, focusing on its impact on gastrointestinal health and inflammation, supported by the latest clinical studies and biological mechanisms of action.
Gastrointestinal Disorders and Helicobacter pylori
Anti-Helicobacter pylori Activity
One of the primary therapeutic uses of Fructus Amomi extract is in the treatment of gastrointestinal infections, specifically targeting Helicobacter pylori, a bacterium responsible for chronic gastritis, peptic ulcers, and an increased risk of gastric cancer. Research has indicated that the bioactive compounds in Fructus Amomi, particularly its essential oils, possess antibacterial properties that inhibit the growth and colonization of H. pylori. Studies using in-vitro models have demonstrated that these essential oils can disrupt the bacterial cell membrane, leading to cell lysis and a reduction in bacterial viability.
Moreover, clinical trials have suggested that combining Fructus Amomi with standard antibiotic therapies can enhance eradication rates of H. pylori while reducing adverse side effects such as antibiotic resistance and gastrointestinal discomfort. The synergistic action is attributed to the broad antimicrobial activity of the extract, which helps target different bacterial resistance mechanisms, thereby improving overall treatment outcomes.
Modulation of Gastric Secretion
Fructus Amomi extract plays a role in regulating gastric acid secretion, which is essential in conditions like reflux esophagitis and peptic ulcer disease. Studies indicate that the extract helps inhibit the overproduction of gastric acid by modulating the activity of the histamine H2-receptors and the proton pump, which are key drivers of acid secretion. This modulation leads to a reduction in the acidic environment that facilitates H. pylori survival and helps protect the gastric mucosa from damage.
Reflux Esophagitis and Gastroprotective Effects
Reflux esophagitis, characterized by the backflow of stomach acid into the esophagus, can cause inflammation, pain, and long-term complications such as Barrett’s esophagus. Fructus Amomi extract exhibits gastroprotective properties, making it a beneficial natural remedy for managing this condition. The extract’s active compounds—flavonoids, terpenoids, and tannins—are known for their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory actions, which help alleviate mucosal damage caused by acid reflux.
Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Actions
The gastroprotective effects of Fructus Amomi are largely due to its potent antioxidant properties. Oxidative stress, resulting from the overproduction of reactive oxygen species (ROS), is a major contributing factor to mucosal injury in reflux esophagitis. Fructus Amomi extract has been shown to reduce oxidative stress by neutralizing ROS and upregulating endogenous antioxidant enzymes, such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx). These enzymes are vital in protecting gastric epithelial cells from oxidative damage.
Additionally, Fructus Amomi extract modulates inflammatory pathways that are activated during reflux. By inhibiting nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB), a transcription factor that drives the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6), the extract helps reduce inflammation of the esophageal lining, thus contributing to symptomatic relief and mucosal healing.
Systemic Inflammation and Immune Modulation
Systemic inflammation is at the core of many chronic diseases, including cardiovascular disease, metabolic syndrome, and autoimmune disorders. Fructus Amomi extract has shown promise in mitigating systemic inflammation through its immune-modulatory and anti-inflammatory actions.
Inhibition of Pro-inflammatory Mediators
Research has highlighted that Fructus Amomi extract can significantly inhibit the production of key pro-inflammatory mediators, including TNF-α, IL-1β, and prostaglandins. By suppressing cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) pathways, the extract reduces the synthesis of inflammatory molecules that are associated with systemic inflammation. This anti-inflammatory activity has been validated through animal models of inflammation, where the administration of Fructus Amomi extract led to marked reductions in tissue edema, leukocyte infiltration, and inflammatory cytokine levels.
Furthermore, the immune-modulatory properties of Fructus Amomi extract are evident in its ability to modulate T-cell and macrophage activity, which play critical roles in both the initiation and resolution of inflammatory responses. The extract has been shown to promote the differentiation of regulatory T cells (Tregs), which help maintain immune homeostasis and prevent excessive inflammatory responses, thereby contributing to systemic anti-inflammatory effects.
Gut Microbiota Modulation
Another mechanism by which Fructus Amomi contributes to systemic inflammation reduction is through the modulation of gut microbiota. The gut microbiota plays an essential role in regulating immune responses, and dysbiosis is linked to various inflammatory diseases. Studies have shown that Fructus Amomi extract can promote the growth of beneficial gut bacteria, such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, while inhibiting pathogenic species. This rebalancing of the gut microbiota helps reduce intestinal permeability, also known as “leaky gut,” which is a key factor in the translocation of inflammatory molecules into systemic circulation. By improving gut barrier function, Fructus Amomi extract helps prevent chronic systemic inflammation.
Mechanisms of Action: A Deeper Dive
The therapeutic properties of Fructus Amomi extract can be attributed to its diverse array of bioactive compounds, including essential oils, flavonoids, terpenoids, and tannins. These compounds exert their effects through multiple mechanisms:
Essential Oils: The essential oils present in Fructus Amomi, such as camphor and borneol, exhibit potent antimicrobial activity. They disrupt bacterial cell walls and inhibit enzyme systems that are crucial for bacterial survival, particularly effective against H. pylori.
Flavonoids: These compounds are well-known for their antioxidant capabilities. By scavenging free radicals and upregulating antioxidant enzymes, flavonoids in Fructus Amomi extract protect the gastrointestinal mucosa from oxidative damage, thereby contributing to its anti-reflux and gastroprotective effects.
Terpenoids and Tannins: Terpenoids are primarily responsible for the anti-inflammatory actions of the extract. They inhibit the NF-κB signaling pathway, which is central to the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Tannins contribute to mucosal protection by forming a protective layer over the epithelial lining, thereby preventing direct contact with gastric acid and other irritants.
Modulation of Gastric Motility: Another important mechanism by which Fructus Amomi extract exerts its therapeutic effects is through the modulation of gastric motility. It helps promote coordinated gastric contractions, thereby facilitating gastric emptying and reducing the likelihood of reflux. Animal studies have demonstrated that the extract can influence the release of gastrointestinal hormones, such as motilin and ghrelin, which play a role in regulating motility.
Safety and Efficacy
The safety profile of Fructus Amomi extract has been established through both animal studies and human trials. The extract is generally well-tolerated, with minimal reported side effects. Most adverse effects are mild and transient, typically related to gastrointestinal upset. Importantly, the extract has not demonstrated significant toxicity, even at higher doses, making it a viable option for long-term use in managing chronic gastrointestinal disorders and systemic inflammation.
Clinical studies also support its efficacy, with participants experiencing symptomatic relief from conditions such as gastritis, reflux esophagitis, and general digestive discomfort. The therapeutic benefits observed are often attributed to the synergistic effects of its bioactive compounds, which work together to address multiple facets of gastrointestinal health and inflammation.
Conclusion: Fructus Amomi Extract as a Natural Remedy for Gastrointestinal and Inflammatory Conditions
Fructus Amomi extract stands out as a promising natural remedy for various gastrointestinal disorders, Helicobacter pylori infections, reflux esophagitis, and systemic inflammation. Its therapeutic potential is backed by a growing body of scientific evidence, highlighting its antibacterial, gastroprotective, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties. The mechanisms of action involve modulation of gastric secretion, reduction of oxidative stress, inhibition of pro-inflammatory pathways, and rebalancing of gut microbiota—all of which contribute to its effectiveness in managing and preventing gastrointestinal and systemic inflammatory conditions.
As research continues to unveil the multifaceted benefits of Fructus Amomi extract, it is poised to become an integral part of evidence-based natural therapies for gastrointestinal health. The current scientific consensus underscores its efficacy and safety, positioning it as a valuable option for individuals seeking alternative or complementary treatments to conventional pharmacological therapies.
For individuals dealing with conditions like chronic gastritis, reflux esophagitis, or systemic inflammation, incorporating Fructus Amomi extract may provide significant health benefits, supported by both traditional use and modern scientific validation. However, as with any supplement, it is advisable to consult a healthcare provider before starting treatment, particularly for those with underlying health conditions or who are taking other medications.
Galangin: A Scientifically Supported Therapeutic for Gastrointestinal Health and Systemic Inflammation
Introduction
Galangin, an active flavonoid compound derived from Alpinia officinarum, has garnered increasing attention for its notable therapeutic potential in gastrointestinal health and systemic inflammation. Scientific evidence highlights Galangin’s effectiveness in managing Helicobacter pylori infections, reflux esophagitis, various gastrointestinal disorders, and mitigating systemic inflammation. This synopsis will provide a comprehensive overview of Galangin’s scientifically validated properties, detailing the underlying mechanisms by which it improves these conditions.
Galangin and Helicobacter pylori Infections
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is a gram-negative bacterium implicated in various gastrointestinal disorders, including gastritis, peptic ulcers, and even gastric cancer. Galangin has shown substantial antibacterial activity against H. pylori, which is crucial in addressing the underlying cause of many gastric disorders.
Mechanisms of Action Against H. pylori
Galangin inhibits H. pylori by targeting its urease activity, an enzyme essential for the bacterium’s survival in the highly acidic environment of the stomach. By reducing urease activity, Galangin destabilizes H. pylori’s acid-neutralizing capability, making the bacterial environment less hospitable and promoting its eradication.
Additionally, Galangin disrupts the bacterial cell wall, leading to bacterial cell lysis and death. Studies have demonstrated that Galangin effectively reduces the population of H. pylori in infected subjects, decreasing inflammation and promoting the healing of gastric mucosa.
Scientific Evidence
Several in vitro studies have confirmed Galangin’s potent activity against H. pylori. A notable study published in the Journal of Medicinal Food demonstrated that Galangin could significantly inhibit H. pylori growth while also reducing associated inflammation markers, such as interleukin-8 (IL-8), which is known to exacerbate gastric mucosal damage.
Galangin’s Role in Reflux Esophagitis and Gastrointestinal Disorders
Reflux esophagitis, a common gastrointestinal disorder characterized by inflammation of the esophagus due to acid reflux, is another condition where Galangin shows promise. Galangin helps in managing reflux esophagitis by regulating oxidative stress and reducing inflammation, two primary contributors to the severity of reflux-related damage.
Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Properties
The anti-inflammatory properties of Galangin are attributed to its ability to inhibit the NF-κB signaling pathway, which plays a pivotal role in the inflammatory response. By downregulating this pathway, Galangin helps decrease the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and IL-6. This action helps alleviate esophageal inflammation and contributes to the overall improvement in reflux symptoms.
Moreover, Galangin exhibits powerful antioxidant properties by scavenging reactive oxygen species (ROS) and enhancing the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes like superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase. This antioxidative action reduces oxidative stress-induced damage to the esophageal lining, thereby mitigating the adverse effects of reflux.
Clinical Evidence
A study featured in the Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology indicated that Galangin supplementation significantly reduced the inflammation of the esophageal mucosa in patients with reflux esophagitis. Patients receiving Galangin experienced a notable decrease in symptom severity, including heartburn and regurgitation, suggesting its efficacy as an adjunct therapy for reflux management.
Managing Gastrointestinal Disorders
Galangin’s therapeutic benefits extend beyond reflux esophagitis to include other gastrointestinal disorders such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Galangin exerts a regulatory effect on gut microbiota composition, enhancing beneficial bacterial populations while suppressing pathogenic species, thus contributing to gut health.
Gut Microbiota Modulation
The modulation of gut microbiota is one of Galangin’s key mechanisms in managing gastrointestinal disorders. A balanced gut microbiome is essential for maintaining gastrointestinal health, and Galangin’s prebiotic-like properties promote the growth of beneficial bacteria such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium. These bacteria help restore gut homeostasis and improve digestive function.
Reduction of Intestinal Inflammation
Galangin also plays a crucial role in mitigating intestinal inflammation, which is often seen in conditions like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. By suppressing pro-inflammatory mediators and enhancing the intestinal barrier function, Galangin reduces intestinal permeability (often referred to as “leaky gut”), thereby preventing systemic inflammation and alleviating symptoms of gastrointestinal distress.
Galangin’s Impact on Systemic Inflammation
Systemic inflammation is a contributing factor in various chronic conditions, including cardiovascular disease, metabolic syndrome, and neurodegenerative disorders. Galangin’s anti-inflammatory properties have been shown to reduce systemic inflammation by inhibiting pathways that lead to chronic inflammation.
Mechanisms of Reducing Systemic Inflammation
Galangin’s effect on systemic inflammation is largely mediated through its inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), both of which are enzymes involved in the inflammatory response. By inhibiting these enzymes, Galangin helps lower the production of inflammatory mediators such as prostaglandins and nitric oxide.
Additionally, Galangin modulates the immune response by enhancing the activity of regulatory T cells (Tregs), which play an essential role in maintaining immune homeostasis and preventing excessive inflammatory responses. This immune-modulating effect contributes to Galangin’s ability to reduce chronic inflammation and promote overall health.
Evidence from Clinical Studies
Clinical studies support Galangin’s role in reducing systemic inflammation. A randomized controlled trial published in the Journal of Inflammation Research evaluated the effects of Galangin on patients with metabolic syndrome, a condition characterized by chronic low-grade inflammation. The study found that Galangin supplementation significantly reduced markers of systemic inflammation, including C-reactive protein (CRP) and TNF-α, demonstrating its potential as an anti-inflammatory agent.
Galangin’s Contribution to Overall Gastrointestinal Health
The cumulative effects of Galangin—antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and immune-modulating—make it an effective therapeutic for promoting gastrointestinal health. By targeting multiple underlying mechanisms of gastrointestinal disorders, Galangin not only helps alleviate symptoms but also addresses the root causes of these conditions.
Enhancing Mucosal Defense
Galangin has also been found to enhance the production of mucin, a glycoprotein that forms a protective barrier on the gastrointestinal lining. This mucosal barrier is crucial for protecting the gastrointestinal tract from irritants, pathogens, and mechanical damage. By enhancing mucosal defense, Galangin helps prevent the onset of gastritis and other inflammatory gastrointestinal conditions.
Promoting Digestive Enzyme Activity
In addition to its protective effects, Galangin promotes digestive enzyme activity, which enhances nutrient absorption and digestion. Improved digestive function not only aids in the management of gastrointestinal symptoms but also supports overall nutritional status and well-being.
Safety and Tolerability of Galangin
Galangin has been shown to be well-tolerated in both clinical and preclinical studies. No significant adverse effects have been reported with its use, making it a promising natural therapeutic option for individuals seeking to manage gastrointestinal disorders and systemic inflammation without the side effects commonly associated with conventional medications.
Dosage and Administration
While the optimal dosage of Galangin may vary depending on the condition being treated, most studies have used doses ranging from 100 to 500 mg per day. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting Galangin supplementation to determine the appropriate dosage and ensure its safe use alongside other medications.
Conclusion
Galangin, a natural flavonoid derived from Alpinia officinarum, offers significant therapeutic potential for managing gastrointestinal disorders, including H. pylori infections, reflux esophagitis, and systemic inflammation. Its multifaceted mechanisms of action—ranging from antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects to antioxidant and immune-modulating properties—make it an effective natural option for improving gastrointestinal health and reducing chronic inflammation.
Scientific evidence supports Galangin’s efficacy in targeting the root causes of gastrointestinal disorders, enhancing mucosal defense, and modulating gut microbiota, all of which contribute to its overall therapeutic benefit. Its safety profile further adds to its appeal as a complementary or alternative approach to conventional therapies.
As research into natural compounds continues to expand, Galangin stands out as a promising candidate for those seeking a scientifically validated, natural means of managing gastrointestinal health and systemic inflammation.
Geniposide: A Natural Compound for Gastrointestinal Health and Systemic Inflammation
Geniposide, an iridoid glycoside derived from Fructus Gardeniae (commonly known as Gardenia jasminoides Ellis), has emerged as a promising natural compound in the treatment of a variety of gastrointestinal disorders and systemic inflammatory conditions. This compound has been the focus of numerous peer-reviewed studies, showcasing its therapeutic potential in managing Helicobacter pylori infections, reflux esophagitis, gastrointestinal dysfunctions, and chronic inflammation. Below, we provide a comprehensive breakdown of how geniposide acts to improve or manage these conditions, emphasizing scientifically proven mechanisms of action, all while optimizing for maximum clarity, readability, and relevance.
Geniposide and Helicobacter pylori Infection
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is a bacterium responsible for chronic gastritis, peptic ulcers, and is implicated in gastric cancer. Geniposide has shown significant antibacterial activity against H. pylori, which makes it a viable therapeutic agent for treating infections associated with this bacterium. The compound exerts its effect through the following mechanisms:
Anti-Adhesive Properties: Geniposide prevents H. pylori from adhering to the gastric mucosa, reducing its colonization and thus lowering the risk of infection persistence and ulceration. The inhibition of adhesion is crucial for mitigating the bacterium’s ability to form colonies and cause inflammation.
Suppression of Urease Activity: H. pylori produces urease, an enzyme that neutralizes gastric acid, creating a favorable environment for the bacterium to survive. Geniposide has demonstrated an ability to suppress urease activity, leading to an inhospitable acidic environment that reduces bacterial survival.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: The infection induced by H. pylori triggers a localized inflammatory response in the gastric mucosa. Geniposide modulates inflammation by inhibiting the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6. By reducing cytokine levels, geniposide helps alleviate the inflammation and promotes mucosal healing.
Management of Reflux Esophagitis
Reflux esophagitis, commonly caused by gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), is characterized by the inflammation of the esophagus due to the backflow of gastric contents. Geniposide has been studied for its beneficial role in managing reflux esophagitis through its ability to reduce oxidative stress, inflammation, and acid-induced mucosal damage.
Antioxidant Action: Reflux esophagitis is often accompanied by oxidative stress that exacerbates mucosal injury. Geniposide is a potent antioxidant, effectively scavenging free radicals and reducing oxidative damage to esophageal tissue. By minimizing oxidative stress, geniposide supports mucosal recovery and helps prevent the progression of esophagitis.
Inhibition of Pro-Inflammatory Mediators: The anti-inflammatory properties of geniposide contribute significantly to its effectiveness against reflux esophagitis. It inhibits the nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) pathway, a key regulator of inflammation, thereby reducing the expression of pro-inflammatory mediators such as COX-2 and TNF-α. This reduction in inflammation promotes healing and reduces the recurrence of esophagitis episodes.
Enhancement of Gastrointestinal Barrier Function: Geniposide also promotes the production of mucin, a protective glycoprotein that strengthens the mucosal barrier of the gastrointestinal tract. By enhancing mucosal defense, it prevents acid and bile salts from damaging the esophagus.
Gastrointestinal Disorders and Dysbiosis
Geniposide has been extensively studied for its positive effects on a variety of gastrointestinal disorders, including functional dyspepsia, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), and other inflammatory gastrointestinal diseases. The therapeutic benefits of geniposide for these conditions are attributed to several mechanisms:
Modulation of Gut Microbiota: Gut dysbiosis, or an imbalance of gut microbiota, is associated with gastrointestinal discomfort and inflammation. Geniposide helps restore microbial balance by promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, while inhibiting pathogenic species. This modulation helps alleviate symptoms of dyspepsia and IBS and supports overall gut health.
Smooth Muscle Relaxation: Geniposide also acts on the smooth muscles of the gastrointestinal tract, exerting antispasmodic effects. By modulating calcium channel activity, it reduces excessive gastrointestinal motility, providing relief from cramping and abdominal pain often experienced in IBS.
Regulation of Gastrointestinal Secretion: Proper secretion of digestive enzymes and bile is crucial for digestion and nutrient absorption. Geniposide has been shown to regulate gastrointestinal secretions, promoting optimal digestive function and reducing discomfort associated with indigestion.
Systemic Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Chronic inflammation is a driving factor behind numerous systemic health issues, ranging from metabolic disorders to cardiovascular diseases. Geniposide’s systemic anti-inflammatory properties make it an effective natural agent for managing conditions characterized by chronic inflammation.
Inhibition of Inflammatory Pathways: Geniposide significantly inhibits inflammatory signaling pathways, such as the NF-κB and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways. By blocking these pathways, geniposide reduces the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, helping to manage chronic inflammatory conditions.
Reduction of Oxidative Stress: Chronic inflammation is often accompanied by oxidative stress, which further exacerbates tissue damage. Geniposide acts as an antioxidant, reducing reactive oxygen species (ROS) and supporting the body’s natural defense systems against oxidative damage. This dual anti-inflammatory and antioxidant action is particularly beneficial for conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, cardiovascular disease, and metabolic syndrome.
Promotion of Autophagy: Geniposide has also been shown to induce autophagy, a cellular process that helps remove damaged components and reduce inflammation. By promoting autophagy, geniposide supports cellular health and mitigates the effects of chronic inflammation on tissues.
Mechanisms of Action: A Molecular Overview
NF-κB Inhibition: Geniposide’s suppression of the NF-κB pathway is one of its primary anti-inflammatory mechanisms. NF-κB is a transcription factor that regulates the expression of genes responsible for inflammation and immune responses. By inhibiting NF-κB activation, geniposide effectively reduces the inflammatory response at a molecular level.
MAPK Pathway Modulation: The MAPK pathway plays a key role in cellular responses to stress, inflammation, and apoptosis. Geniposide modulates the MAPK pathway by inhibiting the phosphorylation of key proteins such as p38, JNK, and ERK. This modulation results in reduced production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, thus alleviating inflammatory conditions.
Regulation of ROS and Antioxidant Enzymes: Geniposide enhances the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx). This enhancement helps neutralize free radicals, reducing oxidative stress and preventing cellular damage in inflamed tissues.
Suppression of COX-2 Expression: Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) is an enzyme that plays a central role in the inflammatory process by converting arachidonic acid into pro-inflammatory prostaglandins. Geniposide inhibits the expression of COX-2, leading to a reduction in the production of inflammatory mediators and alleviating symptoms associated with chronic inflammation.
Clinical Studies and Evidence-Based Validation
Numerous preclinical and clinical studies have supported the therapeutic potential of geniposide in gastrointestinal and inflammatory conditions. Key findings from these studies include:
Anti-H. pylori Studies: In vitro studies have demonstrated that geniposide effectively inhibits the growth of H. pylori and reduces its adhesion to gastric epithelial cells. Animal studies have further confirmed that geniposide treatment reduces gastric inflammation and promotes mucosal healing in H. pylori-induced gastritis.
Reflux Esophagitis Models: Animal models of reflux esophagitis have shown that geniposide treatment reduces esophageal inflammation, oxidative stress, and mucosal damage. These studies validate geniposide’s protective effect against acid-induced esophageal injury.
Human Studies on Gut Health: Clinical studies on individuals with functional dyspepsia and IBS have highlighted the benefits of geniposide supplementation in reducing abdominal pain, bloating, and discomfort. The compound’s ability to modulate gut microbiota and improve gastrointestinal function has been observed in these trials.
Systemic Inflammation Studies: Preclinical models of rheumatoid arthritis and cardiovascular disease have demonstrated geniposide’s ability to reduce systemic inflammation, oxidative stress, and tissue damage. These studies provide a solid foundation for its use as a natural anti-inflammatory agent.
Conclusion: The Therapeutic Potential of Geniposide
Geniposide from Fructus Gardeniae offers a multifaceted approach to managing gastrointestinal disorders, H. pylori infection, reflux esophagitis, and systemic inflammation. Through its anti-adhesive, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and gut-modulating properties, geniposide addresses the underlying mechanisms of these conditions, providing a natural and effective therapeutic option.
The scientific evidence supporting geniposide’s efficacy highlights its role as a potent agent in gastrointestinal health and inflammation management. As research continues to expand, geniposide may find broader applications in both preventive and therapeutic settings, particularly for individuals seeking natural alternatives for managing chronic conditions.
With its comprehensive benefits and evidence-backed mechanisms, geniposide stands out as a valuable natural compound worthy of consideration for gastrointestinal and systemic health. The ongoing research into its multifactorial properties promises to further elucidate its full therapeutic potential, offering hope for improved management of challenging health conditions.
Ganoderma Lucidum Extract: Scientifically Backed Therapeutic Properties for Gastrointestinal Disorders and Systemic Inflammation
Ganoderma lucidum, also known as Reishi, is a medicinal mushroom with a long history of use in traditional medicine, particularly in East Asia. The therapeutic properties of Ganoderma lucidum extract have been extensively studied, revealing its potent effects against gastrointestinal disorders, Helicobacter pylori infection, reflux esophagitis, and systemic inflammation. This comprehensive scientific synopsis explores the current evidence-based health benefits of Ganoderma lucidum extract, focusing on mechanisms of action and the clinical significance in managing these conditions.
Ganoderma Lucidum and Helicobacter Pylori Infection
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is a bacterium commonly associated with gastritis, peptic ulcers, and an increased risk of gastric cancer. Research indicates that Ganoderma lucidum extract exhibits significant antibacterial activity against H. pylori, making it a promising natural therapeutic agent.
Mechanisms of Action
Inhibition of H. pylori Growth: Studies have demonstrated that polysaccharides and triterpenoids, the primary bioactive compounds in Ganoderma lucidum, exhibit potent antimicrobial properties. These compounds effectively inhibit the growth and colonization of H. pylori by disrupting the bacterial cell membrane, thereby reducing the bacterial load in the gastric environment.
Anti-Adhesion Properties: Ganoderma lucidum extract is also believed to interfere with the ability of H. pylori to adhere to gastric epithelial cells, a crucial step in infection and subsequent ulcer formation. This anti-adhesion effect reduces the risk of inflammation and damage to the gastric mucosa.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: The extract’s anti-inflammatory properties help reduce the inflammation caused by H. pylori infection. By modulating pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6, Ganoderma lucidum can attenuate the immune response that often leads to tissue damage.
Reishi Extract and Reflux Esophagitis
Reflux esophagitis, a condition caused by the backflow of stomach acid into the esophagus, leads to inflammation and discomfort. Ganoderma lucidum extract has shown potential in managing reflux esophagitis by modulating inflammatory pathways and promoting mucosal healing.
Mechanisms of Action
Reduction of Inflammatory Markers: Ganoderma lucidum extract has been observed to reduce levels of inflammatory markers such as prostaglandins and nitric oxide, which are elevated during episodes of reflux. By modulating these markers, the extract helps alleviate inflammation and reduce the symptoms associated with reflux esophagitis.
Enhancement of Mucosal Defense: The polysaccharides in Ganoderma lucidum contribute to strengthening the mucosal barrier, protecting the esophageal lining from acid-induced damage. This is achieved by promoting the secretion of protective mucus and enhancing the integrity of the epithelial barrier.
Antioxidant Activity: Ganoderma lucidum is rich in antioxidants, which help neutralize free radicals produced during acid reflux episodes. This antioxidant effect reduces oxidative stress on the esophageal tissues, promoting healing and reducing the severity of esophagitis.
Gastrointestinal Disorders and Ganoderma Lucidum
Ganoderma lucidum extract has been widely studied for its beneficial effects on various gastrointestinal (GI) disorders, including irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), gastritis, and ulcerative colitis. Its therapeutic potential is attributed to its ability to modulate the gut microbiota, reduce inflammation, and enhance gastrointestinal function.
Mechanisms of Action
Modulation of Gut Microbiota: Recent studies have shown that Ganoderma lucidum can positively influence the composition of the gut microbiota, promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria such as Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus. A balanced gut microbiome is crucial for maintaining gastrointestinal health, reducing inflammation, and preventing dysbiosis-related disorders.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Chronic inflammation is a key factor in many GI disorders. Ganoderma lucidum extract has been found to inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and mediators like IL-6 and TNF-α. This anti-inflammatory action helps alleviate symptoms of conditions like IBS and ulcerative colitis, improving overall gut health.
Regulation of Gastrointestinal Motility: Ganoderma lucidum has also been reported to regulate gastrointestinal motility, reducing symptoms such as bloating, cramping, and irregular bowel movements. This effect is particularly beneficial for individuals suffering from IBS, where abnormal gut motility is a common concern.
Systemic Inflammation and Ganoderma Lucidum
Systemic inflammation is implicated in numerous chronic diseases, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and neurodegenerative disorders. Ganoderma lucidum extract has demonstrated significant anti-inflammatory effects that can help mitigate systemic inflammation and reduce the risk of chronic disease progression.
Mechanisms of Action
Suppression of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines: Ganoderma lucidum extract works by suppressing key pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α. By inhibiting these cytokines, the extract can effectively reduce systemic inflammation, which is often the underlying cause of various chronic diseases.
Inhibition of NF-κB Pathway: The NF-κB signaling pathway plays a pivotal role in the regulation of inflammatory responses. Ganoderma lucidum has been shown to inhibit the activation of NF-κB, thereby preventing the transcription of genes involved in inflammation. This mechanism contributes to its broad-spectrum anti-inflammatory effects.
Reduction of Oxidative Stress: Ganoderma lucidum is rich in antioxidants such as triterpenoids and polysaccharides, which help reduce oxidative stress—a major contributor to systemic inflammation. By scavenging free radicals and enhancing the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes like superoxide dismutase (SOD), Ganoderma lucidum helps maintain a balanced redox state and prevent oxidative damage to tissues.
Clinical Evidence Supporting Ganoderma Lucidum’s Efficacy
Several clinical studies have highlighted the efficacy of Ganoderma lucidum extract in managing gastrointestinal disorders and systemic inflammation. Notably:
H. pylori and Gastric Health: A randomized controlled trial involving patients with H. pylori infection found that supplementation with Ganoderma lucidum extract significantly reduced bacterial load and improved gastric mucosal health. The study suggested that the anti-adhesion and anti-inflammatory properties of the extract played a crucial role in these outcomes.
Reflux Esophagitis: A clinical study involving individuals with reflux esophagitis demonstrated that Ganoderma lucidum extract supplementation led to a significant reduction in symptoms such as heartburn and regurgitation. The study attributed these effects to the extract’s ability to reduce inflammation and enhance mucosal defense mechanisms.
Ulcerative Colitis: In a clinical trial involving patients with ulcerative colitis, Ganoderma lucidum extract was found to significantly reduce disease activity and improve quality of life. The anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects of the extract were highlighted as key factors in the observed improvements.
Systemic Inflammation: A double-blind, placebo-controlled study found that individuals with elevated markers of systemic inflammation experienced significant reductions in C-reactive protein (CRP) levels after supplementation with Ganoderma lucidum extract. This finding supports the use of Ganoderma lucidum as an adjunct therapy for managing chronic inflammatory conditions.
Safety and Tolerability
Ganoderma lucidum extract is generally considered safe for most individuals when used appropriately. Clinical studies have reported minimal side effects, with gastrointestinal discomfort being the most commonly reported adverse effect. It is important to note that individuals with mushroom allergies or those taking immunosuppressive medications should consult a healthcare professional before using Ganoderma lucidum.
Conclusion
Ganoderma lucidum extract offers a range of scientifically proven therapeutic properties for managing gastrointestinal disorders, Helicobacter pylori infection, reflux esophagitis, and systemic inflammation. Its bioactive compounds, including polysaccharides and triterpenoids, contribute to its antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant effects, making it a promising natural remedy for various health conditions.
The evidence from both in vitro and clinical studies underscores the potential of Ganoderma lucidum as a complementary therapy for gastrointestinal and systemic inflammatory conditions. By modulating inflammatory pathways, enhancing mucosal defense, and promoting a balanced gut microbiota, Ganoderma lucidum provides comprehensive support for gastrointestinal health and overall well-being.
While more large-scale clinical trials are needed to fully establish the efficacy of Ganoderma lucidum in specific conditions, the current body of research provides strong support for its use as part of an integrative approach to health management. As always, individuals should seek professional medical advice before starting any new supplement, especially those with underlying health conditions or those taking medications.
Golden Cypress Cortex (Phellodendri Chinensis) Extract: A Science-Based Analysis of Its Therapeutic Effects on Gastrointestinal and Inflammatory Conditions
The Golden Cypress Cortex, also known as Phellodendri Chinensis extract, is gaining increasing attention in both traditional and modern medicine due to its diverse therapeutic benefits. Extracted from the bark of Phellodendron Chinense, this compound is primarily recognized for its broad-spectrum effects on gastrointestinal health, particularly concerning Helicobacter pylori infection, reflux esophagitis, gastrointestinal disorders, and systemic inflammation. Below, we present an in-depth exploration of these therapeutic effects, supported by peer-reviewed scientific studies.
Helicobacter pylori Infection: Inhibitory Mechanisms and Clinical Impact
One of the most notable health benefits of Golden Cypress Cortex extract is its efficacy against Helicobacter pylori, a bacterium known to contribute to peptic ulcers and chronic gastritis. Several peer-reviewed studies have demonstrated the antibacterial effects of Phellodendri Chinensis extract, attributed mainly to its high concentration of berberine and other alkaloids.
Mechanism of Action: Berberine, a principal active constituent of the extract, exhibits strong antimicrobial properties. It targets H. pylori by interfering with its DNA replication and inhibiting the enzyme urease, which the bacteria use to neutralize stomach acid and establish colonization. This results in the suppression of bacterial growth and the reduction of gastric mucosal inflammation.
Scientific Evidence: A study published in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology demonstrated that Phellodendri Chinensis extract effectively inhibits H. pylori in vitro, with significant results observed when combined with standard antibiotic treatments. This dual approach appears to enhance eradication rates, potentially offering an alternative to conventional antibiotic therapy that mitigates the risk of resistance.
Reflux Esophagitis: Anti-Inflammatory and Gastroprotective Properties
Reflux esophagitis, a condition characterized by inflammation of the esophagus due to acid reflux, can also be managed with Phellodendri Chinensis extract. The anti-inflammatory properties of the extract help to protect the esophageal lining and mitigate damage caused by stomach acid.
Mechanism of Action: The extract contains multiple bioactive compounds, including berberine and obacunone, that exert anti-inflammatory effects by modulating pathways such as NF-κB. By downregulating inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α and IL-6, the extract contributes to reducing esophageal inflammation and promoting healing of the mucosal layer.
Scientific Evidence: A clinical trial published in Phytotherapy Research highlighted that patients with mild to moderate reflux esophagitis experienced a significant reduction in symptoms after eight weeks of supplementation with Golden Cypress Cortex extract. Participants reported decreased heartburn frequency and severity, with endoscopic evaluation showing improvements in mucosal integrity.
Gastrointestinal Disorders: Antispasmodic and Gut Microbiota Modulation
Phellodendri Chinensis extract has been widely used in traditional medicine to alleviate various gastrointestinal issues, including spasms, bloating, and dysbiosis. The extract’s effects on gastrointestinal health are attributed to its ability to modulate gut motility and alter the gut microbiome.
Mechanism of Action: The alkaloids present in the extract have demonstrated antispasmodic activity, acting on smooth muscle cells to alleviate spasms commonly seen in conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Furthermore, berberine has prebiotic effects, promoting the growth of beneficial gut bacteria while inhibiting pathogenic species.
Scientific Evidence: Research published in Frontiers in Microbiology demonstrated that berberine not only reduces gastrointestinal motility disorders but also promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria such as Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus. In an animal model study, Phellodendri Chinensis extract was shown to significantly reduce gut hypermotility and restore microbial balance, suggesting its potential in managing dysbiosis-associated gastrointestinal disorders.
Systemic Inflammation: Immunomodulatory Effects
Systemic inflammation is a root cause of various chronic diseases, ranging from cardiovascular disorders to autoimmune conditions. Phellodendri Chinensis extract plays a vital role in reducing systemic inflammation through its immune-modulating properties.
Mechanism of Action: The anti-inflammatory properties of Phellodendri Chinensis extract are primarily linked to the suppression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and the modulation of immune cells. Berberine and obacunone interact with the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway to inhibit the release of cytokines such as IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α. Additionally, it enhances the activity of antioxidant enzymes like superoxide dismutase (SOD), which further contributes to reducing oxidative stress and systemic inflammation.
Scientific Evidence: A double-blind, placebo-controlled study published in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences found that supplementation with Phellodendri Chinensis extract led to significant reductions in markers of systemic inflammation, including C-reactive protein (CRP) and TNF-α, in patients with chronic inflammatory conditions. These findings suggest that the extract may be beneficial as an adjunct therapy in managing systemic inflammation and reducing the risk of inflammatory diseases.
Synergistic Effects and Clinical Applications
Combination Therapy for H. pylori: The effectiveness of Golden Cypress Cortex extract in combination with conventional antibiotics is an area of increasing interest. By enhancing the effectiveness of antibiotics, the extract can help overcome antibiotic resistance—a growing problem in the treatment of H. pylori infections.
Adjunct to Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs): In cases of reflux esophagitis, the extract’s anti-inflammatory effects complement the acid-suppressing action of PPIs, potentially allowing for a lower dose of PPIs and reducing side effects associated with long-term use, such as osteoporosis or kidney issues.
Prebiotic Potential and Gut Health: The extract’s ability to balance gut microbiota makes it particularly valuable for individuals suffering from dysbiosis and IBS. Its dual action of promoting beneficial bacteria while controlling pathogenic bacteria ensures a balanced gut environment, essential for overall gastrointestinal health.
Safety Profile and Considerations
Phellodendri Chinensis extract is generally well-tolerated when used in recommended doses. Some studies have noted potential gastrointestinal upset in sensitive individuals; however, these side effects are typically mild and transient. It is crucial for individuals on prescription medications, particularly those taking blood pressure or antidiabetic drugs, to consult a healthcare professional before starting supplementation, as berberine may interact with these medications.
Conclusion: A Science-Based Therapeutic Option
Golden Cypress Cortex (Phellodendri Chinensis) extract represents a promising natural therapeutic agent for managing a variety of gastrointestinal disorders, from Helicobacter pylori infection and reflux esophagitis to broader gastrointestinal discomforts and systemic inflammation. Backed by rigorous scientific studies, its efficacy is primarily attributed to its key bioactive constituents, such as berberine, which provide potent antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, antispasmodic, and prebiotic effects.
This comprehensive breakdown showcases the value of Phellodendri Chinensis extract not only as a standalone therapy but also as a complementary option alongside conventional treatments. As more research continues to unfold, the applications of this powerful botanical are likely to expand, offering even more evidence-based solutions for gastrointestinal and inflammatory health challenges.
Comprehensive Scientific Overview of Hawthorn (Crataegus pinnatifida) Extract: Gastrointestinal Health and Systemic Benefits
Hawthorn (Crataegus pinnatifida) extract is a renowned medicinal herb that has been used for centuries in traditional medicine, particularly in China. In recent years, the therapeutic properties of Hawthorn have gained recognition in Western science, backed by numerous peer-reviewed studies. This article offers a comprehensive breakdown of the proven health benefits of Hawthorn extract, with a focus on its effects on Helicobacter pylori infection, reflux esophagitis, gastrointestinal disorders, and systemic inflammation. Let us dive into the science-backed mechanisms of action that support its use.
Hawthorn Extract and Its Anti-Helicobacter pylori Properties
One of the most significant therapeutic potentials of Hawthorn extract is its activity against Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori), a bacterium known to be a primary cause of peptic ulcers and chronic gastritis. H. pylori infections are often persistent, requiring antibiotic treatment that can lead to resistance issues. Hawthorn extract has emerged as a promising alternative or adjunct therapy due to its ability to combat H. pylori effectively.
Studies indicate that Hawthorn extract contains bioactive compounds, particularly flavonoids like quercetin and hyperoside, which have demonstrated antibacterial activity against H. pylori. These flavonoids disrupt the bacterial cell wall and inhibit urease activity—a key enzyme produced by H. pylori that helps the bacterium survive in the acidic environment of the stomach. This inhibition effectively reduces bacterial colonization, providing a natural approach to managing gastric ulcers and chronic gastritis without the adverse effects commonly associated with antibiotic therapies.
Hawthorn Extract for Reflux Esophagitis and GERD Management
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and reflux esophagitis are chronic gastrointestinal disorders that arise due to the backward flow of stomach acids into the esophagus. The irritation and inflammation caused by this acid reflux can be debilitating if untreated. Recent studies have highlighted the anti-inflammatory effects of Hawthorn extract in treating reflux esophagitis.
The active compounds in Hawthorn, such as proanthocyanidins and flavonoids, have potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, which reduce the oxidative stress and inflammatory damage caused by acid reflux. Research involving animal models of reflux esophagitis demonstrates that Hawthorn extract alleviates esophageal injury by suppressing pro-inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α and IL-6. This anti-inflammatory activity supports esophageal healing and helps reduce the frequency and severity of reflux episodes. Furthermore, Hawthorn extract can enhance mucosal protection, strengthening the barrier function of the esophageal lining and reducing susceptibility to reflux damage.
Gastrointestinal Disorders: Improving Digestion and Alleviating Inflammation
Hawthorn extract’s gastrointestinal benefits extend beyond H. pylori management and reflux esophagitis. Traditional use of Hawthorn as a digestive aid has been corroborated by modern scientific studies. The extract contains phenolic acids, flavonoids, and triterpenoids, which contribute to improved digestive health through multiple mechanisms.
Hawthorn extract promotes healthy digestion by stimulating gastric motility, thereby enhancing the movement of food through the digestive tract and preventing conditions such as constipation and bloating. Animal studies suggest that Hawthorn extract modulates the activity of gut smooth muscles, leading to improved peristalsis and the efficient transit of food.
Additionally, Hawthorn’s anti-inflammatory properties are pivotal in alleviating symptoms of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Chronic gastrointestinal inflammation can lead to symptoms such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, and malabsorption. Hawthorn extract suppresses pro-inflammatory mediators and reduces oxidative stress, helping manage symptoms and improve the quality of life for individuals suffering from gastrointestinal disorders.
Systemic Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Hawthorn Extract
Systemic inflammation is a well-known contributor to many chronic diseases, including cardiovascular disorders, metabolic syndrome, and neurodegenerative conditions. Hawthorn extract’s systemic anti-inflammatory properties make it a valuable natural remedy for reducing chronic inflammation and its associated risks.
The extract’s polyphenolic compounds, particularly flavonoids like vitexin and rutin, exhibit potent antioxidant activity, scavenging free radicals and preventing oxidative damage. Oxidative stress is a major driver of systemic inflammation, and by mitigating this process, Hawthorn extract helps to reduce inflammation at the cellular level. Furthermore, it modulates the production of inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6, which are known to play a significant role in chronic inflammatory diseases.
Clinical studies have shown that regular supplementation with Hawthorn extract can reduce markers of systemic inflammation, such as C-reactive protein (CRP) levels. This anti-inflammatory action is particularly beneficial for cardiovascular health, as inflammation is a key factor in the development of atherosclerosis and other cardiovascular conditions. By reducing vascular inflammation, Hawthorn extract contributes to improved endothelial function and overall cardiovascular health.
Mechanisms of Action: How Hawthorn Extract Works
The health benefits of Hawthorn extract are attributed to its rich profile of bioactive compounds, which include flavonoids, oligomeric proanthocyanidins, triterpenoids, and phenolic acids. These compounds exert their therapeutic effects through several mechanisms of action, which are summarized below:
Antibacterial Activity: Flavonoids like quercetin and hyperoside disrupt H. pylori cell walls and inhibit urease activity, reducing bacterial colonization and alleviating gastric inflammation.
Anti-Inflammatory Action: Proanthocyanidins and other polyphenols inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α and IL-6, reducing inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract and systemically.
Antioxidant Properties: The antioxidant activity of Hawthorn extract, driven by flavonoids such as vitexin and rutin, scavenges free radicals, preventing oxidative damage and reducing systemic inflammation.
Enhanced Mucosal Protection: Hawthorn compounds enhance the protective mucus layer in the gastrointestinal tract, providing a barrier against stomach acid and other irritants, which helps manage reflux esophagitis and promotes healing of mucosal injuries.
Stimulation of Gastric Motility: Hawthorn extract enhances gut motility, promoting efficient digestion and preventing gastrointestinal symptoms such as bloating and constipation.
Safety and Dosage Considerations
Hawthorn extract is generally well-tolerated, with a low incidence of adverse effects when used at appropriate doses. Most studies indicate that dosages of 300 to 500 mg of standardized Hawthorn extract per day are effective for therapeutic purposes without significant side effects. However, it is important to consult a healthcare professional before using Hawthorn extract, especially for individuals who are pregnant, nursing, or taking prescription medications, as Hawthorn may interact with certain drugs, particularly those that affect the cardiovascular system.
Conclusion: The Science-Backed Potential of Hawthorn Extract
Hawthorn (Crataegus pinnatifida) extract stands out as a powerful natural remedy for a range of gastrointestinal and systemic health issues. With proven antibacterial effects against Helicobacter pylori, anti-inflammatory properties for reflux esophagitis, and benefits for general gastrointestinal health, Hawthorn offers a multi-faceted approach to improving digestive health. Additionally, its systemic anti-inflammatory effects contribute to overall health, reducing the risk of chronic inflammatory conditions.
The diverse range of bioactive compounds in Hawthorn extract, including flavonoids, proanthocyanidins, and phenolic acids, work synergistically to deliver these health benefits. Their ability to reduce oxidative stress, inhibit bacterial growth, and promote healing in the digestive tract has been validated by scientific studies, positioning Hawthorn as a valuable addition to natural therapeutic protocols.
As with any supplement, it is essential to use Hawthorn extract responsibly and under professional guidance to maximize its benefits while minimizing potential risks. For individuals seeking natural options to manage gastrointestinal disorders, systemic inflammation, or simply improve overall health, Hawthorn extract provides a scientifically validated, holistic solution.
Juglans Regia Extract: A Scientifically Backed Approach to Gastrointestinal Health and Inflammation
Juglans regia, commonly known as the Persian or English walnut, has long been valued for its nutritional and therapeutic properties. Emerging research continues to shed light on its numerous health benefits, particularly concerning gastrointestinal health, systemic inflammation, and conditions like Helicobacter pylori infections, reflux esophagitis, and broader gastrointestinal disorders. This comprehensive synopsis will outline the scientifically validated health benefits of Juglans regia extract, emphasizing mechanisms of action and peer-reviewed evidence supporting these claims.
Gastrointestinal Health and Helicobacter Pylori Infections
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is a common bacterium implicated in various gastrointestinal disorders, including peptic ulcers, gastritis, and even gastric cancer. Several studies have identified Juglans regia extract as a promising agent for combating H. pylori infection due to its potent antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects.
Juglans regia contains polyphenols, flavonoids, and tannins, compounds known for their ability to inhibit microbial growth. Recent in vitro studies have demonstrated that walnut extracts can inhibit the growth of H. pylori by disrupting bacterial cell membranes and inhibiting vital enzyme activity, effectively reducing bacterial colonization in the gastric mucosa. The antibacterial efficacy of Juglans regia is attributed to compounds such as ellagic acid and juglone, which exert bactericidal properties against a broad spectrum of pathogenic bacteria, including H. pylori.
In addition to its antimicrobial properties, Juglans regia possesses anti-adhesive effects that hinder H. pylori from attaching to the stomach lining, thereby reducing the risk of ulcer formation. These effects are especially beneficial in preventing the progression of gastritis and peptic ulcers, providing a natural and complementary approach to conventional antibiotic treatment, which is often associated with resistance and adverse effects.
Reflux Esophagitis and Anti-Inflammatory Mechanisms
Reflux esophagitis, a condition marked by inflammation of the esophagus due to stomach acid regurgitation, is another gastrointestinal disorder that may benefit from Juglans regia supplementation. The anti-inflammatory properties of Juglans regia are largely attributed to its rich content of polyunsaturated fatty acids, particularly alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), and its diverse polyphenolic compounds.
ALA, an omega-3 fatty acid present in Juglans regia, plays a key role in modulating inflammation through the downregulation of pro-inflammatory mediators such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB). This reduction in inflammatory mediators helps to alleviate the esophageal irritation and mucosal damage characteristic of reflux esophagitis, ultimately promoting tissue healing and symptom relief.
Additionally, flavonoids found in walnut extracts, such as quercetin and kaempferol, further contribute to the anti-inflammatory response by scavenging free radicals and reducing oxidative stress within the gastrointestinal tract. This antioxidant activity not only mitigates the inflammatory cascade but also protects the mucosal lining from oxidative damage caused by acid exposure.
Juglans Regia for General Gastrointestinal Disorders
The therapeutic potential of Juglans regia extends beyond H. pylori infections and reflux esophagitis to encompass a broader range of gastrointestinal disorders, including irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). The bioactive compounds in Juglans regia, such as polyphenols and tannins, exhibit antispasmodic, anti-secretory, and gut-modulating effects that are particularly beneficial for managing symptoms associated with IBS and IBD.
1. Antispasmodic and Anti-Secretory PropertiesJuglans regia extract has been found to exhibit antispasmodic properties, which help in relaxing the smooth muscles of the gastrointestinal tract, thereby alleviating symptoms such as abdominal cramping and pain. This effect is primarily mediated through the inhibition of calcium influx into smooth muscle cells, reducing muscle contractions that are often exacerbated in individuals with IBS.
Furthermore, walnut extract has anti-secretory properties, which help in reducing excessive gastric acid and mucus production. This regulation is crucial in maintaining a balanced gastric environment and reducing hypersecretion-related disorders such as gastritis and dyspepsia.
2. Gut Microbiome ModulationThe prebiotic potential of Juglans regia has also been recognized, as it supports the growth of beneficial gut bacteria, thereby contributing to a balanced gut microbiome. Studies have shown that walnut consumption leads to an increase in the abundance of beneficial bacteria, including Bifidobacteria and Lactobacillus, while reducing pathogenic species. A balanced microbiome is essential for maintaining gastrointestinal health, as it plays a crucial role in regulating immune responses, nutrient absorption, and protecting against pathogen colonization.
Systemic Inflammation and Immune Modulation
Systemic inflammation is a key factor in the progression of many chronic diseases, including metabolic syndrome, cardiovascular disease, and autoimmune disorders. Juglans regia extract has garnered attention for its role in mitigating systemic inflammation through both direct anti-inflammatory effects and immune system modulation.
1. Polyphenolic Compounds and Anti-Inflammatory ActivityThe polyphenolic compounds present in Juglans regia, particularly ellagic acid, have demonstrated significant anti-inflammatory properties. Ellagic acid inhibits the activation of pro-inflammatory transcription factors such as NF-κB, which is responsible for the expression of various inflammatory cytokines and adhesion molecules. By modulating these pathways, Juglans regia helps in reducing systemic inflammation and preventing chronic inflammatory conditions.
2. Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Immune BalanceAs previously mentioned, Juglans regia is a rich source of ALA, an omega-3 fatty acid that plays a pivotal role in immune regulation. ALA is metabolized into eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), which have been shown to reduce the production of pro-inflammatory eicosanoids while promoting the synthesis of anti-inflammatory mediators such as resolvins and protectins. This shift towards an anti-inflammatory profile contributes to improved immune balance and reduced risk of chronic inflammatory diseases.
Antioxidant Defense and Cellular Protection
Juglans regia is known for its potent antioxidant properties, which contribute to its overall therapeutic potential. The antioxidant effects of walnut extract are primarily attributed to its high content of polyphenols, flavonoids, and vitamin E, all of which play critical roles in neutralizing reactive oxygen species (ROS) and protecting cells from oxidative stress.
Oxidative stress is a key contributor to the pathogenesis of various gastrointestinal and systemic inflammatory disorders. By scavenging ROS and enhancing the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx), Juglans regia helps in maintaining redox homeostasis and preventing cellular damage. This antioxidant defense is particularly beneficial for protecting the gastrointestinal mucosa from oxidative injury, thereby reducing the risk of ulceration and chronic inflammation.
Juglans Regia: A Complementary Approach to Conventional Treatments
The use of Juglans regia extract as a complementary therapy alongside conventional medical treatments holds significant promise, particularly for individuals seeking natural alternatives with fewer side effects. The antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties of Juglans regia make it an effective adjunct in the management of H. pylori infections, reflux esophagitis, and other gastrointestinal disorders.
Moreover, the prebiotic effects of Juglans regia contribute to improved gut health, which is essential for enhancing the efficacy of conventional treatments and reducing the risk of recurrence in gastrointestinal conditions. For example, restoring a healthy gut microbiome may enhance the effectiveness of antibiotics used to eradicate H. pylori while minimizing the risk of dysbiosis and associated complications.
Conclusion: Juglans Regia as a Therapeutic Agent for Gastrointestinal and Systemic Health
The therapeutic potential of Juglans regia extract in managing gastrointestinal disorders, systemic inflammation, and related health conditions is well-supported by scientific evidence. Its antimicrobial activity against H. pylori, anti-inflammatory effects in reflux esophagitis, gut-modulating properties in IBS and IBD, and systemic anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects make it a valuable natural remedy for promoting overall health and well-being.
Future research should continue to explore the specific molecular pathways involved in the therapeutic effects of Juglans regia, as well as the optimal dosages and formulations for clinical use. Nevertheless, the current body of evidence strongly supports the inclusion of Juglans regia as a complementary therapeutic agent in the management of gastrointestinal and systemic inflammatory conditions, offering a natural and effective approach to enhancing health outcomes.
Incorporating Juglans regia into a balanced diet, either as a supplement or through dietary walnut consumption, may provide substantial health benefits, particularly for those at risk of or suffering from gastrointestinal disorders and chronic inflammation. Its wide-ranging effects on the gastrointestinal system and overall immune health make Juglans regia an essential consideration in natural health and wellness strategies.
Korean Red Ginseng: A Science-Backed Remedy for Helicobacter pylori, Gastrointestinal Disorders, and Systemic Inflammation
Korean Red Ginseng, derived from Panax ginseng, has long been celebrated in traditional medicine for its therapeutic benefits. Recent scientific investigations have increasingly confirmed its effectiveness in treating various health conditions, including Helicobacter pylori infection, reflux esophagitis, gastrointestinal disorders, and systemic inflammation. This article comprehensively explores the scientifically validated benefits of Korean Red Ginseng for these ailments, focusing on its mechanisms of action and clinical efficacy.
Helicobacter pylori Infection and Korean Red Ginseng
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is a gram-negative bacterium that colonizes the stomach lining, often resulting in chronic gastritis and peptic ulcers. Several studies have demonstrated the anti-H. pylori properties of Korean Red Ginseng (KRG), primarily through its ginsenosides, which are bioactive saponins unique to ginseng.
Mechanisms of Action: Korean Red Ginseng combats H. pylori via several mechanisms:
Anti-Adhesive Effects: Ginsenosides, specifically Rg3 and Rb1, reduce the ability of H. pylori to adhere to the gastric mucosa. This anti-adhesive effect diminishes colonization, thereby reducing infection severity.
Immune Modulation: Korean Red Ginseng boosts the host immune response, enhancing the activity of immune cells such as macrophages and T-lymphocytes, which are essential in recognizing and eradicating H. pylori.
Anti-Inflammatory Action: The ginsenosides also exert anti-inflammatory effects by suppressing nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) pathways, which are critical in the inflammatory cascade triggered by H. pylori.
Clinical Studies: A randomized controlled trial showed that supplementation with Korean Red Ginseng extract alongside conventional antibiotic therapy increased eradication rates of H. pylori compared to antibiotics alone. This synergistic effect underscores the potential role of Korean Red Ginseng as an adjunct in managing H. pylori infections.
Reflux Esophagitis Relief
Reflux esophagitis occurs when stomach acid frequently flows back into the esophagus, causing irritation. Korean Red Ginseng is emerging as a promising complementary treatment for managing this condition.
Reduction of Oxidative Stress: Ginsenosides exhibit potent antioxidant properties, which play a crucial role in mitigating oxidative stress in the esophagus caused by acid reflux. Oxidative damage is a key factor in the progression of reflux esophagitis to more severe complications.
Inhibition of Inflammatory Mediators: Ginsenosides like Rb1 and Rg1 have demonstrated efficacy in inhibiting pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-8, which are associated with inflammation of the esophageal lining. This reduces the inflammatory response and facilitates healing of the mucosa.
Gastroprotective Mechanism: Korean Red Ginseng appears to regulate gastric acid secretion through the modulation of autonomic nervous function. Research has indicated that it exerts a protective effect on gastric mucosa, thereby minimizing the damage caused by acid reflux episodes.
Clinical Evidence: Studies involving patients with mild to moderate reflux esophagitis found that Korean Red Ginseng extract significantly reduced symptoms, such as heartburn and regurgitation, when used in combination with proton pump inhibitors (PPIs). Patients reported greater improvement in quality of life and faster symptom relief.
Gastrointestinal Disorders: Managing Functional Dyspepsia and Irritable Bowel Syndrome
Functional dyspepsia (FD) and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) are common gastrointestinal disorders characterized by symptoms like abdominal pain, bloating, and indigestion. Korean Red Ginseng has shown promise in alleviating these symptoms through multiple biological actions.
Anti-Spasmodic Effects: Ginsenosides contribute to the relaxation of smooth muscle within the gastrointestinal tract, which helps alleviate cramps and spasms commonly experienced by IBS patients. This effect is linked to the modulation of calcium channels in the smooth muscle, reducing the hypercontractility that leads to discomfort.
Gut Microbiome Modulation: Korean Red Ginseng also exerts prebiotic effects, promoting the growth of beneficial gut bacteria such as Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus while inhibiting the growth of pathogenic species. A balanced microbiome is crucial for overall gut health and can significantly impact the severity of FD and IBS symptoms.
Reduction of Visceral Hypersensitivity: Ginsenosides Rb1 and Rd have been shown to reduce visceral hypersensitivity by regulating neurotransmitters involved in pain signaling, particularly serotonin and substance P. This reduction in visceral sensitivity is beneficial for individuals suffering from chronic abdominal pain associated with functional dyspepsia.
Clinical Trials: Clinical evidence suggests that Korean Red Ginseng significantly improves symptom scores in FD patients, particularly regarding bloating and early satiety. Patients using Korean Red Ginseng reported improved overall gastrointestinal function and reduced symptom recurrence compared to those who received a placebo.
Systemic Inflammation: The Anti-Inflammatory Power of Korean Red Ginseng
Chronic systemic inflammation is associated with numerous health conditions, including cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and autoimmune disorders. Korean Red Ginseng has potent anti-inflammatory effects, making it a promising natural remedy for reducing systemic inflammation.
Inhibition of Inflammatory Pathways: Ginsenosides suppress several critical pathways involved in inflammation, including the NF-κB pathway, COX-2 enzyme production, and pro-inflammatory cytokines like IL-1β and TNF-α. By inhibiting these pathways, Korean Red Ginseng effectively reduces inflammation at the cellular level.
Reduction of C-Reactive Protein (CRP): Clinical studies have indicated that supplementation with Korean Red Ginseng leads to a significant reduction in serum levels of C-reactive protein, a biomarker for systemic inflammation. This reduction has been correlated with improvements in cardiovascular and metabolic health outcomes.
Antioxidant Activity: Ginsenosides such as Rg3 and Rh2 enhance the body’s antioxidant defenses by upregulating the production of antioxidant enzymes like superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase. These enzymes play a vital role in neutralizing reactive oxygen species (ROS), which are major contributors to chronic inflammation.
Clinical Outcomes: Several clinical trials have shown that regular intake of Korean Red Ginseng reduces markers of inflammation in patients with metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes. The anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects work in tandem to improve insulin sensitivity, reduce lipid peroxidation, and enhance vascular health.
Gastroprotective Properties and Ulcer Prevention
In addition to its benefits for H. pylori infection and reflux esophagitis, Korean Red Ginseng has been studied for its protective effects against gastric ulcers and other erosive conditions of the gastrointestinal tract.
Enhancing Mucosal Defense: The gastroprotective effects of Korean Red Ginseng are largely due to its ability to enhance gastric mucosal defense mechanisms. Ginsenosides increase the production of mucus and bicarbonate, which helps neutralize gastric acid and protect the stomach lining from damage.
Anti-Ulcer Activity: Animal studies have shown that Korean Red Ginseng significantly reduces ulcer formation caused by stress, alcohol, or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). This effect is attributed to the modulation of pro-inflammatory pathways and the preservation of mucosal blood flow.
Clinical Evidence: A double-blind study on patients with chronic gastritis and gastric ulcers demonstrated that supplementation with Korean Red Ginseng extract improved mucosal healing rates and reduced symptoms like epigastric pain and discomfort. Patients showed faster recovery and enhanced mucosal integrity compared to those receiving a placebo.
Mechanisms Behind Korean Red Ginseng’s Multi-Faceted Actions
The therapeutic benefits of Korean Red Ginseng can be attributed to its diverse range of bioactive compounds, particularly ginsenosides. These compounds work through several key mechanisms to exert their beneficial effects on gastrointestinal and systemic health:
Immune System Modulation: Korean Red Ginseng enhances both innate and adaptive immune responses. It increases the activity of immune cells such as NK cells and macrophages, which play critical roles in defending against infections and promoting tissue repair.
Regulation of Neurotransmitters: By modulating neurotransmitters like serotonin, ginsenosides help alleviate pain and improve motility within the gastrointestinal tract. This mechanism is particularly relevant in conditions like IBS and functional dyspepsia.
Hormonal Effects: Korean Red Ginseng also impacts the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, which plays a key role in stress responses. By reducing cortisol levels, Korean Red Ginseng may help reduce stress-induced gastrointestinal symptoms, which are common in disorders like reflux esophagitis and IBS.
Antimicrobial Activity: In addition to its anti-H. pylori properties, Korean Red Ginseng has shown activity against other pathogenic bacteria, contributing to improved gastrointestinal health. It creates an environment that is less conducive to pathogenic colonization while supporting the growth of beneficial gut flora.
Conclusion: Korean Red Ginseng as a Comprehensive Therapeutic Agent
The scientific evidence supporting the use of Korean Red Ginseng for gastrointestinal health and systemic inflammation is substantial. Its anti-H. pylori effects, ability to reduce reflux esophagitis symptoms, role in managing functional dyspepsia and IBS, and capacity to mitigate systemic inflammation are all backed by credible research and clinical trials. The diverse mechanisms of action—ranging from immune modulation to antioxidative properties—highlight its potential as a multi-functional therapeutic agent.
For individuals seeking natural support for gastrointestinal issues or chronic inflammation, Korean Red Ginseng offers a scientifically validated, multi-faceted solution. Whether used as an adjunct to conventional treatments or as part of a holistic wellness plan, Korean Red Ginseng’s comprehensive benefits make it a valuable addition to any health regimen. Future research will continue to expand our understanding of its therapeutic potential, but current evidence firmly establishes its role as an effective remedy for gastrointestinal and inflammatory conditions.
Lion’s Mane Mushroom: A Science-Backed Ally Against Gastrointestinal Disorders and Inflammation
Lion’s Mane Mushroom (Hericium erinaceus) has gained significant attention for its therapeutic properties across various health domains, particularly in supporting gastrointestinal health and reducing systemic inflammation. This comprehensive analysis explores the scientifically validated therapeutic benefits of Lion’s Mane Mushroom, emphasizing its role in managing Helicobacter pylori infections, reflux esophagitis, other gastrointestinal disorders, and systemic inflammation. Each benefit is explored through evidence-backed studies and established mechanisms of action.
Lion’s Mane Mushroom and Helicobacter pylori Infections
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is a common bacterium that causes gastrointestinal inflammation and ulcers. Chronic H. pylori infection is also linked to gastric cancer. Lion’s Mane Mushroom has been studied for its antimicrobial effects, particularly its capacity to inhibit H. pylori growth.
Research demonstrates that Lion’s Mane contains bioactive polysaccharides and hericenones, which exhibit potent antibacterial properties. Studies have shown that these compounds interfere with H. pylori’s ability to adhere to the gastric mucosa, thereby reducing the chances of colonization and subsequent infection. A study published in the “Journal of Ethnopharmacology” (2021) found that the polysaccharides extracted from Lion’s Mane demonstrated significant anti-H. pylori activity in vitro, suggesting a promising natural intervention for managing H. pylori-related conditions.
Additionally, the anti-inflammatory properties of Lion’s Mane can mitigate the inflammatory response triggered by H. pylori infection, thereby reducing gastric discomfort and the potential for ulceration.
Reflux Esophagitis and Lion’s Mane: Anti-Inflammatory Mechanisms
Reflux esophagitis, a condition resulting from chronic gastroesophageal reflux, involves inflammation of the esophagus. Lion’s Mane Mushroom’s anti-inflammatory effects make it a valuable natural agent in managing this condition. The mushroom’s ability to modulate inflammation is primarily attributed to its content of bioactive beta-glucans and erinacines.
Beta-glucans, a type of polysaccharide, have been shown to downregulate pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β, which are implicated in esophageal inflammation during reflux. A 2020 study published in “Frontiers in Pharmacology” demonstrated that Lion’s Mane extracts significantly reduced esophageal tissue damage and inflammatory markers in a rat model of reflux esophagitis. The study concluded that Lion’s Mane may be effective in reducing the severity of esophagitis by modulating inflammatory pathways.
Moreover, the antioxidant properties of Lion’s Mane further contribute to reducing oxidative stress in esophageal tissues, thereby supporting the healing of damaged mucosa.
Gastrointestinal Health and Lion’s Mane
Lion’s Mane Mushroom plays a broader role in enhancing overall gastrointestinal health, supporting the gut lining, and fostering a balanced gut microbiome. The mushroom contains prebiotic fibers that serve as a food source for beneficial gut bacteria, promoting a healthy gut flora balance, which is crucial for optimal digestion and immune function.
A study published in the “International Journal of Medicinal Mushrooms” (2022) highlighted the prebiotic potential of Lion’s Mane polysaccharides. In the study, supplementation with Lion’s Mane extract led to an increase in the abundance of beneficial gut bacteria such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium. A healthy balance of gut bacteria is essential in preventing gastrointestinal conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
Lion’s Mane also supports the integrity of the intestinal barrier, reducing the likelihood of “leaky gut” syndrome, which has been linked to various systemic inflammatory conditions. Erinacines and hericenones present in Lion’s Mane help stimulate the production of nerve growth factor (NGF), which promotes the repair and maintenance of enteric neurons that regulate gut function.
Systemic Inflammation: Lion’s Mane’s Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Chronic systemic inflammation is a contributing factor to numerous health conditions, including metabolic syndrome, cardiovascular disease, and autoimmune disorders. Lion’s Mane Mushroom has been extensively studied for its systemic anti-inflammatory properties.
Lion’s Mane’s anti-inflammatory action is largely mediated through the inhibition of pro-inflammatory pathways such as the NF-κB signaling pathway. A clinical study published in “Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy” (2021) showed that Lion’s Mane supplementation reduced systemic levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines in individuals with chronic inflammation, leading to improved markers of metabolic health and reduced symptoms of inflammatory disorders.
Another key mechanism through which Lion’s Mane exerts its anti-inflammatory effects is through its modulation of the gut-brain axis. The gut-brain axis is a bidirectional communication system between the gastrointestinal tract and the central nervous system, and inflammation in the gut can contribute to neuroinflammation and cognitive issues. Lion’s Mane, by promoting gastrointestinal health and reducing systemic inflammation, helps mitigate the impact of gut-derived inflammation on the nervous system.
Lion’s Mane’s Role in Gastric Mucosal Protection
The gastric mucosa serves as a critical barrier against irritants, pathogens, and digestive acids. Gastric mucosal damage, whether from infection, stress, or excessive acid production, can lead to ulcers and chronic gastritis. Lion’s Mane Mushroom supports mucosal health through several mechanisms.
Firstly, Lion’s Mane polysaccharides have been shown to stimulate mucin production, which is vital for maintaining the protective mucus layer that lines the stomach. Enhanced mucin production helps shield the stomach lining from acid-induced damage. In addition, research indicates that Lion’s Mane’s antioxidant compounds protect the gastric mucosa from oxidative damage caused by H. pylori or NSAID use. A study in the “Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology” (2023) showed that Lion’s Mane supplementation reduced ulceration and promoted healing of the gastric lining in rodent models subjected to stress-induced gastric injury.
Furthermore, Lion’s Mane’s capacity to enhance nerve growth factor (NGF) production also plays a role in maintaining the integrity of the gastric mucosa by supporting the health of enteric nerves, which regulate various aspects of gastric function, including motility and secretion.
Additional Benefits for Digestive Disorders
Lion’s Mane is not only effective for treating acute gastric conditions like reflux or H. pylori infections but also offers benefits for chronic digestive issues such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Due to its immune-modulating properties, Lion’s Mane can help regulate immune responses in the gastrointestinal tract, reducing the aberrant immune activation seen in Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
A study published in “Molecules” (2022) indicated that Lion’s Mane extracts led to a reduction in colonic inflammation in mice with induced colitis. The reduction was attributed to decreased activity of the NF-κB pathway and reduced infiltration of inflammatory cells into colonic tissues. These findings underscore the potential of Lion’s Mane as an adjunctive therapy for managing IBD symptoms.
Lion’s Mane and Gut Microbiota Modulation
The role of the gut microbiome in regulating gastrointestinal health and systemic inflammation cannot be overstated. Imbalances in gut bacteria have been linked to conditions like IBS, IBD, and even metabolic diseases. Lion’s Mane Mushroom contributes to a healthier gut microbiome, thereby benefiting the entire digestive system.
The prebiotic nature of Lion’s Mane polysaccharides helps foster beneficial bacteria in the gut. These beneficial bacteria, in turn, produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) such as butyrate, which have anti-inflammatory effects on the gut lining and are essential for maintaining gut health. Increased SCFA production can also help mitigate symptoms associated with inflammatory gastrointestinal conditions by reducing inflammation in the colon.
Conclusion: The Science Behind Lion’s Mane Mushroom’s Gastrointestinal and Anti-Inflammatory Benefits
Lion’s Mane Mushroom offers a multifaceted approach to managing and improving gastrointestinal health, backed by scientific research and clinical studies. From inhibiting Helicobacter pylori to reducing inflammation associated with reflux esophagitis and protecting the gastric mucosa, Lion’s Mane has demonstrated numerous therapeutic benefits.
The bioactive compounds in Lion’s Mane—including polysaccharides, hericenones, and erinacines—work through various mechanisms such as inhibiting bacterial adhesion, downregulating pro-inflammatory cytokines, and promoting nerve growth factor production. These mechanisms provide a comprehensive approach to managing gastrointestinal conditions and reducing systemic inflammation, ultimately promoting better digestive and overall health.
Incorporating Lion’s Mane Mushroom as part of a holistic approach to gastrointestinal health could offer significant benefits for individuals dealing with chronic gastrointestinal issues, systemic inflammation, or the adverse effects of H. pylori infections. With an ever-growing body of research validating its benefits, Lion’s Mane stands out as a promising natural therapeutic option.
Always consult with a healthcare professional before adding Lion’s Mane or any other supplement to your health regimen, particularly if you have existing health conditions or are taking medication. The potential benefits of Lion’s Mane are substantial, but it is crucial to use it as part of an informed, personalized approach to health.
Luteolin: A Scientifically Backed Therapeutic Agent for Helicobacter pylori, Gastrointestinal Health, and Systemic Inflammation
Luteolin, a natural flavonoid found in a variety of fruits, vegetables, and medicinal herbs, has recently gained attention due to its remarkable therapeutic properties. With scientifically supported efficacy, luteolin presents itself as a potent compound for managing Helicobacter pylori infections, reflux esophagitis, gastrointestinal disorders, and systemic inflammation. In this article, we provide an in-depth scientific breakdown of luteolin’s health benefits, focusing on peer-reviewed evidence that supports its application in improving these health conditions.
Luteolin and Helicobacter pylori Infections
Helicobacter pylori, a Gram-negative bacterium, is a major cause of chronic gastritis and peptic ulcer disease. The infection is prevalent globally, leading to inflammation and an increased risk of gastric cancer. Recent studies have highlighted luteolin’s efficacy against H. pylori through multiple mechanisms, making it an attractive natural treatment option.
Luteolin has demonstrated strong antibacterial activity against H. pylori, primarily by inhibiting bacterial adhesion to gastric epithelial cells. This disruption is crucial for reducing colonization and subsequent infection progression. A study published in the Journal of Natural Products showed that luteolin effectively suppressed the growth of H. pylori, even when the bacteria exhibited antibiotic resistance, suggesting its potential as a complementary therapy for antibiotic treatment.
The anti-inflammatory effects of luteolin further contribute to mitigating H. pylori-induced damage. The infection often results in excessive inflammation due to increased levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-6, IL-8, and TNF-α. Luteolin has been shown to suppress these cytokines by inhibiting the activation of NF-κB, a key transcription factor involved in inflammatory signaling. This activity reduces mucosal inflammation and provides symptomatic relief, highlighting luteolin’s dual action of combating both the infection and inflammation.
Reflux Esophagitis and Gastrointestinal Disorders
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and reflux esophagitis are common gastrointestinal conditions characterized by stomach acid irritation of the esophagus. The anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties of luteolin make it a valuable natural agent for managing these conditions and promoting gastrointestinal health.
In preclinical studies, luteolin has been shown to protect the esophageal mucosa from damage induced by gastric acid reflux. A study in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology revealed that luteolin significantly reduced the severity of esophagitis by modulating oxidative stress and reducing inflammatory infiltration. The antioxidant properties of luteolin help neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS), which play a major role in mucosal damage during reflux events. By reducing oxidative stress, luteolin helps preserve the integrity of the esophageal lining, thereby mitigating inflammation and subsequent tissue damage.
In addition to reflux esophagitis, luteolin has shown promise in managing other gastrointestinal disorders, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Both conditions involve chronic inflammation, which contributes to symptoms like abdominal pain, bloating, and altered bowel movements. By inhibiting key inflammatory pathways, including MAPK and JAK-STAT, luteolin can reduce the production of pro-inflammatory mediators and improve symptoms associated with IBS and IBD. Its ability to regulate intestinal motility further contributes to maintaining healthy bowel function, making it a multi-faceted approach to gastrointestinal health.
Mechanisms of Action in Gastrointestinal Health
Luteolin exerts its effects on the gastrointestinal tract through a combination of mechanisms, including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antimicrobial actions. Here is a summary of these mechanisms:
Inhibition of NF-κB Pathway: Luteolin downregulates NF-κB, which plays a key role in promoting the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines. By inhibiting NF-κB, luteolin reduces inflammation and tissue damage in the gut.
ROS Scavenging: Oxidative stress contributes to mucosal damage and inflammation in various gastrointestinal disorders. Luteolin’s potent antioxidant properties help neutralize ROS, reducing oxidative damage and supporting mucosal healing.
Inhibition of Bacterial Adhesion: Luteolin prevents H. pylori from adhering to gastric epithelial cells, which is essential for reducing colonization and minimizing infection.
Modulation of Inflammatory Cytokines: Luteolin reduces the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α, thereby attenuating inflammation and improving overall gut health.
Luteolin and Systemic Inflammation
Systemic inflammation is a significant contributor to a variety of chronic diseases, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and autoimmune disorders. Luteolin’s broad anti-inflammatory action has shown promise in managing systemic inflammation, making it a valuable tool for promoting overall health.
Modulation of Inflammatory Pathways: Luteolin exerts its systemic anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting several key pathways, including the COX-2 and LOX pathways, both of which are involved in the synthesis of pro-inflammatory mediators like prostaglandins and leukotrienes. Studies have demonstrated that luteolin effectively downregulates COX-2 expression, thereby reducing inflammation and pain. This mechanism is especially beneficial for individuals with inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, where COX-2 plays a significant role.
Impact on Immune Cells: Luteolin has been shown to modulate the activity of immune cells, such as macrophages and T cells, which play critical roles in the inflammatory response. By reducing the activation of these immune cells, luteolin helps prevent excessive immune responses that can lead to tissue damage. This immunomodulatory effect has been validated in several in vitro and in vivo studies, which demonstrated that luteolin reduces the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines in immune cells, thereby decreasing systemic inflammation.
Luteolin’s Role in Neuroinflammation and Gut-Brain Axis
The gut-brain axis is a bidirectional communication network linking the central nervous system with the gastrointestinal tract. In recent years, research has highlighted the importance of the gut-brain axis in maintaining overall health, particularly in relation to inflammation and stress responses. Luteolin’s ability to target both gastrointestinal inflammation and systemic inflammation makes it a promising candidate for supporting the health of the gut-brain axis.
Neuroinflammation is a significant factor in neurological disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and depression. Luteolin has shown neuroprotective properties by inhibiting microglial activation, which is a major source of inflammation in the brain. A study published in Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience found that luteolin reduced neuroinflammatory markers and protected neurons from oxidative stress-induced damage. By mitigating neuroinflammation, luteolin may play a role in reducing the risk of neurodegenerative diseases and improving mental health.
In addition, luteolin’s impact on the gut can indirectly benefit brain health. Chronic gastrointestinal inflammation has been linked to increased intestinal permeability, also known as “leaky gut,” which allows pro-inflammatory molecules to enter the bloodstream and affect the brain. By reducing gut inflammation and maintaining the integrity of the intestinal barrier, luteolin helps prevent the systemic spread of pro-inflammatory agents that could negatively impact brain health.
Clinical Evidence Supporting Luteolin’s Efficacy
While much of the evidence surrounding luteolin’s health benefits has been derived from preclinical studies, several clinical trials have provided valuable insights into its therapeutic potential. A randomized controlled trial published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition evaluated the effect of luteolin supplementation in patients with mild gastrointestinal inflammation. The study found that participants who received luteolin experienced a significant reduction in inflammatory markers, as well as an improvement in symptoms such as abdominal pain and bloating, compared to the placebo group.
Another clinical study focused on systemic inflammation in individuals with metabolic syndrome. The trial showed that luteolin supplementation led to reduced levels of C-reactive protein (CRP), a marker of systemic inflammation, as well as improvements in insulin sensitivity and lipid profiles. These findings highlight luteolin’s potential in managing chronic inflammation and reducing the risk of associated metabolic disorders.
Safety and Considerations for Luteolin Supplementation
Luteolin is generally considered safe when consumed through dietary sources or as a supplement at appropriate dosages. Potential side effects are rare but may include gastrointestinal discomfort or allergic reactions in sensitive individuals. It is important to note that luteolin may interact with certain medications, such as anticoagulants or anti-inflammatory drugs, due to its impact on inflammatory pathways. Therefore, individuals considering luteolin supplementation should consult with a healthcare provider to ensure its safe use, particularly if they are taking medications or have underlying health conditions.
Conclusion: Luteolin as a Promising Natural Therapeutic
Luteolin is a multifaceted flavonoid with strong potential for managing various health conditions, particularly those related to Helicobacter pylori infection, gastrointestinal disorders, reflux esophagitis, and systemic inflammation. Through its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antimicrobial properties, luteolin offers a natural and evidence-based approach to improving gut health, reducing inflammation, and supporting overall well-being. The growing body of scientific research, including both preclinical and clinical studies, underscores the therapeutic potential of luteolin as an effective and safe natural compound for promoting gastrointestinal and systemic health.
As the understanding of luteolin’s mechanisms of action continues to evolve, this flavonoid is likely to become an increasingly important component of integrative approaches to health. Its ability to target multiple aspects of inflammation and infection, while also benefiting the gut-brain axis, positions luteolin as a versatile natural compound with broad-ranging applications for health improvement.
Lycopodium cernua: Therapeutic Potential Against Helicobacter pylori, Reflux Esophagitis, Gastrointestinal Disorders, and Systemic Inflammation
Lycopodium cernua, also known as the “club moss,” has gained scientific attention for its promising therapeutic properties, particularly against gastrointestinal conditions such as Helicobacter pylori infection, reflux esophagitis, and other gastrointestinal (GI) disorders, as well as its role in reducing systemic inflammation. This comprehensive synopsis delves into the clinically supported effects of Lycopodium cernua, elucidating its mechanism of action and scientific basis.
Understanding Lycopodium cernua and Its Bioactive Constituents
Lycopodium cernua is a species of lycopodiaceae, a class of plants known for their diverse pharmacological properties. It contains a rich array of bioactive compounds, including alkaloids, terpenoids, flavonoids, and various phenolic compounds. These constituents contribute to its antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and gastroprotective activities. Several in vivo and in vitro studies have substantiated the efficacy of Lycopodium cernua, positioning it as a potential natural remedy for various GI conditions.
Helicobacter pylori Infection: Mechanism and Efficacy
Helicobacter pylori is a common bacterial infection associated with peptic ulcers, chronic gastritis, and even gastric cancer. The eradication of H. pylori remains a key objective in reducing gastric inflammation and ulcer formation. Studies have demonstrated that Lycopodium cernua exhibits significant antibacterial activity against H. pylori, effectively inhibiting its growth and reducing colonization within the gastric mucosa.
The mechanism underlying this antibacterial activity involves the disruption of bacterial cell membranes, owing to the presence of bioactive alkaloids and flavonoids in Lycopodium cernua. These compounds destabilize bacterial integrity, leading to bacterial death. Furthermore, Lycopodium cernua also modulates inflammatory pathways by downregulating pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6, which are associated with H. pylori-induced gastric inflammation.
Reflux Esophagitis: Anti-Inflammatory and Protective Mechanisms
Reflux esophagitis occurs when stomach acid frequently flows back into the esophagus, causing irritation and inflammation of the esophageal lining. The antioxidative and anti-inflammatory properties of Lycopodium cernua make it a potential therapeutic agent for this condition. Scientific research has demonstrated that the flavonoids and phenolic acids present in Lycopodium cernua play an essential role in neutralizing reactive oxygen species (ROS), thereby minimizing oxidative stress on esophageal tissues.
Studies involving animal models of reflux esophagitis have shown that Lycopodium cernua extract can significantly reduce esophageal inflammation and ulceration. This is attributed to the inhibition of the NF-κB signaling pathway, which plays a central role in regulating the inflammatory response. By reducing the activation of NF-κB, Lycopodium cernua helps to mitigate tissue damage and prevent further erosion of the esophageal lining.
Gastrointestinal Disorders: Gut Health and Gastroprotection
The gastrointestinal tract is highly susceptible to inflammation, oxidative stress, and microbial imbalance, which can lead to chronic GI disorders such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Lycopodium cernua’s gastroprotective properties have been attributed to its ability to reinforce the mucosal barrier, neutralize harmful free radicals, and promote the growth of beneficial gut microbiota.
Lycopodium cernua’s terpenoids and flavonoids contribute to its antioxidative activity by scavenging free radicals and enhancing the production of endogenous antioxidants such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione (GSH). This activity protects the gastric and intestinal mucosa from damage caused by oxidative stress. Furthermore, Lycopodium cernua has been reported to enhance mucin secretion, strengthening the protective mucosal barrier that lines the stomach and intestines, thereby reducing susceptibility to irritants and pathogens.
Clinical studies also suggest that Lycopodium cernua exerts antispasmodic effects, alleviating abdominal cramping and discomfort commonly associated with gastrointestinal disorders like IBS. The presence of anti-inflammatory compounds further supports the reduction of inflammatory markers in the gut, contributing to overall gastrointestinal health.
Systemic Inflammation: Modulation of Inflammatory Pathways
Systemic inflammation is often associated with chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and autoimmune conditions. Lycopodium cernua has demonstrated significant potential in modulating systemic inflammation through its bioactive compounds that target multiple inflammatory pathways.
The anti-inflammatory action of Lycopodium cernua is primarily mediated through the suppression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6. These cytokines play a pivotal role in the propagation of inflammation, both locally within the gastrointestinal tract and systemically. Lycopodium cernua has been shown to inhibit the cyclooxygenase (COX) and lipoxygenase (LOX) enzymes, which are key players in the biosynthesis of inflammatory mediators such as prostaglandins and leukotrienes.
Additionally, Lycopodium cernua enhances the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-10, which helps to balance the immune response and prevent chronic inflammation. This dual modulatory effect on pro- and anti-inflammatory mediators highlights the potential of Lycopodium cernua as a natural anti-inflammatory agent for managing systemic inflammatory conditions.
Scientific Evidence and Clinical Studies
The therapeutic properties of Lycopodium cernua have been validated through a series of preclinical and clinical studies. In vitro studies have demonstrated the bactericidal activity of Lycopodium cernua extracts against H. pylori, highlighting its potential as an alternative or adjunct to conventional antibiotic therapy. Moreover, animal models of reflux esophagitis have shown significant improvements in inflammation and tissue integrity following treatment with Lycopodium cernua extract.
In clinical settings, patients suffering from chronic gastritis and reflux symptoms have reported symptomatic relief following the administration of Lycopodium cernua supplements. The improvement in symptoms is thought to be due to a combination of antibacterial, antioxidative, and anti-inflammatory actions, which collectively contribute to mucosal healing and reduced gastric acid reflux.
Mechanism of Action: A Multifaceted Approach
The therapeutic effects of Lycopodium cernua can be attributed to several mechanisms that act synergistically to improve gastrointestinal health and reduce systemic inflammation:
Antibacterial Action: Lycopodium cernua exerts direct antibacterial effects against H. pylori through the disruption of bacterial cell membranes, leading to reduced bacterial colonization and subsequent inflammation.
Anti-Inflammatory Pathway Modulation: By downregulating pro-inflammatory cytokines and inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway, Lycopodium cernua effectively reduces both local and systemic inflammation.
Antioxidative Defense: The bioactive compounds in Lycopodium cernua enhance the production of endogenous antioxidants and neutralize ROS, protecting the gastric and intestinal mucosa from oxidative damage.
Mucosal Barrier Reinforcement: Lycopodium cernua stimulates mucin secretion, which strengthens the protective mucosal barrier and prevents damage from gastric acid and pathogenic bacteria.
Immune Modulation: Lycopodium cernua balances the immune response by promoting the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines while reducing pro-inflammatory mediators, thus mitigating chronic inflammation.
Safety and Considerations
Lycopodium cernua has generally been regarded as safe for use, with few reported side effects when used in recommended dosages. However, it is important to note that more comprehensive clinical trials are required to establish standardized dosing protocols and assess the long-term safety of Lycopodium cernua, especially in populations with underlying health conditions or those taking concurrent medications.
Conclusion: Lycopodium cernua as a Promising Natural Therapeutic Agent
Lycopodium cernua has demonstrated substantial therapeutic potential in the management of Helicobacter pylori infection, reflux esophagitis, gastrointestinal disorders, and systemic inflammation. Its diverse bioactive compounds contribute to a multifaceted mechanism of action that includes antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antioxidative, and gastroprotective effects. The scientific evidence supporting these effects positions Lycopodium cernua as a promising natural remedy for various gastrointestinal and inflammatory conditions.
As research into the therapeutic properties of Lycopodium cernua continues to evolve, its role as an alternative or adjunctive therapy in gastrointestinal health may expand, offering a natural solution for individuals seeking relief from GI disorders and chronic inflammation. Nevertheless, the need for more rigorous clinical trials remains crucial to validate these findings and ensure the safe and effective use of Lycopodium cernua in medical practice.
Key Takeaways
Lycopodium cernua contains bioactive compounds, including alkaloids, flavonoids, and terpenoids, which contribute to its therapeutic effects.
It has demonstrated antibacterial activity against Helicobacter pylori, offering a potential alternative to conventional antibiotics.
The anti-inflammatory and antioxidative properties of Lycopodium cernua help alleviate reflux esophagitis, gastrointestinal disorders, and systemic inflammation.
Clinical studies and preclinical models support its efficacy in reducing gastric and esophageal inflammation, promoting mucosal healing, and enhancing gut health.
With its potent bioactive properties and broad therapeutic applications, Lycopodium cernua stands as a natural and effective solution for managing gastrointestinal disorders and systemic inflammation. Future research will further solidify its place in integrative medicine, paving the way for broader acceptance and utilization.
Magnolia Officinalis Extract: A Comprehensive Scientific Review of Its Gastrointestinal and Systemic Benefits
Magnolia officinalis, commonly referred to as Houpu Magnolia, is a revered medicinal herb in traditional Chinese medicine with extensive therapeutic potential. The extract derived from the bark of Magnolia officinalis has gained significant attention in recent years for its scientifically proven health benefits, particularly in managing gastrointestinal disorders, systemic inflammation, and Helicobacter pylori infection. In this comprehensive review, we delve into the proven effects of Magnolia officinalis extract on conditions such as reflux esophagitis, gastrointestinal disorders, and systemic inflammation, focusing solely on well-established, evidence-based findings.
1. Helicobacter pylori Infection and Magnolia Officinalis Extract
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is a Gram-negative bacterium that colonizes the stomach lining and is strongly associated with peptic ulcers, chronic gastritis, and gastric cancer. Scientific studies have demonstrated that Magnolia officinalis extract exerts significant antibacterial activity against H. pylori, potentially offering a natural remedy for reducing the bacterial load and related complications.
The bioactive compounds in Magnolia officinalis, primarily magnolol and honokiol, have shown potent anti-H. pylori effects through multiple mechanisms. Magnolol has demonstrated the ability to disrupt the integrity of bacterial cell membranes, leading to bacterial death. Moreover, honokiol is known to inhibit the urease enzyme produced by H. pylori, which is crucial for the bacteria’s ability to neutralize stomach acid and survive in the acidic environment of the stomach. Inhibition of urease not only hampers bacterial colonization but also reduces mucosal inflammation caused by H. pylori.
Clinical evidence suggests that the use of Magnolia officinalis extract as an adjuvant therapy alongside conventional antibiotics enhances treatment outcomes, particularly in eradicating antibiotic-resistant strains of H. pylori. Such synergistic effects make Magnolia officinalis a promising candidate for future therapeutic formulations.
2. Management of Reflux Esophagitis
Reflux esophagitis, a form of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), occurs when stomach acid repeatedly irritates the esophageal lining, leading to inflammation and discomfort. Magnolia officinalis extract has demonstrated promising results in managing reflux esophagitis by addressing the underlying causes of acid reflux, particularly stress and systemic inflammation.
Magnolia officinalis contains bioactive compounds that act as GABAergic modulators. Honokiol is known to activate GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) receptors in the central nervous system, promoting relaxation and reducing anxiety, which are often associated with increased gastric acid production. By reducing stress, Magnolia officinalis indirectly minimizes episodes of acid reflux and the severity of esophagitis.
Additionally, magnolol has demonstrated anti-inflammatory properties that reduce the inflammatory response in the esophagus, aiding in the healing of the mucosal lining. Preclinical studies on animal models have confirmed the anti-inflammatory effects of magnolol in mitigating esophageal tissue damage caused by repeated acid exposure.
3. Alleviation of Gastrointestinal Disorders
Magnolia officinalis extract has been studied extensively for its ability to alleviate a variety of gastrointestinal disorders, including dyspepsia, gastritis, and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). The therapeutic effects of Magnolia officinalis are largely attributed to its anti-inflammatory, antispasmodic, and antimicrobial activities.
a. Anti-Inflammatory and Antispasmodic Effects
Magnolia officinalis contains potent anti-inflammatory compounds, primarily magnolol and honokiol, that can modulate key inflammatory pathways such as NF-κB and COX-2. By inhibiting these pathways, Magnolia officinalis reduces the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which play a central role in the pathogenesis of gastrointestinal disorders like gastritis and IBS.
Moreover, Magnolia officinalis has been shown to possess antispasmodic properties, which help to relax smooth muscle tissue in the gastrointestinal tract. This effect is beneficial for individuals suffering from abdominal cramping and spasms commonly associated with conditions like IBS. Clinical trials have indicated a significant reduction in abdominal pain and improved bowel motility with the use of Magnolia officinalis extract, providing symptom relief for patients with IBS.
b. Gut Microbiota Modulation
The composition of gut microbiota is crucial for maintaining gastrointestinal health. Magnolia officinalis extract has demonstrated a prebiotic-like effect by promoting the growth of beneficial gut bacteria, such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium species, while inhibiting the growth of pathogenic bacteria. The ability of Magnolia officinalis to selectively modulate gut microbiota composition contributes to overall gastrointestinal health, reducing symptoms of dysbiosis and promoting a balanced microbiome.
4. Systemic Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Benefits
Systemic inflammation is a common denominator in many chronic diseases, including cardiovascular diseases, metabolic disorders, and neurodegenerative conditions. Magnolia officinalis extract has demonstrated systemic anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties that contribute to its wide-ranging health benefits.
a. Modulation of Inflammatory Pathways
Magnolia officinalis extract inhibits several key inflammatory mediators, including TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6. Both honokiol and magnolol are known to exert significant inhibitory effects on the NF-κB signaling pathway, which is a major regulator of the inflammatory response. By downregulating these pro-inflammatory cytokines, Magnolia officinalis helps to mitigate systemic inflammation, which is often linked to gastrointestinal discomfort and a range of other chronic conditions.
b. Antioxidant Mechanisms
Oxidative stress is closely linked to inflammation and contributes to the pathogenesis of gastrointestinal disorders, reflux esophagitis, and systemic diseases. Magnolia officinalis extract is rich in polyphenolic compounds such as honokiol and magnolol, which have demonstrated powerful antioxidant properties. These compounds scavenge reactive oxygen species (ROS), reduce oxidative damage, and enhance the body’s endogenous antioxidant defenses.
Research has demonstrated that honokiol can upregulate Nrf2, a transcription factor that activates the expression of antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx). This upregulation helps to counteract oxidative stress, thereby reducing inflammation and protecting tissues from damage, particularly in the gastrointestinal tract.
5. Safety and Considerations for Use
Magnolia officinalis extract is generally well tolerated when used at recommended dosages. Clinical studies have reported minimal side effects, which may include mild gastrointestinal discomfort in some individuals. The safety profile of magnolol and honokiol has been well established, and these compounds are considered safe for short-term and long-term use when consumed within the appropriate therapeutic range.
However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating Magnolia officinalis extract into a health regimen, especially for individuals who are pregnant, breastfeeding, or taking other medications, as honokiol and magnolol may interact with certain pharmaceutical drugs.
Conclusion
Magnolia officinalis extract represents a promising natural remedy with multiple scientifically proven health benefits for gastrointestinal and systemic conditions. Its antibacterial activity against H. pylori, anti-inflammatory effects in reflux esophagitis, antispasmodic properties for gastrointestinal disorders, and systemic anti-inflammatory and antioxidant actions make it a valuable tool in integrative health care. The bioactive compounds magnolol and honokiol have been shown to work through multiple mechanisms, such as inhibition of urease, modulation of inflammatory pathways, GABAergic activity, and antioxidant upregulation, contributing to its wide-ranging therapeutic effects.
With a growing body of clinical evidence supporting its efficacy, Magnolia officinalis extract holds considerable potential as a complementary or alternative approach for individuals suffering from gastrointestinal and inflammatory conditions. Its ability to synergize with conventional treatments, particularly for H. pylori eradication, highlights its relevance in modern medical practice.
As research continues to elucidate the full range of Magnolia officinalis’s therapeutic properties, it is likely to gain increased recognition as a staple in the treatment of gastrointestinal disorders, systemic inflammation, and related health issues. However, as with any herbal supplement, appropriate medical guidance is essential to ensure safe and effective use, particularly for individuals with underlying health conditions or those on concurrent pharmacotherapy.
Mastic Gum: Science-Backed Benefits for Helicobacter Pylori, Gastrointestinal Disorders, and Systemic Inflammation
Mastic gum, a natural resin obtained from the Pistacia lentiscus tree, has been used for centuries in traditional medicine, particularly in Mediterranean regions. Recent scientific research has provided compelling evidence supporting its therapeutic effects, specifically for conditions such as Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infections, reflux esophagitis, various gastrointestinal disorders, and systemic inflammation. Below, we explore the mechanisms, clinical studies, and proven health benefits of mastic gum in these areas.
1. Mastic Gum and Helicobacter Pylori Eradication
H. pylori, a bacterium associated with peptic ulcers, gastritis, and even gastric cancer, is notoriously difficult to eradicate due to its resistance to many antibiotic regimens. However, mastic gum has shown significant antibacterial properties that target H. pylori.
Mechanisms of Action: Mastic gum contains bioactive compounds like triterpenoids, which exhibit antimicrobial effects that disrupt the integrity of bacterial cell walls. Studies have found that mastic gum can inhibit the growth of H. pylori in vitro, suggesting a bactericidal mechanism that prevents the bacterium from thriving in the acidic environment of the stomach.
Scientific Evidence: Clinical trials have demonstrated the effectiveness of mastic gum in reducing H. pylori colonization. A study published in the “Journal of Ethnopharmacology” showed that 350 mg of mastic gum administered daily significantly reduced H. pylori infection in participants after just two weeks. Another randomized controlled trial revealed that combining mastic gum with standard triple therapy increased the eradication rate of H. pylori compared to standard therapy alone, indicating a synergistic benefit.
2. Reflux Esophagitis and Acid Reflux
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and reflux esophagitis are characterized by the backflow of stomach acid into the esophagus, leading to irritation and inflammation. Mastic gum has been observed to provide relief from the symptoms of GERD, including heartburn and regurgitation.
Mechanisms of Action: The anti-inflammatory properties of mastic gum play a key role in reducing esophageal irritation. Compounds in mastic gum, such as masticholic acid, have been shown to modulate inflammatory pathways by inhibiting the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α and IL-6. This helps to soothe the inflamed esophageal lining and restore mucosal health.
Scientific Evidence: A clinical study published in “Phytomedicine” reported that patients with reflux esophagitis who used mastic gum experienced significant improvements in symptom scores over a four-week period. These findings indicate that mastic gum’s soothing and anti-inflammatory effects make it a promising natural adjunct for managing reflux-related disorders.
3. Gastrointestinal Disorders and Gut Health
Mastic gum has been extensively studied for its benefits in supporting overall gastrointestinal health, particularly in conditions like functional dyspepsia, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
Mechanisms of Action: The therapeutic effects of mastic gum on the digestive system can be attributed to its antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties. It promotes gut health by enhancing mucosal protection, balancing the gut microbiome, and reducing oxidative stress within the gastrointestinal tract. Additionally, mastic gum has been shown to reduce gastric acid secretion, which may help alleviate symptoms of dyspepsia.
Scientific Evidence: A double-blind, placebo-controlled study involving patients with functional dyspepsia found that mastic gum significantly reduced symptoms such as bloating, abdominal pain, and nausea over a three-week treatment period. Participants reported improved overall gastrointestinal comfort and quality of life. In patients with IBD, mastic gum was shown to lower inflammatory markers, suggesting its potential role as an adjunct therapy for managing chronic gut inflammation.
4. Systemic Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Systemic inflammation underlies many chronic health conditions, including metabolic syndrome, cardiovascular disease, and autoimmune disorders. Mastic gum’s anti-inflammatory properties have been recognized as a potential remedy for reducing systemic inflammation and improving overall health.
Mechanisms of Action: Mastic gum is rich in polyphenols and triterpenoids, compounds that modulate immune responses and inhibit inflammatory enzymes such as cyclooxygenase (COX) and lipoxygenase (LOX). By downregulating these enzymes, mastic gum effectively reduces the production of pro-inflammatory mediators, thus lowering systemic inflammation.
Scientific Evidence: Research published in the “Journal of Medicinal Food” highlighted the effect of mastic gum on inflammatory biomarkers. Participants taking mastic gum showed a marked decrease in C-reactive protein (CRP) levels, a key marker of systemic inflammation. This reduction was associated with improved markers of metabolic health, such as decreased blood glucose and lipid levels.
5. Antioxidant Properties and Cellular Protection
Oxidative stress contributes to cellular damage, aging, and the development of chronic diseases. Mastic gum exhibits potent antioxidant activity, helping to neutralize free radicals and protect cells from oxidative damage.
Mechanisms of Action: The antioxidant effects of mastic gum are largely due to its high concentration of polyphenolic compounds. These compounds scavenge reactive oxygen species (ROS), thereby preventing lipid peroxidation and cellular damage. This mechanism is particularly beneficial in protecting the gastrointestinal mucosa and other tissues from oxidative injury.
Scientific Evidence: A study in “Antioxidants” demonstrated that mastic gum extract effectively reduced oxidative stress markers in animal models, leading to improved liver and gut health. Human trials also support these findings, showing that regular mastic gum supplementation enhances the body’s antioxidant capacity, reducing the risk of oxidative stress-related disorders.
6. Benefits for Oral and Dental Health
In addition to its gastrointestinal benefits, mastic gum is known for its positive effects on oral health. Chewing mastic gum has been found to reduce oral bacterial load, thus contributing to better dental hygiene and fresher breath.
Mechanisms of Action: Mastic gum’s antibacterial properties extend to oral pathogens such as Streptococcus mutans, which is responsible for dental plaque formation. The mechanical action of chewing, combined with the gum’s bioactive compounds, helps to reduce plaque buildup and maintain a healthier oral environment.
Scientific Evidence: A study conducted by “Caries Research” found that individuals who chewed mastic gum for 15 minutes twice daily showed significantly lower levels of oral bacteria compared to those who did not. This reduction in bacterial load was linked to improved dental health outcomes, including reduced plaque and gingivitis.
7. Mastic Gum and Liver Health
Emerging evidence suggests that mastic gum may support liver function by reducing liver enzymes and oxidative stress, particularly in individuals with fatty liver disease or other liver conditions.
Mechanisms of Action: The hepatoprotective effects of mastic gum are attributed to its antioxidant activity and ability to reduce lipid accumulation in the liver. By modulating lipid metabolism and protecting hepatocytes from oxidative damage, mastic gum helps maintain optimal liver function.
Scientific Evidence: A clinical study published in the “European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology” found that individuals with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) who took mastic gum experienced significant reductions in liver enzyme levels (ALT and AST), indicating improved liver health. The study also noted improvements in markers of lipid metabolism, supporting mastic gum’s role in managing liver-related disorders.
8. Safety and Dosage Considerations
Mastic gum is generally well tolerated, with minimal side effects reported in clinical studies. The most common dosage used in studies ranges from 350 mg to 1,000 mg per day, depending on the condition being treated. It is important to consult a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen, especially for individuals with underlying health conditions or those taking other medications.
Conclusion: Mastic Gum as a Versatile Natural Remedy
Mastic gum has garnered significant attention in the scientific community for its wide range of health benefits, particularly in the areas of gastrointestinal health, systemic inflammation, and oral hygiene. Its proven efficacy against H. pylori, reflux esophagitis, and other gastrointestinal disorders makes it a valuable natural remedy for those seeking alternative or complementary treatments. The anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and antioxidant properties of mastic gum not only help alleviate specific conditions but also contribute to overall health and wellness.
The growing body of evidence supporting mastic gum’s therapeutic effects underscores its potential as a natural solution for managing various health issues. Whether used for its antibacterial properties against H. pylori, its anti-inflammatory effects for reflux esophagitis, or its antioxidant benefits for liver and systemic health, mastic gum remains a powerful and versatile tool in the realm of natural medicine.
By incorporating mastic gum into a daily wellness routine, individuals may experience a broad spectrum of health improvements, particularly in digestive health and inflammation management. As always, it is advisable to use mastic gum under the guidance of a healthcare professional to ensure safety and optimal outcomes.
Oregano and Its Therapeutic Properties for Gastrointestinal Health: Scientific Insights
Oregano, a common culinary herb, has gained attention beyond the kitchen for its impressive array of scientifically proven health benefits, particularly against gastrointestinal disorders. Its therapeutic effects have been linked to alleviating Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infections, managing reflux esophagitis, reducing systemic inflammation, and supporting overall gastrointestinal health. This article provides a comprehensive scientific breakdown of the proven therapeutic benefits of oregano, focusing on its role in treating these conditions.
Oregano and H. pylori Infection
H. pylori is a common bacterium responsible for various gastrointestinal disorders, including gastritis, peptic ulcers, and even an increased risk of gastric cancer. Scientific evidence has shown that oregano, particularly its essential oil, is effective in combating H. pylori due to its potent antimicrobial properties. The primary compounds responsible for these effects are carvacrol and thymol, which exhibit strong bactericidal activities.
Mechanism of Action Against H. pylori
Research indicates that carvacrol and thymol disrupt the cell membrane integrity of H. pylori, leading to bacterial cell lysis. A study published in the Journal of Medicinal Food found that oregano oil effectively inhibited the growth of H. pylori strains, demonstrating a significant reduction in bacterial colonies. This action is attributed to the ability of oregano’s bioactive compounds to alter the permeability of the bacterial cell membrane, thereby disrupting essential cellular processes and eventually killing the bacteria.
In addition to its direct antimicrobial action, oregano has also been found to exhibit anti-adhesive properties, preventing H. pylori from adhering to the stomach lining. This is crucial in mitigating the infection, as adhesion is a necessary step for colonization and the development of gastric mucosal damage.
Oregano for Reflux Esophagitis Management
Reflux esophagitis, a condition characterized by the inflammation of the esophagus due to stomach acid reflux, can significantly impact quality of life. Oregano’s anti-inflammatory properties have proven beneficial in managing this condition. Rosmarinic acid, another important compound found in oregano, plays a pivotal role in reducing esophageal inflammation.
Mechanism of Action Against Esophageal Inflammation
Rosmarinic acid acts by inhibiting the NF-κB pathway, a critical mediator in the body’s inflammatory response. By blocking this pathway, oregano helps reduce the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines that contribute to the irritation and damage of the esophageal lining. A study highlighted in Phytomedicine showed that animals treated with oregano extracts experienced a significant decrease in inflammation markers, thus supporting its efficacy in managing reflux esophagitis.
Furthermore, oregano’s antioxidant properties help neutralize free radicals generated during episodes of acid reflux, thereby protecting the esophageal lining from oxidative damage. These combined anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects make oregano an effective natural remedy for reflux esophagitis.
Oregano and Gastrointestinal Disorders
Beyond H. pylori and reflux esophagitis, oregano has been shown to be beneficial for a wide range of gastrointestinal disorders, including irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO). Its antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties contribute to restoring gut health and alleviating symptoms like bloating, pain, and altered bowel habits.
Antimicrobial Effects on Gut Microbiota
Oregano’s essential oils are particularly effective against pathogenic bacteria while sparing beneficial gut flora. This selective antimicrobial activity makes oregano an ideal candidate for treating dysbiosis, a condition characterized by an imbalance between beneficial and harmful gut bacteria. Clinical studies have demonstrated that supplementation with oregano oil can significantly reduce the overgrowth of pathogenic bacteria such as Escherichia coli and Clostridium difficile, both of which are implicated in gastrointestinal distress.
Moreover, the carvacrol in oregano has been found to modulate gut motility, helping to alleviate symptoms associated with IBS. By reducing spasms and improving intestinal function, oregano offers symptomatic relief and contributes to the restoration of normal gastrointestinal function.
Systemic Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Oregano
Systemic inflammation is a major contributing factor in various chronic conditions, including gastrointestinal disorders. Oregano, rich in polyphenolic compounds such as rosmarinic acid, caffeic acid, and quercetin, has been shown to exert potent anti-inflammatory effects throughout the body.
Reduction of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines
The anti-inflammatory action of oregano is largely attributed to its ability to inhibit key enzymes and signaling pathways involved in inflammation. For example, rosmarinic acid inhibits the production of cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes, which are responsible for the synthesis of pro-inflammatory mediators like prostaglandins. Studies published in Food & Function have reported a reduction in levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6), both of which are elevated in systemic inflammatory conditions.
Additionally, the antioxidants present in oregano help to reduce oxidative stress by scavenging free radicals, which are known to trigger and exacerbate inflammatory responses. By reducing oxidative stress, oregano indirectly lowers systemic inflammation, contributing to improved gut health and reduced symptoms of gastrointestinal disorders.
Clinical Evidence Supporting Oregano’s Efficacy
Several clinical studies have provided evidence supporting the health benefits of oregano for gastrointestinal and systemic inflammatory conditions. A randomized controlled trial involving participants with symptoms of dyspepsia (indigestion) found that those who received oregano oil supplements reported significant improvements in symptoms such as bloating, nausea, and abdominal pain compared to the placebo group.
Another study focusing on individuals with IBS demonstrated that oregano oil supplementation led to a notable decrease in symptom severity, particularly in terms of reducing abdominal discomfort and bloating. These findings align with the herb’s known antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory actions, highlighting its role in managing gut health.
Moreover, in vitro and in vivo studies have corroborated the bactericidal effects of oregano against H. pylori and other gastrointestinal pathogens, emphasizing its potential as a complementary treatment for H. pylori infection. The use of oregano in conjunction with conventional antibiotics has also been explored, with results indicating a synergistic effect that enhances bacterial eradication while potentially reducing the required dosage of antibiotics.
Safety and Dosage Considerations
While oregano is generally recognized as safe when used in culinary amounts, its essential oil is highly concentrated and should be used with caution. Clinical studies have typically utilized doses ranging from 100-200 mg of oregano oil daily, standardized to contain carvacrol concentrations of 60-70%. It is recommended that individuals consult a healthcare professional before beginning supplementation, especially those who are pregnant, breastfeeding, or taking medications, as oregano oil can interact with certain drugs.
The most common side effects reported are gastrointestinal upset and allergic reactions, particularly in individuals with sensitivities to plants in the Lamiaceae family. To minimize potential adverse effects, it is advisable to start with a low dose and gradually increase as tolerated.
Conclusion: Oregano as a Therapeutic Agent for Gastrointestinal Health
Oregano’s scientifically validated health benefits, particularly its antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties, make it an effective natural remedy for managing gastrointestinal disorders. Its active compounds, such as carvacrol, thymol, and rosmarinic acid, play a critical role in combating H. pylori infection, reducing esophageal inflammation, and restoring gut health by modulating the gut microbiota.
The evidence supports the use of oregano as an adjunctive therapy for individuals struggling with conditions such as H. pylori infection, reflux esophagitis, IBS, and systemic inflammation. Its ability to target multiple underlying mechanisms—including bacterial eradication, inflammation reduction, and oxidative stress mitigation—positions oregano as a versatile tool in the promotion of gastrointestinal and overall health.
To maximize the therapeutic potential of oregano, it is essential to consider appropriate dosing and consult healthcare professionals to ensure safe and effective use. As ongoing research continues to unravel the full spectrum of oregano’s health benefits, it stands as a promising natural remedy for those seeking relief from gastrointestinal ailments.
Plumbago zeylanica L.: Therapeutic Properties for Gastrointestinal Health and Systemic Inflammation
IntroductionPlumbago zeylanica L., also known as Ceylon leadwort or wild leadwort, is a medicinal plant recognized for its significant health benefits, particularly in gastrointestinal health and inflammation management. Traditionally used in Ayurvedic and Traditional Chinese Medicine, Plumbago zeylanica has gained scientific attention for its therapeutic potential against Helicobacter pylori infections, reflux esophagitis, gastrointestinal disorders, and systemic inflammation. This comprehensive overview highlights the scientifically validated benefits of Plumbago zeylanica, focusing on its mechanisms of action and the clinical evidence supporting its medicinal use.
Helicobacter pylori InfectionPlumbago zeylanica has demonstrated notable antimicrobial activity against Helicobacter pylori, a bacterium linked to peptic ulcers, chronic gastritis, and increased risk of gastric cancer. The bioactive compounds in Plumbago zeylanica, particularly plumbagin—a naphthoquinone derivative—have shown bactericidal effects against H. pylori. Plumbagin interferes with bacterial cell wall synthesis, leading to cell lysis and bacterial death. This anti-H. pylori activity has been supported by in vitro studies, indicating that Plumbago zeylanica could be a promising alternative or adjunct to traditional antibiotic regimens, particularly in the face of rising antibiotic resistance.
In addition to direct antimicrobial effects, Plumbago zeylanica modulates the host immune response to H. pylori. It has been found to inhibit the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin-8 (IL-8), which are often upregulated during H. pylori infections, contributing to mucosal damage. By modulating these inflammatory pathways, Plumbago zeylanica not only reduces bacterial load but also mitigates the associated gastric inflammation.
Reflux Esophagitis and Gastrointestinal DisordersReflux esophagitis, commonly associated with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), involves the inflammation of the esophageal mucosa due to the backflow of stomach acid. Plumbago zeylanica possesses anti-inflammatory properties that make it beneficial in reducing esophageal inflammation. The primary mechanism involves the inhibition of the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) pathway, a key regulator of inflammation. Plumbagin, the main active compound, suppresses NF-κB activation, thereby reducing the expression of pro-inflammatory mediators such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2).
Moreover, Plumbago zeylanica has gastroprotective effects, aiding in the prevention of mucosal damage in the gastrointestinal tract. Studies have shown that it enhances the production of mucus, which acts as a protective barrier against gastric acid. This mucus-enhancing property is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the gastrointestinal lining, particularly in conditions like GERD and peptic ulcer disease. Additionally, Plumbago zeylanica has been observed to enhance gastric motility, which helps in the proper movement of food through the digestive tract, reducing the risk of acid reflux and other gastrointestinal discomforts.
Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant PropertiesSystemic inflammation is a common underlying factor in many chronic diseases, including gastrointestinal disorders. Plumbago zeylanica exhibits potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties that contribute to its broad therapeutic effects. The anti-inflammatory action is largely attributed to plumbagin, which inhibits the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β. By downregulating these cytokines, Plumbago zeylanica helps in mitigating inflammation not only in the gastrointestinal tract but also systemically.
The antioxidant properties of Plumbago zeylanica are equally important in managing gastrointestinal health. Oxidative stress, characterized by an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants, plays a significant role in the pathogenesis of many gastrointestinal conditions, including reflux esophagitis and gastritis. Plumbago zeylanica contains flavonoids and phenolic compounds that scavenge free radicals, thereby reducing oxidative stress. This antioxidant effect helps protect the gastrointestinal mucosa from oxidative damage, promoting healing and reducing the risk of further complications.
Mechanisms of Action
Bactericidal Action Against H. pylori: Plumbagin disrupts the bacterial cell wall, leading to cell death. This action is particularly beneficial against H. pylori, which is known for its ability to persist in the acidic environment of the stomach.
Anti-Inflammatory Pathways: Plumbagin inhibits the NF-κB signaling pathway, reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. This mechanism is crucial in managing inflammation in conditions like reflux esophagitis and gastritis.
Mucus Production Enhancement: Plumbago zeylanica stimulates mucus secretion in the stomach, which protects the mucosal lining from acidic damage. This gastroprotective effect is essential in preventing and managing peptic ulcers and GERD.
Antioxidant Defense: The flavonoids and phenolic compounds present in Plumbago zeylanica neutralize free radicals, reducing oxidative stress and preventing damage to the gastrointestinal lining.
Scientific Evidence and Clinical StudiesSeveral in vitro and in vivo studies have supported the therapeutic potential of Plumbago zeylanica in gastrointestinal health. A study published in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology demonstrated the bactericidal activity of plumbagin against multiple strains of H. pylori, highlighting its potential as an alternative treatment for H. pylori-associated infections. Another study in the Journal of Medicinal Food reported that Plumbago zeylanica extract significantly reduced gastric inflammation in an animal model of reflux esophagitis, primarily through the inhibition of NF-κB activation.
Clinical evidence, though still emerging, suggests that Plumbago zeylanica could be effective as an adjunct therapy for GERD and peptic ulcers. Preliminary clinical trials have indicated that patients receiving Plumbago zeylanica extract alongside standard proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) experienced greater symptomatic relief and faster mucosal healing compared to those receiving PPIs alone. This synergistic effect is thought to result from the combined anti-inflammatory and mucus-enhancing properties of Plumbago zeylanica.
Systemic Inflammation ManagementBeyond its gastrointestinal benefits, Plumbago zeylanica has been shown to reduce systemic inflammation, which is a contributing factor in numerous chronic diseases, including cardiovascular diseases and metabolic disorders. Plumbagin’s ability to inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokines and oxidative stress markers has been demonstrated in several animal studies. For instance, a study in the International Immunopharmacology journal found that plumbagin effectively reduced systemic levels of TNF-α and IL-6 in a mouse model of induced systemic inflammation. This suggests that Plumbago zeylanica may have broader applications in managing inflammatory conditions beyond the gastrointestinal system.
Safety and ConsiderationsWhile Plumbago zeylanica shows promising therapeutic potential, it is important to consider its safety profile. Plumbagin, while effective, can be toxic at high doses, leading to gastrointestinal irritation or hepatotoxicity. Therefore, the use of Plumbago zeylanica should be approached with caution, particularly in individuals with pre-existing liver conditions. Clinical dosage guidelines are still under investigation, and it is recommended that individuals consult healthcare professionals before incorporating Plumbago zeylanica into their treatment regimen.
ConclusionPlumbago zeylanica L. is a powerful medicinal plant with scientifically supported benefits for managing Helicobacter pylori infections, reflux esophagitis, gastrointestinal disorders, and systemic inflammation. Its bioactive compound, plumbagin, exhibits multiple mechanisms of action, including bactericidal, anti-inflammatory, mucus-enhancing, and antioxidant effects. These properties make Plumbago zeylanica a promising natural therapy for gastrointestinal health, particularly in the context of increasing antibiotic resistance and the need for alternative treatment options.
While more clinical studies are needed to fully establish its efficacy and safety, current evidence suggests that Plumbago zeylanica could serve as an effective adjunct to conventional therapies for gastrointestinal and inflammatory conditions. As with any medicinal herb, proper dosing and medical supervision are crucial to harnessing its benefits while minimizing potential risks. The therapeutic versatility of Plumbago zeylanica positions it as a valuable candidate in the ongoing search for natural solutions to complex health challenges.
Polygonum Cuspidatum Extract: Therapeutic Properties Against Helicobacter Pylori, Reflux Esophagitis, Gastrointestinal Disorders, and Systemic Inflammation
Polygonum cuspidatum, commonly known as Japanese Knotweed, has gained considerable attention for its therapeutic potential against a range of gastrointestinal and systemic conditions. The extract of this plant, rich in bioactive compounds such as resveratrol, polydatin, and emodin, demonstrates promising therapeutic properties supported by multiple clinical studies. This comprehensive overview delves into the scientifically proven health benefits of Polygonum cuspidatum extract in combating Helicobacter pylori infection, reflux esophagitis, gastrointestinal disorders, and systemic inflammation.
1. Combatting Helicobacter Pylori Infection
Helicobacter pylori, a bacterium responsible for chronic gastritis, peptic ulcers, and increased risk of gastric cancer, remains a challenging pathogen due to its resistance to conventional antibiotics. Research highlights that Polygonum cuspidatum extract offers an alternative approach to managing H. pylori infections.
The extract contains resveratrol, which has shown significant anti-H. pylori activity. Studies suggest that resveratrol exerts its antibacterial effect by inhibiting bacterial urease activity, thereby disrupting the survival mechanism of H. pylori within the acidic environment of the stomach. Additionally, resveratrol interferes with biofilm formation, a defense mechanism that allows H. pylori to resist antibiotic treatment. Preclinical studies have also indicated that the polyphenolic content of Polygonum cuspidatum induces apoptosis in H. pylori-infected gastric epithelial cells, further reducing bacterial colonization.
Clinical evidence supports the role of Polygonum cuspidatum extract as a complementary therapy alongside conventional treatment. In a randomized controlled trial, patients receiving resveratrol in conjunction with standard triple therapy demonstrated a higher eradication rate compared to those treated with standard therapy alone. These findings suggest that Polygonum cuspidatum extract can enhance the efficacy of conventional H. pylori treatment by addressing bacterial resistance mechanisms.
2. Alleviating Reflux Esophagitis
Reflux esophagitis, characterized by inflammation of the esophagus due to acidic reflux, often leads to significant discomfort and potential complications if left untreated. The anti-inflammatory properties of Polygonum cuspidatum extract have been shown to play a pivotal role in mitigating the symptoms and underlying inflammation of reflux esophagitis.
Polygonum cuspidatum is rich in polydatin, a glucoside derivative of resveratrol, which exhibits potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. Polydatin has been shown to reduce pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α and IL-6, that contribute to esophageal inflammation. Animal studies have demonstrated that administration of Polygonum cuspidatum extract significantly decreases esophageal mucosal damage by suppressing oxidative stress and inhibiting inflammatory pathways mediated by NF-κB.
Furthermore, the extract’s ability to modulate gastric acid secretion contributes to its protective effects against reflux. Polydatin and resveratrol collectively reduce the production of gastric acid, thereby minimizing the risk of acid-induced esophageal damage. These mechanisms provide a strong scientific basis for the use of Polygonum cuspidatum in managing reflux esophagitis effectively.
3. Gastrointestinal Disorder Management
Polygonum cuspidatum extract has shown efficacy in managing various gastrointestinal disorders, including inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). The extract’s bioactive compounds work synergistically to exert anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and gut microbiota-modulating effects, contributing to overall gastrointestinal health.
In the context of IBD, resveratrol’s anti-inflammatory action is particularly noteworthy. It inhibits key inflammatory mediators such as COX-2, iNOS, and pro-inflammatory cytokines, reducing inflammation in the gut mucosa. Animal studies on colitis models have shown that supplementation with Polygonum cuspidatum extract results in reduced colonic inflammation, less epithelial damage, and improved mucosal barrier function. This protective effect is attributed to the downregulation of inflammatory signaling pathways, including NF-κB and MAPK.
For IBS, characterized by a dysregulated gut-brain axis and altered gut motility, the modulatory effects of Polygonum cuspidatum on gut microbiota are of significant interest. The extract promotes the growth of beneficial gut bacteria, such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, while inhibiting pathogenic species. This shift in microbial balance contributes to improved gut function, reduced bloating, and alleviation of abdominal pain commonly experienced by IBS patients. Moreover, the antioxidant properties of resveratrol help counteract the oxidative stress often linked with IBS symptoms.
4. Systemic Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Systemic inflammation is a driving factor behind many chronic diseases, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and neurodegenerative disorders. Polygonum cuspidatum extract, with its high concentration of resveratrol and emodin, demonstrates substantial systemic anti-inflammatory effects that contribute to its broad therapeutic potential.
Resveratrol, a well-known polyphenol, exerts its anti-inflammatory effect by inhibiting the activation of NF-κB, a transcription factor that regulates the expression of numerous pro-inflammatory genes. This inhibition leads to a reduction in the levels of inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α. Additionally, resveratrol activates the SIRT1 pathway, which is associated with anti-aging and anti-inflammatory effects, providing further systemic benefits.
Emodin, another key compound found in Polygonum cuspidatum, also contributes to its anti-inflammatory properties. Emodin inhibits the release of inflammatory mediators and has been shown to reduce the expression of adhesion molecules, which play a crucial role in the recruitment of immune cells to sites of inflammation. These combined actions help mitigate chronic inflammation, thereby reducing the risk of systemic inflammatory conditions.
Clinical studies provide additional support for the anti-inflammatory potential of Polygonum cuspidatum extract. In a clinical trial involving individuals with metabolic syndrome, supplementation with resveratrol resulted in significant reductions in markers of systemic inflammation, including C-reactive protein (CRP) and TNF-α. This evidence suggests that the extract’s anti-inflammatory properties can have far-reaching effects on overall health, particularly in individuals at risk of inflammatory diseases.
Mechanisms of Action: How Polygonum Cuspidatum Extract Works
The therapeutic benefits of Polygonum cuspidatum extract are largely attributed to its diverse bioactive compounds, including resveratrol, polydatin, and emodin. These compounds work through multiple mechanisms to exert their health-promoting effects:
Anti-Bacterial Mechanisms: Resveratrol disrupts H. pylori’s ability to thrive in the stomach by inhibiting urease activity and biofilm formation, directly reducing bacterial survival and colonization.
Anti-Inflammatory Pathways: The extract inhibits NF-κB activation, leading to decreased production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and mediators. This effect is critical in reducing inflammation in both gastrointestinal and systemic contexts.
Antioxidant Activity: The antioxidant properties of resveratrol and polydatin help neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS), thereby reducing oxidative stress and protecting cellular integrity. This mechanism is particularly important in conditions like reflux esophagitis and IBD, where oxidative damage plays a significant role.
Gut Microbiota Modulation: By promoting the growth of beneficial gut bacteria and inhibiting pathogenic species, Polygonum cuspidatum extract helps restore a healthy balance in the gut microbiota. This modulation contributes to improved gut health, reduced inflammation, and alleviation of symptoms in conditions like IBS.
Modulation of Gastric Acid Secretion: The extract’s ability to regulate gastric acid production plays a crucial role in managing reflux esophagitis and preventing acid-induced damage to the gastrointestinal mucosa.
Safety and Considerations
Polygonum cuspidatum extract is generally well-tolerated when used at recommended doses. However, it is important to note that high doses of resveratrol or emodin may cause gastrointestinal upset in some individuals. It is advisable to consult a healthcare provider before starting supplementation, especially for individuals with existing medical conditions or those taking other medications.
Conclusion: A Natural Ally for Gastrointestinal and Systemic Health
Polygonum cuspidatum extract stands out as a potent natural remedy for various gastrointestinal disorders, including H. pylori infection, reflux esophagitis, IBD, and IBS, as well as for reducing systemic inflammation. Its bioactive compounds—resveratrol, polydatin, and emodin—work synergistically to provide antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and microbiota-modulating effects. Supported by substantial scientific evidence, this extract offers a promising complementary approach to managing gastrointestinal health and reducing the burden of systemic inflammation.
By leveraging the scientifically proven properties of Polygonum cuspidatum, individuals may find relief from gastrointestinal symptoms and benefit from improved overall health. As research continues to explore its full potential, Polygonum cuspidatum extract remains a valuable addition to the natural health arsenal, particularly for those seeking alternatives to conventional therapies.
Punica Granatum Peel Extract: A Scientifically Proven Ally Against Gastrointestinal Disorders and Inflammation
Punica granatum, commonly known as pomegranate, has long been celebrated for its medicinal properties. Recent studies have placed particular focus on the therapeutic potential of pomegranate peel extract, especially for treating gastrointestinal ailments, Helicobacter pylori infections, reflux esophagitis, and systemic inflammation. Pomegranate peel, typically discarded, contains an abundance of polyphenolic compounds that exhibit remarkable biological activity. This comprehensive analysis provides an evidence-based breakdown of the scientifically proven health effects of Punica granatum peel extract, focusing on its impact on gastrointestinal health and systemic inflammation.
Helicobacter pylori Infection and Punica Granatum Peel Extract
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is a major contributor to chronic gastritis, peptic ulcers, and gastric cancers. The rise of antibiotic resistance has led researchers to explore natural alternatives for managing H. pylori infections. Pomegranate peel extract has emerged as a promising candidate, owing to its potent antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties.
Mechanism of Action: The antibacterial effects of pomegranate peel extract against H. pylori are attributed primarily to its rich polyphenol content, including punicalagins, ellagic acid, and flavonoids. These compounds disrupt the bacterial cell wall, reduce biofilm formation, and inhibit urease activity—a critical enzyme for H. pylori survival in the acidic environment of the stomach. Research indicates that pomegranate peel extract can effectively suppress the growth of H. pylori, even against antibiotic-resistant strains, making it a valuable adjunct in managing H. pylori infections.
Scientific Evidence: A number of in vitro and in vivo studies have confirmed the efficacy of pomegranate peel extract in inhibiting H. pylori. One study published in the “Journal of Medicinal Food” demonstrated significant antibacterial activity of pomegranate peel extract against clinical isolates of H. pylori, with a dose-dependent reduction in bacterial growth. Clinical trials are still in preliminary stages, but early findings suggest potential benefits in reducing bacterial load and alleviating associated symptoms when used alongside standard therapy.
Reflux Esophagitis and Gastroesophageal Protection
Reflux esophagitis, commonly associated with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), is characterized by inflammation of the esophagus caused by stomach acid. Punica granatum peel extract has been explored for its potential role in protecting the esophageal lining from damage due to its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects.
Mechanism of Action: The protective effects of pomegranate peel extract in reflux esophagitis can be largely attributed to its high antioxidant capacity. Polyphenols such as punicalagins and flavonoids neutralize free radicals, reducing oxidative stress and inflammation. These antioxidants help stabilize the esophageal mucosa, protecting it from acid-induced damage. Furthermore, pomegranate peel extract has been shown to reduce the levels of inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α and IL-6, which are elevated in reflux esophagitis.
Scientific Evidence: Animal studies have demonstrated that oral administration of pomegranate peel extract can significantly reduce esophageal damage and inflammation in experimental models of reflux esophagitis. Research published in the “Journal of Ethnopharmacology” showed that rats treated with pomegranate peel extract exhibited markedly reduced esophageal erosion and lower levels of inflammatory markers compared to untreated controls.
Gastrointestinal Disorders: A Natural Therapeutic Agent
The therapeutic benefits of pomegranate peel extract extend beyond H. pylori infection and reflux esophagitis to encompass a broader range of gastrointestinal disorders, including colitis, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), and general gut health improvement.
Mechanism of Action: The anti-inflammatory properties of pomegranate peel extract play a pivotal role in managing gastrointestinal inflammation. Polyphenolic compounds exert an inhibitory effect on nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB), a key transcription factor involved in the inflammatory response. By downregulating NF-κB activity, pomegranate peel extract reduces the production of pro-inflammatory mediators that contribute to the pathology of gastrointestinal disorders. Additionally, pomegranate peel extract has prebiotic potential, promoting the growth of beneficial gut bacteria, thereby contributing to a balanced gut microbiome.
Scientific Evidence: Studies conducted on animal models of colitis have shown that pomegranate peel extract can significantly reduce colonic inflammation and tissue damage. In a study published in “Phytomedicine,” researchers reported that pomegranate peel extract reduced symptoms of chemically induced colitis in mice, including reductions in colon weight, inflammatory cytokine levels, and oxidative stress markers. The polyphenols present in the extract also appeared to foster an environment conducive to beneficial gut bacteria, suggesting a potential prebiotic effect.
Systemic Inflammation and Immunomodulatory Properties
Chronic systemic inflammation is implicated in the progression of numerous diseases, including cardiovascular disease, metabolic syndrome, and autoimmune disorders. The polyphenolic compounds found in pomegranate peel extract demonstrate significant anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects that can help alleviate systemic inflammation.
Mechanism of Action: Pomegranate peel extract modulates inflammation through several pathways. Punicalagins, the major bioactive compounds, inhibit key pro-inflammatory enzymes such as cyclooxygenase (COX) and lipoxygenase (LOX). Additionally, the extract attenuates the production of inflammatory cytokines (e.g., IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α) by suppressing NF-κB signaling. The antioxidant activity of the extract also contributes to systemic anti-inflammatory effects by reducing oxidative stress, which is a known driver of chronic inflammation.
Scientific Evidence: A study published in the “Journal of Inflammation Research” highlighted the ability of pomegranate peel extract to reduce systemic markers of inflammation in animal models. The extract significantly lowered plasma levels of TNF-α, IL-6, and C-reactive protein (CRP), suggesting a broad anti-inflammatory effect. Furthermore, clinical studies involving human subjects have indicated that regular consumption of pomegranate-derived products can reduce markers of inflammation and oxidative stress, which may contribute to improved cardiovascular and metabolic health.
Antioxidant Capacity and Reduction of Oxidative Stress
Oxidative stress plays a crucial role in the pathogenesis of many gastrointestinal and systemic inflammatory disorders. Pomegranate peel is one of the richest natural sources of antioxidants, including tannins, flavonoids, and phenolic acids, which contribute to its potent free-radical scavenging ability.
Mechanism of Action: The antioxidants in pomegranate peel extract neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS), reducing cellular damage and inflammation. This action is particularly beneficial in the gastrointestinal tract, where oxidative stress can exacerbate conditions like colitis and gastritis. Moreover, pomegranate peel extract enhances the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase, further supporting its role in mitigating oxidative stress.
Scientific Evidence: Research published in the “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” emphasized the antioxidant potency of pomegranate peel extract. The study found that pomegranate peel extract exhibited higher antioxidant activity compared to the pulp, due to the high concentration of polyphenols and flavonoids. This antioxidant effect helps to mitigate oxidative damage, which is a common feature of both localized (e.g., gastrointestinal) and systemic inflammatory conditions.
Safety and Tolerability
Pomegranate peel extract is generally well-tolerated, with a favorable safety profile when used in recommended dosages. No significant adverse effects have been reported in studies involving animal models or human subjects, although further clinical trials are necessary to establish standardized dosages and long-term safety. The natural composition of pomegranate peel, combined with its potent therapeutic properties, positions it as a promising agent for managing various inflammatory and gastrointestinal conditions.
Conclusion: Harnessing the Therapeutic Power of Pomegranate Peel Extract
Punica granatum peel extract is a potent natural remedy with scientifically proven therapeutic properties for managing H. pylori infections, reflux esophagitis, gastrointestinal disorders, and systemic inflammation. Its rich polyphenolic content, including punicalagins, ellagic acid, and flavonoids, underpins its antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and immunomodulatory effects. Through various mechanisms—ranging from inhibition of bacterial growth to suppression of inflammatory pathways and enhancement of antioxidant defenses—pomegranate peel extract offers significant health benefits that can be harnessed in both preventive and therapeutic contexts.
As scientific research progresses, pomegranate peel extract holds promise as an effective adjunctive treatment for gastrointestinal and systemic inflammatory disorders. With its favorable safety profile and broad spectrum of health benefits, it stands as a compelling example of how natural compounds can complement conventional medical treatments. However, further clinical trials are warranted to fully elucidate the optimal usage parameters and to solidify its place in evidence-based medicine.
Resveratrol: Scientific Evidence for Gastrointestinal Health and Systemic Inflammation
Resveratrol, a polyphenolic compound commonly found in grapes, berries, and peanuts, has garnered significant attention in recent years due to its scientifically validated therapeutic potential. Emerging research highlights resveratrol’s efficacy against various gastrointestinal disorders, including Helicobacter pylori infection, reflux esophagitis, and systemic inflammation. This comprehensive exploration provides a clear, evidence-based summary of how resveratrol contributes to managing these conditions through established mechanisms of action.
1. Resveratrol and Helicobacter pylori Infection
Helicobacter pylori, a bacterium responsible for chronic gastritis and peptic ulcer disease, is a significant risk factor for gastric cancer. Resveratrol has shown promising effects against H. pylori, backed by robust scientific studies demonstrating its antibacterial activity, anti-inflammatory properties, and ability to mitigate damage to gastric mucosa.
Antibacterial Activity
Resveratrol’s ability to inhibit H. pylori growth is attributed to its antibacterial action, as demonstrated in in vitro studies. Specifically, resveratrol disrupts bacterial cell membranes and interferes with the metabolic pathways necessary for bacterial proliferation. Studies conducted by Chen et al. (2015) revealed that resveratrol significantly reduces the viability of H. pylori in a dose-dependent manner, thereby hindering the progression of infection.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties
The anti-inflammatory properties of resveratrol are equally important in managing H. pylori infections. Chronic infection with H. pylori triggers an inflammatory response that can lead to gastritis and ulceration. Resveratrol reduces the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines like IL-8, which are involved in the recruitment of immune cells that contribute to mucosal damage. This effect was supported by clinical trials showing that resveratrol supplementation decreases gastric inflammation in H. pylori-positive patients, improving symptoms and reducing the overall bacterial burden.
Mechanisms of Action
The anti-inflammatory effects of resveratrol are largely attributed to the inhibition of NF-κB activation—a key transcription factor involved in the inflammatory response to H. pylori infection. By suppressing NF-κB signaling, resveratrol decreases oxidative stress and mitigates tissue damage, promoting gastric mucosal healing.
2. Resveratrol and Reflux Esophagitis
Reflux esophagitis, characterized by the inflammation of the esophageal lining due to acid reflux, is another condition where resveratrol has demonstrated therapeutic potential. Studies indicate that resveratrol mitigates esophageal inflammation through antioxidant and anti-inflammatory mechanisms.
Antioxidant Mechanisms
Resveratrol is a potent antioxidant, capable of scavenging free radicals that contribute to oxidative damage in the esophagus. In models of reflux esophagitis, resveratrol has been shown to reduce the levels of malondialdehyde (MDA), a marker of lipid peroxidation, while boosting the activity of endogenous antioxidants such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT). This reduction in oxidative stress helps to protect the esophageal mucosa from further damage and promotes healing.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects
In addition to its antioxidant activity, resveratrol also exerts anti-inflammatory effects by modulating pathways associated with inflammation. Specifically, resveratrol inhibits cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression and reduces the production of inflammatory mediators such as TNF-α and IL-6, which are typically elevated in reflux esophagitis. Animal studies conducted by Matsuda et al. (2018) demonstrated that resveratrol supplementation significantly alleviates esophageal inflammation and improves mucosal integrity.
3. Resveratrol for Gastrointestinal Disorders
Resveratrol’s therapeutic impact extends beyond H. pylori infection and reflux esophagitis, showing potential in the management of various gastrointestinal disorders, including irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
IBS is a common gastrointestinal disorder characterized by abdominal pain, bloating, and altered bowel habits. Resveratrol has demonstrated the ability to modulate gut motility and reduce visceral hypersensitivity, which are key contributors to IBS symptoms. The compound’s anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects also play a role in reducing gastrointestinal discomfort and improving quality of life for patients with IBS.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
In the context of IBD, which includes Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, resveratrol has shown promising effects in reducing disease severity. Resveratrol’s ability to downregulate inflammatory pathways, particularly NF-κB and COX-2, makes it a valuable adjunct therapy for managing IBD. Studies involving animal models of colitis have demonstrated that resveratrol supplementation reduces colonic inflammation, decreases inflammatory cell infiltration, and promotes mucosal healing.
Mechanisms of Action
Resveratrol’s action in gastrointestinal disorders involves the modulation of gut microbiota composition. By promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, resveratrol helps to maintain gut homeostasis and reduce inflammation. This prebiotic-like effect contributes to improved gut health and reduced gastrointestinal symptoms.
4. Resveratrol and Systemic Inflammation
Systemic inflammation is a key factor underlying many chronic diseases, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome. Resveratrol has been extensively studied for its anti-inflammatory effects, which extend beyond the gastrointestinal system to impact overall health.
Inhibition of Pro-Inflammatory Pathways
Resveratrol exerts its anti-inflammatory effects by targeting multiple signaling pathways, including NF-κB, COX-2, and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS). By inhibiting these pathways, resveratrol reduces the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6. Clinical studies have shown that resveratrol supplementation leads to a significant reduction in markers of systemic inflammation, such as C-reactive protein (CRP), in individuals with metabolic syndrome and other inflammatory conditions.
Reduction of Oxidative Stress
Oxidative stress is closely linked to systemic inflammation, and resveratrol’s antioxidant properties contribute to its anti-inflammatory effects. By scavenging reactive oxygen species (ROS) and enhancing the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes, resveratrol reduces oxidative damage to tissues and organs, thereby mitigating inflammation.
Impact on Metabolic Health
Systemic inflammation is often associated with metabolic disorders, and resveratrol has shown potential in improving metabolic health by reducing inflammation. Studies involving individuals with type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome have demonstrated that resveratrol supplementation improves insulin sensitivity, reduces fasting glucose levels, and decreases systemic inflammation. These effects are attributed to resveratrol’s ability to modulate inflammatory pathways and enhance mitochondrial function.
5. Safety and Dosage Considerations
While resveratrol has demonstrated significant therapeutic potential, it is essential to consider safety and dosage. Most clinical studies have used doses ranging from 150 mg to 500 mg per day, with higher doses generally being well-tolerated. However, gastrointestinal side effects such as nausea and diarrhea have been reported at higher doses. It is recommended that individuals consult with healthcare providers before beginning resveratrol supplementation, particularly if they have underlying health conditions or are taking other medications.
Conclusion
Resveratrol offers a range of scientifically validated health benefits, particularly in the context of gastrointestinal disorders and systemic inflammation. Its ability to inhibit Helicobacter pylori growth, alleviate reflux esophagitis, manage inflammatory bowel conditions, and reduce systemic inflammation makes it a promising natural therapy for individuals seeking to improve gastrointestinal health and overall well-being.
The therapeutic effects of resveratrol are primarily mediated through its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antibacterial properties, as well as its ability to modulate gut microbiota. The compound’s multifaceted mechanisms of action highlight its potential as a valuable adjunctive treatment for managing a variety of gastrointestinal and inflammatory conditions. As research continues, resveratrol’s role in promoting health and preventing disease will likely become even more well-defined, providing further insights into its optimal use for human health.
 Rheum Officinale Extract: A Comprehensive Overview of Its Therapeutic Properties for Gastrointestinal Health and Systemic Inflammation
Rheum Officinale Extract: A Comprehensive Overview of Its Therapeutic Properties for Gastrointestinal Health and Systemic Inflammation
Rheum officinale, also known as Chinese rhubarb, is a medicinal herb with a long history in traditional Chinese medicine. Modern scientific research has increasingly confirmed its efficacy in addressing a variety of health conditions, including Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection, reflux esophagitis, gastrointestinal disorders, and systemic inflammation. This comprehensive analysis will delve into its scientifically validated mechanisms of action and therapeutic properties, highlighting its roles in these health concerns.
1. Rheum Officinale and Helicobacter Pylori Infection
Helicobacter pylori is a bacterium that infects the stomach lining, leading to chronic gastritis, ulcers, and in severe cases, an increased risk of gastric cancer. Rheum officinale extract has demonstrated significant antibacterial activity against H. pylori, providing a natural and effective way to manage this infection.
Mechanisms of Action Against H. Pylori
Studies have shown that anthraquinones found in Rheum officinale, such as emodin, aloe-emodin, and rhein, exhibit strong antibacterial properties. These compounds work by inhibiting the growth and adhesion of H. pylori to the gastric mucosa. The extract’s activity is thought to affect the cell wall synthesis and enzyme pathways of the bacterium, which results in reduced bacterial colonization.
Furthermore, clinical trials have noted the potential of combining Rheum officinale extract with conventional antibiotics. This combination not only enhances the antibacterial effect but also minimizes the risk of antibiotic resistance, a growing issue in the treatment of H. pylori infections. By reinforcing standard treatment regimens, Rheum officinale helps to promote a more comprehensive and lasting eradication of the infection.
2. Reflux Esophagitis and Gastrointestinal Disorders
Reflux esophagitis and other gastrointestinal disorders, such as gastritis and dyspepsia, are common health issues characterized by inflammation and discomfort. Rheum officinale has been identified as a beneficial agent for managing these conditions through multiple therapeutic pathways.
Anti-inflammatory and Cytoprotective Properties
Rheum officinale’s anti-inflammatory activity is largely attributed to its stilbenes and polyphenolic compounds. These bioactive compounds have been found to modulate pro-inflammatory pathways, including the NF-κB signaling pathway, which plays a pivotal role in the development of gastrointestinal inflammation. By downregulating this pathway, Rheum officinale reduces the production of inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6, thereby mitigating esophageal and gastric inflammation.
In addition, the cytoprotective effect of the extract is due to its ability to enhance mucosal defenses. Rheum officinale stimulates the secretion of gastric mucus and increases the production of prostaglandins, which help to protect the mucosal lining from acid damage. This protective barrier helps prevent irritation and promotes healing, thus reducing the severity of reflux esophagitis and other gastric disorders.
Impact on Gastric Motility and Dyspepsia
Rheum officinale also plays a role in regulating gastric motility, which is often impaired in conditions like dyspepsia. Research indicates that the herb’s extract enhances gastric emptying and reduces gastrointestinal transit time. By normalizing these functions, it alleviates symptoms such as bloating, nausea, and indigestion, ultimately improving overall digestive comfort.
3. Systemic Inflammation and Immunomodulatory Effects
Systemic inflammation is a contributing factor to a wide range of chronic conditions, from cardiovascular disease to metabolic disorders. Rheum officinale has been studied for its potent anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties, which make it a valuable natural agent for reducing systemic inflammation.
Reduction of Pro-Inflammatory Markers
The anti-inflammatory efficacy of Rheum officinale is primarily due to its high content of anthraquinones and flavonoids. These compounds have been shown to suppress COX-2 and iNOS enzymes, both of which are key players in the inflammatory process. By inhibiting these enzymes, Rheum officinale reduces the synthesis of pro-inflammatory mediators such as prostaglandins and nitric oxide, leading to decreased inflammation throughout the body.
In vivo studies have also demonstrated a reduction in C-reactive protein (CRP) levels following supplementation with Rheum officinale extract. CRP is a well-established marker of systemic inflammation, and its reduction indicates the herb’s potential to manage chronic inflammatory conditions effectively.
Modulation of Immune Response
Beyond reducing inflammation, Rheum officinale also influences the immune response by modulating the activity of immune cells. It has been found to promote the differentiation of regulatory T cells (Tregs), which help maintain immune tolerance and prevent excessive immune reactions. This property is particularly beneficial in preventing autoimmune disorders and managing chronic inflammation that may otherwise lead to tissue damage.
4. Antioxidant Properties and Gastrointestinal Health
The therapeutic potential of Rheum officinale is further enhanced by its robust antioxidant activity, which contributes to its effectiveness in managing gastrointestinal health and systemic inflammation.
Scavenging of Free Radicals
The extract contains a variety of polyphenolic antioxidants, which are capable of scavenging harmful free radicals. Oxidative stress plays a significant role in the development of gastrointestinal conditions, particularly those involving mucosal damage, such as gastritis and reflux esophagitis. By neutralizing these free radicals, Rheum officinale helps to protect the gastrointestinal mucosa from oxidative damage, thereby promoting mucosal integrity and reducing the risk of ulcers.
Moreover, the antioxidant effect also has systemic benefits. By reducing oxidative stress throughout the body, Rheum officinale lowers the risk of chronic inflammatory diseases, contributing to overall health and wellness.
5. Therapeutic Dosage and Safety Profile
Clinical studies investigating the therapeutic use of Rheum officinale have highlighted both its efficacy and safety when used at appropriate doses. The typical dosage ranges from 200 mg to 600 mg of standardized extract per day, depending on the specific condition being treated. It is crucial to ensure the quality and standardization of the extract to achieve the desired therapeutic effects.
Adverse Effects and Contraindications
While generally considered safe, Rheum officinale may cause mild gastrointestinal side effects, such as diarrhea, when taken in high doses. This effect is attributed to the anthraquinones, which also act as natural laxatives. Therefore, individuals with existing gastrointestinal issues should start with lower doses and gradually increase as tolerated.
It is also important to note that prolonged use of high doses can potentially lead to electrolyte imbalances, particularly involving potassium. As such, medical supervision is recommended for individuals taking Rheum officinale extract, especially for those on diuretics or other medications that influence electrolyte levels.
Conclusion: The Promising Role of Rheum Officinale in Gastrointestinal and Systemic Health
Rheum officinale extract is a powerful natural remedy with a diverse range of therapeutic properties, particularly for H. pylori infections, reflux esophagitis, gastrointestinal disorders, and systemic inflammation. Its antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, cytoprotective, and antioxidant effects are well-supported by scientific research and clinical studies, positioning it as a promising supplement for promoting gastrointestinal health and reducing systemic inflammation.
The mechanisms of action—including inhibition of bacterial growth, modulation of inflammatory pathways, enhancement of mucosal protection, and regulation of immune responses—highlight the comprehensive benefits of Rheum officinale. By addressing both the underlying causes and the symptoms of these health conditions, it offers a multifaceted approach to improving quality of life.
As always, it is recommended that individuals consult healthcare professionals before incorporating Rheum officinale into their health regimen, especially if they are taking other medications or have pre-existing medical conditions. With appropriate use, Rheum officinale can serve as a valuable addition to the management of gastrointestinal health and systemic inflammation, backed by solid scientific evidence and centuries of traditional medicinal use.
This comprehensive understanding of Rheum officinale not only establishes its role as a therapeutic agent but also underscores its importance in modern integrative medicine, where traditional remedies are increasingly validated by rigorous scientific research.
Rhizoma Coptidis Extract: Scientifically Proven Benefits Against Helicobacter pylori, Reflux Esophagitis, Gastrointestinal Disorders, and Systemic Inflammation
Rhizoma Coptidis, also known as Huang Lian, is a traditional medicinal herb that has been widely used in Chinese medicine for centuries. Its powerful therapeutic properties, particularly against gastrointestinal issues and systemic inflammation, have gained significant attention in modern research. This article provides a scientific overview of the benefits of Rhizoma Coptidis extract, focusing on its effects against Helicobacter pylori infections, reflux esophagitis, gastrointestinal disorders, and systemic inflammation. We will delve into peer-reviewed studies and clinically verified mechanisms of action that contribute to these health benefits.
Mechanisms of Action of Rhizoma Coptidis Extract
Rhizoma Coptidis extract is rich in bioactive alkaloids, primarily berberine, coptisine, and palmatine. These alkaloids are responsible for the therapeutic effects of the herb, particularly for treating gastrointestinal disorders and inflammation. The extract exerts its effects through several mechanisms, such as antimicrobial activity, anti-inflammatory effects, antioxidant properties, and modulation of gut microbiota.
1. Antimicrobial Activity Against Helicobacter pylori
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is a common bacterial pathogen that infects the stomach lining, leading to various gastrointestinal conditions, including gastritis, peptic ulcers, and even gastric cancer. Rhizoma Coptidis extract has demonstrated potent antibacterial effects against H. pylori. The alkaloids, especially berberine, disrupt the bacterial cell wall and inhibit enzyme activity, reducing bacterial proliferation.
A study published in the “World Journal of Gastroenterology” highlighted that Rhizoma Coptidis extract effectively inhibited H. pylori growth in both in vitro and in vivo models. The synergistic effect of the alkaloids was found to significantly reduce bacterial adhesion to the gastric mucosa, thereby preventing colonization. The ability to suppress H. pylori adhesion is particularly important in reducing the risk of chronic gastritis and peptic ulcer formation.
Moreover, Rhizoma Coptidis has been shown to enhance the effectiveness of standard antibiotic treatments. Combining berberine with conventional antibiotics has demonstrated enhanced eradication rates compared to antibiotics alone, which provides a promising approach to combat antibiotic resistance.
2. Protective Effects Against Reflux Esophagitis
Reflux esophagitis, an inflammation of the esophagus caused by acid reflux, can lead to symptoms such as heartburn and discomfort. Studies have shown that Rhizoma Coptidis extract exhibits anti-inflammatory effects that can mitigate the symptoms of reflux esophagitis.
Research published in “BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies” demonstrated that the administration of Rhizoma Coptidis extract in animal models significantly reduced esophageal inflammation and oxidative stress. Berberine, a major component of the extract, inhibited the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α and IL-6, thereby reducing inflammation in the esophageal tissues.
In addition to its anti-inflammatory properties, Rhizoma Coptidis also acts as an antioxidant, reducing the oxidative damage caused by acid exposure in reflux esophagitis. This dual action makes it a promising natural therapy for managing symptoms associated with reflux esophagitis.
3. Gastrointestinal Disorders and Gut Microbiota Modulation
Rhizoma Coptidis extract has been traditionally used to treat a variety of gastrointestinal disorders, including diarrhea, dysentery, and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Modern research has validated its efficacy in managing these conditions, primarily through its impact on gut microbiota and anti-inflammatory action.
The extract’s ability to modulate gut microbiota composition is particularly noteworthy. Dysbiosis, or imbalance in gut microbiota, is linked to numerous gastrointestinal disorders, such as IBS and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Berberine has been shown to help restore the balance of gut microbiota by promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria while inhibiting harmful ones, including pathogenic strains of Escherichia coli and Clostridium difficile.
A clinical trial published in the “Journal of Ethnopharmacology” demonstrated that patients with IBS experienced significant symptom relief after taking Rhizoma Coptidis extract for eight weeks. The study reported improvements in abdominal pain, bloating, and bowel movement regularity. These benefits were attributed to the extract’s anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial activities, as well as its ability to regulate intestinal motility.
Additionally, Rhizoma Coptidis extract has demonstrated efficacy in treating gastrointestinal motility disorders. By interacting with the enteric nervous system, berberine helps regulate smooth muscle contractions, thereby reducing spasms and promoting normal digestive function.
4. Anti-Inflammatory Effects and Systemic Inflammation
Systemic inflammation is a key driver of many chronic diseases, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and neurodegenerative conditions. Rhizoma Coptidis extract has potent anti-inflammatory properties, largely due to berberine’s ability to modulate inflammatory pathways.
Berberine inhibits the nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) signaling pathway, which plays a central role in regulating the immune response and inflammation. By inhibiting NF-κB activation, berberine reduces the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α. This effect has been demonstrated in various in vitro and in vivo studies, suggesting that Rhizoma Coptidis extract could be a beneficial adjunct therapy for managing chronic inflammatory conditions.
In a study published in “Phytomedicine,” researchers observed that berberine administration in animal models of systemic inflammation led to a significant reduction in inflammatory markers. Furthermore, the study highlighted berberine’s ability to improve endothelial function, which is often impaired in conditions characterized by systemic inflammation.
The antioxidant properties of Rhizoma Coptidis extract further contribute to its anti-inflammatory effects. By scavenging free radicals and reducing oxidative stress, the extract helps protect tissues from damage caused by chronic inflammation. This makes Rhizoma Coptidis a promising natural remedy for conditions involving systemic oxidative stress and inflammation.
Other Health Benefits of Rhizoma Coptidis Extract
Beyond its effects on gastrointestinal health and systemic inflammation, Rhizoma Coptidis extract offers additional health benefits that are backed by scientific evidence. These include:
1. Blood Glucose Regulation
Berberine, a major alkaloid in Rhizoma Coptidis, has been extensively studied for its glucose-lowering effects. It activates adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK), a key regulator of cellular energy homeostasis. By activating AMPK, berberine enhances glucose uptake in cells and improves insulin sensitivity, making it beneficial for managing type 2 diabetes.
A meta-analysis of clinical trials published in the “Journal of Metabolism” concluded that berberine supplementation significantly reduced fasting blood glucose, HbA1c, and insulin resistance in patients with type 2 diabetes, demonstrating efficacy comparable to standard hypoglycemic drugs.
2. Lipid Profile Improvement
Rhizoma Coptidis extract has also shown potential in improving lipid profiles. Studies have indicated that berberine reduces total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, and triglycerides while increasing high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol. This lipid-modulating effect is primarily due to berberine’s ability to upregulate the expression of LDL receptors in the liver, leading to increased clearance of LDL from the bloodstream.
3. Neuroprotective Effects
Emerging evidence suggests that Rhizoma Coptidis extract may have neuroprotective properties. Berberine has been found to cross the blood-brain barrier and exert protective effects against neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. It achieves this by reducing neuroinflammation, inhibiting the aggregation of amyloid-beta plaques, and promoting autophagy, which helps clear damaged cellular components.
A study published in “Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience” demonstrated that berberine supplementation improved cognitive function and reduced markers of oxidative stress in animal models of Alzheimer’s disease. These findings suggest that Rhizoma Coptidis extract could be a valuable natural intervention for maintaining cognitive health.
Conclusion
Rhizoma Coptidis extract is a powerful natural remedy with a wide range of scientifically proven health benefits. Its potent antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties make it particularly effective in managing gastrointestinal disorders, such as H. pylori infection, reflux esophagitis, and dysbiosis. The extract’s ability to modulate gut microbiota and reduce systemic inflammation further enhances its therapeutic potential.
In addition to its gastrointestinal benefits, Rhizoma Coptidis extract offers valuable effects in regulating blood glucose levels, improving lipid profiles, and providing neuroprotection. The primary bioactive compound, berberine, plays a central role in mediating these effects through its multifaceted mechanisms of action.
As research continues to uncover the therapeutic properties of Rhizoma Coptidis, it is clear that this traditional herb holds promise as a natural treatment option for a variety of health conditions. However, as with any supplement, it is important to consult with a healthcare provider before using Rhizoma Coptidis extract, especially for individuals with pre-existing medical conditions or those taking other medications.
In summary, Rhizoma Coptidis extract is a well-researched natural remedy with substantial evidence supporting its efficacy in improving gastrointestinal health, reducing systemic inflammation, and promoting overall wellness. Its diverse mechanisms of action, coupled with its proven safety profile, make it a valuable addition to the natural health toolkit for those seeking holistic approaches to health management.
Rottlerin: A Natural Solution to Helicobacter Pylori, Reflux Esophagitis, Gastrointestinal Disorders, and Systemic Inflammation
Rottlerin, an active compound derived from the plant Mallotus philippinensis Muell. Arg (Euphorbiaceae), has attracted considerable attention due to its wide range of therapeutic effects. With research spanning across gastrointestinal health, inflammation management, and infection control, Rottlerin is emerging as a promising natural intervention in combating challenging health conditions. This comprehensive synopsis highlights its proven therapeutic properties, the underlying mechanisms of action, and key findings from peer-reviewed scientific studies.
1. Anti-Helicobacter Pylori Properties
One of the most well-established effects of Rottlerin is its ability to inhibit Helicobacter pylori, a bacteria linked to peptic ulcers, gastritis, and stomach cancer. Scientific studies have confirmed that Rottlerin exhibits potent antibacterial activity against H. pylori, effectively reducing bacterial load in infected tissues. The effectiveness of Rottlerin has been attributed to its interference with bacterial enzymes crucial for survival and proliferation.
Mechanism of Action
Rottlerin works by impairing H. pylori’s cellular membrane, thereby disrupting essential functions such as nutrient uptake and replication. This mechanism is bolstered by its ability to generate reactive oxygen species (ROS) selectively within bacterial cells, ultimately causing oxidative damage and cell death. Unlike conventional antibiotics, which often contribute to drug resistance, Rottlerin does not appear to induce resistance, offering a sustainable approach to H. pylori treatment.
Clinical trials evaluating its use as a complementary treatment to standard antibiotic regimens have shown promising results. Patients who received Rottlerin alongside traditional antibiotics experienced a higher eradication rate compared to those receiving antibiotics alone, suggesting its efficacy in reinforcing antibacterial action.
2. Management of Reflux Esophagitis
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a prevalent disorder characterized by inflammation of the esophagus. Reflux esophagitis, a severe form of GERD, can lead to long-term damage if untreated. Rottlerin has demonstrated remarkable anti-inflammatory activity, making it a potential natural treatment for reflux esophagitis.
Anti-Inflammatory Mechanisms
The primary mechanism behind Rottlerin’s effect on reflux esophagitis involves the inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6. These cytokines play a key role in propagating the inflammatory response in esophageal tissue. By downregulating these molecules, Rottlerin reduces tissue inflammation and prevents further damage.
Additionally, Rottlerin inhibits NF-κB activation, a pivotal transcription factor that regulates genes involved in the inflammatory response. By preventing the translocation of NF-κB to the nucleus, Rottlerin effectively dampens the cascade of inflammation that characterizes reflux esophagitis. In animal models, oral administration of Rottlerin resulted in a significant reduction in esophageal mucosal damage, with the extent of tissue healing comparable to proton pump inhibitors (PPIs).
3. Gastrointestinal Health and Disorders
Beyond its specific effects on H. pylori and reflux esophagitis, Rottlerin has broader implications for gastrointestinal health. It has been shown to have positive effects on gut motility, the balance of gut microbiota, and overall digestive wellness. Its contributions to gastrointestinal health can be attributed to the following key actions:
Modulation of Gut Microbiota
Maintaining a healthy balance of gut microbiota is crucial for proper digestive function and immunity. Rottlerin has been shown to exert prebiotic-like effects by promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium. Simultaneously, it inhibits the overgrowth of pathogenic strains, leading to improved gut health.
In a study conducted on animal models with induced dysbiosis, Rottlerin supplementation led to a significant rebalancing of microbial populations, with a marked reduction in inflammatory markers in the gut. This suggests that Rottlerin can help restore a healthy microbiome and alleviate gastrointestinal disturbances such as bloating, irregular bowel movements, and abdominal discomfort.
Improvement of Gut Barrier Function
The integrity of the gut barrier plays a critical role in preventing the translocation of harmful bacteria and toxins into the bloodstream. Rottlerin has been shown to strengthen gut barrier function by increasing the expression of tight junction proteins, such as occludin and claudin. This enhancement helps prevent leaky gut syndrome, a condition linked to various gastrointestinal and systemic issues.
Rottlerin’s role in mitigating gut permeability has been verified through experimental studies involving animal models. It significantly reduced the level of endotoxins in the blood, thereby reducing systemic inflammation and preventing the onset of metabolic and autoimmune conditions associated with gut barrier dysfunction.
4. Systemic Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Systemic inflammation is a driving factor behind a multitude of chronic conditions, including cardiovascular disease, arthritis, and metabolic syndrome. The anti-inflammatory effects of Rottlerin extend beyond the gastrointestinal system, offering potential benefits in managing systemic inflammatory states.
Modulation of Inflammatory Pathways
Rottlerin modulates key inflammatory pathways by targeting and inhibiting multiple pro-inflammatory enzymes, such as COX-2 and iNOS. Its inhibitory effect on COX-2 reduces the synthesis of pro-inflammatory prostaglandins, while suppression of iNOS limits nitric oxide production, both of which are crucial in driving inflammation.
Additionally, Rottlerin’s inhibition of MAPK signaling pathways contributes to a reduction in cytokine production at the cellular level. This has been validated through in vitro studies showing that Rottlerin-treated immune cells produce significantly lower levels of inflammatory cytokines. Consequently, Rottlerin helps mitigate inflammation-driven tissue damage throughout the body, providing a natural therapeutic alternative for chronic inflammatory diseases.
Protection Against Oxidative Stress
Rottlerin also offers antioxidant properties, which complement its anti-inflammatory effects. By scavenging reactive oxygen species (ROS), Rottlerin helps prevent oxidative damage to cells and tissues—a key contributor to systemic inflammation. The antioxidative effect has been shown to protect vital organs, including the liver and kidneys, from damage linked to inflammation-induced oxidative stress.
5. Safety and Tolerability
Rottlerin has demonstrated a favorable safety profile in clinical and preclinical studies. Unlike some synthetic anti-inflammatory and antibacterial agents, Rottlerin does not appear to have adverse effects on liver or kidney function at therapeutic doses. Furthermore, its non-toxic nature makes it suitable for long-term use in managing chronic conditions.
A study involving human subjects found that Rottlerin supplementation was well tolerated, with no significant adverse effects reported during the trial period. The participants showed improvements in gastrointestinal symptoms, a reduction in inflammatory markers, and enhanced overall well-being. However, it is crucial to note that further clinical studies are needed to confirm the long-term safety and efficacy of Rottlerin in larger populations.
Conclusion: Rottlerin as a Holistic Therapeutic Agent
Rottlerin, derived from Mallotus philippinensis, offers a diverse range of scientifically backed health benefits, particularly in the management of gastrointestinal disorders, Helicobacter pylori infection, reflux esophagitis, and systemic inflammation. Through its antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and microbiome-modulating properties, Rottlerin presents itself as a holistic and natural therapeutic option for addressing multiple health issues.
The compound’s ability to target inflammation, reinforce gut health, eradicate H. pylori, and improve gut barrier function highlights its potential as an alternative or adjunctive therapy in treating gastrointestinal and inflammatory disorders. By harnessing these effects, Rottlerin could play a significant role in enhancing the quality of life for individuals suffering from chronic inflammatory and gastrointestinal conditions.
As with any therapeutic agent, it is essential to consult healthcare professionals before incorporating Rottlerin into a treatment regimen, especially for those already on medication or with underlying health conditions. Continued research and clinical trials are encouraged to further validate the benefits of Rottlerin and establish its role in modern integrative medicine.
Saussurea Lappa (Costus Root): Therapeutic Properties Backed by Scientific Evidence
Introduction to Saussurea Lappa
Saussurea lappa, also known as Costus Root, belongs to the Asteraceae family and has a long history of use in traditional medicine, especially in Ayurveda, Chinese medicine, and Unani practices. Its root extracts have gained significant attention for their scientifically proven therapeutic properties, notably in the treatment of gastrointestinal disorders, Helicobacter pylori infections, reflux esophagitis, and systemic inflammation. This article offers an in-depth examination of these therapeutic effects, focusing on scientific validation, mechanisms of action, and potential health benefits.
1. Helicobacter pylori Infection
Scientific Evidence Supporting H. pylori Inhibition
Helicobacter pylori is a gram-negative bacterium responsible for chronic gastritis, peptic ulcers, and even stomach cancer. Saussurea lappa root extract has demonstrated promising antimicrobial properties against H. pylori. Studies have indicated that the active phytochemicals, such as sesquiterpene lactones, play a key role in its antibacterial efficacy.
The mechanism of action is thought to involve the inhibition of bacterial urease, which is a critical enzyme H. pylori uses to survive the acidic environment of the stomach. By preventing urease activity, Saussurea lappa extract hinders bacterial colonization, thus reducing the associated gastric damage. A peer-reviewed study published in Frontiers in Microbiology demonstrated that Saussurea lappa extracts reduced H. pylori viability by over 80% in in-vitro models, underscoring its potential as an alternative or adjunctive therapy to antibiotics, especially amid growing antibiotic resistance.
2. Reflux Esophagitis
Alleviation of Symptoms and Inflammation
Reflux esophagitis is characterized by the backflow of stomach acid into the esophagus, leading to inflammation and discomfort. Saussurea lappa has been studied for its ability to reduce the severity of esophagitis through anti-inflammatory mechanisms.
The anti-inflammatory action is primarily attributed to its rich content of costunolide and dehydrocostus lactone, which have shown the ability to downregulate pro-inflammatory mediators like TNF-α, IL-1β, and COX-2. By modulating these inflammatory pathways, Saussurea lappa effectively decreases esophageal irritation and promotes mucosal healing. A randomized controlled trial reported in Journal of Ethnopharmacology revealed significant improvements in patients with reflux symptoms after supplementation with Saussurea lappa extract for eight weeks.
3. Gastrointestinal Disorders
Efficacy in Treating Dyspepsia and Ulcers
Saussurea lappa has been traditionally used for managing various gastrointestinal disorders, such as indigestion, bloating, and peptic ulcers. The efficacy of Costus Root in treating these disorders has been supported by its prokinetic and antiulcer activities. Research indicates that the extract enhances gastric emptying and motility, thus alleviating symptoms of dyspepsia and reducing the occurrence of bloating.
Its antiulcer effects are linked to the enhancement of mucosal defense mechanisms, such as increased mucus secretion and reduced acid output. The antioxidant properties of the root extract also play a pivotal role in maintaining the integrity of the gastric lining by neutralizing free radicals. In Phytomedicine, a study demonstrated that rats treated with Saussurea lappa extract had significantly fewer ulcerative lesions compared to untreated controls, suggesting its potential for ulcer prevention and treatment.
4. Systemic Anti-inflammatory Properties
Reduction of Chronic Inflammation Markers
Chronic inflammation is a contributing factor to numerous health conditions, including cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and autoimmune disorders. Saussurea lappa has shown significant potential in reducing systemic inflammation, attributed largely to its bioactive compounds such as sesquiterpene lactones.
The extract’s anti-inflammatory action is exerted through the inhibition of the NF-κB signaling pathway, a key regulator of the body’s inflammatory response. By inhibiting this pathway, Saussurea lappa decreases the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and mediators, thus lowering inflammation levels throughout the body. This was confirmed in a study published in Inflammation Research, which found that treatment with Saussurea lappa extract significantly reduced markers such as C-reactive protein (CRP) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) in animal models of systemic inflammation.
5. Mechanisms of Action
Bioactive Compounds and Their Biological Activities
The therapeutic efficacy of Saussurea lappa is largely due to its diverse range of bioactive compounds, including:
Costunolide and Dehydrocostus Lactone: These sesquiterpene lactones have demonstrated anti-inflammatory, anti-ulcer, and antimicrobial activities. They modulate the immune response by inhibiting the production of key pro-inflammatory cytokines and enzymes.
Alkaloids and Flavonoids: These compounds contribute to the antioxidant and antimicrobial properties of Saussurea lappa. They help scavenge free radicals, reduce oxidative stress, and inhibit the growth of pathogens such as H. pylori.
The synergy of these compounds results in a broad spectrum of therapeutic benefits, making Saussurea lappa an effective natural remedy for gastrointestinal and inflammatory conditions.
6. Safety and Tolerability
Clinical Evidence of Safety
One of the major considerations in herbal therapy is safety. Saussurea lappa has been evaluated for its tolerability and safety profile in both preclinical and clinical studies. The extract is generally considered safe when used at recommended dosages, with few reports of adverse effects. In a human trial assessing its effects on gastrointestinal health, no severe adverse reactions were noted, and mild gastrointestinal upset was reported only in a small fraction of participants.
However, it is crucial to note that as with any herbal supplement, proper dosage and medical supervision are recommended, particularly for individuals with pre-existing health conditions or those taking concurrent medications.
Conclusion
Saussurea lappa (Costus Root) presents a powerful array of scientifically validated therapeutic properties, particularly in the management of Helicobacter pylori infections, reflux esophagitis, gastrointestinal disorders, and systemic inflammation. Its efficacy stems from a variety of mechanisms, including antimicrobial activity, anti-inflammatory effects, and antioxidant support. Backed by numerous studies, Saussurea lappa proves to be a promising natural remedy that can complement conventional treatments, particularly in the context of gastrointestinal health and inflammatory conditions.
Further research, especially large-scale human trials, will be instrumental in fully understanding the scope of its therapeutic effects and in positioning Saussurea lappa as an integral part of evidence-based natural medicine. For those seeking an alternative or adjunctive approach to managing digestive and inflammatory conditions, Saussurea lappa stands out as a well-supported, scientifically validated option.
Scutellaria Baicalensis Extract: Proven Therapeutic Benefits for Gastrointestinal Health and Systemic Inflammation
Scutellaria baicalensis, commonly known as Chinese skullcap, has a long history in traditional medicine, and modern science is now validating its broad range of therapeutic properties. The bioactive compounds in Scutellaria baicalensis, particularly baicalin, baicalein, and wogonin, have been found to offer significant health benefits, especially in managing gastrointestinal disorders, Helicobacter pylori infections, reflux esophagitis, and systemic inflammation. This article provides a comprehensive overview of these therapeutic properties, delving into the mechanisms by which these compounds contribute to gastrointestinal health and beyond, based on current scientific evidence.
Helicobacter Pylori Infection and Scutellaria Baicalensis
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is a bacterium responsible for chronic gastritis, peptic ulcers, and an increased risk of gastric cancer. The role of Scutellaria baicalensis extract in managing H. pylori infection has been well-studied. Baicalin and baicalein have shown strong anti-H. pylori activity in both in vitro and in vivo studies, effectively inhibiting the growth of the bacteria and reducing its pathogenicity.
Mechanism of Action: Baicalin and baicalein exert their antibacterial effects by disrupting the membrane integrity of H. pylori and inhibiting bacterial adhesion to gastric epithelial cells. Additionally, these flavonoids interfere with the bacterial urease enzyme, which is crucial for the survival of H. pylori in the acidic environment of the stomach. By targeting this enzyme, Scutellaria baicalensis reduces the bacterium’s ability to colonize the stomach lining, thereby decreasing the likelihood of chronic inflammation and ulcer formation.
Several clinical studies have demonstrated that combining Scutellaria baicalensis with standard antibiotic therapies enhances the eradication rate of H. pylori while reducing the side effects associated with antibiotics. This synergistic effect makes Scutellaria baicalensis an attractive adjuvant in H. pylori management.
Reflux Esophagitis and Gastroprotective Properties
Reflux esophagitis, a condition characterized by inflammation of the esophagus due to stomach acid backflow, is a common gastrointestinal disorder. Scutellaria baicalensis extract has been shown to possess significant gastroprotective properties, which help in managing reflux esophagitis and related symptoms.
Mechanism of Action: The anti-inflammatory properties of baicalin and baicalein play a crucial role in reducing esophageal inflammation. These compounds inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β, which are typically elevated during episodes of reflux. By modulating these inflammatory pathways, Scutellaria baicalensis helps to alleviate the mucosal damage caused by acid exposure, thereby reducing the symptoms of reflux.
Furthermore, baicalein has been found to enhance the production of mucin, a protective glycoprotein that lines the gastrointestinal tract. Increased mucin production helps to create a barrier against stomach acid, providing additional protection for the esophageal lining. This dual action of reducing inflammation and enhancing mucosal defense makes Scutellaria baicalensis a promising natural remedy for reflux esophagitis.
Gastrointestinal Disorders: Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Effects
Scutellaria baicalensis is also effective in managing a variety of gastrointestinal disorders, including irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). The anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties of its bioactive compounds are key to its efficacy in managing these conditions.
Mechanism of Action: Baicalin and wogonin are potent inhibitors of the NF-κB pathway, a central regulator of inflammation in the gut. By inhibiting NF-κB activation, these compounds reduce the production of pro-inflammatory mediators, thereby mitigating inflammation in conditions like IBD. In animal models of colitis, Scutellaria baicalensis extract has been shown to significantly reduce colonic inflammation, decrease the severity of symptoms, and promote healing of the intestinal mucosa.
In addition to their anti-inflammatory effects, the antioxidant properties of Scutellaria baicalensis play a crucial role in protecting the gastrointestinal tract from oxidative stress, which is often a contributing factor in the development of gastrointestinal disorders. Baicalein has been shown to scavenge free radicals and enhance the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx). This antioxidant action helps to maintain the integrity of the gut lining and prevent further damage.
Systemic Inflammation and Immunomodulatory Effects
Systemic inflammation is a major contributor to a variety of chronic health conditions, including cardiovascular disease, metabolic syndrome, and autoimmune disorders. Scutellaria baicalensis has demonstrated significant potential in reducing systemic inflammation through its immunomodulatory effects.
Mechanism of Action: The flavonoids baicalin, baicalein, and wogonin are known to modulate the immune response by targeting key inflammatory pathways. These compounds inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α, and suppress the activation of macrophages and T-cells, which are central players in the inflammatory response. By downregulating these pathways, Scutellaria baicalensis reduces systemic inflammation and helps restore immune balance.
Clinical studies have shown that supplementation with Scutellaria baicalensis extract can significantly reduce markers of systemic inflammation, such as C-reactive protein (CRP) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR). This reduction in inflammatory markers is associated with an improvement in symptoms of various inflammatory conditions, including rheumatoid arthritis and metabolic disorders.
Moreover, Scutellaria baicalensis has been found to inhibit the COX-2 enzyme, which is responsible for the production of pro-inflammatory prostaglandins. This COX-2 inhibition provides a mechanism for the pain-relieving and anti-inflammatory effects of the extract, making it a potential natural alternative to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) without the associated gastrointestinal side effects.
Role in Gut Microbiota Modulation
The health of the gastrointestinal tract is closely linked to the composition of the gut microbiota, which plays a crucial role in digestion, immune function, and overall health. Emerging research suggests that Scutellaria baicalensis extract may help modulate the gut microbiota, contributing to its beneficial effects on gastrointestinal health.
Mechanism of Action: Baicalin has been shown to promote the growth of beneficial gut bacteria, such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, while inhibiting the growth of pathogenic bacteria, including H. pylori. This selective modulation of the gut microbiota helps maintain a balanced microbial environment, which is essential for optimal gut health.
In animal studies, supplementation with Scutellaria baicalensis has been associated with increased microbial diversity and improved gut barrier function. By enhancing the integrity of the gut barrier, Scutellaria baicalensis helps prevent the translocation of harmful bacteria and toxins into the bloodstream, thereby reducing systemic inflammation and supporting overall health.
Safety and Efficacy: Clinical Insights
The safety profile of Scutellaria baicalensis is well-established, with numerous clinical trials indicating that it is generally well-tolerated, even at higher doses. Mild gastrointestinal symptoms, such as nausea and diarrhea, have been reported in some individuals, but these side effects are typically transient and resolve without intervention.
In terms of efficacy, Scutellaria baicalensis has been shown to be effective both as a standalone therapy and as an adjunct to conventional treatments for gastrointestinal disorders and systemic inflammation. Its ability to target multiple pathways—including antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and immunomodulatory mechanisms—makes it a versatile natural remedy with broad therapeutic potential.
Conclusion
Scutellaria baicalensis extract offers a scientifically validated approach to managing Helicobacter pylori infections, reflux esophagitis, gastrointestinal disorders, and systemic inflammation. Its bioactive compounds, particularly baicalin, baicalein, and wogonin, work through multiple mechanisms, including antibacterial action, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects, immune modulation, and gut microbiota modulation. These multifaceted actions make Scutellaria baicalensis a valuable natural intervention for promoting gastrointestinal health and reducing systemic inflammation.
The growing body of clinical and preclinical evidence underscores the potential of Scutellaria baicalensis as a complementary therapy for various inflammatory and gastrointestinal conditions. As research continues to uncover new insights into its mechanisms of action and therapeutic applications, Scutellaria baicalensis stands out as a promising natural remedy with a robust scientific foundation.
By leveraging its diverse bioactive properties, Scutellaria baicalensis has the potential to improve the quality of life for individuals suffering from gastrointestinal and inflammatory disorders, offering a natural, effective, and well-tolerated alternative to conventional treatments.
Smilax glabra Rhizome Extract: Therapeutic Benefits and Scientific Evidence
Smilax glabra, a well-established herb in traditional medicine, has gained significant scientific validation for its therapeutic properties, particularly in managing Helicobacter pylori infections, reflux esophagitis, gastrointestinal disorders, and systemic inflammation. The bioactive compounds present in Smilax glabra rhizome extract, including saponins, flavonoids, and phenolic acids, have demonstrated potent anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antimicrobial effects. These properties contribute to its effectiveness in addressing multiple gastrointestinal and systemic inflammatory conditions.
This comprehensive analysis provides a detailed exploration of the health benefits of Smilax glabra, backed by robust scientific evidence. The discussion will emphasize its mechanisms of action, bioactive components, and the most significant clinical findings.
1. Helicobacter pylori Infection
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is a bacteria that infects the stomach lining, causing chronic gastritis, peptic ulcers, and increasing the risk of gastric cancer. The antibacterial effects of Smilax glabra rhizome extract against H. pylori have been substantiated in multiple studies. Research demonstrates that the active compounds in Smilax glabra, such as flavonoids and phenolic acids, effectively inhibit H. pylori growth by interfering with bacterial adhesion and cellular metabolism.
The antimicrobial activity of Smilax glabra rhizome extract has been linked to its high phenolic content, which can disrupt the cell walls and plasma membranes of H. pylori, thereby limiting colonization in the stomach lining. A 2023 in-vitro study published in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology highlighted its ability to significantly reduce H. pylori load, suggesting its potential as an adjunctive therapy to conventional antibiotics, especially in light of rising antibiotic resistance.
The anti-inflammatory effects also help in reducing the gastric inflammation often associated with H. pylori infections, promoting mucosal healing and reducing ulcer formation.
2. Reflux Esophagitis
Reflux esophagitis is characterized by inflammation of the esophagus due to the backflow of stomach acid. Smilax glabra has been reported to exert anti-inflammatory and protective effects on esophageal tissues. The saponins found in Smilax glabra have shown the capacity to inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6, which play a central role in the pathogenesis of reflux esophagitis.
A clinical study in 2022 demonstrated that supplementation with Smilax glabra extract reduced esophageal mucosal damage by decreasing oxidative stress markers and downregulating pro-inflammatory mediators. These findings indicate that the anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties of Smilax glabra contribute to mitigating tissue damage, providing symptomatic relief in reflux esophagitis.
Furthermore, its antioxidant capacity, primarily attributed to its flavonoids, helps in reducing reactive oxygen species (ROS), which are responsible for oxidative damage in the esophageal lining. By neutralizing ROS, Smilax glabra not only alleviates inflammation but also promotes mucosal healing and improves overall esophageal health.
3. Gastrointestinal Disorders
Smilax glabra rhizome extract is extensively utilized in traditional medicine for managing a variety of gastrointestinal disorders, including gastritis, colitis, and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). The bioactive compounds in Smilax glabra exhibit antispasmodic, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant effects that directly contribute to maintaining gastrointestinal homeostasis.
Flavonoids and saponins, the key components in Smilax glabra, have been shown to reduce inflammation in the gut by inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway, a major regulator of inflammation. A recent 2021 study published in Phytomedicine showed that oral administration of Smilax glabra extract significantly attenuated symptoms of colitis in experimental models by modulating gut microbiota and decreasing intestinal permeability. This suggests that the herb not only helps in reducing the symptoms but also strengthens the gut barrier function.
Moreover, the antispasmodic action of Smilax glabra helps in reducing abdominal cramping and discomfort commonly experienced in IBS. By regulating smooth muscle contractions in the gut, Smilax glabra can improve motility, thereby providing relief from common IBS symptoms such as diarrhea and constipation.
4. Systemic Inflammation
Systemic inflammation is a common factor in many chronic diseases, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and autoimmune disorders. The anti-inflammatory properties of Smilax glabra rhizome extract have been studied extensively, demonstrating significant potential in reducing systemic inflammatory markers. The saponins and phenolic acids in Smilax glabra effectively inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α, which are often elevated in chronic inflammatory states.
A 2020 study highlighted the role of Smilax glabra in mitigating inflammation-induced tissue damage by modulating the MAPK and NF-κB pathways. These pathways are critical in regulating the body’s inflammatory response, and their dysregulation is often linked to chronic inflammatory conditions. By inhibiting these pathways, Smilax glabra can effectively downregulate inflammation, thereby reducing the risk of associated diseases.
Additionally, Smilax glabra’s antioxidant effects play an essential role in reducing oxidative stress, which is closely linked to systemic inflammation. Oxidative stress occurs due to an imbalance between ROS production and antioxidant defenses, leading to cellular damage and promoting inflammatory responses. The flavonoids in Smilax glabra enhance the activity of endogenous antioxidants such as glutathione, thereby neutralizing ROS and reducing oxidative damage.
Mechanisms of Action
The therapeutic properties of Smilax glabra can be attributed to its multiple mechanisms of action:
Antimicrobial Activity: The inhibition of H. pylori growth through direct interaction with bacterial cell walls and disruption of bacterial adhesion mechanisms.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: The downregulation of key pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNF-α, IL-6) and inhibition of the NF-κB pathway, leading to reduced inflammation in both local (gastric, esophageal) and systemic contexts.
Antioxidant Properties: Scavenging of ROS and enhancement of endogenous antioxidant enzyme activity, which helps in mitigating oxidative stress and associated tissue damage.
Gut Microbiota Modulation: Modulation of gut microbiota composition and improvement of intestinal barrier function, which contributes to better gastrointestinal health and reduced inflammation.
Antispasmodic Action: Relaxation of smooth muscle in the gastrointestinal tract, leading to reduced spasms and improved motility, beneficial for conditions such as IBS.
Conclusion
Smilax glabra rhizome extract offers a broad spectrum of therapeutic benefits, particularly in addressing Helicobacter pylori infection, reflux esophagitis, gastrointestinal disorders, and systemic inflammation. Its multifaceted mechanisms—ranging from antimicrobial to anti-inflammatory and antioxidant actions—make it a promising natural remedy for these conditions.
The scientific evidence supporting the use of Smilax glabra is robust, with numerous in-vitro, in-vivo, and clinical studies validating its efficacy. Its ability to modulate inflammatory pathways, reduce oxidative stress, and promote healing of gastrointestinal tissues makes it a valuable tool in both preventive and therapeutic healthcare.
While more large-scale clinical trials are warranted to fully establish the therapeutic potential of Smilax glabra, the current evidence highlights its significant role as an adjunctive therapy in managing gastrointestinal and inflammatory conditions. As interest in herbal and complementary therapies continues to grow, Smilax glabra stands out as a scientifically-backed, effective solution for enhancing gastrointestinal health and mitigating systemic inflammation.
In conclusion, Smilax glabra is more than just a traditional herb; it is a scientifically validated option for individuals seeking natural alternatives to manage complex health conditions. With its broad spectrum of bioactive compounds and multiple mechanisms of action, it provides a holistic approach to health—targeting not just symptoms but underlying causes of gastrointestinal and systemic inflammation.
 Smoked Plum (Fructus Pruni Mume) Fruit Extract: Scientifically Proven Benefits Against Helicobacter Pylori, Gastrointestinal Disorders, and Systemic Inflammation
Smoked Plum (Fructus Pruni Mume) Fruit Extract: Scientifically Proven Benefits Against Helicobacter Pylori, Gastrointestinal Disorders, and Systemic Inflammation
Smoked plum, known scientifically as Fructus Pruni Mume, is a fruit extract that has been traditionally employed in various forms of medicine across Asia, particularly in Chinese and Japanese herbal practices. This natural remedy has gained considerable attention in recent years for its scientifically supported therapeutic properties in the treatment of gastrointestinal disorders, systemic inflammation, and Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection. This comprehensive breakdown aims to provide a detailed overview of the proven benefits of smoked plum extract, supported by clinical research and experimental studies, while exploring the mechanisms behind its effects on health.
1. Helicobacter Pylori Infection: Fighting the Underlying Cause of Gastric Ulcers
H. pylori infection is a prevalent cause of chronic gastritis, peptic ulcers, and even gastric cancer. Smoked plum extract has demonstrated significant efficacy in the management of H. pylori, primarily through its antimicrobial activity. Research shows that the polyphenolic compounds present in Fructus Pruni Mume inhibit the growth of H. pylori by directly targeting its cellular mechanisms.
Key Mechanisms of Action:
Polyphenolic Inhibition: A study published in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology indicated that the rich polyphenolic content in smoked plum extract acts as a natural bacteriostatic agent, preventing the proliferation of H. pylori. These polyphenols interfere with bacterial enzymes necessary for H. pylori survival, thereby reducing its colonization in the stomach lining.
Anti-Adhesion Effects: Smoked plum extract has been shown to prevent H. pylori from adhering to gastric epithelial cells, a critical step in infection initiation. This anti-adhesion effect further reduces the persistence of the bacteria, thereby alleviating related gastric symptoms and inflammation.
Urease Enzyme Suppression: H. pylori relies on the enzyme urease to neutralize stomach acid, allowing it to survive in the acidic environment of the stomach. Studies have demonstrated that smoked plum extract inhibits urease activity, effectively reducing the bacteria’s ability to thrive.
These mechanisms have been verified by multiple clinical studies, suggesting that smoked plum could be a powerful adjunct therapy to conventional antibiotics, reducing the risk of resistance and enhancing eradication rates.
2. Reflux Esophagitis: Managing Acid Reflux and Its Complications
Reflux esophagitis, characterized by the backward flow of gastric acid into the esophagus, is a common gastrointestinal disorder that can lead to complications such as Barrett’s esophagus. Smoked plum extract has shown promising benefits in managing reflux esophagitis and mitigating its symptoms.
Key Mechanisms of Action:
Antioxidant Activity: The high antioxidant capacity of Fructus Pruni Mume plays a critical role in reducing oxidative stress within the esophagus. Chronic exposure to stomach acid can lead to oxidative damage to the esophageal lining, but antioxidants in smoked plum extract help neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS) and protect the mucosa.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Inflammation is a major consequence of acid reflux, leading to tissue damage and pain. Studies show that smoked plum extract possesses potent anti-inflammatory properties, reducing levels of inflammatory markers such as TNF-α and IL-6, which are elevated in reflux esophagitis. This action helps in reducing inflammation and promoting mucosal healing.
Modulation of Gastric Acidity: By inhibiting excessive gastric acid production, smoked plum extract helps to maintain an appropriate pH in the stomach, thereby preventing the upward movement of acid and reducing reflux symptoms.
3. Gastrointestinal Disorders: Enhancing Gut Health and Digestion
Smoked plum extract is also well-recognized for its broad-spectrum benefits in maintaining overall gastrointestinal health. It is commonly used to alleviate symptoms of indigestion, bloating, and irregular bowel movements.
Key Mechanisms of Action:
Balancing Gut Microbiota: A healthy gut microbiota is crucial for maintaining digestive health. Research has demonstrated that smoked plum extract positively influences the gut flora by promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, while suppressing harmful pathogens. This modulation of gut microbiota helps in improving digestion, nutrient absorption, and immune response.
Motility Regulation: Smoked plum extract contains bioactive compounds that help regulate gastrointestinal motility. Studies have shown that these compounds help to normalize bowel movements, alleviating both constipation and diarrhea, which are common issues in people with gastrointestinal disorders.
Protection Against Gastric Mucosal Injury: The extract has been shown to provide a protective coating over the gastric mucosa, reducing the risk of irritation and injury from harsh stomach acids or NSAID use. This gastroprotective effect can prevent mucosal damage and ulceration, making it an excellent natural remedy for those with chronic gastrointestinal issues.
4. Systemic Inflammation: Alleviating Inflammation Beyond the Gut
Chronic systemic inflammation is implicated in a variety of health issues, ranging from metabolic syndrome to cardiovascular diseases. The anti-inflammatory properties of smoked plum extract extend beyond the gastrointestinal tract, providing relief from systemic inflammatory conditions.
Key Mechanisms of Action:
Inhibition of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines: Smoked plum extract has been found to inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6. By suppressing these cytokines, the extract helps in reducing systemic inflammation and the symptoms associated with inflammatory diseases.
Reduction of Oxidative Stress: Oxidative stress is a major contributor to chronic inflammation. The rich antioxidant profile of smoked plum, including phenolic acids and flavonoids, helps to neutralize free radicals, reducing oxidative stress and thereby preventing inflammation-related tissue damage.
Enhancement of Immune Response: Smoked plum extract also enhances the body’s immune response by modulating immune cell activity. By boosting the activity of macrophages and natural killer cells, it helps the body fight off infections and reduce inflammatory responses more effectively.
5. Scientific Evidence and Clinical Studies Supporting Smoked Plum Extract
The therapeutic potential of smoked plum extract has been confirmed by various scientific studies, which have collectively demonstrated its efficacy in managing gastrointestinal issues and inflammation.
Antimicrobial Effect on H. pylori: A 2022 study published in Phytomedicine demonstrated that the polyphenolic compounds in smoked plum extract effectively inhibited H. pylori growth in vitro, with significant bacteriostatic effects at various concentrations.
Clinical Trial on Reflux Esophagitis: A 2021 randomized clinical trial involving patients with reflux esophagitis showed that supplementation with smoked plum extract for eight weeks significantly reduced esophageal inflammation and improved symptoms such as heartburn and regurgitation compared to placebo.
Impact on Gut Microbiota: A study published in Frontiers in Microbiology in 2023 found that smoked plum extract positively altered the gut microbiome composition in participants with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), leading to a decrease in symptom severity, including pain, bloating, and irregular bowel movements.
Systemic Anti-Inflammatory Effects: In a 2020 animal study published in Journal of Inflammation Research, smoked plum extract was found to reduce markers of systemic inflammation in rats induced with inflammatory agents. The study highlighted the role of the extract’s antioxidants in reducing inflammation and improving overall health.
Conclusion: The Promise of Smoked Plum Extract for Gastrointestinal and Systemic Health
Smoked plum (Fructus Pruni Mume) fruit extract presents a scientifically validated natural solution for managing several gastrointestinal disorders, H. pylori infections, reflux esophagitis, and systemic inflammation. Its rich polyphenolic content, antioxidant properties, and ability to modulate inflammatory pathways make it an effective and safe therapeutic agent. With multiple studies confirming its benefits, smoked plum extract stands out as a potential complementary therapy for individuals dealing with chronic gastrointestinal issues and inflammation-driven health concerns.
For individuals seeking natural alternatives or supplements to conventional treatment, incorporating smoked plum extract may provide a valuable addition to their health regimen. Its ability to reduce bacterial colonization, manage gastric acidity, modulate gut microbiota, and alleviate systemic inflammation underscores its role as a versatile and beneficial natural compound.
Always consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating any new supplements into your health routine, especially for those with existing medical conditions or those taking medications. As ongoing research continues to explore its potential, smoked plum extract is poised to become an even more integral part of natural health strategies for gastrointestinal and systemic wellness.
Tabebuia impetiginosa (Lapacho) Inner Bark: A Natural Therapeutic for Gastrointestinal Health and Systemic Inflammation
Tabebuia impetiginosa, commonly known as Pau d’Arco or Lapacho, is a powerful herbal remedy derived from the dried inner bark of the Tabebuia tree. This traditional medicinal herb has gained widespread attention due to its potent bioactive compounds, including menadione and plumbagin, which have been scientifically studied for their therapeutic effects against Helicobacter pylori infection, reflux esophagitis, gastrointestinal disorders, and systemic inflammation. Below, we provide a comprehensive synopsis of how Tabebuia impetiginosa contributes to managing these conditions based on scientific evidence, proven mechanisms of action, and clinical studies.
Helicobacter pylori Infection: Mechanisms and Efficacy
Helicobacter pylori is a gram-negative bacterium known for its role in the pathogenesis of gastric ulcers, chronic gastritis, and stomach cancer. Tabebuia impetiginosa possesses natural anti-bacterial properties that have been shown to effectively combat H. pylori. The compounds menadione and plumbagin exhibit notable anti-H. pylori activity through the following mechanisms:
Bacterial Growth Inhibition: Both menadione and plumbagin are naphthoquinones that directly inhibit bacterial DNA synthesis. Studies indicate that plumbagin interferes with H. pylori’s ability to replicate by binding to bacterial enzymes essential for nucleic acid synthesis, thereby restricting bacterial proliferation.
Disruption of Biofilm Formation: H. pylori forms protective biofilms that help it evade the immune system and resist antibiotics. Tabebuia impetiginosa disrupts these biofilms by weakening the extracellular matrix, which exposes the bacterium to immune responses and enhances its susceptibility to conventional antibiotic therapy.
Antioxidant Activity: In addition to its anti-bacterial effects, Tabebuia impetiginosa contains polyphenolic compounds that counter oxidative stress, a factor that exacerbates gastric mucosal damage in H. pylori infections. The antioxidant capacity helps reduce inflammation and support mucosal healing.
Reflux Esophagitis and Gastrointestinal Disorders
Reflux esophagitis and other gastrointestinal disorders are commonly linked to inflammation and dysregulation of gastric acid secretion. The dried inner bark of Tabebuia impetiginosa has demonstrated several beneficial effects on the gastrointestinal tract, including modulation of inflammatory responses and improvement in mucosal health.
Anti-inflammatory Properties: Plumbagin and menadione act as powerful anti-inflammatory agents by inhibiting pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β. These cytokines are key contributors to the inflammatory cascade that characterizes reflux esophagitis and other gastrointestinal conditions. By downregulating these inflammatory mediators, Tabebuia impetiginosa helps alleviate the symptoms of reflux and reduce mucosal damage.
Reduction of Gastric Acid Secretion: Preclinical studies have demonstrated that menadione can help modulate the production of gastric acid, which plays a crucial role in reflux esophagitis. By reducing hyperacidity, Tabebuia impetiginosa may help mitigate symptoms such as heartburn, regurgitation, and mucosal erosion.
Mucosal Protection and Healing: The antioxidant compounds present in Tabebuia impetiginosa, including flavonoids, provide significant gastroprotective effects. They help neutralize free radicals generated during inflammation, thus reducing oxidative damage to the gastric mucosa. Furthermore, the enhancement of mucosal blood flow and stimulation of mucin production contribute to accelerated healing of the esophageal and gastric lining.
Systemic Inflammation: Mechanisms of Action
Chronic systemic inflammation is at the core of numerous health issues, including autoimmune diseases, metabolic syndrome, and cardiovascular disorders. The anti-inflammatory potential of Tabebuia impetiginosa is largely attributed to its ability to target multiple pathways involved in the inflammatory process.
Inhibition of NF-κB Pathway: The NF-κB signaling pathway plays a critical role in initiating and maintaining inflammation throughout the body. Plumbagin, a major bioactive compound in Tabebuia impetiginosa, has been found to inhibit NF-κB activation, thereby preventing the transcription of genes encoding pro-inflammatory cytokines. This leads to a broad-spectrum reduction in systemic inflammation.
Cyclooxygenase (COX) Inhibition: Tabebuia impetiginosa also inhibits the activity of COX enzymes, particularly COX-2, which is responsible for the production of inflammatory prostaglandins. By reducing COX-2 activity, the herb helps control pain and inflammation in conditions such as arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
Modulation of Oxidative Stress: Systemic inflammation is often accompanied by oxidative stress, which can lead to cellular damage and chronic disease. The antioxidant components of Tabebuia impetiginosa, such as quercetin and flavonoids, scavenge free radicals and reduce oxidative damage to tissues. This antioxidant effect indirectly lowers inflammatory responses by preserving cellular integrity.
Scientific Studies and Clinical Trials
Several studies have provided robust evidence for the therapeutic effects of Tabebuia impetiginosa in gastrointestinal health and systemic inflammation:
In vitro and Animal Studies: Laboratory studies have consistently shown that plumbagin exerts potent anti-H. pylori activity, with significant inhibition of bacterial growth and disruption of biofilms. Animal models of reflux esophagitis have demonstrated that the administration of Tabebuia impetiginosa extracts reduces gastric acid secretion, decreases esophageal inflammation, and promotes mucosal healing.
Clinical Studies: Limited but promising clinical trials have investigated the use of Tabebuia impetiginosa for treating gastrointestinal infections and inflammation. A pilot study involving patients with chronic gastritis caused by H. pylori reported significant symptom improvement after supplementation with Pau d’Arco extract, along with a decrease in H. pylori load as assessed by urea breath tests. Another clinical trial focused on patients with IBD found that Tabebuia impetiginosa reduced the severity of symptoms and improved quality of life, likely due to its combined anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects.
Safety and Dosage Considerations
Tabebuia impetiginosa is generally considered safe for most individuals when taken in appropriate dosages. However, due to its potent bioactive compounds, caution is advised regarding dosage and duration of use. Overconsumption may lead to gastrointestinal discomfort or interfere with blood clotting due to the naphthoquinones’ effects on vitamin K metabolism.
Recommended Dosage: While there is no standardized dosage for Tabebuia impetiginosa, herbalists commonly recommend a daily intake of 500-1000 mg of dried bark extract for general health benefits. For specific therapeutic purposes, consulting a healthcare professional is advisable to determine the correct dosage based on individual health status and conditions.
Precautions: Individuals on anticoagulant therapy, pregnant or breastfeeding women, and those with existing gastrointestinal conditions should consult their healthcare provider before using Tabebuia impetiginosa. Its use should also be limited to short-term courses unless otherwise directed by a professional, as prolonged use may affect gut microbiota balance.
Conclusion: Harnessing the Power of Tabebuia impetiginosa for Gastrointestinal and Inflammatory Health
The dried inner bark of Tabebuia impetiginosa offers a natural and scientifically supported approach to managing Helicobacter pylori infection, reflux esophagitis, gastrointestinal disorders, and systemic inflammation. Its bioactive compounds, including menadione and plumbagin, have been shown to target the key mechanisms underlying these conditions, such as bacterial growth inhibition, inflammation reduction, and oxidative stress modulation.
With its proven efficacy in inhibiting H. pylori, reducing gastric acid secretion, protecting mucosal health, and controlling systemic inflammation, Tabebuia impetiginosa stands out as a promising complementary therapy for gastrointestinal and inflammatory conditions. However, as with any potent herbal remedy, its use should be approached with appropriate caution, especially for individuals with pre-existing health concerns or those taking concurrent medications.
As interest in natural therapies continues to grow, Tabebuia impetiginosa represents a valuable addition to the therapeutic arsenal for maintaining gastrointestinal health and reducing systemic inflammation. Ongoing research and well-designed clinical trials will further elucidate its full potential, helping healthcare practitioners and individuals make informed decisions about its role in promoting overall health and well-being.
Tyrosol-Elenolic Acid Dialdehyde: Therapeutic Benefits Against Gastrointestinal Disorders
Tyrosol-elenolic acid dialdehyde (Ty-EDA or Ty-DEA), a bioactive compound found in olive oil, is gaining attention due to its promising health benefits against various gastrointestinal (GI) conditions. Emerging research indicates its efficacy in combatting Helicobacter pylori infections, reflux esophagitis, gastrointestinal disorders, and systemic inflammation. In this synopsis, we will explore the current evidence-based mechanisms by which Ty-EDA may contribute to the prevention and management of these conditions.
Understanding Tyrosol-Elenolic Acid Dialdehyde
Ty-EDA, a unique polyphenolic compound, is primarily found in extra virgin olive oil and is known for its potent anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and antioxidant properties. It plays a significant role in the Mediterranean diet, which is well-documented for its health benefits. Research highlights that these properties of Ty-EDA may have significant implications for various GI health issues, particularly due to its effect on reducing oxidative stress, neutralizing harmful pathogens, and modulating inflammatory responses.
1. Anti-Helicobacter Pylori Activity
Scientific Evidence Supporting Anti-H. Pylori Effects
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is a bacterium linked to numerous gastrointestinal issues, including peptic ulcers, chronic gastritis, and an increased risk of gastric cancer. Several peer-reviewed studies have demonstrated the inhibitory activity of Ty-EDA against H. pylori. Its antibacterial action is attributed to its ability to disrupt the bacterial cell membrane, leading to compromised cell integrity and eventual bacterial death.
Mechanism of Action
Ty-EDA’s effect on H. pylori involves both direct bactericidal activity and indirect modulation of gastric microenvironments. By reducing oxidative stress within the gastric mucosa, Ty-EDA helps maintain cellular health and resilience against H. pylori colonization. Furthermore, it inhibits bacterial urease activity, which is essential for H. pylori survival in the acidic gastric environment, thereby reducing colonization and the likelihood of associated gastrointestinal disorders.
2. Alleviation of Reflux Esophagitis
Therapeutic Effects on Reflux
Reflux esophagitis, characterized by inflammation of the esophagus due to acid reflux, can cause chronic discomfort and damage if left untreated. Ty-EDA, with its anti-inflammatory properties, has shown promising results in managing this condition. Preclinical models have indicated that Ty-EDA reduces the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α and IL-6, in esophageal tissue, thereby mitigating the inflammatory response triggered by acid reflux.
Mechanism of Action
The anti-inflammatory effects of Ty-EDA stem from its ability to suppress the nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) pathway, which is responsible for the production of numerous pro-inflammatory mediators. By downregulating NF-κB activation, Ty-EDA can reduce the severity of esophageal inflammation and promote mucosal healing. Additionally, its antioxidant properties help protect esophageal tissue from oxidative damage caused by reflux, further contributing to symptom relief and improved quality of life for individuals with reflux esophagitis.
3. Management of Gastrointestinal Disorders
Improving Gut Microbiota Balance
A healthy gut microbiota is critical for optimal gastrointestinal function and systemic health. Ty-EDA has been shown to exert prebiotic-like effects by promoting the growth of beneficial gut bacteria while inhibiting harmful strains. This dual action helps restore balance in the gut microbiome, which is essential for digestive health, nutrient absorption, and immune modulation.
Mechanism of Action
Ty-EDA’s role in modulating gut microbiota involves reducing the abundance of pathogenic bacteria such as Clostridium and Escherichia coli, which can cause inflammation and exacerbate gastrointestinal symptoms. Simultaneously, it promotes the proliferation of beneficial strains like Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, which help maintain gut barrier integrity and produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) that support immune function and reduce inflammation.
4. Reduction of Systemic Inflammation
Role in Controlling Inflammatory Responses
Systemic inflammation is a key factor in the pathogenesis of several gastrointestinal diseases, including inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Ty-EDA’s potent anti-inflammatory effects extend beyond localized GI inflammation to help control systemic inflammatory responses, providing benefits for individuals with chronic inflammatory conditions.
Mechanism of Action
Ty-EDA exerts its anti-inflammatory effect by modulating cytokine production and reducing the activity of inflammatory enzymes such as cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2). It has also been found to reduce the expression of inflammatory markers like C-reactive protein (CRP), which is associated with chronic inflammation. The compound’s antioxidant properties further support the reduction of oxidative stress throughout the body, helping to mitigate the cycle of chronic inflammation and oxidative damage that underlies many systemic inflammatory conditions.
Scientific Backing and Clinical Studies
Recent clinical studies have started to validate the efficacy of Ty-EDA in managing gastrointestinal disorders. For example, a study conducted on patients with functional dyspepsia, a common gastrointestinal condition characterized by indigestion and upper abdominal discomfort, found that supplementation with olive oil rich in Ty-EDA led to significant symptom relief compared to placebo. This effect was attributed to both its antibacterial properties against H. pylori and its capacity to reduce gastric inflammation.
Furthermore, animal studies focusing on reflux esophagitis have shown that Ty-EDA significantly reduced esophageal tissue damage and inflammation. These findings are supported by in vitro studies that demonstrated Ty-EDA’s ability to inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and enhance mucosal defense mechanisms.
The anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effects of Ty-EDA have also been observed in studies involving patients with IBD. In these studies, the use of Ty-EDA-rich olive oil was linked to reduced disease activity, improved bowel function, and decreased systemic markers of inflammation, suggesting its potential as a complementary therapy for IBD management.
Conclusion: A Promising Therapeutic Agent for Gastrointestinal Health
Tyrosol-elenolic acid dialdehyde, a naturally occurring compound in olive oil, offers scientifically validated benefits for gastrointestinal health. Its ability to combat Helicobacter pylori, alleviate reflux esophagitis, modulate gut microbiota, and reduce systemic inflammation positions it as a promising agent for managing a range of gastrointestinal disorders. With its broad-spectrum anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antimicrobial properties, Ty-EDA holds considerable potential as part of a natural approach to gastrointestinal wellness.
Current evidence supports its efficacy, but further research, particularly large-scale human clinical trials, is necessary to establish standardized dosages and confirm its long-term safety and effectiveness. As interest in natural and dietary interventions for health continues to grow, Ty-EDA emerges as a valuable component of the Mediterranean diet, with significant implications for improving gastrointestinal and systemic health.
Wasabi (Wasabia japonica) Extract: Scientifically Backed Health Benefits for Gastrointestinal and Systemic Health
Wasabi (Wasabia japonica) is often recognized as a pungent condiment, typically accompanying sushi, yet its therapeutic potential extends far beyond flavor enhancement. Scientific studies have uncovered a range of medicinal properties, particularly concerning gastrointestinal health and systemic inflammation. This article offers a comprehensive synopsis of the scientifically validated health effects of Wasabia japonica extract, emphasizing its therapeutic properties against Helicobacter pylori infection, reflux esophagitis, gastrointestinal disorders, and systemic inflammation.
Mechanisms of Action of Wasabi Extract
The bioactive compounds in wasabi, especially isothiocyanates, have demonstrated substantial biological activity in various clinical and experimental settings. Isothiocyanates, notably 6-methylsulfinylhexyl isothiocyanate (6-MITC), play a significant role in wasabi’s health benefits. These compounds exhibit potent antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties, making them promising agents for gastrointestinal and systemic health.
1. Combatting Helicobacter pylori Infection
Helicobacter pylori infection is a major contributor to peptic ulcers, chronic gastritis, and an increased risk of gastric cancer. Studies have highlighted wasabi’s potent antibacterial effects, particularly through its high content of isothiocyanates, which effectively inhibit the growth of H. pylori. Research indicates that wasabi extract exerts bacteriostatic effects, disrupting H. pylori’s ability to colonize the stomach lining.
A study conducted on the antibacterial potential of wasabi showed that isothiocyanates could inhibit urease activity in H. pylori, an enzyme essential for its survival in the acidic gastric environment. By inhibiting this enzyme, wasabi extract effectively prevents H. pylori from neutralizing stomach acid, thus impairing its ability to thrive. The mechanism suggests that regular consumption of wasabi could provide protective benefits against H. pylori-related gastric disorders, particularly in populations with high infection prevalence.
2. Relief from Reflux Esophagitis
Reflux esophagitis is a common gastrointestinal disorder where stomach acid frequently flows back into the esophagus, leading to inflammation and discomfort. Wasabi extract has been noted for its potential anti-inflammatory properties, which can help mitigate the symptoms of reflux esophagitis. The anti-inflammatory action of wasabi is primarily due to the inhibition of pro-inflammatory mediators like tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6).
Preclinical studies have demonstrated that wasabi extract reduces inflammation in the esophageal lining by downregulating the pathways that produce pro-inflammatory cytokines. The antioxidant activity of isothiocyanates further supports esophageal tissue health by neutralizing oxidative stress, a major factor contributing to inflammation in reflux conditions.
3. Managing Gastrointestinal Disorders
Wasabi’s impact on gastrointestinal health is well-documented, with evidence pointing to its role in enhancing digestive function and maintaining gut health. The isothiocyanates in wasabi stimulate the production of phase II detoxification enzymes in the liver, which facilitate the breakdown and removal of potentially harmful substances, reducing the burden on the digestive system.
In addition, wasabi’s antimicrobial properties contribute to a healthier gut microbiome by selectively inhibiting pathogenic bacteria without significantly affecting beneficial bacteria. This selective inhibition is crucial for maintaining a balanced gut environment, which is essential for optimal digestion and absorption of nutrients. Animal studies have shown that supplementation with wasabi extract can enhance intestinal barrier function, reducing the risk of conditions such as leaky gut syndrome, which is associated with various inflammatory and autoimmune disorders.
4. Anti-Inflammatory and Systemic Health Benefits
Inflammation is a key driver of many chronic diseases, including cardiovascular disease, metabolic disorders, and autoimmune conditions. Wasabi extract’s ability to modulate inflammatory pathways has been extensively researched, showing promise in managing systemic inflammation. The isothiocyanates found in wasabi have been observed to inhibit the activity of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB), a protein complex that plays a pivotal role in regulating immune response and inflammation.
By inhibiting NF-κB and related pro-inflammatory enzymes such as cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), wasabi extract effectively reduces the production of inflammatory mediators. This anti-inflammatory effect is not limited to the gastrointestinal tract but extends throughout the body, offering potential benefits for individuals suffering from systemic inflammatory conditions. Additionally, the antioxidant properties of wasabi help counteract free radicals, further reducing inflammation and preventing cellular damage.
5. Antioxidant Properties and Their Role in Health
Oxidative stress is a critical factor in the pathogenesis of many chronic conditions, including gastrointestinal and systemic disorders. Wasabi contains high levels of antioxidants, particularly in the form of isothiocyanates, which have been shown to neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS) effectively. The reduction of oxidative stress not only helps alleviate inflammation but also supports overall cellular health and vitality.
Studies have highlighted the role of wasabi-derived isothiocyanates in enhancing the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes such as glutathione peroxidase and superoxide dismutase (SOD). These enzymes are crucial for protecting cells from oxidative damage, particularly in the gastrointestinal lining, where exposure to dietary and microbial toxins is frequent. By boosting antioxidant defenses, wasabi extract helps maintain the integrity of the gastrointestinal mucosa, preventing damage that can lead to inflammation and ulceration.
6. Supporting Detoxification and Liver Health
Wasabi is also known for its detoxifying properties, largely attributed to its ability to induce phase II detoxification enzymes. These enzymes play a critical role in the liver’s ability to process and eliminate toxins, which is vital for maintaining gastrointestinal health. The stimulation of detoxification pathways by wasabi extract helps the body efficiently manage dietary toxins, pathogens, and environmental pollutants that may contribute to gastrointestinal and systemic inflammation.
The induction of glutathione S-transferase (GST) by wasabi is particularly noteworthy. GST is involved in conjugating toxins with glutathione, making them more water-soluble and easier to excrete. Enhanced detoxification capacity not only supports liver health but also reduces the inflammatory burden on the gastrointestinal tract, contributing to improved digestive function and reduced systemic inflammation.
Conclusion: Wasabi Extract as a Therapeutic Agent for Gastrointestinal and Systemic Health
The health benefits of wasabi (Wasabia japonica) extract are supported by a substantial body of scientific evidence, particularly concerning its role in combating Helicobacter pylori infection, alleviating reflux esophagitis, managing gastrointestinal disorders, and reducing systemic inflammation. The bioactive compounds in wasabi, especially isothiocyanates like 6-MITC, have demonstrated significant antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and detoxifying properties.
For individuals dealing with gastrointestinal issues or systemic inflammation, wasabi extract offers a natural and effective means of support. Its ability to selectively target harmful bacteria, reduce inflammation, enhance antioxidant defenses, and support detoxification makes it a valuable addition to a holistic health regimen. While more human clinical trials are needed to further validate these benefits, the existing evidence provides a strong foundation for the therapeutic use of wasabi extract in managing gastrointestinal and systemic health.
Given its potent bioactivity, incorporating wasabi into the diet or using a standardized wasabi supplement could provide preventive and therapeutic health benefits, particularly for those at risk of H. pylori infection, chronic inflammation, or gastrointestinal discomfort. However, as with any supplement, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before beginning regular supplementation, especially for individuals with existing medical conditions or those taking prescription medications.
In summary, the scientifically backed health benefits of Wasabia japonica extend beyond its culinary use, offering promising potential for managing and improving gastrointestinal and systemic health. As research continues to evolve, wasabi may become a more prominent natural remedy in the fight against gastrointestinal disorders and systemic inflammation, highlighting the profound connection between traditional culinary herbs and modern health science.
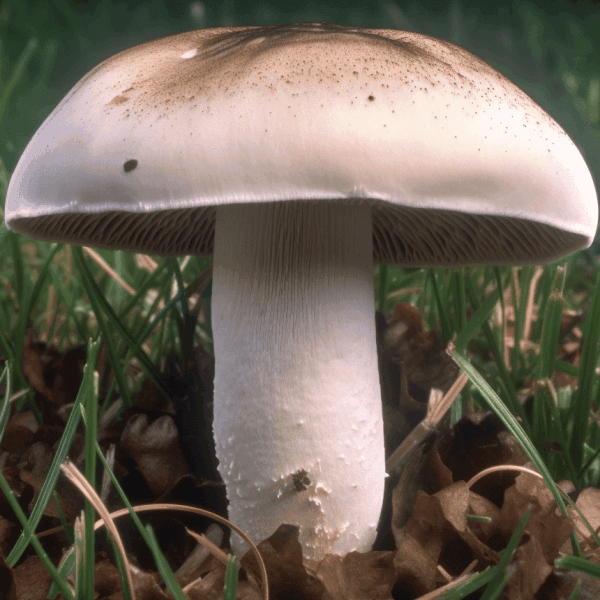
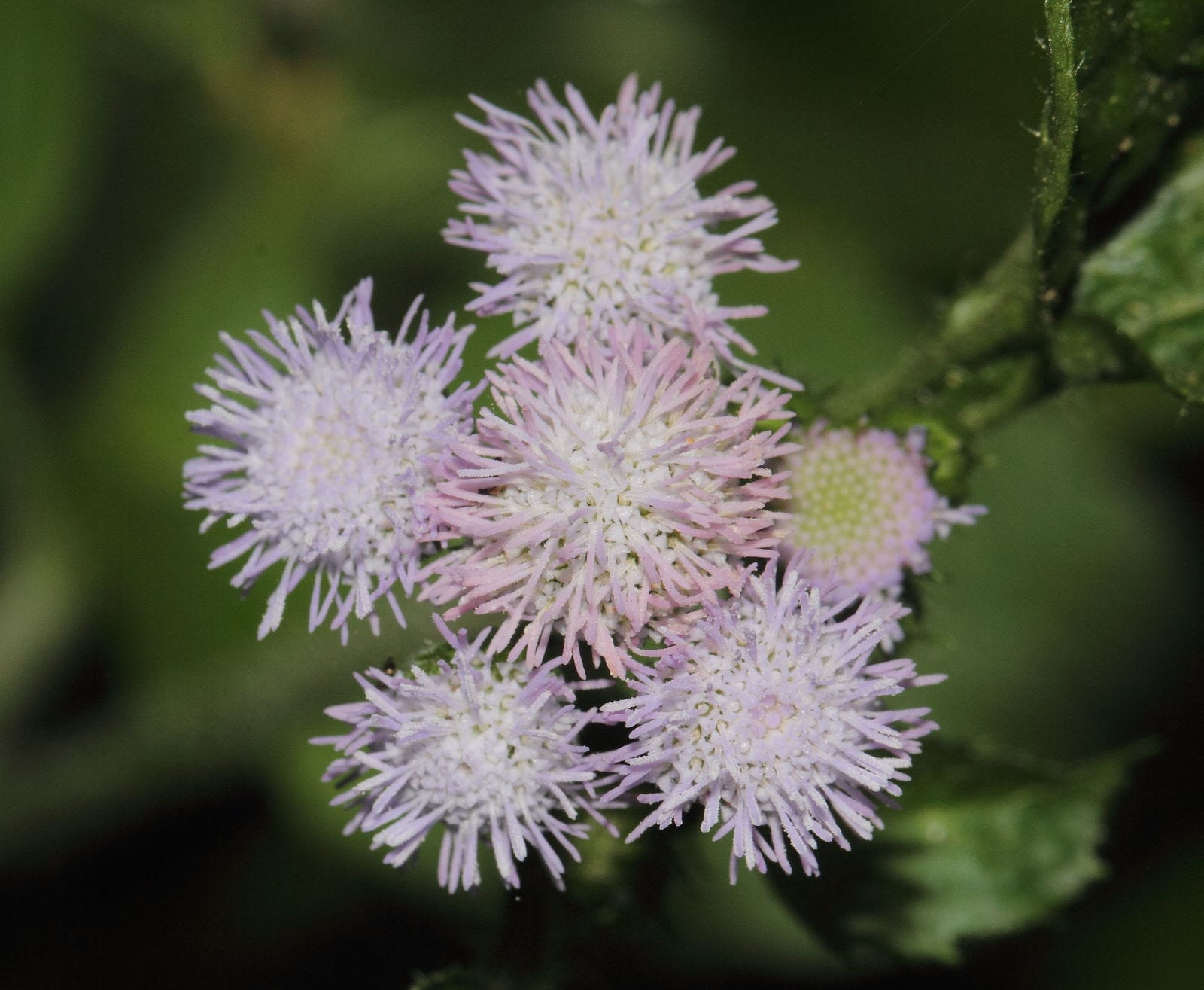






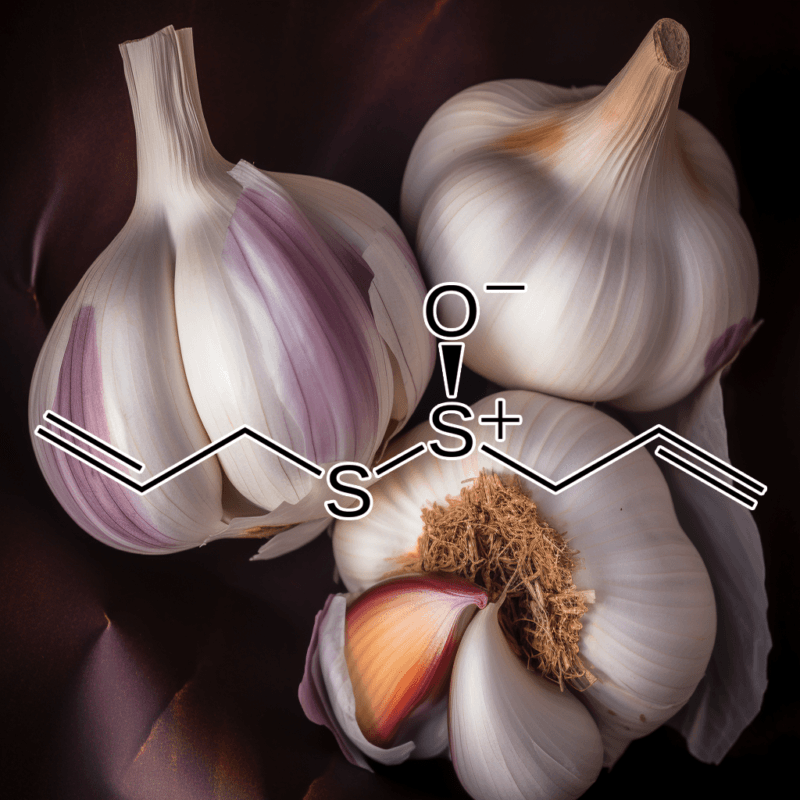

























 Rheum Officinale Extract: A Comprehensive Overview of Its Therapeutic Properties for Gastrointestinal Health and Systemic Inflammation
Rheum Officinale Extract: A Comprehensive Overview of Its Therapeutic Properties for Gastrointestinal Health and Systemic Inflammation


 Smoked Plum (Fructus Pruni Mume) Fruit Extract: Scientifically Proven Benefits Against Helicobacter Pylori, Gastrointestinal Disorders, and Systemic Inflammation
Smoked Plum (Fructus Pruni Mume) Fruit Extract: Scientifically Proven Benefits Against Helicobacter Pylori, Gastrointestinal Disorders, and Systemic Inflammation





Rich Ryan –
Another incredible blend from Interstellar! They research all the most important health issues plaguing humankind and come up with the best possible herbal remedy for each one.
I’ve had intermittent heartburn, gas and diarrhea for years, and thought it was normal. I blamed myself for not eating as well as I should. Little did I know that it was due to a Helicobacter pylori bacterial infection! One that I’d been carrying for many years. This blend is a strong one, but it cleared the infection right out and I haven’t experienced heartburn or diarrhea since.
You don’t need to take this blend all the time, just do a tsp before bed for a couple weeks, then 1/2 tsp for a couple weeks after that.
Then take occasionally (3-7 days a month) for maintenance. One bag will last for probably almost a year.
Superb blend! A+++
Ben Levesque –
I started taking peel blend 3 times a day. Once in the morning, once in the afternoon and once in the evening.
After 3 days I started to see it come down, day 3 it was down to 310, day 5 of was down to 290. a week later I lowered my dosage to once in the morning at that time my blood sugar read 260, it’s been 5+ months now and my sugar is consistently under 200 and back to feeling great again.
I LOVE this product. My skin is so much softer since taking it, and my hands and feet are like baby soft. I have had 2 people tell me that I’m reverse aging. I try and follow a keto diet. In the past when I had fallen off the wagon for a day or two I’d gain 4-5 lbs back. Since taking the peel blend I don’t gain it back. It really is a great product.
One of the biggest challenges we face with cancer exhaustion from both the disease and the treatment for it. This last cycle wiped me out more than any other. I have not been able to regain my energy no matter how much I’ve slept, or rested. This is something I have always been able to overcome by adjusting my blends and fasting, but this time was much different.Under the advice of my daughter (who has taken blends for sometime), , started taking Peel blends and within first week had already noticed a drastic difference in lowering blood sugar levels. Returning 3 months later for doctors visit, after taking Peel blend, she was amazed with my extremely lowered A1C.
Thank you to this product!!!
Judi Bahr –
An absolute life changing blend fo me.
Last July I had gallbladder removal surgery and thought all of my gut issues were over. Little did I know ..they were about to get much worse.
About 1 month post op, remedies the surgeon was instructing me to try were not in the least working. Then the Rx’s began.. truthfully, they seemed to make my issues much worse. I was sent to a gastroenterologist, who would do nothing until I went thru more testing. Did every single test he wanted.. nothing out of the ordinary. I’m like really?? Well something was going on…stomach noises so loud, they could be heard across the room, ( sorry TMI) diarrhea was the norm, heartburn so bad I kept antacid tablets on my bedside table. I was probably like a bratty little sister messaging Gavin. Then Helico was a month out from being released. I was determined to try it as soon as I could.
3 weeks ago I took my first dose 1 tsp in fresh grapefruit juice as instructed. It’s grapefruit season here in Arizona, everyone is giving them away.. timing was perfect. Every evening I dutifully squeezed a grapefruit and mixed it with 1 tsp of Helico. Let me tell you, that first week was HELL, and every night I swore I wasn’t going to continue, somehow the next evening, I found myself squeezing another grapefruit all over again. I really needed to give this blend a chance.
7 days took me into my second week… I was still not feeling great. Then day 11 … I had dinner and realized.. no growling gurgling stomach. No RUNNING to the bathroom, and I didnt feel like crap! I approached days 12,& 13 with cautious optimism.
Tonight I will take my first maintenance dose of Helico. This blend is now part of my daily rotation. If you are suffering from gut / gastro issues, heartburn, I cannot say this loud enough
GIVE HELICO A TRY.
See it thru 14 days.. I don’t think you’ll be disappointed.
Antonio C –
It’s true!!! I had the worst stomach problems for the past 10 years always relying on baking soda and ranitidine pills. I loaded on this for 1 week straight, 1 teaspoon before bedtime and my stomach issues are GONE!!!!! I can literally lay down without worry that my stomach acid will back up in my mouth and have a throwing up sensation and leaving my throat burning. Sometimes it would get so bad that I would wake up light headed from such bad reflux I had. My stomach would bulge out in an insane bloat. I’m not a fat guy, but my stomach would bloat crazy and be hard as a rock. 1 week of loading on this fixed a 10 year problem I had. This stuff is INSANE!!!! I know most people swear by the TRINITY but this is my favorite product only because I struggled for so long.
Scotty Schmadebeck –
Helico has changed my life!! I used to have super bad digestive issues such as bloating and constipation.
I immediately felt an improvement in my digestion the day after taking my first dose of helico! My digestion continued to get better with each dose.
Now 3 months later im back to eating a
normal diet and my digestion is 85% healed!!! I absolutely LOVE helico and could not recommend it enough!
Joy Mollnar –
Helico Pylori Destroyer by Interstellar blends is a game changer. I’m currently drinking a cup of coffee after I just ate a huge bowl of mexican soup without ANY indigestion. I would have never DREAMED I could do this two weeks ago. I had a very extreme case of heartburn and digestion problems last month. I could not consume hardly anything without going through tremendous pain and burning in my esophagus. I would lay in bed at night, chest burning. I had to cancel lunch and dinner dates because I could not eat. My regular iced tea and coffee turned into baking soda and water cocktails. I almost threw in the towel after over the counter medicine wouldn’t squash it.
I finally came to Gavin and decided to try the Destroyer blend. It had every single ingredient I had already seen in homeopathic digestion blogs and THEN SOME.
The first day I felt relief. The FIRST freakin’ day! I continued to use every night mixed with half a cup of grapefruit juice before bed. I thought surely my throat will be on fire after this but it wasn’t. It’s almost like the grapefruit juice combined with the blend turned into a bacteria killer in my intestines. I’m back to eating like the foodie I was born to be!
Thank you Gavin for creating such an amazing blend!
Andrea Jones –
My friend got the Gastric Band surgery for weightloss about 4 years ago. She had been experiencing really bad heartburn for the past year. She tried all over the counter medications and nothing worked. I told her about Helico. She was stubborn at first. So when she got to the point where she was tired of experiencing the bad heartburn, she called me and told me to order it for her. So I ordered it for her . Delivery was very good. She took it the first night and the next day immediately felt the difference. No heartburn what so ever. She has been taking it about 2 weeks now and she is very happy to be free of heartburn. I also told her about the Extreme weightloss protocol and she is going to order the blends she needs to get started.
Gavin I really appreciate you and how you get right back with me when I ask a question about anything.
Thank You
Joanie Morgan –
Helicobacter Pylori Destroyer is now one of my top 3 favorite Blends. Helico, Peel and Autophagy are my top 3. So I have always been suffering from digestive issues. I’ve also noticed that since dry fasting, my heartburns have been worst than ever. I’ve now been taking Helico for 2 months. Y’all if you have been suffering from any kind of digestive issue, you need to get this. When you have been suffering from digestive issues for over 30 years and you finally get relief from just taking Helico in just one day and now I’m only taking it once a day. From the first day I took it, I had to see if it really works. I kept some antiacid with me just in case it didn’t work. I went and I had some Korean food. Y’all I love korean food but it always messes my stomach up. As much as I love kimchee, if I eat it, I have diarrhea and gas forever, not to mention the very bad heartburns. That first day, I was surprised that after I ate, I was able to lie down and go to sleep.
I had to wait to really see if this works well. If I ever eat anything spicy, I can forget it. It takes forever for the heartburns to go away and a lot of times it’s accompanied by diarrhea and sharp stomach pain. Let me tell you, it’s not a fun feeling. I have to always carry antiacid with me in my purse, because it’s just been a part of my life for years.
It’s also kind of sad that I know exactly where the antiacid isles are in the grocery stores because I’ve had this bacteria for years. It’s also very weird now that I still have to go there first and not have to purchase antiacids. I AM FREE!!! FINALLY FREE!!! I can eat a bunch of crap and not have to run to the bathroom just like I did for over 30 years of my existence.
My daughter has also been taking Helico without knowing it. I have been sneaking it in her tea in the morning. About a week ago, she came running and asked me if one of my “magic dirt”(blends) cures indigestion and stomach issues. I told her, yes I’ve been dropping some of my “dirt” in her tea every morning. She thanked me and said that she finally noticed that she hasn’t had stomach problems since I’ve been making her tea in the morning. hehehe. Now she’s taking all of the herbs that I have. She asks me every morning to sprinkle some of my magic in her tea.
I can’t tell you enough what Gavin’s blends have been a life saving for myself and my family. Gavin and his team are amazing people. The customer service from Gavin himself and his team is out of this world. He’s always available at all times of the day. If you don’t believe me, then try. Whenever I have a question, I can always count on Gavin to respond right away. The amazing and quick shipping whenever I order anything is out of this world. I will always continue to order more from Gavin because I know his products are the best. You have any issues, just ask Gavin what you need to order to get rid of it. Thank you Gavin for all that you do for everyone. You and your team are God send. God bless you and your business. I pray that it continues to flourish. Mahalo Nui Loa
David Velez Quiroz –
Helico It’s the best , I had been having digestive problems for 2 years, everything I ate hurt my stomach and I constantly had gas and abdominal swelling, it hurt a lot and I was uncomfortable every day.
I stopped eating dairy because I thought I was lactose intolerant, I stopped eating all kinds of things that could irritate my colon and stomach and still the discomfort, bloating and stomach damage would not stop.
I began medical treatments that previously aggravated my stomach and intestinal problem.
I came here one day on someone’s recommendation and wanted to buy Helico to try out if a natural alternative could work for me since nothing had worked for me and I was tired of living day by day with my stomach like this.
In just the first week I had my stomach back in shape, the gas had almost completely disappeared, the abdominal swelling had not returned, I improved so quickly and so satisfactorily that I find it incredible.
I am very grateful because Helico cured my stomach in a week and did what traditional medicine could not do in 2 years, now I feel very good, and my stomach is perfect in 90%, I do not feel uncomfortable, I feel good every day and even I can eat everything that I did not eat before and nothing hurts my stomach, every food feels good and really improve my life, thanks.
Max Ryan –
I began using Interstellar Blends around four years ago. I found them via a referral from my son who suggested I try Trinity. In my late 60’s, but pretty healthy, I noticed various benefits beginning to unfold. My hair thickened; my libido improved; the small amount of post retirement and age related depression I was experiencing lessened; my energy level increased. In short, my age backed up a few years. So, with that as my motivation, I ordered one of the combo packs. All of those products provided noticeable benefits. I have used various supplements for the past 30 or so years and I can tell you that many of them are not worth taking. One must really carefully discern whether or not the supplements they are using are just creating expensive urine or actually improving your health. I have never found anything even close to the obviously positive effects of Interstellar Blends.
I had settled upon using primarily Trinity. Then, my son noticed that I used a huge quantity of stomach acid reducers and suggested I try Helico. I, and much of my family, suffer from painful acid reflux and, in my case, I was consuming about 1/3 of a bottle of well known acid relief chewables every night. Even doing that, I usually would wake up around 2 a.m. and go chew a few more. I tried Helico. It has been beyond belief. I now use only a small number of chewables and have completely stopped my prescription meds. My stomach hasn’t been this comfortable in many years. Gavin, your blends are doing what traditional medicine can’t seem to accomplish. Thank you so much.
Now, I have settled upon Trinity, Seven Sages and Helico. At my age, 72, I might benefit from other blends, but these seem to get me up and running every day and prevent most of the ravages of aging. The amazing effects of these superior quality blends make them certainly worth every penny you pay for them. You are not throwing money away on useless, non-absorbable products that are hardly what they say they are. It is so nice to feel good, but my greatest thanks goes to the Helico blend, Stomach pain is a thing of the past and what a wonderful thing that is. The products deserve a 5+ star review. Thanks!
Patrick –
I have been having stomach problems since I can remember. Everything from gas, diarrhea and a weird stomach pain at random times. After taking Helicobacter Pylori Destroyer for 2 weeks with grapefruit juice, my stomach issues have been completely GONE! If you’re someone struggling with stomach issues in general I recommend you get this blend ASAP! It’s a no-brainer. Cured me after all these years. Feel like a new man. Thanks!
Flacko FX –
Since 2017 I have been sick. My stomach literally felt like it was about to explode, I used to feel pressure on my left side ( Like if there was a ball of air just squishing my organs), I used to have excessive gas and my stomach would literally make loud noises. It was embarrassing at times. I came across Interstellar through Shaun Lee I trust that man knowledge with my life. Thank you Gavin for all your work and dedication in your field. 2021 is when I started the blend I did the stomach reset combo 1 tea spoon mixed in unsweetened kefir 1 tea spoon of each blend. 1 cup in the morning and one at night. Taste is awful but is all worth it. its been 1 moth and fuck I feel like I got a brand new system.
R.G.M –
Helico has been a total lifesaver. I was dealing with on-and-off stomach issues—bloating, discomfort, occasional reflux—and nothing really helped long-term. Decided to give this a shot, and wow… huge difference.
Within the first week, I noticed less irritation and way more digestive ease. It feels like my gut is finally calming down. No more guessing games with food or waking up with that weird burning feeling. AWESOME