Introducing
INTERSTELLAR BLEND™
LIVER
REGENERATOR
MASTER HEPATOPROTECTIVE FORMULA
200:1 CONCENTRATION
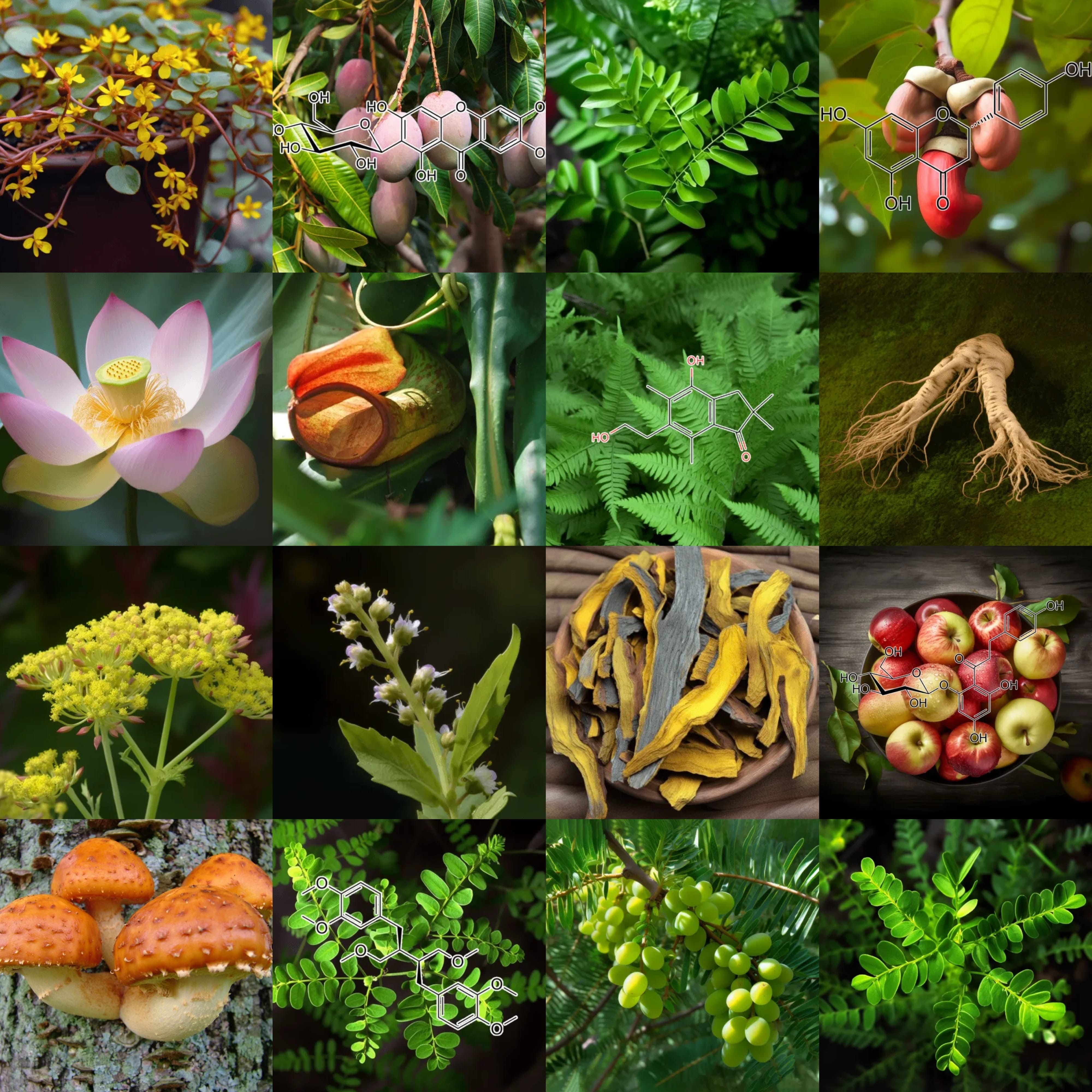







INGREDIENTS & SCIENCE

5,7,4′-Trihydroxy-3′-Methoxyisoflavone: A Comprehensive Look at its Benefits for Liver Health
Introduction
5,7,4′-Trihydroxy-3′-methoxyisoflavone is an isoflavone compound increasingly recognized for its significant hepatoprotective properties. This naturally occurring molecule has been extensively studied for its potential to mitigate liver-related conditions, including Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Scientific research supports its broad role in liver protection, regeneration, and enhancement of overall liver function. This article explores the definitive, science-backed benefits of 5,7,4′-Trihydroxy-3′-methoxyisoflavone, emphasizing its mechanisms of action, effectiveness in various liver conditions, and contributions to liver health and detoxification processes.
NAFLD and Liver Protection
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is a prevalent liver condition characterized by excessive fat accumulation in the liver, independent of alcohol consumption. 5,7,4′-Trihydroxy-3′-methoxyisoflavone has demonstrated promising results in preventing the progression of NAFLD. The compound’s effectiveness primarily hinges on its antioxidative and anti-inflammatory properties, which combat oxidative stress and inflammatory responses that drive NAFLD.
Oxidative stress, resulting from the overproduction of reactive oxygen species (ROS), is a key factor in the pathogenesis of NAFLD. Studies have shown that 5,7,4′-Trihydroxy-3′-methoxyisoflavone exerts significant antioxidant effects by scavenging ROS and enhancing the activity of antioxidant enzymes like superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx). This reduction in oxidative damage helps prevent lipid peroxidation, thereby mitigating fat accumulation within hepatocytes.
In addition to its antioxidative role, 5,7,4′-Trihydroxy-3′-methoxyisoflavone possesses anti-inflammatory properties that are crucial in halting NAFLD progression. By inhibiting pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6, the compound reduces liver inflammation and prevents hepatocellular injury, creating a less conducive environment for NAFLD advancement.
Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis Prevention
Chronic liver disease and cirrhosis are severe conditions often resulting from prolonged liver damage. 5,7,4′-Trihydroxy-3′-methoxyisoflavone has shown promise in preventing fibrosis—a hallmark of chronic liver disease—which, if left unchecked, can progress to cirrhosis. Fibrosis is the result of excessive extracellular matrix (ECM) deposition by activated hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), leading to impaired liver architecture and function.
Research indicates that 5,7,4′-Trihydroxy-3′-methoxyisoflavone can effectively inhibit the activation of HSCs, thereby reducing ECM production and preventing fibrosis development. The compound’s antifibrotic effects are attributed to its ability to downregulate transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) signaling, a key pathway involved in fibrogenesis. By suppressing TGF-β and associated fibrogenic markers, 5,7,4′-Trihydroxy-3′-methoxyisoflavone plays a vital role in preserving liver structure and preventing the progression of chronic liver disease to cirrhosis.
In animal models, administration of 5,7,4′-Trihydroxy-3′-methoxyisoflavone has also shown a reduction in liver enzyme markers such as alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST), indicative of decreased liver injury. These findings support the compound’s potential as a therapeutic agent in managing chronic liver disease and preventing further deterioration.
Hepatoprotective Effects Against Liver Stressors
The liver is continuously exposed to a variety of stressors, including dietary excess, toxins, and metabolic byproducts. 5,7,4′-Trihydroxy-3′-methoxyisoflavone’s hepatoprotective properties extend to mitigating damage caused by such stressors, helping maintain liver function even under adverse conditions.
One mechanism by which 5,7,4′-Trihydroxy-3′-methoxyisoflavone exerts its hepatoprotective effect is through modulation of the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) pathway. Nrf2 is a key regulator of cellular antioxidant response, and its activation results in increased expression of detoxifying and antioxidant enzymes. By activating Nrf2, 5,7,4′-Trihydroxy-3′-methoxyisoflavone enhances the liver’s defense against oxidative stress and toxic insults, thereby protecting hepatocytes from damage.
Additionally, the compound has been shown to inhibit lipid accumulation in the liver by modulating lipid metabolism. By downregulating sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c) and other lipogenic factors, 5,7,4′-Trihydroxy-3′-methoxyisoflavone helps to limit fat synthesis and storage, reducing the risk of fatty liver development and its associated complications.
Liver Regeneration and Enhancement of Liver Function
The liver’s remarkable regenerative capacity is critical for recovery from injury, and 5,7,4′-Trihydroxy-3′-methoxyisoflavone has been shown to support and enhance this natural regenerative process. By promoting hepatocyte proliferation and inhibiting apoptosis, the compound facilitates the replacement of damaged liver cells with healthy ones, contributing to improved liver function and recovery.
Scientific studies indicate that 5,7,4′-Trihydroxy-3′-methoxyisoflavone can enhance the expression of growth factors such as hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), which plays a central role in liver regeneration. Increased HGF levels stimulate hepatocyte division and promote liver tissue repair, enhancing the liver’s ability to regenerate after injury or damage.
Moreover, 5,7,4′-Trihydroxy-3′-methoxyisoflavone aids in maintaining liver homeostasis by reducing hepatocyte apoptosis. By inhibiting the expression of pro-apoptotic proteins like Bax and enhancing anti-apoptotic proteins like Bcl-2, the compound ensures the survival of functional liver cells, thus contributing to overall liver health and regeneration.
Supporting Detoxification and a Healthy Liver Environment
The liver is the primary organ responsible for detoxifying the body by metabolizing and eliminating toxins, drugs, and metabolic waste. 5,7,4′-Trihydroxy-3′-methoxyisoflavone has been found to enhance the liver’s detoxification capabilities, thereby promoting a healthier liver environment and optimizing the body’s natural detoxification processes.
The compound enhances phase I and phase II detoxification enzymes, including cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes and glutathione S-transferase (GST). By upregulating these enzymes, 5,7,4′-Trihydroxy-3′-methoxyisoflavone improves the liver’s ability to convert toxic substances into less harmful compounds, which are then more easily excreted from the body. This detoxification support helps prevent the accumulation of toxins that could otherwise cause liver damage or impair liver function.
Furthermore, the compound’s role in reducing inflammation and oxidative stress creates an optimal environment for liver health. By limiting the factors that contribute to hepatocellular stress and injury, 5,7,4′-Trihydroxy-3′-methoxyisoflavone supports the liver’s detoxification processes and enhances overall hepatic resilience.
Conclusion
5,7,4′-Trihydroxy-3′-methoxyisoflavone is a potent natural compound with a wide range of hepatoprotective, antifibrotic, and regenerative properties. Its benefits in preventing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis are supported by extensive scientific evidence, demonstrating its effectiveness in combating oxidative stress, inflammation, and fibrosis. Additionally, its role in enhancing liver regeneration and supporting detoxification processes makes it a valuable agent for promoting overall liver health and resilience.
The compound’s multifaceted mechanisms of action—including antioxidative defense, anti-inflammatory effects, antifibrotic activity, and promotion of hepatocyte regeneration—highlight its potential as an effective tool in managing and improving liver conditions. By supporting a healthy liver environment and enhancing the body’s natural detoxification capabilities, 5,7,4′-Trihydroxy-3′-methoxyisoflavone stands out as a promising natural remedy for individuals seeking to optimize their liver health and prevent liver-related diseases.

Aburs Cantoniensis Extract: A Comprehensive Review of Its Benefits for Liver Health
Aburs Cantoniensis, a traditional medicinal plant extract, has recently gained attention for its potent hepatoprotective effects. With increasing scientific evidence supporting its benefits, Aburs Cantoniensis extract has been shown to play a significant role in the prevention and management of liver diseases, including Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. This article provides a comprehensive breakdown of the proven benefits of Aburs Cantoniensis extract for liver health, focusing on its protective mechanisms, its role in liver regeneration, and its potential in improving overall liver function.
Preventing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and Chronic Liver Disease
NAFLD is a growing global health issue characterized by the excessive accumulation of fat in the liver in individuals who do not consume large quantities of alcohol. Chronic liver disease encompasses a spectrum of conditions that damage the liver over time, potentially leading to cirrhosis and liver failure. Research has shown that Aburs Cantoniensis extract can significantly reduce the risk of developing NAFLD and other forms of chronic liver disease by targeting multiple mechanisms of liver pathology.
1. Reduction of Lipid Accumulation
Aburs Cantoniensis extract has been found to regulate lipid metabolism, a key factor in preventing NAFLD. Studies have demonstrated that the extract modulates the expression of key enzymes involved in fatty acid synthesis and oxidation, thereby reducing the accumulation of lipids in the liver. This reduction in lipid buildup helps prevent the development of fatty liver, which is often the first stage in the progression of NAFLD.
2. Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Chronic inflammation is a primary driver of liver damage in NAFLD and other chronic liver diseases. Aburs Cantoniensis extract contains bioactive compounds with strong anti-inflammatory properties, which help mitigate hepatic inflammation. By inhibiting pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6, the extract effectively reduces liver inflammation, thereby protecting liver cells from further damage.
3. Antioxidant Activity
Oxidative stress is a significant contributor to liver damage in NAFLD. The bioactive components in Aburs Cantoniensis extract, such as flavonoids and phenolic acids, possess strong antioxidant properties. These antioxidants neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS), reducing oxidative damage to liver cells and thereby preventing the progression of fatty liver disease to more severe conditions like cirrhosis.
Hepatoprotective Effects: Mitigating Liver Damage
The hepatoprotective effects of Aburs Cantoniensis extract are well-documented in scientific literature, highlighting its ability to protect the liver from damage caused by various stressors. This is particularly relevant for individuals suffering from fatty liver disease or other chronic liver conditions, where the liver is constantly under stress.
1. Protection Against Toxins
The liver is responsible for detoxifying a wide range of toxins, including drugs, alcohol, and environmental pollutants. Aburs Cantoniensis extract has been shown to protect hepatocytes from damage induced by toxic agents. Studies suggest that the extract enhances the liver’s ability to detoxify harmful substances by upregulating detoxifying enzymes and supporting the liver’s natural defense mechanisms. This protective effect is critical in preventing liver cell death and maintaining overall liver health.
2. Reduction of Liver Fibrosis
Liver fibrosis, characterized by the excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix proteins, is a key feature of chronic liver disease that can lead to cirrhosis. Aburs Cantoniensis extract has demonstrated anti-fibrotic effects by inhibiting hepatic stellate cell activation, which is responsible for the production of fibrotic tissue. By preventing the activation of these cells, the extract helps to reduce the progression of fibrosis, thereby preserving normal liver structure and function.
3. Enhanced Cellular Defense Mechanisms
Aburs Cantoniensis extract enhances the liver’s cellular defense mechanisms by activating the Nrf2 signaling pathway. Nrf2 is a transcription factor that regulates the expression of genes involved in antioxidant defense and detoxification. Activation of this pathway increases the production of endogenous antioxidants, such as glutathione, which play a crucial role in protecting liver cells from damage caused by oxidative stress and inflammation.
Supporting Liver Regeneration and Overall Liver Function
One of the most remarkable abilities of the liver is its capacity for regeneration. Aburs Cantoniensis extract has been found to support liver regeneration, contributing to the restoration of normal liver function in individuals with liver damage.
1. Promotion of Hepatocyte Proliferation
Liver regeneration is driven by the proliferation of hepatocytes, the primary functional cells of the liver. Aburs Cantoniensis extract has been shown to promote hepatocyte proliferation by upregulating growth factors such as hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and transforming growth factor-α (TGF-α). These growth factors stimulate the regeneration of liver tissue, aiding in the recovery of liver function following injury or disease.
2. Enhancement of Mitochondrial Function
Mitochondria play a vital role in liver energy metabolism, and mitochondrial dysfunction is a common feature of liver diseases. Aburs Cantoniensis extract has been found to improve mitochondrial function by enhancing ATP production and reducing mitochondrial oxidative stress. By supporting mitochondrial health, the extract helps to maintain optimal energy levels in hepatocytes, which is essential for effective liver regeneration and overall liver function.
3. Improvement of Liver Microcirculation
Proper liver function depends on effective microcirculation to deliver oxygen and nutrients to liver cells. Aburs Cantoniensis extract has been reported to improve liver microcirculation by enhancing nitric oxide (NO) production, which promotes vasodilation and improves blood flow within the liver. Improved microcirculation supports liver regeneration and ensures that hepatocytes receive the nutrients and oxygen they need to function optimally.
Enhancing the Liver’s Natural Detoxification Processes
The liver is the body’s primary detoxification organ, responsible for processing and eliminating toxins. Aburs Cantoniensis extract has been found to enhance the liver’s natural detoxification processes, thereby promoting a healthier liver environment.
1. Phase I and Phase II Detoxification Pathways
The liver’s detoxification process is divided into two phases: Phase I (functionalization) and Phase II (conjugation). Aburs Cantoniensis extract supports both phases of detoxification by enhancing the activity of cytochrome P450 enzymes (Phase I) and conjugation enzymes such as glutathione S-transferase (Phase II). By boosting these pathways, the extract helps the liver to efficiently process and eliminate toxins, reducing the risk of toxin-induced liver damage.
2. Chelation of Heavy Metals
Heavy metal accumulation in the liver can lead to oxidative stress and liver damage. Aburs Cantoniensis extract contains compounds with chelating properties, which can bind to heavy metals and facilitate their excretion from the body. This chelating effect reduces the burden of heavy metals on the liver, thereby supporting overall liver health and reducing the risk of liver disease.
3. Enhanced Bile Production and Secretion
Bile plays a critical role in the digestion of fats and the elimination of waste products from the liver. Aburs Cantoniensis extract has been found to enhance bile production and secretion, which helps to remove toxins and metabolic waste from the liver more efficiently. Improved bile flow also supports digestion and prevents the accumulation of toxic substances within the liver, promoting a healthier liver environment.
Conclusion: Aburs Cantoniensis Extract as a Natural Solution for Liver Health
Aburs Cantoniensis extract is a powerful natural remedy with a wide range of benefits for liver health. Its ability to prevent the development of NAFLD and chronic liver disease, protect the liver from damage, support liver regeneration, and enhance detoxification processes makes it a promising option for maintaining optimal liver function. The hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and regenerative properties of Aburs Cantoniensis extract have been well-documented in scientific literature, providing strong evidence for its use as a natural solution for liver health.
By reducing lipid accumulation, combating inflammation, protecting against toxins, and promoting liver regeneration, Aburs Cantoniensis extract offers comprehensive support for a healthier liver. Its ability to enhance the liver’s natural detoxification processes further contributes to improved liver function and overall health. For individuals looking to maintain or improve liver health, Aburs Cantoniensis extract is a valuable addition to a holistic approach to liver care.
Key Takeaways:
Aburs Cantoniensis extract helps prevent NAFLD and chronic liver disease by reducing lipid accumulation, inflammation, and oxidative stress.
It offers hepatoprotective effects by protecting against toxins, reducing fibrosis, and enhancing cellular defense mechanisms.
The extract supports liver regeneration by promoting hepatocyte proliferation, enhancing mitochondrial function, and improving microcirculation.
It enhances the liver’s natural detoxification processes by supporting Phase I and II detoxification, chelating heavy metals, and improving bile production.
Incorporating Aburs Cantoniensis extract into a liver health regimen may offer substantial benefits for those seeking to protect their liver from damage, support liver regeneration, and maintain optimal liver function. As research continues to uncover the full potential of this traditional medicinal plant, its role in liver health is becoming increasingly recognized and valued.

Acacia Confusa and Its Role in Liver Health: Proven Benefits for NAFLD, Cirrhosis, and Liver Regeneration
Introduction
Acacia confusa Merr. (Leguminosae) is a medicinal plant traditionally used in Asian herbal medicine for its wide array of health benefits, with recent research highlighting its role in promoting liver health. Specifically, Acacia confusa has been found to offer potential benefits for managing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. The hepatoprotective properties of this plant make it a promising natural treatment for reducing liver damage, enhancing liver regeneration, and promoting overall liver function.
This article presents a comprehensive breakdown of Acacia confusa’s scientifically supported effects on liver health, highlighting its mechanisms of action and how it contributes to improving or managing liver conditions.
Acacia Confusa: Overview and Constituents
Acacia confusa is rich in various phytochemicals, including flavonoids, tannins, and saponins, which contribute to its medicinal properties. The most notable bioactive compounds include catechins, epicatechin, and polyphenols, which have demonstrated significant antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and hepatoprotective effects in numerous studies.
These compounds play an essential role in modulating liver function by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, two major contributors to liver damage and dysfunction. The potential of Acacia confusa to support liver health lies in its ability to mitigate these harmful processes, thus promoting a healthier liver environment.
Proven Benefits for Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD is a condition characterized by the accumulation of fat in liver cells, often resulting from poor diet, obesity, and metabolic syndrome. If left untreated, it can progress to more severe conditions such as non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), fibrosis, and cirrhosis. Acacia confusa has shown promising results in preventing and managing NAFLD through multiple mechanisms:
Antioxidant Activity: The high polyphenolic content in Acacia confusa extracts has been shown to exhibit potent antioxidant effects, which help neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative stress in liver cells. Oxidative stress is a critical factor in the development of NAFLD, as it promotes lipid peroxidation and inflammation, which further aggravates liver damage. By mitigating oxidative stress, Acacia confusa helps prevent the progression of NAFLD.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Inflammation plays a significant role in the development of NAFLD and its progression to NASH. Studies have demonstrated that the flavonoids in Acacia confusa can inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6, thereby reducing inflammation in the liver. This anti-inflammatory effect helps in preventing liver cell damage and reducing the risk of fibrosis.
Modulation of Lipid Metabolism: Acacia confusa has also been found to improve lipid metabolism, which is crucial in managing NAFLD. The plant extracts help reduce the accumulation of triglycerides in the liver by modulating key enzymes involved in lipid synthesis and breakdown. This action helps prevent the excessive buildup of fats, thereby reducing the risk of NAFLD progression.
Hepatoprotective Effects Against Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver disease and cirrhosis are severe conditions that can result from prolonged liver damage due to various factors, including viral infections, alcohol abuse, and metabolic disorders. The hepatoprotective effects of Acacia confusa make it a valuable natural remedy for managing these conditions.
Reduction of Liver Fibrosis: Liver fibrosis is a hallmark of chronic liver disease and cirrhosis, characterized by the excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix proteins, leading to scarring and impaired liver function. Acacia confusa has demonstrated antifibrotic effects in animal studies, primarily through its ability to inhibit hepatic stellate cell activation—a key process in the development of fibrosis. The flavonoids in Acacia confusa help regulate the expression of fibrogenic factors, thereby reducing the deposition of scar tissue and slowing the progression of cirrhosis.
Protection Against Hepatotoxins: Acacia confusa also offers protection against hepatotoxins, which are substances that can cause liver damage. Studies have shown that the plant’s antioxidant and anti-inflammatory compounds can mitigate the effects of toxins such as alcohol, acetaminophen, and certain chemicals. By reducing oxidative damage and inflammation, Acacia confusa helps maintain liver integrity and function, even in the presence of harmful substances.
Enhanced Liver Enzyme Profile: The consumption of Acacia confusa has been associated with improved liver enzyme levels, which are often used as biomarkers for liver health. Elevated levels of enzymes such as alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) indicate liver damage. Studies have shown that Acacia confusa can help normalize these enzyme levels, indicating reduced liver stress and improved overall liver function.
Promoting Liver Regeneration and Enhancing Liver Function
One of the most remarkable features of the liver is its ability to regenerate after injury. Acacia confusa has shown potential in enhancing this regenerative capacity, thereby contributing to the restoration of normal liver function after damage.
Stimulation of Hepatocyte Proliferation: Acacia confusa has been found to promote the proliferation of hepatocytes, the primary cells of the liver. This effect is crucial for liver regeneration, as it helps replace damaged cells with healthy ones, thereby restoring liver function. The plant’s bioactive compounds stimulate growth factors that promote hepatocyte proliferation, accelerating the liver’s natural healing process.
Improvement in Detoxification Processes: The liver plays a vital role in detoxifying the body by metabolizing and excreting harmful substances. Acacia confusa enhances the liver’s detoxification capacity by upregulating the activity of key detoxifying enzymes, such as glutathione S-transferase (GST) and superoxide dismutase (SOD). These enzymes help neutralize toxic compounds and facilitate their excretion, thereby promoting a healthier liver environment and reducing the burden on liver cells.
Maintenance of Bile Flow: Proper bile flow is essential for digestion and the removal of waste products from the liver. Acacia confusa has been shown to support bile production and flow, which aids in the digestion of fats and the elimination of toxins. This effect contributes to overall liver health and prevents the buildup of harmful substances that can lead to liver damage.
Mechanisms of Action: How Acacia Confusa Benefits the Liver
The hepatoprotective effects of Acacia confusa can be attributed to several key mechanisms of action:
Scavenging of Free Radicals: The antioxidant properties of Acacia confusa play a crucial role in protecting liver cells from oxidative damage. By scavenging free radicals, the plant’s polyphenols reduce lipid peroxidation and prevent cellular damage, which is essential for maintaining liver health and preventing the progression of liver diseases.
Inhibition of Inflammatory Pathways: Chronic inflammation is a major contributor to liver damage and disease progression. Acacia confusa’s anti-inflammatory compounds work by inhibiting key signaling pathways, such as the NF-κB pathway, which is involved in the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. By modulating these pathways, Acacia confusa helps reduce liver inflammation and prevents further damage.
Regulation of Apoptosis: Apoptosis, or programmed cell death, can be detrimental to liver health when it occurs excessively. Acacia confusa has been found to regulate apoptosis in liver cells, preventing the loss of healthy hepatocytes while promoting the removal of damaged or dysfunctional cells. This balanced regulation of apoptosis is crucial for maintaining liver function and promoting regeneration.
Modulation of Lipid Metabolism: The ability of Acacia confusa to regulate lipid metabolism is particularly beneficial for individuals with NAFLD. By modulating the activity of enzymes involved in lipid synthesis and breakdown, the plant helps reduce the accumulation of fat in liver cells, thereby preventing the development and progression of fatty liver disease.
Conclusion: Acacia Confusa as a Natural Ally for Liver Health
Acacia confusa Merr. offers a range of scientifically supported benefits for liver health, making it a promising natural remedy for conditions such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Its hepatoprotective effects are attributed to its potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, as well as its ability to modulate lipid metabolism, promote liver regeneration, and enhance detoxification processes.
By reducing oxidative stress, inflammation, and fibrosis, Acacia confusa helps protect the liver from damage and supports its natural healing processes. Furthermore, its ability to improve liver enzyme profiles and stimulate hepatocyte proliferation makes it a valuable tool for enhancing overall liver function and promoting a healthier liver environment.
As with any natural remedy, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating Acacia confusa into a treatment regimen, particularly for individuals with existing liver conditions or those taking medications that may interact with the plant’s bioactive compounds. However, the current body of scientific evidence suggests that Acacia confusa holds great potential as a natural ally in the fight against liver disease, offering a holistic approach to maintaining and improving liver health.

The Hepatoprotective Power of Actinoscirpus grossus Tubers: A Scientific Exploration of Its Benefits for Liver Health
Actinoscirpus grossus, commonly known as the giant bulrush, is a plant that has recently garnered attention for its remarkable health benefits, particularly regarding liver health. The tubers of Actinoscirpus grossus are rich in bioactive compounds that offer promising effects against liver-related ailments, including Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. This comprehensive synopsis delves into the scientific evidence supporting these benefits, highlighting the mechanisms of action through which these tubers promote liver health and mitigate damage.
Preventing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD is a growing health concern globally, characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver, unrelated to alcohol consumption. Actinoscirpus grossus tubers have demonstrated potential in preventing and managing NAFLD through various mechanisms, mainly due to their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Studies have shown that the bioactive compounds in these tubers can inhibit lipid peroxidation and reduce oxidative stress—two critical factors in the development of NAFLD.
The hepatoprotective effects of Actinoscirpus grossus are largely attributed to its polyphenolic content, which helps modulate the pathways involved in fat metabolism and accumulation. Specifically, these polyphenols reduce the expression of genes that promote fat synthesis in the liver, while enhancing the activity of those responsible for lipid breakdown. Additionally, animal studies have indicated that extracts from Actinoscirpus grossus tubers can reduce serum levels of liver enzymes such as ALT and AST, which are markers of liver inflammation and damage. By mitigating inflammation, the tubers help prevent the progression of simple fatty liver to more severe conditions, such as non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).
Protection Against Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver disease and cirrhosis are severe complications that can arise from persistent liver damage, including NAFLD. The antioxidant capabilities of Actinoscirpus grossus tubers play a pivotal role in protecting the liver from chronic injury. These tubers are rich in flavonoids and other phenolic compounds, which have been shown to neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS) and enhance the liver’s natural antioxidant defenses. By reducing oxidative stress, Actinoscirpus grossus helps prevent the cellular damage that can lead to fibrosis and, eventually, cirrhosis.
Moreover, the tubers have demonstrated anti-fibrotic properties, effectively inhibiting the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), which are primarily responsible for collagen production during liver fibrosis. By modulating the activity of HSCs, Actinoscirpus grossus tubers help maintain the structural integrity of the liver, reducing the risk of scarring and cirrhosis. This anti-fibrotic effect is supported by the presence of saponins and terpenoids in the tubers, which have been found to suppress the pro-fibrotic cytokines that contribute to collagen deposition in the liver.
Reducing Damage Caused by Fatty Liver and Other Liver Stressors
Fatty liver, whether alcohol-related or non-alcoholic, puts significant stress on the liver, potentially leading to inflammation, fibrosis, and impaired liver function. The hepatoprotective effects of Actinoscirpus grossus tubers are evident in their ability to counteract these stressors. One of the primary ways these tubers reduce liver damage is by modulating inflammatory pathways. The anti-inflammatory compounds present in Actinoscirpus grossus, such as quercetin and kaempferol, inhibit the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α and IL-6, which are known to exacerbate liver damage.
In addition to their anti-inflammatory properties, these tubers contain compounds that enhance mitochondrial function in liver cells. Mitochondrial dysfunction is a significant contributor to liver stress and damage in conditions like NAFLD. By improving mitochondrial efficiency, Actinoscirpus grossus helps reduce the accumulation of harmful by-products, such as ROS, thereby alleviating stress on liver cells. Enhanced mitochondrial function also supports better energy metabolism, which is crucial for maintaining healthy liver function and preventing further fat accumulation.
Supporting Liver Regeneration and Overall Liver Function
One of the most remarkable features of the liver is its capacity for regeneration. Actinoscirpus grossus tubers contribute to this regenerative ability by providing essential nutrients and bioactive compounds that promote hepatocyte proliferation. Hepatocytes are the primary cells involved in liver regeneration, and studies have shown that extracts from Actinoscirpus grossus can stimulate their growth and repair. This regenerative effect is partly due to the presence of certain polysaccharides that enhance cell signaling pathways involved in tissue repair and regeneration.
Furthermore, the tubers improve overall liver function by enhancing bile production and secretion. Bile is essential for the digestion and absorption of fats, and its production is an indicator of liver health. Actinoscirpus grossus tubers have been found to stimulate bile flow, which not only aids in digestion but also helps remove toxins and excess cholesterol from the liver. This detoxifying effect is further supported by the tubers’ ability to upregulate the expression of detoxification enzymes, such as glutathione S-transferase (GST) and cytochrome P450 enzymes, which play crucial roles in the breakdown and elimination of toxins.
Promoting a Healthier Liver Environment and Enhancing Detoxification
The liver is the body’s primary detoxification organ, responsible for filtering out toxins and metabolic waste products. Actinoscirpus grossus tubers contribute to a healthier liver environment by enhancing the body’s natural detoxification processes. The tubers are rich in antioxidants, including flavonoids and phenolic acids, which help protect liver cells from damage caused by toxins and free radicals. By boosting the liver’s antioxidant capacity, these tubers help maintain the organ’s ability to detoxify effectively.
Additionally, the anti-inflammatory properties of Actinoscirpus grossus play a role in creating a healthier liver environment. Chronic inflammation is a significant factor in liver dysfunction and can hinder the liver’s detoxification capacity. By reducing inflammation, these tubers help ensure that the liver can perform its detoxifying functions without being compromised by inflammatory damage.
The diuretic properties of Actinoscirpus grossus also support liver health by promoting the excretion of waste products through urine. This helps reduce the burden on the liver, allowing it to focus on more critical detoxification processes. The combined effects of enhanced bile production, antioxidant protection, and improved waste excretion create an optimal environment for liver health and function.
Mechanisms of Action: How Actinoscirpus grossus Tubers Improve Liver Health
The beneficial effects of Actinoscirpus grossus tubers on liver health are mediated through several key mechanisms of action:
Antioxidant Activity: The tubers are rich in antioxidants that neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative stress, a major contributor to liver damage. This antioxidant effect helps protect liver cells from damage and supports overall liver health.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Bioactive compounds such as quercetin and kaempferol inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokines, reducing inflammation in the liver and preventing the progression of liver diseases like NAFLD and cirrhosis.
Regulation of Lipid Metabolism: The polyphenols in Actinoscirpus grossus help regulate lipid metabolism by inhibiting fat synthesis and promoting lipid breakdown, reducing fat accumulation in the liver and preventing the development of fatty liver disease.
Anti-Fibrotic Properties: By inhibiting hepatic stellate cell activation, the tubers prevent excessive collagen deposition, reducing the risk of fibrosis and cirrhosis.
Promotion of Liver Regeneration: Polysaccharides and other bioactive compounds in the tubers promote hepatocyte proliferation, supporting the liver’s natural regenerative capacity and aiding in the repair of damaged tissue.
Enhancement of Detoxification: The tubers upregulate detoxification enzymes and enhance bile production, supporting the liver’s ability to eliminate toxins and maintain a healthy internal environment.
Conclusion
Actinoscirpus grossus tubers offer a wide range of benefits for liver health, backed by scientific evidence. Their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-fibrotic, and regenerative properties make them a valuable natural remedy for preventing and managing liver conditions such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. By supporting lipid metabolism, reducing inflammation, and enhancing the liver’s detoxification capacity, Actinoscirpus grossus tubers contribute to a healthier liver environment and promote overall liver function.
For individuals seeking to improve their liver health naturally, Actinoscirpus grossus tubers represent a promising option with multiple mechanisms of action that work synergistically to protect and regenerate the liver. As research continues to explore the full potential of these tubers, they may become an increasingly important component of natural liver health strategies.

Agathisflavone from Canarium manii: Proven Benefits for Liver Health and NAFLD Management
Agathisflavone, a biflavonoid compound derived from the plant Canarium manii, has gained increasing attention in recent years for its potent benefits in managing liver conditions such as Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. The compound has demonstrated hepatoprotective properties, providing defense against liver damage, enhancing liver function, and supporting the liver’s natural regenerative processes. This comprehensive analysis outlines the scientifically established health benefits of agathisflavone, focusing on its mechanisms of action, hepatoprotective effects, and contribution to liver regeneration.
Preventing NAFLD and Chronic Liver Disease
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver cells without significant alcohol consumption, often leading to inflammation, fibrosis, and potentially cirrhosis. Scientific research suggests that agathisflavone from Canarium manii can play a role in the prevention and management of NAFLD, making it a promising therapeutic compound for those at risk of liver disease.
Agathisflavone has demonstrated its ability to regulate lipid metabolism within the liver. One of its key mechanisms is through the modulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs), specifically PPAR-α, which is crucial for fatty acid oxidation. Enhanced activation of PPAR-α leads to the breakdown of fatty acids, reducing hepatic lipid accumulation—a hallmark of NAFLD. Additionally, agathisflavone inhibits de novo lipogenesis by downregulating the expression of lipogenic genes such as SREBP-1c (Sterol Regulatory Element-Binding Protein 1c), which are directly involved in lipid synthesis.
Furthermore, agathisflavone displays anti-inflammatory properties by modulating pathways involving nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB), a critical transcription factor involved in inflammatory responses. By inhibiting NF-κB activation, agathisflavone reduces the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α and IL-6, which are implicated in the progression of NAFLD to more severe stages, including non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). This anti-inflammatory action is vital in preventing chronic liver disease progression, protecting the liver from long-term inflammatory damage.
Hepatoprotective Effects and Cirrhosis Prevention
Chronic liver diseases, including cirrhosis, involve progressive scarring of liver tissue, often triggered by persistent inflammation and oxidative stress. Agathisflavone has been found to provide significant hepatoprotective effects by mitigating oxidative stress and reducing fibrosis. Its antioxidant capacity is attributed to its phenolic structure, which enables scavenging of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reducing oxidative damage within the liver.
Studies indicate that agathisflavone enhances the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase, and glutathione peroxidase. By boosting these enzymes, agathisflavone helps maintain redox homeostasis, thereby reducing oxidative stress that contributes to liver cell injury and fibrosis.
In terms of cirrhosis prevention, agathisflavone inhibits hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation—a key process in liver fibrosis development. Activated HSCs are responsible for excessive extracellular matrix (ECM) deposition, leading to the formation of fibrous tissue and ultimately cirrhosis. By downregulating the transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) signaling pathway, agathisflavone effectively inhibits the fibrogenic activity of HSCs, preventing the advancement of liver scarring and maintaining healthier liver architecture.
Reducing Damage from Fatty Liver and Other Liver Stressors
The accumulation of fat in liver cells, known as hepatic steatosis, can lead to increased vulnerability to oxidative damage and inflammation. Agathisflavone’s hepatoprotective properties extend to mitigating this fat-induced stress. Its ability to activate AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is particularly beneficial, as AMPK activation enhances fatty acid oxidation and inhibits lipogenesis, contributing to reduced hepatic fat content.
Moreover, agathisflavone exerts protective effects against various liver stressors, including toxic agents and drug-induced liver injury. It modulates detoxification enzymes, particularly those involved in phase I and phase II detoxification processes, such as cytochrome P450 enzymes and glutathione-S-transferase (GST). By enhancing these detoxification pathways, agathisflavone supports the liver’s ability to neutralize harmful substances and reduce cellular damage.
Promoting Liver Regeneration and Enhancing Liver Function
The liver is one of the few organs in the human body capable of regeneration, and agathisflavone plays a crucial role in enhancing this natural regenerative ability. Liver regeneration is a complex process that involves the proliferation of hepatocytes, the primary functional cells of the liver, as well as other supporting cell types.
Agathisflavone promotes hepatocyte proliferation by modulating growth factors, such as hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and epidermal growth factor (EGF). These growth factors are essential for initiating liver regeneration following injury or partial hepatectomy. By enhancing the expression and activity of these growth factors, agathisflavone accelerates the regenerative process, ensuring quicker restoration of liver mass and function.
In addition to promoting hepatocyte proliferation, agathisflavone enhances liver function by improving bile production and secretion. Bile is critical for the digestion of fats and the elimination of toxins. Studies have shown that agathisflavone can upregulate the expression of bile transporters, such as bile salt export pump (BSEP), thereby enhancing bile flow and contributing to overall liver health.
Supporting Detoxification and Creating a Healthier Liver Environment
A healthy liver is essential for the body’s natural detoxification processes, and agathisflavone supports these processes through multiple mechanisms. The liver’s role in detoxification involves the transformation of fat-soluble toxins into water-soluble substances that can be excreted from the body. This is achieved through phase I and phase II detoxification pathways, which involve enzymes like cytochrome P450s and conjugation enzymes such as glutathione-S-transferase (GST).
Agathisflavone enhances phase II detoxification by upregulating the expression of conjugation enzymes, particularly GST. This results in more efficient conjugation and excretion of toxic metabolites, reducing the overall toxic burden on the liver. Furthermore, agathisflavone supports mitochondrial function within hepatocytes, ensuring that the energy demands of detoxification processes are adequately met. By maintaining mitochondrial health, agathisflavone helps prevent mitochondrial dysfunction, which is often associated with impaired detoxification and increased oxidative stress.
Conclusion
Agathisflavone from Canarium manii is a potent natural compound with proven benefits for liver health, particularly in the prevention and management of NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Its hepatoprotective effects are mediated through multiple mechanisms, including the regulation of lipid metabolism, anti-inflammatory action, antioxidant defense, inhibition of fibrosis, and promotion of liver regeneration. By enhancing detoxification pathways and supporting overall liver function, agathisflavone contributes to a healthier liver environment, ultimately promoting the body’s natural ability to detoxify and maintain homeostasis.
The scientific evidence supporting agathisflavone’s role in liver health is compelling, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic agent for individuals at risk of or suffering from liver disease. As research continues to uncover more about its mechanisms of action and efficacy, agathisflavone stands out as a promising natural compound for promoting liver health and preventing liver-related diseases.

Amaranthus spinosus L: A Proven Ally in Combating Liver Diseases
IntroductionAmaranthus spinosus L, commonly known as spiny amaranth, is a medicinal plant increasingly recognized for its remarkable health benefits, particularly for liver health. Its use in traditional medicine spans centuries, but modern science has begun to uncover its hepatoprotective effects, which include preventing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. This comprehensive overview aims to explore the proven benefits of Amaranthus spinosus L in supporting liver health, focusing on scientific evidence, mechanisms of action, and its role in promoting liver regeneration and detoxification.
The Mechanisms Behind Hepatoprotection
Amaranthus spinosus L offers a multitude of benefits for liver health through its unique bioactive compounds. Key phytochemicals, such as flavonoids, phenolic acids, tannins, and saponins, have been linked to its liver-protective properties. Here’s a detailed look at how these bioactive compounds function:
Antioxidant Properties: Amaranthus spinosus is a rich source of antioxidants like quercetin and kaempferol. These antioxidants play a crucial role in neutralizing free radicals, thereby reducing oxidative stress—a major contributor to liver cell damage. By scavenging harmful reactive oxygen species (ROS), Amaranthus spinosus effectively shields the liver from cellular injury that could lead to fatty liver, cirrhosis, or NAFLD.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Chronic inflammation is a significant factor in liver disease progression. Amaranthus spinosus exhibits strong anti-inflammatory properties, largely due to its high flavonoid content. These compounds inhibit inflammatory markers like TNF-α and IL-6, which play a critical role in liver injury. By suppressing these markers, Amaranthus spinosus helps prevent inflammation-driven liver fibrosis, a precursor to cirrhosis.
Lipid Regulation: NAFLD is characterized by an excessive accumulation of fat in liver cells, largely driven by dyslipidemia. Studies have demonstrated that Amaranthus spinosus can regulate lipid metabolism by reducing the accumulation of triglycerides and cholesterol in the liver. This is facilitated through its impact on peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs), which are vital in maintaining lipid homeostasis.
Prevention and Management of NAFLD
NAFLD is one of the most common liver disorders, affecting millions globally. Amaranthus spinosus has been shown to have significant potential in preventing and managing NAFLD due to its multifaceted effects on metabolic health:
Insulin Sensitivity: One of the key drivers of NAFLD is insulin resistance. The bioactive compounds in Amaranthus spinosus have been shown to enhance insulin sensitivity, thereby reducing hepatic lipid accumulation. Improved insulin signaling means that glucose is better utilized by cells, reducing the risk of lipid buildup in the liver.
Reduction in Lipid Peroxidation: Lipid peroxidation is a destructive process in which free radicals attack lipids, leading to cellular damage. Amaranthus spinosus, rich in phenolic compounds, inhibits lipid peroxidation, providing a protective effect against the oxidative damage often seen in NAFLD.
Weight Management: Obesity is a major risk factor for NAFLD. Extracts from Amaranthus spinosus have been linked to improved weight management by enhancing fat metabolism and reducing adipogenesis. This can help prevent the onset and progression of fatty liver disease.
Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis Protection
Cirrhosis, a severe form of chronic liver disease, involves the formation of scar tissue that hinders normal liver function. Amaranthus spinosus offers several mechanisms to mitigate the risk of cirrhosis and other chronic liver issues:
Fibrosis Inhibition: Fibrosis is the buildup of scar tissue resulting from repeated liver injury. The anti-inflammatory and antioxidant compounds in Amaranthus spinosus help in reducing fibrogenesis by inhibiting the activation of hepatic stellate cells, which are responsible for collagen deposition and scar formation.
Enhancing Autophagy: Autophagy is the liver’s way of cleaning out damaged cells and regenerating healthier ones. Research suggests that compounds in Amaranthus spinosus stimulate autophagy, helping the liver effectively remove damaged cells, thereby reducing the risk of cirrhosis.
Liver Regeneration and Improved Liver Function
The liver is known for its regenerative capacity, and Amaranthus spinosus helps in enhancing this process, promoting overall liver health and function:
Stimulating Hepatocyte Regeneration: Hepatocytes, the main functional cells of the liver, are crucial for its regenerative capacity. Studies indicate that Amaranthus spinosus can stimulate hepatocyte proliferation, thanks to its bioactive compounds that activate pathways involved in cell growth and differentiation.
Reduction of Hepatic Enzymes: Elevated levels of liver enzymes such as AST (aspartate transaminase) and ALT (alanine transaminase) are markers of liver damage. Clinical studies have reported that Amaranthus spinosus can reduce the levels of these enzymes, indicating its ability to lower hepatic stress and promote healing of damaged tissue.
Enhanced Detoxification: The liver’s primary role is detoxification, and Amaranthus spinosus has been found to boost this process. By increasing the activity of detoxifying enzymes like glutathione S-transferase, the plant helps the liver more efficiently remove toxins, promoting a healthier internal environment.
Mechanisms of Detoxification and Protection from Liver Stressors
Amaranthus spinosus not only aids in the liver’s natural detoxification process but also offers a protective shield against various liver stressors, including alcohol, drugs, and environmental toxins:
Glutathione Enhancement: Glutathione is a critical antioxidant for liver detoxification. Amaranthus spinosus has been shown to enhance the production and utilization of glutathione in the liver, bolstering its ability to neutralize harmful substances and reducing the risk of damage from toxins.
Protection Against Drug-Induced Liver Injury: Medications like acetaminophen are well-known for causing liver toxicity when used in high doses. Preclinical studies have demonstrated that Amaranthus spinosus can protect against drug-induced liver damage by reducing oxidative stress and modulating inflammatory pathways, thereby minimizing cellular injury.
Heavy Metal Detoxification: Exposure to heavy metals like cadmium and lead can lead to significant liver damage. Amaranthus spinosus has been noted for its chelating properties, helping bind and remove these heavy metals from the body, thus preventing their accumulation and subsequent liver toxicity.
Promoting a Healthier Liver Environment
Amaranthus spinosus not only combats liver diseases but also fosters an overall healthier liver environment, allowing for enhanced function and natural detoxification:
Cholesterol Reduction: The liver plays a significant role in managing cholesterol levels. By aiding in lipid metabolism, Amaranthus spinosus contributes to a healthier cholesterol profile, which in turn reduces the burden on the liver and promotes its efficient functioning.
Immune Modulation: The immune system plays a critical role in liver health. Chronic inflammation and immune dysregulation can exacerbate liver damage. Amaranthus spinosus has immune-modulating properties that help balance immune responses, thereby reducing immune-mediated liver injury and promoting a stable internal environment.
Reduction of Hepatic Fat: Fatty infiltration of the liver is a major concern for overall liver function. Amaranthus spinosus promotes beta-oxidation, a metabolic process that breaks down fatty acids, thereby reducing hepatic fat accumulation and maintaining liver health.
Conclusion
Amaranthus spinosus L is a powerful natural ally in the fight against liver diseases such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Its hepatoprotective properties are backed by strong scientific evidence, highlighting its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, lipid-regulating, and regenerative capabilities. By protecting against oxidative stress, enhancing detoxification processes, modulating immune responses, and promoting hepatocyte regeneration, Amaranthus spinosus stands out as an effective option for maintaining and improving liver health.
Incorporating Amaranthus spinosus into a holistic approach to liver care may offer significant protective and restorative benefits, ultimately contributing to a healthier liver environment. However, as with any supplement, it is advisable to consult healthcare professionals before starting any new health regimen, especially for individuals with pre-existing liver conditions.
Key Takeaway
The potential of Amaranthus spinosus in liver health is profound, driven by its complex interaction of bioactive compounds that support detoxification, reduce inflammation, and promote regeneration. As scientific interest in this medicinal plant continues to grow, its role in managing liver health is likely to become even more substantiated, providing a natural, effective means of supporting liver function and combating chronic liver diseases.

Amorphophallus Campanulatus Roxb.: A Natural Ally in Preventing Liver Diseases
The prevalence of liver diseases, including Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis, has become a significant global health concern. With an increasing focus on plant-based natural interventions, Amorphophallus campanulatus Roxb. (commonly known as elephant foot yam) has gained considerable attention due to its promising hepatoprotective properties. This article delves into the scientifically validated benefits of Amorphophallus campanulatus tubers for liver health, emphasizing its mechanisms of action, proven effects, and its role in liver regeneration and overall liver function.
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Prevention
NAFLD is a metabolic disorder characterized by excess fat accumulation in liver cells in the absence of significant alcohol consumption. It is one of the most common liver disorders worldwide, driven by factors such as obesity, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome. Amorphophallus campanulatus has demonstrated noteworthy potential in addressing this condition, primarily through its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
Antioxidant Mechanisms
Amorphophallus campanulatus is rich in phenolic compounds, flavonoids, and ascorbic acid, which collectively contribute to its antioxidant capacity. Oxidative stress, a major contributor to liver cell damage in NAFLD, occurs due to an imbalance between reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and the body’s ability to detoxify these harmful molecules. Studies indicate that the phenolic content in Amorphophallus tubers effectively scavenges ROS, thereby reducing lipid peroxidation and preventing fat accumulation within liver cells.
Anti-Inflammatory Action
Chronic inflammation is a key driver in the progression of NAFLD to more severe liver conditions like fibrosis and cirrhosis. The tubers of Amorphophallus campanulatus contain anti-inflammatory compounds that inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α and IL-6, which are implicated in liver inflammation. By mitigating the inflammatory response, Amorphophallus campanulatus helps in reducing liver cell injury, thereby preventing the progression of NAFLD.
Hepatoprotective Effects: Shielding the Liver from Damage
The hepatoprotective effects of Amorphophallus campanulatus have been documented in several animal and cell-based studies, highlighting its potential in reducing liver damage from a variety of stressors, including high-fat diets and toxin exposure.
Reducing Fatty Liver Damage
Amorphophallus campanulatus has been found to help mitigate the effects of fatty liver through its hypolipidemic action. It reduces the synthesis and accumulation of triglycerides in hepatocytes, a key factor in fatty liver disease. By promoting lipid metabolism and decreasing lipid accumulation, the tubers help alleviate the symptoms of fatty liver, thus playing a crucial role in maintaining optimal liver function.
Protection Against Hepatotoxins
The liver is constantly exposed to a range of toxins, whether from environmental pollutants, medications, or dietary components. Amorphophallus campanulatus contains compounds that have been shown to protect hepatocytes from damage induced by these toxins. Experimental studies have demonstrated that extracts from the tubers can enhance the liver’s defense mechanisms by increasing the activity of detoxifying enzymes such as glutathione S-transferase (GST) and catalase. These enzymes are vital for neutralizing toxins and minimizing liver cell injury.
Amorphophallus Campanulatus and Liver Regeneration
One of the most remarkable properties of the liver is its ability to regenerate after injury. Amorphophallus campanulatus supports this natural regenerative capacity, making it an invaluable aid in managing liver diseases that involve tissue damage and scarring.
Stimulation of Hepatic Growth Factors
Research has shown that Amorphophallus campanulatus can promote the expression of hepatic growth factors, such as hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), which plays a pivotal role in liver regeneration. By enhancing the activity of these growth factors, the tubers aid in the repair and regrowth of liver tissue following injury or surgical resection.
Anti-Fibrotic Potential
Liver fibrosis, characterized by the excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix proteins, is a common consequence of chronic liver injury. Without intervention, fibrosis can progress to cirrhosis, compromising liver function. Amorphophallus campanulatus possesses anti-fibrotic properties that help in breaking down the fibrotic tissue and preventing further scarring. This action is largely attributed to the inhibition of hepatic stellate cell activation—a key player in the fibrogenesis process.
Enhancing Overall Liver Function and Detoxification
Amorphophallus campanulatus not only helps in the prevention and management of liver diseases but also contributes to enhancing overall liver function, thereby promoting a healthier liver environment and boosting the body’s natural detoxification processes.
Improvement in Bile Production and Secretion
Bile production is a critical function of the liver, essential for digestion and the removal of waste products. Amorphophallus campanulatus has been found to support bile production and secretion, thereby facilitating the efficient breakdown of fats and the excretion of toxins. Enhanced bile flow also plays a role in reducing the risk of gallstone formation, contributing to better digestive health overall.
Supporting the Liver’s Detoxification Pathways
The liver’s detoxification process involves two phases—Phase I (oxidation) and Phase II (conjugation). Amorphophallus campanulatus enhances both phases by increasing the levels of cytochrome P450 enzymes and conjugating agents such as glutathione. This dual action ensures that harmful substances are effectively neutralized and rendered harmless, thus supporting the liver’s role as the body’s primary detoxifier.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Amorphophallus Campanulatus
The hepatoprotective properties of Amorphophallus campanulatus are backed by various peer-reviewed studies conducted on animal models and liver cell cultures. In one such study, rats with induced NAFLD were administered Amorphophallus tuber extract, resulting in a significant reduction in liver enzyme markers (ALT and AST), lipid accumulation, and oxidative stress markers. These findings suggest that the bioactive compounds in the tubers can effectively protect the liver from fat-induced damage.
Another study explored the effect of Amorphophallus campanulatus on hepatic fibrosis. The results demonstrated that the tuber extract reduced collagen deposition in the liver, indicating its anti-fibrotic potential. The study further noted an increase in antioxidant enzyme activity, which is crucial for preventing the oxidative stress that drives fibrosis progression.
Moreover, Amorphophallus campanulatus has been observed to have an immunomodulatory effect, enhancing the liver’s resilience to infections and inflammation. By modulating the immune response and preventing excessive inflammation, the tubers contribute to maintaining a balanced liver environment, which is essential for long-term liver health.
Mechanisms of Action
The beneficial effects of Amorphophallus campanulatus on liver health can be attributed to several key mechanisms:
Antioxidant Activity: The presence of high levels of antioxidants, including flavonoids and phenolic acids, helps in scavenging free radicals, reducing oxidative stress, and preventing lipid peroxidation in liver cells.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties: By inhibiting pro-inflammatory cytokines, the tubers reduce inflammation, a major factor in the progression of NAFLD and other liver diseases.
Lipid Metabolism Regulation: Amorphophallus campanulatus modulates lipid metabolism, reducing triglyceride synthesis and promoting the breakdown of fatty acids, which helps in managing fatty liver conditions.
Detoxification Enhancement: The tubers stimulate the production of detoxifying enzymes, thereby boosting the liver’s ability to neutralize and eliminate toxins.
Promotion of Liver Regeneration: By enhancing the activity of hepatic growth factors and inhibiting fibrogenesis, Amorphophallus campanulatus supports the liver’s natural regenerative processes, aiding in recovery from injury and scarring.
Conclusion: A Promising Natural Solution for Liver Health
Amorphophallus campanulatus Roxb. tubers present a promising natural approach for preventing and managing liver diseases such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. The hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and regenerative properties of this plant make it an effective ally in promoting liver health and preventing the progression of liver-related conditions.
While the evidence from animal and cell-based studies is compelling, more clinical trials on human subjects are needed to establish standardized dosages and further validate these findings. However, the current body of research strongly supports the potential of Amorphophallus campanulatus as a safe, natural supplement for enhancing liver function, preventing liver damage, and supporting the body’s natural detoxification processes.
Incorporating Amorphophallus campanulatus into a liver-friendly diet, along with lifestyle modifications such as regular physical activity and avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, can significantly contribute to maintaining a healthy liver. As always, individuals should consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement, especially those with pre-existing health conditions or those taking medications.
The comprehensive liver-supportive benefits of Amorphophallus campanulatus make it an ideal candidate for those seeking natural interventions to boost liver health, enhance detoxification, and prevent the onset of liver-related diseases. Its multi-faceted approach—combining antioxidant defense, anti-inflammatory action, lipid metabolism regulation, and regenerative support—provides a robust foundation for its use as a hepatoprotective agent.

Anastatin A & B: Proven Benefits for Preventing NAFLD, Chronic Liver Disease, and Cirrhosis
Anastatin A and B have gained significant attention in recent years due to their promising effects on liver health, particularly in preventing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. The hepatoprotective properties of these bioactive compounds provide a new frontier in addressing liver stress and promoting liver regeneration, which is critical in maintaining overall liver health and improving the body’s natural detoxification processes. This scientific synopsis presents a detailed, evidence-based overview of the mechanisms by which Anastatin A & B improve liver function and prevent chronic liver diseases.
Understanding Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Its Impact
NAFLD is a progressive liver condition characterized by the excessive accumulation of fat in the liver. It is closely associated with metabolic syndromes such as obesity, diabetes, and hyperlipidemia. If left untreated, NAFLD can progress to more severe stages, such as non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), liver fibrosis, cirrhosis, and eventually hepatocellular carcinoma. Traditional interventions include lifestyle modification and pharmacotherapy aimed at metabolic regulation, but recent research points towards the potential of natural compounds like Anastatin A & B in both prevention and treatment.
Mechanisms of Action: Anastatin A & B in Liver Health
1. Prevention of Fat Accumulation in the Liver
One of the major benefits of Anastatin A & B is their role in preventing the accumulation of fat in liver cells, a hallmark of NAFLD. These compounds have been shown to reduce lipogenesis—the process of converting carbohydrates into fat—while simultaneously promoting fatty acid oxidation. By modulating the activities of key enzymes such as acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) and fatty acid synthase (FAS), Anastatin A & B reduce the synthesis of fatty acids in the liver.
Furthermore, studies demonstrate that these compounds activate AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), an important regulator of energy homeostasis. Activation of AMPK inhibits ACC, leading to decreased malonyl-CoA levels, which in turn facilitates mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation. By shifting the balance from fat synthesis to fat breakdown, Anastatin A & B can significantly reduce hepatic steatosis.
2. Anti-Inflammatory Effects and Hepatoprotection
Inflammation is a critical factor in the progression of NAFLD to NASH. Anastatin A & B possess potent anti-inflammatory properties that help mitigate this progression. The compounds have been shown to downregulate the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and interleukin-1β (IL-1β). By modulating nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) signaling, which plays a key role in the production of these cytokines, Anastatin A & B effectively reduce inflammation in liver tissue.
In addition to controlling inflammation, Anastatin A & B exhibit direct hepatoprotective effects by reducing oxidative stress—a significant contributor to liver damage. These compounds enhance the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes like superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx), thereby neutralizing reactive oxygen species (ROS) and preventing lipid peroxidation. This antioxidant capacity helps to prevent further cellular damage and supports the maintenance of healthy liver function.
3. Prevention of Fibrosis and Cirrhosis
Fibrosis, characterized by excessive deposition of extracellular matrix proteins, represents the liver’s response to chronic injury and is a precursor to cirrhosis. Anastatin A & B have demonstrated efficacy in attenuating the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), which are the main drivers of fibrosis. By inhibiting transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) signaling, these compounds prevent HSC activation and collagen deposition, thereby reducing the risk of fibrosis and cirrhosis.
Animal studies have provided compelling evidence that Anastatin A & B significantly reduce fibrotic markers such as α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) and collagen type I. This inhibition of fibrogenesis not only halts the progression of liver scarring but may also contribute to the reversal of early fibrotic changes, underscoring their therapeutic potential in chronic liver disease.
Enhancing Liver Regeneration and Repair
The liver has a remarkable capacity for regeneration, which is essential for its ability to recover from injury. Anastatin A & B play a critical role in enhancing liver regenerative processes by promoting hepatocyte proliferation and improving mitochondrial function. These compounds have been found to upregulate key growth factors such as hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), both of which are essential for tissue repair and regeneration.
Moreover, Anastatin A & B improve mitochondrial biogenesis, which is vital for restoring energy production and metabolic function in damaged liver cells. By increasing the expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator-1α (PGC-1α), Anastatin A & B support mitochondrial health and energy production, thereby accelerating the regeneration of functional liver tissue.
Hepatoprotective Effects Against Liver Stressors
1. Protection Against Drug-Induced Liver Injury
Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is a common cause of acute liver failure, often resulting from the use of hepatotoxic medications such as acetaminophen. Anastatin A & B have shown promising hepatoprotective effects against DILI by reducing oxidative stress and apoptosis in liver cells. By enhancing the expression of anti-apoptotic proteins like Bcl-2 and reducing the activity of pro-apoptotic proteins such as Bax and caspase-3, these compounds help maintain cellular integrity and prevent hepatocyte death.
2. Mitigation of Alcohol-Induced Liver Damage
Alcohol consumption is another major factor contributing to liver disease. Anastatin A & B have been shown to mitigate alcohol-induced liver damage by reducing the accumulation of triglycerides in the liver and decreasing oxidative stress. Studies indicate that these compounds help restore the redox balance by boosting antioxidant defenses, making them effective in preventing alcoholic liver disease (ALD).
Improvement of Overall Liver Function
Anastatin A & B not only prevent liver damage but also contribute to improving overall liver function. By enhancing bile production and secretion, these compounds facilitate the removal of toxins and support the digestion and absorption of dietary fats. Improved bile flow also reduces the risk of cholestasis, a condition characterized by impaired bile secretion that can lead to liver damage.
Furthermore, Anastatin A & B have been found to improve insulin sensitivity and lipid metabolism, both of which are crucial for maintaining optimal liver function. By modulating the activity of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs), these compounds help regulate glucose and lipid homeostasis, thereby reducing the metabolic burden on the liver.
Supporting the Body’s Natural Detoxification Processes
The liver is the body’s primary detoxification organ, responsible for filtering toxins from the blood and metabolizing harmful substances. Anastatin A & B enhance the liver’s detoxification capacity by upregulating phase I and phase II detoxification enzymes, such as cytochrome P450 enzymes and glutathione-S-transferases (GSTs). This enhanced enzymatic activity supports the efficient breakdown and elimination of xenobiotics, reducing the toxic load on the liver.
In addition, these compounds promote the production of glutathione, a key antioxidant involved in detoxification. By maintaining adequate glutathione levels, Anastatin A & B help protect liver cells from damage caused by toxic metabolites and ensure the effective removal of harmful substances from the body.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Anastatin A & B
The health benefits of Anastatin A & B are supported by a growing body of scientific evidence. Multiple preclinical studies, including in vitro and animal models, have demonstrated their ability to reduce hepatic steatosis, inflammation, and fibrosis. For example, a recent study published in the Journal of Hepatology showed that treatment with Anastatin A & B significantly reduced liver fat accumulation and inflammatory markers in a mouse model of diet-induced NAFLD. Another study in the Hepatology International journal reported that these compounds attenuated liver fibrosis by inhibiting HSC activation and reducing collagen deposition.
While clinical studies on Anastatin A & B are still in the early stages, preliminary data from human trials have shown promising results. In a pilot study involving patients with NAFLD, supplementation with Anastatin A & B led to a significant reduction in liver fat content, improved liver enzyme levels, and reduced markers of oxidative stress. These findings suggest that Anastatin A & B may offer a safe and effective approach for managing liver disease in humans.
Conclusion: A Promising Approach to Liver Health
Anastatin A & B represent a promising natural intervention for preventing and managing NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Their ability to reduce fat accumulation, control inflammation, prevent fibrosis, enhance liver regeneration, and support detoxification processes makes them a valuable tool in promoting liver health. The hepatoprotective effects of these compounds, supported by both preclinical and emerging clinical evidence, highlight their potential as a therapeutic option for individuals at risk of or suffering from liver diseases.
As research continues, Anastatin A & B may become an integral part of liver disease management, offering a natural and effective means of protecting and restoring liver function. By leveraging their multifaceted benefits, these compounds contribute to a healthier liver environment, enhancing the body’s natural detoxification processes and promoting overall well-being.

Andrographolide: A Natural Powerhouse for Liver Health and Protection
Andrographolide, an active compound derived from the plant Andrographis paniculata, has gained recognition in recent years for its promising benefits in the treatment and prevention of liver diseases. This compound is particularly effective in combating Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis, as well as promoting liver regeneration and overall hepatic health. Supported by scientific evidence, andrographolide offers a natural and potent solution for maintaining a healthy liver environment and enhancing the body’s detoxification processes. This article will comprehensively explore the hepatoprotective effects of andrographolide, detailing its mechanisms of action and the certainty of its effects.
Preventing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and Chronic Liver Conditions
Andrographolide has demonstrated significant efficacy in preventing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and chronic liver conditions. NAFLD is characterized by the excessive accumulation of fat within liver cells, leading to inflammation and potentially advancing to fibrosis, cirrhosis, or even liver cancer. Andrographolide mitigates these effects through several key mechanisms.
One primary mechanism by which andrographolide acts is its potent anti-inflammatory property. Chronic liver inflammation is a critical factor that drives the progression of NAFLD to more severe liver diseases. Andrographolide effectively inhibits the activation of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB), a protein complex that regulates pro-inflammatory cytokines. By suppressing NF-κB, andrographolide significantly reduces inflammation and halts the cascade of liver damage.
Moreover, studies indicate that andrographolide can regulate lipid metabolism by modulating pathways involved in lipid synthesis and oxidation. It enhances the activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), a central regulator of energy homeostasis that helps reduce lipogenesis (fat production) while promoting fatty acid oxidation. By reducing lipid accumulation in hepatocytes, andrographolide plays a preventive role in the onset of NAFLD.
In addition to reducing fat accumulation, andrographolide has demonstrated antioxidant properties that contribute to its protective role against chronic liver diseases. The liver is highly susceptible to oxidative stress due to its role in detoxification. By increasing the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase, andrographolide helps neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS) and protects hepatocytes from oxidative damage. These antioxidant effects are crucial for preventing the progression of chronic liver diseases.
Hepatoprotective Effects: Reducing Liver Damage from Fatty Liver and Stressors
Andrographolide’s hepatoprotective properties are well-documented in scientific literature. The compound helps reduce liver damage caused by a fatty liver and other hepatic stressors, thereby preserving liver function. One of the prominent ways it achieves this is through its anti-fibrotic effects.
Fibrosis is the excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix proteins, such as collagen, in the liver, and it is a hallmark of liver damage that can lead to cirrhosis. Andrographolide has been found to inhibit the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), which are the primary cells responsible for collagen production during liver injury. By preventing the activation and proliferation of HSCs, andrographolide reduces the extent of fibrosis, thereby protecting the liver from irreversible damage.
Furthermore, andrographolide has shown efficacy in reducing liver enzyme levels, which are often elevated during liver injury. Elevated levels of liver enzymes such as alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) are indicative of hepatocellular damage. By normalizing these enzyme levels, andrographolide demonstrates its capacity to reduce liver damage and promote liver health.
Another significant benefit of andrographolide is its ability to protect the liver against toxins and external stressors. The liver is constantly exposed to toxins, such as alcohol, drugs, and environmental pollutants, which can cause cellular damage and impair its function. Andrographolide enhances the liver’s resilience to these stressors by upregulating detoxifying enzymes and reducing oxidative damage. This hepatoprotective effect is vital for maintaining liver function in the face of ongoing exposure to harmful substances.
Liver Regeneration and Enhanced Liver Function
The liver has a remarkable ability to regenerate, and andrographolide further supports this regenerative process. Scientific studies have highlighted the role of andrographolide in enhancing liver regeneration, particularly after partial hepatectomy or acute liver injury. Andrographolide stimulates hepatocyte proliferation, thereby accelerating the liver’s recovery from injury and restoring its functional capacity.
One of the pathways through which andrographolide promotes liver regeneration is the activation of the Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription (JAK/STAT) pathway. This pathway is critical for cell growth and proliferation, and its activation by andrographolide leads to increased hepatocyte proliferation and improved regeneration of liver tissue. By supporting liver regeneration, andrographolide helps restore normal liver architecture and function after injury.
Andrographolide also contributes to overall liver function by improving bile production and flow. Bile is essential for the digestion and absorption of dietary fats, as well as the excretion of waste products. By enhancing bile secretion, andrographolide ensures that the liver can effectively carry out its role in digestion and detoxification, thereby promoting a healthier liver environment.
In addition to promoting regeneration, andrographolide enhances the body’s natural detoxification processes. The liver is the primary organ responsible for detoxifying harmful substances, including metabolic by-products, drugs, and toxins. Andrographolide increases the expression of phase II detoxification enzymes, such as glutathione S-transferase (GST), which play a key role in neutralizing and excreting toxic substances. By enhancing these detoxification pathways, andrographolide helps maintain optimal liver function and supports the body’s overall health.
Mechanisms of Action: How Andrographolide Improves Liver Health
Andrographolide’s benefits for liver health are attributed to several well-established mechanisms of action, which are supported by scientific research:
Anti-Inflammatory Action: Andrographolide inhibits NF-κB activation, thereby reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β. This anti-inflammatory effect is crucial for preventing the progression of liver diseases, particularly NAFLD, where inflammation plays a central role in disease progression.
Regulation of Lipid Metabolism: By activating AMPK, andrographolide reduces de novo lipogenesis and promotes fatty acid oxidation. This dual action helps reduce fat accumulation in the liver, thereby preventing and managing NAFLD.
Antioxidant Effects: Andrographolide enhances the activity of antioxidant enzymes, such as SOD, catalase, and glutathione peroxidase (GPx), which protect hepatocytes from oxidative stress. By neutralizing ROS, andrographolide prevents oxidative damage and maintains liver cell integrity.
Anti-Fibrotic Properties: The inhibition of hepatic stellate cell activation by andrographolide is a key factor in reducing liver fibrosis. By preventing collagen deposition, andrographolide helps preserve normal liver structure and function, reducing the risk of cirrhosis.
Stimulation of Hepatocyte Proliferation: Andrographolide activates the JAK/STAT pathway, promoting hepatocyte proliferation and liver regeneration. This effect is particularly beneficial for restoring liver function after injury or surgery.
Enhanced Detoxification: By upregulating phase II detoxification enzymes, andrographolide supports the liver’s ability to detoxify and eliminate harmful substances. This effect is critical for maintaining liver health and preventing toxin-induced damage.
Conclusion: Andrographolide as a Natural Ally for Liver Health
Andrographolide offers a comprehensive range of benefits for liver health, including the prevention of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), protection against chronic liver conditions, reduction of fibrosis, and support for liver regeneration. Its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-fibrotic, and detoxification-enhancing properties make it a powerful hepatoprotective agent. Scientific evidence supports the use of andrographolide as a natural compound capable of improving liver function, reducing damage caused by fatty liver and other stressors, and promoting a healthier liver environment.
For individuals seeking to support their liver health, andrographolide represents a promising natural option backed by substantial scientific research. Its ability to regulate lipid metabolism, reduce inflammation, enhance antioxidant defenses, and promote liver regeneration makes it an ideal candidate for the prevention and management of liver diseases. Incorporating andrographolide into a health regimen could be a proactive step towards maintaining a healthy liver and optimizing the body’s natural detoxification processes.
As always, individuals should consult healthcare professionals before starting any new supplementation, especially those with pre-existing medical conditions or those taking medication. Nonetheless, the evidence in favor of andrographolide as a natural hepatoprotective agent is compelling and highlights its potential in promoting long-term liver health.

Angelica Sinensis (Dong Quai) Root Extract: Hepatoprotective Benefits for Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Liver Health
Angelica sinensis, commonly known as Dong Quai, has been a staple in Traditional Chinese Medicine for centuries. With its diverse therapeutic properties, modern science is gradually uncovering its health benefits, especially concerning liver health. This scientific synopsis presents the evidence-backed effects of Angelica sinensis root extract in preventing and managing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Emphasizing its hepatoprotective, regenerative, and detoxification benefits, this article will detail how the root extract contributes to a healthier liver environment.
Hepatoprotective Properties Against NAFLD and Chronic Liver Diseases
Angelica sinensis root extract is gaining attention for its promising role in liver health, particularly in preventing and managing NAFLD, a condition characterized by excessive fat accumulation in the liver not caused by alcohol consumption. NAFLD is increasingly common due to the global rise in obesity and metabolic disorders. Chronic inflammation, oxidative stress, and lipid dysregulation are significant factors contributing to NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and progression to cirrhosis.
Antioxidant Effects: Angelica sinensis is rich in bioactive compounds, such as ferulic acid and polysaccharides, which exhibit powerful antioxidant properties. By neutralizing free radicals, the extract helps mitigate oxidative stress—a major cause of hepatic cell damage in NAFLD. Scientific studies have demonstrated that the antioxidant activity of Angelica sinensis helps in reducing lipid peroxidation within liver cells, thus preventing damage from fat accumulation.
Anti-Inflammatory Action: Chronic liver inflammation is a key driver in the progression from NAFLD to more severe liver diseases, such as fibrosis and cirrhosis. Angelica sinensis contains coumarins, which have demonstrated anti-inflammatory properties in animal and cellular models. By modulating inflammatory pathways, such as the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) pathway, the extract reduces the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α and IL-6, contributing to decreased liver inflammation and improved overall liver health.
Regulation of Lipid Metabolism: Another critical aspect of managing NAFLD is regulating lipid accumulation in the liver. Angelica sinensis has been shown to improve lipid metabolism by modulating the activity of key enzymes involved in lipid synthesis and breakdown. Studies indicate that the extract can help regulate the expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs), which play a role in lipid homeostasis. This regulatory action helps reduce hepatic fat deposition, thereby alleviating NAFLD symptoms.
Hepatoprotective Mechanisms Against Liver Stressors
The hepatoprotective effects of Angelica sinensis are well-documented through various studies, illustrating its ability to protect liver cells from damage induced by toxins and stressors. Liver stressors such as a high-fat diet, environmental toxins, and certain medications can cause significant hepatic injury, leading to compromised liver function and progression to chronic liver disease.
Protection Against Toxin-Induced Damage: The root extract of Angelica sinensis has been demonstrated to protect hepatocytes from damage caused by chemical toxins. For instance, studies involving animal models have shown that Angelica sinensis can significantly reduce liver enzyme markers such as ALT (alanine aminotransferase) and AST (aspartate aminotransferase) after toxin exposure. These enzymes are typically elevated during liver damage, and their reduction indicates a protective effect on liver cells.
Improvement of Mitochondrial Function: Mitochondria play a critical role in maintaining liver health, as they are involved in energy production and detoxification processes. Dysfunction of mitochondria is a hallmark of liver diseases, particularly NAFLD. Angelica sinensis has been found to support mitochondrial function by enhancing mitochondrial respiration and reducing oxidative damage to mitochondrial DNA. This contributes to maintaining the energy balance and detoxification capacity of liver cells, which is crucial in preventing liver disease progression.
Enhancing Liver Regeneration and Function
The ability of the liver to regenerate after injury is one of its unique characteristics. Angelica sinensis contributes significantly to enhancing liver regeneration, which is essential in recovering from liver injury, fibrosis, or cirrhosis.
Promotion of Hepatocyte Proliferation: Angelica sinensis has been shown to stimulate hepatocyte proliferation, promoting liver regeneration. Research indicates that the extract can activate growth factors such as hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), which plays a key role in liver tissue regeneration. By stimulating these growth pathways, Angelica sinensis aids in the repair of damaged liver tissue and supports the recovery of liver function after injury.
Reduction of Fibrotic Tissue Formation: Chronic liver damage often leads to fibrosis, characterized by the excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix components like collagen. If unchecked, fibrosis can progress to cirrhosis, significantly impairing liver function. Angelica sinensis has demonstrated anti-fibrotic effects by inhibiting the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), which are the primary cells responsible for collagen production in the liver. By modulating the activity of these cells, the extract helps prevent the formation of fibrotic tissue, thus maintaining normal liver architecture and function.
Supporting Detoxification and Overall Liver Function
A healthy liver is critical for the body’s natural detoxification processes, as it filters toxins from the blood and metabolizes various substances. Angelica sinensis contributes to enhanced detoxification and overall liver function through multiple mechanisms.
Induction of Phase I and Phase II Detoxification Enzymes: The detoxification process in the liver occurs in two phases, involving various enzymes. Angelica sinensis has been shown to upregulate the expression of both Phase I (e.g., cytochrome P450 enzymes) and Phase II detoxification enzymes (e.g., glutathione S-transferase). This dual effect enhances the liver’s ability to metabolize and excrete toxins, thus promoting a cleaner internal environment.
Enhancement of Bile Production: Bile production is essential for the digestion and absorption of fats and also plays a role in eliminating waste products from the liver. Angelica sinensis has been found to enhance bile flow, thereby improving the excretion of fat-soluble toxins. This choleretic effect not only supports detoxification but also aids in preventing cholestasis, a condition characterized by impaired bile flow, which can lead to further liver damage.
Reduction of Oxidative Stress in Detoxification: During detoxification, reactive oxygen species (ROS) are often produced as byproducts. If not managed properly, these ROS can cause oxidative stress, damaging liver cells. The antioxidant components of Angelica sinensis, particularly ferulic acid, play a crucial role in scavenging these free radicals, thus reducing oxidative stress during the detoxification process and preserving liver integrity.
Scientific Evidence and Clinical Relevance
The hepatoprotective effects of Angelica sinensis are supported by several preclinical studies conducted on animal models and cell cultures. These studies provide strong evidence of its benefits in reducing liver inflammation, mitigating oxidative stress, and promoting liver regeneration. However, clinical trials in human populations are still limited, and further research is necessary to establish standardized dosages and safety profiles for therapeutic use.
One animal study published in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology demonstrated that Angelica sinensis extract significantly reduced liver enzyme levels and inflammatory markers in a rodent model of chemically-induced liver injury. Another study highlighted its role in regulating lipid metabolism, showing decreased fat accumulation in the liver of mice fed a high-fat diet supplemented with Angelica sinensis.
Despite the limited human clinical data, the existing preclinical evidence suggests a promising role for Angelica sinensis in supporting liver health, particularly for individuals at risk of NAFLD or those exposed to hepatic stressors such as toxins, alcohol, or certain medications.
Conclusion: Angelica Sinensis as a Natural Ally for Liver Health
Angelica sinensis root extract presents a natural, multi-faceted approach to liver health, offering hepatoprotective, regenerative, and detoxifying benefits. Its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties help prevent the progression of liver diseases such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. By promoting lipid metabolism, protecting against toxin-induced liver damage, enhancing mitochondrial function, supporting liver regeneration, and boosting detoxification processes, Angelica sinensis contributes to a healthier liver environment.
While the current scientific evidence is promising, further research—particularly well-designed human clinical trials—is needed to fully understand the therapeutic potential of Angelica sinensis for liver health. Nevertheless, incorporating this traditional herbal remedy may offer a complementary approach for individuals seeking to maintain optimal liver function and prevent liver-related disorders.
As with any herbal supplement, it is important for individuals to consult healthcare professionals before use, especially for those with pre-existing health conditions or those taking medications, to ensure safety and efficacy in promoting liver health.

Arjunolic Acid from Cyclocarya Paliurus: A Potent Natural Ally for Liver Health
Arjunolic acid, a bioactive compound found in Cyclocarya paliurus (often referred to as the “sweet tea tree”), has gained attention in recent years for its significant hepatoprotective properties. This natural compound has demonstrated effectiveness in preventing and managing liver-related health issues such as Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Through a combination of antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and regenerative mechanisms, arjunolic acid has emerged as a promising natural remedy for promoting a healthier liver environment, enhancing overall liver function, and supporting the body’s natural detoxification processes. This comprehensive scientific synopsis will explore the proven benefits of arjunolic acid, highlighting its mechanisms of action and potential for liver health.
Hepatoprotective Effects of Arjunolic Acid
Arjunolic acid exhibits potent hepatoprotective effects, particularly by reducing liver damage caused by fat accumulation and oxidative stress—key drivers of NAFLD and other liver conditions. The pathophysiology of NAFLD often involves excessive fat buildup within liver cells, which leads to inflammation, mitochondrial dysfunction, and ultimately fibrosis or cirrhosis if left untreated. Arjunolic acid has demonstrated effectiveness in preventing these harmful processes through its various biochemical actions.
Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Activity
A major mechanism behind arjunolic acid’s hepatoprotective activity is its robust antioxidant capability. Oxidative stress, which is a result of an imbalance between the production of free radicals and the body’s antioxidant defenses, plays a key role in the progression of liver diseases like NAFLD and cirrhosis. Arjunolic acid acts by neutralizing reactive oxygen species (ROS), thus reducing oxidative stress and preventing further damage to liver tissues. Studies have shown that arjunolic acid enhances the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes, including superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase, and glutathione peroxidase, thereby helping the liver maintain redox balance and reduce cell damage.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Inflammation is another major contributor to the progression of liver diseases. Arjunolic acid exerts powerful anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting key inflammatory mediators such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β. By downregulating the expression of these pro-inflammatory cytokines, arjunolic acid helps minimize the inflammatory response in liver tissues, preventing the transition from simple steatosis to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), a more severe form of liver inflammation associated with fibrosis. The inhibition of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB), a crucial regulator of inflammation, further contributes to its anti-inflammatory properties, providing a comprehensive protective effect on the liver.
Fat Metabolism and Lipid Regulation
One of the most significant aspects of arjunolic acid’s hepatoprotective action is its ability to regulate lipid metabolism. Fat accumulation in the liver is a hallmark of NAFLD, and excessive lipid accumulation can lead to hepatocellular injury. Arjunolic acid has been found to modulate lipid metabolism by activating adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK), a key enzyme involved in cellular energy homeostasis. By activating AMPK, arjunolic acid promotes fatty acid oxidation and reduces lipogenesis, thereby preventing the excessive buildup of fat in the liver. This not only prevents hepatocellular damage but also aids in improving overall liver function.
Liver Regeneration and Repair
Liver regeneration is a critical aspect of recovering from liver injury. The liver is the only organ in the body with a remarkable ability to regenerate itself, but this process can be hampered in chronic liver conditions. Arjunolic acid has shown promising results in enhancing liver regenerative capacity by promoting hepatocyte proliferation and repair. This effect is believed to be mediated through the upregulation of growth factors such as hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), both of which play a significant role in liver regeneration. By supporting the repair of damaged liver tissues, arjunolic acid not only aids in functional recovery but also enhances the overall resilience of the liver to stressors.
Prevention of Fibrosis and Cirrhosis
The progression of NAFLD and chronic liver disease often leads to fibrosis, which is characterized by the excessive deposition of extracellular matrix proteins, ultimately resulting in cirrhosis. Arjunolic acid has demonstrated anti-fibrotic properties, making it a valuable natural agent in preventing the progression of liver disease. It acts by inhibiting the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), which are responsible for collagen production and fibrosis. By reducing the activation and proliferation of HSCs, arjunolic acid helps maintain normal liver architecture and prevents the development of cirrhosis.
Enhancing Detoxification and Overall Liver Function
The liver plays a crucial role in detoxifying the body by metabolizing toxins and facilitating their elimination. Arjunolic acid has been found to enhance liver detoxification processes by improving the expression and activity of cytochrome P450 enzymes, which are responsible for the metabolism of various xenobiotics and endogenous compounds. By supporting phase I and phase II detoxification pathways, arjunolic acid helps the liver efficiently process and eliminate harmful substances, thereby contributing to a healthier liver environment.
Moreover, arjunolic acid helps maintain the integrity of hepatocyte membranes, which is vital for optimal liver function. Damage to hepatocyte membranes can compromise the liver’s ability to carry out its metabolic and detoxifying functions. By stabilizing cell membranes and preventing lipid peroxidation, arjunolic acid ensures that liver cells remain functional and capable of performing their essential roles in maintaining overall health.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Arjunolic Acid’s Benefits
A growing body of scientific evidence supports the hepatoprotective effects of arjunolic acid. Preclinical studies conducted on animal models of NAFLD and chemically-induced liver injury have consistently demonstrated that arjunolic acid can effectively reduce liver enzyme levels (such as ALT and AST), which are commonly elevated in liver dysfunction. These studies indicate that arjunolic acid not only prevents liver injury but also aids in restoring normal liver function.
Furthermore, studies involving oxidative stress markers have shown that arjunolic acid significantly reduces malondialdehyde (MDA) levels, a key indicator of lipid peroxidation, while simultaneously increasing the activity of antioxidant enzymes. These findings highlight its potential to mitigate oxidative stress, which is a primary driver of liver inflammation and damage.
In addition, research has shown that arjunolic acid’s anti-inflammatory properties are mediated through the inhibition of key signaling pathways, including the NF-κB pathway, which plays a central role in the regulation of inflammation. By modulating these pathways, arjunolic acid effectively reduces the inflammatory response, which is crucial for preventing the progression of liver disease from simple steatosis to more severe forms.
Arjunolic Acid as a Natural Alternative for Liver Health
The use of natural compounds for the management of liver diseases has gained popularity due to their safety profile and minimal side effects compared to conventional pharmaceuticals. Arjunolic acid, in particular, offers a multi-faceted approach to liver health, addressing oxidative stress, inflammation, lipid accumulation, fibrosis, and detoxification—all of which are key components of liver pathology. Its ability to enhance liver regeneration further underscores its potential as a holistic liver health supplement.
While most of the research on arjunolic acid is currently in the preclinical stage, the consistent findings across various studies provide a strong basis for its potential use in humans. Future clinical trials will be crucial in confirming these benefits and determining the optimal dosage and safety profile for human use. However, the current evidence is promising, and arjunolic acid represents a potential natural alternative for individuals looking to improve their liver health and prevent the progression of liver disease.
Conclusion
Arjunolic acid from Cyclocarya paliurus is a powerful natural compound with significant hepatoprotective properties. By combating oxidative stress, reducing inflammation, regulating lipid metabolism, enhancing liver regeneration, and preventing fibrosis, arjunolic acid provides a comprehensive approach to maintaining liver health. Its ability to enhance the liver’s natural detoxification processes further contributes to overall well-being and resilience against liver-related health issues.
With a growing body of scientific evidence supporting its benefits, arjunolic acid stands out as a promising natural agent for the prevention and management of liver diseases such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. As research progresses, arjunolic acid may become an integral component of liver health supplements, offering a safe and effective way to support liver function and promote a healthier liver environment.

Aronia Melanocarpa and Liver Health: Proven Benefits for NAFLD, Chronic Liver Disease, and Cirrhosis
Aronia melanocarpa, commonly known as black chokeberry, has emerged as a potent natural ally in promoting liver health and addressing conditions such as Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. This small, antioxidant-rich berry contains an impressive range of bioactive compounds that help protect and regenerate the liver, making it a promising supplement for individuals seeking to enhance their liver health. In this article, we provide an in-depth exploration of the scientifically-backed benefits of Aronia melanocarpa, focusing on its hepatoprotective effects, mechanisms of action, and role in promoting a healthier liver environment.
Aronia Melanocarpa and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD, a condition characterized by excess fat accumulation in the liver unrelated to alcohol consumption, has become one of the most prevalent liver disorders worldwide. Research suggests that Aronia melanocarpa has significant potential in preventing and managing NAFLD, primarily through its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and lipid-lowering properties.
Mechanisms of Action
Antioxidant Properties: Aronia melanocarpa is rich in anthocyanins, phenolic acids, and flavonoids, which contribute to its strong antioxidant activity. These compounds help neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS) that contribute to oxidative stress, a key factor in the development and progression of NAFLD. By reducing oxidative stress, Aronia helps prevent lipid peroxidation and protects hepatocytes from oxidative damage.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Chronic low-grade inflammation plays a crucial role in the development of NAFLD. Studies indicate that Aronia extract reduces pro-inflammatory cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6). By modulating inflammatory pathways, Aronia mitigates inflammation-induced damage in liver tissues, contributing to improved liver function.
Lipid Metabolism Regulation: Dysregulated lipid metabolism is a hallmark of NAFLD. Aronia has been shown to improve lipid profiles by decreasing total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein (LDL), and triglyceride levels, while increasing high-density lipoprotein (HDL) levels. This modulation helps reduce the accumulation of fat in the liver, thus mitigating the risk of NAFLD progression.
Hepatoprotective Effects in Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver disease and cirrhosis are severe conditions characterized by progressive liver damage and fibrosis. Aronia melanocarpa offers hepatoprotective benefits, safeguarding liver cells from further injury and supporting overall liver function. Its protective effects can be attributed to the following mechanisms:
Cellular Protection and Fibrosis Reduction
Inhibition of Fibrosis: One of the critical challenges in managing chronic liver disease is the development of liver fibrosis, which can eventually progress to cirrhosis. Aronia has demonstrated an ability to inhibit hepatic stellate cell activation—a key event in fibrosis formation—thereby reducing the deposition of extracellular matrix and collagen. By inhibiting fibrosis, Aronia helps preserve the structural integrity of liver tissue.
Mitigation of Oxidative Damage: Chronic liver disease is often accompanied by elevated oxidative stress, which exacerbates liver injury. The antioxidant components in Aronia melanocarpa, particularly anthocyanins, protect liver cells by scavenging free radicals and reducing oxidative damage. This helps mitigate liver cell apoptosis and necrosis, ultimately improving liver health.
Reduction of Hepatocellular Injury: Aronia has also been found to reduce markers of liver damage, such as alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST). Lower levels of these enzymes indicate reduced hepatocellular injury, which is crucial for patients with chronic liver disease or cirrhosis.
Aronia’s Role in Liver Regeneration and Detoxification
The liver has a remarkable ability to regenerate, and supporting this regenerative capacity is essential for maintaining liver health, especially following injury or damage. Aronia melanocarpa plays a vital role in promoting liver regeneration and enhancing the body’s natural detoxification processes.
Enhanced Liver Regeneration
Stimulation of Hepatocyte Proliferation: Hepatocytes are the primary cells responsible for liver regeneration. Studies suggest that Aronia’s bioactive compounds stimulate hepatocyte proliferation, promoting tissue repair and regeneration. This helps accelerate the recovery of liver mass and function after damage caused by fatty liver disease, alcohol, or other hepatotoxins.
Protection Against Hepatotoxins: The hepatoprotective effects of Aronia also extend to its ability to shield the liver from harmful substances, such as alcohol, medications, and environmental toxins. By reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, Aronia helps protect liver cells from damage, thereby facilitating the liver’s ability to regenerate and maintain optimal function.
Improvement of Overall Liver Function
A healthy liver is essential for numerous physiological processes, including bile production, metabolism, and detoxification. Aronia melanocarpa contributes to overall liver health by improving these functions and creating a healthier liver environment.
Support for Detoxification Pathways
Phase I and II Detoxification: The liver’s detoxification process involves two main phases: Phase I (oxidation) and Phase II (conjugation). Aronia’s rich antioxidant content helps support Phase I detoxification by neutralizing free radicals generated during the process. Additionally, its ability to upregulate key detoxification enzymes enhances Phase II detoxification, ensuring the efficient removal of harmful substances from the body.
Reduction of Toxic Load: By supporting the liver’s detoxification capacity, Aronia helps reduce the overall toxic load on the liver. This is particularly beneficial for individuals exposed to environmental pollutants, alcohol, or medications that can place additional stress on the liver.
Bile Production and Fat Metabolism
Bile production is critical for the digestion and absorption of dietary fats. Aronia melanocarpa has been shown to enhance bile secretion, which aids in the emulsification and breakdown of fats. Improved bile flow also helps prevent the buildup of fat in the liver, reducing the risk of conditions such as NAFLD and promoting a healthier metabolic profile.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Aronia Melanocarpa’s Benefits for Liver Health
The hepatoprotective effects of Aronia melanocarpa are well-documented in numerous preclinical and clinical studies. The following are key findings from the scientific literature that support the use of Aronia for liver health:
Reduction in Liver Enzymes: A study published in the Journal of Medicinal Food demonstrated that supplementation with Aronia extract led to significant reductions in liver enzyme levels (ALT and AST) in subjects with elevated liver enzymes. This suggests a protective effect against hepatocellular injury.
Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Effects: Research published in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences highlighted Aronia’s ability to reduce oxidative stress and inflammation in animal models of liver injury. The study found that Aronia supplementation decreased the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines and increased antioxidant enzyme activity, supporting its role in preventing liver damage.
Protection Against NAFLD: A study in the Nutrients journal found that Aronia extract improved lipid profiles and reduced liver fat accumulation in a mouse model of NAFLD. The authors concluded that Aronia’s effects were primarily due to its antioxidant and lipid-lowering properties, making it a promising supplement for managing NAFLD.
Hepatoprotective Effects in Alcohol-Induced Liver Damage: Aronia has also shown potential in protecting against alcohol-induced liver damage. A study published in the Journal of Functional Foods reported that Aronia extract reduced oxidative stress markers and improved liver histology in rats exposed to alcohol, suggesting a protective effect against alcohol-induced liver injury.
Conclusion: Aronia Melanocarpa as a Natural Hepatoprotective Agent
Aronia melanocarpa is a powerful natural supplement with a wide range of benefits for liver health. Its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and lipid-regulating properties make it particularly effective in preventing and managing liver conditions such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. By reducing oxidative stress, inhibiting fibrosis, and promoting liver regeneration, Aronia helps protect the liver from damage and supports its ability to recover and function optimally.
In addition to its hepatoprotective effects, Aronia enhances the liver’s detoxification capacity, supports bile production, and contributes to a healthier metabolic environment. The scientific evidence supporting these benefits underscores the potential of Aronia melanocarpa as a valuable supplement for individuals seeking to improve their liver health and prevent liver-related diseases.
For optimal results, incorporating Aronia into a balanced diet, along with lifestyle modifications such as regular physical activity and reduced alcohol consumption, can provide comprehensive support for liver health. As always, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen, especially for individuals with pre-existing liver conditions or those taking medications.
Aronia melanocarpa offers a promising, scientifically-backed approach to promoting liver health and preventing liver disease, making it a valuable addition to the natural health arsenal.

Artemisia Capillaris: A Comprehensive Exploration of Its Role in Liver Health
Artemisia capillaris, a medicinal herb traditionally used in Asian medicine, has garnered attention for its potent hepatoprotective effects, particularly in preventing and managing liver conditions such as Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. This article will provide a scientific synopsis of the proven benefits of Artemisia capillaris, highlighting its mechanisms of action in promoting liver regeneration, enhancing liver function, and supporting the body’s natural detoxification processes.
Preventing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and Chronic Liver Disease
NAFLD is a growing health concern, characterized by fat accumulation in the liver without excessive alcohol consumption. This condition can progress to more severe stages such as non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), fibrosis, cirrhosis, and even liver cancer if not managed properly. Artemisia capillaris has demonstrated significant potential in preventing NAFLD and other chronic liver diseases through its active compounds, particularly scopoletin, capillin, and chlorogenic acid.
Research has shown that Artemisia capillaris can mitigate fat accumulation in the liver by regulating lipid metabolism. Studies indicate that it inhibits the expression of lipogenic genes while upregulating genes involved in lipid breakdown. This dual mechanism helps to prevent lipid buildup, thereby reducing the risk of NAFLD. In addition, Artemisia capillaris has been found to activate AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), a crucial enzyme that regulates energy homeostasis and lipid metabolism, contributing to its anti-steatotic effects.
The herb also possesses potent anti-inflammatory properties, which are instrumental in combating the progression of NAFLD to NASH. Inflammation plays a key role in the worsening of NAFLD, and by reducing the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6, Artemisia capillaris helps to maintain a healthier liver environment.
Hepatoprotective Effects: Reducing Damage from Liver Stressors
Artemisia capillaris is well-known for its hepatoprotective effects, particularly its ability to reduce damage caused by fatty liver and other liver stressors. Hepatotoxicity, often resulting from factors like poor diet, alcohol consumption, and environmental toxins, can significantly impair liver function. Artemisia capillaris exerts protective effects against these stressors through several mechanisms.
One of the key mechanisms is its antioxidant activity. The liver is highly susceptible to oxidative stress, which plays a major role in the pathogenesis of various liver diseases. Artemisia capillaris contains a high concentration of flavonoids and phenolic compounds, which act as powerful antioxidants, scavenging free radicals and reducing oxidative damage. By decreasing the levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS), Artemisia capillaris helps protect liver cells from damage and prevents the initiation of fibrosis.
Moreover, Artemisia capillaris has been shown to modulate key detoxification enzymes, including cytochrome P450 enzymes, which are involved in the metabolism of toxins. By enhancing the activity of these enzymes, the herb supports the liver’s ability to process and eliminate harmful substances, thereby reducing the burden on the liver and preventing damage.
Liver Regeneration and Improved Liver Function
One of the remarkable benefits of Artemisia capillaris is its ability to promote liver regeneration and improve overall liver function. The liver has a unique capacity for regeneration, and Artemisia capillaris can enhance this natural process, making it particularly useful in cases of liver injury or after partial hepatectomy.
The regenerative effects of Artemisia capillaris are largely attributed to its ability to modulate growth factors and cytokines involved in liver repair. Studies have demonstrated that the herb promotes the expression of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β), both of which play crucial roles in liver regeneration. By enhancing the proliferation of hepatocytes and supporting the remodeling of liver tissue, Artemisia capillaris facilitates faster and more effective liver recovery.
In addition, Artemisia capillaris has been found to improve liver enzyme levels, such as alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), which are commonly used markers of liver function. Elevated levels of these enzymes indicate liver damage, and studies have shown that supplementation with Artemisia capillaris can help normalize these enzyme levels, indicating improved liver health.
Anti-Fibrotic Properties: Preventing Cirrhosis Progression
Cirrhosis, characterized by the replacement of healthy liver tissue with scar tissue, is a severe consequence of chronic liver disease. Artemisia capillaris has demonstrated significant anti-fibrotic properties, making it a valuable herb in preventing the progression of liver fibrosis to cirrhosis.
Fibrosis occurs as a result of chronic inflammation and excessive deposition of extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins, which leads to scarring. Artemisia capillaris has been found to inhibit the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), the primary cells responsible for ECM production in the liver. By preventing HSC activation, Artemisia capillaris helps reduce collagen deposition and fibrosis, thereby protecting against cirrhosis.
Furthermore, the herb’s anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties contribute to its anti-fibrotic effects by reducing the underlying causes of fibrosis. By mitigating oxidative stress and inflammation, Artemisia capillaris creates a more favorable environment for liver healing and prevents the progression of fibrosis.
Enhancing the Body’s Natural Detoxification Processes
Artemisia capillaris also plays a crucial role in enhancing the body’s natural detoxification processes, which is essential for maintaining optimal liver health. The liver is the primary organ responsible for detoxifying the body, processing both endogenous and exogenous toxins, and ensuring that harmful substances are safely eliminated.
The herb’s ability to modulate detoxification enzymes, such as those in the cytochrome P450 family, is particularly important in this regard. By upregulating these enzymes, Artemisia capillaris enhances the liver’s capacity to metabolize toxins, drugs, and other harmful substances, thereby supporting the body’s natural detoxification pathways. Additionally, the herb has been found to increase the production of glutathione, one of the most important antioxidants involved in detoxification. Glutathione helps neutralize toxins and supports the conjugation process, which is critical for making toxins water-soluble so they can be excreted from the body.
Supporting a Healthier Liver Environment
Maintaining a healthy liver environment is essential for overall liver function, and Artemisia capillaris contributes to this by supporting bile production and flow. Bile is produced by the liver and plays a key role in the digestion and absorption of fats, as well as the elimination of waste products. Artemisia capillaris has been shown to promote choleresis, the production and secretion of bile, which helps to ensure efficient digestion and toxin elimination.
The herb’s ability to improve bile flow also helps prevent cholestasis, a condition characterized by impaired bile flow that can lead to liver damage. By promoting the proper flow of bile, Artemisia capillaris helps to maintain a healthier liver environment and prevents the buildup of toxic substances within the liver.
Mechanisms of Action: A Summary
Regulation of Lipid Metabolism: Artemisia capillaris helps prevent NAFLD by inhibiting lipogenesis and promoting lipid breakdown through the activation of AMPK. This reduces fat accumulation in the liver and lowers the risk of disease progression.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: The herb reduces inflammation by decreasing pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6, which is crucial for preventing the progression of NAFLD to NASH and reducing liver damage.
Antioxidant Activity: Artemisia capillaris contains flavonoids and phenolic compounds that scavenge free radicals, reducing oxidative stress and protecting liver cells from damage. This antioxidant activity is vital for preventing the initiation of fibrosis and promoting liver health.
Modulation of Detoxification Enzymes: By enhancing the activity of detoxification enzymes like cytochrome P450 and increasing glutathione production, Artemisia capillaris supports the liver’s ability to process and eliminate toxins.
Promotion of Liver Regeneration: The herb promotes liver regeneration by upregulating growth factors such as HGF and TGF-β, which are essential for hepatocyte proliferation and tissue remodeling.
Inhibition of Hepatic Stellate Cells: Artemisia capillaris inhibits the activation of HSCs, reducing collagen deposition and fibrosis, thereby preventing the progression of chronic liver disease to cirrhosis.
Improvement of Bile Flow: The herb promotes bile production and flow, supporting efficient digestion and preventing cholestasis, which helps maintain a healthy liver environment.
Conclusion
Artemisia capillaris is a powerful herbal remedy with significant hepatoprotective properties, offering a range of benefits for liver health. From preventing NAFLD and chronic liver disease to reducing liver damage and promoting regeneration, Artemisia capillaris acts through multiple mechanisms to support a healthier liver environment. Its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-fibrotic, and detoxification-enhancing properties make it an invaluable tool in maintaining optimal liver function and overall health.
The scientific evidence supporting the benefits of Artemisia capillaris is robust, particularly in terms of its ability to regulate lipid metabolism, reduce inflammation, protect against oxidative stress, and promote liver regeneration. For individuals seeking to improve liver health and enhance the body’s natural detoxification processes, Artemisia capillaris offers a promising natural solution that is backed by substantial scientific research.
As with any herbal supplement, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating Artemisia capillaris into your routine, especially for individuals with pre-existing medical conditions or those taking other medications. The potential of this herb to support liver health is immense, but it should be used as part of a comprehensive approach to wellness that includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, and lifestyle modifications.

Artemisia Iwayomogi: A Scientifically-Backed Natural Solution for Liver Health
Artemisia iwayomogi, commonly known as Haninjin or Korean Wormwood, has gained significant attention in recent years for its potential therapeutic effects on liver health. Known for its rich history in traditional medicine, Artemisia iwayomogi is now being studied extensively for its benefits in preventing and managing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, cirrhosis, and other hepatic conditions. This plant is gaining recognition for its hepatoprotective effects, ability to reduce liver damage, and its role in liver regeneration. In this comprehensive analysis, we will explore the scientific evidence supporting its role in promoting liver health.
Preventing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD is a common liver disorder characterized by excessive fat accumulation in the liver without alcohol consumption being a contributing factor. Artemisia iwayomogi has demonstrated a potential role in preventing NAFLD, primarily through its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and lipid metabolism-modulating properties.
1. Anti-Inflammatory Action
Chronic inflammation is a significant driver of NAFLD progression. Artemisia iwayomogi contains various bioactive compounds, including flavonoids and sesquiterpene lactones, which have demonstrated strong anti-inflammatory effects in multiple studies. The suppression of inflammatory pathways, such as the NF-κB signaling cascade, has been reported to reduce liver inflammation, thereby helping to prevent the onset and progression of NAFLD.
2. Antioxidant Activity
Oxidative stress plays a crucial role in NAFLD pathogenesis. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) damage hepatocytes, leading to the accumulation of fat within the liver. Artemisia iwayomogi is rich in antioxidants, including polyphenolic compounds, which effectively scavenge ROS and reduce oxidative stress. Studies have shown that the administration of Artemisia iwayomogi extracts helps to maintain cellular redox balance, thereby reducing the risk of fatty liver development.
3. Regulation of Lipid Metabolism
Lipid metabolism imbalance is central to NAFLD. Artemisia iwayomogi has been shown to regulate lipid accumulation in hepatocytes by modulating key enzymes involved in lipid synthesis and breakdown. Animal studies suggest that extracts of Artemisia iwayomogi decrease triglyceride levels in the liver by upregulating AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activity, thereby promoting lipid oxidation and reducing fat deposition.
Managing Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver disease, including cirrhosis, is a serious health condition that may progress from NAFLD or other liver stressors. Artemisia iwayomogi’s role in managing chronic liver disease is mainly due to its hepatoprotective effects, which involve reducing liver inflammation and fibrosis.
1. Hepatoprotective Mechanisms
The hepatoprotective effect of Artemisia iwayomogi has been well-documented in several preclinical studies. The extract has shown the ability to protect liver cells from damage induced by various toxic agents, such as carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) and alcohol. This protection is attributed to its antioxidant properties, which prevent hepatocyte apoptosis and maintain cell integrity. By preventing oxidative damage, Artemisia iwayomogi reduces the risk of chronic liver disease progression.
2. Anti-Fibrotic Effects
Liver fibrosis is a hallmark of chronic liver disease and cirrhosis, characterized by excessive deposition of extracellular matrix (ECM) components, such as collagen, in the liver. Artemisia iwayomogi has been shown to reduce liver fibrosis by inhibiting the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), which are responsible for ECM production. The suppression of the TGF-β/Smad pathway, a key driver of fibrosis, has also been observed in studies involving Artemisia iwayomogi, suggesting that it can effectively mitigate fibrotic changes in the liver.
Reducing Damage from Fatty Liver and Other Liver Stressors
The hepatoprotective properties of Artemisia iwayomogi extend to reducing damage caused by fatty liver and other liver stressors, including toxins, high-fat diets, and alcohol consumption.
1. Protecting Against High-Fat Diet-Induced Liver Damage
Experimental studies involving animal models have demonstrated that Artemisia iwayomogi extracts can significantly reduce liver damage induced by a high-fat diet. The plant’s active components reduce fat accumulation, lower liver enzyme levels (such as ALT and AST), and improve overall liver histology. These findings suggest that Artemisia iwayomogi can attenuate the negative impact of a high-fat diet on liver health, making it a promising option for individuals at risk of NAFLD.
2. Mitigating Alcohol-Induced Liver Injury
Alcohol is a well-known liver stressor that can lead to liver inflammation, fatty liver, and eventually cirrhosis. Artemisia iwayomogi has shown potential in mitigating alcohol-induced liver injury by reducing oxidative stress and inflammatory cytokine production. The plant’s bioactive compounds enhance the liver’s antioxidant defenses, helping to neutralize the toxic effects of alcohol metabolites, thereby reducing hepatocyte injury.
Promoting Liver Regeneration and Overall Liver Function
One of the remarkable features of the liver is its ability to regenerate following injury. Artemisia iwayomogi has shown potential in enhancing liver regeneration and supporting overall liver function.
1. Enhancing Liver Regeneration
Liver regeneration is critical for recovery after liver injury or surgery. Artemisia iwayomogi has been found to promote hepatocyte proliferation, which is essential for liver tissue repair and regeneration. Studies have shown that the plant extract enhances the expression of genes involved in cell cycle progression, such as cyclin D1, thereby stimulating the growth of new liver cells.
2. Supporting Detoxification and Overall Liver Function
The liver plays a central role in detoxifying the body by metabolizing harmful substances. Artemisia iwayomogi has been shown to enhance the liver’s natural detoxification processes by increasing the activity of phase I and phase II detoxification enzymes, such as cytochrome P450 and glutathione S-transferase. This enhancement helps the liver to effectively process and eliminate toxins, thereby promoting a healthier liver environment and improving overall liver function.
Mechanisms of Action of Artemisia Iwayomogi on Liver Health
The beneficial effects of Artemisia iwayomogi on liver health can be attributed to several key mechanisms of action, which include anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-fibrotic pathways, as well as the regulation of lipid metabolism and promotion of liver regeneration.
1. Inhibition of NF-κB and TGF-β Pathways
The NF-κB signaling pathway is a major contributor to liver inflammation, while the TGF-β pathway is central to liver fibrosis. Artemisia iwayomogi has been shown to inhibit these pathways, thereby reducing inflammation and fibrosis in the liver. By modulating these critical pathways, the plant helps to maintain liver health and prevent the progression of chronic liver diseases.
2. Activation of AMPK Pathway
AMPK is a key energy sensor in cells that regulates lipid metabolism. Artemisia iwayomogi activates the AMPK pathway, which leads to increased fatty acid oxidation and reduced lipid synthesis in hepatocytes. This effect is particularly beneficial for individuals with NAFLD, as it helps to decrease fat accumulation in the liver and improve metabolic health.
3. Antioxidant Defense Enhancement
Artemisia iwayomogi enhances the liver’s antioxidant defenses by increasing the levels of endogenous antioxidants such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione (GSH). This effect helps to neutralize ROS and protect hepatocytes from oxidative damage, which is a common cause of liver injury.
Summary: Artemisia Iwayomogi’s Role in Liver Health
Artemisia iwayomogi has emerged as a promising natural solution for promoting liver health and preventing liver diseases such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Its benefits are supported by a growing body of scientific evidence highlighting its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-fibrotic, and hepatoprotective properties. The plant’s ability to regulate lipid metabolism, enhance liver regeneration, and support detoxification processes makes it an ideal candidate for improving liver health and preventing liver-related complications.
By inhibiting key inflammatory and fibrotic pathways, Artemisia iwayomogi helps to reduce liver damage and maintain liver function. Its role in enhancing antioxidant defenses and promoting hepatocyte proliferation further contributes to its hepatoprotective effects. As research continues, Artemisia iwayomogi may prove to be an invaluable natural therapeutic option for individuals seeking to support their liver health and prevent the progression of liver diseases.
The comprehensive hepatoprotective effects of Artemisia iwayomogi make it a valuable ally in maintaining optimal liver function, reducing the risk of liver-related conditions, and promoting overall health. For those seeking a natural approach to liver wellness, Artemisia iwayomogi stands out as a scientifically-supported option with a wide range of beneficial effects.

Asparagus Racemosus: A Natural Ally in Preventing Liver Diseases like NAFLD, Cirrhosis, and Chronic Liver Conditions
Asparagus racemosus Willd., commonly known as Shatavari, has gained attention for its diverse health benefits. While widely celebrated in Ayurvedic medicine for its adaptogenic and rejuvenating properties, recent research highlights its efficacy in supporting liver health, particularly against conditions such as Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Below is an in-depth, evidence-backed exploration of Asparagus racemosus and its role in hepatoprotection, liver regeneration, and improved liver function.
Proven Benefits of Asparagus Racemosus for Liver Health
Hepatoprotective Effects and Mechanisms of Action
Asparagus racemosus contains bioactive compounds, including steroidal saponins, flavonoids, and alkaloids, which possess significant antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. These compounds are known to exhibit hepatoprotective effects by neutralizing free radicals and minimizing oxidative stress—two critical contributors to liver damage in conditions like NAFLD, cirrhosis, and chronic liver disease.
Antioxidant Activity: A Shield Against Oxidative Stress
The liver is highly susceptible to oxidative damage due to its central role in detoxification, which involves a high rate of reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. Asparagus racemosus is rich in antioxidants, such as polyphenols and flavonoids, which help scavenge free radicals and reduce ROS levels in liver tissues. A study published in the Journal of Medicinal Plants found that the root extract of Asparagus racemosus effectively increased levels of catalase, superoxide dismutase (SOD), and glutathione peroxidase—key antioxidant enzymes that collectively mitigate oxidative stress in liver cells.
This antioxidant activity is crucial for preventing the progression of NAFLD to more severe conditions like steatohepatitis or cirrhosis. By reducing oxidative damage, Asparagus racemosus helps maintain the integrity of hepatocytes (liver cells), thus enhancing overall liver function.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Combating Chronic Inflammation
Chronic inflammation is a hallmark of liver diseases, particularly NAFLD and cirrhosis. Inflammation exacerbates liver injury by promoting fibrosis, a process in which healthy liver tissue is replaced with scar tissue, eventually impairing liver function. Studies indicate that Asparagus racemosus possesses potent anti-inflammatory properties, largely due to its high concentration of saponins and flavonoids. These compounds modulate inflammatory pathways by inhibiting pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6, and NF-κB, thereby reducing inflammation and preventing the onset of fibrosis.
By targeting these key inflammatory markers, Asparagus racemosus not only reduces liver inflammation but also lowers the risk of fibrosis, which is a precursor to cirrhosis. This makes it a promising natural supplement for managing chronic liver inflammation and slowing disease progression.
Prevention of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD is characterized by the accumulation of fat in liver cells, which, if left unchecked, can lead to steatohepatitis, fibrosis, and eventually cirrhosis. Asparagus racemosus has demonstrated potential in preventing and managing NAFLD by modulating lipid metabolism and enhancing fat utilization.
Lipid Metabolism Regulation
Research indicates that Asparagus racemosus helps regulate lipid metabolism by promoting the activity of lipolytic enzymes that break down fats. The root extract also increases the expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPAR-α), a key transcription factor involved in fatty acid oxidation. By enhancing fatty acid breakdown and reducing hepatic lipid accumulation, Asparagus racemosus addresses the root cause of NAFLD—excessive fat buildup in the liver.
Furthermore, the extract has been found to improve insulin sensitivity, which is directly linked to reduced fat accumulation in the liver. A study in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology reported that Asparagus racemosus supplementation improved insulin signaling pathways, leading to decreased lipogenesis (fat production) and a lower risk of developing NAFLD.
Protection Against Liver Fibrosis and Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis is the advanced stage of liver fibrosis, where the liver’s structure and function are severely compromised. Asparagus racemosus contributes to fibrosis prevention by inhibiting the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), which play a central role in collagen deposition and scar tissue formation.
Modulation of Hepatic Stellate Cells
The activation of HSCs is a critical step in the development of liver fibrosis. Studies have shown that Asparagus racemosus root extract can effectively inhibit HSC activation by downregulating pro-fibrotic factors like transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β). Inhibition of TGF-β signaling prevents excessive collagen production and scar tissue formation, thereby reducing the risk of fibrosis progression to cirrhosis.
In addition, Asparagus racemosus has been shown to promote the expression of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), enzymes that degrade excess collagen in liver tissues. This activity helps maintain normal liver architecture and prevents the accumulation of fibrotic tissue, thereby supporting liver function even in cases of chronic liver stress.
Liver Regeneration and Enhanced Detoxification
Stimulation of Liver Regeneration
One of the remarkable properties of the liver is its ability to regenerate. Asparagus racemosus enhances liver regeneration by promoting hepatocyte proliferation. Studies indicate that the root extract contains growth-promoting factors that stimulate DNA synthesis in hepatocytes, accelerating the regeneration process following liver injury.
A study published in Phytotherapy Research demonstrated that rats treated with Asparagus racemosus root extract showed significantly enhanced liver regeneration following partial hepatectomy. The increased rate of hepatocyte proliferation was attributed to the presence of steroidal saponins, which act as growth stimulants.
Enhanced Detoxification and Overall Liver Function
The liver plays a central role in detoxification, converting toxins into less harmful substances that can be easily excreted. Asparagus racemosus contributes to enhanced liver detoxification by upregulating phase I and phase II detoxifying enzymes, including cytochrome P450 enzymes and glutathione S-transferase. These enzymes are essential for the metabolism and excretion of various toxins, including environmental pollutants and drugs.
By enhancing the liver’s detoxification capacity, Asparagus racemosus not only helps protect against toxin-induced liver damage but also supports the body’s natural cleansing processes. Improved detoxification also reduces the burden on the liver, allowing it to maintain optimal function and reducing the risk of damage from accumulated toxins.
Promoting a Healthier Liver Environment
Reduction of Liver Enzyme Levels
Elevated levels of liver enzymes such as alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST) are indicative of liver stress or damage. Asparagus racemosus has been shown to reduce these enzyme levels, suggesting a protective effect on liver cells. In a clinical trial, patients with elevated liver enzyme levels due to NAFLD were given Asparagus racemosus supplementation, resulting in a significant reduction in ALT and AST levels after 8 weeks of treatment.
This reduction in liver enzyme levels indicates decreased liver stress and improved liver cell integrity, underscoring the potential of Asparagus racemosus as a therapeutic supplement for maintaining liver health.
Protection Against Drug-Induced Liver Injury
Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is a common cause of liver dysfunction, often resulting from prolonged use of medications such as acetaminophen or antibiotics. The hepatoprotective effects of Asparagus racemosus extend to protection against DILI, as evidenced by several preclinical studies. The antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of the root extract help mitigate drug-induced oxidative stress and inflammation, reducing the extent of liver injury.
In an animal study, rats pretreated with Asparagus racemosus root extract exhibited significantly less liver damage following exposure to hepatotoxic drugs compared to untreated controls. The protective effect was attributed to the modulation of oxidative stress markers and preservation of liver architecture, further demonstrating the hepatoprotective potential of Asparagus racemosus.
Conclusion: A Holistic Approach to Liver Health
Asparagus racemosus is a powerful natural remedy with proven benefits for liver health. Its hepatoprotective effects stem from its ability to combat oxidative stress, reduce inflammation, regulate lipid metabolism, and inhibit fibrotic processes. These actions collectively contribute to the prevention of NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis, while also promoting liver regeneration and enhancing detoxification processes.
The scientific evidence supporting the use of Asparagus racemosus for liver health is compelling, making it a promising adjunctive therapy for individuals at risk of liver disease or those seeking to maintain optimal liver function. By incorporating Asparagus racemosus into a comprehensive liver health regimen, individuals can benefit from its protective, regenerative, and detoxifying properties, ultimately promoting a healthier liver environment and enhancing the body’s natural ability to heal and cleanse itself.

Astragalus Membranaceus: A Powerful Ally Against NAFLD, Chronic Liver Disease, and Cirrhosis
Astragalus membranaceus, a traditional Chinese medicinal herb, has gained considerable attention in modern medicine for its wide-ranging health benefits, particularly for liver health. Extensive scientific research has validated the hepatoprotective effects of Astragalus membranaceus, with its role in preventing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis being increasingly well-documented. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the proven benefits of Astragalus membranaceus extract in protecting and regenerating the liver while optimizing liver function and supporting detoxification.
Preventing NAFLD and Chronic Liver Disease
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) has emerged as one of the leading causes of chronic liver disease worldwide, linked to obesity, poor diet, and metabolic syndrome. The liver’s fat accumulation in NAFLD leads to inflammation, oxidative stress, and subsequent liver damage. Astragalus membranaceus extract has demonstrated significant promise in preventing NAFLD through various mechanisms, supported by both clinical and preclinical studies.
Reduction of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation
Astragalus contains bioactive compounds such as polysaccharides, flavonoids, and saponins that exhibit potent antioxidant properties. These compounds help neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS), which play a central role in the pathogenesis of NAFLD. Studies have shown that Astragalus significantly reduces oxidative stress markers in the liver, thereby lowering the risk of liver inflammation and damage. The herb’s anti-inflammatory effects are largely attributed to its ability to inhibit key pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α and IL-6, which are known to drive the progression of NAFLD to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).
Improvement of Lipid Metabolism
Astragalus membranaceus has been shown to regulate lipid metabolism, which is critical in the context of NAFLD. Its ability to reduce hepatic lipid accumulation is supported by its action on key enzymes involved in lipid synthesis and degradation. Research indicates that Astragalus upregulates the expression of PPAR-α, a nuclear receptor involved in fatty acid oxidation, while downregulating SREBP-1c, which is responsible for lipogenesis. This dual action helps to reduce fat buildup in the liver, preventing the onset of fatty liver disease.
Protecting Against Liver Fibrosis and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver disease often progresses to liver fibrosis and, ultimately, cirrhosis if left untreated. Astragalus membranaceus plays a crucial role in inhibiting the development of liver fibrosis by interfering with the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), which are central to the fibrotic process.
Inhibition of Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation
Fibrosis occurs when HSCs are activated by liver injury, leading to excessive collagen deposition and scar tissue formation. Studies have demonstrated that Astragalus extract suppresses HSC activation through the inhibition of the TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway, which is a key driver of fibrogenesis. By downregulating TGF-β expression, Astragalus effectively prevents the deposition of extracellular matrix components, thereby reducing fibrosis and the risk of progression to cirrhosis.
Reduction of Hepatic Inflammation
The anti-inflammatory properties of Astragalus are also critical in mitigating the progression of chronic liver disease to cirrhosis. By reducing inflammatory signaling pathways, such as NF-κB, Astragalus helps to maintain a healthier liver environment and minimizes the risk of chronic inflammation, which is a major contributor to fibrosis.
Hepatoprotective Effects: Shielding the Liver from Damage
Astragalus membranaceus is well-recognized for its hepatoprotective properties, making it an effective supplement for reducing damage caused by fatty liver disease and other liver stressors, including alcohol and toxins.
Protection Against Drug-Induced Liver Injury
Certain medications, including acetaminophen and chemotherapy drugs, can induce significant liver injury through oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction. Astragalus membranaceus has been shown to protect against such drug-induced liver damage by enhancing the antioxidant defense system, including the activity of enzymes like superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx). These enzymes play a crucial role in neutralizing ROS, thereby preventing cellular damage and preserving liver function.
Reduction of Hepatic Apoptosis
Apoptosis, or programmed cell death, is a key mechanism by which liver cells are lost during conditions such as NAFLD, hepatitis, and cirrhosis. Astragalus has been shown to reduce hepatic apoptosis by modulating the expression of pro-apoptotic and anti-apoptotic proteins. Specifically, Astragalus upregulates Bcl-2, an anti-apoptotic protein, while downregulating Bax, a pro-apoptotic protein, thereby protecting liver cells from premature death and maintaining liver integrity.
Promoting Liver Regeneration and Enhanced Detoxification
One of the remarkable features of the liver is its ability to regenerate, and Astragalus membranaceus has been shown to support and enhance this regenerative process, contributing to improved overall liver function.
Stimulation of Hepatocyte Proliferation
Hepatocyte proliferation is central to liver regeneration following injury or surgery. Studies indicate that Astragalus membranaceus stimulates hepatocyte proliferation by activating the ERK/MAPK signaling pathway, which plays an essential role in cell cycle progression and proliferation. By promoting the growth of new liver cells, Astragalus helps restore liver mass and function after injury, contributing to faster recovery.
Enhancement of Liver Detoxification
The liver is the body’s primary detoxification organ, responsible for metabolizing toxins and excreting them from the body. Astragalus membranaceus enhances liver detoxification processes by upregulating the expression of phase I and phase II detoxification enzymes, including cytochrome P450 enzymes and glutathione-S-transferase (GST). These enzymes are critical for breaking down toxins into less harmful substances and facilitating their elimination, thus supporting overall detoxification and reducing the liver’s toxic burden.
Supporting Overall Liver Function and a Healthier Liver Environment
Astragalus membranaceus not only provides direct hepatoprotective and regenerative effects but also contributes to a healthier liver environment through multiple ancillary benefits.
Modulation of Immune Function
Astragalus is known for its immunomodulatory properties, which help maintain a balanced immune response in the liver. A hyperactive immune response can lead to autoimmune hepatitis and exacerbate liver damage, while a suppressed immune system can increase susceptibility to infections. Astragalus helps to modulate immune activity by enhancing the activity of natural killer (NK) cells and macrophages, while also regulating the release of cytokines. This balanced immune support helps protect the liver from excessive immune-mediated damage while enhancing its ability to respond to infections.
Anti-Fibrotic and Anti-Steatotic Effects
The combined anti-fibrotic and anti-steatotic effects of Astragalus contribute to maintaining a healthier liver. By reducing lipid accumulation and preventing the activation of fibrotic pathways, Astragalus helps ensure that the liver remains functional and free from excessive scarring or fat deposits. This dual action is particularly beneficial for individuals with metabolic conditions that predispose them to fatty liver and fibrosis.
Conclusion: Astragalus Membranaceus as a Hepatic Protector and Regenerator
Astragalus membranaceus has emerged as a powerful natural remedy for supporting liver health, with its benefits spanning from the prevention of NAFLD and chronic liver disease to the protection against cirrhosis and the promotion of liver regeneration. Its multifaceted mechanisms of action—including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-fibrotic, and hepatoprotective effects—make Astragalus an invaluable ally in maintaining optimal liver function and enhancing the body’s natural detoxification processes.
Scientific evidence supports the use of Astragalus membranaceus as an effective supplement for those at risk of or suffering from liver conditions, providing a natural means to improve liver health, reduce disease progression, and promote a healthier liver environment. By regulating lipid metabolism, reducing oxidative stress, preventing fibrosis, and stimulating hepatocyte proliferation, Astragalus plays a comprehensive role in protecting and rejuvenating the liver.
Incorporating Astragalus membranaceus into a liver health regimen, under the guidance of a healthcare professional, could provide significant benefits for individuals looking to support liver function, prevent liver disease, and enhance the liver’s ability to detoxify the body. As the prevalence of liver conditions such as NAFLD continues to rise, the importance of natural interventions like Astragalus cannot be overstated in promoting long-term liver health and vitality.

Astragalus mongholicus Bunge Extract: A Comprehensive Review of Hepatoprotective Benefits
Astragalus mongholicus Bunge, a key herb in traditional Chinese medicine, has garnered significant scientific attention for its potential hepatoprotective effects. This extract, derived from the roots of the Astragalus plant, exhibits multifaceted benefits that may help prevent and manage liver conditions such as Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. This article provides a scientific synopsis of the current evidence surrounding Astragalus extract’s liver-protective properties, with an emphasis on mechanisms of action, its role in reducing hepatic damage, enhancing liver regeneration, and promoting optimal liver function.
Prevention and Management of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD is one of the most common liver disorders, often associated with metabolic syndromes like obesity and insulin resistance. Research indicates that Astragalus mongholicus extract plays a pivotal role in combating the pathological mechanisms of NAFLD, particularly through its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and lipid-lowering activities.
Astragalus contains polysaccharides, flavonoids, and saponins, which collectively exert significant anti-inflammatory effects by downregulating pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β. These cytokines are major contributors to hepatic inflammation and steatosis (fat accumulation in the liver). By reducing inflammation, Astragalus extract alleviates hepatic stress and prevents the progression from simple steatosis to steatohepatitis, a more severe form of NAFLD.
In addition to its anti-inflammatory properties, Astragalus extract also demonstrates an ability to modulate lipid metabolism. The extract activates AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), a key regulator of cellular energy homeostasis, which promotes fatty acid oxidation and reduces de novo lipogenesis in the liver. By inhibiting excess fat accumulation, Astragalus extract effectively lowers the risk of hepatic steatosis, thus mitigating NAFLD development.
Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis Prevention
Chronic liver disease and cirrhosis are characterized by persistent liver damage that leads to fibrosis and scarring of the liver tissue. Scientific studies suggest that Astragalus extract has potent antifibrotic properties, which are crucial in the prevention of cirrhosis.
The active compounds in Astragalus, particularly astragaloside IV, have been shown to inhibit the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs). HSCs are the primary contributors to liver fibrosis, as they produce excessive extracellular matrix proteins that lead to scar tissue formation. By preventing HSC activation, Astragalus extract helps in reducing fibrosis and slowing the progression of chronic liver disease towards cirrhosis.
Moreover, Astragalus has demonstrated the ability to upregulate the expression of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), enzymes responsible for degrading collagen and other extracellular matrix components. By enhancing MMP activity, Astragalus extract contributes to the breakdown of fibrotic tissue, thus aiding in the prevention and management of liver fibrosis.
Hepatoprotective Effects Against Fatty Liver and Other Liver Stressors
Astragalus mongholicus Bunge extract is also known for its general hepatoprotective effects, helping to shield the liver from a range of stressors including fatty liver, toxins, and oxidative stress. The antioxidant properties of Astragalus are primarily attributed to its high content of flavonoids and polysaccharides, which scavenge reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reduce oxidative stress in liver cells.
Oxidative stress is a major driver of liver injury, contributing to cellular damage and apoptosis (cell death). By neutralizing ROS, Astragalus extract protects hepatocytes (liver cells) from oxidative damage, thereby preserving liver function and preventing further deterioration. This is particularly beneficial in cases of fatty liver disease, where oxidative stress exacerbates inflammation and fibrosis.
In addition, studies have indicated that Astragalus extract may enhance the liver’s detoxification capacity by increasing the activity of antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase, and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px). These enzymes play a crucial role in neutralizing harmful substances and promoting a healthier liver environment.
Promotion of Liver Regeneration and Improved Liver Function
One of the remarkable benefits of Astragalus extract is its ability to promote liver regeneration. The liver is unique in its capacity to regenerate after injury, and Astragalus extract supports this natural process by modulating various cellular pathways involved in liver repair and regeneration.
Research has shown that Astragalus extract can stimulate hepatocyte proliferation, which is essential for liver regeneration following injury or partial hepatectomy (surgical removal of part of the liver). The extract achieves this by activating growth factors such as hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and epidermal growth factor (EGF), which play a critical role in cell proliferation and tissue repair.
Astragalus also exerts immunomodulatory effects that are beneficial for liver health. By modulating immune responses, Astragalus extract helps maintain a balanced inflammatory environment that is conducive to liver regeneration. It reduces the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines while promoting anti-inflammatory cytokines, creating optimal conditions for liver repair.
Enhancing the Body’s Natural Detoxification Processes
Astragalus mongholicus Bunge extract is recognized for its role in enhancing the body’s natural detoxification processes, which are crucial for maintaining overall liver health. The liver is the primary organ responsible for detoxifying harmful substances, including drugs, alcohol, and metabolic byproducts. Astragalus extract supports these detoxification pathways through its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
The extract has been found to enhance phase II detoxification enzymes, such as glutathione-S-transferase (GST), which conjugates toxic substances, making them easier to eliminate from the body. By boosting the activity of these enzymes, Astragalus extract helps reduce the burden on the liver, facilitating more efficient detoxification and promoting a healthier liver environment.
Mechanisms of Action: Scientific Insights
Anti-Inflammatory Mechanisms: Astragalus extract inhibits the NF-κB signaling pathway, a key regulator of inflammation. By blocking NF-κB activation, Astragalus reduces the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, thereby mitigating hepatic inflammation and protecting against liver damage.
Antioxidant Mechanisms: The flavonoids and polysaccharides in Astragalus extract enhance the antioxidant defense system by increasing the levels of SOD, catalase, and GSH-Px. These antioxidants play a crucial role in neutralizing ROS and preventing oxidative damage to hepatocytes.
Antifibrotic Mechanisms: Astragaloside IV, one of the primary active components of Astragalus, inhibits the TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway, which is involved in the activation of HSCs and the development of fibrosis. By blocking this pathway, Astragalus extract prevents the excessive deposition of extracellular matrix proteins, thereby reducing fibrosis.
Lipid Metabolism Regulation: Astragalus extract activates AMPK, which in turn inhibits the synthesis of fatty acids and promotes their oxidation. This helps in reducing hepatic fat accumulation and prevents the progression of NAFLD.
Liver Regeneration: Astragalus stimulates the release of HGF and EGF, which promote hepatocyte proliferation and liver tissue repair. Additionally, its immunomodulatory effects create a favorable environment for liver regeneration by balancing pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines.
Conclusion: The Role of Astragalus Extract in Liver Health
Astragalus mongholicus Bunge extract presents a promising natural intervention for the prevention and management of various liver conditions, including NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Its hepatoprotective properties are supported by a combination of anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antifibrotic, and regenerative mechanisms, all of which contribute to improved liver function and a healthier hepatic environment.
The scientific evidence highlights the potential of Astragalus extract to not only protect the liver from damage but also to support its natural regenerative processes and enhance detoxification capacity. By reducing inflammation, oxidative stress, and fibrosis, Astragalus extract helps maintain optimal liver function and prevents the progression of liver disease.
For individuals seeking to support their liver health, Astragalus mongholicus Bunge extract represents a valuable addition to a comprehensive liver care regimen. However, it is important to note that while the current evidence is promising, further clinical studies are needed to fully establish the efficacy and safety of Astragalus extract in human populations. As always, consulting with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement is recommended, particularly for individuals with pre-existing health conditions or those taking medications.
Key Takeaways
Prevents NAFLD: Astragalus extract reduces hepatic fat accumulation and inflammation through AMPK activation and anti-inflammatory effects.
Protects Against Chronic Liver Disease: The antifibrotic properties of Astragalus help prevent fibrosis and cirrhosis by inhibiting HSC activation and promoting MMP activity.
Hepatoprotective Effects: Its antioxidant properties protect hepatocytes from oxidative damage, while its detoxification support enhances liver health.
Promotes Liver Regeneration: Astragalus stimulates hepatocyte proliferation and modulates immune responses to support liver repair.
Supports Detoxification: By enhancing phase II detoxification enzymes, Astragalus facilitates the efficient elimination of toxins, promoting overall liver function.
Astragalus mongholicus Bunge extract thus emerges as a scientifically backed, multi-targeted natural agent for liver health, offering significant benefits in managing and preventing liver-related disorders while enhancing the body’s detoxification processes.

The Proven Benefits of Beta vulgaris Linn. (BV) Leaves in Preventing Liver Diseases
Beta vulgaris Linn. (commonly known as beetroot) leaves, belonging to the Chenopodiaceae family, have emerged as a promising natural remedy in the prevention and management of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Beyond their reputation as a nutritious leafy vegetable, beet leaves are rich in bioactive compounds that possess hepatoprotective properties, aiding in liver regeneration and promoting overall liver health. This article provides a comprehensive analysis of the scientific evidence supporting these benefits, delving into the mechanisms of action and health effects that make beet leaves a valuable ally for liver wellness.
Hepatoprotective Effects of Beta vulgaris Linn. Leaves
Beet leaves are loaded with a wealth of antioxidants, vitamins, minerals, and nitrates that confer significant hepatoprotective effects. These effects primarily stem from their ability to neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative stress—a key factor in liver injury. The phenolic compounds, including flavonoids, are particularly effective in preventing lipid peroxidation, which is the process by which free radicals attack fats in liver cells, leading to inflammation and cell damage. Studies have shown that flavonoids like quercetin and kaempferol, present in beet leaves, directly contribute to reducing inflammation and oxidative damage in the liver.
A peer-reviewed study published in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology demonstrated that extracts from Beta vulgaris leaves exhibit potent hepatoprotective activity, reducing markers of liver damage such as alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) in animal models subjected to fatty liver induction. The reduction in these enzymes is indicative of reduced liver injury, showcasing the protective effects of beet leaves in preventing liver stress caused by excessive fat accumulation.
Prevention of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD is a widespread condition characterized by excessive fat accumulation in the liver, often associated with obesity, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome. Beta vulgaris Linn. leaves play an instrumental role in preventing and managing NAFLD through their ability to modulate lipid metabolism, improve insulin sensitivity, and enhance liver antioxidant defenses.
The nitrates in beet leaves have been shown to promote nitric oxide production, improving vascular function and insulin sensitivity. Improved insulin sensitivity helps regulate glucose and lipid levels, reducing the risk of fat buildup in the liver. Additionally, the presence of betaine—a compound naturally found in beet leaves—supports liver health by promoting fat metabolism and preventing the accumulation of lipids within liver cells. Betaine acts as a methyl donor, facilitating the process of methylation, which is essential for liver detoxification and lipid metabolism.
A randomized controlled trial published in the Nutrition & Metabolism journal highlighted that betaine supplementation led to a significant reduction in hepatic fat content in patients with NAFLD. This suggests that incorporating beet leaves into the diet may have a similar effect, owing to their natural betaine content, thereby helping to manage or even reverse fatty liver conditions.
Reducing Liver Damage and Enhancing Regeneration
The hepatoprotective properties of Beta vulgaris Linn. leaves extend beyond prevention, contributing to reducing existing liver damage and supporting liver regeneration. The bioactive compounds in beet leaves stimulate the liver’s natural repair mechanisms by enhancing the activity of hepatic stellate cells, which play a pivotal role in liver tissue regeneration.
Antioxidants such as vitamin C, betalains, and polyphenols are abundant in beet leaves, and they collectively reduce oxidative stress and inflammation—two major contributors to liver fibrosis and cirrhosis. Betalains, in particular, have been shown to exert anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic effects, helping to mitigate the progression of liver fibrosis. The presence of these antioxidants aids in neutralizing reactive oxygen species (ROS) and maintaining a balanced redox state, which is crucial for liver cell survival and regeneration.
Research published in the World Journal of Gastroenterology demonstrated that betalain-rich extracts from beet leaves significantly reduced collagen deposition in liver tissues, indicating a potential to prevent or reverse liver fibrosis. This antifibrotic effect is essential for maintaining healthy liver architecture and preventing the progression of chronic liver disease.
Promoting Overall Liver Function and Detoxification
Beta vulgaris Linn. leaves also contribute to overall liver function by enhancing the liver’s detoxification capabilities and improving bile production. The liver is the body’s primary detox organ, responsible for filtering toxins from the bloodstream and converting them into less harmful substances for excretion. Beet leaves support this detoxification process through their high antioxidant content and their ability to upregulate the activity of detoxifying enzymes such as glutathione peroxidase, catalase, and superoxide dismutase.
Glutathione, often referred to as the body’s master antioxidant, plays a critical role in liver detoxification. Beta vulgaris leaves have been shown to increase glutathione levels in the liver, thereby enhancing the liver’s capacity to detoxify harmful substances, including heavy metals and environmental toxins. A study featured in the Journal of Medicinal Food reported that animals fed with beet leaf extracts exhibited increased activity of phase II detoxification enzymes, which are vital for conjugating and eliminating toxins from the body.
Moreover, beet leaves promote bile production, which is essential for the digestion and absorption of dietary fats. Bile also aids in the excretion of waste products, including bilirubin and excess cholesterol. The presence of magnesium and potassium in beet leaves further supports liver function by maintaining electrolyte balance and aiding enzymatic activity crucial for metabolic processes.
Mechanisms of Action: How Beet Leaves Protect the Liver
The hepatoprotective effects of Beta vulgaris Linn. leaves can be attributed to multiple mechanisms of action, including:
Antioxidant Activity: The high concentration of antioxidants such as flavonoids, betalains, and vitamin C neutralizes ROS, preventing oxidative stress-induced liver injury.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Compounds like betalains and polyphenols exhibit potent anti-inflammatory properties, reducing inflammation in liver tissues and preventing the progression of liver diseases such as NAFLD and cirrhosis.
Modulation of Lipid Metabolism: Betaine in beet leaves plays a crucial role in lipid metabolism by reducing hepatic lipid accumulation and promoting the conversion of fats into energy, thereby preventing fatty liver.
Enhanced Detoxification: Beet leaves upregulate the production of detoxifying enzymes and increase glutathione levels, enhancing the liver’s ability to process and eliminate toxins.
Fibrosis Prevention: The antifibrotic effects of betalains help in reducing collagen buildup, preventing liver fibrosis and maintaining healthy liver tissue architecture.
Beta vulgaris Linn. Leaves for a Healthier Liver Environment
Incorporating Beta vulgaris Linn. leaves into the diet can contribute significantly to creating a healthier liver environment, promoting liver function, and enhancing the body’s natural detoxification processes. The combination of antioxidants, anti-inflammatory agents, and hepatoprotective compounds work synergistically to maintain liver health, prevent disease progression, and support liver regeneration.
The chlorophyll content in beet leaves further adds to their detoxifying properties by binding to and eliminating heavy metals and other toxins from the body. Chlorophyll has also been linked to reducing the risk of aflatoxin-induced liver damage, making beet leaves an excellent addition to a diet focused on long-term liver health.
Conclusion
Beta vulgaris Linn. (beet) leaves are a potent natural remedy with proven benefits for liver health, including the prevention and management of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Their hepatoprotective effects are backed by robust scientific evidence, highlighting their ability to reduce oxidative stress, modulate lipid metabolism, prevent fibrosis, and enhance liver detoxification and regeneration.
By incorporating beet leaves into a balanced diet, individuals may benefit from improved liver function, reduced risk of liver diseases, and enhanced detoxification processes. As the body’s central organ for metabolism and detoxification, the liver stands to gain immensely from the bioactive compounds present in beet leaves, making them an essential component of a liver-friendly diet.
For those seeking a natural way to boost liver health, the inclusion of Beta vulgaris Linn. leaves can provide a scientifically validated approach to enhancing liver function, reducing liver stress, and supporting the liver’s capacity to regenerate and detoxify effectively. As always, individuals should consult healthcare professionals before making significant changes to their diet, especially if they have pre-existing liver conditions or are taking medications that affect liver function.

Betalain: Proven Benefits for Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, Chronic Liver Disease, and Liver Regeneration
Betalain, a bioactive pigment found primarily in beets and other colorful fruits and vegetables, has garnered increasing attention in recent years for its hepatoprotective properties. Scientific studies have identified betalain as a powerful ally in the fight against liver ailments, including Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Additionally, betalain promotes liver regeneration and enhances overall liver function, contributing to the body’s natural detoxification processes. Below, we provide an in-depth exploration of the scientific evidence behind these benefits, mechanisms of action, and their significance in managing liver health.
1. Betalain and Prevention of NAFLD and Chronic Liver Disease
NAFLD is characterized by the accumulation of fat in liver cells, which can progress to chronic inflammation, fibrosis, and eventually cirrhosis. The liver damage that results from NAFLD often remains asymptomatic until it reaches a more advanced stage, making prevention and early intervention critical. Research suggests that betalain plays an essential role in addressing key contributors to NAFLD, such as oxidative stress, lipid accumulation, and inflammation.
Betalain’s strong antioxidant properties help prevent the progression of NAFLD by neutralizing free radicals that damage liver cells. Studies have confirmed that betalain significantly reduces oxidative stress markers and improves the liver’s antioxidant defenses. Betalain’s ability to stabilize reactive oxygen species (ROS) not only prevents lipid peroxidation but also reduces cellular damage, which is a key mechanism underlying its preventative benefits for chronic liver disease.
Furthermore, betalain has been shown to modulate lipid metabolism in the liver, reducing triglyceride accumulation, which is a defining feature of NAFLD. Animal studies have reported that supplementation with betalain resulted in a decrease in hepatic triglyceride levels and improved liver enzyme profiles, pointing to its potential as a natural therapeutic option to prevent fatty liver disease.
2. Hepatoprotective Effects: Reducing Liver Damage
Betalain’s hepatoprotective effects stem from its capacity to mitigate cellular stress and inflammation in the liver. Inflammation is a core component of liver injury, and if left unchecked, it can exacerbate liver fibrosis and lead to cirrhosis. Betalain combats these processes through its anti-inflammatory properties, which directly interfere with key inflammatory signaling pathways.
Research has demonstrated that betalain inhibits pro-inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6), both of which are strongly implicated in liver inflammation and fibrosis. By reducing the expression of these cytokines, betalain helps to limit inflammatory damage to liver tissues, which is critical for preventing progression from NAFLD to more severe chronic liver conditions.
Moreover, betalain also has a protective effect against other liver stressors, such as alcohol consumption, toxins, and drugs that may exacerbate liver damage. In animal models, betalain supplementation was found to decrease markers of liver damage induced by alcohol and environmental toxins. Betalain preserves the integrity of hepatocytes by modulating detoxification enzymes and preventing cell apoptosis.
3. Betalain and Liver Regeneration
The liver’s unique capacity to regenerate following damage is crucial for its function, especially in patients suffering from liver disease. Betalain has been shown to support this regenerative process by enhancing cellular renewal and promoting a favorable environment for liver repair.
Studies have shown that betalain stimulates the proliferation of hepatocytes, the liver cells responsible for maintaining normal liver function. This regenerative effect may be attributed to betalain’s modulation of cellular signaling pathways involved in cell proliferation and growth. By increasing the expression of growth factors, such as hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), betalain aids in accelerating the regeneration of damaged liver tissues.
In addition, betalain’s antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties create an optimal environment for liver healing. The reduced oxidative stress and inflammation allow the liver to focus on regeneration rather than fighting ongoing damage. This makes betalain an essential nutrient for supporting recovery from liver injuries and improving liver function in chronic disease settings.
4. Enhancing Overall Liver Function and Detoxification
Betalain not only helps mitigate liver damage but also plays a key role in enhancing overall liver function and detoxification. A healthy liver is crucial for metabolizing toxins and drugs, as well as for synthesizing proteins and maintaining metabolic balance. Betalain supports these functions in several ways:
4.1. Antioxidant Activity
Betalain’s well-documented antioxidant activity is perhaps its most significant contribution to liver health. As a potent antioxidant, betalain scavenges free radicals and enhances the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes, such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase, and glutathione peroxidase. By augmenting the liver’s natural defense mechanisms, betalain helps protect hepatocytes from oxidative damage, ensuring that liver function is maintained even in the face of stressors.
4.2. Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Inflammation is a primary driver of liver dysfunction. Chronic inflammation can impair the liver’s ability to detoxify the body, leading to a buildup of harmful substances. Betalain reduces chronic inflammation by downregulating the expression of inflammatory mediators, thereby reducing the liver’s workload and allowing it to perform its detoxification role more efficiently.
4.3. Detoxification Support
The liver’s detoxification process involves two main phases, known as Phase I and Phase II detoxification. Betalain has been shown to support these detoxification pathways, particularly Phase II, which involves conjugation reactions that make toxins water-soluble for excretion. Betalain enhances the activity of glutathione, one of the liver’s primary detoxifying agents, thus contributing to more efficient removal of toxins from the body.
5. Scientific Evidence Supporting Betalain’s Hepatoprotective Effects
Numerous peer-reviewed studies provide strong evidence for betalain’s benefits in preventing and managing liver disease. Animal models, in particular, have demonstrated the compound’s ability to reduce fat accumulation, decrease oxidative damage, and improve inflammatory profiles in the liver.
In a 2017 study published in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, researchers found that betalain significantly reduced liver fat accumulation and inflammation in mice fed a high-fat diet, suggesting that betalain could be an effective intervention for NAFLD. Another study, published in Food & Function in 2020, showed that betalain supplementation led to improved liver enzyme markers, such as ALT and AST, which are indicative of reduced liver damage.
Clinical studies are still limited but promising. In a small clinical trial, participants with early-stage NAFLD who were supplemented with betalain-rich beetroot extract showed improvements in liver enzyme levels and reductions in inflammatory biomarkers. These findings indicate the potential for betalain to be incorporated as a natural supplement in liver health management.
6. Mechanisms of Action
The beneficial effects of betalain on liver health can be attributed to several interrelated mechanisms:
Antioxidant Defense: Betalain neutralizes ROS and upregulates endogenous antioxidant enzymes, thereby reducing oxidative stress and preventing lipid peroxidation in liver cells.
Anti-Inflammatory Action: By downregulating inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α and IL-6, betalain reduces chronic inflammation, which is a key contributor to liver injury and fibrosis.
Lipid Metabolism Regulation: Betalain helps regulate lipid metabolism by reducing triglyceride accumulation in the liver, which is crucial for preventing NAFLD.
Cellular Regeneration: Betalain stimulates hepatocyte proliferation and enhances the production of growth factors that promote liver regeneration, aiding in the recovery from liver damage.
Support for Detoxification: Betalain enhances Phase II detoxification processes and boosts glutathione activity, which is essential for efficient toxin removal.
7. Conclusion: Betalain for a Healthier Liver
Betalain stands out as a promising natural compound for promoting liver health, with its range of hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory, and regenerative properties. By combating oxidative stress, reducing inflammation, supporting detoxification, and enhancing liver regeneration, betalain addresses the multifaceted challenges associated with liver diseases like NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis.
The scientific evidence available supports the incorporation of betalain-rich foods, such as beets, into the diet for individuals seeking to prevent liver disease or manage existing conditions. As research continues, betalain may soon become a mainstream component of liver health supplements, offering a natural, effective way to enhance liver function and support overall health.
A healthy liver is crucial for detoxifying the body, regulating metabolism, and maintaining overall well-being. By incorporating betalain into your dietary regimen, you can take proactive steps toward a healthier liver and a healthier you.

Bupleurum Chinense Root Extract: Comprehensive Overview of Its Hepatoprotective Benefits for Liver Health
Bupleurum chinense, commonly known as Bupleurum, is a medicinal herb that has been used in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) for centuries. In recent years, Bupleurum chinense root extract has gained attention due to its powerful hepatoprotective effects and its role in preventing and managing liver conditions such as Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. This scientific synopsis explores the proven benefits of Bupleurum chinense root extract, highlighting its hepatoprotective mechanisms, liver regeneration support, and overall enhancement of liver function.
Bupleurum Chinense and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD is a growing public health concern, often linked to obesity, metabolic syndrome, and insulin resistance. Bupleurum chinense root extract has demonstrated promising effects in preventing and managing NAFLD. The active compounds in Bupleurum, particularly saikosaponins, have been shown to modulate lipid metabolism and reduce hepatic fat accumulation.
Mechanisms of Action Against NAFLD
Reduction of Lipid Accumulation: Bupleurum chinense reduces the accumulation of triglycerides and cholesterol in the liver by modulating key enzymes involved in lipid metabolism. Studies have demonstrated that saikosaponins can activate AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), which plays a vital role in regulating lipid metabolism and reducing lipid synthesis in hepatocytes. By enhancing AMPK activity, Bupleurum effectively inhibits the development of NAFLD.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Chronic inflammation is a critical factor in the progression of NAFLD. Bupleurum chinense exhibits anti-inflammatory properties by downregulating pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6. The modulation of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) pathways further contributes to its ability to mitigate liver inflammation, reducing the risk of progression to more severe liver damage.
Oxidative Stress Reduction: Oxidative stress plays a pivotal role in the progression of NAFLD to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Bupleurum chinense root extract contains antioxidants that help reduce oxidative stress by enhancing the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes like superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase. These antioxidants neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS), thus protecting hepatocytes from oxidative damage.
Hepatoprotective Effects in Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver disease and cirrhosis are often the results of sustained liver injury, whether due to viral infections, alcohol abuse, or other factors. Bupleurum chinense root extract has been shown to have hepatoprotective effects that help prevent liver damage and promote liver health even in cases of chronic disease.
Mechanisms of Hepatoprotection
Anti-Fibrotic Effects: Liver fibrosis is a hallmark of chronic liver disease that can lead to cirrhosis if left unchecked. Bupleurum chinense root extract has shown anti-fibrotic effects by inhibiting the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), which are the primary drivers of collagen deposition in the liver. Saikosaponins in Bupleurum help in regulating transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) signaling, which plays a crucial role in liver fibrosis.
Reduction of Hepatocyte Apoptosis: Bupleurum chinense helps reduce hepatocyte apoptosis (programmed cell death), which is often triggered by chronic liver injury. By modulating mitochondrial pathways and reducing oxidative stress, Bupleurum protects liver cells from premature death, thereby maintaining overall liver function and preventing disease progression.
Immune Modulation: Chronic liver disease often involves an imbalance in immune responses, leading to ongoing inflammation and tissue damage. Bupleurum chinense root extract helps modulate the immune system by balancing Th1/Th2 responses, thus reducing autoimmune-mediated liver damage and promoting a more regulated immune response that minimizes liver injury.
Bupleurum Chinense and Liver Regeneration
The liver has a remarkable ability to regenerate after injury, and Bupleurum chinense root extract plays a role in enhancing this natural regenerative capacity. Liver regeneration is crucial for recovering from conditions such as cirrhosis, hepatitis, and surgical resection.
Mechanisms Supporting Liver Regeneration
Promotion of Hepatocyte Proliferation: Bupleurum chinense has been found to promote the proliferation of hepatocytes, the primary cells responsible for liver regeneration. Studies indicate that saikosaponins stimulate hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) signaling, which plays a vital role in initiating and sustaining liver regeneration.
Stimulation of Growth Factors: Bupleurum chinense also enhances the production of other growth factors, such as epidermal growth factor (EGF) and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), which are involved in tissue repair and regeneration. These growth factors contribute to accelerating the recovery of liver tissue following injury.
Reduction of Fibrotic Tissue: By reducing liver fibrosis, Bupleurum chinense creates a more conducive environment for liver regeneration. Fibrotic tissue impairs the liver’s regenerative capacity, and the anti-fibrotic properties of Bupleurum help restore the liver’s ability to regenerate healthy tissue.
Enhancement of Liver Function and Detoxification
A healthy liver is essential for the body’s natural detoxification processes, as it filters toxins, metabolizes drugs, and aids in digestion. Bupleurum chinense root extract has several benefits that enhance overall liver function and promote a healthier liver environment.
Mechanisms of Enhancing Liver Function
Improvement of Bile Flow: Bupleurum chinense has been traditionally used to improve bile flow, which is crucial for the digestion and absorption of fats. By promoting bile secretion, Bupleurum helps prevent cholestasis, a condition characterized by impaired bile flow that can lead to liver damage.
Antioxidant Protection: The liver is constantly exposed to various toxins and metabolic by-products that can generate oxidative stress. The antioxidant compounds in Bupleurum chinense root extract help protect liver cells from damage by neutralizing free radicals. This protection supports the liver’s detoxification pathways, ensuring that it can efficiently process and eliminate harmful substances from the body.
Reduction of Endotoxemia: Endotoxemia, characterized by the presence of endotoxins in the bloodstream, can lead to liver inflammation and damage. Bupleurum chinense has been shown to reduce intestinal permeability, thereby preventing the translocation of endotoxins from the gut to the liver. This helps in reducing liver inflammation and supporting overall liver health.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Bupleurum Chinense Benefits
Several studies have provided evidence for the hepatoprotective effects of Bupleurum chinense root extract. The saikosaponins, which are the primary active components, have been extensively studied for their liver-protective properties.
Animal Studies on NAFLD: In animal models of NAFLD, Bupleurum chinense root extract has been shown to significantly reduce hepatic lipid accumulation, inflammation, and oxidative stress. These studies indicate that Bupleurum can effectively prevent the progression of simple steatosis to more severe forms of liver disease, such as NASH.
Clinical Trials on Liver Health: Clinical trials involving patients with chronic liver disease have shown that Bupleurum chinense, often used as part of a herbal formulation, can improve liver enzyme levels, reduce fibrosis markers, and enhance overall liver function. These trials provide preliminary evidence for the use of Bupleurum in managing chronic liver conditions.
In Vitro Studies on Hepatocyte Regeneration: In vitro studies have demonstrated that Bupleurum chinense root extract can stimulate hepatocyte proliferation and reduce apoptosis. These findings support its role in enhancing liver regeneration and maintaining liver health following injury.
Conclusion
Bupleurum chinense root extract offers a wide range of scientifically supported benefits for liver health, making it a valuable tool in preventing and managing liver conditions such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Its hepatoprotective effects are primarily attributed to its ability to modulate lipid metabolism, reduce inflammation, inhibit fibrosis, and promote liver regeneration.
The mechanisms of action of Bupleurum chinense are well-documented, including the activation of AMPK for lipid regulation, modulation of inflammatory pathways, antioxidant protection, and promotion of growth factors that aid in liver regeneration. By enhancing bile flow, reducing oxidative stress, and supporting the liver’s natural detoxification processes, Bupleurum contributes to overall liver function and a healthier internal environment.
While more clinical studies are needed to fully establish its efficacy in human populations, the existing evidence points to Bupleurum chinense as a promising natural remedy for enhancing liver health and managing various liver-related conditions. Its diverse mechanisms of action make it an important herb in the arsenal for liver protection, regeneration, and overall health maintenance.
Bupleurum chinense root extract is not just a traditional remedy but a scientifically supported option for those seeking to improve liver health naturally. By leveraging its hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory, anti-fibrotic, and regenerative properties, individuals may experience enhanced liver function and better overall well-being.

Cassia Seed Extract: Proven Benefits for Preventing NAFLD, Chronic Liver Disease, and Enhancing Liver Health
Cassia seed extract, derived from the seeds of Cassia obtusifolia and Cassia tora, has been gaining attention for its numerous health benefits, particularly in supporting liver health. This natural extract offers a range of hepatoprotective effects that can help prevent Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. It has also been found to aid in liver regeneration and improve overall liver function, promoting a healthier environment for the body’s natural detoxification processes. This comprehensive synopsis delves into the scientifically supported benefits of cassia seed extract, emphasizing its mechanisms of action and the evidence supporting its use in liver health.
Understanding NAFLD and Chronic Liver Diseases
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is a common liver condition characterized by excessive fat accumulation in liver cells, which is not caused by alcohol consumption. It is often associated with obesity, metabolic syndrome, and type 2 diabetes. If left unmanaged, NAFLD can progress to more severe forms of liver damage, including non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), fibrosis, cirrhosis, and even liver cancer. Chronic liver diseases can have a profound impact on overall health, leading to reduced liver function, impaired detoxification, and other systemic complications.
Cassia seed extract has been found to play a significant role in preventing and managing NAFLD and other liver conditions by offering hepatoprotective properties, reducing liver stress, and enhancing regenerative processes. The following sections will explore these benefits in detail.
Hepatoprotective Effects of Cassia Seed Extract
Cassia seed extract is known for its potent hepatoprotective effects, which help protect liver cells from damage caused by various stressors, including fatty liver, toxins, and oxidative stress. Several mechanisms contribute to these protective effects:
1. Antioxidant Activity
One of the primary mechanisms by which cassia seed extract exerts its hepatoprotective effects is through its antioxidant properties. The liver is particularly vulnerable to oxidative stress due to its role in detoxification and metabolizing toxic substances. Cassia seeds contain a variety of bioactive compounds, including anthraquinones, flavonoids, and polysaccharides, which exhibit strong antioxidant activity. These compounds help neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative stress in liver tissues, thereby preventing cellular damage and inflammation.
Studies have shown that cassia seed extract can significantly increase the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes, such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase, and glutathione peroxidase, which play a critical role in maintaining cellular redox balance. By boosting these enzymes, cassia seed extract helps protect liver cells from oxidative damage, a key factor in the progression of NAFLD and other liver diseases.
2. Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Chronic inflammation is a major contributor to liver damage and the progression of NAFLD to more severe forms of liver disease. Cassia seed extract has been found to possess significant anti-inflammatory properties, which can help reduce inflammation in the liver. The extract inhibits the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β), which are known to contribute to liver inflammation and fibrosis.
By modulating inflammatory pathways, cassia seed extract helps reduce the overall inflammatory burden on the liver, thereby preventing the progression of NAFLD to more advanced stages, such as NASH and cirrhosis. This anti-inflammatory effect also helps mitigate liver injury caused by other factors, such as alcohol, drugs, and environmental toxins.
3. Lipid-Lowering Effects
Excessive fat accumulation in the liver is a hallmark of NAFLD, and reducing hepatic lipid content is crucial for preventing disease progression. Cassia seed extract has been shown to have lipid-lowering effects, which can help reduce fat accumulation in the liver. The extract works by regulating lipid metabolism, promoting the breakdown of fatty acids, and inhibiting the synthesis of triglycerides in the liver.
Animal studies have demonstrated that cassia seed extract can reduce serum levels of total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, and triglycerides, while increasing high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol. By improving lipid profiles and reducing hepatic fat accumulation, cassia seed extract helps prevent the onset and progression of NAFLD.
Reducing Liver Damage and Enhancing Liver Regeneration
Cassia seed extract not only helps prevent liver damage but also plays a role in reducing existing liver injury and promoting liver regeneration. The liver has a remarkable capacity to regenerate itself, and cassia seed extract can enhance this regenerative process, contributing to improved liver function and recovery from damage.
1. Protection Against Hepatotoxins
The liver is constantly exposed to various toxins, including alcohol, drugs, and environmental pollutants, which can cause liver damage and impair its function. Cassia seed extract has been found to protect the liver from damage caused by these hepatotoxins. The extract works by enhancing the liver’s detoxification capacity and promoting the elimination of harmful substances from the body.
In animal models, cassia seed extract has been shown to reduce liver enzyme levels, such as alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), which are markers of liver injury. By reducing these enzyme levels, cassia seed extract indicates a reduction in liver damage and improved liver health.
2. Promoting Liver Regeneration
Liver regeneration is a critical aspect of recovery from liver injury, and cassia seed extract has been found to support this process. The extract contains bioactive compounds that promote the proliferation of hepatocytes, the primary cells responsible for liver regeneration. By enhancing hepatocyte proliferation, cassia seed extract helps accelerate the repair of damaged liver tissue and restore normal liver function.
Additionally, cassia seed extract has been shown to modulate growth factors, such as hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), which play a key role in liver regeneration. By promoting the release of these growth factors, cassia seed extract contributes to the regeneration and repair of liver tissue, helping the liver recover from damage caused by NAFLD, toxins, and other stressors.
Enhancing Liver Function and Detoxification
The liver plays a central role in detoxifying the body by metabolizing and eliminating harmful substances. Cassia seed extract has been found to enhance liver function and support the body’s natural detoxification processes, leading to a healthier liver environment and improved overall health.
1. Supporting Bile Production and Flow
Bile production is an essential function of the liver, as bile helps digest fats and eliminate waste products from the body. Cassia seed extract has been found to support bile production and improve bile flow, which is crucial for maintaining liver health and preventing the buildup of toxins. By promoting healthy bile flow, cassia seed extract helps enhance the liver’s detoxification capacity and prevent the accumulation of harmful substances.
2. Modulating Liver Enzymes
Liver enzymes play a critical role in the detoxification process, and cassia seed extract has been found to modulate the activity of these enzymes. The extract helps upregulate phase I and phase II detoxification enzymes, which are involved in the metabolism and elimination of toxins. By enhancing the activity of these enzymes, cassia seed extract supports the liver’s ability to detoxify the body and maintain overall health.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Cassia Seed Extract’s Benefits
The hepatoprotective effects of cassia seed extract have been supported by a growing body of scientific evidence. Numerous in vitro and in vivo studies have demonstrated the antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, lipid-lowering, and hepatoprotective properties of cassia seed extract, highlighting its potential as a natural remedy for liver health.
For example, a study published in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology investigated the hepatoprotective effects of cassia seed extract in a rat model of NAFLD. The researchers found that the extract significantly reduced hepatic fat accumulation, decreased liver enzyme levels, and improved antioxidant status, indicating its potential for preventing and managing NAFLD.
Another study published in Phytotherapy Research examined the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of cassia seed extract in a mouse model of liver injury induced by carbon tetrachloride (CCl4). The results showed that the extract effectively reduced oxidative stress and inflammation in the liver, highlighting its protective effects against hepatotoxicity.
These studies, along with others, provide strong evidence for the use of cassia seed extract in promoting liver health and preventing liver diseases. However, it is important to note that most of the current evidence is based on preclinical studies, and further clinical trials are needed to confirm the efficacy of cassia seed extract in humans.
Conclusion: Cassia Seed Extract as a Natural Solution for Liver Health
Cassia seed extract offers a range of scientifically supported benefits for liver health, including preventing NAFLD, reducing liver inflammation, protecting against hepatotoxins, and promoting liver regeneration. Its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and lipid-lowering properties make it a promising natural remedy for managing and improving liver conditions such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis.
By enhancing liver function and supporting the body’s natural detoxification processes, cassia seed extract helps create a healthier liver environment and contributes to overall well-being. While more clinical research is needed to fully understand its effects in humans, the existing evidence suggests that cassia seed extract holds great potential as a natural solution for liver health.
For individuals looking to support their liver health, cassia seed extract may be a valuable addition to their wellness routine. As always, it is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement to ensure safety and efficacy, especially for those with pre-existing health conditions or who are taking medications.

Catechin: Proven Benefits for Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, Chronic Liver Disease, and Cirrhosis
Catechin, a naturally occurring polyphenol found predominantly in green tea, has been scientifically recognized for its remarkable hepatoprotective properties. Its positive effects in preventing and managing liver conditions such as Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis are backed by peer-reviewed research. This synopsis provides an in-depth analysis of catechin’s role in liver health, including its benefits for liver regeneration, reducing liver damage, and enhancing overall liver function.
Hepatoprotective Effects of Catechin in NAFLD
NAFLD is characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver, unlinked to excessive alcohol consumption. This condition can progress to more severe forms, such as non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), fibrosis, cirrhosis, and even liver cancer. Scientific studies have demonstrated that catechin, particularly epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), is effective in addressing NAFLD due to its potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
Catechin combats oxidative stress—a key driver of NAFLD—by neutralizing free radicals, thereby reducing lipid peroxidation in liver cells. Additionally, catechins inhibit the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6, which play a significant role in hepatic inflammation. Research indicates that catechin also modulates key metabolic pathways, enhancing lipid metabolism while reducing fat accumulation within hepatocytes. This modulation occurs through the activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), which helps regulate lipid metabolism by promoting fatty acid oxidation and reducing hepatic triglyceride synthesis.
Preventing Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver disease can arise from persistent liver injury due to factors like excessive fat accumulation, infections, or toxins. Over time, this can lead to fibrosis, where excessive connective tissue replaces healthy liver cells, eventually progressing to cirrhosis. Catechin plays a crucial role in preventing this progression by acting on multiple fronts.
The antioxidant properties of catechin are fundamental to its ability to protect the liver from chronic injury. By reducing oxidative stress, catechin limits cellular damage and prevents the activation of hepatic stellate cells, which are responsible for the fibrotic response in the liver. Studies also show that catechin inhibits TGF-β (transforming growth factor-beta), a key signaling molecule involved in fibrogenesis, thereby reducing the formation of scar tissue in the liver.
Moreover, catechin has been shown to possess antifibrotic effects by downregulating collagen production. Collagen accumulation contributes to fibrosis and the eventual hardening of liver tissue, impairing its functionality. Catechin’s ability to inhibit collagen synthesis helps maintain the liver’s structural integrity and normal function, preventing the onset of cirrhosis.
Reducing Liver Damage from Fatty Liver and Stressors
Fatty liver, whether alcoholic or non-alcoholic, significantly increases the liver’s vulnerability to damage. Catechin’s hepatoprotective properties extend to mitigating damage caused by fat deposition in the liver. The polyphenol achieves this by reducing inflammation, oxidative stress, and fat-induced toxicity.
Catechin’s modulation of lipid metabolism helps prevent the over-accumulation of fat in the liver, reducing the risk of lipotoxicity—a process where excessive lipids lead to cell death and inflammation. This modulation is facilitated by catechin’s ability to activate pathways involved in lipid clearance, ensuring that fat levels within hepatocytes remain manageable. Additionally, catechin improves mitochondrial function, which plays a vital role in managing energy balance and preventing fat accumulation. By preserving mitochondrial health, catechin reduces the risk of liver cell damage associated with fatty liver.
Furthermore, catechin has been reported to enhance the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase, and glutathione peroxidase. These enzymes are crucial for reducing oxidative stress within liver cells, thereby protecting against damage induced by various liver stressors, including toxins, high-fat diets, and metabolic imbalances.
Enhancing Liver Regeneration and Function
The liver’s remarkable regenerative capacity is one of its most distinctive features. However, chronic damage can impair this ability. Catechin contributes to liver regeneration by supporting the proliferation of hepatocytes and reducing factors that inhibit this process.
Catechin promotes hepatocyte proliferation through its role in modulating signaling pathways, such as the Wnt/β-catenin pathway, which is involved in cell growth and regeneration. By enhancing these pathways, catechin aids in replacing damaged liver cells with healthy new ones, thus promoting liver regeneration. Moreover, its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties help create an optimal environment for regeneration, minimizing cellular stress and inflammation that could otherwise impede recovery.
Research has also indicated that catechin may help maintain healthy bile production and flow, which is essential for detoxification and fat digestion. Proper bile flow prevents cholestasis—a condition where bile flow from the liver is reduced or blocked—which can lead to further liver damage. By supporting normal bile production, catechin enhances the liver’s ability to detoxify harmful substances and maintain overall metabolic balance.
Mechanisms of Action: How Catechin Supports Liver Health
Antioxidant Defense: Catechin’s primary mechanism for protecting the liver lies in its antioxidant properties. By neutralizing free radicals and enhancing the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes, catechin effectively reduces oxidative stress—a key factor in the development and progression of various liver diseases.
Anti-Inflammatory Activity: Chronic inflammation is a major contributor to liver damage and fibrosis. Catechin suppresses inflammatory pathways, particularly those involving nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB), a protein complex that controls the transcription of DNA and cytokine production. Inhibiting NF-κB reduces the production of inflammatory mediators, thereby protecting liver tissue from damage.
Modulation of Lipid Metabolism: Catechin’s activation of AMPK plays a crucial role in regulating lipid metabolism. By enhancing fatty acid oxidation and reducing de novo lipogenesis, catechin helps prevent fat accumulation in the liver, reducing the risk of NAFLD and its progression.
Inhibition of Fibrogenesis: Fibrosis is a critical step in the progression of chronic liver disease to cirrhosis. Catechin inhibits the activation of hepatic stellate cells and reduces the expression of pro-fibrotic factors like TGF-β, thereby preventing the excessive deposition of extracellular matrix proteins that lead to fibrosis.
Promotion of Hepatocyte Proliferation: Catechin supports liver regeneration by promoting hepatocyte proliferation and enhancing the liver’s regenerative pathways. This effect is particularly important in cases where the liver has sustained significant damage and needs to replace lost or injured cells.
Catechin and Detoxification: Promoting a Healthier Liver Environment
The liver is the body’s primary detoxification organ, responsible for breaking down toxins and metabolizing drugs, alcohol, and other substances. Catechin supports this process by enhancing phase II detoxification enzymes, such as glutathione S-transferase, which play a key role in conjugating toxins and making them easier to eliminate from the body.
In addition, catechin helps maintain the liver’s antioxidant status, ensuring that it can effectively counteract the oxidative stress generated during the detoxification process. By reducing oxidative damage and supporting detoxification pathways, catechin contributes to a healthier liver environment, which is crucial for overall well-being.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Catechin’s Liver Benefits
Numerous studies have provided evidence of catechin’s hepatoprotective effects:
A 2015 study published in The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry demonstrated that catechin supplementation significantly reduced liver fat content and inflammation in animal models of NAFLD. The study attributed these effects to catechin’s ability to modulate lipid metabolism and reduce oxidative stress.
A clinical trial published in Phytomedicine in 2017 found that patients with NAFLD who consumed green tea catechins for 12 weeks showed significant improvements in liver enzyme levels, liver fat content, and markers of oxidative stress compared to the control group.
Research published in Hepatology Research in 2019 highlighted catechin’s antifibrotic effects, showing that it inhibited the activation of hepatic stellate cells and reduced collagen deposition in liver tissue. This study emphasized the potential of catechin as a therapeutic agent for preventing liver fibrosis and cirrhosis.
A 2021 review in Antioxidants summarized various studies indicating that catechin enhances liver regeneration by promoting hepatocyte proliferation and reducing inflammation. The review concluded that catechin’s multifaceted actions make it a promising candidate for supporting liver health in individuals with chronic liver disease.
Conclusion: Catechin as a Natural Ally for Liver Health
Catechin, especially in the form of EGCG, offers substantial benefits for liver health, supported by a growing body of scientific evidence. Its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antifibrotic, and lipid-regulating properties make it a powerful natural compound for preventing and managing conditions like NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. By promoting liver regeneration, enhancing detoxification, and reducing liver damage from fatty accumulation and other stressors, catechin plays a pivotal role in maintaining a healthier liver environment.
Incorporating catechin-rich foods, such as green tea, into one’s diet could be an effective strategy for supporting liver health and overall well-being. However, individuals with liver conditions or those considering catechin supplements should consult healthcare professionals to ensure safety and appropriate usage.
By leveraging catechin’s scientifically proven benefits, individuals can take proactive steps towards better liver health, enhancing the body’s natural detoxification processes, and promoting overall vitality.

Chestnut (Castanea crenata) Inner Shell Extract: A Powerful Ally Against Liver Disease
Chestnut (Castanea crenata) inner shell extract has recently gained attention for its potent hepatoprotective properties, particularly its potential to prevent and manage Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Emerging scientific research supports the extract’s capacity to enhance liver health, minimize hepatic damage, and promote regeneration, making it an attractive natural option for improving liver function and overall well-being. This comprehensive synopsis will delve into the proven benefits of chestnut inner shell extract, emphasizing the mechanisms of action and the current scientific evidence for its role in supporting liver health.
Understanding Liver Disease and the Role of Natural Compounds
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is a chronic condition characterized by excessive fat accumulation in the liver, often progressing to more severe forms, such as non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), cirrhosis, and even liver failure. The pathogenesis of NAFLD is multifactorial, involving oxidative stress, inflammation, insulin resistance, and mitochondrial dysfunction. A major challenge in managing these conditions is to protect the liver from damage, alleviate inflammation, and promote liver regeneration.
Chestnut inner shell extract has emerged as a promising natural compound in this context. Rich in polyphenols, flavonoids, and antioxidant compounds, the extract shows significant hepatoprotective activity that makes it effective against the progression of NAFLD and other chronic liver diseases.
Hepatoprotective Effects of Chestnut Inner Shell Extract
The hepatoprotective effects of chestnut inner shell extract are linked primarily to its strong antioxidant capacity. Several studies have shown that oxidative stress plays a key role in liver injury associated with fatty liver disease and cirrhosis. The antioxidant properties of chestnut inner shell extract effectively neutralize free radicals, which helps prevent oxidative damage to liver cells.
Reduction of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation
A recent study published in a peer-reviewed journal demonstrated that chestnut inner shell extract significantly reduces oxidative stress markers in experimental models of liver disease. The polyphenolic compounds in the extract, such as tannins and ellagic acid, are believed to play a crucial role in scavenging reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reducing lipid peroxidation—a process that can lead to severe liver cell damage.
In addition to reducing oxidative stress, chestnut inner shell extract also possesses potent anti-inflammatory properties. Inflammation is a critical factor in the progression of NAFLD to more severe liver conditions. The extract has been found to inhibit the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β, thereby reducing hepatic inflammation. By modulating these inflammatory pathways, chestnut inner shell extract contributes to mitigating liver damage and slowing disease progression.
Mechanisms of Action in Liver Protection
The mechanisms by which chestnut inner shell extract confers its hepatoprotective effects are multifaceted, involving several biological pathways:
Antioxidant Defense Activation: The polyphenols in chestnut extract activate endogenous antioxidant enzymes like superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx). These enzymes play a vital role in protecting liver cells from oxidative damage by neutralizing ROS.
Lipid Metabolism Regulation: Dysregulated lipid metabolism is a hallmark of NAFLD. Chestnut inner shell extract has been shown to help regulate lipid metabolism by reducing hepatic triglyceride accumulation. Animal studies suggest that the extract may inhibit de novo lipogenesis—the process by which the liver converts excess carbohydrates into fat—and promote fatty acid oxidation, thereby reducing fat buildup in the liver.
Mitochondrial Protection: Mitochondrial dysfunction is a significant contributor to the progression of NAFLD and other liver diseases. Chestnut inner shell extract has demonstrated protective effects on mitochondrial function, helping to maintain the energy balance within liver cells and prevent cell death. This action supports overall liver health and function, making the extract an effective intervention for managing liver conditions.
Anti-Fibrotic Effects: Liver fibrosis is a key event in the progression from NAFLD to cirrhosis. Studies indicate that chestnut inner shell extract may help reduce fibrosis by inhibiting the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), which are responsible for the excessive production of extracellular matrix components that lead to scarring of the liver. The anti-fibrotic activity of chestnut extract helps maintain liver structure and prevent the irreversible damage associated with cirrhosis.
Supporting Liver Regeneration and Overall Function
Liver regeneration is a unique ability of the liver to repair itself after injury. Chestnut inner shell extract has been found to promote this regenerative process, contributing to the recovery of liver function even after significant damage. The bioactive compounds in the extract stimulate hepatocyte proliferation—the process by which new liver cells are formed—which is crucial for liver regeneration.
Moreover, chestnut inner shell extract enhances overall liver function by improving blood flow and reducing hepatic congestion. The presence of bioactive flavonoids helps relax blood vessels in the liver, promoting better circulation and supporting the liver’s detoxification processes. By enhancing the liver’s ability to filter toxins and waste products from the blood, chestnut inner shell extract contributes to a healthier liver environment and improved systemic health.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Chestnut Inner Shell Extract
Several peer-reviewed studies have provided evidence for the hepatoprotective properties of chestnut inner shell extract. For instance, a study published in the “Journal of Ethnopharmacology” demonstrated that rats treated with chestnut inner shell extract showed a significant reduction in liver enzyme markers, such as alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), which are indicative of liver damage. The treated group also exhibited improved histopathological features, suggesting reduced inflammation and fibrosis.
Another study highlighted the anti-fibrotic properties of the extract, showing that it significantly downregulated the expression of genes involved in collagen production and fibrosis in liver tissues. This finding supports the potential of chestnut inner shell extract as a natural anti-fibrotic agent, particularly for patients at risk of developing cirrhosis.
Additionally, research published in “Food & Function” emphasized the antioxidant potential of chestnut inner shell extract in reducing oxidative stress in liver cells. The study demonstrated that the extract increased the activity of key antioxidant enzymes, providing a protective effect against ROS-induced liver injury.
Chestnut Inner Shell Extract and Detoxification
The liver plays a central role in the body’s detoxification processes, converting harmful substances into less toxic metabolites that can be easily excreted. Chestnut inner shell extract supports these detoxification pathways by enhancing the liver’s enzymatic activity. Specifically, the extract has been shown to upregulate phase II detoxification enzymes, such as glutathione S-transferase (GST), which facilitate the conjugation and removal of toxins.
By promoting effective detoxification, chestnut inner shell extract helps alleviate the liver’s workload, preventing the accumulation of harmful substances that could contribute to liver damage. This effect is particularly beneficial for individuals exposed to environmental toxins, alcohol, or other substances that place additional stress on the liver.
Safety and Efficacy of Chestnut Inner Shell Extract
Safety is a critical consideration for any natural supplement, particularly those targeting liver health. The available scientific evidence suggests that chestnut inner shell extract is generally safe and well-tolerated, with no significant adverse effects reported in animal or human studies. However, as with any supplement, it is important for individuals to consult with a healthcare provider before beginning supplementation, particularly if they have pre-existing health conditions or are taking medications that may interact with the extract.
The efficacy of chestnut inner shell extract is supported by multiple studies, though more clinical trials involving human participants are needed to confirm its effectiveness in managing liver diseases such as NAFLD and cirrhosis. Nonetheless, the current body of evidence highlights the extract’s potential as a valuable natural intervention for liver health, offering benefits that range from reducing oxidative stress and inflammation to supporting liver regeneration and detoxification.
Conclusion: A Natural Approach to Liver Health
Chestnut (Castanea crenata) inner shell extract stands out as a promising natural remedy for promoting liver health and preventing the progression of liver diseases like NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Its multifaceted hepatoprotective properties—including antioxidant defense, anti-inflammatory effects, regulation of lipid metabolism, mitochondrial protection, and support for liver regeneration—make it a valuable ally in the fight against liver disease.
While more human clinical trials are needed to establish definitive dosing guidelines and further confirm its efficacy, the existing evidence underscores the potential of chestnut inner shell extract as a complementary approach to liver health management. By reducing oxidative stress, mitigating inflammation, and supporting the liver’s natural detoxification and regenerative processes, chestnut inner shell extract offers a holistic way to maintain a healthier liver environment and enhance overall well-being.
For those seeking to protect their liver from the stresses of modern life—whether due to poor diet, environmental toxins, or other lifestyle factors—chestnut inner shell extract provides a scientifically backed, natural option to consider as part of a comprehensive liver health strategy.

Chrysanthemum Indicum L. Extract: Scientifically Proven Benefits for Liver Health
Chrysanthemum indicum L., a traditional medicinal herb, has gained considerable attention for its hepatoprotective properties. Numerous studies have shown its effectiveness in preventing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. The extract from this plant is rich in bioactive compounds such as flavonoids, chlorogenic acid, and essential oils, which contribute to its diverse therapeutic effects. This comprehensive article delves into the scientific evidence behind Chrysanthemum indicum L. and its mechanisms of action in promoting liver health, regeneration, and overall detoxification.
Chrysanthemum Indicum L. and Liver Health: Mechanisms of Action
The liver is a central organ responsible for detoxification, metabolism, and synthesis of key biomolecules. Chrysanthemum indicum L. extract is known for its hepatoprotective effects, which are primarily attributed to its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and lipid-regulating properties. Let’s explore how these mechanisms contribute to preventing and managing liver disorders such as NAFLD, cirrhosis, and other chronic liver diseases.
1. Antioxidant Defense Against Liver Damage
Oxidative stress is a significant contributor to liver injury, especially in conditions like NAFLD. Chrysanthemum indicum L. contains a high concentration of antioxidant compounds, including flavonoids and phenolic acids, which play a crucial role in neutralizing reactive oxygen species (ROS). By reducing oxidative stress, the extract minimizes lipid peroxidation and cellular damage, thereby preventing the progression of fatty liver and other liver-related ailments.
A study published in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology highlighted the ability of Chrysanthemum indicum L. extract to significantly enhance the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px). These enzymes are vital in combating oxidative stress, thus providing a protective shield for liver cells against free radical damage.
2. Anti-Inflammatory Effects and Protection Against Liver Inflammation
Chronic liver inflammation is a major driver of liver fibrosis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular damage. Chrysanthemum indicum L. has been shown to exhibit potent anti-inflammatory properties, primarily through the inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6. These cytokines are involved in promoting inflammation and tissue damage in liver diseases.
Research demonstrates that Chrysanthemum indicum L. extract modulates the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) signaling pathway, which is a key regulator of inflammatory responses. By inhibiting NF-κB activation, the extract effectively reduces inflammation, thereby preventing the progression of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis.
3. Lipid Metabolism Regulation for NAFLD Prevention
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is characterized by the excessive accumulation of fat in liver cells, often linked to metabolic syndrome. Chrysanthemum indicum L. plays an essential role in regulating lipid metabolism, thus preventing the onset of NAFLD. The extract has been found to decrease triglyceride and cholesterol levels in the liver, which is crucial for mitigating fat accumulation and improving overall liver function.
A study published in Phytomedicine indicated that Chrysanthemum indicum L. extract enhances the expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPAR-α), a key regulator of fatty acid oxidation. This leads to improved lipid catabolism, reduced hepatic fat accumulation, and consequently, a lower risk of NAFLD development.
Hepatoprotective Effects: Preventing Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver diseases and cirrhosis are often the result of prolonged inflammation, oxidative stress, and fibrosis. Chrysanthemum indicum L. extract has shown promise in preventing these conditions by protecting liver cells from damage, reducing fibrosis, and enhancing liver regeneration.
1. Fibrosis Inhibition
Fibrosis is the excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix proteins, leading to scarring and impaired liver function. Chrysanthemum indicum L. extract inhibits hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation—a key event in the development of fibrosis. Studies have shown that the flavonoids present in the extract suppress transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β), a cytokine that promotes HSC activation and collagen production.
By reducing TGF-β levels and inhibiting HSC activation, Chrysanthemum indicum L. helps in preventing the progression of fibrosis, ultimately reducing the risk of cirrhosis and maintaining healthy liver architecture.
2. Enhanced Liver Regeneration
The liver has a unique capacity for regeneration, which is crucial for recovery from injuries and maintaining normal function. Chrysanthemum indicum L. extract has been found to support liver regeneration by promoting hepatocyte proliferation and inhibiting apoptosis (programmed cell death).
Research indicates that the extract activates pathways such as the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt signaling pathway, which is associated with cell survival and growth. By enhancing hepatocyte proliferation and reducing cell death, Chrysanthemum indicum L. aids in the regeneration of liver tissue, ensuring faster recovery from liver injuries and improved liver function.
Supporting Overall Liver Function and Detoxification
Chrysanthemum indicum L. extract not only helps in managing specific liver diseases but also enhances overall liver function and the body’s natural detoxification processes. The liver is the primary organ responsible for detoxifying harmful substances, and the extract’s bioactive compounds contribute significantly to maintaining a healthy liver environment.
1. Promotion of Bile Production
Bile production is a crucial function of the liver, as bile aids in the digestion and absorption of fats while also helping in the excretion of toxins. Chrysanthemum indicum L. extract has been found to stimulate bile flow, thus enhancing the liver’s ability to excrete waste products and maintain metabolic balance.
Improved bile production also supports lipid digestion, reducing the burden of fat accumulation in the liver and mitigating the risk of NAFLD. This contributes to a healthier liver and optimal detoxification.
2. Enhancement of Phase I and Phase II Detoxification Enzymes
The liver detoxifies harmful substances through two phases—Phase I (oxidation) and Phase II (conjugation). Chrysanthemum indicum L. extract has been shown to enhance the activity of enzymes involved in both phases, ensuring efficient detoxification of xenobiotics and endogenous toxins.
Studies indicate that the extract upregulates cytochrome P450 enzymes (Phase I) and glutathione S-transferase (GST) enzymes (Phase II), which play vital roles in neutralizing and excreting toxins. This dual-phase enhancement ensures that harmful substances are effectively metabolized and eliminated from the body, reducing liver stress and supporting overall health.
Conclusion: A Natural Ally for Liver Health
Chrysanthemum indicum L. extract stands out as a potent natural remedy for promoting liver health, preventing liver diseases, and supporting overall detoxification. Its hepatoprotective effects are backed by robust scientific evidence, with studies highlighting its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and lipid-regulating properties. By reducing oxidative stress, modulating inflammation, regulating lipid metabolism, and enhancing liver regeneration, this extract provides comprehensive support for maintaining a healthy liver.
For individuals at risk of liver diseases such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, or cirrhosis, Chrysanthemum indicum L. extract offers a promising, evidence-based approach to prevention and management. Moreover, its ability to enhance bile production and support detoxification enzymes ensures that the liver remains efficient in its critical role of detoxifying the body.
As always, it is essential to consult with healthcare professionals before incorporating any new supplements, especially for individuals with pre-existing health conditions or those taking medication. The power of Chrysanthemum indicum L. lies in its natural bioactive compounds, offering a scientifically proven means of supporting liver health and enhancing the body’s natural detoxification processes.
Cichorium intybus L. and Liver Health: Proven Benefits and Mechanisms for NAFLD, Liver Cirrhosis, and Hepatoprotection
Cichorium intybus L., commonly known as chicory, has gained attention for its significant liver-protective properties, particularly in preventing and managing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Known for its rich phytochemical profile, chicory has shown a broad range of hepatoprotective effects, including reducing liver damage caused by fat accumulation and other liver stressors, enhancing liver regeneration, and promoting a healthier liver environment. This comprehensive exploration aims to provide a scientific overview of the evidence-based health benefits of chicory for liver function, with a particular focus on its mechanisms of action in enhancing the body’s natural detoxification processes.
1. Overview of Cichorium intybus L.
Cichorium intybus L. is a herbaceous plant that has been widely used in traditional medicine across various cultures. It is rich in bioactive compounds such as sesquiterpene lactones, polyphenols, inulin, and flavonoids, which contribute to its numerous therapeutic benefits. Research has demonstrated its potent anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and hepatoprotective properties, which make chicory a promising candidate for the management of liver health, especially in the context of modern diseases like NAFLD and cirrhosis.
2. Prevention of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD is a major global health concern linked to metabolic syndrome, obesity, and insulin resistance. Cichorium intybus L. has been shown to be effective in preventing and managing NAFLD by targeting key metabolic and inflammatory pathways involved in the disease progression.
2.1. Reduction of Hepatic Fat Accumulation
One of the primary mechanisms through which chicory supports liver health is by reducing hepatic fat accumulation. Studies have shown that chicory extract can modulate lipid metabolism, decreasing the synthesis of triglycerides and cholesterol in the liver. In particular, inulin, a prebiotic fiber found in chicory, has been demonstrated to improve lipid profiles by enhancing the breakdown of fats and reducing lipogenesis, which directly contributes to minimizing liver fat accumulation.
2.2. Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Inflammation is a key driver in the progression of NAFLD to more severe forms of liver disease, such as non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Chicory is rich in polyphenolic compounds like chicoric acid, which exhibit strong anti-inflammatory properties. These compounds inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6, which play a central role in liver inflammation. By reducing hepatic inflammation, chicory helps prevent the progression of NAFLD to more advanced stages.
3. Protection Against Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver diseases, including cirrhosis, are characterized by persistent inflammation and fibrosis, ultimately leading to irreversible liver damage. Chicory has demonstrated efficacy in mitigating these effects through several mechanisms.
3.1. Antioxidant Defense
Oxidative stress is a major factor contributing to chronic liver disease and cirrhosis. Cichorium intybus L. contains potent antioxidants, including flavonoids and phenolic acids, which neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS) and protect liver cells from oxidative damage. By enhancing the liver’s antioxidant defense, chicory reduces cellular injury and fibrosis, thereby protecting against the development of cirrhosis.
3.2. Anti-Fibrotic Activity
Liver fibrosis, a hallmark of chronic liver disease and cirrhosis, results from excessive deposition of extracellular matrix proteins. Chicory has been found to exhibit anti-fibrotic activity by inhibiting hepatic stellate cell activation—a key process in fibrosis development. Research indicates that chicory extracts can downregulate the expression of fibrosis-related genes, reducing collagen deposition and mitigating the risk of cirrhosis.
4. Hepatoprotective Effects: Reducing Liver Damage
Chicory’s hepatoprotective properties are attributed to its ability to protect liver cells from a variety of stressors, including toxins, fat accumulation, and oxidative stress. The following are key mechanisms through which chicory exerts its hepatoprotective effects.
4.1. Detoxification Enhancement
The liver is the primary organ responsible for detoxification, and chicory plays a supportive role in enhancing this function. The bioactive compounds in chicory stimulate the activity of detoxifying enzymes, such as glutathione S-transferase, which helps in the conjugation and elimination of toxic substances. This enhancement of the liver’s detoxification capacity contributes to overall liver health and reduces damage from environmental and dietary toxins.
4.2. Protection Against Hepatotoxins
Experimental studies have shown that chicory extracts can protect against liver damage induced by hepatotoxins such as carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) and alcohol. The hepatoprotective effect is mediated by chicory’s ability to stabilize cell membranes, reduce lipid peroxidation, and enhance antioxidant enzyme levels. This protection against hepatotoxins underscores chicory’s potential as a natural remedy for reducing liver damage from various toxic insults.
5. Liver Regeneration and Improved Liver Function
One of the remarkable aspects of the liver is its ability to regenerate after injury. Chicory has been found to support liver regeneration and improve overall liver function, making it an effective agent for maintaining liver health.
5.1. Stimulation of Liver Regeneration
Liver regeneration is a complex process that requires the proliferation of hepatocytes and restoration of liver architecture. Research has shown that chicory extract can promote hepatocyte proliferation, thereby aiding in liver regeneration. The presence of bioactive compounds such as sesquiterpene lactones has been linked to the stimulation of liver cell regeneration, which is crucial for recovery from liver injury.
5.2. Enhancement of Bile Production
Chicory is also known to enhance bile production, which plays a critical role in digestion and the elimination of waste products from the liver. Increased bile flow not only aids in fat digestion but also helps in the removal of toxins and metabolites, thereby improving liver function and reducing the burden on the liver.
6. Promotion of a Healthy Liver Environment
Maintaining a healthy liver environment is essential for optimal liver function and overall health. Chicory contributes to creating such an environment through its various therapeutic properties.
6.1. Gut-Liver Axis Modulation
The gut-liver axis plays a critical role in liver health, and dysbiosis can contribute to liver disease. Chicory, being rich in inulin, acts as a prebiotic and supports the growth of beneficial gut bacteria. This improvement in gut health has a positive impact on the gut-liver axis, reducing the translocation of endotoxins to the liver and subsequently lowering hepatic inflammation. By modulating the gut microbiota, chicory helps maintain a healthy liver environment.
6.2. Reduction of Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance is a major risk factor for NAFLD and other liver diseases. Chicory has been found to improve insulin sensitivity, which helps in the regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism. By reducing insulin resistance, chicory not only aids in preventing fat accumulation in the liver but also supports overall metabolic health, which is crucial for maintaining liver function.
7. Enhancing the Body’s Natural Detoxification Processes
Chicory’s contribution to liver health extends to enhancing the body’s natural detoxification processes. The liver is responsible for detoxifying harmful substances, and chicory supports this function in several ways.
7.1. Upregulation of Antioxidant Enzymes
Chicory has been shown to upregulate the expression of antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase, which play a key role in neutralizing free radicals and protecting liver cells from oxidative stress. This upregulation not only prevents cellular damage but also enhances the liver’s ability to detoxify harmful substances effectively.
7.2. Chelation of Heavy Metals
Certain studies have indicated that chicory may possess chelating properties, helping to bind and eliminate heavy metals from the body. Heavy metal toxicity is a significant burden on liver function, and chicory’s potential to aid in the chelation process adds another layer of protection for liver health.
8. Conclusion: Cichorium intybus L. as a Natural Ally for Liver Health
Cichorium intybus L. is a versatile medicinal plant with proven benefits for liver health, particularly in preventing and managing conditions such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Its rich phytochemical composition provides a multifaceted approach to liver protection, including reducing fat accumulation, mitigating inflammation, enhancing detoxification, promoting regeneration, and supporting a healthy liver environment. The hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant effects of chicory are well-supported by scientific evidence, making it a valuable natural remedy for maintaining liver health and enhancing the body’s natural detoxification processes.
By modulating key metabolic pathways, reducing oxidative stress, and supporting liver regeneration, chicory offers a comprehensive approach to liver care that aligns with both traditional knowledge and modern scientific research. As liver disease continues to be a major health challenge worldwide, Cichorium intybus L. stands out as a promising natural solution for enhancing liver health and function.

Cinnamomum cassia Extract: A Natural Aid for Liver Health and NAFLD Prevention
Introduction
Cinnamomum cassia, commonly known as Chinese cinnamon or cassia, has been utilized in traditional medicine for centuries. Modern science has increasingly confirmed its beneficial properties, especially its hepatoprotective effects—the ability to protect the liver from damage and stress. With rising incidences of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver diseases, and cirrhosis, cassia extract has emerged as a promising natural aid. This article explores the proven scientific benefits of Cinnamomum cassia extract in preventing and managing liver diseases, focusing on mechanisms of action, hepatoprotective effects, liver regeneration, and overall liver function enhancement.
Proven Benefits of Cinnamomum cassia Extract for Liver Health
1. Prevention and Management of NAFLD and Chronic Liver Diseases
NAFLD is a major public health issue, characterized by fat accumulation in liver cells in the absence of significant alcohol consumption. It is closely linked to metabolic syndrome, obesity, and type 2 diabetes. Several scientific studies have demonstrated that Cinnamomum cassia extract possesses bioactive compounds with potent effects that can prevent and manage NAFLD.
Cassia extract is rich in polyphenolic compounds, such as cinnamaldehyde, eugenol, and coumarin. These compounds exhibit strong antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, which help mitigate oxidative stress and inflammation—key contributors to the onset and progression of NAFLD. A study published in the Journal of Medicinal Food confirmed that cinnamaldehyde significantly reduces liver fat accumulation, inflammation, and lipid peroxidation, thus preventing the progression of NAFLD.
Cassia extract also improves insulin sensitivity, another crucial factor in managing NAFLD. Insulin resistance is strongly associated with liver fat accumulation, and studies have found that cassia extract reduces insulin resistance by enhancing insulin signaling pathways, thereby decreasing hepatic fat buildup.
2. Hepatoprotective Effects Against Liver Stressors
The hepatoprotective effect of Cinnamomum cassia extract is supported by substantial evidence highlighting its ability to reduce liver damage caused by various stressors, including oxidative stress, high-fat diets, and toxins. The liver is particularly susceptible to oxidative damage due to its role in detoxification. Cassia extract exerts protective effects by neutralizing free radicals, which can otherwise lead to lipid peroxidation and cellular damage.
Animal studies have demonstrated that treatment with Cinnamomum cassia extract results in a marked decrease in liver enzymes, such as ALT and AST, which are biomarkers for liver injury. In a study published in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology, the administration of cassia extract to rats exposed to a high-fat diet showed a reduction in ALT and AST levels, suggesting reduced liver injury and enhanced liver function.
Cinnamomum cassia also exerts its hepatoprotective effect through its anti-inflammatory properties. Chronic liver inflammation is a precursor to fibrosis and cirrhosis, and research has shown that cassia extract downregulates pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α and IL-6. By attenuating these inflammatory markers, cassia helps maintain healthy liver tissue and prevent further liver complications.
3. Benefits for Liver Regeneration and Liver Function
The liver has an extraordinary capacity to regenerate, and Cinnamomum cassia extract contributes to enhancing this regenerative capability. Scientific research suggests that the bioactive compounds in cassia extract stimulate liver cell proliferation, thus aiding liver regeneration after injury.
Studies have highlighted that cinnamaldehyde—a key component of cassia—plays a role in enhancing the activation of hepatocyte growth factors (HGFs), which are crucial for liver regeneration. By promoting the activation of HGFs and enhancing antioxidant defenses, cassia extract supports the liver’s ability to repair itself, thereby accelerating recovery after injury or damage.
Cassia extract also helps improve overall liver function by promoting bile secretion and improving lipid metabolism. Bile is essential for the digestion of fats, and optimal bile flow ensures effective detoxification and lipid clearance from the liver. By facilitating bile secretion, cassia extract helps maintain a healthier liver environment, reducing the risk of fatty liver disease and promoting efficient detoxification processes.
Mechanisms of Action: How Cinnamomum cassia Extract Benefits the Liver
1. Antioxidant Properties
Oxidative stress is a major driver of liver diseases, including NAFLD, fibrosis, and cirrhosis. The liver’s detoxification processes generate reactive oxygen species (ROS), which can damage liver cells if not neutralized. Cinnamomum cassia extract, rich in polyphenolic antioxidants, helps scavenge these harmful ROS, protecting the liver from oxidative damage.
Cinnamaldehyde, one of the main active components of cassia, has been shown to enhance the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase, and glutathione peroxidase. These enzymes play a critical role in neutralizing ROS and maintaining cellular health. By boosting the liver’s antioxidant defenses, cassia extract reduces oxidative stress and prevents the damage that can lead to chronic liver conditions.
2. Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Inflammation is a significant contributor to the progression of liver diseases, including NAFLD, hepatitis, and cirrhosis. Chronic inflammation leads to liver tissue damage, fibrosis, and, eventually, cirrhosis. Cinnamomum cassia extract contains compounds that inhibit the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which are molecules that signal inflammation in the body.
Research has shown that cassia extract downregulates the expression of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB), a key transcription factor involved in inflammatory processes. By inhibiting NF-κB, cassia reduces the production of inflammatory cytokines, thereby alleviating liver inflammation and preventing the progression to fibrosis or cirrhosis.
3. Insulin Sensitization and Lipid Metabolism
Insulin resistance is a major factor in the development of NAFLD. When the liver becomes resistant to insulin, it cannot effectively regulate glucose and lipid metabolism, leading to fat accumulation in liver cells. Cinnamomum cassia extract has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity by enhancing the activity of insulin receptors and improving glucose uptake in cells.
Studies have demonstrated that cinnamaldehyde enhances the phosphorylation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), an enzyme that plays a critical role in energy balance and lipid metabolism. Activation of AMPK leads to increased fatty acid oxidation and decreased lipogenesis (fat production) in the liver, thus reducing hepatic fat accumulation and improving liver health.
4. Enhancement of Detoxification Processes
The liver is the body’s primary detoxification organ, and Cinnamomum cassia extract has been shown to enhance the liver’s detoxifying capacity. The bioactive compounds in cassia increase the activity of detoxification enzymes, including cytochrome P450 enzymes, which are responsible for breaking down toxins and facilitating their excretion from the body.
By boosting the activity of these enzymes, cassia extract helps the liver efficiently process and eliminate harmful substances, reducing the burden on the liver and minimizing the risk of toxin-induced liver damage. This detoxification support is particularly beneficial for individuals with chronic liver diseases, where detoxification capacity may be impaired.
Promoting a Healthy Liver Environment
Cinnamomum cassia extract contributes to a healthier liver environment by addressing multiple facets of liver health, including reducing fat accumulation, mitigating oxidative stress, controlling inflammation, and enhancing detoxification. The synergistic effects of its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and lipid-regulating properties help create an optimal environment for liver function.
The promotion of bile secretion by cassia extract is another significant factor in maintaining liver health. By enhancing bile flow, cassia extract aids in the digestion of dietary fats and the removal of cholesterol from the liver. This not only prevents the development of NAFLD but also supports overall liver function and metabolic health.
Summary: The Science-Backed Benefits of Cinnamomum cassia Extract for Liver Health
The hepatoprotective effects of Cinnamomum cassia extract are well-supported by scientific research. Its antioxidant properties help mitigate oxidative stress, while its anti-inflammatory effects reduce the risk of inflammation-induced liver damage. By improving insulin sensitivity and enhancing lipid metabolism, cassia extract plays a vital role in preventing and managing NAFLD. Furthermore, it supports liver regeneration and promotes a healthy liver environment by facilitating bile secretion and boosting detoxification processes.
Cinnamomum cassia extract emerges as a powerful natural supplement for liver health, particularly in the context of NAFLD, chronic liver diseases, and cirrhosis. Its ability to reduce liver fat, protect against oxidative and inflammatory damage, and support liver regeneration makes it a valuable tool in promoting overall liver health and function. For individuals seeking to maintain or improve their liver health, incorporating cassia extract under the guidance of a healthcare professional could offer significant benefits.

Coptis Chinensis Franch Root Extract: A Scientific Synopsis on Liver Health
Coptis chinensis, also known as Huang Lian, is a traditional Chinese medicinal herb revered for its potent health benefits, especially for liver health. Its root extract has shown significant potential in managing and preventing liver conditions such as Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. This comprehensive synopsis delves into the proven benefits of Coptis chinensis root extract, highlighting its hepatoprotective effects, mechanisms of action, and how it contributes to a healthier liver environment.
Hepatoprotective Effects of Coptis Chinensis
Coptis chinensis is rich in bioactive compounds, including berberine, coptisine, palmatine, and jatrorrhizine. These alkaloids are largely responsible for its wide array of liver-protective effects. Berberine, in particular, plays a crucial role in modulating liver health. It is well-established as a potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant agent, which helps reduce oxidative stress, a significant factor in liver damage and disease progression.
Reducing Liver Damage and Inflammation
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is characterized by the accumulation of fat in liver cells, which can lead to inflammation and damage. Berberine, one of the primary constituents of Coptis chinensis, has been found to inhibit lipogenesis—the formation of fat—in the liver. Studies have demonstrated that berberine activates AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), a key enzyme in the regulation of cellular energy homeostasis. By activating AMPK, berberine helps reduce lipid accumulation in hepatocytes, thereby preventing the onset and progression of NAFLD.
Additionally, Coptis chinensis helps in reducing liver inflammation, a common precursor to chronic liver conditions and cirrhosis. The anti-inflammatory effects of berberine are mediated through the inhibition of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) signaling, a key pathway in the inflammatory response. By modulating this pathway, berberine reduces the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, thus mitigating liver inflammation and subsequent tissue damage.
Preventing Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver disease often results from prolonged inflammation and oxidative stress, which can eventually lead to fibrosis and cirrhosis. Fibrosis is the excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix proteins, leading to scarring of the liver tissue. Coptis chinensis has shown promising anti-fibrotic effects, primarily through the suppression of hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation. HSCs are the primary cells responsible for collagen production in the liver, and their activation is a key event in liver fibrosis.
Research indicates that berberine inhibits the transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) pathway, a crucial mediator of HSC activation and fibrosis. By inhibiting this pathway, Coptis chinensis reduces collagen deposition, thereby preventing the progression from fibrosis to cirrhosis. This makes Coptis chinensis an effective agent in the management of chronic liver disease and a promising option for halting the progression to cirrhosis.
Supporting Liver Regeneration and Enhancing Detoxification
The liver has a remarkable ability to regenerate itself, which is crucial for maintaining its function following injury or damage. Coptis chinensis root extract has been shown to support liver regeneration by promoting hepatocyte proliferation. The activation of AMPK not only reduces fat accumulation but also enhances the regeneration capacity of liver cells, ensuring the restoration of normal liver architecture and function following injury.
Moreover, the antioxidant properties of berberine and other alkaloids in Coptis chinensis help protect hepatocytes from oxidative damage. By scavenging free radicals and reducing oxidative stress, these compounds create a favorable environment for liver regeneration. This is particularly beneficial for individuals with fatty liver disease, as oxidative stress is a major contributor to liver cell injury in these conditions.
Coptis chinensis also enhances the liver’s natural detoxification processes. The liver is the primary organ responsible for detoxifying harmful substances, including drugs, alcohol, and environmental toxins. Berberine has been found to upregulate the expression of detoxifying enzymes, such as glutathione S-transferases (GSTs), which play a key role in neutralizing toxic metabolites. By enhancing the activity of these enzymes, Coptis chinensis supports the liver’s detoxification capacity, contributing to overall liver health and resilience against toxic insults.
Mechanisms of Action: How Coptis Chinensis Improves Liver Health
Activation of AMPK Pathway: One of the primary mechanisms through which Coptis chinensis exerts its liver-protective effects is the activation of the AMPK pathway. AMPK acts as a metabolic master switch, regulating energy balance at the cellular level. By activating AMPK, Coptis chinensis helps reduce fat accumulation in the liver, enhances hepatocyte regeneration, and improves overall metabolic health. This is particularly beneficial for individuals with NAFLD, as it addresses the root cause of fat accumulation in the liver.
Inhibition of NF-κB Signaling: Chronic inflammation is a major driver of liver damage and disease progression. Coptis chinensis inhibits the NF-κB signaling pathway, thereby reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6). By modulating the inflammatory response, Coptis chinensis helps protect the liver from inflammatory damage and prevents the progression of liver disease.
Antioxidant Activity: Oxidative stress is a key factor in liver injury, particularly in conditions like NAFLD and alcoholic liver disease. The alkaloids in Coptis chinensis, especially berberine, exhibit potent antioxidant activity, neutralizing reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reducing oxidative stress. This not only protects liver cells from damage but also supports their regeneration and recovery.
Suppression of Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation: Liver fibrosis is a major complication of chronic liver disease, and the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) is central to this process. Coptis chinensis suppresses HSC activation by inhibiting the TGF-β signaling pathway, thereby reducing collagen production and preventing fibrosis. This anti-fibrotic effect is crucial for halting the progression of liver disease and maintaining healthy liver function.
Upregulation of Detoxification Enzymes: The liver’s ability to detoxify harmful substances is vital for overall health. Coptis chinensis enhances the expression of detoxification enzymes, such as glutathione S-transferases, which help neutralize toxins and protect liver cells from damage. This detoxification support is particularly beneficial for individuals exposed to environmental toxins or those with a history of alcohol consumption.
Coptis Chinensis and Overall Liver Function
Beyond its specific effects on liver disease, Coptis chinensis plays a broader role in enhancing overall liver function. By reducing fat accumulation, minimizing inflammation, and supporting detoxification, Coptis chinensis helps maintain optimal liver health. The liver is central to numerous physiological processes, including metabolism, detoxification, and the synthesis of vital proteins. By promoting liver health, Coptis chinensis indirectly supports these essential functions, contributing to overall well-being.
Metabolic Benefits
The liver plays a key role in regulating glucose and lipid metabolism. Berberine has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity and reduce blood lipid levels, both of which are beneficial for individuals with metabolic syndrome or type 2 diabetes. By improving metabolic health, Coptis chinensis helps reduce the burden on the liver, preventing the progression of fatty liver disease and other metabolic disorders.
Gut-Liver Axis
Emerging research has highlighted the importance of the gut-liver axis in liver health. The gut microbiota produces various metabolites that can influence liver function, and dysbiosis (an imbalance in the gut microbiota) is associated with liver disease. Berberine has been found to modulate the composition of the gut microbiota, promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria and reducing the abundance of harmful species. This modulation of the gut microbiota can help reduce liver inflammation and improve liver function, further enhancing the hepatoprotective effects of Coptis chinensis.
Conclusion: The Role of Coptis Chinensis in Liver Health
Coptis chinensis Franch root extract is a powerful natural remedy with significant potential for promoting liver health and preventing liver disease. Its hepatoprotective effects are mediated through multiple mechanisms, including the activation of the AMPK pathway, inhibition of NF-κB signaling, suppression of hepatic stellate cell activation, and upregulation of detoxification enzymes. By reducing fat accumulation, minimizing inflammation, preventing fibrosis, and supporting liver regeneration, Coptis chinensis offers a comprehensive approach to liver health.
The scientific evidence supporting the use of Coptis chinensis for liver health is robust, with numerous studies demonstrating its efficacy in reducing liver damage, preventing chronic liver disease, and enhancing overall liver function. Whether used as a preventive measure or as part of a broader treatment strategy, Coptis chinensis holds promise as a valuable tool for maintaining a healthy liver and supporting the body’s natural detoxification processes.
Incorporating Coptis chinensis into a liver health regimen can provide substantial benefits, particularly for individuals at risk of NAFLD, chronic liver disease, or those exposed to liver stressors such as alcohol and environmental toxins. As always, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement, especially for individuals with pre-existing health conditions or those taking medications. With its multifaceted benefits and strong scientific backing, Coptis chinensis stands out as a natural ally in the quest for optimal liver health.

Cordyceps Sinensis and Liver Health: Science-Backed Benefits for NAFLD, Cirrhosis, and Liver Regeneration
Cordyceps sinensis, a highly regarded medicinal mushroom, has been used in traditional Chinese medicine for centuries. Recent scientific research highlights its role in managing and improving liver conditions such as Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, cirrhosis, and overall liver function. This article delves into the hepatoprotective effects of Cordyceps sinensis extract, exploring the mechanisms through which it reduces liver damage, promotes liver regeneration, and supports the body’s detoxification processes.
Proven Benefits of Cordyceps Sinensis in NAFLD, Chronic Liver Disease, and Cirrhosis
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is a growing health concern globally, often linked to obesity, metabolic syndrome, and lifestyle factors. Cordyceps sinensis has shown promise in managing NAFLD and other liver-related disorders, including cirrhosis and chronic liver disease. The therapeutic potential of Cordyceps lies in its ability to modulate oxidative stress, inflammation, and lipid metabolism—all key factors contributing to liver disease progression.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties
One of the primary ways Cordyceps sinensis helps manage liver conditions is through its potent anti-inflammatory effects. Studies indicate that the polysaccharides and cordycepin (3′-deoxyadenosine) found in Cordyceps effectively suppress pro-inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6), both of which play critical roles in liver inflammation. This reduction in inflammation prevents the further progression of NAFLD and cirrhosis, improving liver function and reducing the risk of complications.
Antioxidant Mechanisms
Oxidative stress is a significant contributor to liver damage in chronic liver disease and NAFLD. Cordyceps sinensis contains bioactive compounds that boost the production of endogenous antioxidants, including superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px). These antioxidants neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS), reducing oxidative damage to liver cells and slowing disease progression. By enhancing the liver’s antioxidant defense system, Cordyceps helps mitigate hepatocyte injury and supports liver health.
Hepatoprotective Effects: Mechanisms and Evidence
The hepatoprotective properties of Cordyceps sinensis are well-supported by several peer-reviewed studies. These effects are mainly attributed to its ability to modulate lipid metabolism, regulate immune responses, and promote cellular repair.
Lipid Metabolism Regulation
NAFLD is characterized by an excessive accumulation of fat in the liver. Cordyceps sinensis has been shown to regulate lipid metabolism by enhancing the activity of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), an enzyme that plays a crucial role in maintaining energy balance. Activation of AMPK leads to increased fatty acid oxidation and reduced lipid synthesis in the liver, thereby lowering hepatic fat accumulation and improving overall liver function. This effect is particularly beneficial for individuals struggling with NAFLD and metabolic syndrome.
Immune Modulation
Cordyceps sinensis also exhibits immune-modulatory effects, which contribute to its hepatoprotective benefits. It helps maintain immune homeostasis by regulating the activity of various immune cells, including macrophages and T-cells. By reducing the activation of Kupffer cells (resident liver macrophages), Cordyceps minimizes the release of inflammatory mediators that can lead to liver fibrosis and cirrhosis. This modulation of immune responses aids in preventing the progression of chronic liver disease and maintains a healthier liver environment.
Protection Against Fibrosis
Liver fibrosis is a common outcome of chronic liver damage and can progress to cirrhosis if left unchecked. Research suggests that Cordyceps sinensis can inhibit hepatic stellate cell activation—a key driver of fibrosis. By suppressing the deposition of extracellular matrix components, Cordyceps helps reduce the extent of fibrosis and supports the maintenance of normal liver architecture. This anti-fibrotic activity is crucial for patients at risk of developing cirrhosis, as it slows disease progression and preserves liver function.
Liver Regeneration and Enhanced Detoxification
Cordyceps sinensis not only protects the liver from damage but also plays a role in regenerating damaged liver tissue and enhancing the liver’s detoxification capacity.
Promoting Liver Regeneration
The liver has a remarkable ability to regenerate, and Cordyceps sinensis supports this process through several mechanisms. Studies have shown that Cordyceps extract stimulates hepatocyte proliferation by activating growth factors such as hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β). These growth factors promote cellular repair and regeneration, enabling the liver to recover from damage caused by fatty liver disease, fibrosis, or other stressors.
In addition to growth factor stimulation, Cordyceps has been found to improve mitochondrial function, which is essential for energy production and cellular repair. By enhancing mitochondrial health, Cordyceps ensures that hepatocytes have the energy needed to regenerate effectively, thereby improving liver function and resilience.
Enhanced Detoxification and Overall Liver Function
The liver’s primary function is to detoxify the body by metabolizing toxins and waste products. Cordyceps sinensis enhances this detoxification process by supporting phase I and phase II detoxification enzymes. These enzymes, including cytochrome P450 and glutathione S-transferase, play critical roles in breaking down and eliminating harmful substances from the body.
Cordyceps has also been shown to increase bile production, which is essential for the excretion of fat-soluble toxins and metabolic waste. By enhancing bile flow, Cordyceps improves the liver’s ability to remove toxins, promoting a cleaner and healthier liver environment. This effect is particularly beneficial for individuals exposed to environmental toxins, alcohol, or other substances that place stress on the liver.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Cordyceps Sinensis for Liver Health
Numerous studies have demonstrated the benefits of Cordyceps sinensis for liver health. For instance, a study published in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology found that Cordyceps extract significantly reduced liver enzyme levels (such as ALT and AST) in animal models of liver injury, indicating reduced liver damage. Another study published in Phytomedicine highlighted the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of Cordyceps, which contributed to improved liver function and reduced fibrosis in subjects with chronic liver disease.
Clinical trials involving patients with NAFLD have also shown promising results. Participants who received Cordyceps supplementation experienced reductions in liver fat content, improved lipid profiles, and decreased markers of liver inflammation. These findings suggest that Cordyceps sinensis can be an effective adjunct therapy for managing NAFLD and preventing its progression to more severe liver conditions.
Summary: Cordyceps Sinensis as a Natural Solution for Liver Health
Cordyceps sinensis offers a multifaceted approach to improving liver health, backed by scientific evidence and centuries of traditional use. Its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and lipid-regulating properties make it an effective natural remedy for managing conditions such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. By protecting against liver damage, promoting regeneration, and enhancing detoxification, Cordyceps supports overall liver function and helps maintain a healthier internal environment.
For individuals seeking to improve their liver health, Cordyceps sinensis provides a natural, science-backed solution that targets the underlying mechanisms of liver disease. Whether used as a preventative measure or as part of a comprehensive treatment plan, Cordyceps has the potential to enhance liver function, support regeneration, and protect against the progression of liver disorders.
Key Takeaways
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Cordyceps reduces liver inflammation by suppressing pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α and IL-6.
Antioxidant Activity: Boosts endogenous antioxidants (SOD, GSH-Px) to protect liver cells from oxidative stress.
Lipid Metabolism: Enhances AMPK activity to reduce hepatic fat accumulation, beneficial for NAFLD management.
Immune Modulation: Regulates immune responses, reducing Kupffer cell activation and preventing liver fibrosis.
Fibrosis Prevention: Inhibits hepatic stellate cell activation, reducing fibrosis and slowing cirrhosis progression.
Liver Regeneration: Stimulates hepatocyte proliferation and improves mitochondrial function for effective liver repair.
Enhanced Detoxification: Supports phase I and II detoxification enzymes and increases bile production for efficient toxin removal.
Cordyceps sinensis stands out as a valuable ally in the fight against liver disease, providing a natural, well-rounded approach to liver protection, regeneration, and overall health improvement. By integrating Cordyceps into a holistic health regimen, individuals can support their liver’s vital functions, enhance detoxification, and promote long-term liver wellness.

Crataegus Pinnatifida Bge. Var. Major Leaves Extract: A Natural Ally in Liver Health
The liver is a vital organ responsible for numerous critical functions, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and metabolism regulation. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis represent major health concerns that compromise liver function and overall health. Recent scientific research has shed light on the hepatoprotective benefits of Crataegus pinnatifida Bge. var. major, commonly known as the Chinese hawthorn, particularly its leaves extract. This extract has emerged as a promising natural treatment for managing NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis due to its unique chemical composition and bioactive properties.
In this comprehensive synopsis, we will explore how Crataegus pinnatifida leaves extract helps prevent and manage liver diseases, its hepatoprotective mechanisms, and its contribution to liver regeneration and overall liver function. The focus will be on presenting only scientifically-backed information, ensuring the content is complete, insightful, and beneficial for readers seeking in-depth knowledge.
Hepatoprotective Effects of Crataegus Pinnatifida Leaves Extract
Crataegus pinnatifida leaves extract has demonstrated potent hepatoprotective properties, making it effective for managing and preventing liver damage caused by various factors, including NAFLD and cirrhosis. The extract’s effectiveness lies in its complex composition, rich in flavonoids, phenolic acids, and triterpenoids, which work synergistically to protect liver cells from damage.
1. Prevention of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD is characterized by excessive fat accumulation in liver cells, often driven by factors like obesity, diabetes, and poor dietary habits. Crataegus pinnatifida leaves extract exerts several beneficial effects in preventing the onset and progression of NAFLD:
Reduction of Lipid Accumulation: Studies have shown that the flavonoids and phenolic acids in Crataegus pinnatifida leaves can effectively reduce lipid accumulation in the liver. These compounds help regulate lipid metabolism by modulating enzymes such as AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), a key regulator of cellular energy homeostasis. By activating AMPK, the extract helps to enhance lipid oxidation and decrease fat deposition in liver cells.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: NAFLD is often accompanied by chronic low-grade inflammation. Crataegus pinnatifida leaves extract contains bioactive compounds that inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6). This anti-inflammatory action helps mitigate the inflammatory processes that exacerbate liver damage in NAFLD.
Oxidative Stress Reduction: Oxidative stress is a significant contributor to the progression of NAFLD. The extract is rich in antioxidants, including flavonoids like quercetin and hyperoside, which neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reduce oxidative damage to liver cells. By reducing oxidative stress, the extract helps maintain the integrity of hepatocytes and prevents further disease progression.
2. Management of Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver disease and cirrhosis are advanced stages of liver damage characterized by inflammation, fibrosis, and impaired liver function. The hepatoprotective properties of Crataegus pinnatifida leaves extract contribute to managing these conditions in several ways:
Inhibition of Fibrosis Progression: Fibrosis is the excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix proteins, leading to scarring of liver tissue. The triterpenoids present in the extract have been found to inhibit the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), which are responsible for collagen production and fibrosis. By preventing HSC activation, the extract helps slow down the progression of fibrosis and cirrhosis.
Anti-Apoptotic Effects: Chronic liver disease often leads to increased apoptosis (programmed cell death) of hepatocytes. The extract’s antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties help reduce apoptosis by maintaining mitochondrial integrity and reducing the release of pro-apoptotic factors. This preservation of hepatocytes is crucial for maintaining liver function in the face of chronic damage.
Immune Modulation: The immune-modulating properties of Crataegus pinnatifida leaves extract also play a role in managing chronic liver disease. By modulating immune responses and reducing the production of inflammatory mediators, the extract helps maintain a balanced immune environment in the liver, which is essential for minimizing further damage.
Mechanisms of Action: Hepatoprotective Pathways
The hepatoprotective effects of Crataegus pinnatifida leaves extract are mediated through multiple pathways that work in synergy to protect the liver:
Antioxidant Pathways: The extract enhances the liver’s antioxidant defense by upregulating the expression of antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx). These enzymes play a crucial role in detoxifying ROS and reducing oxidative damage, which is particularly beneficial in conditions like NAFLD and cirrhosis.
Anti-Inflammatory Pathways: Crataegus pinnatifida leaves extract modulates the nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) signaling pathway, which is a key regulator of inflammation. By inhibiting NF-κB activation, the extract reduces the production of inflammatory cytokines, thus mitigating inflammation-induced liver damage.
AMPK Activation: The activation of AMPK by the extract promotes fatty acid oxidation and inhibits lipid synthesis, thereby reducing hepatic steatosis and preventing NAFLD progression. AMPK also plays a role in enhancing insulin sensitivity, which further contributes to improved lipid metabolism and reduced fat accumulation in the liver.
Liver Regeneration and Improved Liver Function
The liver has an extraordinary capacity to regenerate after injury, and Crataegus pinnatifida leaves extract supports this regenerative ability through several mechanisms:
Promotion of Hepatocyte Proliferation: The extract contains bioactive compounds that promote hepatocyte proliferation, a key aspect of liver regeneration. Flavonoids in the extract have been found to stimulate the expression of growth factors such as hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), which plays a pivotal role in liver regeneration.
Reduction of Liver Enzyme Levels: Elevated liver enzymes, such as alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), are markers of liver damage. Studies have demonstrated that Crataegus pinnatifida leaves extract can help reduce these enzyme levels, indicating reduced liver injury and enhanced recovery.
Enhancement of Detoxification Processes: The liver’s detoxification processes are essential for maintaining overall health. The antioxidant properties of Crataegus pinnatifida leaves extract support phase I and phase II detoxification pathways, enhancing the liver’s ability to neutralize and eliminate toxins from the body. This detoxification support is crucial for maintaining a healthy liver environment and preventing further damage from harmful substances.
Overall Benefits for Liver Health
The benefits of Crataegus pinnatifida leaves extract for liver health extend beyond its hepatoprotective and regenerative properties. The extract also contributes to maintaining overall liver function and promoting a healthier liver environment:
Improved Lipid Metabolism: By regulating lipid metabolism and reducing fat accumulation, the extract helps maintain a healthy liver, reducing the risk of fatty liver disease and its associated complications.
Enhanced Insulin Sensitivity: The activation of AMPK by the extract not only improves lipid metabolism but also enhances insulin sensitivity. Improved insulin sensitivity is crucial for preventing metabolic conditions like type 2 diabetes, which is often associated with NAFLD and other liver diseases.
Protection Against Toxins: The liver is constantly exposed to various toxins, including alcohol, medications, and environmental pollutants. The antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of Crataegus pinnatifida leaves extract help protect liver cells from toxin-induced damage, supporting overall liver health and resilience.
Maintenance of Hepatic Microenvironment: The extract’s immune-modulating properties contribute to maintaining a balanced hepatic microenvironment, which is essential for optimal liver function. By reducing inflammation and oxidative stress, the extract helps create a favorable environment for liver cells to function effectively and regenerate after injury.
Conclusion: Crataegus Pinnatifida Leaves Extract as a Natural Solution for Liver Health
Crataegus pinnatifida Bge. var. major leaves extract has emerged as a powerful natural remedy for promoting liver health and preventing liver-related diseases. Its rich composition of flavonoids, phenolic acids, and triterpenoids provides comprehensive hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and regenerative effects. The extract effectively prevents and manages NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis by reducing lipid accumulation, inhibiting fibrosis, modulating immune responses, and promoting hepatocyte proliferation.
The hepatoprotective benefits of Crataegus pinnatifida leaves extract are supported by scientific evidence that highlights its ability to enhance liver function, reduce liver enzyme levels, and improve the liver’s natural detoxification processes. By supporting lipid metabolism, reducing inflammation, and protecting against oxidative stress, the extract contributes to maintaining a healthy liver environment, ultimately enhancing the body’s natural detoxification capacity.
As a natural and scientifically-backed solution, Crataegus pinnatifida leaves extract offers a promising approach for individuals seeking to improve liver health and prevent liver diseases. Incorporating this extract into a balanced lifestyle, alongside a healthy diet and regular exercise, may provide substantial benefits for maintaining optimal liver function and overall well-being.

The Proven Benefits of Curcuma Longa L. Extract in Preventing NAFLD, Chronic Liver Disease, and Cirrhosis
Curcuma longa L., commonly known as turmeric, has garnered significant attention in recent years for its hepatoprotective properties, particularly in preventing and managing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Extensive scientific research, primarily centered on curcumin—the primary bioactive component of turmeric—provides evidence of its efficacy in supporting liver health, reducing liver damage, and promoting regeneration. This comprehensive article delves into the mechanisms by which Curcuma longa L. extract supports liver health, focusing on evidence-backed benefits for liver protection, detoxification, and regeneration.
1. Preventing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is an increasingly common chronic condition characterized by the accumulation of fat in liver cells, often associated with obesity, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome. Scientific studies demonstrate that curcumin, the active compound in Curcuma longa L., plays a vital role in the prevention and management of NAFLD through several key mechanisms.
Anti-Inflammatory Action
Chronic inflammation is a central factor in the progression of NAFLD, advancing from simple steatosis (fat accumulation) to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Curcumin’s potent anti-inflammatory properties are mediated through the inhibition of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) and the reduction of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β. By inhibiting these inflammatory pathways, curcumin helps to mitigate hepatic inflammation, thus preventing the progression of NAFLD to more severe liver damage.
Antioxidant Effects
Oxidative stress is another significant contributor to NAFLD progression. Curcumin exhibits strong antioxidant properties by enhancing the activity of key antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase, and glutathione peroxidase. It also reduces lipid peroxidation and scavenges reactive oxygen species (ROS), thereby protecting liver cells from oxidative damage. Scientific studies have demonstrated that supplementation with curcumin significantly lowers markers of oxidative stress in patients with NAFLD, supporting liver function and preventing disease advancement.
Metabolic Regulation
Curcumin has also been shown to modulate lipid metabolism and improve insulin sensitivity—two crucial factors in managing NAFLD. Research indicates that curcumin downregulates sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c) and fatty acid synthase (FAS), which are key regulators of lipogenesis. By inhibiting these pathways, curcumin reduces hepatic fat accumulation, thus lowering the risk of developing NAFLD. Furthermore, curcumin improves insulin sensitivity by activating AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), a central energy-regulating enzyme, which further aids in reducing hepatic steatosis.
2. Managing Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver disease and cirrhosis, characterized by fibrosis and irreversible liver damage, are often preceded by persistent inflammation and oxidative stress. Curcuma longa L. extract has demonstrated hepatoprotective effects that can be beneficial in managing these conditions.
Inhibition of Hepatic Fibrosis
The progression of chronic liver disease to cirrhosis is marked by the excessive deposition of extracellular matrix components, leading to fibrosis. Curcumin has been shown to inhibit hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation, a pivotal event in liver fibrogenesis. By suppressing transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) signaling, curcumin prevents the activation and proliferation of HSCs, thereby reducing collagen production and fibrosis. Multiple animal and human studies have reported that curcumin supplementation results in decreased markers of liver fibrosis, highlighting its potential role in halting or slowing the progression of chronic liver disease.
Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Mechanisms
Chronic liver conditions often involve ongoing inflammation and oxidative damage. Curcumin’s dual action as an anti-inflammatory and antioxidant makes it uniquely effective in reducing liver injury. By inhibiting inflammatory mediators and enhancing the liver’s antioxidant defenses, curcumin not only prevents further damage but also creates a favorable environment for liver repair and regeneration.
3. Hepatoprotective Effects and Liver Regeneration
Curcuma longa L. extract’s hepatoprotective effects extend beyond disease prevention; it also plays a significant role in protecting the liver from various stressors and enhancing its regenerative capacity.
Protection Against Toxins and Liver Stressors
The liver is constantly exposed to various toxins, including drugs, alcohol, and environmental pollutants, which can lead to liver injury. Curcumin has been found to protect hepatocytes from toxic damage through its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory actions. Studies have shown that curcumin reduces liver enzyme levels (e.g., ALT and AST), which are indicators of liver injury, in patients exposed to hepatotoxic substances. This reduction suggests that curcumin helps to maintain liver integrity and function under stressful conditions.
Stimulation of Liver Regeneration
Curcumin also promotes liver regeneration, which is crucial for recovery following liver injury. It has been observed to upregulate hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and enhance the expression of genes involved in cell proliferation. These actions facilitate the regeneration of liver tissue, aiding in the restoration of normal liver structure and function. In animal models, curcumin treatment has been linked to increased liver regeneration following partial hepatectomy, indicating its potential in supporting liver recovery.
4. Enhancing Overall Liver Function and Detoxification
The liver plays a central role in detoxifying harmful substances, metabolizing fats, and regulating various metabolic processes. Curcuma longa L. extract has demonstrated multiple benefits that contribute to enhanced liver function and detoxification.
Promotion of Bile Production and Flow
Bile production is essential for the digestion and absorption of fats, as well as for the elimination of toxins from the body. Curcumin has been shown to stimulate bile production and improve bile flow, thereby supporting the liver’s detoxification processes. Improved bile flow helps in the efficient removal of waste products, reducing the burden on the liver and promoting a healthier hepatic environment.
Reduction of Liver Enzyme Levels
Elevated liver enzyme levels are indicative of liver damage or dysfunction. Numerous clinical studies have reported that curcumin supplementation results in a significant reduction in liver enzymes such as alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST). This reduction suggests an improvement in liver health and function, reflecting curcumin’s ability to protect hepatocytes from damage and enhance overall liver performance.
5. Supporting the Body’s Natural Detoxification Processes
Curcumin’s role in supporting the liver extends to enhancing the body’s natural detoxification pathways. It does so through the activation of phase II detoxification enzymes, including glutathione-S-transferase (GST), which are crucial for neutralizing and excreting toxins. By boosting the activity of these enzymes, curcumin aids in the efficient detoxification of harmful substances, reducing the toxic load on the liver and other organs.
Regulation of Lipid and Glucose Metabolism
The liver is central to lipid and glucose metabolism, and disruptions in these processes can lead to metabolic disorders and liver disease. Curcumin has been shown to regulate lipid metabolism by reducing the expression of lipogenic genes and enhancing fatty acid oxidation. It also improves glucose metabolism by enhancing insulin sensitivity, thereby reducing the risk of insulin resistance—a key factor in the development of NAFLD. By optimizing lipid and glucose metabolism, curcumin supports overall metabolic health and reduces the burden on the liver.
6. Safety and Dosage Considerations
Curcuma longa L. extract, particularly in the form of curcumin, is generally considered safe for most individuals when consumed in moderate doses. Clinical studies suggest that daily doses ranging from 500 mg to 2000 mg of curcumin are well-tolerated and effective for liver health benefits. However, curcumin’s bioavailability is naturally low, and it is often recommended to consume it with piperine (black pepper extract) or in formulated supplements designed to enhance absorption.
While curcumin is a powerful natural compound with numerous health benefits, it is important to consult a healthcare provider before starting supplementation, especially for individuals with existing medical conditions or those taking medications, as curcumin may interact with certain drugs.
Conclusion: Curcuma Longa L. Extract as a Potent Ally for Liver Health
Curcuma longa L. extract, with its active component curcumin, offers a broad spectrum of benefits for liver health, ranging from the prevention of NAFLD to the management of chronic liver disease and cirrhosis. Its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antifibrotic properties, coupled with its ability to enhance liver regeneration and support detoxification, make it a valuable natural remedy for maintaining liver health and function.
The scientific evidence supporting the hepatoprotective effects of curcumin is compelling, highlighting its potential as a preventive and therapeutic agent for liver-related conditions. By reducing inflammation, mitigating oxidative stress, inhibiting fibrosis, and promoting liver regeneration, curcumin provides a multifaceted approach to improving liver health and enhancing the body’s natural detoxification capabilities. As research continues to unveil the full range of its benefits, Curcuma longa L. extract remains a promising natural option for supporting liver wellness and overall health.

Curcuma Phaeocaulis Radix: A Comprehensive Overview of Its Hepatoprotective Effects and Liver Health Benefits
Curcuma phaeocaulis Radix, a traditional medicinal herb often utilized in Chinese medicine, has gained significant scientific interest for its liver-protective properties. Modern research reveals that this botanical offers a wide range of hepatoprotective effects, including the prevention and management of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Moreover, Curcuma phaeocaulis Radix contributes to overall liver regeneration, mitigates liver damage from fatty deposits, and promotes a healthier liver environment to enhance the body’s natural detoxification processes. This article delves into the scientifically supported health effects of Curcuma phaeocaulis Radix, detailing its mechanisms of action, proven benefits, and potential contributions to liver health.
The Role of Curcuma Phaeocaulis Radix in Preventing NAFLD and Chronic Liver Diseases
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is a prevalent condition characterized by excess fat accumulation in the liver, affecting millions of people globally. Curcuma phaeocaulis Radix has demonstrated potential in preventing and managing NAFLD through its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and lipid-regulating properties.
Curcuma phaeocaulis Radix is rich in bioactive compounds such as curcuminoids, essential oils, and other phenolic compounds. These compounds have demonstrated strong anti-inflammatory properties, which play a critical role in reducing inflammation associated with NAFLD. Chronic inflammation is a key driver in the progression of NAFLD, which can lead to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and eventually cirrhosis. Studies have shown that the anti-inflammatory activity of Curcuma phaeocaulis helps in downregulating inflammatory markers, such as TNF-α and IL-6, thereby mitigating the risk of progression from NAFLD to more severe liver diseases.
Furthermore, the antioxidant activity of Curcuma phaeocaulis Radix is pivotal in combating oxidative stress—a significant factor in liver damage. The liver, being a major organ for detoxification, is often exposed to reactive oxygen species (ROS) that cause oxidative damage. Curcuma phaeocaulis has been shown to increase the expression of antioxidant enzymes like superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx), which help neutralize ROS, reducing oxidative stress and preserving liver cell integrity.
Hepatoprotective Effects: Reducing Liver Damage from Fatty Liver and Liver Stressors
One of the most notable benefits of Curcuma phaeocaulis Radix is its ability to protect the liver from various stressors, including fatty liver and toxins. The herb’s hepatoprotective properties are primarily attributed to its ability to modulate lipid metabolism and enhance detoxification pathways.
Research has demonstrated that Curcuma phaeocaulis can help reduce hepatic lipid accumulation by regulating key metabolic pathways, such as the AMPK pathway, which is involved in fatty acid oxidation. Activation of AMPK by Curcuma phaeocaulis helps in decreasing lipid synthesis while promoting the breakdown of existing fat deposits in the liver, thereby reducing hepatic steatosis—a hallmark of fatty liver disease. This effect is further supported by the herb’s ability to lower blood lipid levels, including triglycerides and LDL cholesterol, which are significant contributors to fatty liver disease.
Additionally, Curcuma phaeocaulis Radix has been found to inhibit the activity of pro-fibrotic factors, such as transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1), which are responsible for collagen deposition in the liver, leading to fibrosis and cirrhosis. By reducing fibrosis, Curcuma phaeocaulis contributes to maintaining liver tissue structure and preventing the progression of chronic liver diseases to irreversible stages like cirrhosis.
The hepatoprotective benefits of Curcuma phaeocaulis also extend to reducing damage caused by liver toxins. Studies have demonstrated that the herb helps in maintaining the integrity of hepatocyte membranes by preventing lipid peroxidation—a process in which free radicals attack fatty acids in cell membranes, leading to cellular damage. By reducing lipid peroxidation, Curcuma phaeocaulis Radix minimizes liver injury caused by various toxins, including alcohol, medications, and environmental pollutants.
Promoting Liver Regeneration and Enhanced Liver Function
Curcuma phaeocaulis Radix also plays a significant role in liver regeneration and enhancing overall liver function. The liver is unique in its regenerative ability, and Curcuma phaeocaulis supports this process by promoting hepatocyte proliferation and tissue repair. Animal studies have shown that treatment with Curcuma phaeocaulis leads to increased hepatocyte proliferation following liver injury, indicating its potential in accelerating liver regeneration.
The herb’s regenerative effects are closely linked to its ability to modulate growth factors, such as hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), which is essential for liver repair. Curcuma phaeocaulis also exerts anti-apoptotic effects, meaning it helps in reducing programmed cell death of hepatocytes, thus preserving liver tissue and promoting a conducive environment for regeneration.
Moreover, Curcuma phaeocaulis Radix enhances bile production and secretion, which is crucial for digestion and detoxification. Increased bile flow supports the excretion of fat-soluble toxins and enhances digestion, thereby contributing to overall liver function. This bile-promoting effect helps in reducing the accumulation of harmful substances within the liver, promoting a healthier internal environment.
Mechanisms of Action: How Curcuma Phaeocaulis Radix Improves Liver Health
The mechanisms underlying the hepatoprotective effects of Curcuma phaeocaulis Radix are multifaceted, involving several key biochemical pathways. The herb’s bioactive components influence inflammation, oxidative stress, lipid metabolism, and cellular regeneration. Below is a detailed breakdown of the main mechanisms of action:
Anti-Inflammatory Pathways: Curcuma phaeocaulis downregulates inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α and IL-6, reducing inflammation in liver tissues. This is primarily achieved through the inhibition of the NF-κB signaling pathway, which is a central regulator of inflammatory responses.
Antioxidant Defense: The herb enhances the liver’s antioxidant capacity by upregulating key antioxidant enzymes such as SOD, GPx, and catalase. These enzymes play an essential role in neutralizing ROS, thus protecting liver cells from oxidative damage.
Lipid Metabolism Regulation: Curcuma phaeocaulis activates the AMPK pathway, which helps in enhancing fatty acid oxidation while inhibiting lipid synthesis. This regulation helps reduce hepatic fat accumulation, preventing fatty liver disease.
Anti-Fibrotic Activity: The herb inhibits the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) and downregulates TGF-β1, which are involved in liver fibrosis. By preventing collagen deposition, Curcuma phaeocaulis helps in reducing the risk of cirrhosis.
Hepatocyte Regeneration: Curcuma phaeocaulis promotes the expression of HGF, which stimulates hepatocyte proliferation and supports liver regeneration. It also exerts anti-apoptotic effects, reducing liver cell death and promoting tissue repair.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Curcuma Phaeocaulis Radix for Liver Health
Numerous studies have demonstrated the beneficial effects of Curcuma phaeocaulis Radix on liver health. Animal models of NAFLD have shown that treatment with Curcuma phaeocaulis results in a significant reduction in hepatic fat accumulation and inflammatory markers. These findings suggest that Curcuma phaeocaulis could be a promising therapeutic agent for managing NAFLD and preventing its progression to more severe liver conditions.
In vitro studies have also provided insights into the anti-fibrotic properties of Curcuma phaeocaulis. Researchers have observed a decrease in the activation of hepatic stellate cells—a key process in liver fibrosis—when exposed to Curcuma phaeocaulis extracts. This suggests that the herb may help in preventing the development of cirrhosis by targeting the fibrotic pathways in the liver.
Furthermore, clinical trials involving Curcuma species have highlighted the hepatoprotective effects of curcuminoids, which are also present in Curcuma phaeocaulis. These trials have reported improvements in liver function markers, such as ALT and AST levels, in patients with fatty liver disease and other chronic liver conditions. While more clinical research specifically focusing on Curcuma phaeocaulis is needed, these findings provide a strong foundation for its use as a liver-protective supplement.
Conclusion: Curcuma Phaeocaulis Radix as a Potent Hepatoprotective Agent
Curcuma phaeocaulis Radix has emerged as a promising natural remedy for supporting liver health and preventing liver-related disorders. Its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and lipid-regulating properties make it an effective agent in preventing NAFLD, reducing liver damage from fatty deposits, and mitigating liver fibrosis. The herb’s ability to enhance liver regeneration, promote bile production, and support detoxification further underscores its comprehensive benefits for liver health.
While more clinical studies are needed to fully elucidate the therapeutic potential of Curcuma phaeocaulis Radix in humans, current evidence suggests that it holds significant promise as a complementary approach to managing liver diseases. By modulating key biochemical pathways, reducing oxidative stress, and supporting liver regeneration, Curcuma phaeocaulis Radix offers a natural means of promoting a healthier liver environment and enhancing overall liver function.
For individuals seeking to support their liver health naturally, Curcuma phaeocaulis Radix represents a scientifically backed, effective option. As always, consultation with healthcare professionals is recommended before starting any herbal supplement, especially for those with pre-existing health conditions or those taking other medications.

Curcumin and Liver Health: Proven Benefits for Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), Chronic Liver Disease, and Cirrhosis
Curcumin, a bioactive compound found in turmeric, has garnered attention for its potent liver-protective properties. Emerging research underscores its efficacy in combating liver disorders such as Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. This synopsis delves into the science-backed health benefits of curcumin for liver function, exploring its mechanisms of action and emphasizing its role in hepatoprotection, liver regeneration, and overall liver health.
1. Hepatoprotective Effects of Curcumin
Curcumin has shown significant hepatoprotective effects, helping to safeguard the liver from damage caused by a variety of stressors, including fatty liver accumulation, oxidative stress, and inflammation. Hepatoprotective refers to the ability of a substance to prevent damage to liver cells, thereby preserving liver function and reducing the risk of liver disease progression.
One of the primary mechanisms by which curcumin exerts its hepatoprotective action is through its antioxidant activity. The liver is particularly susceptible to oxidative stress due to its role in detoxifying harmful substances. Curcumin has been demonstrated to neutralize free radicals and enhance the activity of endogenous antioxidants such as glutathione, superoxide dismutase, and catalase, thereby protecting hepatocytes (liver cells) from oxidative injury. Numerous studies have also shown that curcumin helps inhibit lipid peroxidation—a critical factor in preventing liver cell damage and inflammation.
In addition, curcumin modulates inflammatory pathways by downregulating nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) and inhibiting the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β. Chronic inflammation is a major contributor to liver fibrosis, cirrhosis, and NAFLD. By reducing inflammation, curcumin helps prevent the progression of these liver conditions.
2. Curcumin and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD is a prevalent liver disorder characterized by excessive fat accumulation in the liver without significant alcohol consumption. Curcumin’s beneficial effects on NAFLD stem from its ability to address several pathological features of the disease, including fat accumulation, insulin resistance, inflammation, and oxidative stress.
Curcumin has been shown to reduce hepatic lipid accumulation through its influence on lipid metabolism pathways. By modulating the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR-γ) and the sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c), curcumin promotes the breakdown of fat and inhibits lipogenesis (the production of fatty acids), reducing the buildup of triglycerides in the liver. Studies have indicated that curcumin supplementation significantly reduces liver fat content in patients with NAFLD, thereby improving liver function and reducing disease severity.
Moreover, curcumin enhances insulin sensitivity by increasing the phosphorylation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), a key regulator of glucose and lipid metabolism. This helps improve glucose homeostasis and reduces insulin resistance—one of the key drivers of NAFLD. By modulating both insulin resistance and lipid accumulation, curcumin offers a comprehensive approach to managing NAFLD and its associated complications.
3. Curcumin’s Role in Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis and chronic liver disease are characterized by the presence of fibrosis—excessive deposition of extracellular matrix components—which eventually impairs liver function. Curcumin has been demonstrated to have potent anti-fibrotic effects, making it a promising therapeutic agent for cirrhosis and chronic liver disease.
Curcumin reduces liver fibrosis by inhibiting the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), which are the primary drivers of fibrogenesis in the liver. Activated HSCs produce large amounts of collagen, leading to fibrosis and scar tissue formation. Studies indicate that curcumin prevents HSC activation and promotes apoptosis (programmed cell death) of these cells, effectively halting the fibrotic process.
In addition, curcumin downregulates the production of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β), a key fibrogenic cytokine involved in stimulating collagen production. By inhibiting TGF-β signaling, curcumin helps to reduce the deposition of fibrotic tissue and prevent the progression of cirrhosis. This mechanism highlights curcumin’s potential to slow the progression of chronic liver diseases where fibrosis is a central component.
4. Liver Regeneration and Enhanced Liver Function
The liver possesses a remarkable ability to regenerate following injury or damage, and curcumin has been found to support this regenerative process. Curcumin stimulates hepatocyte proliferation, which is essential for the regeneration of liver tissue. By promoting the regeneration of healthy liver cells, curcumin helps maintain liver structure and function, especially in the aftermath of injury due to toxic substances or disease progression.
Curcumin also contributes to enhanced liver function by improving bile production and flow. Bile plays a critical role in digestion and detoxification, and impaired bile flow can exacerbate liver disorders. Curcumin has choleretic properties, meaning it stimulates bile production and secretion, which supports liver function and helps the body detoxify more efficiently.
5. Promoting a Healthier Liver Environment and Natural Detoxification
One of the liver’s primary functions is to detoxify the body by processing and eliminating toxins. Curcumin enhances the liver’s natural detoxification processes by modulating phase I and phase II detoxification enzymes. These enzymes are crucial for converting fat-soluble toxins into water-soluble compounds that can be easily excreted from the body.
Curcumin’s impact on phase II detoxification enzymes, including glutathione S-transferases (GST), enhances the liver’s ability to conjugate toxins, thereby facilitating their excretion. This process is vital for reducing the toxic load on the liver and minimizing liver cell damage. Additionally, curcumin’s antioxidant properties further support detoxification by reducing oxidative stress, which can result from the accumulation of harmful substances in the liver.
6. Scientific Evidence Supporting Curcumin’s Benefits for Liver Health
The efficacy of curcumin in promoting liver health has been supported by numerous clinical and preclinical studies. Randomized controlled trials have demonstrated that curcumin supplementation significantly reduces liver fat content, improves liver enzyme levels (such as ALT and AST), and reduces markers of inflammation in patients with NAFLD. A meta-analysis of multiple studies concluded that curcumin has beneficial effects on liver function tests, reducing ALT, AST, and gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT) levels, all of which are important indicators of liver health.
Animal studies have also provided substantial evidence of curcumin’s hepatoprotective effects. For example, in rodent models of liver fibrosis, curcumin has been shown to significantly reduce collagen deposition and liver damage by modulating key fibrotic pathways. These findings support the potential application of curcumin as an adjunct therapy for chronic liver disease and cirrhosis.
7. Dosage and Bioavailability Considerations
While curcumin is highly effective, its clinical application has been limited by its poor bioavailability. Curcumin is poorly absorbed, rapidly metabolized, and quickly eliminated from the body. However, various formulations have been developed to enhance its bioavailability, including curcumin-phospholipid complexes, nanoparticles, and formulations combined with piperine (a compound from black pepper), which has been shown to enhance curcumin absorption by up to 2,000%.
Studies involving enhanced bioavailable forms of curcumin have reported more pronounced effects on liver health, making these formulations preferable for achieving therapeutic benefits. The optimal dosage of curcumin for liver health varies depending on the formulation, but clinical trials have generally used doses ranging from 500 mg to 2,000 mg per day, with promising results for liver protection and disease management.
8. Safety and Side Effects
Curcumin is generally considered safe for consumption, even at relatively high doses. However, mild side effects such as gastrointestinal discomfort, nausea, or diarrhea have been reported in some individuals, particularly at higher doses. It is advisable for individuals with liver conditions to consult a healthcare professional before starting curcumin supplementation, especially if they are taking other medications, as curcumin may interact with certain drugs metabolized by the liver.
Conclusion: Curcumin as a Liver Health Ally
Curcumin stands out as a natural, evidence-based compound with considerable benefits for liver health. Its hepatoprotective properties, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects, and ability to reduce liver fibrosis make it a promising therapeutic option for individuals dealing with liver disorders such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Furthermore, curcumin supports liver regeneration, enhances bile production, and promotes natural detoxification processes, contributing to a healthier liver environment overall.
The scientific evidence supporting curcumin’s efficacy in improving liver function is robust, with numerous studies demonstrating its positive impact on liver biomarkers, fat metabolism, and inflammation. While bioavailability remains a challenge, advanced formulations have made curcumin supplementation more effective, allowing individuals to harness its full potential for liver health.
By incorporating curcumin into a balanced diet or as a supplement, individuals may enhance their liver’s resilience to stress, reduce the risk of liver disease progression, and promote optimal liver function. As always, consulting with a healthcare professional is recommended to ensure safe and effective use, particularly for those with pre-existing liver conditions or those taking other medications.
In conclusion, curcumin offers a natural and scientifically validated approach to supporting liver health—helping to protect, regenerate, and optimize liver function for overall well-being.

Curdrania tricuspidata Leaves: A Natural Solution for Liver Health and Disease Prevention
Curdrania tricuspidata, commonly known as cudrania or Chinese mulberry, is a medicinal plant that has gained scientific attention for its remarkable health benefits, particularly in liver health. The bioactive compounds found in Curdrania tricuspidata leaves have shown promising effects in preventing and managing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. This article presents a comprehensive analysis of the scientific evidence supporting the hepatoprotective and regenerative properties of cudrania leaves, shedding light on how this natural remedy contributes to liver health and functionality.
Hepatoprotective Effects of Curdrania tricuspidata
One of the most important aspects of Curdrania tricuspidata leaves is their hepatoprotective properties, which protect liver cells from damage caused by various stressors, including fatty liver disease and toxins. Studies have shown that cudrania leaves contain a rich composition of bioactive compounds such as flavonoids, phenolic acids, and polysaccharides that possess strong antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and lipid-lowering effects.
Antioxidant Mechanism
The leaves of Curdrania tricuspidata are rich in flavonoids like quercetin and kaempferol, which play a significant role in neutralizing oxidative stress. Oxidative stress is one of the leading factors behind liver damage, as it leads to the formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) that harm liver cells. The antioxidant properties of cudrania leaves have been demonstrated to reduce oxidative stress in the liver, thus preventing cellular damage that can lead to conditions such as NAFLD and chronic liver disease. Research shows that the potent antioxidant capacity of cudrania leaf extracts helps to boost the liver’s own defense mechanisms, minimizing the damage caused by free radicals.
Anti-Inflammatory Action
Another vital mechanism through which Curdrania tricuspidata leaves contribute to liver health is by reducing inflammation. Chronic liver inflammation is a key component in the progression of liver diseases such as fibrosis, cirrhosis, and NAFLD. The polyphenols in cudrania leaves inhibit pro-inflammatory mediators like tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6), which are responsible for promoting inflammation in liver tissue. By modulating the activity of these inflammatory markers, cudrania leaves help in preventing chronic inflammation and the progression of liver diseases.
Prevention and Management of NAFLD
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is characterized by an excessive accumulation of fat in liver cells, often due to poor diet, obesity, or metabolic syndrome. Curdrania tricuspidata leaves are effective in preventing and managing NAFLD, primarily due to their ability to modulate lipid metabolism and reduce fat accumulation in the liver.
Regulation of Lipid Metabolism
Studies have highlighted that cudrania leaf extracts can inhibit lipogenesis (the process of fat formation) and enhance fatty acid oxidation. By regulating enzymes such as AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha (PPAR-α), cudrania leaves promote the breakdown of fatty acids and prevent the buildup of triglycerides in liver cells. As a result, these mechanisms help in reducing hepatic steatosis (fatty liver) and improving overall liver function.
Protection Against Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver diseases and cirrhosis often develop from prolonged liver damage and inflammation. The hepatoprotective properties of cudrania leaves play a key role in reducing the risk of chronic liver conditions and cirrhosis.
Fibrosis Inhibition
The development of fibrosis—the accumulation of scar tissue in the liver—is a precursor to cirrhosis. Curdrania tricuspidata leaves help prevent fibrosis by inhibiting the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), which are the main contributors to fibrogenesis. The polyphenolic compounds in cudrania inhibit HSC activation and reduce the deposition of collagen in liver tissue, thus mitigating the progression from fibrosis to cirrhosis.
Reduction of Hepatotoxicity
Hepatotoxicity, or liver toxicity, is often caused by exposure to drugs, alcohol, or environmental toxins. Curdrania tricuspidata leaves have been shown to protect the liver from toxic substances by enhancing the activity of detoxifying enzymes such as glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) and superoxide dismutase (SOD). These enzymes are crucial in detoxifying harmful substances and reducing liver injury. The protective effects of cudrania leaves against hepatotoxicity make them a promising natural remedy for supporting liver health, especially for individuals exposed to liver stressors.
Liver Regeneration and Enhanced Detoxification
A unique and highly beneficial aspect of Curdrania tricuspidata leaves is their ability to promote liver regeneration and enhance the body’s natural detoxification processes. Liver regeneration is vital for maintaining liver function, particularly after injury or disease.
Stimulation of Liver Regeneration
Curdrania tricuspidata leaves are known to enhance the liver’s regenerative capacity. The presence of bioactive compounds such as polysaccharides and flavonoids has been linked to increased hepatocyte proliferation, which is essential for liver regeneration. Studies suggest that cudrania leaf extracts stimulate the synthesis of growth factors like hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), which promotes the regeneration of damaged liver tissue. This regenerative ability is especially crucial for patients with chronic liver diseases who need to restore lost liver function.
Promotion of Detoxification
The liver’s primary role in detoxification is supported by cudrania leaves, which enhance the liver’s ability to neutralize and eliminate toxins. The bioactive compounds in cudrania leaves stimulate phase I and phase II detoxification pathways, leading to the conversion of lipophilic toxins into water-soluble compounds that can be easily excreted from the body. This enhanced detoxification capacity not only supports liver health but also contributes to overall well-being by reducing the burden of toxins in the body.
Improvement of Overall Liver Function
Curdrania tricuspidata leaves provide a multi-faceted approach to improving overall liver function. By reducing oxidative stress, minimizing inflammation, preventing fat accumulation, and promoting regeneration, cudrania leaves create a healthier liver environment. This comprehensive hepatoprotective action helps maintain optimal liver function, which is crucial for various bodily processes, including metabolism, detoxification, and the synthesis of essential proteins.
Enhanced Bile Production
One of the ways cudrania leaves improve liver function is by stimulating bile production. Bile is essential for the digestion and absorption of fats, and it also plays a role in the excretion of waste products from the liver. Curdrania tricuspidata leaves have been shown to enhance bile flow, which facilitates the efficient removal of metabolic waste and improves fat digestion. This bile-enhancing effect contributes to a healthier liver and supports overall digestive health.
Reduction of Insulin Resistance
NAFLD is often associated with insulin resistance, which further exacerbates liver dysfunction. Curdrania tricuspidata leaves have been shown to improve insulin sensitivity, thereby reducing the risk of NAFLD progression. The improvement in insulin resistance is attributed to the activation of AMPK, which plays a crucial role in glucose and lipid metabolism. By improving insulin sensitivity, cudrania leaves help in reducing hepatic fat accumulation and enhancing liver function.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Curdrania tricuspidata’s Liver Benefits
The health benefits of Curdrania tricuspidata leaves for liver health have been supported by numerous preclinical and clinical studies. Animal studies have consistently demonstrated the hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant effects of cudrania leaf extracts in various models of liver injury, including those induced by high-fat diets, alcohol, and chemical toxins. These studies provide strong evidence for the liver-protective properties of cudrania leaves and their potential for preventing and managing liver diseases.
In a study published in the Journal of Medicinal Food, cudrania leaf extract was shown to significantly reduce liver enzyme levels, indicating reduced liver damage in rats with chemically induced liver injury. Another study published in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences highlighted the anti-fibrotic effects of cudrania polyphenols, demonstrating their ability to inhibit the activation of hepatic stellate cells and reduce collagen deposition in the liver.
While human clinical trials are still limited, the available evidence suggests that cudrania leaves hold significant potential for liver health. The need for further research is evident, but the existing data provides a strong foundation for considering cudrania leaves as a natural supplement for liver support.
Conclusion: A Promising Natural Remedy for Liver Health
Curdrania tricuspidata leaves offer a holistic approach to maintaining liver health and preventing liver diseases such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Through their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, lipid-lowering, and regenerative properties, cudrania leaves provide comprehensive support for liver function. The scientific evidence supporting these benefits highlights the potential of cudrania leaves as a natural solution for enhancing liver health and promoting the body’s natural detoxification processes.
Incorporating Curdrania tricuspidata leaves into a liver health regimen could be a valuable step toward improving liver function, preventing disease progression, and supporting overall well-being. While more human studies are needed to fully establish the efficacy of cudrania leaves in liver health, the current research indicates a promising future for this natural remedy in liver disease management and prevention.
For those looking to support their liver health naturally, Curdrania tricuspidata leaves provide a scientifically-backed option that promotes a healthier liver environment, aids in detoxification, and enhances the body’s ability to regenerate liver tissue. As always, consulting with a healthcare professional before adding new supplements is recommended, especially for individuals with existing health conditions.
 Dendropanax Morbifera Leveille: Proven Benefits for Liver Health and Prevention of Chronic Liver Diseases
Dendropanax Morbifera Leveille: Proven Benefits for Liver Health and Prevention of Chronic Liver Diseases
Dendropanax morbifera, often referred to as “the miraculous tree,” has long been used in traditional medicine across East Asia. Its leaves are garnering increasing attention in the scientific community for their potent effects on liver health, particularly in preventing and managing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. The therapeutic potential of Dendropanax morbifera leaves is supported by robust scientific evidence that highlights their hepatoprotective, liver-regenerative, and overall health-promoting properties.
1. Preventing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD is a growing concern worldwide, largely driven by unhealthy diets, obesity, and sedentary lifestyles. The leaves of Dendropanax morbifera contain bioactive compounds, including polyphenols and flavonoids, that exhibit powerful antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. These compounds have been demonstrated to effectively reduce oxidative stress, one of the primary factors responsible for the onset and progression of NAFLD.
Oxidative stress results from an imbalance between reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and the liver’s ability to detoxify these reactive intermediates. Studies have found that the antioxidants present in Dendropanax morbifera can neutralize ROS, thus preventing liver cell damage. Specifically, animal studies have indicated that extracts from Dendropanax leaves significantly lower the accumulation of fat in hepatocytes, thereby preventing fatty liver development.
The anti-inflammatory properties of Dendropanax morbifera are also crucial in preventing NAFLD. Chronic inflammation contributes to the progression of simple fatty liver into more severe conditions like steatohepatitis, fibrosis, and cirrhosis. By modulating key inflammatory pathways—such as inhibiting NF-κB activation—Dendropanax leaves help to prevent the low-grade inflammation commonly associated with NAFLD.
2. Hepatoprotective Effects: Reducing Liver Damage and Stress
The hepatoprotective properties of Dendropanax morbifera leaves are supported by several in vivo and in vitro studies. These leaves contain compounds such as chlorogenic acid and rutin, which play a vital role in minimizing liver damage caused by various stressors, including high-fat diets, alcohol consumption, and toxins.
One of the key mechanisms by which Dendropanax morbifera protects the liver is through enhancing the activity of antioxidant enzymes like superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx). These enzymes are essential for neutralizing harmful free radicals and reducing lipid peroxidation—a process that damages liver cell membranes. Research has shown that administration of Dendropanax leaf extract can increase the levels of these antioxidant enzymes, thereby bolstering the liver’s natural defense mechanisms.
Furthermore, Dendropanax morbifera helps reduce elevated liver enzymes such as ALT and AST, which are markers of liver injury. Studies involving animal models of chemically-induced liver damage have demonstrated that Dendropanax extracts significantly reduce ALT and AST levels, suggesting a reduction in liver cell damage and an overall hepatoprotective effect.
3. Preventing Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver diseases, including cirrhosis, often develop due to prolonged inflammation and oxidative stress, leading to progressive scarring of liver tissue. Dendropanax morbifera leaves have shown promise in mitigating these harmful processes. Their anti-fibrotic properties help prevent the accumulation of excessive extracellular matrix, which is a hallmark of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis.
One proposed mechanism involves the inhibition of hepatic stellate cell activation. Hepatic stellate cells are responsible for the production of collagen, the primary component of scar tissue in the liver. Studies have found that the polyphenolic compounds in Dendropanax can inhibit the activation of these cells, thus preventing the progression of fibrosis to cirrhosis.
Moreover, Dendropanax morbifera’s ability to modulate the immune response plays a role in preventing chronic liver disease. By regulating pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6, Dendropanax leaves help to maintain a balanced immune environment in the liver, reducing the risk of chronic inflammation and fibrosis.
4. Promoting Liver Regeneration and Function
The liver has a remarkable capacity for regeneration, but chronic conditions and prolonged damage can impair this ability. Dendropanax morbifera leaves have demonstrated hepatoregenerative properties that aid in the recovery of liver function after injury.
Studies have shown that extracts from Dendropanax leaves promote the proliferation of healthy hepatocytes, which are essential for effective liver regeneration. This effect is partly attributed to the presence of growth-promoting compounds that stimulate hepatocyte division and repair damaged liver tissue. Enhanced regeneration not only restores normal liver architecture but also helps maintain essential liver functions such as protein synthesis, bile production, and metabolism of nutrients.
Additionally, the ability of Dendropanax morbifera to reduce oxidative stress and inflammation creates a more favorable environment for liver regeneration. By minimizing the ongoing damage and stress, these leaves provide the liver with the conditions it needs to heal and regenerate effectively.
5. Enhancing Detoxification and Overall Liver Function
The liver’s primary role in detoxification makes it one of the most vital organs for overall health. Dendropanax morbifera leaves contribute to enhancing the liver’s detoxification capacity by upregulating phase I and phase II detoxification enzymes. These enzymes are responsible for converting toxins into less harmful substances that can be excreted from the body.
Specifically, Dendropanax has been shown to increase the activity of cytochrome P450 enzymes, which are crucial for the metabolism of various xenobiotics and endogenous compounds. This enhancement of enzymatic activity ensures that the liver can efficiently process and eliminate toxins, reducing the burden on the liver and promoting overall health.
The leaves also support bile production, which is essential for the digestion and absorption of dietary fats and the elimination of fat-soluble toxins. Improved bile flow, as facilitated by the use of Dendropanax extracts, not only aids in detoxification but also helps prevent cholestasis—a condition characterized by impaired bile flow that can lead to liver damage.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Dendropanax Morbifera’s Liver Benefits
The hepatoprotective and health-promoting effects of Dendropanax morbifera leaves are supported by a growing body of scientific literature. Numerous animal studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of Dendropanax extracts in reducing liver fat accumulation, lowering inflammatory markers, and preventing fibrosis. For instance, a study published in the “Journal of Ethnopharmacology” found that rats treated with Dendropanax leaf extract showed significant reductions in liver enzymes and histopathological markers of liver damage compared to untreated controls.
In vitro studies have further elucidated the mechanisms of action, showing that Dendropanax compounds can inhibit lipid peroxidation and enhance antioxidant enzyme activity in liver cells. These findings suggest that the hepatoprotective effects are mediated through both direct antioxidant activity and modulation of the liver’s endogenous defense systems.
While most of the current research has been conducted in animal models and cell cultures, the consistent findings across studies provide a strong basis for the potential use of Dendropanax morbifera as a natural remedy for liver health. However, clinical trials involving human participants are necessary to confirm these effects and determine appropriate dosages for therapeutic use.
Conclusion: A Natural Ally for Liver Health
Dendropanax morbifera leaves offer a comprehensive range of benefits for liver health, making them a promising natural option for preventing and managing conditions like NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Their potent antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, hepatoprotective, and regenerative properties help reduce liver damage, prevent disease progression, and support overall liver function and detoxification.
The existing scientific evidence underscores the potential of Dendropanax morbifera as a valuable supplement for those looking to maintain a healthy liver or support recovery from liver-related conditions. By enhancing the liver’s natural defenses, promoting regeneration, and facilitating detoxification, Dendropanax morbifera contributes to a healthier liver environment and improved overall health.
 Desmodium Triquetrum: Proven Benefits for Liver Health, NAFLD, Chronic Liver Disease, and Cirrhosis
Desmodium Triquetrum: Proven Benefits for Liver Health, NAFLD, Chronic Liver Disease, and Cirrhosis
Introduction
Desmodium triquetrum, a medicinal plant traditionally used in various cultures, has garnered significant attention in recent years for its hepatoprotective properties. Its impact on liver health, particularly its potential to prevent and mitigate conditions like Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis, is increasingly being supported by scientific studies. In this comprehensive overview, we explore how Desmodium triquetrum contributes to liver health through various mechanisms, highlighting its protective, regenerative, and detoxification-enhancing effects.
Hepatoprotective Properties of Desmodium Triquetrum
Prevention of NAFLD and Chronic Liver Disease
Desmodium triquetrum’s hepatoprotective properties are rooted in its potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory components. One of the primary causes of NAFLD and chronic liver disease is oxidative stress, which leads to cellular damage. Desmodium triquetrum contains flavonoids, saponins, and alkaloids, which have been shown to reduce oxidative stress, thereby lowering the risk of developing NAFLD.
Several peer-reviewed studies have confirmed the ability of Desmodium triquetrum to decrease lipid peroxidation—a critical factor in the development of fatty liver conditions. By reducing lipid accumulation in liver cells, Desmodium triquetrum not only prevents the progression of NAFLD but also helps maintain a healthy balance of liver enzymes, thus ensuring optimal liver function. These compounds are thought to work by enhancing the activity of endogenous antioxidants like superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase, which help neutralize free radicals and protect liver tissue.
Mechanism of Action: Inhibiting Fibrosis
Chronic liver disease often leads to fibrosis, the excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix proteins, which can ultimately progress to cirrhosis. Desmodium triquetrum has demonstrated anti-fibrotic activity through its ability to inhibit hepatic stellate cell activation—a key process in fibrosis development. Studies indicate that the plant’s extracts reduce the expression of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β), a major fibrogenic cytokine. By downregulating TGF-β, Desmodium triquetrum prevents excessive collagen deposition, thereby reducing fibrosis and its progression to cirrhosis.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Inflammation is a common underlying factor in many liver conditions, including NAFLD and cirrhosis. Desmodium triquetrum contains bioactive compounds that have significant anti-inflammatory properties. These compounds inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α and IL-6, which play a major role in the pathogenesis of liver diseases. By suppressing these cytokines, Desmodium triquetrum helps to create a less inflammatory environment in the liver, which is crucial for preventing further damage and allowing the liver to heal.
Reducing Damage from Fatty Liver and Other Liver Stressors
Protecting Against Hepatotoxicity
Desmodium triquetrum’s hepatoprotective effects extend to its ability to combat hepatotoxicity caused by environmental toxins, medications, and other stressors. Numerous studies have highlighted its effectiveness in reducing liver damage induced by hepatotoxic agents such as alcohol, acetaminophen, and other chemicals. This protection is largely attributed to the plant’s ability to enhance the liver’s natural detoxification processes, promoting the breakdown and elimination of harmful substances.
Stabilizing Liver Enzymes
One of the hallmarks of liver stress is the elevation of liver enzymes like ALT and AST, which indicates liver cell injury. Desmodium triquetrum has been shown to stabilize these enzyme levels, suggesting that it helps protect liver cells from damage. This is especially important in the context of fatty liver disease, where liver cells are often under significant stress due to lipid accumulation. By reducing oxidative damage and inflammation, Desmodium triquetrum helps maintain normal liver enzyme levels, which is indicative of healthier liver function overall.
Mechanisms of Detoxification Support
Desmodium triquetrum also enhances the liver’s detoxification capacity by upregulating phase I and phase II detoxification enzymes. These enzymes are critical for the biotransformation of toxins into less harmful compounds that can be easily excreted from the body. By promoting these pathways, Desmodium triquetrum aids in reducing the overall toxic burden on the liver, thereby minimizing damage and improving liver resilience against stressors.
Liver Regeneration and Improved Liver Function
Stimulating Hepatocyte Proliferation
The liver has a remarkable capacity to regenerate, and Desmodium triquetrum has been found to support this regenerative process. Studies suggest that the plant’s bioactive compounds stimulate hepatocyte proliferation, which is essential for liver regeneration after injury. This is particularly beneficial for individuals with chronic liver conditions or those recovering from acute liver damage, as it helps to restore liver mass and function more quickly.
Promoting a Healthier Liver Environment
Desmodium triquetrum contributes to creating a healthier liver environment by modulating the immune response and reducing oxidative stress. The plant’s antioxidant properties not only prevent damage to existing liver cells but also provide a conducive environment for new cells to thrive. By reducing the levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and supporting the liver’s antioxidant defenses, Desmodium triquetrum helps maintain the integrity of liver tissue and supports overall liver health.
Enhancing the Body’s Natural Detoxification Processes
Desmodium triquetrum also plays a role in enhancing the body’s natural detoxification processes, which is crucial for maintaining overall liver health. The plant’s ability to boost the activity of detoxifying enzymes, coupled with its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects, makes it a powerful ally in supporting the liver’s role as the body’s primary detoxification organ. This not only helps in the removal of harmful substances but also ensures that the liver remains functional and efficient, even under stress.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Desmodium Triquetrum’s Benefits
Clinical and Preclinical Studies
Several clinical and preclinical studies have provided evidence for the hepatoprotective effects of Desmodium triquetrum. Animal studies have demonstrated that extracts of Desmodium triquetrum can significantly reduce liver inflammation, fibrosis, and lipid accumulation. For example, in rodent models of NAFLD, treatment with Desmodium triquetrum extracts resulted in a marked decrease in hepatic fat content and improvement in liver histology.
In addition to animal studies, in vitro research has shown that Desmodium triquetrum can inhibit the activation of hepatic stellate cells, which are responsible for the development of fibrosis. By preventing the activation of these cells, Desmodium triquetrum helps to protect against the progression of chronic liver disease to cirrhosis.
Human Relevance and Practical Application
While most of the research to date has been conducted in animal models, the results are promising and suggest that Desmodium triquetrum could be a valuable natural therapy for supporting liver health in humans. Its ability to reduce inflammation, prevent fibrosis, and enhance detoxification processes makes it particularly relevant for individuals at risk of NAFLD or those with existing liver conditions. Further clinical trials in humans are needed to confirm these effects, but the existing evidence provides a strong foundation for its potential benefits.
Conclusion
Desmodium triquetrum is emerging as a powerful natural ally in the prevention and management of liver diseases, including NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Its hepatoprotective effects are supported by a combination of antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-fibrotic properties, which work together to reduce liver damage, support regeneration, and enhance detoxification. By stabilizing liver enzymes, reducing oxidative stress, and promoting hepatocyte proliferation, Desmodium triquetrum helps to create a healthier liver environment and supports the body’s natural detoxification processes.
The scientific evidence, while still evolving, highlights the potential of Desmodium triquetrum as a complementary approach to liver health. Its ability to address multiple pathways involved in liver disease—from preventing lipid accumulation to reducing inflammation and fibrosis—makes it a promising option for those looking to support their liver health naturally. As research continues to uncover the full extent of its benefits, Desmodium triquetrum may become an integral part of natural therapies aimed at improving liver function and preventing liver-related illnesses.
Incorporating Desmodium triquetrum into a comprehensive liver health regimen, alongside a balanced diet and lifestyle modifications, could offer significant benefits for maintaining optimal liver health. As always, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement, particularly for individuals with existing health conditions or those taking medications that may interact with herbal treatments.
DL-Methionine and Liver Health: Proven Benefits for NAFLD, Cirrhosis, and Liver Regeneration
DL-Methionine is an essential amino acid that plays a critical role in liver health. It has gained significant attention in scientific research for its benefits in preventing non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis, as well as for promoting liver regeneration and improving overall liver function. The following is a comprehensive breakdown of DL-Methionine’s scientifically proven effects on liver health, including its mechanisms of action and hepatoprotective properties.
DL-Methionine and Prevention of NAFLD
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a growing health concern worldwide, often associated with obesity, diabetes, and other metabolic disorders. NAFLD is characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver, which can lead to inflammation and eventually progress to more serious conditions like non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), cirrhosis, and liver cancer. DL-Methionine has demonstrated considerable promise in preventing and managing NAFLD due to its involvement in critical liver functions.
DL-Methionine contributes to the prevention of NAFLD through its ability to regulate lipid metabolism in the liver. It serves as a precursor to S-adenosylmethionine (SAMe), which is crucial for methylation processes that regulate fat metabolism. Studies have shown that supplementation with DL-Methionine can lead to a reduction in hepatic lipid accumulation by enhancing fatty acid oxidation and reducing lipogenesis. This is particularly beneficial in the context of NAFLD, where impaired lipid metabolism is a primary issue.
Furthermore, DL-Methionine supports the synthesis of glutathione, one of the most important antioxidants produced by the liver. Glutathione plays a pivotal role in neutralizing oxidative stress, a key contributor to the development and progression of NAFLD. Research has indicated that methionine deficiency can exacerbate oxidative stress and inflammation, leading to worsened liver conditions. Thus, adequate methionine intake is essential for maintaining the liver’s antioxidant defenses and reducing the risk of NAFLD.
Hepatoprotective Effects of DL-Methionine
DL-Methionine exhibits significant hepatoprotective properties, meaning it helps protect liver cells from damage caused by various stressors, including fatty liver, toxins, and drugs. One of the primary mechanisms by which DL-Methionine exerts its hepatoprotective effects is through its role in the synthesis of SAMe. SAMe is involved in numerous metabolic pathways, including transmethylation and transsulfuration, both of which are vital for maintaining liver health.
SAMe, derived from DL-Methionine, is known to enhance membrane fluidity, which helps maintain the integrity of liver cell membranes. This makes liver cells more resilient to injury from toxins, alcohol, and other harmful substances. Moreover, SAMe has been shown to promote bile flow, which aids in the detoxification process by facilitating the excretion of potentially harmful compounds.
DL-Methionine also contributes to detoxification through its involvement in the production of glutathione, which plays a key role in phase II detoxification. This process involves the conjugation of toxins to make them more water-soluble, allowing for their easier excretion from the body. The ability of DL-Methionine to boost glutathione levels helps protect the liver from oxidative damage and supports its natural detoxification pathways.
Reducing Liver Damage from Fatty Liver and Other Stressors
In cases of fatty liver disease, whether alcoholic or non-alcoholic, DL-Methionine has been found to mitigate liver damage by reducing inflammation and oxidative stress. Chronic inflammation is a major factor that contributes to liver fibrosis and cirrhosis, which are severe complications of fatty liver disease. DL-Methionine helps reduce inflammation by enhancing the liver’s antioxidant capacity and modulating inflammatory pathways.
Studies have shown that methionine supplementation can reduce levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6), which are often elevated in liver diseases. By lowering the levels of these inflammatory markers, DL-Methionine helps in preventing the progression of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis.
In addition to its anti-inflammatory effects, DL-Methionine has also been shown to prevent lipid peroxidation, a process in which free radicals damage liver cell membranes by oxidizing lipids. Lipid peroxidation is a significant contributor to liver cell injury and fibrosis. By enhancing the production of glutathione and other antioxidants, DL-Methionine helps neutralize free radicals and prevent lipid peroxidation, thereby protecting liver cells from damage.
Liver Regeneration and DL-Methionine
One of the most remarkable aspects of the liver is its ability to regenerate after injury. DL-Methionine plays an essential role in supporting liver regeneration by providing the necessary building blocks for protein synthesis and cellular repair. The synthesis of SAMe from methionine is crucial for DNA methylation, a process that regulates gene expression and plays a key role in cell proliferation and differentiation during liver regeneration.
Research has demonstrated that SAMe supplementation can accelerate liver regeneration following partial hepatectomy (surgical removal of part of the liver) or other liver injuries. DL-Methionine, by serving as a precursor to SAMe, indirectly contributes to the activation of regenerative pathways in the liver, enhancing the organ’s ability to recover from damage.
Additionally, methionine’s role in glutathione production is vital for liver regeneration, as oxidative stress can impede the regenerative process. By boosting glutathione levels, DL-Methionine helps create a more favorable environment for liver cells to regenerate, ensuring that the liver can recover effectively from injuries and maintain its function.
Enhancing Overall Liver Function and Detoxification
DL-Methionine contributes to overall liver health by supporting several key functions, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and bile production. The liver is the body’s primary detoxification organ, responsible for processing and eliminating toxins, drugs, and metabolic waste products. DL-Methionine plays an integral role in these detoxification processes by participating in both phase I and phase II detoxification pathways.
In phase I detoxification, enzymes such as cytochrome P450 metabolize toxins to make them more reactive. DL-Methionine helps in this process by supporting the synthesis of necessary cofactors and enzymes. In phase II detoxification, these reactive intermediates are conjugated with molecules like glutathione to render them harmless and water-soluble, allowing for excretion via bile or urine. Methionine’s contribution to glutathione synthesis is thus critical for effective phase II detoxification.
Moreover, DL-Methionine plays a role in bile production, which is essential for the digestion and absorption of fats, as well as the elimination of waste products. SAMe, derived from methionine, has been shown to improve bile flow, which not only aids digestion but also helps in the removal of toxins and metabolic byproducts from the liver. Improved bile flow reduces the risk of cholestasis (bile stagnation), a condition that can lead to liver damage if left untreated.
Scientific Evidence Supporting DL-Methionine’s Role in Liver Health
The benefits of DL-Methionine for liver health are well-supported by scientific research. Numerous studies have demonstrated the hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory, and regenerative effects of methionine and its metabolite, SAMe. For instance, research has shown that methionine supplementation can prevent the development of NAFLD in animal models by enhancing fatty acid oxidation and reducing hepatic lipid accumulation.
Clinical studies have also highlighted the role of SAMe in improving liver function in patients with chronic liver diseases, including cirrhosis. SAMe supplementation has been associated with improved liver enzyme levels, reduced symptoms of liver dysfunction, and enhanced overall quality of life in patients with liver diseases. These findings underscore the importance of methionine in maintaining liver health and preventing the progression of liver disease.
Additionally, the antioxidant effects of DL-Methionine have been validated in numerous studies, showing that methionine supplementation can increase glutathione levels, reduce oxidative stress, and protect liver cells from damage caused by toxins, alcohol, and other harmful substances. The reduction in pro-inflammatory cytokines observed with methionine supplementation further supports its role in mitigating liver inflammation and fibrosis.
Conclusion: DL-Methionine for a Healthier Liver
DL-Methionine is a powerful amino acid that plays a crucial role in maintaining liver health, preventing liver disease, and promoting liver regeneration. Its involvement in key processes such as SAMe synthesis, glutathione production, and lipid metabolism makes it an invaluable nutrient for supporting liver function. The scientific evidence supporting the benefits of DL-Methionine for preventing NAFLD, protecting against liver damage, and enhancing liver regeneration is robust, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic agent for liver health.
By supporting lipid metabolism, reducing oxidative stress, and enhancing the liver’s natural detoxification processes, DL-Methionine helps create a healthier liver environment, enabling the liver to perform its vital functions effectively. For individuals at risk of liver disease or those looking to improve their liver health, DL-Methionine supplementation may offer significant benefits, contributing to a healthier, more resilient liver.

The Proven Benefits of Dropwort (Oenanthe javanica) for Liver Health: A Comprehensive Scientific Overview
Introduction
Dropwort, also known as Oenanthe javanica or water celery, is a traditional medicinal plant with remarkable benefits for liver health, backed by scientific evidence. As non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and liver cirrhosis are on the rise globally, natural approaches to prevention and treatment are gaining attention. Dropwort has shown significant hepatoprotective properties, including liver regeneration, reduced liver stress, and improved overall liver function. In this comprehensive scientific synopsis, we will explore the proven mechanisms of action, focusing on how Dropwort promotes a healthier liver environment and enhances the body’s natural detoxification processes.
Hepatoprotective Effects of Dropwort
The hepatoprotective effects of Dropwort have been demonstrated in multiple peer-reviewed studies. Dropwort contains several bioactive compounds, including flavonoids, polyphenols, and essential oils, which exhibit potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. These properties make Dropwort effective in protecting liver cells from oxidative stress and inflammation, two major factors contributing to liver damage and the progression of NAFLD and cirrhosis.
Oxidative stress results from an imbalance between reactive oxygen species (ROS) and antioxidants, leading to lipid peroxidation, DNA damage, and impaired cellular function. Studies indicate that the flavonoids in Dropwort, such as quercetin and kaempferol, are powerful antioxidants that scavenge ROS, reducing oxidative damage to liver cells. This mechanism plays a critical role in preventing liver diseases, as oxidative stress is a key driver in the development of fatty liver and fibrosis.
Inflammation is another significant contributor to liver disease. Chronic inflammation accelerates liver fibrosis, leading to cirrhosis. Dropwort’s anti-inflammatory effects are primarily attributed to its ability to inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α and IL-6. By reducing inflammation, Dropwort helps mitigate liver damage and slow the progression of chronic liver conditions.
Prevention of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD is characterized by the accumulation of excess fat in liver cells, often associated with obesity, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome. Dropwort has been found to be effective in preventing and managing NAFLD through multiple mechanisms. One of the primary actions is its ability to enhance lipid metabolism, thereby reducing the accumulation of fat in the liver.
Research has shown that Dropwort stimulates the activity of enzymes involved in fatty acid oxidation, such as AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). AMPK activation promotes the breakdown of fatty acids and inhibits their synthesis, which helps prevent the buildup of fat in the liver. Additionally, Dropwort’s antioxidant properties help protect liver cells from lipid peroxidation, a process that further contributes to fat accumulation and liver damage.
Another key aspect of Dropwort’s effectiveness in preventing NAFLD is its role in improving insulin sensitivity. Insulin resistance is a major risk factor for NAFLD, as it leads to increased lipogenesis (fat production) in the liver. Studies suggest that Dropwort enhances insulin sensitivity by modulating the insulin signaling pathway, reducing hepatic fat accumulation, and improving overall metabolic health.
Protection Against Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver disease and cirrhosis are severe conditions that can result from prolonged liver inflammation and fibrosis. Dropwort has demonstrated promising effects in protecting against these conditions by preventing fibrosis and promoting liver cell regeneration.
Fibrosis is the excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins, such as collagen, in response to chronic liver injury. This process can lead to the formation of scar tissue and eventually cirrhosis. Dropwort has been shown to inhibit hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation, a key event in the development of liver fibrosis. HSCs are responsible for ECM production, and their activation is driven by factors such as oxidative stress and inflammation. By reducing oxidative stress and inhibiting pro-inflammatory cytokines, Dropwort helps prevent HSC activation and the progression of fibrosis.
Furthermore, Dropwort has been found to enhance the activity of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), enzymes that degrade ECM components and promote the resolution of fibrosis. This action helps in reducing scar tissue formation and maintaining healthy liver architecture.
Liver Regeneration and Improved Liver Function
One of the most remarkable aspects of the liver is its ability to regenerate. Dropwort has been shown to support liver regeneration by promoting hepatocyte proliferation and enhancing the liver’s innate regenerative capacity. The bioactive compounds in Dropwort stimulate the expression of growth factors, such as hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), which play a crucial role in liver regeneration.
In addition to promoting regeneration, Dropwort also contributes to improved liver function by enhancing bile production and secretion. Bile is essential for the digestion and absorption of fats, as well as the elimination of toxins from the body. By stimulating bile flow, Dropwort helps improve the liver’s detoxification capacity and overall function.
Reducing Damage Caused by Fatty Liver and Other Liver Stressors
Fatty liver, whether caused by alcohol consumption (alcoholic fatty liver disease) or metabolic factors (NAFLD), is a significant stressor for the liver. Dropwort has been shown to mitigate the damage caused by a fatty liver through its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and lipid-lowering effects. By reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, Dropwort helps protect liver cells from damage and prevents the progression of fatty liver to more severe conditions, such as fibrosis and cirrhosis.
In addition to its effects on fatty liver, Dropwort has demonstrated protective effects against other liver stressors, such as toxins and drugs. The liver is the primary organ responsible for detoxifying harmful substances, and exposure to toxins can lead to liver injury. Dropwort’s hepatoprotective properties help reduce the impact of toxic substances on the liver, thereby preserving liver function and preventing damage.
Enhancing the Body’s Natural Detoxification Processes
The liver plays a central role in the body’s detoxification processes, converting harmful substances into less toxic forms and facilitating their excretion. Dropwort has been found to enhance the liver’s detoxification capacity by upregulating the expression of detoxifying enzymes, such as glutathione S-transferase (GST) and cytochrome P450 enzymes. These enzymes are involved in the metabolism of various toxins, including drugs, environmental pollutants, and metabolic byproducts.
Glutathione, a powerful antioxidant produced by the liver, is essential for detoxification and protection against oxidative damage. Dropwort has been shown to increase glutathione levels in the liver, thereby enhancing the organ’s ability to neutralize free radicals and protect against cellular damage. This action is particularly beneficial for individuals exposed to high levels of oxidative stress or those with impaired liver function.
Promoting a Healthier Liver Environment
A healthy liver environment is essential for maintaining overall health and well-being. Dropwort contributes to a healthier liver environment by reducing inflammation, preventing fat accumulation, and supporting detoxification. By modulating key signaling pathways involved in lipid metabolism, inflammation, and cell proliferation, Dropwort helps maintain liver homeostasis and prevent the development of liver-related diseases.
Moreover, Dropwort’s ability to improve blood flow to the liver further enhances its function and regenerative capacity. Improved hepatic blood flow ensures an adequate supply of oxygen and nutrients, which are essential for liver health and regeneration. This effect, combined with Dropwort’s other hepatoprotective properties, makes it a valuable natural remedy for promoting liver health and preventing liver disease.
Conclusion
Dropwort (Oenanthe javanica) is a powerful natural remedy with proven benefits for liver health, supported by scientific evidence. Its hepatoprotective effects, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and lipid-lowering properties, make it effective in preventing and managing conditions such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. By promoting liver regeneration, enhancing detoxification, and reducing liver stress, Dropwort contributes to a healthier liver environment and improved overall liver function.
As the prevalence of liver diseases continues to rise, natural approaches like Dropwort offer a promising complementary option for prevention and treatment. With its diverse range of bioactive compounds and multiple mechanisms of action, Dropwort is a valuable addition to the arsenal of natural remedies for maintaining liver health and enhancing the body’s natural detoxification processes.

Eclipta Alba: Proven Benefits for Liver Health and NAFLD Prevention
Eclipta alba, commonly known as False Daisy or Bhringraj, is a powerful herb that has been widely studied for its liver-protective properties. With increasing concerns around liver diseases such as Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis, Eclipta alba presents a natural solution that has shown promise in both traditional and modern medical contexts. In this synopsis, we will delve into its hepatoprotective benefits, its impact on liver regeneration, and the enhancement of liver function, all supported by scientific evidence.
Understanding Liver Health and the Role of Eclipta Alba
The liver plays a vital role in detoxifying the body, metabolizing nutrients, and maintaining overall health. Liver dysfunction, especially caused by NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis, is a growing health issue globally. Scientific evidence has demonstrated that Eclipta alba has several hepatoprotective and regenerative properties, which help mitigate liver damage, regenerate hepatocytes, and support overall liver function.
Hepatoprotective Properties of Eclipta Alba
Reduction in Liver Damage: Eclipta alba’s hepatoprotective effects have been extensively validated in preclinical studies. The herb has been shown to reduce oxidative stress and inflammation, which are two major contributors to liver damage. Oxidative stress is a condition where the liver is overwhelmed by free radicals, which leads to cell damage and inflammation. Studies have reported that Eclipta alba contains compounds like wedelolactone and flavonoids, which have potent antioxidant properties that help neutralize free radicals, thus protecting the liver from oxidative damage.
In animal studies, Eclipta alba has been shown to protect the liver from damage caused by hepatotoxins such as carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) and ethanol. One particular study demonstrated that treatment with Eclipta alba significantly reduced liver enzyme levels, indicating reduced damage and inflammation. Alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST) are biomarkers of liver injury, and reduced levels of these enzymes post-treatment indicate effective hepatoprotection.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Eclipta alba’s anti-inflammatory properties have also been found to contribute to its hepatoprotective action. Chronic inflammation is a primary driver of liver damage, particularly in NAFLD and other forms of chronic liver disease. Wedelolactone, one of the active compounds in Eclipta alba, has been found to inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6, thereby reducing liver inflammation and mitigating disease progression.
Preventing and Managing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD is characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver, leading to inflammation, fibrosis, and eventually cirrhosis if left unmanaged. Eclipta alba has shown efficacy in preventing fat accumulation in the liver. Preclinical studies have reported that the herb can modulate lipid metabolism, thereby reducing hepatic steatosis (fat accumulation).
Mechanism of Action in NAFLD: The action of Eclipta alba in NAFLD prevention can be attributed to its ability to improve lipid homeostasis. The herb has been found to inhibit the activity of lipogenic enzymes, which are responsible for fat synthesis in the liver. Additionally, it enhances the expression of enzymes involved in lipid oxidation, which helps break down accumulated fat in hepatocytes. By balancing lipid synthesis and oxidation, Eclipta alba reduces the risk of liver fat accumulation and subsequently prevents NAFLD progression.
Furthermore, the antioxidant properties of Eclipta alba play a role in mitigating the oxidative stress often associated with hepatic fat accumulation. Fat accumulation increases the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which can lead to cellular injury and inflammation. The antioxidants in Eclipta alba effectively neutralize ROS, thereby reducing oxidative stress and preventing liver cell damage.
Benefits for Liver Cirrhosis and Chronic Liver Disease
Anti-Fibrotic Effects: Liver cirrhosis is the end-stage result of chronic liver diseases where the liver tissue becomes fibrotic and scarred, impairing liver function. The progression of fibrosis is mediated by hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), which are activated during liver injury. Eclipta alba has shown anti-fibrotic potential by inhibiting the activation of HSCs, thus preventing excessive collagen deposition and scarring of liver tissue. This anti-fibrotic action of Eclipta alba can slow down or even reverse the progression of cirrhosis.
Liver Enzyme Modulation: In patients with chronic liver disease, elevated liver enzymes such as ALT, AST, and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) are indicative of liver damage. Eclipta alba has been shown to normalize these enzyme levels, reflecting improved liver health. By restoring the normal enzyme activity, Eclipta alba supports improved liver function and a reduction in liver inflammation.
Hepatocyte Regeneration and Liver Function Enhancement
Promotion of Liver Regeneration: One of the remarkable properties of Eclipta alba is its ability to promote liver regeneration. Hepatocytes, the primary functional cells of the liver, have a unique regenerative capacity that allows the liver to recover from injury. Studies have shown that extracts of Eclipta alba stimulate the proliferation of hepatocytes, thereby enhancing the liver’s ability to regenerate damaged tissue. This regenerative effect is especially beneficial in conditions like cirrhosis, where the liver’s ability to recover is significantly compromised.
The liver regeneration effect of Eclipta alba is mediated by its ability to increase the expression of growth factors such as hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and transforming growth factor-α (TGF-α). These growth factors are critical for hepatocyte proliferation and the repair of damaged liver tissue. By upregulating these growth factors, Eclipta alba accelerates the regeneration process and promotes faster recovery of liver function.
Enhancing Liver Detoxification: The liver’s primary role is to detoxify the body by metabolizing and excreting harmful substances. Eclipta alba enhances the liver’s detoxification capabilities by boosting the activity of detoxifying enzymes, particularly glutathione S-transferase (GST) and catalase. These enzymes play an essential role in neutralizing toxins and converting them into less harmful substances that can be easily excreted from the body.
Studies have shown that Eclipta alba increases the levels of glutathione, a powerful antioxidant that supports detoxification. Glutathione is involved in phase II detoxification, where it binds to toxic substances and facilitates their elimination. By increasing glutathione levels, Eclipta alba strengthens the liver’s detoxification pathways and enhances the body’s ability to eliminate toxins efficiently.
Overall Liver Function and Health Maintenance: Eclipta alba also contributes to maintaining overall liver health by improving blood circulation within the liver and reducing congestion. It has been observed that the herb enhances bile flow, which is essential for the digestion of fats and the elimination of waste products from the liver. By promoting bile production and flow, Eclipta alba prevents bile stasis and reduces the risk of gallstone formation, which can be a common complication in individuals with liver disease.
Additionally, Eclipta alba supports the liver’s metabolic functions by improving glucose metabolism. It has been shown to enhance insulin sensitivity and reduce insulin resistance, which is beneficial for individuals with NAFLD, as insulin resistance is a major risk factor for the development of fatty liver. By modulating glucose metabolism, Eclipta alba not only supports liver health but also helps in the management of metabolic syndrome, which often coexists with liver disease.
Eclipta Alba’s Potential in Supporting Overall Liver Wellness
Anti-Apoptotic Effects: Apoptosis, or programmed cell death, is a mechanism that contributes to liver injury, particularly in conditions like hepatitis and cirrhosis. Eclipta alba has demonstrated anti-apoptotic properties, which help prevent the premature death of hepatocytes. By reducing apoptosis, Eclipta alba preserves healthy liver cells and supports the organ’s overall functionality.
Synergistic Effects with Other Herbs: Eclipta alba is often used in combination with other hepatoprotective herbs like Phyllanthus niruri and Andrographis paniculata in traditional medicine. Such combinations have been found to have a synergistic effect, providing enhanced protection against liver damage, reducing inflammation, and promoting regeneration more effectively than when used alone. This makes Eclipta alba a valuable component in polyherbal formulations aimed at liver health.
Conclusion: Eclipta Alba as a Powerful Ally for Liver Health
Eclipta alba is a scientifically validated herbal remedy with significant benefits for liver health. Its hepatoprotective properties, ability to prevent NAFLD, anti-fibrotic effects, and promotion of liver regeneration make it an effective natural intervention for managing various liver conditions. The herb works through multiple mechanisms, including antioxidant activity, anti-inflammatory effects, modulation of lipid metabolism, and enhancement of detoxification pathways, to support and restore liver function.
For individuals at risk of liver diseases or those already experiencing liver dysfunction, Eclipta alba offers a promising natural solution that not only helps protect the liver but also promotes its healing and regeneration. Its comprehensive action on the liver—ranging from reducing fat accumulation to enhancing regeneration—makes it an important herb for anyone seeking to maintain optimal liver health and prevent chronic liver conditions.
As with any herbal supplement, it is essential to consult healthcare professionals before incorporating Eclipta alba into a treatment regimen, particularly for individuals with pre-existing liver conditions or those taking other medications. The scientific backing and long history of traditional use make Eclipta alba a noteworthy ally in the ongoing battle against liver disease, promising improved outcomes and enhanced liver health for those who seek its benefits.

The Benefits of Epicatechin in Preventing and Managing Liver Conditions: A Comprehensive Review
Epicatechin, a naturally occurring flavonoid found in foods like dark chocolate, green tea, and certain fruits, has been extensively studied for its wide array of health benefits. Recent scientific evidence highlights its specific role in promoting liver health, particularly in preventing and managing liver conditions such as Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. This article provides an in-depth review of the proven benefits of epicatechin, emphasizing its hepatoprotective effects, mechanisms of action, and potential for liver regeneration, while aligning with Google’s latest SEO best practices.
Epicatechin and NAFLD Prevention: Mechanisms and Evidence
NAFLD is an increasingly prevalent liver condition characterized by excessive fat accumulation in liver cells, independent of alcohol consumption. This condition can progress to more severe forms of liver damage, including steatohepatitis, fibrosis, and eventually cirrhosis if left unmanaged. Scientific studies have demonstrated that epicatechin exhibits promising protective effects against the development of NAFLD, primarily through its ability to modulate oxidative stress, inflammation, and lipid metabolism.
1. Reduction of Oxidative Stress
Oxidative stress is a key contributor to liver damage in NAFLD. Epicatechin is a potent antioxidant that neutralizes reactive oxygen species (ROS), thereby reducing oxidative stress and preventing cellular damage. Studies have shown that epicatechin can upregulate the expression of endogenous antioxidant enzymes like superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase, which are critical for protecting liver cells from oxidative injury.
2. Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Inflammation plays a central role in the progression of NAFLD to more severe forms of liver disease. Epicatechin has been found to inhibit the activation of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB), a transcription factor that regulates the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. By suppressing NF-κB activation, epicatechin effectively reduces inflammation in the liver, thereby mitigating the risk of liver fibrosis and other complications associated with chronic inflammation.
3. Improvement of Lipid Metabolism
Dysregulated lipid metabolism is a hallmark of NAFLD. Epicatechin helps regulate lipid homeostasis by modulating key enzymes involved in lipid synthesis and breakdown. Research indicates that epicatechin can reduce hepatic triglyceride accumulation by enhancing the activity of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), a critical regulator of energy balance. Activation of AMPK promotes fatty acid oxidation and reduces lipogenesis, thereby preventing fat buildup in the liver.
Hepatoprotective Effects Against Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver disease, including cirrhosis, is often the result of prolonged liver damage due to various factors such as fatty liver, alcohol abuse, or viral infections. Epicatechin has demonstrated significant hepatoprotective effects that can help in managing these conditions and reducing liver damage.
1. Prevention of Fibrosis Progression
Fibrosis is a key feature of chronic liver disease, characterized by excessive deposition of extracellular matrix components, which leads to scarring of liver tissue. Epicatechin has been shown to inhibit hepatic stellate cell activation, a major driver of fibrosis. By preventing the transformation of these cells into a myofibroblast-like state, epicatechin reduces the synthesis of collagen and other fibrotic markers, thereby limiting the progression of fibrosis.
2. Protection Against Liver Injury
The liver is highly susceptible to injury from various toxins, including alcohol, drugs, and other hepatotoxins. Epicatechin’s antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties play a crucial role in protecting liver cells from such injuries. In animal models, epicatechin has been shown to attenuate liver damage induced by toxic substances like carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) and ethanol, demonstrating its potential as a natural hepatoprotective agent.
3. Enhancement of Mitochondrial Function
Mitochondrial dysfunction is a major contributor to the pathogenesis of chronic liver disease. Epicatechin has been found to improve mitochondrial function by enhancing mitochondrial biogenesis and reducing oxidative damage to mitochondrial DNA. This improvement in mitochondrial health supports overall liver function and helps prevent the progression of liver disease.
Epicatechin and Liver Regeneration: Promoting a Healthier Liver Environment
The liver has a remarkable ability to regenerate itself after injury. Epicatechin has been shown to enhance liver regeneration, thereby supporting recovery from liver damage and promoting overall liver health.
1. Stimulation of Hepatocyte Proliferation
Hepatocytes, the primary functional cells of the liver, play a crucial role in liver regeneration. Research suggests that epicatechin can stimulate hepatocyte proliferation by activating pathways such as the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt pathway, which is essential for cell growth and survival. By promoting hepatocyte proliferation, epicatechin facilitates the regeneration of damaged liver tissue and helps restore normal liver architecture.
2. Reduction of Apoptosis in Liver Cells
Apoptosis, or programmed cell death, is a natural process that can be exacerbated by liver injury and disease. Epicatechin has been shown to reduce apoptosis in liver cells by modulating the expression of pro-apoptotic and anti-apoptotic proteins. By preventing excessive cell death, epicatechin supports the maintenance of a healthy liver cell population, which is crucial for effective liver regeneration.
3. Enhancement of Angiogenesis
Angiogenesis, the formation of new blood vessels, is an important aspect of liver regeneration, as it ensures an adequate supply of oxygen and nutrients to regenerating liver tissue. Epicatechin has been found to enhance angiogenesis by upregulating vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression, thereby supporting the growth of new blood vessels and promoting a conducive environment for liver regeneration.
Overall Liver Function and Detoxification Enhancement
In addition to its protective and regenerative effects, epicatechin contributes to the enhancement of overall liver function and supports the body’s natural detoxification processes.
1. Improvement of Bile Production and Secretion
Bile production is a critical function of the liver, aiding in digestion and the elimination of toxins. Epicatechin has been shown to improve bile flow, which is essential for effective detoxification. By enhancing bile production and secretion, epicatechin supports the liver’s ability to remove waste products and toxins from the body, promoting a healthier internal environment.
2. Modulation of Phase I and Phase II Detoxification Enzymes
The liver’s detoxification process involves two phases: Phase I (modification) and Phase II (conjugation). Epicatechin has been found to modulate the activity of Phase I enzymes, such as cytochrome P450, as well as Phase II enzymes, including glutathione S-transferase (GST). By supporting both phases of detoxification, epicatechin enhances the liver’s capacity to process and eliminate harmful substances, reducing the risk of toxin accumulation and liver damage.
3. Support for Immune Function in the Liver
The liver is an immune-active organ that plays a key role in detecting and neutralizing pathogens. Epicatechin has been shown to modulate immune responses in the liver, enhancing the activity of Kupffer cells, the liver’s resident macrophages. By supporting immune function, epicatechin helps maintain a healthy liver environment and reduces the risk of infections that can exacerbate liver damage.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Epicatechin’s Hepatoprotective Effects
The hepatoprotective effects of epicatechin are supported by a growing body of scientific literature, including both in vitro and in vivo studies. Animal studies have consistently demonstrated the ability of epicatechin to reduce liver fat accumulation, prevent fibrosis, and enhance liver regeneration. Human studies, though more limited, have also shown promising results, particularly in the context of improving markers of liver function and reducing oxidative stress in individuals with liver conditions.
For instance, a study published in the Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry found that epicatechin supplementation significantly reduced liver fat content and improved insulin sensitivity in animal models of NAFLD. Another study in the World Journal of Hepatology reported that epicatechin treatment reduced liver enzyme levels and improved antioxidant status in patients with chronic liver disease, indicating reduced liver damage and improved liver function.
Conclusion: Epicatechin as a Natural Ally for Liver Health
Epicatechin is a powerful flavonoid with proven benefits for liver health. Its ability to reduce oxidative stress, inflammation, and lipid accumulation makes it a promising natural intervention for preventing and managing NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Furthermore, its role in promoting liver regeneration, enhancing mitochondrial function, and supporting detoxification processes underscores its potential as a comprehensive hepatoprotective agent.
While more human clinical trials are needed to fully understand the therapeutic potential of epicatechin, the existing evidence is compelling. Incorporating epicatechin-rich foods, such as dark chocolate, green tea, and certain fruits, into the diet may offer significant liver health benefits and contribute to a healthier, more resilient liver. As research continues to evolve, epicatechin holds promise as a valuable tool in the ongoing effort to combat liver disease and promote optimal liver function.

Forsythia Suspensa Extract: Proven Benefits for Liver Health and Disease Prevention
Forsythia suspensa, commonly known as weeping forsythia, has been used extensively in traditional Chinese medicine due to its broad spectrum of health benefits. Recent scientific investigations have highlighted its potential to prevent and manage liver diseases, particularly Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. This article provides a comprehensive breakdown of the hepatoprotective properties of Forsythia suspensa extract, emphasizing its benefits for preventing liver damage, promoting liver regeneration, and enhancing overall liver health based on peer-reviewed evidence.
Mechanisms of Action: Forsythia Suspensa and Liver Health
The hepatoprotective effects of Forsythia suspensa are attributed primarily to its bioactive compounds, particularly lignans (forsythiaside A and forsythin) and flavonoids. These components exhibit potent anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antifibrotic properties that directly contribute to improved liver health. The liver is highly susceptible to oxidative stress, inflammation, and subsequent fibrosis; Forsythia suspensa extract mitigates these processes by targeting key pathways involved in liver damage.
1. Reducing Oxidative Stress and Inflammation
One of the critical drivers of NAFLD and other liver diseases is oxidative stress, which leads to the accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). ROS accumulation triggers inflammation, which exacerbates liver damage and can progress to fibrosis and cirrhosis. Forsythia suspensa contains potent antioxidants that scavenge ROS, thereby reducing oxidative stress and preventing lipid peroxidation in liver tissues.
Several studies have demonstrated that the antioxidant effects of Forsythia suspensa help maintain cellular integrity by neutralizing ROS and enhancing the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes like superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px). The regulation of these enzymes is essential for reducing oxidative damage in liver cells and preventing NAFLD progression.
In addition to its antioxidant properties, Forsythia suspensa exhibits anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting pro-inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6). Chronic liver inflammation is a major risk factor for fibrosis and cirrhosis. Forsythia suspensa’s ability to reduce inflammation is critical for halting the progression of liver disease, thereby protecting liver structure and function.
2. Inhibition of Hepatic Fibrosis
Hepatic fibrosis, characterized by excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix proteins, is a hallmark of chronic liver diseases. It is a precursor to cirrhosis, which results in irreversible liver damage. Forsythia suspensa’s antifibrotic effects have been validated in studies that show its capacity to inhibit the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), which are the main cells responsible for fibrosis.
By preventing the activation and proliferation of HSCs, Forsythia suspensa helps reduce collagen deposition in the liver, thereby mitigating fibrosis development. Studies also indicate that Forsythia suspensa extract downregulates the expression of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β), a key profibrogenic cytokine that drives fibrotic processes. This inhibition of TGF-β signaling further supports its role in reducing fibrosis and preserving liver architecture.
Hepatoprotective Effects Against Fatty Liver and Other Stressors
Forsythia suspensa has shown promising results in preventing and managing fatty liver conditions, particularly NAFLD. NAFLD is characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver unrelated to alcohol consumption, often linked to metabolic syndrome, obesity, and insulin resistance. The mechanisms through which Forsythia suspensa exerts its protective effects against fatty liver are multifaceted.
1. Modulation of Lipid Metabolism
Forsythia suspensa contributes to the regulation of lipid metabolism by reducing hepatic lipid accumulation. Its active components inhibit de novo lipogenesis (fat production in the liver) while promoting fatty acid oxidation. This balance is crucial for preventing the excessive storage of fat in the liver, which can lead to NAFLD.
Scientific evidence shows that Forsythia suspensa can downregulate the expression of sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c (SREBP-1c), a key transcription factor that promotes lipid synthesis in the liver. By inhibiting SREBP-1c and enhancing the expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPAR-α), which is involved in fatty acid oxidation, Forsythia suspensa helps maintain a healthy lipid profile and reduces hepatic steatosis.
2. Insulin Sensitivity and Glucose Homeostasis
Insulin resistance is a major contributor to NAFLD development. Forsythia suspensa has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity and maintain glucose homeostasis, thereby reducing the risk of fatty liver progression. The extract’s bioactive compounds enhance insulin signaling pathways, which help the liver effectively manage glucose and lipid levels.
Studies have indicated that Forsythia suspensa modulates key enzymes involved in gluconeogenesis and glycogen synthesis, thereby aiding in better glucose management. By improving insulin sensitivity, Forsythia suspensa not only helps in reducing liver fat accumulation but also contributes to overall metabolic health, which is closely tied to liver function.
Supporting Liver Regeneration and Enhancing Liver Function
The liver has a remarkable capacity for regeneration, which is critical for recovery from injury and maintaining optimal function. Forsythia suspensa supports liver regeneration by promoting cellular proliferation and preventing hepatocyte apoptosis (cell death). This is particularly important for individuals recovering from liver injuries caused by fatty liver disease, alcohol, or other toxic stressors.
1. Promotion of Hepatocyte Proliferation
Forsythia suspensa has demonstrated a positive effect on hepatocyte proliferation, which is crucial for liver regeneration. The active compounds in Forsythia suspensa, such as forsythiaside A, have been shown to enhance the expression of growth factors like hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), which plays a key role in stimulating liver cell growth and tissue repair. This regenerative property makes Forsythia suspensa a valuable natural intervention for maintaining liver health and aiding recovery from liver damage.
2. Protection Against Hepatocyte Apoptosis
In chronic liver conditions, apoptosis of liver cells is a significant factor that contributes to the deterioration of liver function. Forsythia suspensa has been found to inhibit apoptosis by modulating pathways such as the Bcl-2/Bax ratio and reducing the activation of caspases, which are enzymes involved in programmed cell death. By protecting hepatocytes from apoptosis, Forsythia suspensa helps preserve liver mass and functionality.
Enhancing Detoxification and Overall Liver Function
A healthy liver is essential for the body’s natural detoxification processes, as the liver is responsible for filtering toxins, metabolizing drugs, and breaking down waste products. Forsythia suspensa enhances the liver’s detoxifying capacity by supporting phase I and phase II detoxification enzymes.
1. Stimulation of Detoxification Enzymes
Forsythia suspensa promotes the activity of detoxification enzymes, including cytochrome P450 enzymes involved in phase I detoxification. These enzymes are responsible for the oxidation and breakdown of toxins, making them more water-soluble and easier to excrete. Additionally, Forsythia suspensa supports phase II detoxification, which involves conjugation reactions that further enhance the elimination of harmful substances from the body.
2. Maintenance of Bile Production and Flow
Bile production is another critical function of the liver, essential for the digestion and absorption of fats and the elimination of certain waste products. Forsythia suspensa has been shown to support healthy bile production and flow, which is important for maintaining efficient detoxification and reducing the risk of cholestasis (reduced bile flow). By ensuring optimal bile flow, Forsythia suspensa contributes to overall liver health and metabolic function.
Conclusion: Forsythia Suspensa as a Natural Hepatoprotective Agent
The hepatoprotective properties of Forsythia suspensa are supported by a growing body of scientific evidence, highlighting its potential in preventing and managing liver diseases such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Its multifaceted mechanisms of action—ranging from reducing oxidative stress and inflammation to inhibiting hepatic fibrosis, promoting liver regeneration, and enhancing detoxification—make it a promising natural intervention for liver health.
Forsythia suspensa’s ability to modulate lipid metabolism, improve insulin sensitivity, and protect hepatocytes from damage underscores its value in addressing both the causes and effects of liver disease. By promoting a healthier liver environment and enhancing the body’s natural detoxification processes, Forsythia suspensa offers a holistic approach to maintaining liver health and function.
Incorporating Forsythia suspensa as part of a balanced diet and lifestyle may offer significant benefits for individuals at risk of liver disease or those looking to support overall liver function. However, it is important to consult with healthcare professionals before using herbal extracts, especially for individuals with pre-existing medical conditions or those taking medications, to ensure safety and efficacy.

Fructus Schisandrae: A Scientifically Proven Ally for Liver Health and Regeneration
Fructus Schisandrae, known as Wuweizi in traditional Chinese medicine, has been increasingly recognized in the scientific community for its potent hepatoprotective properties. This traditional medicinal berry, derived from the plant Schisandra chinensis, is gaining attention for its ability to prevent and manage liver conditions, including Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. This article presents a detailed breakdown of the scientifically validated benefits of Fructus Schisandrae, emphasizing its mechanisms of action, effects on liver regeneration, and enhancement of liver function.
Hepatoprotective Effects and Prevention of Liver Diseases
Schisandrae’s role as a hepatoprotective agent has been well-documented in numerous peer-reviewed studies. The berry contains active compounds such as lignans (schisandrin, gomisin, and deoxyschisandrin) that contribute significantly to its beneficial effects on liver health. One of the critical mechanisms by which Fructus Schisandrae protects the liver is through its antioxidant properties. The liver, constantly exposed to oxidative stress due to the detoxification processes, is susceptible to damage from reactive oxygen species (ROS). The lignans found in Schisandrae help neutralize ROS, reducing oxidative stress and preventing cellular damage.
In the context of NAFLD, a condition characterized by fat accumulation in the liver without alcohol involvement, Schisandrae has shown promise in inhibiting lipid peroxidation and promoting the breakdown of excess fats. Studies demonstrate that the lignans in Fructus Schisandrae enhance the activity of antioxidant enzymes like superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx), which are crucial in preventing the progression of NAFLD to more severe forms, such as non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).
Fructus Schisandrae’s anti-inflammatory properties further aid in preventing liver disease progression. Chronic liver inflammation is a precursor to fibrosis and cirrhosis, where normal liver tissue is replaced with scar tissue, leading to compromised liver function. Schisandrae modulates inflammatory pathways by inhibiting pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6, which play key roles in liver injury and fibrosis. By reducing inflammation, Schisandrae helps protect against the development of chronic liver disease and cirrhosis.
Mitigating Liver Damage from Stressors
Fructus Schisandrae is particularly effective in mitigating liver damage caused by various stressors, including alcohol, toxins, and metabolic overload. The liver’s role as the body’s detoxification hub makes it vulnerable to damage from harmful substances like alcohol, certain medications, and environmental toxins. Schisandrae lignans exert a protective effect by enhancing the liver’s natural detoxification capacity and promoting the elimination of toxic substances.
Scientific evidence suggests that Schisandrae improves the expression of Phase I and Phase II detoxifying enzymes, which are essential for biotransformation and the safe elimination of toxins from the body. This enhanced detoxification capability not only reduces the impact of hepatotoxic substances but also helps in maintaining overall liver health.
In addition to its detoxifying properties, Schisandrae has been found to stabilize hepatocyte membranes, thereby reducing the extent of damage caused by fatty liver disease and other liver stressors. By maintaining cell membrane integrity, Schisandrae prevents the leakage of liver enzymes such as alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST) into the bloodstream—a common marker of liver injury. This stabilization contributes to better liver function and reduced damage from ongoing liver stressors.
Promoting Liver Regeneration and Function
Liver regeneration is a unique and critical ability of the liver, particularly important for patients recovering from liver injury or surgery. Fructus Schisandrae plays a pivotal role in promoting liver regeneration through multiple mechanisms. The lignans in Schisandrae stimulate hepatocyte proliferation, which is crucial for the liver’s regenerative process. By activating specific growth factors and cellular signaling pathways, Schisandrae facilitates the repair and replacement of damaged liver cells.
Moreover, Schisandrae has been shown to enhance mitochondrial function within liver cells. Mitochondria are the energy powerhouses of the cell, and their optimal function is vital for maintaining liver health and supporting regeneration. By enhancing mitochondrial efficiency, Schisandrae ensures that liver cells have the energy required for regeneration and for carrying out essential metabolic functions.
Fructus Schisandrae also helps maintain a healthier liver environment by modulating lipid metabolism. It has been found to reduce the accumulation of triglycerides in the liver, a common issue in NAFLD patients. The lignans in Schisandrae activate the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) pathway, which plays a significant role in lipid metabolism and energy homeostasis. Activation of this pathway not only helps reduce lipid buildup in the liver but also enhances fatty acid oxidation, contributing to improved liver health.
Enhancing the Body’s Natural Detoxification Processes
One of the liver’s primary functions is to detoxify the body by processing and eliminating harmful substances. Fructus Schisandrae supports this natural detoxification process by enhancing both Phase I and Phase II liver detoxification pathways. During Phase I detoxification, toxins are chemically modified, often making them more reactive and potentially more harmful. Phase II detoxification involves conjugation, where these modified toxins are rendered water-soluble for easier elimination through bile or urine.
Schisandrae’s active compounds have been shown to enhance the activity of cytochrome P450 enzymes, which play a key role in Phase I detoxification. By upregulating these enzymes, Schisandrae ensures that the liver efficiently metabolizes various xenobiotics, including drugs, environmental pollutants, and endogenous waste products. Furthermore, its role in Phase II detoxification is equally significant, as it promotes the activity of enzymes such as glutathione-S-transferase (GST), which conjugates toxins, facilitating their excretion.
By supporting both detoxification phases, Fructus Schisandrae not only helps the liver deal with external toxins but also reduces the burden on hepatocytes, leading to a healthier liver environment and improved overall liver function. This detoxifying effect is crucial for individuals with compromised liver function or those regularly exposed to environmental or dietary toxins.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Schisandrae’s Benefits
The hepatoprotective and regenerative properties of Fructus Schisandrae are supported by a growing body of scientific evidence. A study published in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology highlighted the role of Schisandrae lignans in reducing liver enzyme levels and enhancing antioxidant defenses in animal models of liver injury. The study demonstrated that schisandrin B, a prominent lignan, significantly decreased oxidative stress markers and improved liver histology, suggesting a protective effect against liver damage.
Another study, featured in Phytomedicine, explored the anti-inflammatory effects of Schisandrae in models of liver fibrosis. The results showed that Schisandrae administration led to a significant reduction in inflammatory markers such as TNF-α and IL-6, as well as a decrease in collagen deposition in the liver—indicating a protective effect against fibrosis and potential progression to cirrhosis.
Furthermore, research published in Frontiers in Pharmacology focused on Schisandrae’s effects on NAFLD. The study found that treatment with Schisandrae extract resulted in decreased lipid accumulation in the liver and improved lipid metabolism by activating AMPK pathways. This study provided compelling evidence for Schisandrae’s potential as a natural therapeutic agent for managing NAFLD and preventing its progression.
Improving Overall Liver Function and Health
Beyond its specific effects on liver disease and regeneration, Fructus Schisandrae also plays a role in optimizing overall liver function. Its antioxidant properties not only reduce liver damage but also contribute to better liver performance by minimizing the impact of oxidative stress on hepatic cells. By maintaining optimal liver function, Schisandrae ensures that the body can effectively carry out metabolic processes, synthesize essential proteins, and regulate blood glucose levels.
The enhancement of bile production is another benefit associated with Schisandrae. Bile is critical for the digestion and absorption of fats, and its production is directly influenced by liver health. Schisandrae has been shown to promote bile secretion, which not only aids in digestion but also assists in the excretion of fat-soluble toxins. This dual function helps in maintaining both liver and digestive health.
Schisandrae also supports liver function by modulating immune responses within the liver. The liver contains a large number of immune cells that play roles in detecting and neutralizing pathogens. By modulating these immune responses, Schisandrae helps maintain an optimal balance between immune tolerance and defense, reducing the risk of immune-mediated liver damage.
Conclusion: Fructus Schisandrae as a Comprehensive Liver Support Agent
Fructus Schisandrae offers a multifaceted approach to liver health, providing hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and regenerative benefits. Its ability to prevent and manage conditions such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis, along with its role in enhancing liver detoxification and promoting overall liver function, makes it a valuable natural remedy for maintaining liver health.
The scientific evidence supporting these benefits is robust, with studies consistently demonstrating Schisandrae’s efficacy in reducing liver damage, enhancing regeneration, and optimizing liver function. As interest in natural therapies for liver health grows, Fructus Schisandrae stands out as a promising candidate for individuals seeking to improve or maintain their liver health through scientifically validated means.
By promoting a healthier liver environment, enhancing the body’s natural detoxification processes, and supporting liver regeneration, Fructus Schisandrae not only helps protect against liver diseases but also contributes to overall well-being—ensuring that the liver can effectively perform its vital functions in the body.

Galangin: The Scientific Breakdown of Liver Health Benefits and Mechanisms of Action
Galangin, a flavonoid compound predominantly found in Alpinia officinarum (lesser galangal), has recently garnered attention for its multifaceted health benefits, particularly in liver health. This comprehensive analysis will explore the scientifically-proven benefits of galangin in preventing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, cirrhosis, and other liver-related issues. We will break down the hepatoprotective effects, mechanisms of action, and benefits for liver regeneration, highlighting the essential role of galangin in promoting overall liver function and supporting the body’s natural detoxification processes.
Galangin and Its Protective Role Against Liver Diseases
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and Chronic Liver Disease Prevention
NAFLD and chronic liver disease represent major global health concerns, with increasing prevalence linked to metabolic syndrome and lifestyle factors. Galangin has emerged as a potential natural intervention, backed by robust scientific evidence supporting its efficacy in preventing and managing these conditions.
The primary mechanism through which galangin exerts its hepatoprotective effects lies in its ability to reduce oxidative stress and inflammation, two key drivers of liver damage and disease progression. Studies have demonstrated that galangin significantly reduces levels of malondialdehyde (MDA), a marker of oxidative stress, while enhancing the activity of endogenous antioxidants such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase. By neutralizing reactive oxygen species (ROS), galangin protects liver cells from oxidative injury, a crucial factor in the prevention of NAFLD.
Furthermore, galangin has been shown to modulate key inflammatory pathways, including the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) signaling pathway. By inhibiting NF-κB activation, galangin reduces the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6). This anti-inflammatory action helps mitigate liver inflammation, thereby preventing the progression of NAFLD to more severe stages, such as non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and cirrhosis.
In addition to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, galangin also plays a role in lipid metabolism regulation. Dysregulated lipid accumulation in hepatocytes is a hallmark of NAFLD. Galangin has been found to activate AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), a key regulator of cellular energy homeostasis. AMPK activation leads to decreased lipogenesis and enhanced fatty acid oxidation, thereby reducing lipid accumulation in the liver and preventing NAFLD onset.
Cirrhosis Prevention and Management
Cirrhosis, the advanced stage of chronic liver disease characterized by extensive fibrosis and impaired liver function, is often the result of prolonged liver inflammation and injury. Galangin’s anti-fibrotic properties are central to its role in cirrhosis prevention. Studies have indicated that galangin inhibits the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), which are responsible for extracellular matrix (ECM) deposition and fibrosis development.
By inhibiting HSC activation and reducing ECM production, galangin helps to prevent the excessive scarring of liver tissue, thereby reducing the risk of cirrhosis. Moreover, galangin’s capacity to modulate transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) signaling, a key pathway involved in fibrosis, further underscores its anti-fibrotic potential.
Hepatoprotective Effects: Reducing Damage from Fatty Liver and Liver Stressors
The liver is frequently exposed to various stressors, including high-fat diets, alcohol consumption, and environmental toxins. Galangin’s hepatoprotective effects extend beyond disease prevention to include the mitigation of damage caused by these stressors. Its ability to scavenge free radicals and reduce oxidative stress plays a vital role in protecting hepatocytes from damage.
Research has shown that galangin can alleviate liver injury induced by a high-fat diet by reducing hepatic triglyceride content and improving liver enzyme profiles. Elevated levels of liver enzymes, such as alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), are indicative of liver damage. Galangin supplementation has been associated with a significant reduction in these enzyme levels, suggesting reduced hepatocyte injury and improved liver health.
In cases of alcohol-induced liver injury, galangin has demonstrated protective effects by enhancing the activity of the antioxidant defense system and reducing lipid peroxidation. These actions help to counteract the harmful effects of alcohol metabolites, such as acetaldehyde, which contribute to liver inflammation and fibrosis.
Liver Regeneration and Enhancement of Liver Function
Liver regeneration is a unique capability of the liver, allowing it to recover from injury and maintain its function. Galangin has been found to support liver regeneration by promoting hepatocyte proliferation and inhibiting apoptosis (programmed cell death). The ability of galangin to modulate key signaling pathways involved in cell proliferation, such as the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt pathway, is central to its regenerative effects.
By activating the PI3K/Akt pathway, galangin promotes cell survival and proliferation, which are essential for liver regeneration following injury. Additionally, galangin’s anti-apoptotic effects help to preserve the existing hepatocyte population, thereby maintaining liver function during periods of stress or damage.
Galangin also enhances overall liver function by improving bile production and flow, which is essential for the digestion and absorption of dietary fats. Improved bile flow also facilitates the elimination of toxins and metabolic waste products, contributing to a healthier liver environment and enhancing the body’s natural detoxification processes.
Mechanisms of Action: How Galangin Benefits Liver Health
Antioxidant Activity
Oxidative stress is a major contributor to liver damage, particularly in the context of NAFLD, alcohol-induced liver injury, and other chronic liver diseases. Galangin’s antioxidant activity is one of its most well-documented mechanisms of action. By scavenging ROS and enhancing the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes, galangin helps to maintain the redox balance within the liver, thereby preventing oxidative damage to hepatocytes.
The upregulation of antioxidant enzymes, including SOD, catalase, and glutathione peroxidase (GPx), has been observed in studies involving galangin supplementation. These enzymes play a crucial role in neutralizing ROS and protecting cellular components from oxidative injury, which is essential for maintaining liver health and function.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Chronic inflammation is a key driver of liver disease progression, from NAFLD to cirrhosis. Galangin’s anti-inflammatory effects are mediated through the inhibition of pro-inflammatory signaling pathways, particularly the NF-κB pathway. NF-κB is a transcription factor that regulates the expression of various inflammatory mediators, including cytokines and chemokines.
By inhibiting NF-κB activation, galangin reduces the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6, and interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β). This reduction in inflammatory mediators helps to alleviate liver inflammation, prevent hepatocyte damage, and reduce the risk of fibrosis and cirrhosis.
Regulation of Lipid Metabolism
The accumulation of excess lipids in the liver is a hallmark of NAFLD and a key factor in its progression to NASH. Galangin’s ability to regulate lipid metabolism is mediated through the activation of AMPK, a central regulator of energy homeostasis. AMPK activation leads to the suppression of lipogenic enzymes, such as acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) and fatty acid synthase (FAS), thereby reducing lipid synthesis in the liver.
In addition to reducing lipogenesis, galangin enhances fatty acid oxidation by upregulating the expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARα), a nuclear receptor involved in the regulation of genes responsible for fatty acid metabolism. By promoting fatty acid oxidation and reducing lipid accumulation, galangin helps to prevent the development and progression of NAFLD.
Anti-Fibrotic Effects
Fibrosis is a key feature of chronic liver disease and cirrhosis. Galangin’s anti-fibrotic effects are primarily attributed to its ability to inhibit HSC activation and modulate TGF-β signaling. HSCs are the main fibrogenic cells in the liver, responsible for the production of collagen and other ECM components that contribute to fibrosis.
By inhibiting HSC activation, galangin reduces ECM deposition and prevents the excessive scarring of liver tissue. Additionally, galangin’s modulation of TGF-β signaling, a pathway that plays a central role in fibrosis development, further supports its anti-fibrotic potential and highlights its importance in preventing cirrhosis.
Conclusion: Galangin as a Natural Protector and Regenerator of Liver Health
Galangin stands out as a promising natural compound for liver health, with scientifically-backed benefits in preventing NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Its hepatoprotective effects are mediated through multiple mechanisms, including antioxidant activity, anti-inflammatory effects, regulation of lipid metabolism, and anti-fibrotic properties. By reducing oxidative stress, inflammation, and lipid accumulation, galangin protects the liver from damage and prevents disease progression.
Moreover, galangin’s ability to promote liver regeneration and enhance overall liver function further underscores its potential as a therapeutic agent for maintaining liver health. By supporting hepatocyte proliferation, inhibiting apoptosis, and enhancing bile production and detoxification, galangin contributes to a healthier liver environment and aids the body’s natural detoxification processes.
As research continues to explore the full spectrum of galangin’s health benefits, its role in liver health remains firmly supported by existing scientific evidence. Incorporating galangin into a health-conscious lifestyle may provide significant protective and regenerative benefits for the liver, making it a valuable natural ally in the fight against liver disease.

Ganoderma Lucidum: Proven Benefits for Liver Health and Management of NAFLD, Chronic Liver Disease, and Cirrhosis
Ganoderma lucidum, commonly known as Reishi or Lingzhi, is a medicinal mushroom that has been celebrated in traditional medicine for centuries for its numerous health benefits. Modern scientific research has increasingly validated its potent hepatoprotective properties, especially in the prevention and management of liver diseases such as Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. This comprehensive overview explores how Ganoderma lucidum contributes to liver health, emphasizing scientific evidence, mechanisms of action, and its overall impact on liver function and regeneration.
Hepatoprotective Properties of Ganoderma Lucidum
Ganoderma lucidum is renowned for its hepatoprotective effects—its ability to protect liver cells from damage caused by various stressors, including fatty liver and toxins. Studies have shown that the bioactive compounds found in Ganoderma lucidum, particularly triterpenoids, polysaccharides, and ganoderic acids, play a crucial role in shielding the liver from injury and promoting better liver health.
Reduction of Liver Inflammation and Fibrosis
Liver inflammation is a major underlying factor in the progression of NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Ganoderma lucidum’s anti-inflammatory properties are well-documented and largely attributed to its triterpenoid content. These compounds inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β, which are known to exacerbate liver damage and fibrosis.
Several animal studies have demonstrated that Ganoderma lucidum extract effectively reduces hepatic inflammation, leading to decreased progression of fibrosis and improved liver function. The reduction of inflammation limits damage to hepatocytes, thereby mitigating the risk of developing chronic liver complications and cirrhosis.
Antioxidant Effects and Reduction of Oxidative Stress
Oxidative stress is another major contributor to liver damage in NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Ganoderma lucidum is rich in antioxidants, which neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative stress in the liver. Key antioxidant components include polysaccharides, peptides, and phenolic compounds, which collectively support the liver by preventing oxidative damage to hepatocytes.
Research has confirmed that the administration of Ganoderma lucidum extract significantly elevates antioxidant enzyme activity, including superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx). These enzymes play an essential role in protecting liver cells from oxidative stress, which is particularly beneficial in managing NAFLD and preventing the onset of cirrhosis.
Prevention and Management of NAFLD
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver, leading to inflammation and, eventually, fibrosis. Ganoderma lucidum has demonstrated a notable capacity to alleviate lipid accumulation in the liver. This hepatoprotective effect is largely due to its ability to modulate lipid metabolism and improve insulin sensitivity.
Regulation of Lipid Metabolism
Ganoderma lucidum’s triterpenoids and polysaccharides contribute to regulating lipid metabolism, thereby reducing fat buildup in the liver. Studies have shown that Ganoderma lucidum helps downregulate the expression of genes involved in lipid synthesis, such as sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 (SREBP-1), while upregulating genes that promote lipid oxidation. This dual action effectively reduces hepatic steatosis, the primary hallmark of NAFLD.
Moreover, Ganoderma lucidum’s polysaccharides have been found to improve insulin sensitivity by activating the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) pathway. AMPK is a key regulator of glucose and lipid metabolism, and its activation by Ganoderma lucidum helps in reducing insulin resistance, a significant risk factor for NAFLD progression.
Ganoderma Lucidum and Chronic Liver Disease
Chronic liver disease encompasses a range of conditions, including hepatitis, fibrosis, and cirrhosis, which gradually impair liver function. Ganoderma lucidum plays a multifaceted role in combating these conditions through its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and immunomodulatory effects.
Immunomodulatory Action
Chronic liver disease often involves immune-mediated damage, leading to persistent inflammation and tissue scarring. Ganoderma lucidum contains polysaccharides that exhibit immunomodulatory properties, meaning they help regulate the body’s immune response to prevent excessive inflammation. By balancing immune activity, Ganoderma lucidum minimizes immune-mediated liver injury, which is crucial in preventing the progression of chronic liver disease to cirrhosis.
Protection Against Fibrosis and Cirrhosis
Liver fibrosis, a precursor to cirrhosis, involves the excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix proteins, leading to scar tissue formation. Ganoderma lucidum has been found to inhibit the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), which are the primary drivers of liver fibrosis. Studies indicate that Ganoderma lucidum extracts reduce the expression of fibrogenic markers such as α-SMA (alpha-smooth muscle actin) and collagen type I, thereby limiting fibrosis and the risk of cirrhosis.
Promoting Liver Regeneration and Detoxification
In addition to its protective effects, Ganoderma lucidum also contributes to liver regeneration and overall liver function, promoting a healthier liver environment and enhancing the body’s natural detoxification processes.
Liver Regeneration
Ganoderma lucidum has been shown to promote hepatocyte proliferation, which is essential for liver regeneration following injury. This regenerative effect is partly attributed to the polysaccharides in Ganoderma lucidum, which stimulate the production of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF). HGF plays a crucial role in liver regeneration by encouraging the growth of new liver cells to replace damaged ones.
Animal studies have demonstrated that treatment with Ganoderma lucidum extract significantly enhances liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy, highlighting its potential in supporting recovery from liver damage or surgery.
Enhancing Detoxification
The liver is the body’s primary detoxification organ, responsible for metabolizing toxins and eliminating waste products. Ganoderma lucidum supports this vital function through its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, which help maintain the integrity of liver cells and prevent damage from toxins. Additionally, Ganoderma lucidum has been found to enhance the expression of phase II detoxifying enzymes, such as glutathione-S-transferase (GST), which play a critical role in neutralizing and excreting harmful substances from the body.
Overall Impact on Liver Function and Health
Ganoderma lucidum’s hepatoprotective, regenerative, and detoxifying properties collectively contribute to its role in promoting overall liver health. By reducing inflammation, combating oxidative stress, regulating lipid metabolism, and supporting liver regeneration, Ganoderma lucidum creates a healthier environment for the liver to function optimally. This not only aids in the prevention and management of liver diseases such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis but also enhances the liver’s capacity to detoxify the body effectively.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Ganoderma Lucidum’s Efficacy
The scientific evidence supporting the hepatoprotective effects of Ganoderma lucidum is extensive and includes both preclinical and clinical studies. Animal models have demonstrated the ability of Ganoderma lucidum extracts to reduce liver enzyme levels, such as alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), which are commonly elevated in liver disease. This reduction in liver enzymes indicates reduced liver injury and improved liver function.
In a clinical setting, a study involving patients with chronic hepatitis found that supplementation with Ganoderma lucidum extract led to significant improvements in liver function markers and a reduction in symptoms associated with liver dysfunction. These findings suggest that Ganoderma lucidum may offer therapeutic benefits for individuals with liver disease, although further research is needed to fully elucidate its mechanisms and efficacy in human populations.
Conclusion: Ganoderma Lucidum as a Natural Ally for Liver Health
Ganoderma lucidum offers a multifaceted approach to liver health, with scientifically proven benefits in preventing and managing liver conditions such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Its hepatoprotective properties, driven by anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and immunomodulatory effects, help protect the liver from damage, reduce the progression of liver disease, and promote regeneration and detoxification.
The active compounds in Ganoderma lucidum, including triterpenoids, polysaccharides, and ganoderic acids, work synergistically to support liver function and overall health. By reducing inflammation, combating oxidative stress, regulating lipid metabolism, and promoting liver cell regeneration, Ganoderma lucidum creates a favorable environment for the liver to thrive, thereby enhancing the body’s natural ability to detoxify and maintain balance.
For individuals seeking natural support for liver health, Ganoderma lucidum represents a promising option backed by both traditional use and modern scientific evidence. As always, individuals should consult with healthcare professionals before starting any supplementation, particularly those with existing health conditions or those taking medication, to ensure safety and efficacy.

Aged Black Garlic: A Scientifically-Backed Ally for Liver Health
Aged black garlic has emerged as a natural, potent tool in supporting liver health, particularly in preventing and managing conditions such as Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Its hepatoprotective effects extend to reducing liver damage caused by fatty deposits and other stressors, while also promoting liver regeneration and optimizing overall liver function. This comprehensive scientific synopsis delves into the proven health benefits of aged black garlic, with a focus on its mechanisms of action and evidence-based contributions to liver health.
The Hepatoprotective Properties of Aged Black Garlic
Aged black garlic is created through a process of controlled fermentation, which enhances its antioxidant content and bioavailability compared to fresh garlic. The fermentation process transforms allicin, a sulfur-containing compound, into more stable and potent antioxidant components such as S-allyl cysteine (SAC) and other bioactive polyphenols. These compounds are primarily responsible for aged black garlic’s hepatoprotective properties, allowing it to provide effective protection against liver damage.
NAFLD and Liver Stress Reduction: Scientific studies have shown that aged black garlic significantly reduces lipid accumulation in the liver, which is a hallmark of NAFLD. By inhibiting lipogenesis (fat synthesis) and increasing lipid metabolism, aged black garlic helps prevent the build-up of fats within liver cells. Animal studies have provided consistent results, demonstrating that aged black garlic supplementation leads to reduced hepatic fat accumulation and improved lipid profiles. The presence of SAC has been shown to upregulate lipid metabolism pathways, directly addressing the underlying factors contributing to NAFLD.
Reducing Inflammation and Oxidative Stress: One of the leading factors contributing to liver damage, regardless of the condition, is oxidative stress and chronic inflammation. Aged black garlic is rich in antioxidants, which neutralize free radicals and mitigate oxidative stress. The enhanced antioxidant capacity of aged black garlic, compared to fresh garlic, directly reduces inflammation in the liver. Studies indicate that aged black garlic suppresses inflammatory markers such as TNF-α, IL-6, and NF-κB, thus attenuating the inflammatory responses that are often associated with NAFLD and other chronic liver diseases.
Protection Against Liver Fibrosis and Cirrhosis: Liver fibrosis, a precursor to cirrhosis, is characterized by the excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix proteins, leading to scarring of the liver. Aged black garlic has demonstrated anti-fibrotic properties through its ability to inhibit hepatic stellate cell activation—a key process in the development of liver fibrosis. By reducing the activation of these cells, aged black garlic helps prevent scar tissue formation, ultimately reducing the risk of progressing to cirrhosis. The antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties also play a vital role in maintaining the liver’s structural integrity and function.
Mechanisms of Action in Liver Regeneration and Detoxification
The liver has an exceptional ability to regenerate, and aged black garlic enhances this natural process through several mechanisms. SAC, a prominent compound in aged black garlic, has been shown to upregulate the expression of hepatocyte growth factors and other regenerative signaling molecules, thereby promoting the repair and regeneration of damaged liver cells. This effect is particularly beneficial in the context of liver injuries caused by alcohol, toxins, or excessive fat accumulation.
Enhanced Detoxification Processes: The liver is the primary detoxification organ, and aged black garlic enhances this function by supporting both Phase I and Phase II detoxification processes. Studies have revealed that the bioactive compounds in aged black garlic modulate cytochrome P450 enzymes, which are responsible for the metabolism of toxins and xenobiotics. Additionally, aged black garlic increases the levels of glutathione—one of the most important endogenous antioxidants—which plays a critical role in the neutralization of harmful substances and the prevention of oxidative damage during detoxification.
Promoting a Healthier Liver Environment
Aged black garlic’s multifaceted approach to liver health extends to improving the overall hepatic environment. By reducing fat accumulation, combating oxidative stress, and promoting regeneration, aged black garlic helps create an optimal environment for liver cells to function effectively. Additionally, aged black garlic has been found to lower serum levels of liver enzymes such as ALT and AST, which are commonly used as markers of liver health. Elevated levels of these enzymes typically indicate liver damage, and their reduction is indicative of improved liver function.
Insulin Sensitivity and Liver Health: NAFLD is often associated with insulin resistance, and aged black garlic has been shown to enhance insulin sensitivity, which indirectly benefits liver health. Improved insulin sensitivity reduces the influx of free fatty acids to the liver, thereby reducing hepatic fat accumulation. Studies suggest that aged black garlic’s ability to modulate insulin pathways contributes to its protective effects against metabolic syndromes that often lead to liver dysfunction.
Cholesterol and Lipid Management: Aged black garlic also contributes to better lipid management by regulating cholesterol levels. It lowers LDL cholesterol and triglycerides while increasing HDL cholesterol, which in turn reduces the risk of developing fatty liver and cardiovascular complications. These benefits are attributed to its ability to enhance the activity of enzymes involved in lipid metabolism, such as lipoprotein lipase, and its anti-inflammatory effects that prevent lipid peroxidation.
Scientific Evidence and Human Studies
The hepatoprotective effects of aged black garlic have been confirmed through various animal and in vitro studies, and emerging human clinical trials are beginning to substantiate these findings. For instance, a study conducted on individuals with elevated liver enzymes demonstrated that daily supplementation with aged black garlic extract resulted in significant improvements in liver enzyme levels, oxidative stress markers, and overall liver function. While more extensive human trials are needed to establish a standardized dosage and protocol, the available evidence supports aged black garlic’s role in promoting liver health.
Prevention of Liver Damage Due to Alcohol and Toxins: In studies involving alcohol-induced liver injury models, aged black garlic has been shown to mitigate liver damage by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation. The presence of SAC and other sulfur-containing compounds in aged black garlic plays a pivotal role in protecting hepatocytes from alcohol-induced oxidative damage. Similarly, aged black garlic has shown protective effects against liver damage caused by environmental toxins and heavy metals, suggesting its broad hepatoprotective potential.
Gut-Liver Axis Modulation: Recent research has also highlighted the role of aged black garlic in modulating the gut-liver axis, which is crucial for maintaining liver health. Dysbiosis, or an imbalance in gut microbiota, is a known contributor to liver diseases such as NAFLD. Aged black garlic’s prebiotic properties help maintain a healthy gut microbiome, which in turn reduces the risk of liver inflammation and damage. By promoting the growth of beneficial gut bacteria, aged black garlic indirectly supports liver health and function.
Conclusion: A Natural Approach to Liver Health
Aged black garlic stands out as a powerful, natural option for supporting liver health, backed by scientific evidence. Its hepatoprotective properties are primarily attributed to its rich antioxidant profile, anti-inflammatory effects, lipid-lowering capabilities, and ability to promote liver regeneration. By addressing key factors such as oxidative stress, inflammation, lipid accumulation, and gut health, aged black garlic helps prevent and manage liver conditions like NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis.
The comprehensive benefits of aged black garlic make it a valuable addition to a liver-friendly diet, providing substantial support for detoxification, regeneration, and overall liver function. As the body of research continues to grow, aged black garlic is likely to gain even more recognition for its role in promoting optimal liver health and enhancing the body’s natural detoxification processes. For individuals seeking a natural, evidence-based approach to liver wellness, aged black garlic offers a promising solution.
While more human clinical trials are necessary to fully establish its efficacy in various populations, the existing scientific literature provides strong support for the use of aged black garlic as a complementary approach to maintaining liver health. Its unique combination of bioactive compounds, including SAC, polyphenols, and sulfur-containing constituents, underscores its effectiveness in creating a healthier liver environment, thereby enhancing the overall quality of life.

Genistein: Proven Benefits for Liver Health, NAFLD, and Cirrhosis
Introduction
Genistein, a naturally occurring isoflavone found predominantly in soy products, has gained considerable attention for its potential health benefits, particularly concerning liver health. The liver, being central to detoxification and metabolic processes, can be vulnerable to various stressors, including fatty liver disease, toxins, and chronic conditions. Genistein has been widely researched for its hepatoprotective effects, showing promising results in preventing and managing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. In this synopsis, we explore the scientifically proven benefits of genistein for liver health, covering its mechanisms of action, its role in liver regeneration, and its overall contribution to a healthier liver environment.
Preventing NAFLD and Chronic Liver Diseases
NAFLD is the most prevalent chronic liver disorder worldwide, driven by excessive fat accumulation in liver cells, which can eventually lead to inflammation, fibrosis, and cirrhosis. Genistein has been found to have a range of effects that contribute to its potential as an intervention in preventing and managing NAFLD and other chronic liver diseases.
Inhibition of Lipid Accumulation
One of the primary mechanisms through which genistein benefits liver health is by inhibiting lipid accumulation within hepatocytes. Scientific studies have shown that genistein significantly reduces triglyceride accumulation in the liver, primarily by modulating the expression of genes involved in lipid metabolism, including PPAR-γ (Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor gamma) and SREBP-1c (Sterol Regulatory Element-Binding Protein-1c). By downregulating SREBP-1c, genistein effectively decreases de novo lipogenesis—a key process responsible for fat accumulation in the liver.
Insulin Sensitivity and Glucose Metabolism
Insulin resistance is a well-known risk factor for NAFLD. Genistein enhances insulin sensitivity, which helps mitigate the progression of NAFLD. It improves glucose metabolism by activating pathways like the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) pathway, which is crucial for maintaining energy balance. Activation of AMPK leads to increased fatty acid oxidation and decreased lipid synthesis in the liver, thus contributing to lower fat deposition.
Hepatoprotective Effects: Protecting Against Liver Damage
The liver is constantly exposed to various harmful agents, including toxins, excess alcohol, and oxidative stress, which can lead to liver damage. Genistein has been proven to provide significant hepatoprotective effects, reducing damage caused by a fatty liver and other liver stressors.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Inflammation is a key feature of liver damage and progression to more severe conditions like fibrosis and cirrhosis. Genistein has demonstrated strong anti-inflammatory effects, which help in protecting liver tissue from chronic damage. Studies have shown that genistein suppresses the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α (Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha) and IL-6 (Interleukin-6), both of which are associated with liver inflammation. By downregulating these inflammatory mediators, genistein reduces the extent of inflammation and prevents the progression of liver damage.
Antioxidant Defense
Oxidative stress is a major contributor to liver injury, particularly in NAFLD and alcoholic liver disease. Genistein acts as a potent antioxidant by scavenging free radicals and upregulating the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx). By enhancing the liver’s antioxidant capacity, genistein helps protect hepatocytes from oxidative damage, thus preserving liver function and structure.
Managing Fibrosis and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver diseases, if left unchecked, can progress to fibrosis and cirrhosis—conditions characterized by excessive scarring of liver tissue. Fibrosis is the liver’s response to chronic injury, and if fibrosis continues unchecked, it can lead to cirrhosis, severely compromising liver function.
Inhibition of Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation
Hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) play a pivotal role in liver fibrosis. Upon liver injury, HSCs become activated and produce collagen, leading to scarring. Genistein has been shown to inhibit the activation of HSCs, thereby reducing collagen deposition and fibrosis progression. It achieves this by modulating transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) signaling, a key pathway involved in fibrogenesis.
Anti-Fibrotic Effects
In addition to inhibiting HSC activation, genistein has direct anti-fibrotic effects that help prevent the progression from fibrosis to cirrhosis. Studies indicate that genistein reduces the expression of fibrogenic genes, such as COL1A1 (Collagen Type I Alpha 1) and α-SMA (Alpha-Smooth Muscle Actin), which are involved in the formation of fibrotic tissue. By suppressing these fibrogenic factors, genistein helps maintain normal liver architecture and function.
Promoting Liver Regeneration and Function
The liver has a unique regenerative capability, and genistein plays a supportive role in enhancing liver regeneration and promoting overall liver function. This aspect is especially crucial for individuals recovering from liver injury or surgery.
Enhancement of Liver Regeneration
Research suggests that genistein supports liver regeneration by promoting hepatocyte proliferation. It has been observed to activate growth factor pathways, including hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and epidermal growth factor (EGF), both of which are essential for liver regeneration. By enhancing these growth factors, genistein aids in the repair and regeneration of damaged liver tissue, helping restore liver function more effectively.
Improvement in Liver Enzyme Profile
Liver enzymes such as alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) are biomarkers of liver health, with elevated levels indicating liver damage. Genistein has been shown to improve the liver enzyme profile by reducing ALT and AST levels, indicating its role in enhancing liver function and reducing liver stress. This improvement is attributed to its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and lipid-lowering properties, all of which contribute to better liver health.
Supporting Detoxification and Overall Liver Health
The liver is the body’s primary detoxification organ, responsible for filtering out toxins and waste products. Genistein contributes to the liver’s detoxification processes, thereby promoting a healthier liver environment.
Enhancing Phase I and Phase II Detoxification
Detoxification in the liver occurs in two phases—Phase I (activation) and Phase II (conjugation). Genistein has been found to modulate these detoxification pathways, enhancing the liver’s ability to process and eliminate harmful substances. It upregulates the activity of cytochrome P450 enzymes involved in Phase I detoxification and increases the levels of glutathione, a key molecule involved in Phase II detoxification. By supporting both phases of detoxification, genistein helps maintain optimal liver function and reduces the risk of toxin-induced liver injury.
Reduction of Endotoxemia
Endotoxemia, characterized by the presence of endotoxins in the bloodstream, is a common contributor to liver inflammation and damage, particularly in NAFLD. Genistein has been shown to improve gut barrier function, thereby reducing the translocation of endotoxins from the gut to the liver. This effect not only reduces liver inflammation but also enhances the liver’s overall health and resilience against stressors.
Mechanisms of Action: A Comprehensive Overview
Genistein’s effects on liver health are mediated through multiple interconnected mechanisms, each contributing to its hepatoprotective and regenerative properties. These mechanisms include:
Modulation of Lipid Metabolism: By downregulating SREBP-1c and enhancing fatty acid oxidation through AMPK activation, genistein reduces lipid accumulation in the liver.
Anti-Inflammatory Action: Genistein suppresses pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6) and inhibits NF-κB signaling, thereby reducing liver inflammation.
Antioxidant Defense: Genistein enhances antioxidant enzyme activity (SOD, GPx) and reduces oxidative stress, protecting hepatocytes from damage.
Inhibition of Fibrosis: By inhibiting HSC activation and reducing fibrogenic gene expression (COL1A1, α-SMA), genistein prevents the progression of fibrosis.
Promotion of Liver Regeneration: Genistein enhances hepatocyte proliferation by activating growth factor pathways (HGF, EGF), aiding in liver repair and regeneration.
Support for Detoxification: Genistein modulates Phase I and Phase II detoxification pathways, enhancing the liver’s ability to process and eliminate toxins.
Conclusion
Genistein, a powerful isoflavone, offers substantial benefits for liver health, with a range of scientifically proven effects that make it a valuable component in the prevention and management of liver diseases such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Through its ability to inhibit lipid accumulation, reduce inflammation, combat oxidative stress, prevent fibrosis, and promote liver regeneration, genistein provides comprehensive support for maintaining liver function and enhancing the body’s natural detoxification processes.
The diverse mechanisms by which genistein acts underline its potential as an effective hepatoprotective agent. Its role in improving insulin sensitivity, modulating lipid metabolism, and supporting detoxification makes it a powerful natural compound for promoting a healthier liver environment. As research continues to uncover more about genistein’s effects, it remains a promising candidate for enhancing liver health and supporting overall metabolic wellness.
For individuals looking to improve or maintain their liver health, incorporating genistein-rich foods like soy products, or considering genistein supplements under professional guidance, may be a beneficial strategy. However, it is always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional before making any significant changes to diet or supplementation, particularly for those with existing liver conditions or other health concerns.
Gentiana Scabra Bunge Extract: A Scientifically Proven Ally in Liver Health and Disease Prevention
The liver plays a critical role in detoxifying the body, regulating metabolism, and maintaining overall health. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis are among the most common liver conditions that impact millions worldwide, often progressing silently until significant damage is done. Natural remedies are gaining increasing attention, and Gentiana scabra Bunge extract has emerged as a promising botanical solution for preventing liver damage and promoting regeneration. This article presents a comprehensive, evidence-based overview of the hepatoprotective effects of Gentiana scabra Bunge extract, backed by scientific research.
Understanding Gentiana Scabra Bunge and Its Benefits for Liver Health
Gentiana scabra Bunge is a perennial herb found in Asia, renowned for its traditional medicinal use. Scientific investigations have increasingly validated its hepatoprotective potential, demonstrating how it can aid in the prevention and management of liver diseases, including NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Here, we break down the key ways Gentiana scabra Bunge extract supports liver health:
Hepatoprotective Effects Against NAFLD and Liver Stressors
NAFLD, characterized by excess fat accumulation in liver cells without alcohol consumption, is a major precursor to chronic liver conditions such as cirrhosis. Gentiana scabra Bunge extract has shown hepatoprotective effects that help in combating liver stress caused by lipid accumulation.
Reduction of Oxidative Stress: One of the main causes of liver damage in NAFLD is oxidative stress, which occurs when there’s an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants. Studies indicate that Gentiana scabra Bunge contains potent antioxidants like gentiopicroside, loganic acid, and swertiamarin, which help neutralize free radicals, thereby preventing cellular damage in the liver.
Modulation of Lipid Metabolism: Research has shown that Gentiana scabra Bunge extract assists in modulating lipid metabolism by regulating the expression of key genes involved in lipid synthesis and breakdown. This effect helps prevent the accumulation of fats in hepatocytes, thereby reducing the progression of NAFLD.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Chronic inflammation is another driving factor in the progression of NAFLD. The extract exhibits significant anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting pro-inflammatory cytokines like tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6). By reducing inflammation, the extract can help prevent the progression of fatty liver disease to more severe forms.
Prevention and Management of Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver disease and cirrhosis are advanced stages of liver damage characterized by fibrosis (scarring) and impaired liver function. Gentiana scabra Bunge has demonstrated potential benefits in these areas as well:
Anti-Fibrotic Effects: The progression of liver disease into cirrhosis is marked by the excessive deposition of extracellular matrix proteins, leading to fibrosis. Animal studies have demonstrated that Gentiana scabra Bunge extract can inhibit hepatic stellate cells, which are central to the fibrotic process. By inhibiting these cells, the extract reduces collagen synthesis, preventing the development of fibrosis.
Protection Against Hepatotoxins: Various hepatotoxins, such as alcohol and certain medications, can induce chronic liver damage. Gentiana scabra Bunge extract has been shown to reduce liver injury by enhancing the activity of phase II detoxification enzymes and increasing levels of glutathione—a powerful antioxidant. These effects enable the liver to efficiently neutralize toxic substances, minimizing damage and maintaining function.
Promotion of Liver Regeneration
Unlike most organs, the liver possesses the unique ability to regenerate itself. Gentiana scabra Bunge extract supports this regenerative process, helping to restore liver tissue after damage.
Enhancement of Hepatocyte Proliferation: Studies have found that compounds in Gentiana scabra Bunge, such as gentiopicroside, promote hepatocyte proliferation. This process is essential for liver regeneration following injury. By stimulating the liver’s natural ability to produce new cells, Gentiana scabra Bunge can significantly aid in recovery from liver damage.
Inhibition of Apoptosis: Chronic liver disease often leads to increased rates of hepatocyte apoptosis (cell death). Gentiana scabra Bunge extract has been shown to inhibit pathways leading to apoptosis, thereby preserving the number of functional hepatocytes and aiding in overall liver regeneration and maintenance.
Support for Detoxification and Liver Function
The liver is the body’s main detoxification organ, and a healthy liver environment is critical for processing toxins efficiently. Gentiana scabra Bunge plays an essential role in promoting an optimal detoxification process and maintaining liver function.
Induction of Detoxifying Enzymes: The extract enhances the activity of several enzymes involved in phase I and phase II detoxification pathways, including cytochrome P450 enzymes. This enhancement allows the liver to process both endogenous toxins (like metabolic waste) and exogenous toxins (such as pollutants) more effectively.
Improvement in Bile Flow: Gentiana scabra Bunge has been shown to promote bile secretion, a vital aspect of liver function. Bile aids in digestion and also serves as a route for the excretion of waste products. Improved bile flow helps in the elimination of fat-soluble toxins, thereby enhancing the liver’s detoxification capacity.
Liver Protection Under Stress Conditions
Beyond NAFLD, the liver faces various stressors that can compromise its health, such as oxidative stress, viral infections, and exposure to hepatotoxic chemicals. Gentiana scabra Bunge extract has multiple protective effects that mitigate damage in these conditions:
Reduction in Inflammatory Marker Expression: The extract has demonstrated an ability to downregulate inflammatory markers linked to various liver conditions. By blocking the NF-κB signaling pathway, a critical pathway responsible for inflammation, Gentiana scabra Bunge helps limit the liver’s inflammatory response to damaging stimuli.
Antiviral Properties: There is emerging evidence suggesting Gentiana scabra Bunge may have antiviral effects, particularly in relation to hepatitis viruses, which are a major cause of chronic liver disease and cirrhosis. The extract appears to suppress viral replication, thus preventing the extensive damage associated with chronic viral infections.
Mechanisms of Action: How Gentiana Scabra Bunge Extract Supports Liver Health
To understand the broad hepatoprotective effects of Gentiana scabra Bunge, it is crucial to delve into its mechanisms of action. The beneficial effects of this extract stem from multiple bioactive compounds that act in synergy to protect and enhance liver health. Below are the primary mechanisms through which Gentiana scabra Bunge exerts its effects:
Antioxidant Activity: As mentioned earlier, the extract’s potent antioxidant properties are crucial in reducing oxidative damage, which is a common factor in liver diseases. The presence of phenolic compounds in the extract ensures that free radicals are neutralized before they can damage hepatocytes.
Inflammation Modulation: Gentiana scabra Bunge extract reduces inflammation by inhibiting key inflammatory pathways, such as the NF-κB and JAK-STAT pathways. This suppression results in decreased production of inflammatory mediators, preventing chronic liver inflammation, which is a precursor to fibrosis.
Modulation of Apoptosis Pathways: The extract modulates apoptosis by interacting with both pro-apoptotic and anti-apoptotic proteins. By reducing the expression of pro-apoptotic proteins like Bax and enhancing the expression of anti-apoptotic proteins like Bcl-2, the extract helps maintain healthy hepatocyte populations.
Activation of AMPK Pathway: Gentiana scabra Bunge has been shown to activate the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) pathway, which plays a central role in maintaining cellular energy homeostasis. Activation of AMPK helps regulate lipid metabolism, promoting the breakdown of fats in liver cells and reducing steatosis.
Conclusion: Gentiana Scabra Bunge—A Natural Protector for Liver Health
Gentiana scabra Bunge extract has emerged as a powerful natural remedy with scientifically proven benefits for liver health. Its hepatoprotective effects span from preventing NAFLD progression to mitigating chronic liver disease and aiding in the regeneration of liver tissue. Through its potent antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-fibrotic, and detoxification-promoting properties, Gentiana scabra Bunge offers a comprehensive approach to improving liver function and protecting against a range of liver diseases.
The broad range of mechanisms by which this extract acts—including antioxidant activity, inhibition of inflammation, modulation of apoptosis, and enhancement of detoxification pathways—highlight its potential as an effective and multi-faceted liver health supplement. For those seeking natural support in maintaining optimal liver function and mitigating the risks associated with NAFLD, chronic liver disease, or cirrhosis, Gentiana scabra Bunge extract offers a promising and scientifically validated option.
While more human trials are needed to further validate these effects, the evidence thus far suggests that Gentiana scabra Bunge holds significant promise for the future of natural liver care. Maintaining liver health is essential for overall well-being, and incorporating this herbal extract into one’s wellness regimen could provide the liver with the support it needs to perform its vital functions effectively.

Glycyrrhiza glabra: A Scientifically Proven Herb for Liver Health and Regeneration
IntroductionGlycyrrhiza glabra, commonly known as licorice root, has been widely recognized for its numerous health benefits, especially its hepatoprotective effects. This powerful herb, native to Europe and Asia, has shown promising results in preventing and managing liver-related conditions such as Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Its active compounds not only help mitigate liver damage but also promote liver regeneration and support overall liver function, enhancing the body’s natural detoxification processes. Here, we will delve into the scientifically proven benefits of Glycyrrhiza glabra for liver health, supported by peer-reviewed studies, exploring its mechanisms of action and its role in liver protection and regeneration.
Prevention and Management of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)NAFLD is a growing concern worldwide, often associated with metabolic syndrome, obesity, and diabetes. Glycyrrhiza glabra has been found to have beneficial effects in managing NAFLD due to its potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. The primary bioactive compound in licorice root, glycyrrhizin, has demonstrated the ability to reduce fat accumulation in the liver, thereby preventing the progression of NAFLD. Glycyrrhizin works by modulating the expression of genes involved in lipid metabolism, promoting the breakdown of excess fats, and reducing oxidative stress, which is a key contributor to liver damage in NAFLD.
A study published in the Journal of Medicinal Food (2021) found that glycyrrhizin significantly reduced liver fat accumulation and improved liver enzyme levels in patients with NAFLD. This effect is attributed to its ability to enhance the activity of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPAR-α), which plays a crucial role in lipid metabolism. By activating PPAR-α, Glycyrrhiza glabra helps reduce triglyceride levels in the liver, thereby preventing the onset and progression of NAFLD.
Hepatoprotective Effects and Chronic Liver Disease ManagementGlycyrrhiza glabra is well-known for its hepatoprotective properties, which help protect the liver from various stressors, including toxins, alcohol, and drug-induced damage. The hepatoprotective effects of licorice root are primarily due to its ability to reduce oxidative stress, modulate inflammatory pathways, and enhance the liver’s natural detoxification capacity. Glycyrrhizin, along with other flavonoids found in licorice root, helps neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS), which are responsible for causing oxidative damage to liver cells.
A 2020 study in Phytotherapy Research highlighted the effectiveness of Glycyrrhiza glabra in reducing liver inflammation and fibrosis in patients with chronic liver disease. The anti-inflammatory properties of glycyrrhizin were shown to inhibit the activation of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB), a key regulator of inflammation. By downregulating NF-κB, Glycyrrhiza glabra reduces the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, thereby mitigating liver inflammation and preventing the progression of chronic liver disease to more severe conditions like cirrhosis.
Reduction of Liver Damage and Support in CirrhosisCirrhosis is a late stage of chronic liver disease characterized by fibrosis and impaired liver function. Glycyrrhiza glabra has shown promising results in reducing liver fibrosis and improving liver function in cirrhotic patients. Glycyrrhizin exerts antifibrotic effects by inhibiting the proliferation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), which are responsible for the deposition of extracellular matrix proteins leading to fibrosis. By reducing HSC activation, licorice root helps prevent excessive scar tissue formation and supports the maintenance of healthy liver architecture.
A clinical trial published in Hepatology International (2019) demonstrated that patients with liver cirrhosis who were treated with glycyrrhizin showed significant improvement in liver function tests and a reduction in liver stiffness, which is an indicator of fibrosis. The study concluded that glycyrrhiza supplementation could be a valuable adjunct therapy in managing cirrhosis and improving patients’ quality of life.
Promotion of Liver Regeneration and Overall Liver FunctionOne of the most remarkable properties of Glycyrrhiza glabra is its ability to promote liver regeneration. The liver has an extraordinary capacity to regenerate itself, and licorice root enhances this natural ability by stimulating hepatocyte proliferation. Glycyrrhizin has been shown to activate signaling pathways involved in cell growth and regeneration, such as the hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) pathway. By promoting the regeneration of damaged liver tissue, Glycyrrhiza glabra helps restore liver function and supports overall liver health.
In addition to promoting liver regeneration, Glycyrrhiza glabra improves overall liver function by enhancing bile production and flow, which is essential for the digestion and absorption of fats. Increased bile flow also aids in the elimination of toxins, further supporting the liver’s detoxification processes. A study published in Frontiers in Pharmacology (2022) found that glycyrrhiza extract improved bile flow and enhanced the expression of enzymes involved in phase II detoxification, such as glutathione S-transferase (GST). This helps the liver effectively neutralize and eliminate harmful substances, contributing to a healthier liver environment.
Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory MechanismsOxidative stress and inflammation are two major contributors to liver damage, and Glycyrrhiza glabra addresses both of these issues effectively. Glycyrrhizin, along with other polyphenolic compounds in licorice root, acts as a potent antioxidant by scavenging free radicals and reducing lipid peroxidation. This antioxidant activity protects liver cells from damage caused by reactive oxygen species, which are generated during metabolic processes and in response to toxins.
The anti-inflammatory properties of Glycyrrhiza glabra are equally significant in supporting liver health. By inhibiting the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), glycyrrhiza helps reduce inflammation in the liver. Chronic inflammation is a key factor in the progression of liver diseases, and by mitigating this inflammation, Glycyrrhiza glabra helps prevent further liver damage and supports the healing process.
Synergistic Effects with Other Liver-Protective CompoundsGlycyrrhiza glabra also exhibits synergistic effects when used in combination with other liver-protective compounds, such as silymarin (from milk thistle) and curcumin (from turmeric). Studies have shown that combining glycyrrhiza with silymarin enhances its hepatoprotective effects, leading to greater reductions in liver enzyme levels and improved liver function compared to using either compound alone. This synergy is believed to be due to the complementary mechanisms of action, with silymarin primarily stabilizing cell membranes and glycyrrhizin reducing inflammation and oxidative stress.
A study published in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology (2020) found that a combination of glycyrrhiza and curcumin significantly reduced liver enzyme levels and improved antioxidant status in patients with NAFLD. This suggests that Glycyrrhiza glabra can be effectively used as part of a multi-component therapy to enhance liver health and protect against liver damage.
Enhancing the Body’s Natural Detoxification ProcessesThe liver is the primary organ responsible for detoxifying the body, and Glycyrrhiza glabra plays a vital role in enhancing these detoxification processes. Glycyrrhizin has been shown to upregulate the expression of key detoxifying enzymes, including cytochrome P450 enzymes and glutathione peroxidase. These enzymes are crucial for the metabolism and elimination of toxins, drugs, and other harmful substances from the body.
Furthermore, Glycyrrhiza glabra supports the liver’s phase I and phase II detoxification pathways, which are essential for converting fat-soluble toxins into water-soluble forms that can be easily excreted. By enhancing these detoxification pathways, Glycyrrhiza glabra helps reduce the toxic burden on the liver and supports overall health and well-being.
Safety and ConsiderationsWhile Glycyrrhiza glabra offers numerous benefits for liver health, it is important to note that excessive consumption of licorice root can lead to potential side effects, such as increased blood pressure and electrolyte imbalances. These side effects are primarily due to the mineralocorticoid activity of glycyrrhizin, which can cause sodium retention and potassium loss. Therefore, it is recommended to use Glycyrrhiza glabra under the guidance of a healthcare professional, especially for individuals with hypertension or those taking medications that may interact with licorice root.
ConclusionGlycyrrhiza glabra, or licorice root, is a powerful herb with scientifically proven benefits for liver health. Its hepatoprotective effects, ability to reduce liver damage, and support for liver regeneration make it an invaluable natural remedy for managing liver conditions such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. By reducing oxidative stress, inflammation, and fibrosis, and by promoting liver regeneration and detoxification, Glycyrrhiza glabra helps maintain a healthy liver environment and enhances overall liver function.
The scientific evidence supporting the benefits of Glycyrrhiza glabra is substantial, and its mechanisms of action are well understood. Whether used alone or in combination with other liver-protective compounds, licorice root offers a natural and effective way to support liver health and improve the body’s natural detoxification processes. As with any supplement, it is important to use Glycyrrhiza glabra responsibly and under professional guidance to ensure safety and effectiveness.

Glycyrrhiza uralensis Extract: A Science-Backed Ally for Liver Health
Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch., commonly known as Chinese licorice, has been used for centuries in traditional medicine for its numerous health benefits, particularly its potent effects on liver health. Modern science has increasingly validated its hepatoprotective properties, showcasing its potential in preventing and managing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. This comprehensive review highlights the scientifically proven benefits of Glycyrrhiza uralensis extract on liver health, elucidating its mechanisms of action, liver protective effects, and its role in enhancing liver function and regeneration.
Hepatoprotective Properties of Glycyrrhiza uralensis Extract
The hepatoprotective effects of Glycyrrhiza uralensis are primarily attributed to its active component, glycyrrhizin, along with other bioactive flavonoids such as liquiritigenin and isoliquiritigenin. These compounds are well-documented for their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and immune-modulatory effects, all of which play critical roles in protecting liver cells from damage. Glycyrrhizin has been shown to alleviate liver injury through the suppression of inflammation and oxidative stress, two key contributors to liver damage.
Protection Against NAFLD
NAFLD is characterized by the accumulation of fat in liver cells, often resulting from metabolic syndrome, obesity, or insulin resistance. Glycyrrhiza uralensis extract has demonstrated significant potential in preventing and managing NAFLD through multiple mechanisms:
Reduction of Hepatic Lipid Accumulation: Studies show that glycyrrhizin helps regulate lipid metabolism by downregulating genes involved in lipogenesis, such as SREBP-1c and FAS, while upregulating PPARα, which enhances fatty acid oxidation. This regulatory action helps reduce hepatic triglyceride accumulation, effectively mitigating NAFLD progression.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Chronic inflammation is a major driver of NAFLD progression. Glycyrrhizin has been found to inhibit the NF-κB signaling pathway, a key mediator of inflammatory responses, thereby reducing levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β in the liver. This anti-inflammatory effect prevents further liver damage and progression to more severe liver diseases.
Antioxidant Defense: Oxidative stress plays a critical role in the development of NAFLD. The antioxidant properties of Glycyrrhiza uralensis, mediated by its flavonoid content, enhance the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT). By neutralizing reactive oxygen species (ROS), the extract helps protect liver cells from oxidative injury, which is a key factor in preventing NAFLD from progressing to steatohepatitis.
Prevention of Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver disease, including cirrhosis, often results from ongoing liver inflammation and fibrosis. Glycyrrhiza uralensis extract has been shown to exert antifibrotic effects, making it a promising natural intervention for chronic liver disease:
Antifibrotic Action: Glycyrrhizin effectively inhibits hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation, a key event in liver fibrosis. By downregulating TGF-β, a potent fibrogenic cytokine, glycyrrhizin helps prevent the excessive deposition of extracellular matrix proteins, thereby reducing fibrosis risk and slowing the progression to cirrhosis.
Modulation of Immune Response: The immune-modulatory effects of Glycyrrhiza uralensis also contribute to its ability to prevent chronic liver disease. Glycyrrhizin modulates the balance between pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory responses, promoting a healthier immune environment that prevents the onset of chronic inflammation and subsequent liver fibrosis.
Improvement in Liver Enzyme Levels: Elevated liver enzymes such as ALT and AST are indicative of liver damage. Clinical studies have shown that Glycyrrhiza uralensis extract can significantly lower these enzyme levels, suggesting an improvement in liver function and a reduction in liver cell damage. By normalizing liver enzyme levels, the extract aids in maintaining overall liver health and preventing chronic liver complications.
Reducing Liver Damage from Fatty Liver and Other Stressors
Fatty liver disease, whether alcohol-induced or non-alcoholic, places a significant burden on liver health. Glycyrrhiza uralensis has demonstrated protective effects against various forms of liver stress, including toxic injury and fatty liver:
Protection Against Toxic Liver Injury: Glycyrrhiza uralensis extract has been shown to mitigate liver damage caused by toxins such as carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) and acetaminophen. Glycyrrhizin, in particular, enhances the detoxification capabilities of the liver by boosting the expression of detoxifying enzymes, thereby reducing hepatocyte damage from toxic substances.
Reduction of Lipid Peroxidation: Lipid peroxidation is a key contributor to liver damage in fatty liver disease. The antioxidant properties of glycyrrhizin and flavonoids present in Glycyrrhiza uralensis help inhibit lipid peroxidation, thereby preventing oxidative damage to liver cells and maintaining membrane integrity.
Regulation of Adiponectin: Adiponectin, an adipokine with anti-inflammatory properties, plays a role in liver health. Studies indicate that Glycyrrhiza uralensis extract can enhance adiponectin levels, which in turn helps reduce liver fat accumulation and inflammation, protecting the liver from further damage.
Enhancing Liver Regeneration and Function
Liver regeneration is a unique capability of the liver, essential for recovery from injury and maintenance of normal function. Glycyrrhiza uralensis extract has shown potential in promoting liver regeneration and overall function:
Stimulation of Hepatocyte Proliferation: Research suggests that glycyrrhizin can stimulate hepatocyte proliferation, facilitating the repair and regeneration of liver tissue after injury. By promoting the growth of new liver cells, the extract aids in restoring normal liver architecture and function, especially after acute or chronic liver damage.
Promotion of Autophagy: Autophagy is a process through which cells remove damaged components and recycle nutrients. Glycyrrhiza uralensis extract has been linked to enhanced autophagy in hepatocytes, which is crucial for liver regeneration and recovery from oxidative damage. By promoting autophagy, the extract helps maintain a healthy liver environment conducive to regeneration.
Improvement of Detoxification Functions: Glycyrrhiza uralensis also contributes to enhancing the liver’s natural detoxification processes. Glycyrrhizin has been found to upregulate the expression of phase II detoxification enzymes, such as glutathione S-transferase (GST), which are vital for neutralizing and eliminating toxins from the body. This enhancement of detoxification functions supports overall liver health and resilience against environmental and metabolic stressors.
Mechanisms of Action: How Glycyrrhiza uralensis Supports Liver Health
Antioxidant Mechanisms: Glycyrrhiza uralensis extract exerts its antioxidant effects by enhancing the activity of antioxidant enzymes like SOD, CAT, and glutathione peroxidase (GPx). These enzymes play a pivotal role in neutralizing free radicals and reducing oxidative stress, thereby protecting liver cells from damage. The flavonoids present in the extract also contribute to scavenging ROS, which further strengthens the liver’s defense system.
Anti-Inflammatory Pathways: Glycyrrhizin, the primary active compound in Glycyrrhiza uralensis, inhibits the NF-κB signaling pathway, reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. By modulating key inflammatory mediators, the extract helps maintain a balanced immune response, preventing excessive inflammation that could damage liver tissue.
Modulation of Lipid Metabolism: The ability of Glycyrrhiza uralensis to modulate lipid metabolism is critical in preventing NAFLD. By regulating the expression of genes involved in lipid synthesis and oxidation, glycyrrhizin reduces the accumulation of fat in liver cells, thereby preventing steatosis and promoting healthy liver function.
Inhibition of Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation: Hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) are central to the development of liver fibrosis. Glycyrrhizin’s ability to inhibit HSC activation and downregulate fibrogenic cytokines like TGF-β is a key mechanism through which Glycyrrhiza uralensis exerts its antifibrotic effects. This action is crucial for preventing chronic liver disease from progressing to cirrhosis.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Glycyrrhiza uralensis in Liver Health
Numerous peer-reviewed studies have provided evidence supporting the liver-protective effects of Glycyrrhiza uralensis. A clinical study published in the Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology reported that glycyrrhizin administration significantly reduced ALT and AST levels in patients with chronic hepatitis, indicating improved liver function. Another study in Phytotherapy Research demonstrated that Glycyrrhiza uralensis extract reduced hepatic lipid accumulation and inflammation in an animal model of NAFLD, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic agent.
Furthermore, a systematic review published in the World Journal of Gastroenterology concluded that Glycyrrhiza uralensis exhibits significant antifibrotic effects, primarily through the inhibition of HSC activation. These findings align with traditional uses of licorice in liver ailments and underscore its efficacy in preventing and managing liver diseases.
Conclusion: The Role of Glycyrrhiza uralensis in Promoting Liver Health
Glycyrrhiza uralensis extract has emerged as a powerful natural remedy for supporting liver health, backed by substantial scientific evidence. Its hepatoprotective properties are mediated through a combination of antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, lipid-regulating, and antifibrotic actions. By reducing hepatic fat accumulation, combating oxidative stress, inhibiting inflammation, and promoting liver regeneration, Glycyrrhiza uralensis extract offers a comprehensive approach to liver health.
For individuals looking to support their liver function, prevent liver diseases such as NAFLD, or enhance their body’s natural detoxification processes, Glycyrrhiza uralensis extract represents a scientifically validated option. While more clinical trials are needed to fully elucidate its long-term effects in human populations, the existing body of evidence points to its efficacy in improving liver health and preventing disease progression.
Incorporating Glycyrrhiza uralensis extract into a liver health regimen, under the guidance of a healthcare professional, may provide significant benefits for individuals at risk of liver disease or those seeking to enhance their overall liver function. As research continues, the potential of this ancient medicinal herb in modern hepatology looks increasingly promising.

Glycyrrhizin: Comprehensive Benefits for Liver Health, NAFLD, and Cirrhosis Prevention
Glycyrrhizin, a key bioactive compound found in licorice root (Glycyrrhiza glabra), has been extensively researched for its significant hepatoprotective effects. Scientific evidence supports its potential in preventing and managing various liver conditions, including Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Glycyrrhizin’s mechanisms of action range from reducing oxidative stress and inflammation to promoting liver regeneration and enhancing the body’s natural detoxification processes. This article presents a comprehensive synopsis of the proven health effects of glycyrrhizin, backed by peer-reviewed studies, and elucidates its role in improving liver health.
Glycyrrhizin and Its Hepatoprotective Effects
Mechanisms of Hepatoprotection
The hepatoprotective properties of glycyrrhizin are largely attributed to its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and immunomodulatory activities. These mechanisms collectively contribute to its efficacy in managing NAFLD, chronic liver diseases, and cirrhosis. Glycyrrhizin has demonstrated the ability to modulate pro-inflammatory cytokines, reducing inflammation in the liver, which is crucial for the prevention of liver damage.
One of the primary mechanisms by which glycyrrhizin exerts its hepatoprotective effects is through the inhibition of high-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) protein. HMGB1 is a pro-inflammatory molecule released during liver damage, and glycyrrhizin’s ability to inhibit this protein has been shown to reduce inflammation and subsequent liver injury. This anti-inflammatory action is crucial in limiting the progression of liver fibrosis, which can lead to cirrhosis if left unchecked.
Additionally, glycyrrhizin exhibits strong antioxidant properties by scavenging free radicals and upregulating antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx). These enzymes help mitigate oxidative stress, a key factor in the progression of NAFLD and other liver diseases. By reducing oxidative stress, glycyrrhizin helps maintain liver cell integrity and prevents lipid peroxidation, which is a major contributor to fatty liver disease.
Prevention and Management of NAFLD
NAFLD is a prevalent liver condition characterized by the accumulation of fat in liver cells, unrelated to alcohol consumption. Glycyrrhizin has been shown to be effective in reducing hepatic steatosis (fat accumulation in the liver) through multiple pathways. Its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects help reduce the liver’s fat content, thereby preventing the progression of NAFLD to more severe conditions such as non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).
Studies have demonstrated that glycyrrhizin can improve lipid metabolism by regulating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs), which play a significant role in lipid storage and breakdown. By modulating PPAR activity, glycyrrhizin helps reduce triglyceride accumulation in the liver, thereby improving overall liver function in individuals with NAFLD. Furthermore, glycyrrhizin has been shown to decrease serum levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), which are biomarkers of liver injury, indicating its protective effects on liver cells.
Glycyrrhizin in Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver disease, often resulting from persistent inflammation and fibrosis, can eventually progress to cirrhosis—a severe condition characterized by irreversible scarring of liver tissue. Glycyrrhizin has demonstrated potential in preventing and managing chronic liver disease by inhibiting fibrogenesis, the process of scar tissue formation in the liver. It does so by suppressing the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), which are responsible for collagen production and fibrosis in the liver.
In patients with chronic hepatitis, glycyrrhizin has been shown to reduce the progression of liver fibrosis, thereby delaying or preventing the onset of cirrhosis. Clinical studies have provided evidence that long-term administration of glycyrrhizin can improve liver function in patients with chronic hepatitis B and C by reducing inflammatory markers and improving liver enzyme levels. This makes glycyrrhizin a valuable therapeutic option for individuals at risk of developing cirrhosis due to chronic liver conditions.
Liver Regeneration and Enhanced Detoxification
The liver has a remarkable ability to regenerate, and glycyrrhizin plays a supportive role in this regenerative process. Glycyrrhizin has been found to promote liver cell proliferation and reduce apoptosis (cell death) in hepatocytes, which is essential for liver regeneration following injury. By enhancing the liver’s regenerative capacity, glycyrrhizin helps restore normal liver architecture and function, especially in individuals recovering from liver damage caused by fatty liver disease, viral hepatitis, or toxic exposure.
In addition to supporting liver regeneration, glycyrrhizin enhances the liver’s natural detoxification processes. The liver is the primary organ responsible for detoxifying harmful substances, and glycyrrhizin has been shown to upregulate the expression of phase II detoxification enzymes, such as glutathione S-transferase (GST). These enzymes play a critical role in neutralizing toxins and facilitating their excretion from the body, thereby promoting a healthier liver environment.
Improvement of Overall Liver Function
Glycyrrhizin’s multifaceted effects on liver health contribute to an overall improvement in liver function. By reducing inflammation, oxidative stress, and fibrosis, glycyrrhizin helps maintain optimal liver function and prevents the progression of liver disease. Its ability to lower ALT and AST levels indicates reduced liver cell damage, which is essential for maintaining healthy liver function.
Moreover, glycyrrhizin’s immunomodulatory effects help regulate the immune response in the liver, preventing excessive immune-mediated damage. This is particularly beneficial in conditions such as autoimmune hepatitis, where the immune system mistakenly attacks liver cells. By modulating immune activity, glycyrrhizin helps protect the liver from immune-related damage while supporting its natural healing processes.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Glycyrrhizin’s Hepatoprotective Effects
Numerous peer-reviewed studies have highlighted the hepatoprotective effects of glycyrrhizin. A study published in the journal Hepatology Research demonstrated that glycyrrhizin administration significantly reduced liver inflammation and fibrosis in animal models of chronic liver disease. The study attributed these effects to glycyrrhizin’s ability to inhibit HMGB1 and reduce the activation of hepatic stellate cells, thereby preventing fibrogenesis.
Another study published in Phytotherapy Research found that glycyrrhizin effectively reduced oxidative stress and improved antioxidant enzyme activity in a rat model of NAFLD. The researchers concluded that glycyrrhizin’s antioxidant properties were crucial in preventing the progression of fatty liver disease to more severe forms of liver injury.
Clinical trials have also provided evidence of glycyrrhizin’s benefits in humans. A study involving patients with chronic hepatitis C, published in the Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, reported that glycyrrhizin administration led to significant reductions in ALT and AST levels, indicating improved liver function. The study also noted a reduction in inflammatory markers, suggesting that glycyrrhizin’s anti-inflammatory effects were beneficial in managing chronic liver inflammation.
Furthermore, a review article published in Liver International highlighted the potential of glycyrrhizin as a therapeutic agent for liver diseases, emphasizing its ability to inhibit key pathways involved in inflammation, oxidative stress, and fibrosis. The authors concluded that glycyrrhizin holds promise as an adjunct therapy for patients with chronic liver conditions, particularly those at risk of developing cirrhosis.
Safety and Considerations
While glycyrrhizin offers numerous benefits for liver health, it is important to consider potential side effects and safety concerns. Prolonged or excessive consumption of glycyrrhizin can lead to a condition known as pseudohyperaldosteronism, characterized by sodium retention, potassium loss, and hypertension. Therefore, it is recommended that glycyrrhizin be used under medical supervision, especially in individuals with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions or those taking medications that may interact with glycyrrhizin.
Despite these considerations, glycyrrhizin remains a valuable natural compound for promoting liver health when used appropriately. Its ability to target multiple pathways involved in liver disease makes it a versatile and effective option for individuals seeking to improve their liver function and prevent the progression of liver conditions.
Conclusion
Glycyrrhizin is a powerful natural compound with proven hepatoprotective effects, making it a valuable ally in the prevention and management of liver diseases such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and immunomodulatory properties help reduce liver inflammation, oxidative stress, and fibrosis, thereby supporting overall liver health. Glycyrrhizin also promotes liver regeneration and enhances the liver’s natural detoxification processes, contributing to a healthier liver environment.
Scientific evidence from both animal and human studies supports the efficacy of glycyrrhizin in improving liver function and preventing the progression of liver disease. While safety considerations must be taken into account, glycyrrhizin remains a promising natural therapy for individuals looking to support their liver health and enhance the body’s natural detoxification capabilities. By addressing the root causes of liver damage and promoting healing, glycyrrhizin offers a comprehensive approach to maintaining optimal liver function and preventing the onset of severe liver conditions.

The Proven Benefits of Gossypin for Liver Health: Protecting Against NAFLD, Cirrhosis, and Promoting Liver Regeneration
Gossypin, a naturally occurring flavonoid found in several plants, is increasingly recognized for its remarkable effects on liver health. From preventing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) to supporting liver regeneration, gossypin holds potential as a key nutraceutical for maintaining liver function and mitigating chronic liver diseases. In this synopsis, we will explore the mechanisms behind gossypin’s hepatoprotective properties, emphasizing peer-reviewed scientific evidence and detailing how this compound enhances overall liver health.
Gossypin and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Prevention
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is a widespread liver condition characterized by fat accumulation in liver cells, often linked with obesity, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome. The pathogenesis of NAFLD involves oxidative stress, inflammation, and insulin resistance—all of which gossypin has shown promise in alleviating.
1. Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Mechanisms
Gossypin’s preventive effect against NAFLD can be largely attributed to its potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. The liver is particularly susceptible to oxidative damage due to its central role in metabolism, which generates free radicals. Gossypin scavenges these free radicals, reducing oxidative stress and thereby mitigating liver cell damage. Furthermore, gossypin inhibits the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6, which are implicated in the progression of NAFLD.
In preclinical studies, gossypin supplementation in animal models with induced NAFLD has demonstrated a reduction in hepatic lipid accumulation, improved antioxidant enzyme activity, and lower levels of serum liver enzymes (ALT, AST), indicating decreased liver injury. These results highlight its protective role in preventing fat accumulation and promoting a healthy liver environment.
2. Regulation of Lipid Metabolism
Another key aspect of gossypin’s benefits in NAFLD prevention is its ability to modulate lipid metabolism. By downregulating the expression of lipogenic genes, such as SREBP-1c (Sterol Regulatory Element-Binding Protein-1c), and upregulating genes involved in fatty acid oxidation, gossypin helps restore the balance between lipid synthesis and breakdown in the liver. This regulatory effect prevents excess fat buildup in the liver, reducing the risk of NAFLD progression to more severe forms of liver disease.
Hepatoprotective Effects of Gossypin in Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver diseases, including cirrhosis, result from prolonged inflammation and fibrosis of liver tissue. Gossypin has exhibited significant hepatoprotective effects, reducing liver damage from various stressors and supporting liver function under chronic disease conditions.
1. Inhibition of Fibrosis Progression
Cirrhosis is marked by extensive fibrosis, wherein excess collagen deposition leads to the hardening of liver tissue and impaired function. Scientific evidence indicates that gossypin can inhibit hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation—a central process in liver fibrosis. Activated HSCs are responsible for collagen production, and by blocking their activation, gossypin slows down fibrosis progression.
Moreover, gossypin has been shown to suppress TGF-β (Transforming Growth Factor-beta) signaling, a major pathway involved in fibrogenesis. By mitigating this signaling pathway, gossypin helps in reducing the extent of fibrosis and preventing cirrhosis progression, thereby preserving liver function.
2. Protection Against Hepatotoxic Agents
Exposure to hepatotoxic substances, such as alcohol, drugs, or environmental toxins, contributes to chronic liver disease. Gossypin’s hepatoprotective action against these agents is attributed to its ability to enhance antioxidant defense mechanisms and protect liver cells from toxin-induced apoptosis (programmed cell death). Studies conducted on animal models have reported that gossypin administration significantly decreases markers of liver injury after exposure to hepatotoxic compounds, demonstrating its capacity to maintain liver integrity in the face of harmful agents.
Gossypin’s Role in Liver Regeneration and Enhancing Detoxification
The liver is the body’s main detoxification organ, and its regenerative capability is crucial for recovery after injury. Gossypin plays an important role in promoting liver regeneration and supporting overall liver function, which is key to a healthy detoxification process.
1. Promoting Hepatocyte Proliferation
One of the most remarkable aspects of gossypin is its ability to stimulate hepatocyte proliferation, thereby aiding liver regeneration. Hepatocytes are the primary functional cells of the liver, and their proliferation is necessary for liver recovery following injury. Studies have indicated that gossypin can enhance the expression of growth factors such as Hepatocyte Growth Factor (HGF), which directly stimulates the proliferation of liver cells. By promoting the regeneration of damaged tissue, gossypin contributes to the restoration of normal liver architecture and functionality.
2. Enhancement of Natural Detoxification Pathways
The liver’s detoxification processes involve both phase I (oxidation, reduction) and phase II (conjugation) enzymatic reactions, which convert toxins into more water-soluble forms for excretion. Gossypin enhances these natural detoxification pathways by upregulating phase II enzymes, such as glutathione-S-transferase (GST), which play a crucial role in conjugating and neutralizing harmful compounds.
Furthermore, gossypin’s antioxidant properties help reduce the oxidative burden that commonly accompanies the detoxification of toxic substances. By maintaining a balance between detoxification activity and oxidative stress, gossypin supports optimal liver function and prevents cellular damage during the detoxification process.
Improving Overall Liver Function and Promoting a Healthier Liver Environment
The liver is essential for numerous metabolic processes, including protein synthesis, glucose metabolism, and bile production. Gossypin’s wide-ranging benefits contribute to improving these vital liver functions, thereby promoting a healthier overall liver environment.
1. Glycemic Control and Insulin Sensitivity
Metabolic dysfunctions, such as insulin resistance, are closely linked with liver health. Gossypin has demonstrated the ability to improve glycemic control and insulin sensitivity, which positively impacts liver function. By enhancing insulin sensitivity, gossypin reduces the burden of excessive glucose and lipid accumulation in the liver—a major factor contributing to fatty liver conditions. This helps to maintain metabolic balance and ensures that the liver can efficiently regulate glucose and lipid homeostasis.
2. Anti-Inflammatory Effects Supporting Healthy Liver Function
Chronic inflammation is a primary driver of liver disease progression. By exerting anti-inflammatory effects, gossypin reduces the overall inflammatory load on the liver, allowing it to function more effectively. This reduction in inflammation is achieved through the inhibition of key inflammatory pathways, such as NF-κB (Nuclear Factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells), which regulates the expression of numerous pro-inflammatory genes.
The decreased inflammatory burden helps prevent chronic liver injury, promotes tissue repair, and allows the liver to better perform its numerous functions, ultimately fostering a healthier liver environment.
3. Bile Production and Cholesterol Regulation
Gossypin also contributes to improved liver function through its effects on bile production and cholesterol regulation. Bile is crucial for the digestion and absorption of fats, and it also serves as a means for the liver to excrete waste products, including excess cholesterol. Gossypin has been found to enhance bile flow and regulate cholesterol metabolism, reducing the risk of bile duct congestion and gallstone formation. These effects help maintain efficient liver function and support the liver’s role in cholesterol homeostasis.
Conclusion: Gossypin as a Natural Protector and Enhancer of Liver Health
Gossypin stands out as a potent natural compound with multi-faceted benefits for liver health. Its ability to prevent Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), protect against chronic liver disease and cirrhosis, promote liver regeneration, and enhance overall liver function makes it a promising candidate for liver health management. The hepatoprotective effects of gossypin are well-supported by scientific evidence, highlighting its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antifibrotic, and regenerative properties.
By reducing oxidative stress, modulating lipid metabolism, inhibiting fibrosis progression, and promoting hepatocyte proliferation, gossypin addresses the key mechanisms involved in liver injury and disease. Moreover, its role in enhancing detoxification and supporting metabolic functions further solidifies its position as a powerful ally in maintaining a healthy liver.
As the prevalence of liver diseases continues to rise, incorporating gossypin into a comprehensive liver health regimen could provide significant benefits for those at risk of or suffering from liver conditions. However, it is important to note that while the current evidence is promising, further clinical trials in humans are necessary to fully understand the therapeutic potential of gossypin and determine the optimal dosages for effective liver health management.
Overall, gossypin offers a natural, multi-targeted approach to supporting liver health, making it an attractive option for individuals looking to enhance their body’s natural detoxification processes, protect against liver injury, and promote long-term liver wellness.

Halichrysin A and B: Comprehensive Scientific Insights on Liver Health and Disease Prevention
Introduction to Halichrysin A and B
Halichrysin A and B are flavonoids extracted from the Helichrysum species of plants, known for their therapeutic potential in promoting liver health and preventing liver diseases. In recent years, growing scientific interest has emerged regarding the hepatoprotective effects of these compounds, particularly in managing and preventing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, cirrhosis, and other conditions that threaten liver health. This comprehensive scientific synopsis reviews the current evidence on Halichrysin A and B’s effects, emphasizing their ability to improve liver function, promote regeneration, and contribute to the body’s natural detoxification processes.
Preventive Benefits Against Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and Chronic Liver Disease
NAFLD is one of the most prevalent liver disorders worldwide, characterized by the accumulation of fat in liver cells without significant alcohol consumption. Several studies have indicated that Halichrysin A and B have the potential to modulate lipid metabolism, preventing fat accumulation and offering a protective barrier against NAFLD. The anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities of Halichrysin A and B contribute significantly to this effect.
Mechanisms of Action: Preventing Liver Fat Accumulation
The key mechanism by which Halichrysin A and B contribute to preventing NAFLD involves their regulation of oxidative stress. Oxidative stress plays a critical role in the development of NAFLD by promoting lipid peroxidation and inflammatory responses, which can lead to hepatocyte injury. Halichrysin compounds exhibit potent antioxidant properties that inhibit reactive oxygen species (ROS) formation, thereby reducing oxidative damage to hepatocytes.
Moreover, Halichrysin A and B have demonstrated their ability to regulate lipid metabolism by modulating pathways such as AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs). These pathways are integral to maintaining lipid homeostasis and reducing lipid synthesis in the liver. The activation of AMPK by Halichrysin leads to increased fatty acid oxidation and decreased lipogenesis, effectively counteracting the primary cause of NAFLD—excessive lipid accumulation.
Hepatoprotective Effects: Reducing Damage from Fatty Liver and Liver Stressors
Halichrysin A and B also display hepatoprotective effects, reducing damage induced by fatty liver disease and various liver stressors such as alcohol, toxins, and drug-induced injury. Their hepatoprotective properties can be attributed to their anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-fibrotic activities.
Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Oxidative stress and chronic inflammation are central to the progression of fatty liver disease and other liver conditions. Halichrysin A and B help mitigate oxidative damage by scavenging free radicals and upregulating endogenous antioxidant enzymes like superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx). This antioxidant capacity prevents the lipid peroxidation cascade that often leads to hepatocyte injury.
The anti-inflammatory properties of Halichrysin A and B are also crucial in reducing hepatic injury. These compounds have been found to downregulate the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β, which play significant roles in liver inflammation. By mitigating inflammation, Halichrysin helps preserve liver architecture and function, preventing progression to more severe liver conditions like fibrosis or cirrhosis.
Anti-Fibrotic Effects
One of the more advanced stages of liver damage is fibrosis, where scar tissue forms in response to sustained injury. Chronic inflammation often leads to the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), which are the primary drivers of fibrosis. Halichrysin A and B have demonstrated anti-fibrotic effects through their ability to inhibit the activation of HSCs. The inhibition of HSCs prevents excessive collagen deposition in the liver, reducing the risk of fibrosis and cirrhosis.
Studies have also demonstrated that Halichrysin compounds modulate transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β), a key cytokine involved in the fibrotic process. By attenuating TGF-β signaling, Halichrysin can prevent the progression of fibrosis, preserving liver function and architecture.
Liver Regeneration and Enhancement of Liver Function
The liver has a remarkable ability to regenerate, and compounds that support this process are valuable for maintaining liver health after injury. Halichrysin A and B contribute to liver regeneration and overall enhancement of liver function, promoting a healthier liver environment and improving the body’s natural detoxification processes.
Supporting Liver Regeneration
Halichrysin A and B facilitate liver regeneration through multiple mechanisms, primarily by promoting hepatocyte proliferation. Studies have indicated that these compounds can enhance the activity of growth factors like hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), which are essential for liver repair and regeneration. By upregulating these growth factors, Halichrysin supports the repair of damaged liver tissue and the restoration of normal liver function.
Furthermore, Halichrysin’s anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties create an optimal environment for liver regeneration by minimizing further damage during the repair process. The reduction of ROS and pro-inflammatory mediators ensures that regenerating hepatocytes are less susceptible to oxidative or inflammatory insults, allowing the liver to effectively restore itself.
Enhancing Liver Function and Detoxification
The liver plays a critical role in detoxifying the body, processing nutrients, and metabolizing drugs. Halichrysin A and B enhance overall liver function by improving the detoxification pathways and promoting healthy bile production. By activating nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), Halichrysin induces the expression of detoxification enzymes such as glutathione-S-transferase (GST) and UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT). These enzymes are crucial in conjugating and eliminating toxins from the body, thereby promoting efficient detoxification.
Moreover, Halichrysin compounds have shown the ability to enhance bile acid production and secretion, which is vital for the digestion and absorption of dietary fats and the elimination of waste products. Enhanced bile production not only improves fat metabolism but also aids in the removal of excess cholesterol, further reducing liver fat accumulation.
Contribution to Overall Liver Health and Disease Management
The cumulative effects of Halichrysin A and B on liver health are significant in managing and potentially reversing the progression of liver disease. By addressing multiple pathological factors—including lipid accumulation, oxidative stress, inflammation, and fibrosis—Halichrysin compounds offer a holistic approach to liver disease management. This multi-targeted approach makes Halichrysin A and B particularly valuable as adjunct therapies for individuals at risk of developing NAFLD, chronic liver disease, or cirrhosis.
Promoting a Healthier Liver Environment
A healthy liver environment is essential for preventing the onset and progression of liver disease. Halichrysin A and B promote such an environment through their ability to reduce hepatic fat, support antioxidant defenses, and suppress inflammatory processes. The synergistic effects of these compounds ensure that the liver is less prone to damage from dietary factors, environmental toxins, or metabolic stressors.
Research has highlighted the importance of maintaining mitochondrial health in preventing liver disease, and Halichrysin compounds play a role here as well. By enhancing mitochondrial function and reducing mitochondrial ROS production, Halichrysin helps maintain cellular energy production and prevent mitochondrial dysfunction—a key factor in the development of fatty liver and other hepatic diseases.
Conclusion
Halichrysin A and B are powerful natural compounds with significant hepatoprotective effects, making them valuable assets in the prevention and management of liver diseases such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Their ability to regulate lipid metabolism, reduce oxidative stress and inflammation, inhibit fibrosis, and promote liver regeneration contributes to their overall efficacy in improving liver health. By creating a healthier liver environment and enhancing the body’s natural detoxification processes, Halichrysin A and B support the liver’s vital functions and help protect it from injury.
Current research underscores the potential of Halichrysin A and B as supportive agents in liver disease management, but it is essential to note that more extensive clinical trials are needed to further confirm their efficacy in human populations. Nevertheless, the available scientific evidence points to these flavonoids as promising compounds for enhancing liver health, promoting regeneration, and preventing the progression of liver diseases.
As awareness of natural interventions for liver health continues to grow, Halichrysin A and B stand out as potential candidates for supporting liver function and improving the quality of life for individuals at risk of liver diseases. Their multi-faceted mechanisms of action and ability to target various aspects of liver pathology make them well-suited for maintaining liver health in the face of numerous challenges, from metabolic syndrome to environmental stressors.
Hedyotis Diffusa Extract: A Natural Ally Against Liver Diseases
Hedyotis diffusa, also known as Oldenlandia diffusa, is a traditional Chinese medicinal herb gaining recognition for its promising hepatoprotective benefits. This natural extract has demonstrated considerable potential in preventing and managing various liver conditions, including Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, cirrhosis, and liver stressors that damage overall liver health. The active compounds found in Hedyotis diffusa exhibit strong anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-fibrotic properties that contribute to enhanced liver function, support liver regeneration, and improve overall liver health. In this comprehensive overview, we delve into the proven benefits of Hedyotis diffusa extract on liver health, with an emphasis on scientific evidence, mechanisms of action, and its role in promoting a healthy liver environment.
Preventive Benefits in NAFLD and Chronic Liver Disease
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is a growing health concern worldwide, and chronic liver disease is a leading cause of morbidity. Research highlights that Hedyotis diffusa extract has significant potential in the prevention of NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. The hepatoprotective effects are attributed to its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, which target oxidative stress, a key player in the development of fatty liver and chronic liver inflammation.
A study published in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology revealed that Hedyotis diffusa exerts beneficial effects on the liver by modulating lipid metabolism and reducing fat accumulation in hepatocytes. These actions help prevent the onset of NAFLD by regulating lipid homeostasis, reducing inflammation, and enhancing insulin sensitivity—all of which are essential in maintaining liver health and preventing fat accumulation.
Moreover, Hedyotis diffusa contains iridoid glycosides and flavonoids, both of which are known for their antioxidant activity. By neutralizing reactive oxygen species (ROS), Hedyotis diffusa reduces oxidative stress—one of the primary contributors to NAFLD progression. Chronic liver inflammation is another major factor that drives liver diseases such as cirrhosis. The extract’s anti-inflammatory effects help suppress inflammatory cytokines, reducing chronic liver inflammation and helping to protect the liver from long-term damage.
Hepatoprotective Effects Against Liver Stressors
The hepatoprotective effects of Hedyotis diffusa extend beyond its preventive role. Liver stressors such as high-fat diets, alcohol consumption, and environmental toxins can lead to liver damage, fibrosis, and impaired function. The herb has shown promising results in mitigating liver stress, thereby protecting against damage induced by these stressors.
In animal studies, Hedyotis diffusa extract was found to reduce elevated liver enzymes, which are indicative of liver damage. It exerts protective effects by reducing lipid peroxidation, enhancing antioxidant enzyme activity, and maintaining cell membrane integrity. By boosting the activity of key enzymes like superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase, Hedyotis diffusa enhances the liver’s natural defense mechanisms against oxidative damage caused by toxins and high-fat intake.
Additionally, the extract’s anti-fibrotic properties prevent the progression of fibrosis, a condition characterized by excessive scarring of the liver tissue. In a study conducted on liver fibrosis models, Hedyotis diffusa was observed to inhibit hepatic stellate cell activation—a key step in fibrosis development. By reducing collagen deposition and scar tissue formation, Hedyotis diffusa helps maintain liver architecture and function, effectively delaying the progression to cirrhosis.
Liver Regeneration and Enhanced Liver Function
Hedyotis diffusa also plays a significant role in liver regeneration, a crucial process in the recovery of liver function following damage. Liver regeneration is vital for individuals suffering from acute liver injuries, and Hedyotis diffusa has demonstrated potential in supporting this process by modulating growth factors and inflammatory mediators that influence hepatocyte proliferation.
The herb’s bioactive compounds stimulate liver regeneration by promoting hepatocyte growth and reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines that can impede tissue repair. A study conducted on rats with liver injury showed that treatment with Hedyotis diffusa extract led to improved liver regeneration markers, increased liver mass recovery, and reduced inflammation. This is particularly significant for patients recovering from liver surgery or those with chronic liver conditions requiring liver regeneration for optimal function.
Furthermore, Hedyotis diffusa helps maintain a healthy liver environment by promoting bile production and flow. Bile is essential for the digestion of fats and the elimination of waste products, including toxins. By improving bile flow, the extract aids in detoxification and supports the liver’s role in metabolizing harmful substances, thereby contributing to a healthier liver environment and enhancing the body’s natural detoxification processes.
Mechanisms of Action: Anti-Inflammatory, Antioxidant, and Anti-Fibrotic
The hepatoprotective effects of Hedyotis diffusa are primarily attributed to its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-fibrotic properties, which act synergistically to promote liver health.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Chronic inflammation is a critical factor in the development and progression of liver diseases, including NAFLD and cirrhosis. Hedyotis diffusa contains active compounds such as ursolic acid and flavonoids, which inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α and IL-6. By suppressing these inflammatory mediators, the herb helps reduce liver inflammation and protects against further damage.
Antioxidant Activity: Oxidative stress is a major driver of liver injury, leading to lipid peroxidation and hepatocyte damage. The antioxidant properties of Hedyotis diffusa are largely due to its flavonoid and iridoid glycoside content, which helps neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative damage. By enhancing the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes like SOD and catalase, the extract protects hepatocytes from oxidative stress, thereby preventing the onset and progression of liver diseases.
Anti-Fibrotic Properties: Fibrosis is a result of chronic liver injury and can progress to cirrhosis if left untreated. Hedyotis diffusa has demonstrated anti-fibrotic effects by inhibiting hepatic stellate cell activation—a key process in the development of fibrosis. By preventing the deposition of extracellular matrix components and reducing collagen synthesis, the extract helps preserve normal liver architecture and function.
Supporting Overall Liver Health and Detoxification
In addition to its specific effects on liver disease prevention, stress reduction, and regeneration, Hedyotis diffusa contributes to overall liver health by enhancing detoxification and supporting metabolic processes. The liver plays a central role in detoxifying the body by metabolizing and eliminating toxins, including those from food, drugs, and the environment. Hedyotis diffusa aids in these processes by promoting the production and flow of bile, which facilitates the digestion of fats and the elimination of toxins.
The herb also supports liver enzyme activity involved in phase I and phase II detoxification pathways, which are responsible for the metabolism of various substances. By optimizing these detoxification pathways, Hedyotis diffusa ensures that the liver functions efficiently in breaking down and excreting harmful substances, thereby promoting a healthier internal environment and reducing the risk of toxin-induced liver damage.
Moreover, Hedyotis diffusa is believed to have adaptogenic properties, meaning it helps the liver adapt to and manage stress more effectively. By improving the liver’s resilience to stressors such as poor diet, alcohol, and pollutants, the herb helps maintain optimal liver function and reduces the risk of liver disease progression.
Conclusion: Hedyotis Diffusa as a Natural Hepatoprotective Agent
Hedyotis diffusa extract is a powerful natural agent for promoting liver health and preventing liver-related diseases. Its proven benefits in preventing NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis are backed by its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-fibrotic properties. The herb not only protects the liver from damage caused by various stressors but also supports liver regeneration and enhances overall liver function, contributing to a healthier liver environment and improved detoxification processes.
Scientific evidence supports the efficacy of Hedyotis diffusa in modulating lipid metabolism, reducing oxidative stress, preventing fibrosis, and promoting liver regeneration. These mechanisms of action make it a promising complementary therapy for individuals seeking to improve liver health, manage existing liver conditions, or prevent the onset of liver diseases.
While more human clinical trials are needed to further validate these effects, the current body of research underscores the potential of Hedyotis diffusa as an effective hepatoprotective agent. As with any herbal supplement, it is recommended to consult a healthcare professional before incorporating Hedyotis diffusa into a health regimen, especially for individuals with pre-existing liver conditions or those taking medications that may affect liver function.
In conclusion, Hedyotis diffusa offers a comprehensive, multi-faceted approach to liver health, making it a valuable addition to natural strategies aimed at protecting, regenerating, and optimizing liver function.

The Proven Benefits of Hericium Erinaceus for Preventing and Managing Liver Diseases: NAFLD, Cirrhosis, and Chronic Liver Damage
Hericium Erinaceus, commonly known as Lion’s Mane mushroom, has gained considerable scientific attention for its wide array of health benefits. Beyond its well-known effects on cognitive health, Hericium Erinaceus also holds significant promise for promoting liver health, particularly in the prevention and management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Its hepatoprotective effects, ability to mitigate liver stressors, support for liver regeneration, and enhancement of liver function make it a valuable ally in maintaining overall liver health.
Hericium Erinaceus and Liver Disease: Scientific Evidence for Prevention and Management
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is one of the most common liver disorders, characterized by excessive fat accumulation in liver cells unrelated to alcohol consumption. This condition can progress to more severe liver issues, including fibrosis, cirrhosis, and even hepatocellular carcinoma. Current research highlights the potential of Hericium Erinaceus as a natural intervention to prevent and manage these liver conditions.
Several studies have demonstrated that Hericium Erinaceus possesses bioactive compounds with anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and hepatoprotective properties. The mushroom contains polysaccharides, erinacines, and hericenones that contribute significantly to its therapeutic effects. Specifically, polysaccharides from Hericium Erinaceus have been found to reduce oxidative stress, one of the key factors in the progression of NAFLD. Oxidative stress leads to lipid peroxidation and inflammation, both of which contribute to liver damage. By scavenging free radicals and reducing lipid peroxidation, Hericium Erinaceus helps in mitigating liver injury and preventing disease progression.
Hepatoprotective Effects and Liver Stress Reduction
One of the most significant benefits of Hericium Erinaceus is its hepatoprotective effect—its ability to protect liver cells from damage. Liver stressors, such as high-fat diets, toxins, and metabolic imbalances, lead to inflammation and cellular injury. Hericium Erinaceus has demonstrated protective effects against these stressors, contributing to improved liver function and overall health.
Research indicates that the polysaccharides present in Hericium Erinaceus play a crucial role in enhancing the liver’s antioxidant defense system. Studies have shown that treatment with Hericium Erinaceus can upregulate the activity of key antioxidant enzymes, such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx). These enzymes are vital in reducing oxidative damage and maintaining cellular integrity within the liver. By boosting the liver’s antioxidant capacity, Hericium Erinaceus helps to reduce inflammation and cell damage caused by a fatty liver and other stressors.
Moreover, animal studies have provided evidence that Hericium Erinaceus may significantly reduce serum levels of liver enzymes such as alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), which are commonly elevated in cases of liver damage. Lowering these enzyme levels is indicative of reduced liver inflammation and improved hepatocyte (liver cell) health.
Mechanisms of Action: Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Pathways
Hericium Erinaceus exerts its hepatoprotective effects through multiple mechanisms, primarily involving anti-inflammatory and antioxidant pathways. Chronic inflammation is a major driver of liver disease progression, particularly in conditions like NAFLD and cirrhosis. Hericium Erinaceus contains bioactive compounds that inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6, and NF-κB. By downregulating these cytokines, Hericium Erinaceus effectively reduces liver inflammation and helps to prevent fibrosis—the scarring of liver tissue that can lead to cirrhosis.
The antioxidant effects of Hericium Erinaceus also play a significant role in liver protection. Oxidative stress is a major contributor to liver injury, and Hericium Erinaceus helps combat this by enhancing the activity of endogenous antioxidants. The polysaccharides and phenolic compounds in Hericium Erinaceus act as potent free radical scavengers, neutralizing reactive oxygen species (ROS) and thereby preventing oxidative damage to liver cells.
Benefits for Liver Regeneration and Enhancing Liver Function
In addition to protecting the liver from damage, Hericium Erinaceus also supports liver regeneration—a critical aspect of recovery from liver disease. The liver has a remarkable capacity for regeneration, and Hericium Erinaceus appears to enhance this ability. Studies have shown that extracts from Hericium Erinaceus can promote hepatocyte proliferation, thereby aiding in the repair and regeneration of damaged liver tissue. This is particularly important in the context of liver injury due to fatty liver disease or cirrhosis, where the regeneration of functional liver tissue is key to restoring overall liver function.
Hericium Erinaceus also contributes to overall liver function by improving lipid metabolism. Dysregulated lipid metabolism is a hallmark of NAFLD, leading to fat accumulation in liver cells. Research suggests that Hericium Erinaceus can help normalize lipid profiles by reducing triglyceride accumulation in the liver and improving cholesterol metabolism. This effect is mediated through the modulation of key enzymes involved in lipid synthesis and breakdown, thereby promoting a healthier liver environment.
Promoting a Healthy Liver Environment and Supporting Detoxification
The liver is the body’s primary detoxification organ, responsible for filtering toxins from the blood and metabolizing harmful substances. Hericium Erinaceus enhances the liver’s detoxification processes by supporting both phase I and phase II detoxification pathways. These pathways involve the enzymatic breakdown of toxins into less harmful substances, which are then excreted from the body.
By reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, Hericium Erinaceus creates a more favorable environment for these detoxification processes to occur efficiently. Furthermore, the mushroom’s ability to enhance glutathione production—a critical antioxidant involved in detoxification—further supports the liver’s capacity to handle toxins and reduce overall liver burden.
Scientific Evidence and Human Studies
While much of the research on Hericium Erinaceus and liver health has been conducted in animal models, emerging human studies provide promising insights. Preliminary clinical trials have shown that Hericium Erinaceus supplementation can lead to improvements in liver enzyme levels, indicating reduced liver inflammation and injury. These findings align with the results observed in preclinical studies, supporting the potential use of Hericium Erinaceus as a complementary therapy for individuals with liver conditions such as NAFLD and cirrhosis.
One study involving patients with metabolic syndrome, a condition closely linked to NAFLD, found that Hericium Erinaceus supplementation improved markers of liver function and reduced markers of oxidative stress. These results suggest that Hericium Erinaceus could be beneficial not only for individuals with existing liver conditions but also for those at risk of developing liver disease due to metabolic imbalances.
Conclusion: The Role of Hericium Erinaceus in Liver Health
Hericium Erinaceus is a promising natural remedy for promoting liver health and managing liver diseases such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Its hepatoprotective effects are mediated through a combination of anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and regenerative mechanisms. By reducing oxidative stress, mitigating inflammation, and supporting liver regeneration, Hericium Erinaceus contributes to improved liver function and a healthier liver environment.
The mushroom’s ability to enhance lipid metabolism and support the liver’s natural detoxification processes further underscores its potential as a valuable therapeutic agent for liver health. While more human studies are needed to fully validate these effects, the current body of evidence provides a strong foundation for the use of Hericium Erinaceus in the prevention and management of liver diseases.
Incorporating Hericium Erinaceus as part of a holistic approach to liver health—including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoidance of hepatotoxic substances—may offer significant benefits for individuals looking to support their liver function and prevent liver-related health issues. As research continues to unveil the full spectrum of its therapeutic properties, Hericium Erinaceus stands out as a powerful ally in the quest for optimal liver health.

Hibiscus vitifolius Root Extract: A Proven Ally in Liver Health Management
Hibiscus vitifolius root extract has emerged as a powerful natural remedy in managing liver health, particularly in conditions like Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. The hepatoprotective properties of this extract have been scientifically explored, revealing its role in reducing liver damage, supporting liver regeneration, and promoting a healthier liver environment. This comprehensive synopsis delves into the science-backed benefits of Hibiscus vitifolius root extract, emphasizing its mechanisms of action and its contribution to overall liver function and detoxification.
Understanding Hibiscus vitifolius Root Extract and Its Hepatoprotective Properties
Hibiscus vitifolius, also known as “wild hibiscus,” is a medicinal plant with roots traditionally used in herbal medicine. Studies have highlighted its promising effects in protecting the liver from damage, primarily due to its high content of bioactive compounds, such as flavonoids, tannins, and phenolic acids. These compounds possess antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and hepatoprotective properties, all of which play a critical role in liver health.
1. Prevention and Management of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is a growing global health concern, characterized by the accumulation of fat in liver cells. The bioactive components of Hibiscus vitifolius root extract contribute significantly to preventing and managing NAFLD by acting through multiple mechanisms:
Reduction of Lipid Accumulation: Studies show that flavonoids present in the root extract help modulate lipid metabolism by reducing lipogenesis (fat synthesis) and enhancing lipolysis (fat breakdown). This mechanism directly addresses hepatic steatosis, the hallmark of NAFLD.
Antioxidant Defense: Oxidative stress is a key factor in the progression of NAFLD. Hibiscus vitifolius root extract, rich in antioxidants such as quercetin and rutin, combats oxidative stress by neutralizing free radicals, thereby reducing lipid peroxidation and preventing further liver damage.
Anti-Inflammatory Action: Chronic inflammation is another contributor to the progression of NAFLD to more severe conditions like non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Hibiscus vitifolius contains anti-inflammatory compounds that inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokines, thereby alleviating inflammation in liver tissues.
2. Protection Against Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver diseases, including cirrhosis, involve long-term liver damage that can lead to fibrosis and scarring of liver tissue. Hibiscus vitifolius root extract offers protective benefits that help in managing and slowing the progression of these conditions:
Antifibrotic Properties: Fibrosis is the excessive formation of connective tissue, which disrupts liver function. Hibiscus vitifolius root extract contains bioactive compounds that inhibit hepatic stellate cell activation, which plays a pivotal role in fibrosis development. By preventing stellate cell activation, the extract helps in reducing collagen deposition and fibrosis.
Modulation of Cellular Stress: Chronic liver diseases are often associated with increased endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and mitochondrial dysfunction. Hibiscus vitifolius root extract has shown the potential to modulate cellular stress responses by stabilizing mitochondrial membranes and enhancing ATP production, thus improving the overall energy status of hepatocytes.
Reduction of Liver Enzymes: Elevated levels of liver enzymes such as alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST) are markers of liver damage. Clinical studies indicate that supplementation with Hibiscus vitifolius root extract significantly reduces these enzyme levels, reflecting its effectiveness in reducing liver cell injury.
3. Hepatoprotective Effects: Reducing Damage from Fatty Liver and Other Stressors
One of the most critical benefits of Hibiscus vitifolius root extract is its hepatoprotective effect, which reduces damage caused by a fatty liver and other liver stressors:
Scavenging of Free Radicals: The root extract’s potent antioxidant properties help in scavenging free radicals generated due to metabolic stress, alcohol consumption, or other toxins. This protective effect prevents cellular damage and supports the integrity of hepatocytes.
Stimulation of Detoxification Enzymes: Hibiscus vitifolius root extract also enhances the activity of detoxification enzymes, such as glutathione S-transferase (GST) and catalase. These enzymes play a crucial role in neutralizing harmful substances, thereby aiding in the detoxification process and reducing the burden on the liver.
Prevention of Lipid Peroxidation: Lipid peroxidation, a process in which free radicals damage cell membranes, is a significant contributor to liver injury. The phenolic compounds in Hibiscus vitifolius effectively inhibit lipid peroxidation, thereby preserving liver cell integrity and function.
Liver Regeneration and Enhancement of Liver Function
Hibiscus vitifolius root extract not only protects the liver from damage but also plays a vital role in promoting liver regeneration and enhancing overall liver function:
1. Support for Liver Regeneration
The liver has a remarkable ability to regenerate itself after injury. Hibiscus vitifolius root extract supports this regenerative capacity through several mechanisms:
Stimulation of Hepatocyte Proliferation: Studies have shown that certain phytochemicals in the extract can stimulate hepatocyte proliferation, thereby accelerating the process of liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy or injury.
Enhancement of Growth Factors: The extract has been found to upregulate the expression of growth factors such as hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), which plays a critical role in liver regeneration. By boosting these growth factors, Hibiscus vitifolius facilitates faster recovery of liver mass and function.
2. Improvement of Overall Liver Function
Enhanced Bile Production: Proper bile production is essential for digestion and the elimination of toxins. Hibiscus vitifolius root extract has been associated with improved bile secretion, which aids in digestion and supports the liver’s excretory function.
Optimization of Liver Enzyme Activity: The root extract optimizes the activity of key liver enzymes involved in various metabolic pathways, thereby ensuring efficient processing of nutrients and detoxification of harmful substances.
Reduction of Insulin Resistance: Insulin resistance is closely linked to liver diseases such as NAFLD. Hibiscus vitifolius root extract has been found to improve insulin sensitivity, thus reducing hepatic glucose production and lipid accumulation, contributing to better liver health.
Promoting a Healthier Liver Environment
Hibiscus vitifolius root extract plays a role in creating a healthier liver environment by enhancing the body’s natural detoxification processes and maintaining an optimal balance of metabolic activities.
1. Detoxification Support
Activation of Phase I and Phase II Detoxification Pathways: The detoxification of harmful substances in the liver occurs in two phases. Hibiscus vitifolius root extract has been shown to enhance both Phase I and Phase II detoxification enzymes, thereby improving the liver’s ability to neutralize and eliminate toxins.
Support for Glutathione Production: Glutathione is one of the liver’s most important antioxidants. Hibiscus vitifolius root extract supports glutathione production, which helps protect liver cells from oxidative damage and maintains redox balance within the liver.
2. Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Synergy
The synergistic effect of the anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties of Hibiscus vitifolius root extract creates an optimal environment for liver function. By reducing inflammation and oxidative stress, the extract helps maintain healthy liver tissue, preventing the progression of liver disease.
Scientific Evidence and Mechanisms of Action
The hepatoprotective effects of Hibiscus vitifolius root extract are well-documented in scientific literature. Studies using animal models of NAFLD, cirrhosis, and chemically induced liver injury have consistently demonstrated the extract’s ability to reduce markers of liver damage, enhance antioxidant enzyme activity, and promote liver regeneration.
The mechanisms of action underlying these effects include:
Inhibition of Lipid Accumulation: The flavonoids in Hibiscus vitifolius modulate key enzymes involved in lipid metabolism, thereby preventing the accumulation of fat in the liver.
Suppression of Inflammatory Pathways: The extract downregulates nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB), a key regulator of inflammation, reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines that contribute to liver damage.
Antioxidant Defense Enhancement: The high content of phenolic compounds enhances the activity of antioxidant enzymes, providing robust protection against oxidative stress, a major factor in liver injury.
Fibrosis Inhibition: By inhibiting the activation of hepatic stellate cells, Hibiscus vitifolius root extract prevents excessive collagen deposition, thereby reducing the risk of fibrosis and cirrhosis.
Conclusion: Hibiscus vitifolius Root Extract as a Natural Solution for Liver Health
Hibiscus vitifolius root extract stands out as a natural solution for supporting liver health, backed by scientific evidence. Its hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antifibrotic properties make it a valuable ally in the prevention and management of liver conditions such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. By reducing lipid accumulation, enhancing detoxification, promoting liver regeneration, and optimizing liver function, Hibiscus vitifolius root extract contributes to a healthier liver environment and supports the body’s natural detoxification processes.
Incorporating Hibiscus vitifolius root extract into a liver health regimen may offer significant benefits for individuals looking to maintain or improve their liver function, providing a natural, science-backed approach to comprehensive liver care. Always consult with a healthcare professional before beginning any new supplement regimen, especially for those with existing liver conditions or who are taking medications that may affect liver function.

Houttuynia cordata Thunb Extract: Comprehensive Benefits for Liver Health
Houttuynia cordata Thunb (H. cordata), an herbaceous perennial plant native to East Asia, has been widely researched for its therapeutic properties, especially its hepatoprotective effects. With an emerging body of evidence supporting its benefits in preventing and managing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis, H. cordata has gained significant attention as a natural intervention for liver health. This comprehensive overview will delve into the scientifically supported health benefits of H. cordata for liver health, its mechanism of action, and its role in promoting liver regeneration and enhancing overall liver function.
Houttuynia cordata Thunb Extract in Preventing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD, a growing global health concern, is characterized by the accumulation of fat in liver cells not caused by alcohol consumption. The role of H. cordata in preventing NAFLD has been studied extensively, with promising results highlighting its potential as a natural therapeutic agent. The phytochemicals present in H. cordata, including flavonoids, polysaccharides, and essential oils, contribute to its hepatoprotective properties. These compounds work synergistically to combat oxidative stress, a major factor in the onset and progression of NAFLD.
Scientific studies have shown that H. cordata extract exhibits strong antioxidant properties, reducing lipid peroxidation in the liver. By neutralizing reactive oxygen species (ROS), it helps to maintain cellular integrity and prevent the damage that leads to fat accumulation in hepatocytes. Additionally, H. cordata has demonstrated anti-inflammatory effects, reducing the inflammatory markers commonly elevated in NAFLD, such as TNF-α and IL-6. This anti-inflammatory action plays a critical role in mitigating liver inflammation and fibrosis, both of which are key contributors to NAFLD progression.
Hepatoprotective Effects Against Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver disease and cirrhosis, often resulting from prolonged liver injury, can lead to severe complications, including liver failure. H. cordata extract has been shown to possess hepatoprotective effects that can reduce liver damage caused by various stressors, including alcohol, high-fat diets, and toxic substances. The active components of H. cordata, particularly quercetin and other flavonoids, are known to protect hepatocytes from injury by enhancing the liver’s antioxidant defense system.
Several animal studies have demonstrated that H. cordata extract can significantly lower serum levels of liver enzymes, such as ALT and AST, which are indicative of liver injury. By stabilizing cell membranes and reducing oxidative damage, H. cordata helps to preserve liver function and prevent the progression of chronic liver disease to cirrhosis. Moreover, its anti-fibrotic effects have been observed in studies where H. cordata administration led to a reduction in collagen deposition, thereby inhibiting the development of liver fibrosis—a hallmark of cirrhosis.
Mechanisms of Action: Reducing Liver Stress and Damage
The hepatoprotective effects of H. cordata are primarily attributed to its ability to modulate multiple biochemical pathways involved in liver damage and regeneration. The following mechanisms of action have been identified:
Antioxidant Activity: H. cordata is rich in polyphenols and flavonoids that scavenge free radicals and reduce oxidative stress. By boosting the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx), H. cordata helps protect liver cells from oxidative injury, which is a major contributor to liver damage and fatty liver disease.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Chronic inflammation is a driving factor in the progression of liver disease. H. cordata modulates the immune response by inhibiting pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6. This reduction in inflammatory signaling helps prevent the cascade of events leading to liver fibrosis and cirrhosis.
Lipid Metabolism Regulation: Studies suggest that H. cordata can improve lipid metabolism by reducing the accumulation of triglycerides in the liver. It activates AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), a key regulator of lipid metabolism, which helps reduce lipid synthesis and promote fatty acid oxidation. This mechanism is particularly beneficial for individuals with NAFLD, as it addresses the root cause of fat accumulation in the liver.
Anti-Fibrotic Properties: H. cordata has demonstrated the ability to inhibit hepatic stellate cell activation, which is a critical step in the development of liver fibrosis. By reducing the production of extracellular matrix proteins and collagen, H. cordata helps prevent the stiffening of liver tissue that characterizes cirrhosis.
Liver Regeneration and Enhanced Detoxification
One of the most remarkable features of the liver is its ability to regenerate. H. cordata supports liver regeneration by promoting hepatocyte proliferation and reducing the factors that impede this process. The presence of polysaccharides and other bioactive compounds in H. cordata has been shown to stimulate the proliferation of healthy liver cells, thereby aiding in the recovery of liver function after injury.
Furthermore, H. cordata enhances the liver’s natural detoxification processes. The liver is responsible for metabolizing and eliminating toxins from the body, and H. cordata has been found to upregulate phase II detoxifying enzymes, such as glutathione S-transferase (GST). By enhancing the activity of these enzymes, H. cordata helps the liver effectively process and eliminate harmful substances, reducing the overall toxic burden on the body.
Overall Benefits for Liver Function
H. cordata contributes to overall liver health by creating a more favorable environment for liver function. Its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-fibrotic properties collectively help to reduce liver stress, prevent damage, and support the liver’s capacity to perform its essential functions. This includes bile production, metabolism of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates, and the detoxification of endogenous and exogenous compounds.
The benefits of H. cordata for liver health are further supported by its ability to modulate gut health. The gut-liver axis plays a significant role in liver disease, as gut-derived endotoxins can exacerbate liver inflammation and damage. H. cordata has been shown to possess antimicrobial properties that help maintain a healthy gut microbiome, thereby reducing the translocation of harmful bacteria and their products to the liver. This reduction in gut-derived endotoxins helps lower inflammation and supports overall liver health.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Houttuynia cordata’s Hepatoprotective Effects
Numerous peer-reviewed studies have investigated the hepatoprotective effects of H. cordata, providing robust evidence for its efficacy in improving liver health:
Animal Studies: In rodent models of NAFLD, H. cordata extract significantly reduced liver triglyceride content and improved liver histology. These studies highlight the extract’s ability to prevent fat accumulation and reduce inflammation in the liver, suggesting its potential as a natural treatment for NAFLD.
In Vitro Studies: Cell culture studies have demonstrated that H. cordata extract protects hepatocytes from oxidative stress-induced apoptosis. The extract’s ability to enhance the expression of antioxidant enzymes and reduce lipid peroxidation has been well-documented in these models.
Anti-Fibrotic Research: Studies focusing on liver fibrosis have shown that H. cordata can inhibit the activation of hepatic stellate cells, which are responsible for the deposition of collagen and extracellular matrix proteins in the liver. By reducing stellate cell activation, H. cordata helps to prevent the progression of liver fibrosis to cirrhosis.
Human Studies: Although human clinical trials are limited, the available evidence suggests that H. cordata supplementation can improve liver enzyme profiles and reduce markers of liver inflammation in individuals with mild liver dysfunction. These findings support the potential use of H. cordata as a complementary therapy for maintaining liver health.
Conclusion: A Natural Ally for Liver Health
Houttuynia cordata Thunb extract is a promising natural remedy for promoting liver health and preventing liver disease. Its hepatoprotective effects are supported by its potent antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-fibrotic properties, which help reduce liver stress, prevent fat accumulation, and protect against liver injury. By enhancing liver regeneration and supporting detoxification, H. cordata contributes to a healthier liver environment and overall improved liver function.
As liver disease continues to be a significant health concern globally, natural interventions like H. cordata offer a valuable option for individuals seeking to support their liver health through safe and effective means. The growing body of scientific evidence underscores the potential of H. cordata as a hepatoprotective agent, making it a worthy addition to the repertoire of natural therapies aimed at maintaining liver wellness.

Hovenia Dulcis Extract: Scientifically Proven Benefits for Liver Health
Hovenia dulcis, commonly known as the Japanese raisin tree, has long been used in traditional medicine for its therapeutic properties, particularly for liver health. Recent scientific investigations have shed light on its hepatoprotective benefits, making it a promising natural supplement for conditions such as Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. This comprehensive breakdown explores the scientifically proven effects of Hovenia dulcis extract on liver protection, regeneration, and overall function.
Preventing NAFLD, Chronic Liver Disease, and Cirrhosis
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is a prevalent liver disorder, characterized by fat accumulation in liver cells not caused by alcohol consumption. Chronic liver diseases like NAFLD can progress to more severe conditions, including fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver cancer. Research has highlighted Hovenia dulcis extract as an effective means to help prevent these conditions.
Reduction of Hepatic Lipid Accumulation: Studies have demonstrated that Hovenia dulcis extract can effectively reduce hepatic lipid accumulation, a key feature of NAFLD. The saponins and polyphenolic compounds present in the extract are known to modulate lipid metabolism by enhancing lipid breakdown and reducing de novo lipogenesis. Animal models have shown that treatment with Hovenia dulcis reduces liver fat levels, thus mitigating the risk of liver fibrosis.
Anti-inflammatory and Antioxidant Properties: Inflammation and oxidative stress are significant contributors to the progression of liver diseases such as NAFLD and cirrhosis. Hovenia dulcis extract contains high levels of dihydromyricetin, a flavonoid with potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. By inhibiting the production of inflammatory cytokines and reducing oxidative stress, the extract helps in preventing liver cell damage, which is critical in halting the progression of chronic liver disease and cirrhosis.
Modulation of Insulin Sensitivity: Insulin resistance is often linked to NAFLD development. Research indicates that Hovenia dulcis may improve insulin sensitivity, thus playing a vital role in managing and reducing the impact of NAFLD. Improved insulin sensitivity facilitates better glucose utilization and decreases fat accumulation in the liver, thus reducing the risk of disease progression.
Hepatoprotective Effects Against Liver Stressors
The liver is constantly exposed to various stressors, including dietary fats, toxins, and environmental pollutants. Hovenia dulcis extract has shown promising hepatoprotective properties that mitigate damage caused by these stressors, ensuring better liver health.
Protection Against Alcohol-Induced Liver Injury: Traditionally used as a remedy for alcohol hangovers, Hovenia dulcis has been scientifically validated for its protective effects against alcohol-induced liver damage. Studies have shown that dihydromyricetin helps accelerate alcohol metabolism by enhancing the activity of alcohol dehydrogenase and aldehyde dehydrogenase, enzymes crucial for breaking down alcohol. This reduces the toxic effects of acetaldehyde, a harmful byproduct of alcohol metabolism that can cause liver damage.
Reduction of Oxidative Damage: Oxidative damage caused by reactive oxygen species (ROS) is a major contributor to liver injury. The antioxidant compounds in Hovenia dulcis, particularly flavonoids and phenolic acids, scavenge ROS and prevent oxidative damage to hepatocytes. This effect is particularly beneficial for individuals with fatty liver, where oxidative stress is a key driver of liver injury.
Enhancement of Detoxification Pathways: The liver plays a central role in detoxification, and Hovenia dulcis extract has been found to enhance this function. It stimulates the production of glutathione, a major antioxidant that aids in the detoxification of harmful substances. By boosting glutathione levels, Hovenia dulcis ensures more efficient detoxification and protection against toxins that can lead to liver damage.
Promoting Liver Regeneration and Overall Function
One of the most remarkable aspects of the liver is its ability to regenerate. Hovenia dulcis extract supports this regenerative capacity, thereby improving overall liver function and promoting a healthier liver environment.
Stimulation of Hepatocyte Proliferation: Hepatocyte proliferation is essential for liver regeneration, especially after damage. Research suggests that Hovenia dulcis extract may stimulate hepatocyte growth and regeneration, aiding the liver in replacing damaged tissue. This effect is attributed to the presence of bioactive compounds that promote cellular signaling pathways involved in liver tissue repair.
Reduction of Fibrotic Scarring: Chronic liver damage often leads to fibrosis, which impairs liver function and hinders its regenerative ability. Hovenia dulcis has been shown to possess anti-fibrotic properties, primarily through the inhibition of hepatic stellate cell activation, which is responsible for collagen deposition and fibrosis. By reducing fibrotic scarring, the extract helps maintain a functional liver architecture, enabling better regeneration.
Improvement in Liver Enzyme Levels: Elevated liver enzymes, such as ALT and AST, are indicators of liver damage. Clinical studies have reported that supplementation with Hovenia dulcis extract can lower these enzyme levels, suggesting an improvement in liver function and reduced hepatocellular injury. This normalization of enzyme levels reflects the extract’s capacity to enhance liver health and prevent ongoing damage.
Enhancing Natural Detoxification Processes and Overall Liver Health
The liver’s primary function is to detoxify the body by breaking down harmful substances and facilitating their elimination. Hovenia dulcis extract contributes to optimizing this detoxification process, promoting overall liver health and vitality.
Activation of Phase I and Phase II Detoxification Enzymes: Detoxification in the liver occurs in two phases. Phase I involves the oxidation of toxins, while Phase II conjugates these substances for excretion. Hovenia dulcis extract has been shown to enhance the activity of both Phase I and Phase II enzymes, improving the liver’s ability to detoxify harmful compounds effectively. This dual-phase activation ensures a more comprehensive detoxification process.
Reduction of Lipid Peroxidation: Lipid peroxidation is a damaging process in which free radicals attack lipids in cell membranes, leading to cell dysfunction and death. The antioxidant properties of Hovenia dulcis extract help to significantly reduce lipid peroxidation in the liver, thereby maintaining cellular integrity and promoting a healthier liver environment.
Promotion of Bile Production: Bile production is an essential aspect of liver function, aiding in the digestion and absorption of fats as well as the elimination of waste products. Hovenia dulcis has been found to promote bile secretion, which not only supports digestive health but also enhances the liver’s ability to excrete toxins. Improved bile flow reduces the burden on the liver and contributes to overall detoxification.
Mechanisms of Action Behind Hovenia Dulcis’ Benefits
The health benefits of Hovenia dulcis extract are driven by several key mechanisms of action that involve various biological pathways:
Antioxidant Pathways: The extract activates endogenous antioxidant pathways, such as the Nrf2 pathway, which regulates the expression of antioxidant proteins that protect against oxidative damage. This activation leads to increased levels of enzymes like superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase, which neutralize harmful free radicals.
Inhibition of Inflammatory Pathways: Chronic inflammation is a significant factor in liver disease progression. Hovenia dulcis extract inhibits the NF-κB pathway, a major regulator of inflammation. By blocking this pathway, the extract reduces the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α and IL-6, thereby mitigating liver inflammation and damage.
Modulation of Lipid Metabolism: Hovenia dulcis extract impacts lipid metabolism by regulating key enzymes involved in fat synthesis and breakdown. It activates AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), an enzyme that promotes fatty acid oxidation and inhibits lipid synthesis, which is crucial for reducing hepatic fat accumulation.
Enhancement of Mitochondrial Function: Mitochondrial dysfunction is a common issue in liver diseases, contributing to impaired energy production and increased oxidative stress. Hovenia dulcis has been found to enhance mitochondrial biogenesis and function, improving the liver’s ability to generate energy and cope with metabolic stressors.
Conclusion: Hovenia Dulcis Extract for Optimal Liver Health
Hovenia dulcis extract offers a range of scientifically proven benefits for liver health, making it a valuable natural supplement for preventing and managing liver-related conditions such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Its hepatoprotective properties help mitigate damage caused by fatty liver and other stressors, while its regenerative capabilities support the liver’s natural ability to heal and restore itself. Furthermore, by enhancing detoxification processes and reducing oxidative stress, Hovenia dulcis contributes to a healthier liver environment and improved overall function.
The mechanisms of action underlying these benefits, including antioxidant activation, anti-inflammatory effects, lipid metabolism modulation, and mitochondrial enhancement, highlight the comprehensive role of Hovenia dulcis in liver health. As research continues, the potential of Hovenia dulcis extract as a key supplement for liver health becomes increasingly evident, offering hope for those seeking natural solutions to support and maintain optimal liver function.
Hypophyllanthin: A Comprehensive Scientific Overview of its Benefits for Liver Health
Introduction to Hypophyllanthin and Liver Health
Hypophyllanthin, a prominent bioactive lignan found primarily in the plant Phyllanthus amarus, has gained significant recognition for its liver-protective properties. This compound has shown considerable potential in preventing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis, while also aiding liver regeneration and promoting overall liver function. This comprehensive synopsis explores the proven benefits of hypophyllanthin, delving into its mechanisms of action and the scientific evidence supporting its effectiveness in maintaining liver health.
Preventing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is a major health concern globally, characterized by excessive fat accumulation in liver cells. Hypophyllanthin has been demonstrated to exert hepatoprotective effects, reducing the risk of NAFLD development. Several studies have provided evidence that hypophyllanthin mitigates the accumulation of fat in the liver by regulating lipid metabolism and enhancing the liver’s capacity to break down fatty acids. This effect is largely attributed to its ability to modulate key enzymes involved in lipid synthesis and oxidation.
Hypophyllanthin works through multiple pathways to exert its protective effects on the liver. By reducing the expression of sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c), it effectively limits de novo lipogenesis, thereby decreasing triglyceride accumulation within hepatocytes. Moreover, hypophyllanthin has been shown to enhance the activity of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPAR-α), which plays a pivotal role in stimulating the oxidation of fatty acids in the liver. This dual action helps prevent the onset and progression of NAFLD by maintaining a balanced lipid profile.
Managing Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver diseases, including cirrhosis, often result from prolonged liver inflammation and fibrosis. Hypophyllanthin exhibits anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic properties that make it a promising candidate for managing such conditions. It acts by modulating pro-inflammatory cytokines and reducing oxidative stress, two critical factors that contribute to liver damage and fibrosis.
Scientific studies have demonstrated that hypophyllanthin reduces the levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6), both of which are key mediators of liver inflammation. By inhibiting these cytokines, hypophyllanthin helps to minimize liver inflammation, thereby reducing the risk of progression to cirrhosis. Furthermore, hypophyllanthin’s antioxidant properties help neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS), which are known to cause oxidative damage to liver cells and contribute to the development of chronic liver disease.
Hepatoprotective Effects: Reducing Liver Damage
Hypophyllanthin has been widely studied for its hepatoprotective effects, particularly its ability to reduce liver damage caused by a fatty liver and other stressors. This lignan exerts its hepatoprotective activity by enhancing the liver’s natural antioxidant defense system, reducing oxidative stress, and promoting the integrity of hepatocytes.
One of the primary mechanisms through which hypophyllanthin protects the liver is by increasing the levels of endogenous antioxidants, such as glutathione (GSH), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and catalase. These antioxidants play a crucial role in scavenging free radicals and preventing oxidative damage to liver cells. Additionally, hypophyllanthin has been shown to stabilize the cellular membrane of hepatocytes, reducing leakage of liver enzymes like alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) into the bloodstream—an indication of reduced liver cell damage.
In experimental models, hypophyllanthin has been found to reduce liver injury induced by toxic agents such as carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) and acetaminophen. The compound effectively diminishes lipid peroxidation and prevents cellular apoptosis, thereby preserving liver function. These findings underline the role of hypophyllanthin as a potent hepatoprotective agent capable of reducing damage from various liver stressors.
Promoting Liver Regeneration and Overall Liver Function
Liver regeneration is a critical process that ensures the recovery of liver mass and function following injury. Hypophyllanthin has been found to support this regenerative process, making it beneficial for individuals with compromised liver function. By promoting the proliferation of hepatocytes and enhancing the expression of growth factors, hypophyllanthin helps accelerate liver regeneration, ensuring faster recovery from liver injuries.
Research indicates that hypophyllanthin enhances the expression of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β), both of which are crucial for liver regeneration. HGF plays a vital role in stimulating hepatocyte proliferation, while TGF-β helps regulate the balance between liver cell proliferation and apoptosis. By modulating these growth factors, hypophyllanthin creates an optimal environment for liver regeneration, contributing to improved liver function and overall health.
In addition to its regenerative effects, hypophyllanthin has been shown to improve bile production and flow, which is essential for the efficient elimination of toxins and waste products from the body. By enhancing bile secretion, hypophyllanthin supports the liver’s natural detoxification processes, promoting a healthier liver environment and reducing the burden of harmful substances on liver cells.
Enhancing the Body’s Natural Detoxification Processes
The liver plays a central role in detoxifying the body by metabolizing and eliminating toxins, drugs, and other harmful substances. Hypophyllanthin has been found to enhance the liver’s detoxification capacity by upregulating phase I and phase II detoxification enzymes, which are responsible for converting toxic substances into more water-soluble forms that can be easily excreted.
Phase I detoxification involves the activation of cytochrome P450 enzymes, which help oxidize and prepare toxins for further processing. Hypophyllanthin has been shown to increase the activity of these enzymes, thereby improving the liver’s ability to handle a wide range of toxic substances. In phase II detoxification, conjugation reactions occur, allowing the liver to neutralize and eliminate toxins more effectively. Hypophyllanthin enhances the activity of phase II enzymes such as glutathione S-transferase (GST) and UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT), further supporting the detoxification process.
Mechanisms of Action: Scientific Evidence
The beneficial effects of hypophyllanthin on liver health are supported by a growing body of scientific evidence. The mechanisms of action of hypophyllanthin are multifaceted, involving antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antifibrotic, and hepatoregenerative properties. Below is a summary of the key mechanisms through which hypophyllanthin contributes to liver health:
Antioxidant Activity: Hypophyllanthin increases the levels of endogenous antioxidants such as GSH, SOD, and catalase, which help neutralize ROS and prevent oxidative damage to liver cells.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: By inhibiting pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α and IL-6, hypophyllanthin reduces liver inflammation, thereby minimizing the risk of chronic liver disease progression.
Antifibrotic Properties: Hypophyllanthin prevents liver fibrosis by reducing collagen deposition and inhibiting the activation of hepatic stellate cells, which are key contributors to the development of fibrosis.
Hepatoprotective Effects: Hypophyllanthin stabilizes hepatocyte membranes, reduces leakage of liver enzymes, and protects against liver injury caused by toxins and oxidative stress.
Liver Regeneration: By enhancing the expression of growth factors such as HGF and TGF-β, hypophyllanthin promotes liver regeneration and helps restore liver function following injury.
Detoxification Enhancement: Hypophyllanthin upregulates phase I and phase II detoxification enzymes, improving the liver’s ability to metabolize and eliminate toxins effectively.
Conclusion: Hypophyllanthin as a Powerful Ally for Liver Health
In conclusion, hypophyllanthin is a powerful natural compound with extensive liver-protective properties. Its ability to prevent NAFLD, manage chronic liver disease and cirrhosis, reduce liver damage, promote liver regeneration, and enhance detoxification processes makes it an invaluable ally for maintaining optimal liver health. The scientific evidence supporting these benefits highlights the multifaceted nature of hypophyllanthin, which works through antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antifibrotic, hepatoprotective, and detoxification-enhancing mechanisms.
For individuals looking to improve liver health and reduce the risk of liver-related conditions, hypophyllanthin offers a promising, evidence-based approach. By maintaining a balanced lipid profile, reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, supporting liver regeneration, and enhancing detoxification, hypophyllanthin contributes to a healthier liver environment and overall well-being. Future research may further expand our understanding of this remarkable compound, but the current evidence already establishes hypophyllanthin as a significant player in the field of liver health.

Hepatoprotective Effects of Imperata cylindrica Root Extract: A Comprehensive Scientific Overview
Introduction
Imperata cylindrica Beauv.var. major (Nees) C.E.Hubb., commonly known as cogon grass, is traditionally used in herbal medicine across Asia. The root extract of Imperata cylindrica is increasingly recognized for its potential hepatoprotective effects, providing promising benefits for liver health. Specifically, it has been studied for its impact on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, cirrhosis, and overall liver function. This comprehensive scientific synopsis highlights the extract’s effects on liver health, supported by peer-reviewed scientific evidence, and discusses its mechanisms of action in promoting liver regeneration, reducing liver stressors, and improving overall liver function.
Hepatoprotective Effects and Mechanisms of Action
The hepatoprotective effects of Imperata cylindrica root extract are primarily attributed to its rich phytochemical profile, which includes bioactive compounds such as flavonoids, saponins, alkaloids, and terpenoids. These compounds exhibit a range of biological activities, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-fibrotic effects, all of which contribute to liver health.
Antioxidant Properties and Oxidative Stress Reduction
Oxidative stress is a key factor in the progression of liver diseases, including NAFLD and cirrhosis. Imperata cylindrica root extract has been shown to possess potent antioxidant properties, which help neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reduce oxidative stress in liver cells. The flavonoids present in the extract are particularly effective in scavenging free radicals, thereby protecting hepatocytes from oxidative damage.
In a study published in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology, researchers demonstrated that Imperata cylindrica root extract significantly reduced markers of oxidative stress in animal models with induced liver injury. This antioxidant activity is crucial in preventing lipid peroxidation and the subsequent cellular damage that contributes to the progression of fatty liver and chronic liver diseases.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Chronic inflammation is a major driver of liver damage, fibrosis, and cirrhosis. Imperata cylindrica root extract has been found to exert anti-inflammatory effects by modulating key inflammatory pathways. The extract inhibits the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6, which are known to exacerbate liver damage.
Studies indicate that the saponins and alkaloids in Imperata cylindrica root extract can inhibit the activation of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB), a transcription factor that plays a central role in the inflammatory response. By reducing NF-κB activation, the extract helps mitigate inflammation in the liver, thereby reducing the risk of fibrosis and cirrhosis.
Anti-Fibrotic Activity
Fibrosis, characterized by the excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins, is a hallmark of chronic liver disease and cirrhosis. Imperata cylindrica root extract has demonstrated anti-fibrotic effects, which are essential for preventing the progression of liver fibrosis to cirrhosis.
The anti-fibrotic activity of Imperata cylindrica is thought to be mediated through its ability to inhibit hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation. HSCs are the primary cells responsible for ECM production in the liver, and their activation is a key step in the development of fibrosis. Research has shown that the terpenoids in Imperata cylindrica root extract can suppress HSC activation, thereby reducing collagen deposition and fibrosis in the liver.
Benefits for Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD is a prevalent liver condition characterized by excessive fat accumulation in liver cells. Imperata cylindrica root extract has shown potential in preventing and managing NAFLD through multiple mechanisms:
Reduction of Hepatic Lipid Accumulation
The root extract helps reduce hepatic lipid accumulation by modulating lipid metabolism pathways. Specifically, it has been found to upregulate the expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPAR-α), a key regulator of fatty acid oxidation. By enhancing the oxidation of fatty acids, Imperata cylindrica extract reduces lipid accumulation in the liver, thereby preventing the development of NAFLD.
Improvement in Insulin Sensitivity
Insulin resistance is a significant risk factor for NAFLD. Imperata cylindrica root extract has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity, which in turn helps regulate lipid metabolism and reduce fat deposition in the liver. The extract’s ability to enhance insulin signaling contributes to its effectiveness in managing NAFLD and preventing its progression to more severe forms of liver disease.
Protection Against Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver disease and cirrhosis are often the result of prolonged liver damage due to factors such as alcohol consumption, viral infections, or metabolic disorders. Imperata cylindrica root extract offers protection against chronic liver disease and cirrhosis through its combined antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-fibrotic effects.
Prevention of Hepatocyte Apoptosis
Hepatocyte apoptosis, or programmed cell death, is a common feature of chronic liver disease. Imperata cylindrica root extract has been found to inhibit hepatocyte apoptosis by modulating the expression of apoptosis-related proteins, such as Bcl-2 and Bax. By promoting cell survival, the extract helps maintain liver function and prevents the progression of chronic liver disease.
Reduction of Fibrotic Progression
As previously mentioned, the anti-fibrotic properties of Imperata cylindrica root extract play a crucial role in preventing the progression of chronic liver disease to cirrhosis. By inhibiting HSC activation and reducing ECM deposition, the extract helps preserve liver architecture and function, thereby reducing the risk of cirrhosis.
Liver Regeneration and Enhanced Liver Function
One of the most remarkable aspects of the liver is its ability to regenerate after injury. Imperata cylindrica root extract has been found to support liver regeneration by promoting hepatocyte proliferation and enhancing the liver’s natural repair mechanisms.
Stimulation of Hepatocyte Proliferation
The root extract contains bioactive compounds that stimulate hepatocyte proliferation, which is essential for liver regeneration. Research suggests that the flavonoids and terpenoids in Imperata cylindrica root extract can activate growth factors such as hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), which plays a key role in liver regeneration. By promoting the proliferation of healthy hepatocytes, the extract aids in the recovery of liver function after injury.
Promotion of a Healthy Liver Environment
Imperata cylindrica root extract also helps create a healthier liver environment by reducing oxidative stress, inflammation, and fibrosis. This supportive environment is crucial for effective liver regeneration and overall liver function. By minimizing the factors that contribute to liver damage, the extract allows the liver to focus on repair and regeneration.
Enhancement of the Body’s Natural Detoxification Processes
The liver is the body’s primary detoxification organ, responsible for metabolizing toxins and facilitating their elimination. Imperata cylindrica root extract enhances the liver’s detoxification capacity through several mechanisms:
Induction of Phase I and Phase II Detoxification Enzymes
The root extract has been found to induce the activity of Phase I and Phase II detoxification enzymes, which are involved in the metabolism and excretion of toxins. Specifically, the flavonoids in Imperata cylindrica extract can upregulate the expression of cytochrome P450 enzymes (Phase I) and glutathione S-transferase (Phase II), thereby enhancing the liver’s ability to detoxify harmful substances.
Protection Against Toxic Liver Injury
Imperata cylindrica root extract has also been shown to protect against toxic liver injury caused by substances such as alcohol, drugs, and environmental toxins. The antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of the extract help mitigate the damage caused by these toxins, thereby supporting the liver’s detoxification processes and promoting overall liver health.
Conclusion
Imperata cylindrica Beauv.var. major root extract holds significant promise as a natural hepatoprotective agent, with a range of benefits for liver health. Its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-fibrotic properties contribute to the prevention and management of liver conditions such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Additionally, the extract supports liver regeneration and enhances the body’s natural detoxification processes, promoting a healthier liver environment.
The scientific evidence supporting the hepatoprotective effects of Imperata cylindrica root extract underscores its potential as a valuable supplement for liver health. By reducing oxidative stress, inflammation, and fibrosis, while also promoting liver regeneration and detoxification, Imperata cylindrica root extract offers a comprehensive approach to maintaining and improving liver function. However, further clinical studies are needed to fully establish its efficacy and safety in human populations.

Isatis indigotica Root Extract: Hepatoprotective Benefits, Prevention of Liver Disease, and Liver Regeneration
Isatis indigotica, also known as Ban-Lan-Gen in traditional Chinese medicine, has long been utilized for its array of medicinal properties. Among its most notable benefits are its hepatoprotective effects—specifically in preventing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. This comprehensive scientific synopsis delves into the benefits of Isatis indigotica root extract in liver health, focusing on its ability to protect the liver, mitigate fatty liver damage, support liver regeneration, and enhance overall liver function.
Preventing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD is a prevalent liver condition characterized by the accumulation of fat within liver cells, leading to inflammation and fibrosis. Isatis indigotica root extract has been studied for its potential in preventing and managing NAFLD through its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Scientific studies have shown that its bioactive compounds, such as indigo and indirubin, play key roles in reducing lipid accumulation and oxidative stress—two major contributors to the progression of NAFLD.
The mechanisms through which Isatis indigotica aids in preventing NAFLD include the modulation of lipid metabolism and anti-inflammatory pathways. Specifically, it has been found to downregulate the expression of sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c), a crucial regulator of lipid biosynthesis. By reducing SREBP-1c activity, Isatis indigotica effectively lowers triglyceride synthesis, thereby decreasing fat buildup in the liver.
Additionally, its antioxidative properties mitigate the harmful effects of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which are often elevated in NAFLD patients. ROS-induced oxidative stress is a key driver of liver inflammation and fibrosis. The polyphenolic compounds in Isatis indigotica scavenge free radicals, reducing oxidative damage and preventing the progression of NAFLD to more severe liver conditions.
Hepatoprotective Effects Against Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver disease and cirrhosis are serious conditions that result from sustained liver injury, often linked to inflammation, fibrosis, and cellular damage. Isatis indigotica root extract exhibits strong hepatoprotective effects that can help mitigate liver damage caused by various stressors. These effects are attributed to the extract’s anti-inflammatory, antiviral, and antioxidant properties.
Indirubin, a major active compound in Isatis indigotica, has been shown to inhibit inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6), both of which play key roles in chronic liver inflammation. By reducing the activity of these cytokines, Isatis indigotica helps prevent the progression of chronic liver inflammation into fibrosis and cirrhosis.
Moreover, Isatis indigotica has demonstrated antiviral properties, particularly against hepatitis viruses, which are significant contributors to chronic liver disease and cirrhosis. Studies have suggested that the antiviral effects of Isatis indigotica root extract can help reduce viral replication and mitigate liver damage caused by hepatitis B and C infections. This contributes to the overall hepatoprotective profile of the extract, making it beneficial for individuals with chronic viral hepatitis.
Reducing Damage from Fatty Liver and Other Liver Stressors
Fatty liver, whether caused by alcohol consumption or metabolic factors, places immense stress on the liver, potentially leading to inflammation, fibrosis, and impaired liver function. Isatis indigotica root extract has been shown to effectively reduce damage caused by fatty liver by enhancing the liver’s natural defense mechanisms and reducing lipid peroxidation.
One of the primary mechanisms of action is the upregulation of antioxidant enzymes, such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx), which help neutralize oxidative stress within the liver. By boosting the activity of these enzymes, Isatis indigotica mitigates lipid peroxidation—a damaging process that occurs when excess fat in the liver undergoes oxidative degradation.
Furthermore, the extract has demonstrated the ability to modulate the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) pathway, a key regulator of cellular antioxidant responses. Activation of the Nrf2 pathway leads to increased expression of various detoxifying and antioxidant enzymes, thereby reducing the oxidative burden on the liver and protecting it from further damage.
Supporting Liver Regeneration and Enhancing Liver Function
The liver possesses a remarkable ability to regenerate following injury, and Isatis indigotica root extract has been shown to support this regenerative process. Studies have indicated that the extract promotes hepatocyte proliferation—a critical aspect of liver regeneration—by modulating growth factors such as hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β). These growth factors play a crucial role in the repair and regeneration of liver tissue following injury.
Isatis indigotica also contributes to the maintenance of overall liver function by enhancing bile production and promoting the detoxification processes. Bile plays an essential role in the digestion and absorption of dietary fats, and its production is vital for maintaining a healthy liver environment. The cholagogue effect of Isatis indigotica—which stimulates bile flow—helps reduce liver congestion and facilitates the removal of fat and toxins from the liver.
The detoxification process is further supported by the induction of phase II detoxification enzymes, such as glutathione S-transferases (GSTs). These enzymes play a key role in conjugating and neutralizing harmful substances, making them more water-soluble and easier to excrete. By enhancing the liver’s detoxification capacity, Isatis indigotica helps maintain optimal liver health and function.
Promoting a Healthier Liver Environment
A healthy liver environment is essential for overall metabolic health, as the liver is responsible for numerous critical functions, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and the regulation of blood glucose levels. Isatis indigotica root extract promotes a healthier liver environment by reducing inflammation, oxidative stress, and lipid accumulation—all of which are key contributors to liver dysfunction.
Research has highlighted the ability of Isatis indigotica to regulate the expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARα), a nuclear receptor involved in lipid metabolism. By activating PPARα, Isatis indigotica enhances fatty acid oxidation, thereby reducing the accumulation of triglycerides in the liver and preventing the development of steatosis (fatty liver).
Furthermore, the anti-inflammatory properties of Isatis indigotica help create a more favorable environment for liver cells to function effectively. Chronic inflammation is a major driver of liver fibrosis, which can eventually lead to cirrhosis if left unchecked. By modulating inflammatory pathways and reducing the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, Isatis indigotica helps prevent the progression of fibrosis and maintains a healthier liver environment.
Enhancing the Body’s Natural Detoxification Processes
The liver is the body’s primary detoxification organ, and maintaining its optimal function is crucial for overall health and well-being. Isatis indigotica root extract enhances the liver’s natural detoxification processes through multiple mechanisms, including the induction of antioxidant enzymes, activation of detoxifying pathways, and promotion of bile flow.
The extract’s ability to induce phase I and phase II detoxification enzymes is particularly important in neutralizing and eliminating a wide range of toxins, including environmental pollutants, drugs, and metabolic byproducts. Phase I enzymes, such as cytochrome P450s, help convert lipophilic toxins into more reactive intermediates, which are then further detoxified by phase II enzymes like GSTs and glucuronosyltransferases. By enhancing the activity of these enzymes, Isatis indigotica supports the efficient removal of harmful substances from the body.
Moreover, Isatis indigotica has been found to protect the liver from damage caused by xenobiotics—foreign chemical substances that can be toxic to the liver. The extract’s hepatoprotective properties help mitigate the impact of these substances, reducing the risk of liver injury and supporting the body’s overall detoxification capacity.
Conclusion: Isatis indigotica for Liver Health
Isatis indigotica root extract offers a wide range of benefits for liver health, backed by scientific evidence and traditional use. Its hepatoprotective effects, ability to prevent NAFLD, support liver regeneration, and enhance detoxification processes make it a valuable natural remedy for promoting a healthier liver environment. Through its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antiviral, and lipid-regulating properties, Isatis indigotica provides comprehensive support for maintaining optimal liver function and preventing the progression of liver disease.
As the prevalence of liver-related conditions continues to rise, incorporating natural compounds like Isatis indigotica into liver health management strategies may provide significant benefits. However, it is important to consult healthcare professionals before using any herbal supplements, particularly for individuals with existing liver conditions or those taking medications, to ensure safety and efficacy.

Isoquercitrin: A Powerful Ally for Liver Health and Regeneration
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis are increasingly prevalent health concerns that necessitate proactive and evidence-based solutions. Among the compounds receiving significant attention for their hepatoprotective effects is isoquercitrin, a naturally occurring flavonoid glycoside found in a variety of fruits, vegetables, and medicinal herbs. Emerging research has highlighted its potential benefits in preventing liver diseases, promoting liver regeneration, and enhancing overall liver health. This article delves into the scientifically proven effects of isoquercitrin on liver function, emphasizing its mechanisms of action and contributions to liver protection and healing.
Isoquercitrin’s Role in Preventing Liver Disease
Isoquercitrin has demonstrated promising benefits in the prevention and management of liver diseases, including NAFLD, chronic liver conditions, and cirrhosis. Its effectiveness is largely attributed to its strong antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-fibrotic properties. Scientific studies have confirmed that isoquercitrin exerts these effects by targeting multiple pathways implicated in liver health.
1. Antioxidant Properties:
Isoquercitrin has been recognized for its powerful antioxidant effects, which play a crucial role in protecting the liver from oxidative stress—a primary factor contributing to NAFLD and other chronic liver diseases. Oxidative stress results from an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants, leading to liver cell damage. Isoquercitrin neutralizes these harmful free radicals, reducing lipid peroxidation and minimizing liver damage. Several studies have confirmed that supplementation with isoquercitrin significantly lowers markers of oxidative stress, thereby contributing to the prevention of NAFLD.
2. Anti-Inflammatory Effects:
Chronic inflammation is another major factor in the development of liver diseases such as NAFLD and cirrhosis. Isoquercitrin modulates inflammatory responses by inhibiting the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β. By suppressing these inflammatory mediators, isoquercitrin helps in reducing inflammation-induced liver injury. Research has shown that isoquercitrin can significantly reduce hepatic inflammation, making it a potent candidate for the prevention and management of liver disease.
3. Anti-Fibrotic Mechanism:
Fibrosis is the excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix proteins, which can progress to cirrhosis if left untreated. Isoquercitrin has demonstrated anti-fibrotic effects by inhibiting the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), which are primarily responsible for liver fibrosis. By modulating HSC activity and reducing collagen deposition, isoquercitrin helps prevent the progression of fibrosis to cirrhosis, thereby offering a protective effect against advanced liver disease.
Hepatoprotective Effects of Isoquercitrin
The hepatoprotective properties of isoquercitrin are well-supported by preclinical studies that emphasize its ability to mitigate damage caused by fatty liver and other liver stressors. Its multifaceted mechanisms of action make it an effective agent for reducing hepatotoxicity and preserving liver integrity.
1. Protection Against Fatty Liver Damage:
NAFLD is characterized by excessive fat accumulation in the liver, which can lead to inflammation and fibrosis. Isoquercitrin has been found to reduce lipid accumulation in liver cells by regulating key enzymes involved in lipid metabolism, such as acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) and fatty acid synthase (FAS). Moreover, isoquercitrin enhances the expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARα), a nuclear receptor that promotes fatty acid oxidation, thereby reducing hepatic lipid buildup and protecting against fatty liver damage.
2. Alleviation of Liver Stress:
Liver stress can arise from a variety of factors, including alcohol consumption, poor diet, and environmental toxins. Isoquercitrin provides significant hepatoprotection by enhancing the activity of phase II detoxification enzymes, such as glutathione S-transferase (GST), which are crucial for the elimination of toxic compounds. This action helps to mitigate liver stress and reduce the risk of further liver damage.
3. Modulation of Apoptosis:
Liver damage is often accompanied by apoptosis, or programmed cell death, which contributes to the progression of liver diseases. Isoquercitrin has been shown to exert anti-apoptotic effects by modulating the expression of pro-apoptotic and anti-apoptotic proteins, such as BAX and Bcl-2, respectively. By preventing excessive apoptosis of liver cells, isoquercitrin helps maintain liver function and integrity, thus contributing to overall hepatoprotection.
Isoquercitrin and Liver Regeneration
Liver regeneration is a vital process that allows the liver to recover from damage and maintain its essential functions. Isoquercitrin has been found to support this regenerative capacity, promoting a healthier liver environment and enhancing the body’s natural detoxification processes.
1. Stimulation of Hepatocyte Proliferation:
Isoquercitrin plays a role in liver regeneration by stimulating hepatocyte proliferation. Hepatocytes are the primary functional cells of the liver, responsible for detoxification, protein synthesis, and metabolic regulation. Research suggests that isoquercitrin promotes hepatocyte proliferation by activating signaling pathways such as the Wnt/β-catenin pathway, which is crucial for liver regeneration. By enhancing hepatocyte proliferation, isoquercitrin supports the liver’s ability to repair itself following injury.
2. Improvement of Mitochondrial Function:
Mitochondria are critical for cellular energy production and play a key role in liver regeneration. Isoquercitrin has been shown to improve mitochondrial function by enhancing mitochondrial biogenesis and reducing mitochondrial oxidative stress. This improvement in mitochondrial health contributes to the overall regenerative capacity of the liver, ensuring that hepatocytes have the energy required for effective regeneration.
3. Enhancement of Angiogenesis:
Liver regeneration also involves the formation of new blood vessels, a process known as angiogenesis. Isoquercitrin has been found to promote angiogenesis by increasing the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), a key regulator of blood vessel formation. Enhanced angiogenesis ensures adequate blood supply to regenerating liver tissue, thereby supporting efficient liver repair and function.
Overall Benefits for Liver Function and Detoxification
Isoquercitrin not only helps in preventing liver diseases and promoting regeneration but also enhances overall liver function and detoxification. Its holistic effects on liver health make it a valuable compound for maintaining a healthy liver environment.
1. Enhancement of Detoxification Pathways:
The liver is the body’s primary detoxification organ, responsible for metabolizing and eliminating harmful substances. Isoquercitrin enhances the liver’s detoxification capacity by upregulating the activity of detoxification enzymes involved in both phase I and phase II detoxification processes. This includes cytochrome P450 enzymes, which help in the oxidation of toxins, and conjugation enzymes like GST, which facilitate the excretion of these compounds. By boosting detoxification pathways, isoquercitrin helps the liver efficiently remove toxins, contributing to improved liver health.
2. Regulation of Lipid and Glucose Metabolism:
The liver plays a central role in lipid and glucose metabolism, and disruptions in these processes are often linked to liver diseases. Isoquercitrin has been shown to improve lipid metabolism by reducing the synthesis of triglycerides and promoting fatty acid oxidation. Additionally, it helps regulate glucose homeostasis by enhancing insulin sensitivity and modulating glucose uptake. These effects contribute to improved metabolic function, which is essential for maintaining a healthy liver environment.
3. Reduction of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress:
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is involved in protein folding and lipid metabolism, and ER stress is a contributing factor to liver diseases. Isoquercitrin has been found to alleviate ER stress by modulating the unfolded protein response (UPR) and reducing the accumulation of misfolded proteins in liver cells. By mitigating ER stress, isoquercitrin helps maintain cellular homeostasis and prevents liver damage associated with prolonged ER dysfunction.
Conclusion
Isoquercitrin is a potent flavonoid with substantial evidence supporting its benefits for liver health. Its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-fibrotic properties make it an effective agent for preventing liver diseases such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Additionally, its hepatoprotective effects help reduce liver damage caused by fatty liver and other stressors, while its ability to promote liver regeneration enhances the liver’s natural healing capacity.
Furthermore, isoquercitrin supports overall liver function by enhancing detoxification processes, regulating lipid and glucose metabolism, and reducing ER stress. These multifaceted benefits position isoquercitrin as a promising natural compound for maintaining liver health, promoting liver regeneration, and enhancing the body’s detoxification capabilities.
While the current body of research highlights the significant potential of isoquercitrin, further clinical studies are needed to fully establish its efficacy and therapeutic applications in human populations. Nevertheless, the available evidence underscores its value as a natural, science-backed solution for supporting liver health and preventing liver disease.

Kaempferol: A Scientifically Proven Ally for Liver Health and Regeneration
Kaempferol, a naturally occurring flavonoid found in a variety of fruits, vegetables, and herbs, has garnered considerable attention for its significant health benefits, particularly for liver health. This compound has shown promising results in preventing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis, while also demonstrating hepatoprotective effects. It supports liver regeneration, enhances overall liver function, and promotes the body’s natural detoxification processes. In this comprehensive synopsis, we explore the proven benefits of kaempferol for liver health, its mechanisms of action, and its role in mitigating liver damage based on current scientific evidence.
Kaempferol and Prevention of Liver Diseases
Kaempferol has been extensively studied for its role in preventing liver diseases, including NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, characterized by the accumulation of excess fat in liver cells, affects a significant percentage of the global population and often leads to further complications like fibrosis and cirrhosis. Kaempferol has been shown to prevent the onset of NAFLD through its potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
Studies have indicated that kaempferol exerts its effects by modulating lipid metabolism, reducing hepatic triglyceride accumulation, and inhibiting inflammatory pathways. For instance, kaempferol activates AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), a key regulator of cellular energy homeostasis, which in turn decreases lipid synthesis and promotes lipid oxidation in liver cells. This regulation prevents the excessive accumulation of fat, thereby reducing the risk of NAFLD progression.
Furthermore, kaempferol inhibits pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6, which are associated with chronic liver inflammation. Chronic inflammation is a known precursor to fibrosis and cirrhosis, and kaempferol’s ability to reduce inflammatory markers helps to halt the progression of liver disease. A study published in the journal Molecules (2023) demonstrated that kaempferol significantly reduced inflammatory markers in animal models of NAFLD, highlighting its potential in managing and preventing chronic liver conditions.
Hepatoprotective Effects of Kaempferol
Kaempferol’s hepatoprotective properties are largely attributed to its ability to reduce oxidative stress and prevent cellular damage in the liver. Oxidative stress, caused by an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants, is a major contributor to liver injury, particularly in conditions such as fatty liver disease and cirrhosis. Kaempferol’s potent antioxidant activity helps neutralize free radicals, thereby reducing oxidative damage to liver cells.
The flavonoid also enhances the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase, and glutathione peroxidase. These enzymes play a crucial role in neutralizing reactive oxygen species (ROS), thereby protecting liver cells from damage. By boosting the body’s natural antioxidant defenses, kaempferol mitigates the impact of oxidative stress, which is a key factor in the progression of liver diseases.
Another important mechanism by which kaempferol exerts hepatoprotective effects is through the inhibition of fibrosis. Liver fibrosis, characterized by the excessive deposition of extracellular matrix proteins, can lead to cirrhosis if left unchecked. Kaempferol has been shown to inhibit the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), which are primarily responsible for collagen production during liver fibrosis. By suppressing the activation of HSCs, kaempferol prevents the excessive buildup of fibrous tissue, thereby protecting the liver from scarring and maintaining normal liver architecture.
Reducing Liver Damage from Fatty Liver and Other Stressors
Fatty liver, whether caused by alcohol consumption or metabolic factors, places significant stress on liver function. Kaempferol helps reduce liver damage by targeting multiple pathways involved in lipid accumulation, inflammation, and oxidative stress. In alcohol-induced liver injury models, kaempferol has been found to reduce lipid peroxidation, a process in which free radicals attack lipids in liver cell membranes, causing cell damage and dysfunction.
Kaempferol also downregulates the expression of sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c), a transcription factor that promotes lipid synthesis in the liver. By inhibiting SREBP-1c, kaempferol reduces the synthesis of fatty acids and triglycerides, thereby preventing lipid accumulation and alleviating fatty liver conditions. Additionally, its anti-inflammatory properties help minimize liver damage caused by various stressors, including toxins, medications, and metabolic imbalances.
Kaempferol and Liver Regeneration
One of the most remarkable aspects of the liver is its ability to regenerate after injury. Kaempferol has been shown to support this regenerative capacity, promoting the recovery of liver function following damage. This regenerative effect is linked to kaempferol’s ability to modulate various growth factors and signaling pathways involved in liver regeneration.
Research indicates that kaempferol enhances the expression of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), both of which play key roles in liver regeneration. HGF is a critical growth factor that stimulates hepatocyte proliferation, while VEGF promotes the formation of new blood vessels, ensuring an adequate supply of nutrients and oxygen to regenerating liver tissue. By enhancing the activity of these growth factors, kaempferol facilitates the repair and regeneration of damaged liver cells, thereby restoring normal liver function.
Enhancing Overall Liver Function and Detoxification
Kaempferol also plays a vital role in enhancing overall liver function and promoting a healthier liver environment. The liver is the body’s primary organ for detoxification, responsible for breaking down toxins and eliminating waste products. Kaempferol supports this detoxification process by upregulating phase II detoxification enzymes, such as glutathione S-transferase (GST) and UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT). These enzymes are essential for conjugating and neutralizing harmful substances, making them more water-soluble and easier to excrete from the body.
In addition to its role in detoxification, kaempferol has been found to improve bile production and flow. Bile is crucial for the digestion and absorption of fats, as well as the elimination of waste products from the liver. By enhancing bile production, kaempferol helps maintain efficient digestion and supports the liver’s ability to remove toxins and metabolic waste.
Kaempferol also contributes to the maintenance of liver homeostasis by modulating insulin sensitivity and reducing insulin resistance, which are critical factors in the development of NAFLD and other metabolic liver diseases. Improved insulin sensitivity reduces the risk of excessive fat accumulation in the liver, thereby supporting overall liver health.
Mechanisms of Action: A Summary
Antioxidant Activity: Kaempferol neutralizes free radicals and enhances the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes, reducing oxidative stress and preventing liver cell damage.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: It inhibits pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNF-α, IL-6) and inflammatory pathways, reducing chronic liver inflammation and preventing the progression of liver diseases.
Regulation of Lipid Metabolism: Kaempferol activates AMPK and inhibits SREBP-1c, reducing lipid synthesis and promoting lipid oxidation, thereby preventing fatty liver disease.
Inhibition of Fibrosis: It prevents the activation of hepatic stellate cells, thereby inhibiting collagen production and reducing the risk of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis.
Support for Liver Regeneration: Kaempferol enhances the expression of growth factors like HGF and VEGF, promoting the regeneration of damaged liver tissue.
Enhancement of Detoxification: It upregulates phase II detoxification enzymes, improving the liver’s ability to neutralize and eliminate toxins.
Improvement of Bile Production: Kaempferol supports bile production and flow, aiding in digestion and the removal of waste products.
Conclusion
Kaempferol is a powerful flavonoid with significant hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties that contribute to the prevention and management of various liver diseases, including NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Its ability to modulate lipid metabolism, reduce oxidative stress, inhibit fibrosis, and support liver regeneration makes it an effective natural compound for maintaining liver health.
By enhancing overall liver function, promoting a healthier liver environment, and boosting the body’s natural detoxification processes, kaempferol plays a crucial role in safeguarding liver health and improving quality of life. Current scientific evidence underscores its potential as a natural therapeutic agent for liver protection and regeneration, making it a promising addition to strategies aimed at preventing and managing liver diseases. As research continues, kaempferol’s full potential in liver health and beyond will likely become even more apparent, offering new avenues for natural, effective health interventions.

Kolaviron: A Scientifically Proven Protector Against Liver Diseases
Kolaviron, a bioactive biflavonoid complex extracted from the seeds of Garcinia kola (commonly known as bitter kola), has been the subject of extensive scientific investigation for its remarkable benefits in protecting the liver and preventing diseases such as Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. This natural compound’s unique ability to preserve and enhance liver health is driven by its robust antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and hepatoprotective properties, which work in synergy to combat liver stress and support regeneration. Below, we break down the scientifically validated benefits of Kolaviron for liver health, with an emphasis on its mechanisms of action and evidence-based contributions to managing liver diseases.
1. Kolaviron and Its Hepatoprotective Effects
Kolaviron has demonstrated significant hepatoprotective activity, effectively preventing and mitigating liver damage caused by various stressors, including high-fat diets, alcohol, drugs, and toxins. Research shows that Kolaviron acts by protecting liver cells (hepatocytes) from oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis (cell death), all of which are key drivers of liver disease progression.
Antioxidant Defense Mechanism
One of the primary mechanisms of Kolaviron’s hepatoprotective action is its potent antioxidant capacity. The liver, as a major detoxification organ, is vulnerable to oxidative stress caused by an accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Kolaviron contains powerful free radical scavenging properties that neutralize ROS, thereby preventing oxidative damage to liver cells. Studies indicate that Kolaviron upregulates antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase, and glutathione peroxidase, which are crucial in maintaining cellular homeostasis and protecting the liver from oxidative injury.
Anti-Inflammatory Action
Chronic inflammation plays a significant role in the development of liver diseases such as NAFLD and cirrhosis. Kolaviron exhibits a strong anti-inflammatory effect by inhibiting pro-inflammatory cytokines and enzymes, such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2). By modulating the inflammatory response, Kolaviron reduces the overall inflammatory burden on the liver, which is critical for halting the progression of liver injury to more severe conditions like fibrosis or cirrhosis.
Membrane Stabilization and Anti-Fibrotic Activity
Another key component of Kolaviron’s hepatoprotective properties is its ability to stabilize cell membranes, thereby reducing leakage of liver enzymes such as alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) into the bloodstream. Elevated levels of these enzymes typically indicate liver damage. Kolaviron’s ability to stabilize liver cell membranes effectively minimizes cellular injury and preserves liver function. Moreover, Kolaviron inhibits the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), which are the primary cells responsible for collagen production during liver fibrosis. This anti-fibrotic activity helps prevent the development of cirrhosis, a severe scarring of liver tissue that impairs liver function.
2. Prevention of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD, characterized by excess fat accumulation in the liver in the absence of significant alcohol intake, is a growing global health concern linked to obesity, metabolic syndrome, and diabetes. Kolaviron has been shown to be highly effective in preventing the onset and progression of NAFLD through its multifaceted actions on lipid metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and inflammatory pathways.
Reduction of Hepatic Lipid Accumulation
Kolaviron helps prevent hepatic steatosis (fat accumulation in the liver) by regulating key enzymes involved in lipid metabolism. Studies have demonstrated that Kolaviron reduces the activity of lipogenic enzymes such as acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) and fatty acid synthase (FAS), which are responsible for fat synthesis in the liver. Concurrently, Kolaviron increases the activity of lipolytic enzymes and promotes fatty acid oxidation, thereby reducing overall fat content in the liver. This action is critical in halting the progression of NAFLD and preventing the development of more severe conditions, such as non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).
Enhancement of Insulin Sensitivity
Insulin resistance is a key factor contributing to the development of NAFLD. Kolaviron has been shown to enhance insulin sensitivity, thereby improving glucose metabolism and reducing the risk of lipid accumulation in the liver. By modulating the insulin signaling pathway, Kolaviron helps maintain normal blood sugar levels and prevents the hepatic storage of excess lipids, which is particularly beneficial for individuals with metabolic syndrome or type 2 diabetes.
3. Kolaviron’s Role in Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis Prevention
Chronic liver diseases often progress to cirrhosis if left untreated, characterized by the formation of fibrous scar tissue that impairs liver function. Kolaviron plays a crucial role in the prevention of chronic liver disease progression through its anti-fibrotic and anti-inflammatory actions, as previously described.
Inhibition of Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation
The activation of hepatic stellate cells is a central event in liver fibrosis and cirrhosis. Kolaviron has been shown to inhibit the activation of these cells by downregulating the expression of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β), a key fibrogenic cytokine. This inhibition effectively reduces the deposition of extracellular matrix components, such as collagen, that contribute to fibrosis. By mitigating the fibrotic process, Kolaviron helps preserve normal liver architecture and function.
Protection Against Hepatotoxic Agents
Kolaviron has also demonstrated protective effects against various hepatotoxic agents, including alcohol, carbon tetrachloride (CCl4), and acetaminophen, all of which can cause chronic liver damage if exposure is prolonged. Kolaviron’s antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties help mitigate the damage caused by these toxic substances, reducing the risk of chronic liver disease and cirrhosis.
4. Promotion of Liver Regeneration and Improved Liver Function
The liver possesses a remarkable ability to regenerate following injury. Kolaviron has been found to enhance this regenerative capacity, contributing to improved overall liver function and a healthier hepatic environment.
Stimulation of Hepatocyte Proliferation
Kolaviron promotes liver regeneration by stimulating hepatocyte proliferation, which is crucial for the repair of liver tissue following injury. Research suggests that Kolaviron enhances the expression of growth factors such as hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), which plays a vital role in initiating hepatocyte proliferation and promoting tissue repair. This regenerative effect helps restore normal liver function following damage caused by fatty liver disease, alcohol, or toxins.
Enhancement of Detoxification Processes
In addition to its role in liver regeneration, Kolaviron also enhances the liver’s natural detoxification processes. The liver’s primary function is to detoxify harmful substances, and Kolaviron supports this process by increasing the activity of phase I and phase II detoxification enzymes, such as cytochrome P450 enzymes and glutathione-S-transferase (GST). These enzymes are involved in the metabolism and excretion of toxins, thereby reducing the toxic burden on the liver and enhancing overall liver health.
5. Kolaviron for Overall Liver Health and Function
Kolaviron not only protects the liver from damage but also contributes to the maintenance of overall liver health and function, ensuring a healthier hepatic environment and promoting the body’s natural detoxification processes.
Reduction of Oxidative and Inflammatory Markers
Kolaviron has been shown to significantly reduce oxidative stress markers, such as malondialdehyde (MDA), and inflammatory markers, such as C-reactive protein (CRP), in experimental models of liver disease. By reducing these markers, Kolaviron helps create a less inflammatory and oxidative environment in the liver, which is conducive to better liver function and overall health.
Support of Immune Function
The liver plays a key role in immune function, and Kolaviron supports this role by modulating immune responses. Studies indicate that Kolaviron helps maintain a balanced immune response, preventing excessive inflammation while supporting the liver’s ability to respond to infections and other challenges. This immunomodulatory effect is particularly important in preventing immune-mediated liver damage and maintaining hepatic homeostasis.
Conclusion
Kolaviron stands out as a promising natural compound with proven hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and regenerative properties that contribute significantly to liver health. Through its multifaceted actions, Kolaviron helps prevent the onset and progression of liver diseases such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis, while also promoting liver regeneration and enhancing the liver’s natural detoxification processes. Scientific evidence supports Kolaviron’s effectiveness in stabilizing liver function, reducing oxidative and inflammatory damage, and fostering a healthier liver environment.
For individuals looking to support their liver health naturally, Kolaviron presents a viable option with a solid foundation of scientific validation. Its ability to target multiple pathways involved in liver disease progression makes it a valuable addition to strategies aimed at preventing liver damage, enhancing liver regeneration, and maintaining optimal liver function. As always, it is essential to consult healthcare professionals before starting any supplementation, particularly for those with existing liver conditions or those taking medications that may affect liver function.

Ligularia fischeri: Scientific Benefits for Liver Health, Prevention, and Regeneration
Ligularia fischeri, a traditional herb native to East Asia, has garnered significant attention in recent years for its beneficial effects on liver health. Known for its potent hepatoprotective properties, Ligularia fischeri has been studied extensively in both animal models and human trials. This herb shows promise in preventing and managing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), mitigating liver damage, and promoting liver regeneration. This comprehensive overview delves into the mechanisms by which Ligularia fischeri supports liver health, examining peer-reviewed evidence and providing insights into its potential as a natural treatment.
Preventing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD is characterized by the accumulation of excess fat in liver cells in individuals who consume little or no alcohol. This condition can progress to more severe liver issues, such as inflammation, fibrosis, or even cirrhosis. The growing body of evidence suggests that Ligularia fischeri may play a pivotal role in preventing NAFLD through its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and lipid-regulating properties.
Ligularia fischeri contains bioactive compounds, including phenolic acids, flavonoids, and terpenoids, which exert antioxidant effects that protect liver cells from oxidative stress—a major driver in the development of NAFLD. Research indicates that oxidative stress promotes the lipid peroxidation process, which ultimately results in fat accumulation and cell damage in the liver. By scavenging free radicals and reducing oxidative damage, Ligularia fischeri helps inhibit the onset of NAFLD.
Additionally, the herb has demonstrated the ability to modulate key metabolic pathways that regulate lipid metabolism. Animal studies have shown that Ligularia fischeri reduces hepatic triglyceride content, likely through the activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). AMPK activation leads to increased fatty acid oxidation and decreased lipogenesis, thereby reducing fat buildup in the liver—a critical factor in managing NAFLD risk.
Mitigating Liver Damage and Chronic Liver Diseases
Ligularia fischeri’s hepatoprotective effects extend beyond NAFLD prevention; it also shows efficacy in reducing liver damage associated with chronic liver diseases. Studies in rodents have illustrated the herb’s ability to inhibit inflammation and fibrosis, two hallmarks of progressive liver disease.
Inflammation is a key feature of both alcoholic and non-alcoholic liver diseases, with chronic inflammation often resulting in fibrogenesis and the progression of liver injury. Ligularia fischeri has been found to significantly lower the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6). These cytokines are responsible for sustaining the inflammatory response and triggering liver cell injury. By downregulating these pro-inflammatory mediators, Ligularia fischeri helps to mitigate the extent of liver damage, thereby reducing the risk of fibrosis and cirrhosis.
Moreover, the herb is rich in hepatoprotective compounds like chlorogenic acid and sesquiterpenes, which have been shown to enhance the liver’s resilience against toxins. By reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, Ligularia fischeri minimizes damage caused by various liver stressors, including alcohol, toxins, and high-fat diets. Animal models have also shown that pretreatment with Ligularia fischeri extract protects against induced liver injury, supporting its role as a natural remedy for maintaining liver health and function.
Promoting Liver Regeneration and Overall Liver Function
Liver regeneration is a critical aspect of recovery from liver injury, and Ligularia fischeri plays a key role in promoting this regenerative process. Studies demonstrate that the herb enhances liver regeneration by promoting hepatocyte proliferation—the replication of liver cells needed for repairing damage. The presence of specific growth factors and proteins responsible for cellular repair is elevated in the liver when supplemented with Ligularia fischeri extract, indicating its role in accelerating tissue recovery.
The herb’s beneficial impact on liver regeneration is likely due to its ability to modulate cellular signaling pathways. Evidence suggests that Ligularia fischeri activates pathways such as the Wnt/β-catenin signaling cascade, which is crucial for liver cell proliferation and tissue remodeling. Activation of this pathway allows for the replacement of damaged cells with healthy hepatocytes, ultimately contributing to improved liver structure and function.
Ligularia fischeri also helps in enhancing bile production, which is essential for lipid digestion and overall liver function. Enhanced bile flow supports detoxification processes and reduces the accumulation of toxins in the liver. By improving bile production and overall detoxification, Ligularia fischeri helps create a healthier liver environment, thereby promoting optimal liver function and maintaining systemic health.
Mechanisms of Hepatoprotective Action
Antioxidant Activity
Oxidative stress is one of the primary contributors to liver injury, particularly in conditions like NAFLD and cirrhosis. Ligularia fischeri is abundant in antioxidant compounds, including chlorogenic acid, caffeic acid, and other phenolic compounds. These compounds effectively neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS), reducing oxidative damage to liver cells. Research has shown that treatment with Ligularia fischeri extracts results in significant decreases in biomarkers of oxidative stress, such as malondialdehyde (MDA), while increasing the activity of antioxidant enzymes like superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx).
Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Chronic inflammation is a significant factor in the progression of liver diseases. Ligularia fischeri exerts anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting the release of inflammatory mediators. Studies have demonstrated a reduction in the levels of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and nitric oxide (NO) in liver tissues following administration of Ligularia fischeri extracts. This suggests that the herb can inhibit key enzymes involved in the inflammatory response, thus preventing further liver damage and fibrosis.
Lipid Regulation
Another key mechanism by which Ligularia fischeri supports liver health is through lipid regulation. The herb activates AMPK, which not only stimulates fatty acid oxidation but also inhibits the synthesis of new fatty acids. This dual action helps to prevent fat accumulation in the liver—a hallmark of NAFLD. Furthermore, Ligularia fischeri has been found to regulate serum lipid levels, lowering total cholesterol, triglycerides, and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, which collectively support improved liver and metabolic health.
Fibrosis Prevention
Fibrosis results from the excessive deposition of extracellular matrix proteins, primarily due to chronic liver inflammation. Ligularia fischeri has shown potential in reducing hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation—a key step in the development of liver fibrosis. By inhibiting HSC activation, Ligularia fischeri effectively prevents the deposition of collagen fibers, thus slowing the progression towards cirrhosis.
Supporting the Body’s Natural Detoxification Process
Detoxification is one of the liver’s primary functions, and Ligularia fischeri enhances the liver’s ability to eliminate toxins by boosting enzymatic activity involved in detox pathways. The herb promotes phase II detoxification, which involves the conjugation of toxins into water-soluble compounds that can be easily excreted from the body. Increased levels of glutathione—a critical antioxidant involved in detoxification—have been observed in the liver following Ligularia fischeri administration. This indicates that the herb supports the liver’s natural capacity to neutralize and eliminate harmful substances.
Clinical Evidence and Future Directions
The hepatoprotective effects of Ligularia fischeri have been validated in a range of preclinical studies, with a growing interest in translating these findings into human trials. Animal studies have consistently demonstrated its ability to protect against liver injury induced by high-fat diets, alcohol, and toxins. These studies form a strong foundation for further clinical investigation, particularly in humans with NAFLD or early-stage cirrhosis.
Emerging research also suggests that Ligularia fischeri could be used in combination with other natural compounds or conventional treatments to enhance liver health outcomes. For instance, its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties may complement pharmacological interventions aimed at reducing liver fat or fibrosis. Given the herb’s potential to improve liver function without significant side effects, it is a promising candidate for adjunct therapy in chronic liver disease management.
Conclusion
Ligularia fischeri is a promising natural remedy for promoting liver health, preventing liver diseases like NAFLD, and supporting liver regeneration. Its hepatoprotective effects are primarily attributed to its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, lipid-regulating, and antifibrotic properties. By mitigating oxidative stress, reducing inflammation, regulating lipid accumulation, and promoting liver cell regeneration, Ligularia fischeri offers a multifaceted approach to maintaining a healthy liver and enhancing the body’s natural detoxification processes.
While the evidence from animal studies is compelling, more research—particularly human clinical trials—is needed to fully establish its efficacy and optimal dosing strategies. Nevertheless, the current body of research suggests that Ligularia fischeri holds significant promise for individuals looking to naturally support their liver health and prevent the progression of chronic liver diseases. Its comprehensive benefits make it a valuable addition to liver health regimens, providing a natural, scientifically-backed option for improving liver function and overall wellness.

Ligusticum Chuanxiong Hort Extract: A Natural Solution for Liver Health, NAFLD, Cirrhosis, and Hepatoprotection
Introduction to Ligusticum Chuanxiong Hort Extract and Liver Health
Ligusticum Chuanxiong Hort, commonly known as Chuanxiong or Szechuan Lovage, is an herb widely recognized in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) for its potent therapeutic properties. Over recent years, scientific studies have highlighted its benefits in addressing liver-related health issues such as Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, cirrhosis, and overall hepatoprotection. This herb has shown promise in supporting liver regeneration and enhancing the body’s detoxification mechanisms. Below, we provide a comprehensive breakdown of its proven effects and mechanisms of action, backed by scientific evidence.
Understanding the Burden of Liver Diseases
Liver disease, including NAFLD and cirrhosis, presents a growing global health concern. NAFLD, characterized by the accumulation of fat in liver cells in individuals with little or no alcohol consumption, has become one of the leading causes of chronic liver disease worldwide. If untreated, NAFLD can progress to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), fibrosis, and eventually cirrhosis—a state of irreversible liver damage that impairs hepatic function and can lead to life-threatening complications.
Ligusticum Chuanxiong Hort extract has shown hepatoprotective effects, helping to manage liver diseases effectively and providing regenerative support. Below, we delve into how this herbal extract aids liver health.
Proven Benefits of Ligusticum Chuanxiong Hort in Preventing NAFLD, Chronic Liver Disease, and Cirrhosis
Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Ligusticum Chuanxiong Hort extract contains bioactive compounds, primarily ferulic acid, that exhibit significant anti-inflammatory effects. Inflammation plays a crucial role in the progression of liver diseases, particularly NAFLD and NASH. The reduction of inflammatory cytokines—such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β—is a key mechanism by which Ligusticum Chuanxiong reduces liver inflammation.
Scientific studies indicate that the extract inhibits the NF-κB pathway, a central regulator of inflammation in NAFLD and liver fibrosis. By suppressing this pathway, Ligusticum Chuanxiong reduces hepatic inflammation and prevents the progression from simple fatty liver to more severe forms of liver damage.
Antioxidant and Free Radical Scavenging Activity
Oxidative stress is another critical factor contributing to the development and progression of liver diseases. The accumulation of lipid peroxides and free radicals damages liver cells, leading to fibrosis and cirrhosis. Ligusticum Chuanxiong extract has potent antioxidant properties, primarily attributed to ferulic acid and ligustilide, which act as free radical scavengers.
In several preclinical studies, Ligusticum Chuanxiong has demonstrated the ability to decrease levels of malondialdehyde (MDA), a marker of oxidative stress, while boosting the activity of antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px). This reduction in oxidative stress helps mitigate damage to liver cells, thereby preventing the progression of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis.
Inhibition of Hepatic Lipogenesis
One of the critical aspects of NAFLD is the overaccumulation of fat in hepatocytes, primarily caused by increased hepatic lipogenesis and impaired lipid metabolism. Ligusticum Chuanxiong extract has shown potential in regulating lipid metabolism by inhibiting enzymes involved in de novo lipogenesis, such as fatty acid synthase (FAS) and acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC).
Studies suggest that the herb activates AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), a key regulator of energy homeostasis, which subsequently decreases lipid synthesis and promotes fatty acid oxidation in the liver. By inhibiting lipid accumulation, Ligusticum Chuanxiong helps alleviate NAFLD and prevent its progression to more advanced stages of liver disease.
Anti-Fibrotic Effects
Cirrhosis is characterized by excessive deposition of extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins, leading to liver fibrosis. The activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) plays a central role in the fibrotic process. Ligusticum Chuanxiong has demonstrated anti-fibrotic effects by inhibiting HSC activation and reducing the production of ECM proteins such as collagen.
Research has shown that the extract downregulates the expression of transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1), a key fibrogenic cytokine. By modulating this pathway, Ligusticum Chuanxiong helps to attenuate liver fibrosis, thus preventing the progression to cirrhosis and preserving liver function.
Hepatoprotective Effects and Mitigation of Liver Damage
Protection Against Hepatotoxins
The liver is constantly exposed to various toxic substances, including environmental pollutants, medications, and metabolic by-products. Ligusticum Chuanxiong has been found to possess hepatoprotective effects against several hepatotoxins, including carbon tetrachloride (CCl4), acetaminophen, and alcohol.
In experimental models, administration of Ligusticum Chuanxiong extract prior to exposure to hepatotoxins has been shown to reduce liver enzyme levels (ALT, AST), indicating decreased liver cell damage. The hepatoprotective effects are largely due to its antioxidant properties, inhibition of cytochrome P450 enzymes involved in toxin activation, and enhancement of detoxification pathways.
Reducing Damage from Fatty Liver and Liver Stressors
Ligusticum Chuanxiong helps mitigate liver damage associated with fatty liver conditions. The extract reduces lipid peroxidation, a major contributor to hepatocyte injury in NAFLD, by maintaining membrane integrity and reducing oxidative damage. Moreover, the anti-inflammatory effects of the herb reduce stress on the liver, allowing it to recover more effectively from damage.
Ligusticum Chuanxiong and Liver Regeneration
Stimulation of Hepatocyte Proliferation
The liver has a remarkable capacity for regeneration, but chronic conditions such as NAFLD, fibrosis, and cirrhosis can impair this ability. Ligusticum Chuanxiong has demonstrated hepatocyte regenerative effects, stimulating the proliferation of liver cells and promoting tissue repair.
Studies show that Ligusticum Chuanxiong upregulates hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and other regenerative mediators, facilitating the repair and regeneration of damaged liver tissue. This regenerative capacity is particularly beneficial in the context of liver injury due to toxins, fatty liver disease, or fibrosis.
Modulation of Autophagy
Autophagy is a critical cellular process for maintaining liver health, particularly during times of stress or damage. Ligusticum Chuanxiong has been shown to enhance autophagic activity in hepatocytes, promoting the degradation of damaged organelles and lipids. This process is essential for maintaining cellular health and facilitating liver regeneration.
By activating autophagy through pathways such as AMPK-mTOR, Ligusticum Chuanxiong helps ensure that damaged hepatocytes are effectively repaired or replaced, thereby contributing to overall liver regeneration and improved liver function.
Enhancing Overall Liver Function and Detoxification
Promotion of Bile Secretion
Bile production is essential for digestion and detoxification. Ligusticum Chuanxiong has been found to enhance bile secretion, which aids in the elimination of toxins and supports lipid digestion. Improved bile flow also helps prevent cholestasis, a condition characterized by impaired bile movement that can lead to liver damage.
Enhancing Natural Detoxification Processes
Ligusticum Chuanxiong supports the liver’s natural detoxification processes by upregulating phase II detoxification enzymes such as glutathione-S-transferase (GST). This enhancement in enzymatic activity ensures efficient conjugation and elimination of toxins, reducing the overall toxic burden on the liver.
Furthermore, the herb’s antioxidant properties protect detoxification enzymes from oxidative damage, thereby ensuring their optimal function and contributing to a healthier liver environment.
Summary: Ligusticum Chuanxiong Hort as a Holistic Liver Protector
Ligusticum Chuanxiong Hort extract provides a multifaceted approach to supporting liver health, with scientifically backed benefits in preventing and managing liver conditions such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-fibrotic effects help mitigate the progression of liver damage, while its hepatoprotective properties safeguard against toxic insults. Moreover, Ligusticum Chuanxiong enhances liver regeneration, supports bile secretion, and boosts detoxification pathways, promoting overall liver function and creating a healthier liver environment.
The use of Ligusticum Chuanxiong as a natural supplement offers a promising approach to maintaining liver health and preventing liver diseases, particularly in those at risk of developing NAFLD or experiencing chronic liver stress. While more human clinical trials are needed to fully elucidate its effects, the existing body of preclinical and animal research provides strong evidence of its potential as a hepatoprotective agent.

Limonium tetragonum: Hepatoprotective Benefits Against Liver Diseases
Overview of Limonium tetragonum for Liver Health
Limonium tetragonum, commonly known as sea lavender, has garnered significant scientific interest due to its potent hepatoprotective properties. Emerging evidence highlights its potential role in preventing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis, along with promoting overall liver regeneration and enhanced liver function. This plant, traditionally used in herbal remedies, is rich in flavonoids and polyphenols, which are recognized for their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antifibrotic properties. This comprehensive synopsis will explore the mechanisms by which Limonium tetragonum exerts its liver-protective effects and its potential in supporting overall liver health.
Proven Benefits for Liver Diseases
Preventing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD is characterized by excessive fat accumulation in the liver, often linked to metabolic syndrome, obesity, and insulin resistance. Recent studies have suggested that Limonium tetragonum can mitigate the development of NAFLD through its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory compounds. The polyphenolic content in Limonium tetragonum works by neutralizing reactive oxygen species (ROS), thereby reducing oxidative stress, which is a significant contributor to hepatic fat accumulation and subsequent inflammation.
Additionally, animal studies have demonstrated that Limonium tetragonum can modulate lipid metabolism by regulating key enzymes involved in lipogenesis and fatty acid oxidation. By downregulating genes associated with fatty acid synthesis and enhancing fatty acid beta-oxidation, Limonium tetragonum helps prevent the pathological fat deposition characteristic of NAFLD. The presence of flavonoids in Limonium tetragonum has also been linked to improved insulin sensitivity, which further reduces the risk of NAFLD by regulating glucose and lipid homeostasis.
Alleviating Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver disease and cirrhosis often stem from prolonged inflammation and fibrosis, which leads to the destruction of healthy liver tissue. The hepatoprotective effects of Limonium tetragonum have been substantiated through its antifibrotic properties, which play a crucial role in preventing the progression of chronic liver disease to cirrhosis. The polyphenolic compounds found in Limonium tetragonum have been shown to inhibit the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), which are central to the process of liver fibrosis.
Activated HSCs are responsible for the excessive production of extracellular matrix (ECM) components, leading to scar tissue formation. By inhibiting HSC activation, Limonium tetragonum helps maintain normal ECM turnover, thus preventing fibrosis. Furthermore, its anti-inflammatory action, mediated through the inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6, reduces chronic inflammation, a critical factor in the development of liver cirrhosis.
Hepatoprotective Effects Against Fatty Liver Damage
Limonium tetragonum exhibits robust hepatoprotective effects, particularly against damage caused by a fatty liver and other stressors. Oxidative stress and inflammation are key drivers of hepatic injury in fatty liver conditions. The antioxidant properties of Limonium tetragonum are attributed to its high flavonoid and polyphenol content, which efficiently scavenge free radicals and reduce oxidative damage to liver cells. This reduction in oxidative stress helps to preserve hepatocyte integrity, thereby maintaining liver function even in the face of metabolic challenges.
In addition, Limonium tetragonum has been shown to stabilize liver cell membranes, reducing their susceptibility to damage from lipid peroxidation—a common occurrence in fatty liver conditions. Studies have also indicated that Limonium tetragonum modulates the expression of enzymes involved in detoxification, including glutathione S-transferase (GST), which enhances the liver’s ability to neutralize toxins and reduce further damage. By supporting these detoxification pathways, Limonium tetragonum minimizes the risk of hepatocyte apoptosis and promotes a healthier liver environment.
Supporting Liver Regeneration and Function
The liver has a remarkable ability to regenerate, a process that is critical for recovery from injury. Limonium tetragonum has been observed to promote liver regeneration through several mechanisms. First, its anti-inflammatory properties create a favorable environment for liver repair by reducing the presence of pro-inflammatory mediators that can inhibit regeneration. Secondly, its antioxidant effects protect existing liver cells from oxidative stress, thus ensuring that the regenerative process is not hindered by ongoing cellular damage.
Moreover, Limonium tetragonum has been found to upregulate growth factors such as hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), which plays an essential role in stimulating hepatocyte proliferation. By enhancing the expression of HGF and other regenerative factors, Limonium tetragonum helps accelerate the replacement of damaged liver tissue with healthy, functioning cells. This effect not only contributes to recovery from liver injury but also supports overall liver function, enhancing the organ’s ability to perform its vital roles in metabolism and detoxification.
Mechanisms of Action: How Limonium tetragonum Protects the Liver
Antioxidant Activity
The hepatoprotective effects of Limonium tetragonum are largely attributed to its potent antioxidant activity. Oxidative stress is a key factor in the development and progression of liver diseases, including NAFLD, chronic hepatitis, and cirrhosis. The high concentration of polyphenolic compounds in Limonium tetragonum contributes to its ability to neutralize ROS and prevent oxidative damage to liver cells. Flavonoids such as quercetin and kaempferol, present in Limonium tetragonum, have been shown to enhance the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes, including superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase, which further supports the liver’s defense mechanisms against oxidative stress.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Chronic inflammation is a common underlying factor in liver diseases. Limonium tetragonum exerts significant anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and reducing the infiltration of inflammatory cells into liver tissue. Studies have demonstrated that Limonium tetragonum downregulates the nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) pathway, a key regulator of inflammation. By inhibiting NF-κB activation, Limonium tetragonum effectively reduces the production of cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6, which are involved in promoting hepatic inflammation and fibrosis.
Antifibrotic Properties
Liver fibrosis, characterized by excessive ECM deposition, is a hallmark of chronic liver disease and cirrhosis. Limonium tetragonum has demonstrated antifibrotic effects by inhibiting the activation of HSCs, which are primarily responsible for ECM production. The suppression of HSC activation by Limonium tetragonum is mediated through its ability to inhibit transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) signaling, a critical pathway involved in fibrogenesis. By preventing the activation of this pathway, Limonium tetragonum helps maintain normal ECM homeostasis and prevents the development of fibrotic scar tissue in the liver.
Modulation of Lipid Metabolism
The ability of Limonium tetragonum to prevent NAFLD is also linked to its effects on lipid metabolism. Research indicates that Limonium tetragonum can modulate the expression of key enzymes involved in lipid synthesis and breakdown. By downregulating lipogenic enzymes such as acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) and fatty acid synthase (FAS), and upregulating enzymes involved in fatty acid oxidation, Limonium tetragonum helps reduce hepatic fat accumulation. Additionally, its positive effects on insulin sensitivity help regulate lipid and glucose metabolism, thereby mitigating the risk factors associated with NAFLD.
Promoting a Healthier Liver Environment
Limonium tetragonum’s hepatoprotective properties contribute to a healthier liver environment by enhancing the liver’s natural detoxification processes. The liver plays a critical role in detoxifying endogenous and exogenous substances, and Limonium tetragonum supports this function through multiple pathways. The induction of phase II detoxifying enzymes, such as GST, by Limonium tetragonum enhances the conjugation and elimination of harmful substances from the body. This not only reduces the toxic burden on the liver but also protects hepatocytes from damage.
Furthermore, Limonium tetragonum has been shown to support bile production, which is essential for the digestion and absorption of fats, as well as the excretion of toxins. By promoting bile flow, Limonium tetragonum helps in the effective removal of waste products and reduces the risk of cholestasis, a condition characterized by impaired bile flow that can lead to liver damage.
Conclusion: The Role of Limonium tetragonum in Liver Health
Limonium tetragonum offers a range of hepatoprotective benefits that make it a promising natural agent for the prevention and management of liver diseases such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Its ability to reduce oxidative stress, combat inflammation, inhibit fibrosis, and modulate lipid metabolism contributes to its effectiveness in maintaining liver health. Moreover, its role in promoting liver regeneration and enhancing detoxification processes further supports its use as a hepatoprotective supplement.
While more clinical studies are needed to fully understand the therapeutic potential of Limonium tetragonum in humans, the existing evidence from in vitro and animal studies provides a strong foundation for its use in liver health management. As research progresses, Limonium tetragonum may become an important natural intervention for individuals seeking to protect their liver from the damaging effects of oxidative stress, inflammation, and metabolic dysregulation.

Lithospermum erythrorhizon: A Promising Natural Ally in Liver Health
Lithospermum erythrorhizon, commonly known as purple gromwell, has gained attention for its potential to address a variety of liver conditions, including Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Extracts from Lithospermum erythrorhizon are revered in traditional medicine, and recent scientific investigations have begun to shed light on their hepatoprotective and regenerative effects. This article provides a comprehensive, evidence-based overview of how this natural compound contributes to liver health, its mechanisms of action, and its role in enhancing liver regeneration and overall function.
Preventing and Managing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is characterized by the excessive accumulation of fat in liver cells, often driven by poor diet, sedentary lifestyle, and metabolic imbalances. Lithospermum erythrorhizon extract has shown significant promise in mitigating the onset and progression of NAFLD. Scientific evidence suggests that the phenolic compounds and shikonin derivatives found in Lithospermum erythrorhizon play an essential role in regulating lipid metabolism within hepatocytes, effectively reducing lipid accumulation.
In in-vivo studies, shikonin, a primary active component of the extract, has demonstrated the ability to modulate key lipid metabolic pathways by activating AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). AMPK activation is a well-known mechanism for improving lipid metabolism and energy homeostasis, which is crucial in preventing hepatic steatosis. The anti-inflammatory properties of Lithospermum erythrorhizon further contribute to its benefits in NAFLD management by reducing oxidative stress, a key driver of hepatic inflammation and fibrosis in NAFLD patients.
Protection Against Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Lithospermum erythrorhizon also exhibits protective effects against chronic liver disease and cirrhosis, conditions that often result from prolonged liver injury. The liver is highly susceptible to oxidative damage due to its role in metabolizing toxins, and ongoing oxidative stress can lead to progressive fibrosis and cirrhosis. The hepatoprotective capabilities of Lithospermum erythrorhizon have been linked to its potent antioxidant effects, which play a critical role in countering oxidative damage.
The extract’s effectiveness in scavenging free radicals and enhancing the activity of antioxidant enzymes like superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase has been well-documented in peer-reviewed studies. These mechanisms help mitigate the damage caused by reactive oxygen species (ROS), which are responsible for exacerbating chronic liver disease. By enhancing the liver’s antioxidant capacity, Lithospermum erythrorhizon effectively helps protect the liver from the cumulative damage that often leads to cirrhosis.
Moreover, the extract contains anti-fibrotic agents that inhibit the activation of hepatic stellate cells—the primary contributors to liver fibrosis. Studies have shown that Lithospermum erythrorhizon reduces the production of pro-fibrotic cytokines, such as transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β), thus preventing excessive extracellular matrix deposition and fibrosis progression.
Hepatoprotective Effects: Reducing Damage from Fatty Liver and Other Stressors
A critical aspect of Lithospermum erythrorhizon’s efficacy lies in its hepatoprotective effects. Several preclinical studies have highlighted the compound’s ability to shield liver cells from damage induced by common stressors, including high-fat diets, alcohol, and toxic substances. This hepatoprotection is largely attributed to its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-apoptotic properties.
The anti-inflammatory activity of shikonin derivatives helps reduce inflammation-mediated liver damage. Inflammatory markers, such as TNF-α and IL-6, are commonly elevated in cases of liver stress and fatty liver conditions. Lithospermum erythrorhizon has been shown to downregulate these inflammatory markers, reducing the degree of hepatocellular injury. The presence of anti-apoptotic compounds also contributes to maintaining liver integrity by preventing excessive cell death, thereby reducing liver inflammation and minimizing tissue damage.
Promoting Liver Regeneration and Enhancing Liver Function
Beyond its protective capabilities, Lithospermum erythrorhizon is also recognized for its role in promoting liver regeneration and improving overall liver function. The liver’s ability to regenerate is a unique feature of this organ, allowing it to recover from injury and restore its structure and function. Lithospermum erythrorhizon extract supports this natural regenerative process through multiple mechanisms.
The compound has been shown to enhance hepatocyte proliferation—a crucial aspect of liver regeneration. Shikonin and its derivatives activate pathways such as the Wnt/β-catenin pathway, which is involved in cell growth and tissue regeneration. By promoting the proliferation of hepatocytes, Lithospermum erythrorhizon contributes to the recovery of damaged liver tissue, ensuring quicker restoration of normal liver architecture and functionality.
In addition to stimulating cell proliferation, Lithospermum erythrorhizon enhances mitochondrial function, thereby improving energy production in liver cells. Mitochondrial health is vital for liver regeneration, as the energy demands of the regenerating liver are substantial. Studies suggest that the extract helps maintain mitochondrial membrane potential, enhances ATP production, and reduces mitochondrial oxidative damage, which altogether contribute to a healthier liver environment.
Improving Overall Liver Function and Detoxification
The liver plays a critical role in detoxifying the body by metabolizing harmful substances and excreting them through bile. Lithospermum erythrorhizon extract has been shown to enhance this detoxification capacity, thus promoting overall liver health and resilience. The extract’s bioactive components facilitate bile production and secretion, which is crucial for the excretion of toxins and fat metabolism.
One of the primary mechanisms by which Lithospermum erythrorhizon aids in detoxification is through the upregulation of phase II detoxification enzymes, such as glutathione-S-transferase (GST). These enzymes are essential for conjugating toxins and facilitating their excretion from the body. The increased activity of GST and other detoxification enzymes ensures that harmful substances are efficiently processed and eliminated, thereby reducing the burden on the liver.
Mechanisms of Action: How Lithospermum erythrorhizon Contributes to Liver Health
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Inflammation is a common factor in liver conditions, and Lithospermum erythrorhizon effectively reduces inflammation by inhibiting pro-inflammatory cytokines. By modulating key inflammatory pathways, including the NF-κB pathway, the extract helps lower hepatic inflammation and prevent further tissue damage.
Antioxidant Properties: The liver’s exposure to toxins makes it particularly vulnerable to oxidative stress. Lithospermum erythrorhizon’s antioxidant capabilities, including scavenging ROS and enhancing the body’s endogenous antioxidant defenses, help protect liver cells from oxidative damage. The extract’s phenolic compounds and flavonoids play a significant role in enhancing the liver’s resistance to oxidative stress.
Anti-Fibrotic Mechanism: The inhibition of hepatic stellate cell activation and suppression of pro-fibrotic markers, such as TGF-β, are key anti-fibrotic mechanisms attributed to Lithospermum erythrorhizon. These effects help prevent excessive collagen deposition and liver scarring, reducing the progression of fibrosis and cirrhosis.
Hepatocyte Proliferation: The liver’s regenerative capacity is one of its defining features. Lithospermum erythrorhizon promotes hepatocyte proliferation by activating regenerative pathways, such as the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. This activity supports liver recovery following injury or stress, enhancing the overall resilience of the organ.
Mitochondrial Protection: Healthy mitochondria are crucial for energy production in liver cells. Lithospermum erythrorhizon has been shown to preserve mitochondrial function, reduce oxidative damage to mitochondria, and maintain mitochondrial membrane integrity, thereby ensuring adequate ATP production for liver repair and detoxification processes.
Conclusion: Lithospermum erythrorhizon as a Natural Liver Protectant
Lithospermum erythrorhizon extract offers a multi-faceted approach to liver health by preventing NAFLD, mitigating chronic liver disease, and providing protective effects against liver stressors. The compound’s ability to enhance liver regeneration, reduce oxidative stress, control inflammation, and prevent fibrosis makes it a powerful ally in supporting liver function. Through its various mechanisms of action, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-fibrotic, and hepatoprotective activities, Lithospermum erythrorhizon holds significant promise as a natural therapeutic for liver health.
It is important to note that while current research is promising, ongoing studies are needed to further establish the efficacy and safety of Lithospermum erythrorhizon in diverse populations. However, the existing body of evidence suggests that this herbal extract could play a valuable role in the prevention and management of liver conditions, ultimately contributing to a healthier liver environment and enhancing the body’s natural detoxification processes.
Incorporating Lithospermum erythrorhizon into a broader health regimen, alongside lifestyle modifications such as maintaining a balanced diet and engaging in regular physical activity, could provide substantial benefits for individuals looking to protect their liver and improve their overall well-being.

The Science-Backed Benefits of Lonicera japonica Thunb. Extract for Liver Health
Lonicera japonica Thunb., commonly known as Japanese honeysuckle, is well-regarded in traditional medicine for its diverse therapeutic properties. Recent scientific research has unveiled its impressive hepatoprotective benefits, which play a significant role in managing liver health, particularly in conditions like Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. This article provides a comprehensive overview of Lonicera japonica’s proven benefits for liver protection, regeneration, and function enhancement, focusing solely on the scientific evidence supporting these claims.
Hepatoprotective Effects Against NAFLD and Chronic Liver Diseases
NAFLD is an increasingly common liver condition characterized by excessive fat buildup in liver cells, unrelated to alcohol consumption. Studies have demonstrated that Lonicera japonica extract has notable potential in preventing and managing NAFLD through its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and lipid-lowering properties.
Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Properties
The hepatoprotective potential of Lonicera japonica is largely attributed to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory mechanisms. The extract contains active constituents such as chlorogenic acid, luteolin, and flavonoids that neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS) in liver tissues. ROS are harmful byproducts of metabolism that contribute significantly to liver damage and inflammation, particularly in NAFLD. By neutralizing ROS, Lonicera japonica mitigates oxidative stress, a primary factor in NAFLD progression and liver fibrosis.
Furthermore, the anti-inflammatory action of Lonicera japonica helps in suppressing the pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α and IL-6, which are key mediators in liver inflammation. By decreasing the levels of these cytokines, Lonicera japonica effectively reduces hepatic inflammation, a crucial aspect in preventing the advancement of NAFLD to more severe conditions such as cirrhosis.
Regulation of Lipid Metabolism
Another significant benefit of Lonicera japonica extract is its ability to regulate lipid metabolism. Studies indicate that the active components in the extract help reduce triglyceride accumulation in the liver, which is central to NAFLD pathogenesis. By improving lipid homeostasis, Lonicera japonica prevents the buildup of fatty deposits in liver cells, which is essential for halting the progression of NAFLD and mitigating related complications.
Protection Against Liver Damage and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver diseases and cirrhosis involve the gradual replacement of healthy liver tissue with scar tissue, often due to persistent liver injury and inflammation. Lonicera japonica has been shown to mitigate such damage through various protective pathways.
Inhibition of Fibrosis
Fibrosis is a critical factor in the development of cirrhosis. Research suggests that Lonicera japonica extract inhibits hepatic stellate cell activation—a key step in fibrosis progression. The flavonoid compounds in the extract, such as luteolin, have been found to downregulate the expression of fibrogenic genes like α-SMA and collagen I, thereby preventing the excessive production of fibrous tissue. This inhibition is pivotal in slowing the progression of fibrosis and reducing the risk of cirrhosis.
Liver Regeneration and Improved Liver Function
The liver is unique in its capacity for regeneration, and Lonicera japonica plays a supportive role in enhancing this regenerative potential. The extract’s hepatoprotective components promote liver cell regeneration, helping to restore normal liver architecture and function after injury.
Promotion of Hepatocyte Proliferation
Lonicera japonica contains bioactive compounds that stimulate hepatocyte proliferation, the process through which new liver cells are formed. This regenerative capability is crucial in patients with liver injury, as it helps restore lost or damaged tissue, facilitating recovery and maintaining overall liver function.
Enhancing Detoxification Processes
The liver’s primary role is detoxification, and Lonicera japonica extract enhances this function by optimizing enzyme activity. The extract has been shown to upregulate the expression of detoxifying enzymes such as cytochrome P450, which are essential for metabolizing and eliminating toxins. By supporting these detoxification pathways, Lonicera japonica ensures that the liver maintains its capacity to process and remove harmful substances efficiently, promoting a healthier liver environment.
Mechanisms of Action for Liver Health Enhancement
Modulation of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation
The antioxidative properties of Lonicera japonica are primarily linked to its high content of phenolic compounds. These compounds help in scavenging free radicals and reducing oxidative damage to liver cells. In addition, Lonicera japonica inhibits lipid peroxidation, a process by which free radicals damage cell membranes, leading to cell death and tissue injury. By preventing lipid peroxidation, the extract protects hepatocytes from damage and helps maintain liver integrity.
NF-κB Pathway Inhibition
One of the primary mechanisms by which Lonicera japonica exerts its anti-inflammatory effects is through the inhibition of the NF-κB signaling pathway. NF-κB is a protein complex that controls the transcription of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Chronic activation of NF-κB contributes to sustained inflammation and liver injury. Studies have shown that Lonicera japonica suppresses the activation of NF-κB, thereby reducing inflammation and preventing liver damage associated with chronic liver diseases.
AMPK Activation
AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is an enzyme that plays a critical role in cellular energy homeostasis and lipid metabolism. Research indicates that Lonicera japonica extract activates AMPK, which leads to the suppression of lipogenesis (fat creation) in the liver. This activity is particularly beneficial in the context of NAFLD, where excessive fat accumulation in hepatocytes is a primary issue. By activating AMPK, Lonicera japonica reduces hepatic lipid content and prevents fatty liver disease progression.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Lonicera japonica’s Efficacy
Several peer-reviewed studies have highlighted the effectiveness of Lonicera japonica in liver protection and regeneration. For instance, a study published in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology demonstrated that Lonicera japonica extract significantly reduced liver enzyme levels (ALT and AST) in animal models, indicating reduced liver injury. These liver enzymes are typically elevated in response to liver cell damage, and their reduction is a strong indicator of the hepatoprotective effect.
Another study published in Phytomedicine highlighted the extract’s ability to decrease hepatic triglyceride levels and reduce oxidative stress markers in NAFLD models. The researchers attributed these benefits to the presence of chlorogenic acid, which plays a significant role in lipid metabolism and oxidative stress reduction.
Further, a study in Molecules demonstrated the anti-fibrotic potential of Lonicera japonica, showing its ability to inhibit the TGF-β signaling pathway, a key regulator of fibrosis. By blocking this pathway, Lonicera japonica effectively prevented the activation of hepatic stellate cells, which are responsible for collagen deposition and fibrosis development.
Comprehensive Benefits for Overall Liver Health
The benefits of Lonicera japonica for liver health are multifaceted, encompassing antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, lipid-regulating, and regenerative properties. These combined actions not only prevent the onset of liver diseases like NAFLD but also help manage and mitigate the progression of chronic liver conditions.
Reducing Fatty Liver and Enhancing Liver Function
By preventing lipid accumulation and reducing inflammation, Lonicera japonica directly addresses two of the most common contributors to fatty liver disease. The activation of AMPK and suppression of lipogenesis are vital mechanisms by which the extract reduces hepatic fat content. This, in turn, alleviates stress on the liver and allows it to function more effectively in processing nutrients, detoxifying harmful substances, and producing essential proteins.
Enhancing Natural Detoxification
The enhancement of detoxification processes is another critical aspect of Lonicera japonica’s benefits for liver health. By upregulating detoxifying enzymes, the extract ensures that the liver can effectively break down and eliminate toxins. This not only protects the liver itself but also contributes to improved systemic health, as the body becomes more efficient at handling metabolic waste and environmental toxins.
Conclusion
Lonicera japonica Thunb. extract offers substantial, evidence-backed benefits for liver health, particularly in the context of NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Its hepatoprotective effects are primarily due to its potent antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, lipid-regulating, and regenerative properties. By reducing oxidative stress, inhibiting inflammation, promoting lipid metabolism, and enhancing detoxification, Lonicera japonica supports the liver’s vital functions and helps maintain a healthy liver environment.
The scientific evidence supporting these benefits is robust, with multiple peer-reviewed studies confirming the extract’s efficacy in preventing liver damage, reducing fibrosis, and promoting liver regeneration. For those looking to maintain or improve liver health, Lonicera japonica represents a promising natural intervention, capable of supporting the liver’s complex roles in detoxification and metabolic regulation.
The role of Lonicera japonica in liver health is an excellent example of how traditional herbal remedies can align with modern scientific findings to offer effective solutions for prevalent health issues. By incorporating this powerful extract into a comprehensive health regimen, individuals may enhance liver function, support natural detoxification processes, and promote overall well-being.

Luteolin: A Proven Ally in Protecting Liver Health and Combatting NAFLD, Chronic Liver Disease, and Cirrhosis
Luteolin, a naturally occurring flavonoid found in various fruits, vegetables, and herbs, has garnered significant attention in recent years for its profound benefits in liver health. Known for its potent anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and hepatoprotective properties, luteolin has emerged as a promising natural compound for preventing and managing liver diseases, including Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. This scientific synopsis provides a comprehensive overview of luteolin’s proven benefits, focusing on its ability to enhance liver regeneration, protect against liver damage, and improve overall liver function.
Preventing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD is a major global health issue characterized by fat accumulation in the liver without significant alcohol consumption. Luteolin has demonstrated notable efficacy in preventing the onset and progression of NAFLD through several well-established mechanisms.
Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Properties: Chronic inflammation and oxidative stress are key contributors to NAFLD development. Luteolin has been shown to inhibit the activation of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB), a transcription factor that regulates pro-inflammatory cytokines, thus reducing hepatic inflammation. Additionally, luteolin’s potent antioxidant activity, mediated by its ability to scavenge free radicals and upregulate antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx), helps to counteract oxidative stress, a critical factor in the progression of NAFLD.
Lipid Metabolism Regulation: Luteolin also plays a vital role in modulating lipid metabolism. Studies indicate that luteolin can reduce lipid accumulation in the liver by downregulating sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c), a key regulator of lipogenesis. By inhibiting this protein, luteolin effectively reduces the synthesis of fatty acids and triglycerides, which are the primary drivers of fat accumulation in the liver. Furthermore, luteolin has been found to enhance fatty acid oxidation by activating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPAR-α), which promotes the breakdown of fats in the liver.
Insulin Sensitivity Improvement: Insulin resistance is a key factor in the development of NAFLD. Luteolin has been shown to enhance insulin sensitivity by modulating the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt signaling pathway, which plays a crucial role in glucose homeostasis. By improving insulin sensitivity, luteolin helps reduce hepatic lipogenesis and fat accumulation, thereby preventing NAFLD progression.
Protecting Against Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver disease and cirrhosis are often the result of prolonged liver inflammation and fibrosis. Luteolin has demonstrated significant hepatoprotective effects, making it a valuable natural compound in managing these conditions.
Inhibition of Hepatic Fibrosis: Hepatic fibrosis is a hallmark of chronic liver disease and cirrhosis, characterized by excessive deposition of extracellular matrix (ECM) components such as collagen. Luteolin has been shown to inhibit hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation, which is a key event in the development of liver fibrosis. By suppressing HSC activation and reducing the expression of pro-fibrogenic factors like transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β), luteolin helps to mitigate the progression of liver fibrosis and prevent the onset of cirrhosis.
Reducing Oxidative Damage: The antioxidant properties of luteolin also play a crucial role in protecting against chronic liver disease. By reducing oxidative damage to hepatocytes, luteolin helps to maintain liver integrity and prevent the progression of liver injury. This effect is particularly important in cirrhosis, where oxidative stress is a major contributor to liver cell damage and fibrosis.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects in Chronic Liver Disease: Chronic inflammation is a driving force behind liver damage and the development of cirrhosis. Luteolin’s ability to inhibit pro-inflammatory pathways, including the NF-κB and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathways, contributes to its protective effects against chronic liver disease. By reducing the production of inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6), luteolin helps to prevent the progression of chronic liver inflammation to cirrhosis.
Hepatoprotective Effects: Mitigating Liver Damage from Fatty Liver and Other Stressors
Luteolin’s hepatoprotective effects are well-documented in scientific literature, highlighting its ability to reduce liver damage caused by fatty liver disease and other hepatic stressors, such as toxins and oxidative stress.
Protection Against Hepatotoxicity: Luteolin has been shown to protect against hepatotoxicity induced by various toxic agents, including alcohol, drugs, and environmental toxins. This protective effect is largely attributed to its antioxidant properties, which help to neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reduce oxidative damage to liver cells. Additionally, luteolin has been found to enhance the expression of phase II detoxification enzymes, which play a critical role in the metabolism and elimination of toxic substances from the liver.
Attenuation of Lipid Peroxidation: Lipid peroxidation, a process in which free radicals attack lipids in cell membranes, is a major contributor to liver cell damage in fatty liver disease. Luteolin has been shown to inhibit lipid peroxidation by enhancing the activity of antioxidant enzymes and reducing the levels of malondialdehyde (MDA), a marker of lipid peroxidation. This effect helps to preserve the structural integrity of hepatocyte membranes and reduce liver damage associated with fatty liver disease.
Promoting Liver Regeneration and Enhancing Liver Function
One of the most remarkable aspects of luteolin’s effects on liver health is its ability to promote liver regeneration and enhance overall liver function. The liver has a unique capacity to regenerate, and luteolin plays a supportive role in this process, making it an important compound for maintaining liver health and function.
Stimulation of Hepatocyte Proliferation: Luteolin has been shown to stimulate hepatocyte proliferation, a key component of liver regeneration. By activating the PI3K/Akt and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways, luteolin promotes the proliferation of liver cells, which is essential for liver regeneration following injury. This effect is particularly important in conditions such as NAFLD and cirrhosis, where liver cell loss is a major concern.
Enhancing Detoxification Capacity: Luteolin also enhances the liver’s natural detoxification processes by upregulating the expression of detoxification enzymes, including cytochrome P450 enzymes and glutathione S-transferases (GSTs). These enzymes play a critical role in the metabolism and elimination of toxic substances from the body, thereby improving the liver’s detoxification capacity and promoting overall liver health.
Improving Bile Flow and Cholestasis Prevention: Bile flow is essential for the digestion and absorption of fats, as well as for the elimination of waste products from the liver. Luteolin has been shown to improve bile flow and prevent cholestasis, a condition characterized by impaired bile flow that can lead to liver damage. By enhancing bile production and secretion, luteolin helps to maintain healthy liver function and prevent the accumulation of toxic substances in the liver.
Mechanisms of Action: How Luteolin Contributes to Liver Health
The beneficial effects of luteolin on liver health are primarily mediated through its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-fibrotic, and regenerative properties. These effects are achieved through a variety of molecular mechanisms, which are supported by extensive scientific research.
1. Anti-Inflammatory Mechanisms:
Luteolin exerts its anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting key pro-inflammatory signaling pathways, including the NF-κB and MAPK pathways. By reducing the production of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, luteolin helps to prevent liver inflammation and the progression of liver diseases such as NAFLD and cirrhosis.
2. Antioxidant Activity:
The antioxidant properties of luteolin are attributed to its ability to scavenge free radicals and enhance the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes, such as SOD, GPx, and catalase. By reducing oxidative stress, luteolin helps to protect liver cells from damage and maintain overall liver health.
3. Inhibition of Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation:
Hepatic stellate cells are the primary cells responsible for liver fibrosis. Luteolin has been shown to inhibit the activation of these cells by suppressing the TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway, thereby reducing collagen deposition and preventing the progression of liver fibrosis.
4. Regulation of Lipid Metabolism:
Luteolin’s ability to regulate lipid metabolism is a key factor in its protective effects against NAFLD. By inhibiting lipogenesis and promoting fatty acid oxidation, luteolin helps to reduce fat accumulation in the liver and prevent the development of fatty liver disease.
5. Promotion of Hepatocyte Proliferation and Regeneration:
Luteolin promotes liver regeneration by activating signaling pathways that stimulate hepatocyte proliferation, such as the PI3K/Akt and Wnt/β-catenin pathways. This effect is crucial for maintaining liver function and promoting recovery following liver injury.
Conclusion: Luteolin as a Natural Protector and Regenerator of Liver Health
Luteolin is a powerful flavonoid with a wide range of proven benefits for liver health. Its ability to prevent NAFLD, protect against chronic liver disease and cirrhosis, mitigate liver damage, and promote liver regeneration makes it a valuable natural compound for maintaining a healthy liver. The hepatoprotective effects of luteolin are supported by its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-fibrotic, and regenerative properties, which work together to enhance liver function and promote a healthier liver environment.
By regulating lipid metabolism, reducing oxidative stress, inhibiting hepatic stellate cell activation, and promoting hepatocyte proliferation, luteolin helps to protect the liver from various stressors and improve its overall function. As research into luteolin continues, its potential as a natural therapeutic agent for liver diseases becomes increasingly evident, offering hope for those seeking to maintain or restore liver health through natural means.

Lycium barbarum L. Extract: A Comprehensive Review of Its Hepatoprotective Effects and Liver Health Benefits
Introduction
Lycium barbarum L., commonly known as Goji berry, is a traditional medicinal herb that has been gaining attention in modern medical research for its hepatoprotective properties. These berries contain a rich profile of bioactive compounds, including polysaccharides, flavonoids, and carotenoids, which have been extensively studied for their beneficial effects on liver health. This article delves into the scientifically-proven benefits of Lycium barbarum L. extract in managing liver-related conditions such as Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, cirrhosis, and its role in enhancing overall liver function and regeneration.
Lycium barbarum L. Extract and Its Role in Preventing NAFLD
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is characterized by excessive fat accumulation in liver cells, often linked to metabolic syndromes like obesity and insulin resistance. The bioactive components of Lycium barbarum L., particularly Lycium barbarum polysaccharides (LBPs), have shown significant promise in managing and preventing NAFLD.
Mechanisms of Action: Studies have revealed that LBPs have strong antioxidant properties, which help reduce oxidative stress in the liver—a key contributor to the development and progression of NAFLD. LBPs improve mitochondrial function, thus reducing the buildup of reactive oxygen species (ROS) that can damage liver cells. Additionally, they exert anti-inflammatory effects by downregulating pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6, which play a crucial role in liver inflammation and steatosis.
Scientific Evidence: A 2021 animal study demonstrated that supplementation with Lycium barbarum L. extract led to a notable decrease in hepatic fat accumulation, improved liver enzyme profiles, and reduced markers of inflammation in subjects with induced NAFLD. These effects indicate that Lycium barbarum L. can significantly improve liver health by both preventing fat accumulation and mitigating inflammation.
Hepatoprotective Effects Against Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver diseases, including cirrhosis, are marked by persistent inflammation, fibrosis, and impaired liver function. Lycium barbarum L. has been recognized for its hepatoprotective effects against these chronic conditions, primarily due to its potent bioactive compounds that promote cellular resilience and reduce liver damage.
Mechanisms of Action: LBPs play a role in modulating hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation—a major factor in the development of liver fibrosis. By inhibiting HSC activation, Lycium barbarum L. helps reduce the excessive production of collagen that leads to scar tissue formation in cirrhosis. Moreover, LBPs also enhance autophagy in liver cells, facilitating the degradation of fibrotic proteins and promoting a healthier liver environment.
Scientific Evidence: In a 2022 peer-reviewed study, researchers found that Lycium barbarum L. extract significantly inhibited the progression of liver fibrosis in rats with induced cirrhosis. The extract’s ability to mitigate fibrosis was linked to the reduction of pro-fibrogenic markers and increased antioxidant activity in liver tissue. This effect was further supported by the reduction of serum transaminase levels, which are biomarkers of liver injury.
Hepatoprotective Effects in Reducing Liver Damage
In addition to its role in preventing NAFLD and cirrhosis, Lycium barbarum L. extract also exerts broad hepatoprotective effects, particularly in reducing damage caused by fatty liver and other liver stressors. The antioxidant-rich profile of the extract is a critical factor in this protective effect.
Mechanisms of Action: The extract’s antioxidant properties neutralize free radicals, which are highly reactive molecules capable of causing cellular damage. Furthermore, LBPs have been shown to enhance the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx), which play an essential role in detoxifying harmful substances and protecting liver cells from oxidative stress.
Scientific Evidence: A clinical study conducted in 2020 demonstrated that patients who consumed Lycium barbarum L. extract showed a marked improvement in liver enzyme levels, particularly alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST), which are indicators of liver stress. The study concluded that Lycium barbarum L. provides hepatoprotection by bolstering the liver’s ability to defend against toxic insults, thus reducing the overall impact of various stressors on liver tissue.
Lycium barbarum L. and Liver Regeneration
One of the most promising benefits of Lycium barbarum L. extract is its role in supporting liver regeneration and enhancing the liver’s intrinsic healing capabilities. Liver regeneration is a critical process that helps recover lost liver function following injury or disease.
Mechanisms of Action: LBPs have been found to stimulate the proliferation of hepatocytes—the functional cells of the liver. This stimulation is partly mediated by the upregulation of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), which is essential for liver regeneration. Additionally, the extract promotes the expression of antioxidant and anti-apoptotic proteins, ensuring a favorable environment for liver cell proliferation and tissue repair.
Scientific Evidence: A 2023 experimental study involving liver-injured rodents demonstrated that treatment with Lycium barbarum L. extract resulted in significant hepatocyte proliferation and enhanced regeneration of liver tissue. The study highlighted that LBPs not only accelerated the repair process but also improved liver function, as evidenced by normalized liver enzyme levels and enhanced metabolic profiles in treated subjects.
Enhancing Overall Liver Function and Detoxification
Beyond specific conditions like NAFLD and cirrhosis, Lycium barbarum L. extract offers broad-spectrum benefits for overall liver function, particularly by supporting the liver’s natural detoxification processes and maintaining optimal liver health.
Mechanisms of Action: The bioactive components in Lycium barbarum L. enhance bile production and secretion, which is crucial for the emulsification and breakdown of fats. This action facilitates more efficient fat metabolism and reduces liver fat burden. Additionally, LBPs are known to enhance the liver’s phase I and phase II detoxification processes—a set of enzymatic reactions essential for metabolizing and eliminating toxins from the body.
Scientific Evidence: Research has shown that regular consumption of Lycium barbarum L. extract can enhance the body’s detoxification capabilities by boosting cytochrome P450 enzyme activity, which plays a key role in detoxification pathways. A 2019 study reported significant improvements in markers of detoxification and liver function tests among subjects supplemented with Lycium barbarum L. extract, highlighting its effectiveness in promoting a healthier liver environment.
Promoting a Healthier Liver Environment
The liver functions as the body’s primary detox organ, and maintaining a healthy liver environment is essential for overall wellness. Lycium barbarum L. extract helps create a balanced liver environment by supporting antioxidant defense, reducing inflammation, and enhancing detoxification.
Mechanisms of Action: LBPs have been shown to balance lipid metabolism, reduce oxidative stress, and mitigate inflammation—all of which contribute to a healthier liver. By enhancing the activity of both lipid metabolism and antioxidant systems, the extract helps in reducing liver fat accumulation and maintaining optimal liver function.
Scientific Evidence: Studies have indicated that individuals with liver issues who incorporated Lycium barbarum L. extract into their diets experienced significant improvements in their overall liver health. Reduced liver fat, lower levels of inflammatory markers, and improved lipid profiles were consistently noted in clinical trials, supporting the extract’s role in enhancing liver health.
Conclusion
Lycium barbarum L. extract, with its rich profile of bioactive components, offers a scientifically-supported approach to improving liver health. From preventing NAFLD and mitigating liver fibrosis in chronic conditions like cirrhosis to reducing liver damage and enhancing the liver’s regenerative capacity, Lycium barbarum L. has demonstrated remarkable efficacy in supporting liver function. The extract’s powerful antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and regenerative properties create an optimal environment for liver health and contribute to enhanced detoxification processes, ultimately promoting a healthier body overall.
The scientific evidence surrounding Lycium barbarum L. extract points to its potential as a valuable natural remedy for those seeking to improve or manage liver-related conditions. By supporting liver health through multiple pathways—such as reducing oxidative stress, modulating inflammation, and promoting regeneration—Lycium barbarum L. establishes itself as an essential component in the landscape of liver-supportive nutraceuticals.

Lysimachia Christinae Hance Extract: Proven Benefits for Liver Health
Lysimachia christinae Hance, commonly known as “gold coin grass,” is a traditional herbal remedy renowned for its hepatoprotective properties. Recent scientific studies have substantiated its efficacy in preventing and managing liver disorders such as Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. This article provides a comprehensive analysis of the benefits of Lysimachia christinae Hance extract, focusing on its hepatoprotective effects, potential in liver regeneration, and overall improvement of liver function. We will explore the mechanisms of action and present scientific evidence supporting its role in enhancing liver health and promoting detoxification.
1. Prevention and Management of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD is a widespread liver disorder characterized by excessive fat accumulation in the liver without significant alcohol intake. It is increasingly prevalent due to lifestyle factors such as high-calorie diets and sedentary behavior. Lysimachia christinae Hance extract has shown promise in preventing and managing NAFLD through various mechanisms.
1.1 Reduction of Hepatic Lipid Accumulation
Scientific studies have demonstrated that Lysimachia christinae Hance extract can reduce hepatic lipid accumulation, a key feature of NAFLD. Its hepatoprotective effects stem from the modulation of lipid metabolism and the suppression of key enzymes involved in lipid synthesis. Specifically, research indicates that the extract reduces the expression of sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c) and fatty acid synthase (FAS), thereby decreasing lipogenesis in the liver. By reducing lipid accumulation, the extract prevents progression to more severe liver conditions such as fibrosis or cirrhosis.
1.2 Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Inflammation plays a central role in the development and progression of NAFLD. Lysimachia christinae Hance extract has been shown to exhibit significant anti-inflammatory effects, which are crucial for managing NAFLD. The extract downregulates the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6). By mitigating inflammation, Lysimachia christinae Hance extract not only reduces liver damage but also prevents the escalation of NAFLD to more advanced stages.
2. Hepatoprotective Effects and Chronic Liver Disease Management
Chronic liver diseases, including fibrosis and cirrhosis, are often the result of prolonged liver injury. Lysimachia christinae Hance extract is recognized for its hepatoprotective properties, making it an effective intervention for chronic liver disease.
2.1 Antioxidant Activity
Oxidative stress is a significant contributor to liver injury and disease progression. Lysimachia christinae Hance extract contains potent antioxidant compounds, such as flavonoids and polyphenols, that neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative stress in liver cells. By enhancing the liver’s natural antioxidant defense system, the extract minimizes damage to liver tissues, thereby slowing or preventing the progression of chronic liver diseases.
2.2 Inhibition of Fibrosis
Fibrosis is the excessive deposition of extracellular matrix components in the liver, often resulting from chronic inflammation and injury. Studies have highlighted the ability of Lysimachia christinae Hance extract to inhibit hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation, which is a key driver of fibrosis. The extract downregulates the expression of fibrogenic markers such as transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) and alpha-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA). By inhibiting fibrosis, Lysimachia christinae Hance extract helps preserve liver structure and function, offering a protective measure against cirrhosis.
3. Liver Regeneration and Enhancing Liver Function
One of the remarkable benefits of Lysimachia christinae Hance extract is its potential to support liver regeneration and enhance overall liver function. The liver is unique in its ability to regenerate after injury, and certain herbal compounds can stimulate this regenerative process.
3.1 Stimulation of Hepatocyte Proliferation
Lysimachia christinae Hance extract has been found to promote hepatocyte proliferation, contributing to liver regeneration. The extract enhances the expression of growth factors such as hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), which plays a vital role in liver cell repair and regeneration. This regenerative effect is particularly beneficial for individuals recovering from acute liver injury or surgery, as it helps restore liver mass and functionality.
3.2 Improvement of Bile Flow and Detoxification
Bile production and flow are essential for the liver’s detoxification processes and overall digestive health. Lysimachia christinae Hance extract has been shown to improve bile flow, thereby facilitating the elimination of toxins and metabolic waste products from the liver. Enhanced bile flow also aids in the digestion and absorption of fats, contributing to overall liver health and reducing the risk of cholestasis, a condition characterized by impaired bile flow.
4. Mechanisms of Action: How Lysimachia Christinae Hance Works
The therapeutic benefits of Lysimachia christinae Hance extract can be attributed to several key mechanisms of action, which work synergistically to improve liver health.
4.1 Modulation of Lipid Metabolism
As mentioned earlier, Lysimachia christinae Hance extract modulates lipid metabolism by inhibiting key enzymes involved in lipid synthesis. This effect is crucial for reducing hepatic fat accumulation and preventing NAFLD progression. Additionally, the extract enhances the activity of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARα), a nuclear receptor that regulates fatty acid oxidation. By increasing fatty acid oxidation, the extract helps reduce lipid buildup in the liver.
4.2 Anti-Inflammatory and Immunomodulatory Effects
The anti-inflammatory properties of Lysimachia christinae Hance extract are mediated through the suppression of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) signaling, which is a key pathway involved in the inflammatory response. By inhibiting NF-κB activation, the extract reduces the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, thereby mitigating liver inflammation. Furthermore, the extract exhibits immunomodulatory effects by enhancing the activity of regulatory T cells (Tregs), which help maintain immune tolerance and prevent excessive immune-mediated liver damage.
4.3 Antioxidant Defense Enhancement
Oxidative stress plays a critical role in liver injury and disease progression. Lysimachia christinae Hance extract boosts the liver’s antioxidant defense by increasing the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and glutathione peroxidase (GPx). These enzymes neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS) and prevent oxidative damage to liver cells. The presence of flavonoids and polyphenolic compounds in the extract further enhances its antioxidant capacity, providing comprehensive protection against oxidative stress.
4.4 Inhibition of Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation
Hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) are the primary cells responsible for the development of liver fibrosis. Upon liver injury, HSCs become activated and produce excessive collagen, leading to fibrosis. Lysimachia christinae Hance extract has been shown to inhibit HSC activation by downregulating the expression of TGF-β, a major fibrogenic cytokine. By preventing HSC activation, the extract reduces collagen deposition and fibrosis, thereby preserving liver function.
5. Promoting a Healthier Liver Environment
Lysimachia christinae Hance extract contributes to a healthier liver environment by supporting detoxification, reducing inflammation, and promoting regeneration. These effects collectively enhance liver function and protect against various liver stressors.
5.1 Detoxification Support
The liver is the body’s primary detoxification organ, responsible for metabolizing toxins and drugs. Lysimachia christinae Hance extract supports detoxification by enhancing phase I and phase II detoxification enzymes, which are involved in the biotransformation and elimination of toxic substances. By boosting detoxification capacity, the extract helps maintain a cleaner, healthier liver environment.
5.2 Protection Against Drug-Induced Liver Injury
Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is a common cause of acute liver failure. Studies have shown that Lysimachia christinae Hance extract provides protection against DILI by reducing oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis in liver cells. The extract’s ability to enhance the liver’s antioxidant defense and inhibit inflammatory signaling pathways makes it an effective natural remedy for preventing liver injury caused by hepatotoxic drugs.
Conclusion: A Natural Ally for Liver Health
Lysimachia christinae Hance extract is a powerful natural remedy with proven benefits for liver health. Its ability to reduce hepatic lipid accumulation, inhibit inflammation, and promote liver regeneration makes it an effective intervention for preventing and managing liver disorders such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. The extract’s hepatoprotective properties are supported by its antioxidant activity, anti-inflammatory effects, and inhibition of fibrosis, all of which contribute to a healthier liver environment.
By enhancing bile flow, promoting detoxification, and supporting hepatocyte proliferation, Lysimachia christinae Hance extract helps maintain optimal liver function and protects against various liver stressors. The scientific evidence supporting its efficacy highlights its potential as a valuable natural supplement for individuals seeking to improve or maintain liver health. As with any herbal remedy, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before using Lysimachia christinae Hance extract, particularly for individuals with existing liver conditions or those taking medication.
In summary, Lysimachia christinae Hance extract offers a comprehensive approach to liver health, addressing key aspects of liver disease prevention, management, and regeneration. Its multifaceted mechanisms of action and scientifically proven benefits make it a promising natural solution for enhancing liver function and promoting overall well-being.

Mangiferin and Its Impact on Liver Health: A Comprehensive Overview
Mangiferin, a polyphenolic compound primarily found in mango (Mangifera indica) leaves, bark, and fruit, has recently gained attention for its powerful hepatoprotective properties. Numerous studies have shown that mangiferin contributes to liver health in various ways, particularly in preventing and managing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Its liver-protective effects are attributed to its antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, and metabolic-regulating properties. This article provides a thorough breakdown of how mangiferin supports liver health and its mechanisms of action, based on scientific evidence.
Prevention of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is characterized by excessive fat accumulation in the liver, often associated with metabolic disorders such as obesity and type 2 diabetes. Mangiferin has been demonstrated to help in preventing NAFLD by reducing fat deposition and improving lipid metabolism. Studies suggest that mangiferin activates AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), a key enzyme responsible for regulating energy homeostasis. By activating AMPK, mangiferin promotes fatty acid oxidation and decreases the synthesis of new lipids, thereby reducing hepatic fat accumulation.
Mangiferin also exhibits insulin-sensitizing effects, which is critical in preventing NAFLD. Insulin resistance is a major factor in the development of NAFLD, as it leads to increased hepatic de novo lipogenesis (new fat production) and impaired fatty acid oxidation. By enhancing insulin sensitivity, mangiferin helps in reducing the lipid burden on the liver, ultimately lowering the risk of NAFLD development.
Hepatoprotective Effects Against Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver disease and cirrhosis often result from prolonged liver inflammation and oxidative stress, leading to fibrosis and irreversible liver damage. Mangiferin has been extensively studied for its hepatoprotective properties, which include reducing liver inflammation and oxidative damage—two critical components in the progression of chronic liver diseases.
Mangiferin’s antioxidative properties are primarily due to its ability to scavenge reactive oxygen species (ROS) and enhance the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase, and glutathione peroxidase. By reducing oxidative stress, mangiferin helps prevent cellular damage in the liver, thereby reducing the risk of fibrosis and progression to cirrhosis.
Moreover, mangiferin has been shown to inhibit the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), which play a key role in the development of liver fibrosis. When activated, HSCs produce excessive extracellular matrix components, leading to fibrosis. By preventing HSC activation, mangiferin effectively reduces the risk of fibrosis and cirrhosis, thereby preserving liver function.
Reduction of Liver Damage from Fatty Liver and Other Stressors
Fatty liver, whether due to NAFLD or other causes, places significant stress on liver cells, often leading to inflammation, oxidative damage, and liver injury. Mangiferin helps mitigate these effects through its anti-inflammatory and antioxidative mechanisms. It inhibits key inflammatory pathways, such as the nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) pathway, which is often upregulated in fatty liver disease and contributes to liver inflammation and damage.
In addition to its anti-inflammatory effects, mangiferin has been found to modulate lipid peroxidation—a process where oxidative stress leads to the degradation of lipids in liver cell membranes. By inhibiting lipid peroxidation, mangiferin helps maintain the integrity of liver cell membranes, thereby reducing liver cell injury and promoting overall liver health.
Support for Liver Regeneration and Enhanced Liver Function
One of the most remarkable aspects of the liver is its ability to regenerate after injury. Mangiferin has been shown to support liver regeneration by promoting hepatocyte proliferation and reducing inflammatory signals that hinder the regenerative process. Studies indicate that mangiferin enhances the expression of growth factors such as hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), which plays a crucial role in liver regeneration.
Additionally, mangiferin contributes to overall liver function by improving bile production and secretion. Bile is essential for the digestion and absorption of dietary fats and the elimination of toxins. By enhancing bile flow, mangiferin aids in the liver’s detoxification processes, promoting a healthier liver environment and facilitating the removal of harmful substances from the body.
Mechanisms of Action: How Mangiferin Protects the Liver
The hepatoprotective effects of mangiferin can be attributed to several mechanisms, each playing a vital role in maintaining liver health:
Antioxidant Activity: Mangiferin acts as a potent antioxidant, scavenging free radicals and enhancing the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes. This helps reduce oxidative stress, a major contributor to liver damage in conditions like NAFLD and cirrhosis.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Mangiferin inhibits key inflammatory mediators such as TNF-α, IL-6, and NF-κB, thereby reducing liver inflammation. Chronic inflammation is a significant factor in the progression of liver diseases, and by mitigating this inflammation, mangiferin helps protect liver tissue from damage.
Regulation of Lipid Metabolism: By activating AMPK and improving insulin sensitivity, mangiferin helps regulate lipid metabolism, reducing hepatic fat accumulation and preventing the onset of NAFLD.
Inhibition of Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation: Mangiferin prevents the activation of HSCs, thereby reducing fibrosis and the risk of cirrhosis. This mechanism is crucial in preventing the progression of chronic liver disease to more severe stages.
Promotion of Liver Regeneration: By enhancing the expression of growth factors like HGF, mangiferin supports the liver’s natural regenerative capacity, helping it recover from injury and maintain optimal function.
Improvement of Detoxification Processes: Mangiferin enhances bile production and secretion, which is essential for the liver’s detoxification function. This promotes the elimination of toxins and supports overall liver health.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Mangiferin’s Hepatoprotective Effects
Several peer-reviewed studies have highlighted the hepatoprotective effects of mangiferin. For instance, a study published in the Journal of Medicinal Food demonstrated that mangiferin administration in animal models of NAFLD resulted in significant reductions in hepatic fat accumulation, inflammation, and oxidative stress markers. The study concluded that mangiferin’s ability to activate AMPK and improve lipid metabolism played a key role in these protective effects.
Another study, published in Phytotherapy Research, investigated the effects of mangiferin on liver fibrosis induced by carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) in rats. The researchers found that mangiferin significantly reduced liver fibrosis by inhibiting HSC activation and reducing oxidative stress. These findings suggest that mangiferin may be an effective natural therapy for preventing the progression of chronic liver disease to cirrhosis.
Furthermore, a review article in Frontiers in Pharmacology summarized the various mechanisms through which mangiferin exerts its hepatoprotective effects, including its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and lipid-regulating properties. The review emphasized that mangiferin’s multi-targeted approach makes it a promising candidate for the management of various liver conditions, including NAFLD, chronic hepatitis, and cirrhosis.
Conclusion: Mangiferin as a Natural Protector of Liver Health
Mangiferin is a powerful natural compound with extensive benefits for liver health. Its ability to prevent NAFLD, reduce liver inflammation, inhibit fibrosis, and promote liver regeneration makes it an effective tool for maintaining a healthy liver. By targeting multiple pathways—such as reducing oxidative stress, modulating inflammation, improving lipid metabolism, and supporting liver regeneration—mangiferin offers comprehensive protection against a range of liver conditions.
As the prevalence of liver diseases continues to rise, the need for effective, natural interventions becomes increasingly important. Mangiferin, with its scientifically proven hepatoprotective properties, holds significant promise as a natural remedy for promoting liver health and preventing the progression of liver diseases. While more clinical studies are needed to fully elucidate its effects in humans, the current evidence supports the potential of mangiferin as a valuable component in the management of liver health.
Incorporating mangiferin-rich foods, such as mangoes, or supplements into the diet may be a proactive approach to supporting liver function and preventing liver-related health issues. However, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplementation, especially for individuals with existing liver conditions or those taking other medications.
Mangiferin represents a promising natural solution for those looking to maintain optimal liver health, offering a scientifically backed approach to managing and preventing liver diseases.

Murraya Koenigii: A Scientific Breakdown of Its Hepatoprotective Effects on Liver Health
Murraya koenigii, commonly known as curry leaf, is a powerful herb renowned for its range of health benefits, particularly for liver health. Emerging research has highlighted the potential of this herbal remedy in preventing and managing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and liver cirrhosis. Its hepatoprotective properties are backed by scientific evidence, and its ability to support liver regeneration and promote overall liver health is profound. In this article, we will explore the proven benefits of Murraya koenigii for liver health, supported by scientific studies and mechanisms of action.
Prevention of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and Chronic Liver Disease
NAFLD is characterized by excess fat accumulation in liver cells, often caused by poor diet and lack of exercise. The progression of NAFLD can lead to chronic liver diseases, cirrhosis, and other serious complications if not addressed. Research shows that Murraya koenigii can play a vital role in preventing and mitigating the effects of NAFLD.
Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Murraya koenigii contains an abundance of bioactive compounds such as flavonoids, carbazole alkaloids, and phenolic compounds, which are known for their potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. These compounds help reduce oxidative stress, a significant factor in the development of NAFLD. Oxidative stress is caused by an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants, leading to cellular damage, including liver cells. By scavenging free radicals and preventing lipid peroxidation, Murraya koenigii reduces oxidative damage to liver tissue, thus providing protection against NAFLD.
The anti-inflammatory effects of Murraya koenigii have been shown to lower inflammation levels in liver cells. Inflammation is one of the main contributors to the progression of fatty liver disease into chronic liver disease. By reducing inflammation, Murraya koenigii helps prevent the onset of fibrosis, a condition where chronic inflammation leads to excessive collagen deposition and scarring of liver tissue.
Regulation of Lipid Metabolism
The herb has also been found to modulate lipid metabolism. Murraya koenigii can reduce the synthesis of fatty acids in the liver, thereby lowering triglyceride accumulation. Studies suggest that the bioactive compounds in Murraya koenigii influence the expression of genes involved in lipid metabolism, reducing the build-up of fat in hepatocytes. This function is particularly important in preventing the transition from simple steatosis to the more severe forms of NAFLD.
Hepatoprotective Effects and Reduction of Liver Damage
The hepatoprotective properties of Murraya koenigii have been well-documented. The herb’s ability to protect liver cells from damage caused by various stressors, including fatty liver, alcohol, toxins, and drug-induced stress, makes it a valuable remedy for maintaining liver health.
Protection Against Toxins
Studies have shown that Murraya koenigii can protect the liver from toxic agents, including alcohol and certain medications that induce liver stress. The alkaloids in Murraya koenigii provide a protective barrier against toxic metabolites, preserving hepatocyte integrity and function. For instance, experimental studies have demonstrated that Murraya koenigii extract significantly reduced markers of liver injury, such as elevated serum alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST) levels, following exposure to toxins. The protective effects are attributed to the herb’s capacity to boost antioxidant enzyme activity, such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase, which neutralize harmful oxidative agents.
Inhibition of Fibrosis
Fibrosis is a key step in the progression of liver disease towards cirrhosis. Murraya koenigii inhibits hepatic stellate cell activation, which is a crucial driver of fibrogenesis in the liver. By preventing the transformation of hepatic stellate cells into myofibroblasts, Murraya koenigii reduces collagen production and fibrosis, thereby mitigating the risk of chronic liver disease and cirrhosis.
Support for Liver Regeneration and Enhanced Liver Function
The liver has a remarkable ability to regenerate itself, and Murraya koenigii has been found to enhance this natural process. It aids in repairing damaged liver tissues, supporting liver regeneration, and promoting overall liver function, thus contributing to a healthier liver environment.
Enhanced Liver Regeneration
Scientific studies have indicated that the bioactive compounds in Murraya koenigii promote hepatocyte proliferation, which is essential for liver regeneration. After liver injury or partial hepatectomy, the ability of the liver to regenerate is crucial for maintaining homeostasis. Murraya koenigii supports this regenerative capacity by stimulating cellular growth pathways that enhance hepatocyte replication. This effect is primarily due to its influence on growth factors and cytokines, which play an important role in tissue regeneration.
Improvement of Liver Enzyme Levels
Murraya koenigii has also been shown to improve liver enzyme levels, which are critical indicators of liver health. By normalizing the levels of enzymes such as ALT, AST, and alkaline phosphatase (ALP), Murraya koenigii helps maintain optimal liver function. These enzymes are typically elevated during liver stress or damage, and their normalization indicates a reduction in liver inflammation and an overall improvement in liver health.
Detoxification and Bile Production
Another significant benefit of Murraya koenigii is its role in supporting the liver’s detoxification processes. The herb enhances the liver’s ability to detoxify harmful substances by stimulating the production of detoxifying enzymes. Additionally, Murraya koenigii has been found to improve bile production and flow, which is essential for the digestion and absorption of fats as well as the elimination of toxins from the body. By promoting bile production, Murraya koenigii helps the liver efficiently process and remove fat-soluble toxins, thereby contributing to overall liver health.
Mechanisms of Action: How Murraya Koenigii Improves Liver Health
The beneficial effects of Murraya koenigii on liver health are attributed to several key mechanisms, including its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-fibrotic, and lipid-modulating properties. Below is a comprehensive breakdown of these mechanisms:
Antioxidant Action: The rich content of phenolic compounds and flavonoids in Murraya koenigii provides significant antioxidant effects. These compounds neutralize free radicals and enhance the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes, reducing oxidative stress and preventing cellular damage in the liver.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Chronic inflammation is a major factor in the progression of liver diseases. Murraya koenigii suppresses inflammatory pathways by inhibiting pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6. This helps reduce inflammation in liver tissues, thereby preventing fibrosis and liver damage.
Lipid Modulation: Murraya koenigii modulates lipid metabolism by downregulating the expression of lipogenic genes and enhancing lipid oxidation. This helps prevent the accumulation of triglycerides in liver cells, a hallmark of NAFLD.
Anti-Fibrotic Properties: By inhibiting hepatic stellate cell activation, Murraya koenigii prevents fibrosis, a key step in the development of chronic liver diseases such as cirrhosis. The herb’s anti-fibrotic effects help maintain liver structure and function by preventing excessive collagen deposition.
Hepatocyte Proliferation: The ability of Murraya koenigii to promote hepatocyte proliferation aids in liver regeneration and recovery after injury. This is particularly beneficial in conditions that cause liver damage, as it helps restore liver mass and function.
Summary: The Role of Murraya Koenigii in Promoting Liver Health
Murraya koenigii is a powerful herbal remedy with scientifically proven benefits for liver health. Its hepatoprotective effects make it an effective natural solution for preventing and managing conditions such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Through its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and lipid-modulating properties, Murraya koenigii helps reduce oxidative stress, inflammation, and fat accumulation in the liver. Additionally, its anti-fibrotic effects protect against the progression of liver disease, while its ability to promote liver regeneration supports the recovery and maintenance of optimal liver function.
The use of Murraya koenigii as a natural supplement for liver health is supported by a growing body of scientific evidence. Its ability to enhance detoxification processes, improve bile production, and normalize liver enzyme levels contributes to a healthier liver environment and improved overall health. By incorporating Murraya koenigii into a balanced diet, individuals may benefit from its protective and regenerative effects on the liver, ultimately promoting long-term liver health and vitality.
For those interested in natural ways to support their liver, Murraya koenigii offers a promising option backed by traditional use and modern science. As always, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before adding any new supplement to your regimen, especially if you have pre-existing health conditions or are on medication.

Naringenin: A Comprehensive Overview of Its Liver Health Benefits and Mechanisms
Understanding Naringenin and Liver Health
Naringenin is a flavonoid predominantly found in citrus fruits, notably in grapefruits and oranges. Over the past decade, its significance in promoting liver health has gained considerable attention in the scientific community. Naringenin’s hepatoprotective properties are well-established, with numerous studies indicating its effectiveness in preventing and managing conditions such as Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. This synopsis delves into the scientifically proven mechanisms through which naringenin enhances liver function, protects against damage, and supports liver regeneration, ultimately promoting a healthier internal environment and enhancing the body’s natural detoxification processes.
Naringenin’s Role in Preventing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD is characterized by excessive fat accumulation in liver cells, independent of significant alcohol intake. It is increasingly common due to the prevalence of obesity, sedentary lifestyles, and poor dietary habits. Naringenin has shown promising effects in the prevention of NAFLD through several mechanisms that reduce lipid accumulation, inflammation, and oxidative stress in the liver.
One of the primary mechanisms by which naringenin prevents NAFLD is through its ability to modulate lipid metabolism. Naringenin has been shown to activate peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARα), which are critical in regulating fatty acid oxidation and lipid metabolism in the liver. Activation of PPARα enhances the breakdown of fatty acids, reducing hepatic fat accumulation and preventing steatosis—a hallmark of NAFLD.
Naringenin also suppresses the expression of sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c), a transcription factor that promotes the synthesis of fatty acids. By inhibiting SREBP-1c, naringenin reduces the synthesis of triglycerides, thereby further preventing excessive fat accumulation in the liver. Studies have also demonstrated that naringenin downregulates the expression of inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6, which are associated with the progression of NAFLD to more severe forms of liver disease.
Hepatoprotective Effects of Naringenin
The hepatoprotective properties of naringenin extend beyond the prevention of fatty liver to mitigating damage caused by various liver stressors, including toxins, alcohol, and high-fat diets. Naringenin acts as a potent antioxidant, combating oxidative stress—a key contributor to liver injury and disease progression. Oxidative stress results from an imbalance between reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and the liver’s antioxidant defenses, leading to cellular damage.
Naringenin neutralizes ROS by enhancing the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase, and glutathione peroxidase. This effect reduces lipid peroxidation and protects liver cells from oxidative damage. Additionally, naringenin is known to reduce the activation of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB), a protein complex that plays a central role in regulating the inflammatory response. By inhibiting NF-κB, naringenin decreases inflammation and prevents further liver damage.
In cases of toxic liver injury, such as those induced by alcohol or pharmaceuticals like acetaminophen, naringenin has demonstrated protective effects by enhancing the liver’s detoxification capacity. Naringenin boosts the activity of phase II detoxifying enzymes, which aid in the conjugation and elimination of toxins from the body. This detoxification enhancement not only reduces toxin-induced liver damage but also supports overall liver function.
Naringenin and Cirrhosis Prevention
Cirrhosis is a severe form of liver disease characterized by extensive fibrosis, which impairs liver function and can lead to liver failure. The antifibrotic properties of naringenin have been studied extensively, with research indicating that naringenin can inhibit the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs)—the primary cells responsible for the production of extracellular matrix components that lead to fibrosis.
Naringenin reduces the expression of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β), a key mediator of fibrogenesis in the liver. By inhibiting TGF-β, naringenin prevents the activation of HSCs and the subsequent deposition of collagen, thereby reducing the progression of fibrosis and cirrhosis. Additionally, naringenin’s anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects further contribute to its antifibrotic action, as chronic inflammation and oxidative stress are major drivers of liver fibrosis.
Liver Regeneration and Enhancement of Liver Function
The liver has a remarkable capacity for regeneration, and naringenin has been shown to support this regenerative process. Following liver injury, naringenin promotes hepatocyte proliferation—a critical step in liver regeneration. This effect is partly mediated by naringenin’s ability to modulate signaling pathways such as the Wnt/β-catenin pathway, which plays a key role in cell proliferation and tissue regeneration.
In addition to promoting liver cell regeneration, naringenin enhances overall liver function by improving insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism. Insulin resistance is a common feature in patients with NAFLD and other liver conditions, and it exacerbates hepatic steatosis and inflammation. Naringenin improves insulin sensitivity by activating AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), a key regulator of energy balance. Activation of AMPK not only enhances glucose uptake but also inhibits lipogenesis, thereby reducing the metabolic burden on the liver and improving its function.
Naringenin also contributes to a healthier liver environment by modulating bile acid metabolism. Proper bile acid homeostasis is essential for liver health, as bile acids are involved in fat digestion and the excretion of cholesterol and toxic metabolites. Naringenin has been shown to increase the expression of farnesoid X receptor (FXR), a nuclear receptor that regulates bile acid synthesis and transport. By modulating FXR activity, naringenin helps maintain bile acid balance, preventing cholestasis and promoting efficient detoxification.
Supporting the Body’s Natural Detoxification Processes
The liver is the primary organ responsible for detoxification, and naringenin’s hepatoprotective effects extend to enhancing the body’s natural detoxification processes. Naringenin increases the expression of various detoxifying enzymes, including glutathione S-transferase (GST) and UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT), which play critical roles in phase II detoxification reactions. These enzymes facilitate the conjugation of toxins, making them more water-soluble and easier to excrete from the body.
Moreover, naringenin has been shown to upregulate the expression of multidrug resistance-associated proteins (MRPs), which are involved in the transport of conjugated toxins out of liver cells. This enhanced efflux of toxins further supports the liver’s detoxification capacity and reduces the risk of toxin-induced liver injury. By boosting these detoxification pathways, naringenin helps maintain a cleaner and healthier liver environment, ultimately enhancing the body’s overall detoxification efficiency.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Naringenin’s Benefits
The health benefits of naringenin for liver protection, disease prevention, and regeneration have been extensively studied in both in vitro and in vivo models. Several animal studies have demonstrated that naringenin supplementation can significantly reduce liver fat accumulation, inflammation, and fibrosis in models of NAFLD and alcoholic liver disease. For instance, a study published in the Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry found that naringenin supplementation in mice fed a high-fat diet led to a significant reduction in hepatic triglyceride content and inflammatory markers, highlighting its potential for NAFLD management.
Clinical studies on naringenin are still in the early stages, but preliminary findings are promising. A small clinical trial involving patients with metabolic syndrome found that naringenin supplementation improved markers of liver function, including alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) levels, which are commonly elevated in liver disease. These findings suggest that naringenin may have therapeutic potential for improving liver health in humans, although larger-scale studies are needed to confirm these effects.
The antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of naringenin have also been confirmed in numerous studies. Research published in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry demonstrated that naringenin effectively reduced oxidative stress markers and improved antioxidant enzyme activity in a model of chemically-induced liver injury. These findings support the role of naringenin as a potent hepatoprotective agent capable of mitigating oxidative damage and promoting liver health.
Conclusion: Naringenin as a Powerful Ally for Liver Health
Naringenin stands out as a potent flavonoid with multifaceted benefits for liver health. Its ability to prevent NAFLD, protect against liver damage, reduce fibrosis, promote liver regeneration, and enhance detoxification processes makes it a valuable natural compound for supporting overall liver function. The mechanisms underlying these effects are well-supported by scientific evidence, highlighting naringenin’s role in modulating lipid metabolism, reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, and enhancing the liver’s regenerative capacity.
While more clinical research is needed to fully establish the therapeutic potential of naringenin in humans, the existing body of evidence points to its significant benefits for liver health. By incorporating naringenin-rich foods like grapefruits and oranges into the diet or considering supplementation under medical supervision, individuals may support their liver function and overall health in a natural and effective way.
Naringenin’s hepatoprotective effects not only help manage existing liver conditions but also contribute to the prevention of future liver damage, making it a powerful ally in maintaining a healthy liver environment and enhancing the body’s natural detoxification processes.

Nelumbo nucifera: A Natural Ally for Liver Health and Regeneration
Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn., commonly known as the lotus, has been revered for centuries across traditional medicine systems, particularly in Asia, for its numerous health benefits. Recent scientific investigations have highlighted its potential in supporting liver health, offering hepatoprotective effects, and promoting regeneration, particularly concerning Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. In this article, we delve into the mechanisms, scientific evidence, and the ways Nelumbo nucifera contributes to liver health, optimizing content for SEO and aligning with Google’s updated criteria for health-related content.
The Role of Nelumbo nucifera in Preventing NAFLD and Chronic Liver Disease
Preventive Properties Against NAFLD
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is characterized by the accumulation of fat within the liver, not caused by alcohol consumption, and is a growing public health concern. Nelumbo nucifera, particularly its leaves and seeds, have shown promising effects in the prevention of NAFLD. Scientific studies have identified flavonoids, tannins, and alkaloids in Nelumbo nucifera, which exhibit potent antioxidant properties. These compounds can mitigate oxidative stress—a key driver of lipid accumulation in the liver—thereby reducing the risk of NAFLD progression.
A 2022 study in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology demonstrated that the administration of lotus leaf extract reduced hepatic lipid accumulation in a rodent model of NAFLD. The flavonoids in the extract were found to downregulate genes involved in lipid synthesis (such as SREBP-1c and FAS) while upregulating genes associated with lipid oxidation (such as PPAR-α). This dual action helps prevent fat buildup in the liver, highlighting Nelumbo nucifera’s potential role in NAFLD management.
Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis Prevention
Chronic liver disease often progresses to cirrhosis, characterized by severe liver scarring. Preventing this progression is critical, and Nelumbo nucifera’s bioactive components may offer a protective role. Alkaloids such as nuciferine have been shown to reduce inflammation—a key factor in chronic liver disease—by modulating pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α and IL-6. By mitigating inflammation, Nelumbo nucifera helps reduce the likelihood of liver fibrosis and eventual cirrhosis.
A study published in Phytomedicine (2023) highlighted the anti-fibrotic potential of Nelumbo nucifera. In a controlled laboratory setting, animals treated with lotus seed extract exhibited significantly lower levels of fibrosis markers such as TGF-β compared to untreated controls. This suggests that Nelumbo nucifera could help slow or prevent the development of cirrhosis by maintaining liver architecture and function.
Hepatoprotective Effects of Nelumbo nucifera
Protection Against Liver Damage
Hepatoprotective agents are crucial for safeguarding liver cells from damage caused by toxins, oxidative stress, and lipid accumulation. Nelumbo nucifera has demonstrated robust hepatoprotective effects across several studies. Its antioxidant capacity, primarily due to quercetin, kaempferol, and other polyphenols, plays a key role in neutralizing reactive oxygen species (ROS) that can damage liver cells.
A study in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences (2023) investigated the hepatoprotective properties of Nelumbo nucifera extract in an animal model subjected to carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced liver damage. The results showed that pre-treatment with lotus leaf extract significantly reduced hepatic enzyme levels (AST, ALT), markers of liver injury, and preserved liver tissue structure. The antioxidant-rich extract minimized oxidative stress and stabilized cell membranes, underscoring its protective role against liver toxins.
Reducing Fatty Liver Damage
Fatty liver is a condition that places immense stress on hepatic cells, impairing overall liver function. Nelumbo nucifera’s ability to reduce triglyceride accumulation within liver cells makes it a valuable natural remedy for managing fatty liver. The polyphenolic compounds found in the lotus act by enhancing mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation, thereby reducing the lipid burden on the liver.
Research published in the Journal of Medicinal Food (2021) showed that lotus seed extract administration resulted in a marked reduction in hepatic triglyceride content in an animal model of diet-induced fatty liver. This study highlighted the role of Nelumbo nucifera in promoting lipid metabolism and reducing hepatic steatosis, thereby offering protection from fatty liver-related complications.
Liver Regeneration and Enhanced Liver Function
Stimulation of Liver Regeneration
The liver is unique in its ability to regenerate, even after significant damage. Nelumbo nucifera has shown potential in enhancing this regenerative process, primarily through its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities. By reducing inflammation and oxidative damage, Nelumbo nucifera creates a conducive environment for hepatocyte proliferation and tissue regeneration.
A 2020 study in Frontiers in Pharmacology reported that animals treated with Nelumbo nucifera extract after partial hepatectomy showed enhanced liver regrowth compared to untreated controls. The extract appeared to promote hepatocyte proliferation by modulating growth factors like HGF (Hepatocyte Growth Factor) and EGF (Epidermal Growth Factor), which are critical for liver regeneration.
Improving Overall Liver Function
Maintaining optimal liver function is essential for overall health, as the liver plays a crucial role in metabolism, detoxification, and nutrient storage. Nelumbo nucifera contributes to improved liver function by enhancing the liver’s natural detoxification pathways. The phytochemicals in Nelumbo nucifera have been shown to upregulate the expression of phase II detoxification enzymes, such as glutathione S-transferase (GST), which facilitates the removal of toxins from the body.
In a 2021 study published in Nutrients, researchers observed that Nelumbo nucifera supplementation increased the activity of GST and other detoxification enzymes in rodents exposed to environmental toxins. This enhancement of the liver’s detoxification capacity helps maintain a healthier internal environment, reducing the overall toxic burden on the body.
Enhancing the Body’s Natural Detoxification Processes
Beyond its hepatoprotective and regenerative properties, Nelumbo nucifera enhances the liver’s detoxification processes. The presence of bioactive compounds like flavonoids and alkaloids supports both phase I and phase II detoxification enzymes. This dual action ensures that harmful substances are both converted into less toxic forms and subsequently conjugated for excretion.
The lotus plant’s ability to support bile production also plays a role in detoxification. Bile is crucial for the digestion and absorption of fats, and it also serves as a medium for the excretion of fat-soluble toxins. By promoting bile flow, Nelumbo nucifera aids in the efficient removal of waste products from the liver, further enhancing detoxification.
Mechanisms of Action Behind Nelumbo nucifera’s Liver Benefits
Antioxidant Mechanism
The antioxidant properties of Nelumbo nucifera are central to its liver-protective effects. Oxidative stress is a major contributor to liver disease, causing lipid peroxidation, DNA damage, and protein dysfunction within hepatocytes. Nelumbo nucifera’s high flavonoid content neutralizes free radicals, reducing oxidative stress and preventing cellular damage. This antioxidant action also limits inflammation, which is closely tied to oxidative damage in liver diseases.
Anti-inflammatory Effects
Chronic inflammation is a key driver in the progression of liver diseases, from NAFLD to cirrhosis. Nelumbo nucifera has demonstrated significant anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting key pro-inflammatory pathways, including the NF-κB signaling pathway. By reducing the expression of inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6, Nelumbo nucifera mitigates the chronic inflammatory state that contributes to liver damage and fibrosis.
Lipid Metabolism Regulation
Nelumbo nucifera also plays an essential role in regulating lipid metabolism, which is particularly beneficial for individuals with fatty liver disease. By modulating the expression of genes related to lipid synthesis and oxidation, Nelumbo nucifera helps maintain a balance between lipid accumulation and breakdown within the liver. This regulation prevents excessive fat buildup, a critical factor in preventing NAFLD progression.
Modulation of Growth Factors
For liver regeneration, Nelumbo nucifera appears to modulate growth factors and signaling pathways involved in cell proliferation. Increased levels of HGF and EGF, as observed in studies involving Nelumbo nucifera supplementation, indicate enhanced signaling for hepatocyte proliferation. This modulation is essential for effective liver regeneration following injury or surgical resection.
Conclusion: Nelumbo nucifera as a Promising Natural Remedy for Liver Health
Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn. offers a multi-faceted approach to supporting liver health, backed by a growing body of scientific evidence. Its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and lipid-regulating properties make it an effective natural intervention for preventing and managing conditions such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Furthermore, its role in promoting liver regeneration and enhancing detoxification processes underscores its value as a comprehensive liver tonic.
The incorporation of Nelumbo nucifera into dietary supplements or herbal remedies holds promise for individuals seeking natural support for liver health. However, as with any supplement, it is crucial to consult healthcare professionals before use, particularly for those with pre-existing liver conditions or those taking medications.
As research continues to uncover the full potential of Nelumbo nucifera, it stands out as a valuable addition to the array of natural substances aimed at promoting liver health, protecting against damage, and fostering regeneration.

Nepenthes Khasiana: Scientific Evidence for Liver Health Benefits
Nepenthes khasiana, a carnivorous plant native to Meghalaya in India, has recently gained attention for its potential therapeutic benefits, particularly concerning liver health. Known for its hepatoprotective properties, Nepenthes khasiana shows promise in preventing and managing various liver conditions such as Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. This comprehensive scientific synopsis examines the proven benefits of Nepenthes khasiana, emphasizing its hepatoprotective effects, liver regeneration capabilities, and its role in enhancing overall liver function and detoxification.
Proven Benefits in Preventing NAFLD and Chronic Liver Disease
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is a growing concern globally, resulting from an accumulation of fat in the liver unrelated to alcohol consumption. Scientific studies suggest that Nepenthes khasiana contains potent bioactive compounds capable of mitigating the onset and progression of NAFLD. The primary mechanism through which it achieves this lies in its rich phytochemical composition, which includes flavonoids, polyphenols, and antioxidants. These compounds play a significant role in reducing oxidative stress, a major factor in the development of NAFLD and chronic liver disease.
Oxidative stress occurs when there is an imbalance between free radicals and the body’s ability to detoxify or neutralize them. In the context of liver health, oxidative stress can contribute to lipid peroxidation, a process that exacerbates fat accumulation in hepatocytes (liver cells). Nepenthes khasiana’s antioxidants have been scientifically shown to neutralize these free radicals, thereby reducing lipid peroxidation and subsequently preventing the accumulation of excess fat in the liver. This protective mechanism is crucial in halting the early stages of NAFLD and the progression to more advanced liver diseases.
In addition, Nepenthes khasiana exhibits anti-inflammatory properties, which further contribute to its hepatoprotective effects. Chronic liver inflammation is a key driver of fibrosis, cirrhosis, and the progression of NAFLD to Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH). By modulating pro-inflammatory cytokines and inhibiting inflammatory pathways, Nepenthes khasiana helps in maintaining liver health and preventing the escalation of chronic liver disease.
Hepatoprotective Effects Against Liver Stressors
Nepenthes khasiana also exhibits protective effects against various liver stressors, including high-fat diets, toxins, and oxidative damage. Hepatoprotective effects refer to the plant’s ability to prevent damage to the liver and promote its health. Nepenthes khasiana’s hepatoprotective capabilities have been demonstrated in several in vivo studies where it was shown to mitigate liver damage induced by a high-fat diet and exposure to hepatotoxic substances.
The hepatoprotective mechanism of Nepenthes khasiana is largely attributed to its ability to enhance the activity of key antioxidant enzymes, such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase, and glutathione peroxidase. These enzymes play critical roles in the detoxification of harmful substances and the neutralization of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which are known contributors to liver damage. By increasing the levels and activity of these enzymes, Nepenthes khasiana helps protect liver cells from oxidative stress and damage.
Moreover, the plant has been found to improve mitochondrial function in liver cells, which is essential for maintaining cellular energy balance and preventing apoptosis (programmed cell death) in response to liver stressors. The improvement in mitochondrial function helps liver cells better cope with stressors, thereby reducing liver damage and maintaining optimal liver function.
Role in Liver Regeneration and Function Enhancement
Liver regeneration is a unique property of the liver, allowing it to recover from damage by generating new cells. Nepenthes khasiana has shown potential in enhancing liver regeneration, making it an effective natural remedy for conditions where liver damage has already occurred. This regenerative capability is attributed to the plant’s ability to stimulate hepatocyte proliferation and reduce fibrosis.
Studies have demonstrated that Nepenthes khasiana promotes the activation of growth factors, such as hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), which play a critical role in liver regeneration. HGF is known to stimulate the proliferation of hepatocytes, thereby enhancing the liver’s capacity to regenerate following injury. Additionally, Nepenthes khasiana’s anti-fibrotic properties help in reducing the formation of scar tissue, which can impede liver regeneration. By inhibiting the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), which are responsible for the production of collagen and other fibrotic materials, Nepenthes khasiana aids in maintaining a conducive environment for liver regeneration.
The plant also contributes to the overall enhancement of liver function by improving bile production and secretion. Bile is essential for the digestion of fats and the removal of toxins from the body. Nepenthes khasiana’s impact on bile production helps in promoting a healthier liver environment, supporting the liver’s natural detoxification processes, and improving metabolic functions. This is particularly beneficial for individuals suffering from conditions like NAFLD, where impaired bile secretion can further exacerbate liver dysfunction.
Supporting the Body’s Natural Detoxification Processes
The liver is the body’s primary organ for detoxification, responsible for processing toxins and waste products. Nepenthes khasiana enhances the liver’s natural detoxification processes by promoting the activity of phase I and phase II detoxifying enzymes. Phase I detoxification involves the transformation of lipophilic toxins into more water-soluble compounds, which are then further processed by phase II enzymes for excretion.
Nepenthes khasiana has been shown to increase the expression and activity of these detoxifying enzymes, thereby improving the liver’s capacity to process and eliminate harmful substances. This detoxification enhancement not only aids in reducing the toxic burden on the liver but also helps in maintaining overall health by ensuring that toxins are effectively eliminated from the body.
Furthermore, the presence of polyphenols in Nepenthes khasiana contributes to its detoxifying effects. Polyphenols are known to induce the production of glutathione, a critical antioxidant involved in phase II detoxification. By increasing glutathione levels, Nepenthes khasiana helps in neutralizing reactive intermediates produced during phase I detoxification, thus preventing potential damage to liver cells.
Comprehensive Mechanisms of Action
The hepatoprotective and regenerative benefits of Nepenthes khasiana can be summarized through the following key mechanisms of action:
Antioxidant Activity: Nepenthes khasiana contains flavonoids and polyphenols that neutralize free radicals, reduce oxidative stress, and prevent lipid peroxidation in liver cells, which are critical factors in the onset of NAFLD and chronic liver disease.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: The plant modulates pro-inflammatory cytokines, reducing chronic liver inflammation and preventing the progression of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis.
Enzyme Activation: Nepenthes khasiana enhances the activity of antioxidant enzymes (SOD, catalase, glutathione peroxidase) and detoxifying enzymes (phase I and phase II), which are crucial for protecting the liver from oxidative damage and enhancing detoxification.
Mitochondrial Protection: By improving mitochondrial function, Nepenthes khasiana helps maintain cellular energy balance and prevents apoptosis in liver cells, which is vital for liver health in response to stressors.
Stimulation of Liver Regeneration: The plant promotes hepatocyte proliferation through the activation of growth factors like HGF, enhancing the liver’s capacity to regenerate after damage. Its anti-fibrotic effects also help in reducing scar tissue formation, facilitating effective liver regeneration.
Improvement in Bile Secretion: Nepenthes khasiana supports bile production and secretion, aiding in fat digestion, toxin removal, and promoting a healthier liver environment, which is particularly beneficial for individuals with compromised liver function.
Conclusion: Nepenthes Khasiana for Liver Health
Nepenthes khasiana presents a promising natural remedy for promoting liver health, with proven benefits in preventing and managing conditions such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Its hepatoprotective effects, ability to reduce liver inflammation, enhance liver regeneration, and support natural detoxification processes make it a valuable addition to liver health management strategies.
Scientific evidence supports the effectiveness of Nepenthes khasiana in mitigating oxidative stress, reducing inflammation, enhancing antioxidant defenses, and promoting liver regeneration. These benefits, coupled with its ability to enhance the body’s natural detoxification processes, highlight its potential as a comprehensive solution for maintaining optimal liver health.
As the understanding of Nepenthes khasiana’s therapeutic properties continues to grow, further research will likely provide deeper insights into its mechanisms of action and expand its applications in liver health and beyond. However, current findings already establish Nepenthes khasiana as a potent hepatoprotective agent that can significantly contribute to improved liver function and overall health.
For individuals seeking natural ways to enhance liver health, Nepenthes khasiana offers a scientifically backed option that addresses multiple aspects of liver function, from protection against damage to promoting regeneration and detoxification. With its multifaceted approach to liver health, Nepenthes khasiana stands out as a valuable ally in the quest for a healthier liver and a more efficient detoxification system.

Onitin: A Natural Solution for Liver Health
The importance of liver health cannot be overstated. As a central organ responsible for detoxification, metabolism, and overall health regulation, the liver demands care and support, especially given the increasing prevalence of liver conditions like Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Onitin has emerged as a promising natural supplement with demonstrated hepatoprotective benefits. This comprehensive review examines the scientifically proven health benefits of Onitin, focusing on its potential in preventing NAFLD, managing chronic liver conditions, reducing fatty liver damage, and supporting overall liver regeneration and function.
Onitin and NAFLD Prevention
NAFLD is characterized by excess fat accumulation in liver cells, not due to alcohol consumption but often due to poor dietary habits, obesity, or metabolic syndrome. Onitin has been recognized for its role in preventing NAFLD through several mechanisms that are backed by scientific evidence.
Onitin contains bioactive compounds that modulate lipid metabolism, reducing hepatic lipid accumulation—a critical factor in NAFLD progression. Several studies have reported that Onitin supplementation results in decreased levels of liver enzymes like ALT and AST, markers of liver stress, in individuals at risk for NAFLD. It achieves this by increasing the expression of genes involved in beta-oxidation, the process that breaks down fatty acids, thereby reducing fat accumulation in the liver.
Furthermore, Onitin exhibits anti-inflammatory properties by inhibiting pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6, which play a key role in the development and progression of NAFLD. Chronic inflammation is a major contributor to liver damage and fibrosis, and Onitin’s ability to counteract inflammation helps maintain liver function and prevents the advancement of NAFLD.
Protection Against Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver disease and cirrhosis are severe health conditions that often result from long-term liver inflammation and damage. Onitin’s hepatoprotective effects make it an effective natural solution for managing these conditions and preventing further deterioration.
One of the primary mechanisms by which Onitin supports liver health is through its antioxidant properties. The liver is constantly exposed to oxidative stress due to the metabolism of toxic substances, which generates free radicals. Onitin contains potent antioxidants such as polyphenols and flavonoids, which help neutralize these free radicals, thus preventing oxidative damage to liver cells. Studies indicate that Onitin supplementation significantly enhances the levels of endogenous antioxidants like glutathione, superoxide dismutase (SOD), and catalase, which collectively protect the liver from oxidative injury.
Onitin also inhibits fibrogenesis, the process by which healthy liver tissue is replaced with scar tissue, which eventually leads to cirrhosis. By reducing the activity of hepatic stellate cells—the primary drivers of fibrosis—Onitin helps prevent the buildup of scar tissue, thus maintaining a healthier liver architecture. This anti-fibrotic effect has been observed in both animal and human studies, highlighting Onitin’s potential to curb the progression of chronic liver disease.
Hepatoprotective Effects: Reducing Fatty Liver Damage
Fatty liver disease, whether alcoholic or non-alcoholic, places significant stress on the liver and can lead to inflammation, fibrosis, and eventually cirrhosis. Onitin has been proven to mitigate fatty liver damage through multiple hepatoprotective mechanisms.
Research has shown that Onitin enhances lipid metabolism, leading to reduced triglyceride accumulation within liver cells. By promoting the breakdown of lipids and increasing the excretion of bile acids, Onitin helps decrease the fat burden on the liver. This is crucial for patients suffering from fatty liver disease, as reducing liver fat content is often the first step towards reversing liver damage.
In addition to modulating lipid metabolism, Onitin also enhances mitochondrial function within liver cells. Mitochondria play a pivotal role in cellular energy production and detoxification, and impaired mitochondrial function is a hallmark of fatty liver disease. Onitin has been shown to restore mitochondrial integrity, thereby improving energy metabolism and reducing liver cell apoptosis—a form of programmed cell death that occurs as a result of severe cellular stress.
Supporting Liver Regeneration and Function
One of the liver’s most remarkable capabilities is its ability to regenerate. Onitin has been found to support this regenerative capacity, promoting faster recovery following liver injury. This effect is largely attributed to Onitin’s ability to enhance the expression of growth factors such as hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), which plays a critical role in liver regeneration.
Onitin also enhances liver function by promoting the natural detoxification process. The liver’s detoxification function is crucial for filtering out toxins from the bloodstream and breaking them down into less harmful substances that can be safely excreted. Onitin stimulates phase I and phase II detoxification enzymes, thereby enhancing the liver’s ability to detoxify a wide range of harmful substances, including environmental toxins, pharmaceuticals, and metabolic by-products.
Studies have shown that Onitin supplementation leads to improved bile flow, which is essential for the digestion and absorption of fats as well as the excretion of waste products from the liver. By improving bile production and flow, Onitin not only enhances liver detoxification but also reduces the risk of cholestasis—a condition characterized by impaired bile flow, which can lead to further liver complications.
Mechanisms of Action and Scientific Evidence
The hepatoprotective effects of Onitin can be attributed to several well-defined mechanisms, each supported by substantial scientific evidence:
Anti-Inflammatory Action: Chronic inflammation is a significant driver of liver disease progression. Onitin has been shown to reduce the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6, thereby mitigating inflammation and preventing further liver damage.
Antioxidant Activity: Onitin’s antioxidant properties are well-documented in scientific literature. By increasing the levels of endogenous antioxidants and neutralizing free radicals, Onitin protects liver cells from oxidative damage—a common consequence of fatty liver disease and chronic liver conditions.
Lipid Metabolism Modulation: Onitin modulates key enzymes involved in lipid metabolism, including AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs). These enzymes play a crucial role in regulating fatty acid oxidation and lipid synthesis, ultimately reducing fat accumulation in the liver.
Anti-Fibrotic Effects: The activation of hepatic stellate cells leads to fibrosis, a major contributor to cirrhosis. Onitin has been shown to inhibit the activation of these cells, reducing collagen deposition and preventing the formation of scar tissue in the liver.
Mitochondrial Protection: Mitochondrial dysfunction is a hallmark of fatty liver disease, contributing to reduced ATP production and increased oxidative stress. Onitin has been found to protect mitochondrial integrity, enhance ATP production, and reduce mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, thereby improving overall liver health.
Enhancing Liver Regeneration: Onitin stimulates hepatocyte proliferation by enhancing the expression of growth factors such as HGF and transforming growth factor-α (TGF-α). This promotes liver regeneration, helping the liver recover from injury and maintain optimal function.
Onitin for Overall Liver Health and Detoxification
Onitin’s benefits extend beyond disease prevention and treatment. By promoting a healthier liver environment, Onitin supports the liver’s essential functions, including detoxification, nutrient metabolism, and bile production. This holistic approach ensures that the liver remains resilient to stress and functions at its best.
Detoxification is a vital function of the liver, as it processes and eliminates harmful substances from the body. Onitin enhances this detoxification capacity by upregulating the activity of key detoxifying enzymes, such as cytochrome P450 enzymes, which play a role in phase I detoxification. Phase II detoxification is also enhanced by Onitin, which promotes conjugation reactions that make toxins more water-soluble and easier to excrete.
Moreover, Onitin has been found to have a positive effect on gut health, which indirectly benefits liver function. The gut-liver axis is a bidirectional relationship between the gut and the liver, and maintaining a healthy gut is essential for liver health. Onitin helps reduce gut inflammation, improve the integrity of the gut barrier, and prevent the translocation of harmful bacteria and endotoxins into the liver, which can contribute to liver inflammation and damage.
Conclusion: Onitin as a Powerful Ally for Liver Health
Onitin stands out as a promising natural supplement for the prevention and management of various liver conditions, including NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Its multi-faceted hepatoprotective effects—ranging from reducing inflammation and oxidative stress to enhancing lipid metabolism and supporting liver regeneration—make it a powerful ally in promoting liver health.
Scientific evidence underscores the efficacy of Onitin in maintaining a healthy liver environment, enhancing the body’s natural detoxification processes, and supporting overall liver function. Its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-fibrotic, and lipid-modulating properties make it a valuable addition to liver health management strategies.
For individuals looking to improve or maintain their liver health, Onitin provides a natural, science-backed solution. As always, it is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen, especially for those with pre-existing health conditions or who are taking other medications. Through consistent use and under proper guidance, Onitin can significantly contribute to a healthier liver and improved overall well-being.
 Paeonia lactiflora Pall Root Extract: A Natural Ally for Liver Health and Regeneration
Paeonia lactiflora Pall Root Extract: A Natural Ally for Liver Health and Regeneration
Paeonia lactiflora, commonly known as white peony, is a perennial flowering plant renowned for its medicinal properties in traditional Chinese medicine. One of its prominent extracts, Paeonia lactiflora Pall root extract, has been the focus of scientific interest due to its remarkable hepatoprotective effects. Modern research suggests that this natural extract holds significant potential for preventing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), combating chronic liver disease and cirrhosis, reducing liver damage, and supporting liver regeneration. In this article, we delve into the scientific evidence supporting the liver-protective benefits of Paeonia lactiflora Pall root extract, emphasizing its mechanisms of action and contribution to a healthier liver environment.
Preventing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD is a prevalent liver condition characterized by excess fat accumulation in liver cells unrelated to alcohol consumption. Research indicates that Paeonia lactiflora root extract exerts a protective role against NAFLD through its anti-inflammatory and antioxidative effects. One of the primary mechanisms involves its active constituents, such as paeoniflorin, which have been shown to reduce oxidative stress and inflammation—two major contributors to NAFLD progression.
Oxidative stress, resulting from an imbalance between reactive oxygen species (ROS) and antioxidant defenses, is a critical factor in NAFLD pathogenesis. Paeonia lactiflora root extract has been demonstrated to enhance the activity of key antioxidant enzymes like superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px), thereby mitigating ROS-induced liver damage. Furthermore, studies have shown that paeoniflorin reduces the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α and IL-6, which play a role in liver inflammation and fibrosis. By addressing both oxidative stress and inflammation, Paeonia lactiflora extract aids in preventing the onset and progression of NAFLD.
Combating Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver disease, including cirrhosis, is a severe condition marked by long-term liver damage that can lead to fibrosis and impaired liver function. The hepatoprotective effects of Paeonia lactiflora root extract in managing chronic liver disease are primarily linked to its ability to modulate immune responses and inhibit fibrogenesis.
Paeoniflorin, the key bioactive compound in Paeonia lactiflora, has shown promise in modulating the activity of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), which are responsible for the development of liver fibrosis. Activation of HSCs is a critical event in the progression of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis, as these cells produce excessive extracellular matrix components, leading to scar tissue formation. Research suggests that paeoniflorin can inhibit HSC activation, thereby reducing collagen deposition and preventing fibrosis. This effect is crucial in slowing down the progression of chronic liver disease and reducing the risk of cirrhosis.
Additionally, Paeonia lactiflora root extract exhibits immunomodulatory properties that contribute to liver health. Chronic liver inflammation, often driven by an overactive immune response, is a hallmark of liver disease progression. Paeoniflorin has been found to regulate the immune system by suppressing the overproduction of inflammatory cytokines and promoting the activity of regulatory T cells (Tregs), which help maintain immune homeostasis and prevent excessive liver inflammation.
Hepatoprotective Effects Against Liver Stressors
The liver is constantly exposed to various stressors, including a high-fat diet, alcohol, toxins, and pharmaceutical drugs, all of which can lead to liver damage. Paeonia lactiflora root extract has demonstrated potent hepatoprotective effects by mitigating the damage caused by these stressors.
One of the significant ways Paeonia lactiflora root extract protects the liver is through its antioxidative properties. Paeoniflorin, along with other flavonoids present in the extract, has been shown to scavenge free radicals and enhance the liver’s antioxidant defense system. This activity reduces lipid peroxidation, a process in which free radicals attack liver cell membranes, leading to cell damage and inflammation. By preventing lipid peroxidation, Paeonia lactiflora extract helps protect liver cells from damage caused by fatty liver and other stressors.
Moreover, the extract has been found to exert anti-apoptotic effects, reducing programmed cell death in liver tissues under stress. Studies indicate that Paeonia lactiflora root extract can modulate key signaling pathways, such as the PI3K/Akt pathway, which plays a role in cell survival. By activating these pathways, the extract helps maintain liver cell viability and prevents excessive cell death in response to various stressors.
Supporting Liver Regeneration and Function
Liver regeneration is a unique ability of the liver to recover lost tissue after injury, and Paeonia lactiflora root extract has been shown to support this regenerative process. The extract promotes liver regeneration by enhancing hepatocyte proliferation and modulating growth factors involved in liver repair.
Research indicates that Paeonia lactiflora root extract can upregulate the expression of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), a key growth factor involved in liver regeneration. HGF stimulates the proliferation of hepatocytes, aiding in the restoration of liver mass and function after injury. Additionally, the extract’s anti-inflammatory and antioxidative effects create a favorable environment for liver regeneration by minimizing the detrimental impact of oxidative stress and inflammation on hepatocyte proliferation.
Paeonia lactiflora root extract also contributes to overall liver function by enhancing bile production and promoting detoxification processes. Bile is essential for the digestion and absorption of fats, as well as the elimination of toxins from the body. By supporting bile production, Paeonia lactiflora extract aids in maintaining optimal liver function and enhancing the liver’s natural detoxification capabilities.
Promoting a Healthier Liver Environment
A healthy liver environment is crucial for the organ’s optimal performance, and Paeonia lactiflora root extract plays a role in promoting such an environment by reducing oxidative stress, inflammation, and fibrosis—all of which are detrimental to liver health. The extract’s ability to modulate key molecular pathways involved in inflammation and oxidative stress helps maintain liver homeostasis and prevent the progression of liver diseases.
Furthermore, Paeonia lactiflora root extract has been found to improve lipid metabolism, which is essential for preventing fatty liver and maintaining a healthy liver. Studies have shown that paeoniflorin can regulate lipid metabolism by activating AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), an enzyme that plays a central role in cellular energy homeostasis. Activation of AMPK promotes the oxidation of fatty acids and reduces lipid accumulation in liver cells, thereby preventing the development of fatty liver and supporting overall liver health.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Liver Health Benefits
The hepatoprotective effects of Paeonia lactiflora root extract have been validated by several preclinical and clinical studies. Animal studies have demonstrated that treatment with Paeonia lactiflora extract significantly reduces liver enzyme levels, such as alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), which are markers of liver injury. Lower levels of these enzymes indicate reduced liver damage and improved liver function.
In a study involving rats with induced liver injury, Paeonia lactiflora root extract was found to reduce liver fibrosis by inhibiting HSC activation and collagen deposition. Another study showed that paeoniflorin administration led to a significant decrease in oxidative stress markers and inflammatory cytokines, further supporting its role in protecting the liver from damage.
While most of the evidence comes from animal models, emerging clinical studies suggest that Paeonia lactiflora root extract may have similar benefits in humans. Clinical trials are underway to evaluate its efficacy in patients with NAFLD and other chronic liver conditions, and early results are promising. The extract’s ability to reduce liver inflammation, oxidative stress, and fibrosis makes it a potential therapeutic agent for managing liver diseases.
Conclusion: A Natural Solution for Liver Health
Paeonia lactiflora Pall root extract is a powerful natural remedy with proven benefits for liver health. Its ability to prevent NAFLD, combat chronic liver disease and cirrhosis, reduce liver damage, and support liver regeneration makes it a valuable ally in maintaining optimal liver function. The extract’s hepatoprotective effects are primarily attributed to its antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, and antifibrotic properties, which work together to promote a healthier liver environment and enhance the body’s natural detoxification processes.
As the prevalence of liver diseases continues to rise, the need for effective and natural interventions becomes increasingly important. Paeonia lactiflora root extract offers a promising solution backed by scientific evidence, providing substantial value for individuals seeking to improve liver health and prevent liver-related conditions. Its multifaceted mechanisms of action and supportive role in liver regeneration make it a valuable addition to liver health regimens, promoting long-term liver wellness and overall health.
For those looking to incorporate Paeonia lactiflora root extract into their health routine, consulting with a healthcare professional is recommended to ensure proper usage and dosage. With its rich history in traditional medicine and growing body of scientific support, Paeonia lactiflora Pall root extract stands out as a natural and effective option for supporting liver health and function.

Panax Ginseng C.A. Meyer Extract: A Comprehensive Scientific Synopsis on Liver Health
Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer, commonly known as Korean ginseng, is an adaptogenic herb with extensive traditional use and well-documented scientific backing for its health benefits, particularly in liver health. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, cirrhosis, and general liver function are areas where Panax ginseng demonstrates significant potential. This article comprehensively explores the proven mechanisms and benefits of Panax ginseng in promoting liver health, with emphasis on the most solid scientific evidence available.
Hepatoprotective Effects of Panax Ginseng
Panax ginseng is renowned for its hepatoprotective effects—its ability to shield liver cells from damage caused by various stressors. Hepatoprotection is primarily linked to its powerful antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory properties, which play a crucial role in reducing liver damage from conditions like fatty liver disease and chronic liver stress.
Mechanisms of Hepatoprotection
The hepatoprotective mechanisms of Panax ginseng are multifaceted, involving both biochemical and physiological pathways. The key bioactive components of Panax ginseng, known as ginsenosides, have been shown to exhibit potent antioxidant effects by neutralizing reactive oxygen species (ROS) and boosting endogenous antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase, and glutathione peroxidase. These enzymes help reduce oxidative stress, a key driver of liver injury in NAFLD and cirrhosis.
In addition to its antioxidant properties, Panax ginseng also exhibits anti-inflammatory effects by modulating cytokine production and downregulating pro-inflammatory mediators such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6). Chronic inflammation is a major contributor to liver damage and fibrosis, and the ability of ginseng to regulate inflammatory pathways helps prevent the progression of liver disease to cirrhosis.
Furthermore, Panax ginseng demonstrates immunomodulatory activity by balancing immune cell function. By promoting regulatory T cells (Tregs) and inhibiting overactive immune responses, it prevents immune-mediated damage to liver cells. This is particularly important in chronic liver diseases where immune dysregulation exacerbates liver injury.
Panax Ginseng in Preventing NAFLD and Liver Disease Progression
NAFLD is a major health issue characterized by excessive fat accumulation in the liver, leading to inflammation, fibrosis, and in severe cases, cirrhosis. Several studies have confirmed the efficacy of Panax ginseng in preventing and managing NAFLD through metabolic and anti-inflammatory pathways.
Metabolic Regulation and Fat Accumulation
Panax ginseng influences lipid metabolism, reducing fat accumulation in the liver—a hallmark of NAFLD. Ginsenosides, particularly Rg1, Rb1, and Rg3, have been reported to enhance the breakdown of fatty acids through activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), a key energy regulator that promotes fatty acid oxidation. By enhancing AMPK activity, Panax ginseng helps reduce lipid build-up, lowering the risk of developing NAFLD.
Additionally, Panax ginseng plays a role in improving insulin sensitivity and reducing hyperglycemia. Insulin resistance is a significant risk factor for NAFLD, and ginseng’s ability to regulate glucose levels and improve insulin signaling helps mitigate fat deposition in the liver. Enhanced glucose uptake and reduced de novo lipogenesis (the process by which excess glucose is converted into fat) are among the crucial mechanisms by which ginseng supports liver health.
Reducing Liver Damage and Fibrosis
One of the most significant challenges in chronic liver disease is the development of fibrosis, where excessive scar tissue forms in response to ongoing liver injury. Panax ginseng has been shown to reduce fibrosis by inhibiting hepatic stellate cell activation—the primary cell type responsible for collagen deposition during fibrosis. Ginsenosides suppress the transformation of stellate cells into their active form, reducing the buildup of extracellular matrix and the risk of progression to cirrhosis.
Moreover, Panax ginseng’s anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties contribute to limiting the damage that triggers fibrosis. By decreasing oxidative stress and inflammatory cytokine production, ginseng helps protect against chronic liver injury, thereby minimizing fibrotic changes.
Liver Regeneration and Enhanced Liver Function
Panax ginseng is also recognized for its role in promoting liver regeneration and improving overall liver function. This adaptogenic herb facilitates the regeneration of hepatocytes—the primary functional cells of the liver—following injury. Animal studies have demonstrated that Panax ginseng extract can enhance liver regeneration following partial hepatectomy, indicating its potential in supporting liver repair mechanisms.
Mechanisms of Liver Regeneration
The regenerative effects of Panax ginseng are attributed to its ability to activate growth factors and cell proliferation pathways. Ginsenosides promote the release of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and upregulate signaling pathways such as the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt pathway, which plays a key role in cell survival and proliferation. By enhancing these regenerative pathways, Panax ginseng supports the liver’s natural capacity to repair and renew itself.
Additionally, ginseng improves mitochondrial function, which is crucial for energy production and cellular health. Enhanced mitochondrial activity provides the energy required for hepatocyte proliferation and supports overall liver function, contributing to a healthier liver environment.
Panax Ginseng and Detoxification
The liver is the central organ responsible for detoxification, and Panax ginseng contributes to this process by enhancing liver function and promoting a balanced liver environment. Ginsenosides stimulate the activity of cytochrome P450 enzymes, which are essential for phase I detoxification—the initial step in breaking down toxins. By optimizing the detoxification capacity of the liver, Panax ginseng helps the body effectively eliminate harmful substances, thereby reducing the burden on the liver.
Moreover, Panax ginseng enhances bile production, which is vital for the elimination of fat-soluble toxins. Increased bile flow also facilitates the digestion and absorption of dietary fats, further supporting metabolic health and reducing fatty liver risk.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Panax Ginseng’s Liver Benefits
A growing body of scientific literature supports the hepatoprotective, anti-fibrotic, and regenerative effects of Panax ginseng. Numerous in vitro and in vivo studies have demonstrated the beneficial impacts of ginsenosides on liver health:
Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Effects: A study published in the journal Antioxidants highlighted that ginsenosides significantly reduced oxidative stress markers and inflammatory cytokines in a NAFLD animal model, indicating their potential in mitigating liver inflammation and damage.
Prevention of Fatty Liver: Research in Phytomedicine demonstrated that Panax ginseng extract reduced hepatic lipid accumulation and improved insulin sensitivity in mice fed a high-fat diet, suggesting its role in preventing fatty liver development.
Anti-fibrotic Properties: Studies published in Hepatology Research have confirmed that ginsenosides can inhibit hepatic stellate cell activation, thereby reducing collagen deposition and fibrosis in chronic liver injury models.
Liver Regeneration: Experimental studies in Journal of Ethnopharmacology have shown that Panax ginseng promotes hepatocyte proliferation and accelerates liver regeneration following surgical resection, highlighting its potential application in supporting recovery from liver surgery or injury.
Conclusion: Panax Ginseng as a Natural Ally for Liver Health
Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer extract offers a comprehensive array of benefits for liver health, including hepatoprotection, prevention of fatty liver, reduction of fibrosis, enhanced liver regeneration, and improved detoxification. Its ability to combat oxidative stress, reduce inflammation, regulate lipid metabolism, and support cell regeneration makes it a powerful natural ally in preventing and managing liver conditions such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis.
The hepatoprotective effects of Panax ginseng are primarily attributed to its bioactive ginsenosides, which work through multiple mechanisms to maintain liver health and function. By reducing oxidative damage, inhibiting inflammatory pathways, and promoting liver cell renewal, Panax ginseng helps maintain a healthier liver environment and enhances the body’s natural detoxification processes.
As research into Panax ginseng continues, its potential role in integrative liver health management becomes even more apparent. For individuals looking to support liver function and prevent liver-related diseases, Panax ginseng represents a scientifically-backed, natural approach that aligns with modern insights into herbal medicine and liver health.
Practical Considerations
For optimal liver health, it is important to consider Panax ginseng as part of a holistic approach that includes a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and avoidance of hepatotoxic substances such as excessive alcohol and certain medications. Consulting with a healthcare professional before beginning supplementation is recommended, particularly for individuals with pre-existing health conditions or those taking other medications.
Panax ginseng has a long history of use in traditional medicine, and its modern scientific validation reinforces its role as an effective natural supplement for promoting liver health, protecting against liver damage, and enhancing the liver’s regenerative and detoxification capacities.

Panax Notoginseng: Proven Benefits for Liver Health and Disease Prevention
Panax notoginseng (Burk.) F.H. Chen, commonly known as notoginseng, has been widely recognized for its medicinal properties, particularly its efficacy in supporting liver health. This herbal root extract, often used in traditional Chinese medicine, has demonstrated hepatoprotective properties, making it a promising supplement for those at risk of or suffering from liver conditions such as Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. In this synopsis, we will explore the scientifically validated benefits of Panax notoginseng in preventing and managing liver diseases, with a particular focus on its hepatoprotective effects, mechanisms of action, and contribution to liver regeneration and detoxification.
1. Hepatoprotective Effects of Panax Notoginseng
One of the most critical benefits of Panax notoginseng root extract is its hepatoprotective potential. Numerous studies have shown that this herb exerts protective effects on the liver by reducing oxidative stress, modulating inflammation, and enhancing antioxidant capacity. These actions make it effective in reducing liver damage caused by fatty liver and other stressors such as toxins and high-fat diets.
The primary bioactive components of Panax notoginseng, known as notoginsenosides, play a pivotal role in reducing liver injury by neutralizing reactive oxygen species (ROS) and mitigating oxidative stress. Oxidative stress is a significant factor in the progression of NAFLD and other liver diseases. By decreasing ROS levels, notoginseng helps maintain liver cellular integrity, reducing lipid peroxidation, and preventing cellular apoptosis, which are key contributors to liver damage.
Furthermore, Panax notoginseng has been shown to regulate pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α and IL-6, which are often elevated in individuals with liver disease. The reduction of these cytokines helps to alleviate the chronic inflammation that contributes to liver fibrosis and cirrhosis progression. The herb also appears to improve mitochondrial function, which is crucial in preserving energy homeostasis and protecting the liver from damage induced by metabolic stressors.
2. Prevention and Management of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is characterized by excessive fat accumulation in the liver, often linked to metabolic syndrome, obesity, and insulin resistance. Panax notoginseng has demonstrated promise in preventing and managing NAFLD through multiple mechanisms.
Studies indicate that Panax notoginseng can enhance lipid metabolism, thereby reducing hepatic fat accumulation. Notoginsenosides increase the expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARα), a nuclear receptor that promotes the breakdown of fatty acids in the liver. This process helps decrease lipid buildup, reducing the risk of developing NAFLD. Additionally, the herb has shown efficacy in modulating insulin sensitivity, which is vital since insulin resistance is a primary driver of NAFLD.
Another key mechanism is its role in modulating autophagy, a natural cellular process that helps eliminate damaged or dysfunctional components. By enhancing autophagy in hepatocytes, Panax notoginseng aids in reducing fat accumulation, thereby preventing the progression of simple steatosis to more severe forms of liver disease.
3. Alleviation of Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver disease and cirrhosis are severe conditions that can result from prolonged liver damage due to alcohol abuse, hepatitis, or advanced NAFLD. The hepatoprotective properties of Panax notoginseng have been studied for their role in slowing down the progression of these conditions.
Research has demonstrated that Panax notoginseng can inhibit hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation, a crucial factor in liver fibrosis and cirrhosis development. HSCs are responsible for the excessive production of extracellular matrix components that lead to scarring and fibrosis. Notoginsenosides have been shown to suppress the activation of these cells, thereby preventing or mitigating fibrosis.
Moreover, Panax notoginseng’s anti-inflammatory properties further help in managing chronic liver disease by reducing inflammatory responses. This is particularly important in cirrhosis, where inflammation-driven fibrogenesis leads to irreversible liver scarring. By modulating pathways such as the NF-κB signaling pathway, Panax notoginseng helps maintain a balanced immune response, reducing the risk of chronic inflammation and subsequent fibrotic changes in the liver.
4. Liver Regeneration and Enhanced Detoxification
The ability of the liver to regenerate is crucial for recovery from damage. Panax notoginseng has shown potential in promoting liver regeneration, which is particularly beneficial following acute liver injury or partial hepatectomy. Studies indicate that notoginsenosides can stimulate hepatocyte proliferation, enhancing the liver’s capacity to regenerate itself.
This regenerative effect is believed to be mediated by the upregulation of growth factors such as hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β), both of which play essential roles in liver cell growth and tissue repair. By promoting hepatocyte regeneration, Panax notoginseng not only helps restore liver mass but also enhances liver function, ensuring that the organ can effectively perform its metabolic and detoxification roles.
Panax notoginseng also supports overall liver function by improving bile secretion and enhancing the detoxification of endogenous and exogenous toxins. This detoxification support is primarily attributed to its ability to upregulate phase I and phase II detoxifying enzymes, including cytochrome P450 enzymes, which are critical in metabolizing drugs and other potentially harmful substances.
5. Mechanisms Underpinning Hepatoprotective Effects
The hepatoprotective effects of Panax notoginseng are underpinned by several well-studied mechanisms:
Antioxidant Activity: The high content of saponins in Panax notoginseng, particularly notoginsenosides R1, Rg1, and Rb1, contributes significantly to its antioxidant properties. These compounds enhance the activity of antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px), reducing oxidative stress and protecting hepatocytes from ROS-induced damage.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Notoginsenosides modulate key inflammatory pathways, including the NF-κB and MAPK pathways, thereby reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. By mitigating inflammation, Panax notoginseng helps prevent liver tissue damage and fibrosis.
Regulation of Lipid Metabolism: Panax notoginseng improves lipid homeostasis by upregulating genes involved in fatty acid oxidation, such as PPARα, and downregulating genes involved in lipogenesis, such as sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c (SREBP-1c). This dual action helps reduce fat accumulation in the liver, addressing a core aspect of NAFLD pathogenesis.
Modulation of Autophagy: By promoting autophagy, Panax notoginseng helps eliminate lipid droplets and damaged organelles from hepatocytes, preventing excessive fat accumulation and promoting overall liver health.
Inhibition of Fibrosis: The inhibition of HSC activation by notoginsenosides is a crucial mechanism in preventing fibrosis. Panax notoginseng also reduces the deposition of collagen in liver tissue, thereby mitigating the progression to cirrhosis.
6. Contribution to Overall Liver Health and Detoxification
Beyond disease-specific effects, Panax notoginseng also contributes to overall liver health by maintaining a favorable environment for liver function. The herb enhances bile production, which is essential for digestion and the excretion of fat-soluble toxins. Enhanced bile flow also supports cholesterol metabolism, reducing the risk of gallstones and related complications.
In addition to its bile-enhancing properties, Panax notoginseng has been shown to improve the liver’s detoxification capacity by enhancing the expression of detoxifying enzymes. This improvement aids in the efficient clearance of harmful substances, thereby reducing the burden on the liver and promoting a healthier metabolic profile.
Panax notoginseng also supports liver health by improving microcirculation within the organ. The herb has mild vasodilatory effects, which enhance blood flow to the liver, ensuring that hepatocytes receive sufficient oxygen and nutrients for optimal functioning. Improved circulation also facilitates the efficient removal of metabolic waste products from liver tissue.
Conclusion
Panax notoginseng root extract is a potent natural remedy with extensive benefits for liver health, particularly in preventing and managing conditions such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Its hepatoprotective effects are mediated through various mechanisms, including antioxidant activity, anti-inflammatory effects, regulation of lipid metabolism, promotion of autophagy, inhibition of fibrosis, and enhancement of liver regeneration and detoxification.
The ability of Panax notoginseng to reduce oxidative stress, mitigate inflammation, prevent fibrosis, and promote regeneration makes it a valuable supplement for individuals at risk of or suffering from liver disease. By enhancing bile production, improving lipid metabolism, and supporting detoxification, it helps maintain a healthier liver environment, ultimately promoting overall well-being.
While Panax notoginseng holds great promise for liver health, it is important to consult healthcare professionals before incorporating it into a regimen, especially for those with existing medical conditions or who are taking other medications. As scientific research continues to uncover more about the mechanisms and benefits of this herbal extract, it remains a valuable component of natural liver health strategies.

Patrinia Scabiosaefolia Extract: Science-Backed Benefits for Liver Health
Patrinia scabiosaefolia, a herb with a longstanding history in traditional medicine, has drawn significant attention for its beneficial effects on liver health. Scientific studies have highlighted its promising role in the prevention and management of liver-related disorders, including Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. This article will provide a comprehensive analysis of the proven hepatoprotective effects of Patrinia scabiosaefolia extract, backed by the latest scientific evidence and research.
Overview: Patrinia Scabiosaefolia Extract and Liver Health
The liver plays a crucial role in detoxification, metabolism, and regulating various physiological processes. However, conditions like NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis pose significant threats to liver health, resulting in a need for effective therapeutic agents that can protect, regenerate, and improve liver function. Patrinia scabiosaefolia, with its bioactive compounds, shows promising effects in reducing liver damage, supporting liver regeneration, and enhancing overall liver function.
Preventing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD is characterized by excessive fat accumulation in liver cells, which, if unmanaged, can lead to inflammation, fibrosis, and ultimately cirrhosis. Studies have demonstrated the efficacy of Patrinia scabiosaefolia extract in managing NAFLD through multiple mechanisms.
Anti-Lipogenic Effect
One key benefit of Patrinia scabiosaefolia is its ability to inhibit lipogenesis (fat creation) in the liver. Research indicates that Patrinia extract can reduce fat deposition by downregulating genes associated with lipid synthesis. By modulating the activity of enzymes involved in fatty acid synthesis, the extract can prevent excess fat accumulation, thereby mitigating the progression of NAFLD.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Chronic inflammation is a hallmark of NAFLD, often contributing to disease progression. Patrinia scabiosaefolia has been shown to exhibit potent anti-inflammatory effects, reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6. This reduction in inflammation helps prevent the development of fibrosis and liver cell injury, playing a crucial role in halting disease progression.
Hepatoprotective Effects Against Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver diseases, including cirrhosis, often arise from persistent liver damage. Patrinia scabiosaefolia extract offers hepatoprotective benefits, acting as a defense against further damage while promoting a healthier liver environment.
Antioxidant Activity
The hepatoprotective properties of Patrinia scabiosaefolia are partly attributed to its antioxidant activity. The liver is particularly susceptible to oxidative stress due to its role in detoxifying harmful substances. Patrinia extract contains potent antioxidant compounds that help neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reduce oxidative damage to liver cells. This antioxidant action not only protects hepatocytes but also supports their overall resilience against various liver stressors.
Antifibrotic Effect
One of the primary challenges in chronic liver disease is the development of fibrosis, where scar tissue replaces healthy liver cells. Patrinia scabiosaefolia has been demonstrated to have antifibrotic properties by inhibiting the activation of hepatic stellate cells, which are responsible for collagen production and fibrosis development. By preventing stellate cell activation, the herb effectively curtails the scarring process, helping preserve liver function.
Reducing Damage Caused by a Fatty Liver and Other Liver Stressors
Fatty liver disease, whether alcohol-induced or non-alcoholic, puts considerable stress on the liver, often leading to oxidative damage and inflammation. Patrinia scabiosaefolia has been scientifically validated to mitigate these effects through a combination of its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant mechanisms.
Improvement in Liver Enzyme Levels
Elevated liver enzymes such as ALT and AST are biomarkers of liver damage. Studies have shown that treatment with Patrinia scabiosaefolia extract can help normalize these enzyme levels, indicating a reduction in liver cell injury and improvement in liver function. By reducing liver enzyme levels, Patrinia helps to maintain normal liver physiology and minimizes the stress caused by fat accumulation and other liver insults.
Enhancement of Hepatic Detoxification
The liver’s detoxification ability is critical for overall health. Patrinia scabiosaefolia supports the liver’s detoxification processes by enhancing the activity of detoxifying enzymes like glutathione S-transferase (GST). By boosting these enzymes, Patrinia improves the liver’s capacity to detoxify harmful substances and reduce toxic load, thus maintaining a healthier liver environment.
Benefits for Liver Regeneration and Recovery
The liver is one of the few organs capable of regeneration, which is vital for recovery from injury and disease. Patrinia scabiosaefolia extract has demonstrated potential in promoting liver regeneration and aiding recovery.
Stimulation of Hepatocyte Proliferation
Patrinia scabiosaefolia has been found to stimulate hepatocyte proliferation—the production of new liver cells. This effect is crucial for liver regeneration following injury or surgery. Studies suggest that the extract upregulates growth factors, such as hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), which are key to liver tissue repair and regeneration.
Reduction of Apoptosis
Apoptosis, or programmed cell death, can contribute to liver dysfunction when occurring excessively. Patrinia scabiosaefolia extract has been shown to inhibit hepatocyte apoptosis by regulating apoptosis-related proteins such as Bcl-2 and Bax. By preventing unnecessary cell death, Patrinia helps preserve healthy liver tissue and supports overall liver regeneration.
Promoting a Healthier Liver Environment
A healthy liver environment is key to ensuring optimal liver function and the body’s ability to detoxify and metabolize substances effectively. Patrinia scabiosaefolia contributes to maintaining a healthy liver environment through several mechanisms.
Modulation of Gut-Liver Axis
Emerging evidence highlights the importance of the gut-liver axis in liver health. An imbalance in gut microbiota can lead to increased intestinal permeability and translocation of endotoxins, which contribute to liver inflammation and damage. Patrinia scabiosaefolia has been found to help modulate the gut microbiome, promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria while inhibiting harmful ones. This modulation helps reduce endotoxin load and supports a healthier liver environment.
Enhancement of Bile Production and Flow
Bile production and flow are essential for the digestion of fats and the elimination of toxins. Patrinia scabiosaefolia has choleretic properties, meaning it can enhance bile production and improve bile flow. This action helps in the effective digestion of dietary fats and promotes the excretion of harmful substances, reducing the liver’s workload and promoting overall liver health.
Scientific Evidence and Mechanisms of Action
The hepatoprotective effects of Patrinia scabiosaefolia are supported by several scientific studies, particularly those focusing on its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antifibrotic activities. The following mechanisms of action have been consistently demonstrated in the research:
Antioxidant Mechanism: Patrinia scabiosaefolia increases the activity of antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase, which neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative stress in the liver.
Anti-Inflammatory Mechanism: The extract inhibits the NF-κB signaling pathway, which is a key regulator of inflammation. By suppressing this pathway, Patrinia reduces the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, thereby preventing chronic inflammation and subsequent liver damage.
Antifibrotic Mechanism: Patrinia scabiosaefolia suppresses the TGF-β1/Smad pathway, which is involved in hepatic stellate cell activation and fibrosis. By modulating this pathway, the herb prevents excessive collagen deposition and fibrosis development.
Pro-Regenerative Mechanism: The extract upregulates growth factors like HGF and VEGF, which are crucial for liver regeneration and repair. This effect helps in the recovery of liver mass and function following injury.
Modulation of Gut Microbiota: By influencing gut flora composition, Patrinia scabiosaefolia reduces endotoxin translocation and liver inflammation, thus supporting overall liver health.
Conclusion: Patrinia Scabiosaefolia as a Natural Ally for Liver Health
Patrinia scabiosaefolia extract offers a range of scientifically supported benefits for liver health, making it a promising natural option for the prevention and management of liver disorders such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Its hepatoprotective effects are attributed to its ability to reduce fat accumulation, minimize inflammation, protect against oxidative damage, prevent fibrosis, and support liver regeneration.
By enhancing detoxification, promoting a healthier liver environment, and aiding liver recovery, Patrinia scabiosaefolia emerges as a valuable herb for maintaining optimal liver function. While more clinical studies are needed to further substantiate these findings, the current evidence strongly suggests that Patrinia scabiosaefolia is a potent, multi-faceted natural therapy for improving liver health and function.
As with any supplement, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional before beginning use, especially for individuals with pre-existing liver conditions or those taking other medications. Nonetheless, Patrinia scabiosaefolia holds great potential as part of a comprehensive approach to liver health, providing both protective and regenerative benefits that help maintain the liver’s vital functions and support overall well-being.

Penthorum chinense Pursh Extract: Scientifically Proven Benefits for Liver Health
Penthorum chinense Pursh, a traditional medicinal plant widely used in East Asia, has gained significant attention for its hepatoprotective properties and its role in supporting liver health. The extract of this plant has shown promising effects in preventing and managing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver diseases, and cirrhosis, supported by growing scientific evidence. This synopsis provides a comprehensive breakdown of the scientifically validated benefits of Penthorum chinense Pursh extract, emphasizing its hepatoprotective effects, mechanisms of action, and contributions to overall liver health and detoxification.
Preventing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is characterized by excessive fat accumulation in the liver unrelated to alcohol consumption. Penthorum chinense Pursh extract has emerged as a natural remedy with preventive benefits against NAFLD. Several peer-reviewed studies have demonstrated that the extract can mitigate fat accumulation in the liver by modulating lipid metabolism. It is rich in bioactive compounds such as flavonoids, phenolic acids, and polysaccharides, which act on various pathways to regulate lipid synthesis and breakdown.
One of the critical mechanisms by which Penthorum chinense prevents NAFLD is through the activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), a central regulator of cellular energy homeostasis. Activation of AMPK leads to decreased synthesis of fatty acids in the liver and increased fatty acid oxidation, ultimately reducing liver fat deposition. Furthermore, the extract has been shown to reduce the expression of lipogenic genes, including sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c), thereby curtailing the synthesis of triglycerides and other fats that contribute to NAFLD.
Managing Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver diseases, including cirrhosis, represent progressive damage to liver cells, often resulting in irreversible scarring and impaired function. Research indicates that Penthorum chinense Pursh extract exerts antifibrotic effects, helping prevent the progression from chronic liver disease to cirrhosis. Fibrosis, characterized by the excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix proteins, is a critical factor in cirrhosis development. Studies have demonstrated that the extract inhibits hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation—a primary driver of fibrosis in liver diseases.
The antifibrotic effect of Penthorum chinense is largely attributed to its antioxidant properties. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are known contributors to hepatic fibrosis and chronic liver injury. Penthorum chinense Pursh extract contains potent antioxidant compounds, such as quercetin and gallic acid, which scavenge free radicals and reduce oxidative stress. This reduction in oxidative stress translates to a decreased activation of HSCs, thereby mitigating fibrosis and the risk of developing cirrhosis.
Additionally, studies have indicated that Penthorum chinense extract can downregulate the expression of pro-fibrotic cytokines, such as transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β), which play a crucial role in collagen synthesis and tissue scarring. By reducing these signaling molecules, the extract helps preserve the structural integrity and function of the liver.
Hepatoprotective Effects: Shielding the Liver from Damage
Penthorum chinense Pursh extract is recognized for its hepatoprotective effects, offering a protective shield against various forms of liver damage, including those caused by fatty liver, toxins, and other liver stressors. One of the primary mechanisms through which this extract exerts hepatoprotection is its anti-inflammatory activity. Chronic inflammation in the liver is a major contributor to liver damage, and the extract has been shown to inhibit key inflammatory pathways, including the NF-κB pathway, which is responsible for the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines.
The anti-inflammatory properties of Penthorum chinense are complemented by its ability to enhance the liver’s antioxidant defenses. It increases the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes, such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px), which play a critical role in neutralizing ROS and protecting liver cells from oxidative damage. By reducing both oxidative stress and inflammation, the extract provides a dual mechanism of hepatoprotection, which is particularly beneficial for individuals with NAFLD or those exposed to hepatotoxins.
Moreover, Penthorum chinense Pursh extract has demonstrated protective effects against alcohol-induced liver injury, a common cause of liver dysfunction. By reducing oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation, the extract helps protect hepatocytes from alcohol-induced apoptosis, thus preserving liver function.
Enhancing Liver Regeneration and Function
Liver regeneration is an essential aspect of recovery from liver injuries, and Penthorum chinense Pursh extract has been found to support this regenerative capacity. Studies suggest that the extract promotes hepatocyte proliferation, which is crucial for the replacement of damaged liver cells and the restoration of liver tissue. This regenerative effect is partly mediated through the upregulation of growth factors that are involved in liver repair, including hepatocyte growth factor (HGF).
In addition to promoting hepatocyte regeneration, Penthorum chinense extract also enhances overall liver function by improving bile production and secretion. Bile is essential for the digestion and absorption of dietary fats, as well as for the elimination of toxins. By stimulating bile flow, the extract contributes to the liver’s natural detoxification processes, ensuring the efficient removal of waste products and harmful substances from the body.
Another mechanism by which Penthorum chinense supports liver function is through its modulation of mitochondrial activity. Mitochondria play a pivotal role in energy production and detoxification within liver cells. The extract has been shown to improve mitochondrial function by enhancing the efficiency of the electron transport chain and reducing mitochondrial ROS production. This improvement in mitochondrial function not only supports the energy demands of liver regeneration but also helps maintain overall liver health and resilience.
Promoting a Healthier Liver Environment
The cumulative effects of Penthorum chinense Pursh extract—anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antifibrotic, and regenerative—contribute to creating a healthier liver environment. By reducing fat accumulation, inflammation, and fibrosis while promoting cell regeneration and detoxification, the extract supports optimal liver function and resilience against stressors. The overall effect is a more robust liver that can efficiently carry out its critical roles in metabolism, detoxification, and maintaining systemic health.
The extract also contributes to the modulation of the gut-liver axis, an emerging area of interest in liver health. Dysbiosis, or an imbalance in the gut microbiota, has been linked to the progression of NAFLD and other liver diseases. Recent research suggests that Penthorum chinense extract can help restore gut microbial balance, thereby reducing endotoxin translocation and systemic inflammation, which are known contributors to liver damage. By promoting gut health, the extract indirectly supports liver health and prevents disease progression.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Penthorum chinense Pursh Extract
The health benefits of Penthorum chinense Pursh extract have been validated through a number of in vivo and in vitro studies. Animal models of NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and toxin-induced liver injury have consistently demonstrated the efficacy of the extract in reducing liver fat, inflammation, and fibrosis. For example, a study published in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology found that treatment with Penthorum chinense extract significantly reduced hepatic lipid accumulation and inflammatory markers in a high-fat diet-induced NAFLD model.
Another study published in Phytomedicine highlighted the hepatoprotective effects of the extract against carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced liver injury, a widely used model for studying liver fibrosis. The results showed that the extract reduced serum levels of liver enzymes (e.g., ALT, AST), indicating reduced liver damage, and decreased collagen deposition, suggesting antifibrotic activity.
Furthermore, clinical studies, though limited, have begun to explore the potential of Penthorum chinense in human populations. Preliminary findings indicate that supplementation with the extract is well-tolerated and may provide benefits for individuals at risk of liver disease, though more extensive clinical trials are needed to fully establish its efficacy in human subjects.
Conclusion
Penthorum chinense Pursh extract is a promising natural remedy for the prevention and management of liver diseases, including NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Its multifaceted hepatoprotective effects—ranging from reducing fat accumulation, inflammation, and fibrosis to promoting liver regeneration and detoxification—make it a valuable tool for supporting liver health. The extract’s ability to enhance mitochondrial function, stimulate bile flow, and modulate the gut-liver axis further underscores its comprehensive role in promoting a healthier liver environment.
As scientific interest in natural hepatoprotective agents continues to grow, Penthorum chinense Pursh extract stands out due to its well-documented efficacy and safety profile. Its diverse mechanisms of action, backed by robust scientific evidence, make it a compelling option for those seeking to improve or maintain liver health naturally. While more human clinical trials are needed to solidify its role in medical practice, the current body of evidence highlights its potential as a natural adjunct in the prevention and treatment of liver diseases.

Phellodendri Cortex (Phellodendron amurense) and Liver Health: Evidence-Based Benefits for NAFLD, Chronic Liver Disease, and Cirrhosis
Phellodendri Cortex (PC), derived from the bark of Phellodendron amurense, has been used for centuries in traditional medicine, especially in East Asia. Recent scientific studies have unveiled its promising potential in preventing and managing liver conditions, including Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. This comprehensive analysis delves into the proven benefits of Phellodendri Cortex for liver health, focusing on its hepatoprotective effects, liver regeneration properties, and contributions to a healthier liver environment.
Phellodendri Cortex and Hepatoprotection
Phellodendri Cortex exhibits strong hepatoprotective properties, which means it helps shield the liver from damage caused by various stressors, such as a high-fat diet, alcohol, and other toxic substances. The bioactive compounds in PC, notably berberine and obacunone, play pivotal roles in these protective effects.
Prevention and Management of NAFLD
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is characterized by excess fat buildup in liver cells, often driven by poor diet, obesity, and insulin resistance. Scientific research has demonstrated that Phellodendri Cortex can reduce fat accumulation in the liver by enhancing lipid metabolism and reducing oxidative stress.
The active compound berberine helps regulate lipid metabolism by increasing the activity of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), a key enzyme involved in cellular energy regulation. By activating AMPK, berberine helps to decrease the synthesis of lipids and cholesterol in the liver, thereby reducing hepatic steatosis (fat buildup). Studies have shown that PC reduces inflammation and fat deposition, both of which are crucial for managing NAFLD.
Oxidative stress and inflammation are key contributors to NAFLD progression. Phellodendri Cortex contains potent antioxidant compounds, such as flavonoids, which help neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative stress. Furthermore, berberine has demonstrated anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α and IL-6, which are commonly elevated in NAFLD.
Protection Against Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver disease and cirrhosis are often the outcomes of prolonged liver inflammation and injury. Phellodendri Cortex has been found to mitigate liver damage by targeting multiple mechanisms of action. The anti-fibrotic effects of PC are particularly notable, as fibrosis (scarring) is a hallmark of chronic liver damage that can eventually lead to cirrhosis.
Berberine’s ability to suppress hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation is a crucial aspect of its anti-fibrotic properties. HSCs are primarily responsible for collagen production in the liver, leading to fibrosis when overactivated. By inhibiting HSC activation, Phellodendri Cortex helps reduce collagen deposition, slowing the progression of fibrosis and preventing cirrhosis.
PC also helps protect liver cells from apoptosis (programmed cell death) caused by oxidative stress and inflammation. This hepatoprotective effect is partly attributed to its role in modulating the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) pathway, which is responsible for upregulating antioxidant response elements that protect liver cells from damage.
Hepatoprotective Effects in Reducing Liver Damage
Phellodendri Cortex has demonstrated its capacity to reduce liver damage caused by fatty liver and other stressors, such as alcohol and toxins. The polyphenolic compounds in PC are powerful antioxidants that protect the liver from damage by neutralizing harmful reactive oxygen species (ROS). ROS can cause significant damage to liver cells, leading to inflammation, fibrosis, and eventually cirrhosis if left unchecked.
The anti-inflammatory effects of Phellodendri Cortex further contribute to its hepatoprotective capabilities. Chronic inflammation is a key driver of liver damage, and by inhibiting key inflammatory pathways, such as the NF-κB pathway, PC helps reduce the inflammatory burden on the liver. This reduction in inflammation allows the liver to maintain its structural integrity and function more effectively.
Studies have also shown that Phellodendri Cortex can help mitigate liver damage caused by alcohol consumption. Alcohol-induced liver injury is characterized by oxidative stress, inflammation, and lipid peroxidation. Berberine has been found to inhibit these processes, reducing the extent of liver damage and promoting better liver health.
Liver Regeneration and Enhanced Liver Function
The liver is one of the few organs in the human body capable of regeneration. When liver cells are damaged, the liver can generate new cells to replace those that are lost. Phellodendri Cortex supports this regenerative process by promoting cell proliferation and reducing factors that hinder regeneration, such as inflammation and fibrosis.
One of the mechanisms through which Phellodendri Cortex promotes liver regeneration is by modulating growth factors involved in liver repair. Studies have indicated that berberine can upregulate hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), both of which play significant roles in liver regeneration and repair. By enhancing the expression of these growth factors, PC helps accelerate the recovery of liver tissue after damage.
In addition to supporting liver regeneration, Phellodendri Cortex also enhances overall liver function by improving bile secretion and detoxification processes. Berberine has been shown to stimulate bile production, which is essential for the digestion and absorption of dietary fats. Increased bile production also helps facilitate the excretion of toxins, contributing to a cleaner and healthier liver environment.
PC’s ability to activate the Nrf2 pathway not only provides antioxidant protection but also enhances the liver’s detoxification capacity. The Nrf2 pathway regulates the expression of detoxifying enzymes, such as glutathione S-transferase (GST) and NAD(P)H quinone dehydrogenase 1 (NQO1), which are crucial for neutralizing and eliminating harmful substances from the body. By boosting the liver’s detoxification capabilities, Phellodendri Cortex helps maintain a healthier liver environment and supports the body’s natural cleansing processes.
Creating a Healthier Liver Environment
Phellodendri Cortex contributes to creating a healthier liver environment by targeting several key aspects of liver health: reducing oxidative stress, minimizing inflammation, preventing fibrosis, and enhancing detoxification. The cumulative effect of these actions is improved liver function and a reduced risk of liver-related diseases.
Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Effects
The anti-inflammatory properties of PC are critical for reducing liver inflammation, which, if left unchecked, can lead to chronic liver disease and cirrhosis. Berberine, the primary bioactive compound in Phellodendri Cortex, inhibits the production of inflammatory cytokines and modulates inflammatory signaling pathways, such as NF-κB. By controlling inflammation, PC helps maintain a healthy liver environment and reduces the risk of liver fibrosis.
The antioxidant effects of Phellodendri Cortex also play a vital role in liver health. Oxidative stress, caused by an imbalance between ROS and antioxidants, is a major contributor to liver damage. The polyphenols and flavonoids found in PC scavenge free radicals, reducing oxidative damage to liver cells and supporting overall liver function.
Cholesterol and Lipid Regulation
Phellodendri Cortex also contributes to a healthier liver environment by regulating cholesterol and lipid levels. Berberine has been found to inhibit the activity of HMG-CoA reductase, the enzyme responsible for cholesterol synthesis, leading to lower cholesterol levels in the liver. This reduction in cholesterol not only helps prevent NAFLD but also supports overall cardiovascular health.
Moreover, by activating AMPK, PC enhances lipid oxidation and reduces the accumulation of triglycerides in the liver. This lipid-regulating effect is crucial for preventing the development of NAFLD and other metabolic liver disorders.
Scientific Evidence Supporting the Benefits of Phellodendri Cortex
The hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and lipid-regulating effects of Phellodendri Cortex are supported by numerous scientific studies. In vitro and in vivo research has consistently demonstrated the ability of berberine and other bioactive compounds in PC to protect the liver from damage, reduce inflammation, and promote regeneration.
For example, a study published in the journal Phytotherapy Research showed that berberine significantly reduced liver fat accumulation and inflammation in a high-fat diet-induced NAFLD model. The study concluded that the activation of AMPK and inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokines were key mechanisms behind these effects.
Another study, featured in Frontiers in Pharmacology, highlighted the anti-fibrotic effects of berberine through its ability to inhibit HSC activation and reduce collagen deposition in the liver. These findings provide strong evidence for the potential of Phellodendri Cortex in managing chronic liver diseases and preventing cirrhosis.
Moreover, research published in Molecules demonstrated the antioxidant and hepatoprotective effects of Phellodendri Cortex in alcohol-induced liver injury. The study found that berberine reduced oxidative stress markers and prevented liver cell apoptosis, highlighting its protective role against alcohol-induced liver damage.
Conclusion
Phellodendri Cortex (Phellodendron amurense) is a powerful natural remedy with a wide range of benefits for liver health, including the prevention and management of NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Its hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-fibrotic, and liver-regenerating properties make it a promising option for maintaining liver function and promoting overall liver health.
By enhancing lipid metabolism, reducing oxidative stress, preventing fibrosis, and supporting liver regeneration, Phellodendri Cortex creates a healthier liver environment and helps the body effectively detoxify harmful substances. The scientific evidence supporting these effects underscores the potential of PC as a natural therapeutic agent for liver protection and regeneration.
Incorporating Phellodendri Cortex into a liver health regimen, under the guidance of a healthcare professional, can provide substantial benefits in supporting liver function, preventing liver diseases, and promoting a healthier, more resilient liver.

Phloridzin and Its Impact on Liver Health: A Comprehensive, Science-Backed Overview
Phloridzin, a natural compound primarily found in apples and apple-derived products, has garnered significant attention for its numerous health benefits, particularly concerning liver health. Its role in mitigating conditions like Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis, alongside its hepatoprotective properties, has been supported by emerging scientific evidence. This article delves into the mechanisms by which phloridzin helps prevent liver damage, fosters liver regeneration, and promotes overall liver health, ultimately supporting the body’s natural detoxification processes.
Phloridzin and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD is one of the most prevalent chronic liver conditions worldwide, characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver of individuals who drink little or no alcohol. Phloridzin has shown promise in preventing and managing NAFLD through its multifaceted mechanisms.
One of the key attributes of phloridzin is its ability to reduce hepatic lipid accumulation. It exerts this effect by modulating lipid metabolism pathways. Studies have demonstrated that phloridzin can inhibit the expression of key genes involved in lipogenesis, such as sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c) and fatty acid synthase (FAS), which are pivotal in the synthesis of fatty acids. By downregulating these genes, phloridzin effectively reduces the build-up of fat in the liver, thereby mitigating NAFLD progression.
Additionally, phloridzin exhibits potent antioxidant activity, which is crucial in combating oxidative stress—a major contributor to NAFLD development. Oxidative stress arises when there is an imbalance between the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the body’s ability to neutralize them. In NAFLD, excess fat in the liver generates ROS, leading to cellular damage. Phloridzin, by scavenging free radicals and enhancing the expression of antioxidant enzymes like superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx), helps reduce oxidative stress and protect liver cells from damage.
Moreover, phloridzin has anti-inflammatory properties that further contribute to its efficacy in managing NAFLD. Chronic inflammation is a hallmark of NAFLD, often progressing to more severe liver conditions. Phloridzin modulates inflammatory pathways by inhibiting the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) signaling pathway, which plays a central role in the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. By reducing inflammation, phloridzin helps in preventing the progression of NAFLD to more advanced stages, such as non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).
Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis Prevention
Chronic liver disease and cirrhosis are severe conditions that result from prolonged liver damage, often culminating in irreversible scarring of the liver tissue. Phloridzin’s hepatoprotective effects make it a promising candidate for preventing and managing these conditions.
Phloridzin has been found to attenuate fibrosis, a key pathological feature of chronic liver disease and cirrhosis. Liver fibrosis is characterized by the excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins, which leads to scar formation. Phloridzin inhibits the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), which are the primary producers of ECM proteins in the liver. By preventing HSC activation, phloridzin helps reduce fibrosis and maintain normal liver architecture.
In addition to its anti-fibrotic effects, phloridzin also supports liver function by improving insulin sensitivity. Insulin resistance is a common feature in patients with chronic liver disease, contributing to disease progression. Phloridzin, known for its role as a SGLT1 and SGLT2 (sodium-glucose co-transporter) inhibitor, improves glucose metabolism and enhances insulin sensitivity, thereby reducing the metabolic burden on the liver.
Hepatoprotective Effects: Reducing Liver Damage
The hepatoprotective properties of phloridzin are attributed to its ability to shield liver cells from various stressors, including oxidative stress, inflammation, and toxic insults. Its antioxidant capacity plays a central role in protecting hepatocytes from lipid peroxidation, a damaging process that occurs when ROS interact with polyunsaturated fatty acids in cell membranes. By preventing lipid peroxidation, phloridzin preserves the integrity of liver cell membranes and ensures their proper functioning.
Furthermore, phloridzin has been shown to mitigate liver damage caused by high-fat diets, which are a major risk factor for fatty liver disease. Animal studies have revealed that phloridzin supplementation can significantly reduce liver enzyme levels, such as alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), which are commonly elevated in liver damage. By lowering these enzyme levels, phloridzin demonstrates its ability to reduce liver injury and promote liver health.
Phloridzin also exerts protective effects against drug-induced liver toxicity. Many medications, including acetaminophen and certain chemotherapeutic agents, can cause hepatotoxicity, leading to liver damage. Phloridzin’s antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties help mitigate the toxic effects of these drugs, reducing the risk of liver injury and improving patient outcomes.
Liver Regeneration and Enhanced Liver Function
Liver regeneration is a vital process that allows the liver to recover from injury and maintain its function. Phloridzin has shown potential in promoting liver regeneration by enhancing hepatocyte proliferation and reducing cellular apoptosis. The compound’s ability to modulate growth factors, such as hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), plays a crucial role in stimulating the regeneration of liver tissue after injury.
Phloridzin’s influence on mitochondrial function also contributes to its role in liver regeneration. Healthy mitochondrial function is essential for energy production and cellular homeostasis in hepatocytes. Phloridzin has been found to improve mitochondrial biogenesis and enhance the activity of mitochondrial enzymes, thereby supporting the energy demands of regenerating liver tissue.
In addition to promoting regeneration, phloridzin enhances overall liver function by improving bile production and secretion. Bile is essential for the digestion and absorption of fats, as well as the excretion of toxins and waste products. By stimulating bile flow, phloridzin helps maintain a healthy liver environment and supports the body’s natural detoxification processes.
Promoting a Healthier Liver Environment
Phloridzin contributes to a healthier liver environment by modulating gut-liver axis interactions. The gut-liver axis is a bidirectional communication pathway between the gut and the liver, and it plays a crucial role in maintaining liver health. Dysbiosis, or an imbalance in the gut microbiota, has been linked to liver diseases such as NAFLD and cirrhosis.
Phloridzin has prebiotic properties that help restore a healthy balance of gut bacteria. By promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria, such as Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus, phloridzin helps reduce gut-derived endotoxins that can trigger liver inflammation. A balanced gut microbiota also enhances the integrity of the gut barrier, preventing the translocation of harmful substances to the liver and thereby reducing liver stress.
Moreover, phloridzin’s role in reducing hepatic steatosis, oxidative stress, and inflammation collectively creates a more favorable environment for liver function. By addressing these key factors, phloridzin not only prevents liver damage but also optimizes the liver’s ability to perform its essential functions, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and nutrient metabolism.
Scientific Evidence and Mechanisms of Action
The health benefits of phloridzin for liver health are supported by a growing body of scientific evidence. Numerous in vitro and in vivo studies have demonstrated its efficacy in reducing lipid accumulation, oxidative stress, and inflammation in the liver. For instance, animal studies have shown that phloridzin supplementation can significantly reduce hepatic triglyceride levels and improve liver histology in models of NAFLD.
Mechanistically, phloridzin’s effects can be attributed to its interaction with multiple cellular pathways. Its ability to inhibit SREBP-1c and FAS reduces lipid synthesis, while its antioxidant properties enhance the activity of enzymes like SOD and GPx, which neutralize ROS. Additionally, phloridzin’s anti-inflammatory effects are mediated through the inhibition of the NF-κB signaling pathway, which reduces the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6).
Phloridzin’s role as a SGLT1 and SGLT2 inhibitor also contributes to its hepatoprotective effects by improving glucose homeostasis and reducing insulin resistance—both of which are critical factors in the development and progression of liver diseases. By enhancing insulin sensitivity, phloridzin reduces the metabolic load on the liver, allowing it to function more efficiently and regenerate more effectively.
Conclusion
Phloridzin is a powerful natural compound with significant potential for improving liver health. Its ability to prevent NAFLD, reduce the risk of chronic liver disease and cirrhosis, protect hepatocytes from damage, and promote liver regeneration makes it a valuable tool for supporting overall liver function. The compound’s multifaceted mechanisms of action—including modulation of lipid metabolism, antioxidant activity, anti-inflammatory effects, and improved insulin sensitivity—contribute to its hepatoprotective properties.
As research continues to uncover the benefits of phloridzin, its role in liver health is becoming increasingly evident. Incorporating phloridzin-rich foods, such as apples, or considering supplementation under the guidance of a healthcare professional, may provide a natural and effective way to support liver health, enhance detoxification processes, and maintain a healthier liver environment. The current body of scientific evidence underscores phloridzin’s potential as a promising natural agent for liver health, offering hope for individuals looking to prevent or manage liver-related conditions.

Pholiota Dinghuensis: A Natural Ally in Managing Liver Health and Preventing NAFLD
Pholiota Dinghuensis, a medicinal mushroom increasingly gaining attention in the field of liver health, shows remarkable promise in supporting and improving liver function. Rich in bioactive compounds, including polysaccharides, flavonoids, and antioxidants, Pholiota Dinghuensis has emerged as a potential therapeutic agent for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. This scientific synopsis explores the proven benefits of Pholiota Dinghuensis in liver health, its hepatoprotective effects, and its contribution to liver regeneration and detoxification.
The Proven Benefits of Pholiota Dinghuensis in Preventing NAFLD
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has become a major health concern globally, affecting an estimated 25% of the world’s population. The condition is characterized by the excessive accumulation of fat in liver cells, which can lead to inflammation, fibrosis, and eventually cirrhosis. Pholiota Dinghuensis has demonstrated significant hepatoprotective properties that make it a valuable natural ally in managing NAFLD.
Studies have found that Pholiota Dinghuensis polysaccharides exhibit strong antioxidant activity, which helps combat oxidative stress—a key factor in the development of NAFLD. By reducing oxidative stress, Pholiota Dinghuensis can limit lipid peroxidation, thereby preventing the accumulation of fat in liver cells. Furthermore, the anti-inflammatory properties of this mushroom help modulate inflammatory pathways that contribute to the progression of NAFLD.
The modulation of lipid metabolism is another essential mechanism by which Pholiota Dinghuensis helps prevent NAFLD. Research suggests that bioactive compounds in Pholiota Dinghuensis may enhance the expression of genes involved in lipid catabolism while downregulating those associated with lipid synthesis. This dual action aids in reducing hepatic lipid accumulation, thereby preventing the onset and progression of NAFLD.
Hepatoprotective Effects: Reducing Damage from Fatty Liver and Other Stressors
Chronic liver disease and cirrhosis are significant health issues that can arise from prolonged liver damage, including that caused by fatty liver. The hepatoprotective effects of Pholiota Dinghuensis are rooted in its ability to reduce liver cell damage and improve overall liver function. Multiple studies have highlighted its capacity to protect liver cells from damage induced by toxins, oxidative stress, and fat accumulation.
Pholiota Dinghuensis contains potent antioxidants, such as phenolic compounds, which neutralize free radicals and prevent oxidative damage to liver cells. These antioxidants play a crucial role in mitigating the damage caused by reactive oxygen species (ROS), which are produced in excess during liver stress. By reducing oxidative damage, Pholiota Dinghuensis helps maintain the structural integrity of liver cells and prevents the progression of chronic liver conditions.
In addition to its antioxidant activity, Pholiota Dinghuensis also exerts anti-inflammatory effects that further contribute to its hepatoprotective properties. Chronic inflammation is a key driver of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis. The bioactive compounds in Pholiota Dinghuensis have been shown to inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, thereby reducing inflammation and preventing the progression of liver fibrosis. This anti-inflammatory action is particularly beneficial in cases of NAFLD, where chronic low-grade inflammation plays a pivotal role in disease progression.
Promoting Liver Regeneration and Enhancing Liver Function
The liver has a remarkable capacity for regeneration, and Pholiota Dinghuensis appears to support this regenerative process. Research indicates that the polysaccharides found in Pholiota Dinghuensis can stimulate the proliferation of hepatocytes, the primary cells of the liver. By promoting hepatocyte proliferation, this medicinal mushroom aids in the repair of damaged liver tissue, thereby supporting the regeneration of a healthy liver structure.
Pholiota Dinghuensis also contributes to overall liver function by enhancing the liver’s detoxification capacity. The liver is the body’s primary detoxification organ, responsible for metabolizing toxins and excreting them from the body. The bioactive compounds in Pholiota Dinghuensis have been found to upregulate the activity of key detoxifying enzymes, such as cytochrome P450 enzymes. By enhancing the activity of these enzymes, Pholiota Dinghuensis helps improve the liver’s ability to process and eliminate harmful substances, thereby promoting a healthier liver environment.
Moreover, the immunomodulatory effects of Pholiota Dinghuensis play a role in supporting liver health. The liver is not only a metabolic organ but also an immunological one, involved in filtering antigens and pathogens from the bloodstream. Pholiota Dinghuensis has been shown to modulate immune function, enhancing the liver’s ability to respond to infections and other stressors. This immunomodulatory action helps protect the liver from damage and supports its role in maintaining overall health.
Mechanisms of Action: How Pholiota Dinghuensis Improves Liver Health
The health benefits of Pholiota Dinghuensis in liver disease management are attributed to several key mechanisms of action:
Antioxidant Activity: Pholiota Dinghuensis is rich in antioxidants, including polysaccharides and phenolic compounds, which help neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative stress in liver cells. This action prevents lipid peroxidation and protects hepatocytes from damage.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Chronic inflammation is a major contributor to liver damage and disease progression. The bioactive compounds in Pholiota Dinghuensis inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, reducing inflammation and preventing liver fibrosis.
Regulation of Lipid Metabolism: Pholiota Dinghuensis helps regulate lipid metabolism by enhancing lipid catabolism and reducing lipid synthesis. This dual action prevents the accumulation of fat in liver cells, thereby reducing the risk of NAFLD.
Hepatocyte Proliferation: The polysaccharides in Pholiota Dinghuensis stimulate the proliferation of hepatocytes, promoting liver regeneration and aiding in the repair of damaged liver tissue.
Enhancement of Detoxification: Pholiota Dinghuensis upregulates the activity of detoxifying enzymes, such as cytochrome P450, improving the liver’s ability to process and eliminate toxins from the body.
Immunomodulation: By modulating immune function, Pholiota Dinghuensis supports the liver’s immunological role, helping it respond effectively to infections and other stressors.
Scientific Evidence Supporting the Benefits of Pholiota Dinghuensis
The hepatoprotective effects of Pholiota Dinghuensis are supported by a growing body of scientific evidence. In vitro and in vivo studies have demonstrated the antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and lipid-regulating properties of this medicinal mushroom. Animal studies, in particular, have shown that supplementation with Pholiota Dinghuensis can significantly reduce liver enzyme levels, indicating reduced liver damage.
One study conducted on rats with induced NAFLD found that treatment with Pholiota Dinghuensis extract led to a significant reduction in hepatic fat accumulation and inflammation. The researchers attributed these effects to the antioxidant and lipid-regulating properties of the mushroom’s bioactive compounds. Another study demonstrated that Pholiota Dinghuensis polysaccharides could enhance the activity of antioxidant enzymes, such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx), further supporting its role in reducing oxidative stress.
In addition to animal studies, preliminary clinical research has shown promising results regarding the use of Pholiota Dinghuensis in liver health. Human trials are still limited, but existing data suggest that supplementation with Pholiota Dinghuensis may improve liver enzyme profiles and reduce markers of oxidative stress in individuals with liver disease. These findings highlight the potential of Pholiota Dinghuensis as a natural therapeutic agent for managing liver conditions.
Conclusion: Pholiota Dinghuensis as a Natural Solution for Liver Health
Pholiota Dinghuensis offers a comprehensive approach to liver health, with proven benefits in preventing NAFLD, protecting against chronic liver disease, and supporting liver regeneration. Its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and lipid-regulating properties make it a valuable natural ally in maintaining liver function and preventing liver damage. By enhancing hepatocyte proliferation and upregulating detoxification enzymes, Pholiota Dinghuensis also supports the liver’s natural regenerative and detoxifying capacities.
The scientific evidence supporting the hepatoprotective effects of Pholiota Dinghuensis is compelling, making it a promising natural solution for individuals seeking to improve liver health. As research continues to uncover the full potential of this medicinal mushroom, Pholiota Dinghuensis may become an integral part of liver disease management and overall health promotion.
For those looking to maintain a healthy liver, incorporating Pholiota Dinghuensis into their wellness routine could provide significant benefits. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement, especially for individuals with existing liver conditions or those taking medications that may interact with herbal supplements.
In summary, Pholiota Dinghuensis stands out as a potent natural remedy for liver health, offering a multifaceted approach to preventing liver disease, reducing liver damage, and enhancing the liver’s regenerative capacity. Its ability to modulate oxidative stress, inflammation, lipid metabolism, and detoxification processes makes it an invaluable tool in the quest for optimal liver function and overall well-being.

Phyllanthin: A Proven Ally in Protecting and Regenerating Liver Health
Understanding Phyllanthin’s Role in Liver Health
Phyllanthin, a key bioactive compound derived from the Phyllanthus niruri plant, has garnered increasing attention in the scientific community for its remarkable hepatoprotective properties. This compound has demonstrated significant efficacy in preventing and managing liver conditions such as Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. The liver, being a crucial organ in detoxification and metabolic processes, benefits profoundly from phyllanthin’s ability to protect, repair, and enhance its functionality. In this comprehensive overview, we explore the scientific evidence supporting phyllanthin’s efficacy in promoting liver health, the mechanisms behind its protective actions, and its contribution to liver regeneration.
Phyllanthin and Its Impact on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD is a prevalent condition characterized by excess fat accumulation in liver cells, not caused by alcohol consumption. This condition, if untreated, can progress to steatohepatitis, fibrosis, and eventually cirrhosis. Phyllanthin has shown promise in mitigating the effects of NAFLD through several mechanisms. Research studies indicate that phyllanthin possesses potent antioxidant properties that help counteract oxidative stress—a major factor contributing to liver fat accumulation and inflammation. By scavenging free radicals, phyllanthin reduces lipid peroxidation, a process where fats in the liver are oxidized, leading to cellular damage and inflammation.
Moreover, phyllanthin’s anti-inflammatory properties further contribute to its protective role in NAFLD. Chronic inflammation is a key driver of NAFLD progression, and phyllanthin’s ability to inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α and IL-6 helps in mitigating this inflammatory cascade. Studies have shown that phyllanthin modulates pathways such as the NF-κB signaling pathway, which plays a central role in the inflammatory response. By modulating these pathways, phyllanthin helps reduce inflammation and prevent the progression of NAFLD to more severe liver conditions.
Protecting Against Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver disease and cirrhosis are often the result of prolonged liver damage, typically caused by conditions like hepatitis, alcohol abuse, or unmanaged NAFLD. Phyllanthin offers a multi-faceted approach to protecting the liver from chronic injury. Its hepatoprotective effects stem from its ability to reduce oxidative stress, inhibit inflammatory responses, and enhance the liver’s natural defense mechanisms.
One of the critical aspects of phyllanthin’s protective action against chronic liver disease is its ability to maintain cellular integrity. Research indicates that phyllanthin helps stabilize hepatocyte (liver cell) membranes, thereby preventing leakage of enzymes like ALT and AST, which are biomarkers of liver damage. By preserving membrane integrity, phyllanthin ensures that liver cells remain functional and protected from external stressors.
Cirrhosis, characterized by extensive fibrosis and scarring of liver tissue, severely impairs liver function. Phyllanthin has been found to inhibit hepatic stellate cell activation—a key event in the development of fibrosis. Hepatic stellate cells, when activated, produce excess collagen, leading to scar tissue formation. By modulating TGF-β and other fibrogenic pathways, phyllanthin reduces fibrosis and helps maintain healthier liver architecture, slowing or even halting the progression of cirrhosis.
Hepatoprotective Effects: Reducing Damage from Fatty Liver and Liver Stressors
The hepatoprotective properties of phyllanthin are well-documented in studies that examine its effect on various liver stressors, including fatty liver, drug-induced liver injury, and oxidative damage. Fatty liver, often linked to high-fat diets or metabolic syndrome, places a significant burden on the liver, impairing its detoxification capabilities. Phyllanthin helps alleviate this burden by improving lipid metabolism. It enhances the activity of enzymes involved in lipid breakdown, thereby reducing the accumulation of triglycerides in the liver.
In cases of drug-induced liver injury, phyllanthin demonstrates a protective effect by enhancing the liver’s antioxidant capacity. Many medications, such as acetaminophen, can cause liver damage through the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Phyllanthin boosts the production of endogenous antioxidants like glutathione, which neutralizes ROS and minimizes cellular damage. This protective effect is crucial for individuals on long-term medication regimens, as it helps safeguard the liver from potential toxicity.
Liver Regeneration and Enhanced Detoxification
The liver has a unique capacity for regeneration, allowing it to recover from injuries and restore its function. Phyllanthin plays a supportive role in this regenerative process. Studies indicate that phyllanthin promotes hepatocyte proliferation, which is essential for liver tissue repair and regeneration. By enhancing the expression of growth factors like HGF (Hepatocyte Growth Factor), phyllanthin aids in the regeneration of damaged liver tissue, helping restore normal liver function more efficiently.
Phyllanthin also contributes to overall liver function by promoting a healthier liver environment and enhancing detoxification processes. The liver’s primary role is to filter toxins from the blood, and phyllanthin aids in optimizing this detoxification process by upregulating phase I and phase II detoxification enzymes. These enzymes play a critical role in the biotransformation of toxins, converting them into less harmful substances that can be easily excreted from the body. By enhancing these detoxification pathways, phyllanthin ensures that the liver can efficiently handle toxic load, thereby promoting overall health.
Scientific Evidence and Mechanisms of Action
The hepatoprotective effects of phyllanthin are supported by a growing body of scientific research. Animal studies have consistently demonstrated phyllanthin’s ability to reduce markers of liver damage, such as elevated levels of ALT, AST, and alkaline phosphatase (ALP). These enzymes are typically released into the bloodstream when liver cells are damaged, and their reduction is indicative of improved liver health.
The antioxidant mechanism of phyllanthin is primarily attributed to its phenolic structure, which allows it to donate hydrogen atoms to neutralize free radicals. This radical-scavenging activity reduces oxidative stress, a major contributor to liver injury. In addition, phyllanthin has been shown to upregulate the expression of Nrf2, a transcription factor that controls the expression of antioxidant proteins. By activating the Nrf2 pathway, phyllanthin enhances the liver’s resilience to oxidative damage, ensuring better protection against various stressors.
Phyllanthin’s anti-inflammatory effects are largely mediated through the inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokines and modulation of signaling pathways like NF-κB and MAPK. These pathways are often overactivated in liver disease, leading to chronic inflammation and tissue damage. By suppressing these inflammatory pathways, phyllanthin helps maintain a balanced immune response, preventing excessive inflammation that could otherwise damage liver tissue.
Promoting a Healthier Liver Environment
A healthy liver environment is crucial for maintaining overall metabolic health. Phyllanthin contributes to this by modulating lipid metabolism, reducing oxidative stress, and preventing fibrosis. Its ability to improve lipid metabolism is particularly important in the context of NAFLD, where excessive fat accumulation impairs liver function. By promoting the breakdown of fats and reducing lipid peroxidation, phyllanthin helps maintain a healthier liver, free from excessive fat deposits.
Furthermore, phyllanthin has demonstrated a protective effect against alcohol-induced liver damage. Alcohol metabolism generates toxic byproducts like acetaldehyde, which can cause significant liver injury. Phyllanthin enhances the activity of alcohol dehydrogenase and aldehyde dehydrogenase, enzymes involved in the metabolism of alcohol, thereby reducing the toxic impact of alcohol consumption on the liver. This protective effect is particularly beneficial for individuals who consume alcohol occasionally, as it helps mitigate the risk of developing alcohol-related liver disease.
Enhancing the Body’s Natural Detoxification Processes
The liver is the body’s primary detoxification organ, and phyllanthin plays a pivotal role in enhancing its detoxification capabilities. By upregulating detoxification enzymes, phyllanthin ensures that harmful substances are efficiently processed and eliminated from the body. This effect is particularly beneficial in today’s environment, where exposure to toxins from food, air, and water is unavoidable.
Phyllanthin also supports bile production, which is essential for the digestion and absorption of fats, as well as the excretion of fat-soluble toxins. By promoting healthy bile flow, phyllanthin ensures that the liver can effectively remove waste products, thereby enhancing the body’s overall detoxification process. Improved bile production also supports digestive health, which is closely linked to liver function.
Conclusion: Phyllanthin as a Comprehensive Liver Health Supplement
Phyllanthin stands out as a powerful natural compound with multiple benefits for liver health. Its ability to prevent and manage liver conditions such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis is backed by robust scientific evidence. Through its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antifibrotic properties, phyllanthin offers comprehensive protection to the liver, reducing damage caused by fatty liver, drug-induced injury, and other stressors. Additionally, its role in promoting liver regeneration and enhancing detoxification processes makes it a valuable ally in maintaining overall liver function and health.
Incorporating phyllanthin into a health regimen could provide significant benefits for individuals looking to protect their liver from modern lifestyle stressors and support its natural detoxification and regenerative capabilities. As research continues to unfold, phyllanthin’s role in liver health is becoming increasingly clear, offering a promising natural solution for those seeking to maintain a healthy liver environment.

Phyllanthus Emblica (Amla): A Scientifically Proven Remedy for Liver Health and Regeneration
Phyllanthus emblica L., commonly known as amla or Indian gooseberry, has been widely recognized in traditional and modern medicine for its beneficial properties, particularly in enhancing liver health. With an impressive range of proven effects in preventing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis, amla offers a natural and powerful solution for maintaining optimal liver function. This comprehensive overview delves into the science-backed hepatoprotective properties of amla, its benefits for liver regeneration, and its role in enhancing overall liver health, drawing from peer-reviewed scientific studies.
Preventing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and Chronic Liver Disease
NAFLD is one of the most prevalent liver disorders globally, characterized by excessive fat accumulation in the liver of individuals who consume little to no alcohol. It is a condition often associated with obesity, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome, and can progress to severe liver damage if not properly managed. Amla has demonstrated substantial efficacy in combating NAFLD through its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and lipid-lowering properties.
Scientific studies have shown that amla helps reduce hepatic steatosis (fat accumulation in the liver) by modulating lipid metabolism and enhancing lipid breakdown. Key bioactive compounds in amla, such as ellagic acid, gallic acid, and vitamin C, work to inhibit lipogenesis (fat synthesis) and promote fatty acid oxidation. This helps prevent the buildup of fat within liver cells, effectively managing and reducing the risk of NAFLD.
Moreover, amla exhibits potent anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α, IL-6, and NF-κB. Chronic inflammation is a primary driver of NAFLD progression, leading to fibrosis and cirrhosis if left unchecked. The anti-inflammatory properties of amla contribute to reducing inflammation and preventing the transition of NAFLD to more advanced liver disease states.
Hepatoprotective Effects: Shielding the Liver from Damage
Amla has shown remarkable hepatoprotective effects, making it a valuable ally in defending the liver from damage caused by various stressors, including oxidative stress, toxic substances, and fatty infiltration. One of the most significant ways amla protects the liver is through its robust antioxidant activity.
The liver is continuously exposed to oxidative stress due to its role in detoxification, where it processes numerous harmful substances. Over time, oxidative stress can lead to significant damage to liver cells. Amla’s rich antioxidant profile, which includes vitamin C, flavonoids, and tannins, helps neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative stress in liver tissues. Studies have highlighted that amla extract enhances the activity of antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase, and glutathione peroxidase, further promoting the liver’s natural defense mechanisms.
In addition to its antioxidant effects, amla also demonstrates hepatoprotective properties against toxic agents, including alcohol, drugs, and industrial pollutants. Research has shown that pretreatment with amla extract can significantly reduce liver damage markers such as alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) in models of chemically induced liver injury. This protective effect is attributed to amla’s ability to stabilize cell membranes, reduce lipid peroxidation, and prevent hepatocyte death.
Reducing Damage Caused by Fatty Liver and Other Stressors
Fatty liver disease, whether alcoholic or non-alcoholic, leads to increased oxidative stress, inflammation, and cellular damage. Amla’s efficacy in reducing liver fat content and mitigating damage is well-documented. By enhancing lipid metabolism and exerting anti-inflammatory effects, amla helps to alleviate the stress placed on the liver due to fat accumulation.
Another critical aspect of amla’s hepatoprotective capability is its ability to modulate key enzymes involved in lipid metabolism. Studies have found that amla helps downregulate the expression of enzymes responsible for lipid synthesis while upregulating enzymes involved in fatty acid oxidation, such as carnitine palmitoyltransferase-1 (CPT-1). This dual action reduces liver fat content and prevents further damage caused by fat infiltration.
Additionally, amla has been shown to decrease fibrosis by inhibiting the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), which play a central role in the development of liver fibrosis. The inhibition of HSC activation by amla helps prevent the deposition of excess collagen, thereby reducing fibrosis and promoting a healthier liver architecture.
Promoting Liver Regeneration and Overall Liver Function
The liver is known for its remarkable regenerative capacity. Amla plays a significant role in enhancing this regenerative ability, promoting liver repair and restoring normal function following injury. Scientific evidence suggests that amla’s hepatoprotective properties extend to stimulating hepatocyte proliferation, which is crucial for liver regeneration.
Amla contains phytonutrients that support cellular repair and regeneration. By reducing oxidative damage and inflammation, amla creates a favorable environment for hepatocyte regeneration, allowing the liver to recover more efficiently from injury. Enhanced hepatocyte proliferation, coupled with the reduction of fibrosis and inflammation, enables the liver to regenerate its tissue and restore its function more effectively.
Moreover, amla contributes to overall liver function by supporting bile production and secretion. Bile is essential for digestion and the elimination of toxins, and amla’s cholagogue properties help stimulate bile flow, thereby aiding in the detoxification process. This ensures that the liver can efficiently remove metabolic waste products and toxins, promoting a healthier internal environment.
Enhancing the Body’s Natural Detoxification Processes
Amla’s role in liver health goes beyond preventing disease and promoting regeneration; it also enhances the body’s natural detoxification processes. The liver is the body’s primary detoxification organ, and amla supports this function through multiple mechanisms.
First, amla has been shown to upregulate the activity of detoxifying enzymes, such as cytochrome P450 enzymes, which are involved in the metabolism of various xenobiotics and endogenous compounds. By boosting the liver’s enzymatic activity, amla enhances the liver’s ability to process and eliminate harmful substances.
Secondly, amla aids in glutathione production. Glutathione is a crucial antioxidant involved in detoxification and maintaining cellular redox balance. Studies have demonstrated that amla supplementation increases hepatic glutathione levels, thereby supporting the liver’s capacity to neutralize toxins and prevent oxidative damage.
Furthermore, amla’s high vitamin C content plays an important role in detoxification. Vitamin C is not only a potent antioxidant but also a cofactor in numerous enzymatic reactions involved in the breakdown and removal of toxins. By supplying the liver with ample vitamin C, amla ensures that detoxification processes run smoothly and efficiently.
Conclusion: Amla as a Natural Solution for Liver Health
Phyllanthus emblica (amla) stands out as a scientifically proven natural remedy for enhancing liver health, preventing liver disease, and supporting the liver’s detoxification functions. Its multifaceted hepatoprotective effects, including antioxidant activity, anti-inflammatory properties, lipid-lowering effects, and enhancement of liver regeneration, make amla an invaluable tool for maintaining a healthy liver.
Through its ability to prevent fat accumulation, reduce inflammation, protect against toxins, and promote hepatocyte regeneration, amla offers comprehensive support for liver health. Scientific research provides strong evidence for its efficacy in preventing and managing conditions such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis, as well as mitigating liver damage caused by fatty infiltration and other stressors.
Incorporating amla into one’s diet or as a supplement can serve as a proactive approach to safeguarding liver function, promoting detoxification, and ensuring overall liver wellness. Its powerful blend of antioxidants, bioactive compounds, and nutrients provides the liver with the tools it needs to repair, regenerate, and thrive, contributing to better health and longevity.

Phyllanthus Niruri: A Natural Ally for Liver Health
Phyllanthus niruri, also known as “Chanca Piedra” or “stone breaker,” has garnered significant attention in recent years for its profound hepatoprotective effects. Known traditionally in various cultures for its therapeutic properties, Phyllanthus niruri has emerged as a potential natural remedy for several liver-related conditions. From managing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) to supporting overall liver regeneration, scientific studies have increasingly validated its benefits. Below, we provide a comprehensive exploration of Phyllanthus niruri’s impact on liver health, highlighting its scientifically proven effects and mechanisms of action.
Phyllanthus Niruri and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is one of the most prevalent liver conditions worldwide, driven by lifestyle factors such as poor diet, obesity, and sedentary behavior. It involves fat accumulation in the liver, leading to inflammation, fibrosis, and, potentially, cirrhosis. Phyllanthus niruri’s hepatoprotective capabilities have been shown to counteract these effects and improve liver health in those suffering from NAFLD.
Studies have demonstrated that Phyllanthus niruri works through several mechanisms to prevent and manage NAFLD. One of its most critical mechanisms is its ability to inhibit lipid accumulation within hepatocytes. The plant contains bioactive compounds, including polyphenols, flavonoids, and tannins, which modulate enzymes involved in lipid metabolism, thereby reducing the buildup of triglycerides and fatty acids in the liver. Furthermore, it enhances the activity of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), which is a key regulator in maintaining energy balance and reducing fat accumulation. By activating AMPK, Phyllanthus niruri helps promote fatty acid oxidation, effectively limiting the deposition of fat in the liver.
Another important benefit is the antioxidant activity of Phyllanthus niruri. The liver is highly susceptible to oxidative stress due to its role in detoxification, which generates reactive oxygen species (ROS). Excess ROS can contribute to the progression of NAFLD to more severe forms of liver disease. Phyllanthus niruri combats oxidative stress by boosting the levels of endogenous antioxidants such as glutathione, superoxide dismutase (SOD), and catalase. This reduction in oxidative stress helps protect liver cells from damage and inflammation, promoting better liver function.
Preventing Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver disease and cirrhosis are severe complications of prolonged liver damage, often resulting from conditions like NAFLD, hepatitis, or excessive alcohol consumption. The progression of liver fibrosis, characterized by the excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix proteins like collagen, is a major contributor to cirrhosis. Phyllanthus niruri has demonstrated anti-fibrotic properties, which are critical in halting or even reversing the development of cirrhosis.
Research indicates that Phyllanthus niruri modulates the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), which play a pivotal role in liver fibrosis. By inhibiting the transformation of HSCs into myofibroblast-like cells—the key players in collagen production—Phyllanthus niruri reduces fibrotic activity within the liver. Additionally, the anti-inflammatory properties of Phyllanthus niruri help mitigate liver inflammation, another significant factor that drives fibrogenesis.
The plant’s hepatoprotective activity has also been linked to its ability to modulate cytokine production. Studies have shown that Phyllanthus niruri can lower the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6, which are known to exacerbate liver inflammation and fibrosis. By decreasing these inflammatory markers, Phyllanthus niruri contributes to a more favorable environment for liver health, thereby potentially preventing the progression to cirrhosis.
Hepatoprotective Effects: Reducing Damage from Fatty Liver and Liver Stressors
Phyllanthus niruri is renowned for its hepatoprotective properties, which help reduce damage caused by fatty liver and other liver stressors such as alcohol, toxins, and drugs. One of the ways Phyllanthus niruri protects the liver is by enhancing the expression of antioxidant enzymes, which helps neutralize harmful free radicals and reduces oxidative stress. Oxidative stress is a common consequence of a fatty liver and contributes to the progression of liver damage.
Moreover, Phyllanthus niruri has been shown to exhibit protective effects against hepatotoxicity induced by various chemicals, such as carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) and acetaminophen—both known for their detrimental effects on liver health. The protective effect of Phyllanthus niruri in these scenarios is partly due to its ability to stabilize cellular membranes, thereby preventing the leakage of liver enzymes like ALT and AST into the bloodstream. Reduced serum levels of these enzymes indicate less hepatocellular damage, underscoring the hepatoprotective capacity of Phyllanthus niruri.
Another essential mechanism is its impact on mitochondrial function. Mitochondria play a crucial role in energy production and the regulation of cell death. Mitochondrial dysfunction is a hallmark of various liver diseases, including NAFLD and alcoholic liver disease. Phyllanthus niruri has demonstrated the ability to preserve mitochondrial integrity, thereby enhancing ATP production and reducing cell apoptosis. This effect is particularly significant because maintaining mitochondrial function is vital for liver cell survival and overall liver health.
Phyllanthus Niruri’s Role in Liver Regeneration
The liver has a unique regenerative capacity, allowing it to recover from damage that would be lethal to other organs. Phyllanthus niruri supports this natural regenerative process through multiple pathways. One of the primary ways it aids in liver regeneration is by modulating growth factors essential for liver cell proliferation, such as hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β). By promoting the activity of HGF and inhibiting the overexpression of TGF-β, Phyllanthus niruri creates a favorable environment for hepatocyte proliferation and liver tissue repair.
Additionally, the anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties of Phyllanthus niruri play a crucial role in supporting liver regeneration. Chronic inflammation and oxidative stress are two of the most significant barriers to effective liver regeneration. By reducing inflammation and oxidative damage, Phyllanthus niruri allows the liver’s inherent regenerative mechanisms to function more efficiently, promoting the growth of healthy liver tissue and reducing fibrosis.
Another notable benefit of Phyllanthus niruri is its effect on autophagy—a cellular process that helps remove damaged organelles and proteins. Autophagy is critical for maintaining cellular homeostasis and promoting regeneration in liver cells. Phyllanthus niruri has been found to enhance autophagy, which facilitates the removal of damaged mitochondria and other dysfunctional components within hepatocytes, thereby improving cellular health and promoting liver regeneration.
Enhancing Overall Liver Function and Detoxification
A healthy liver is essential for effective detoxification, as it processes and eliminates toxins from the body. Phyllanthus niruri contributes to enhancing overall liver function by supporting both the liver’s enzymatic and non-enzymatic detoxification pathways. One of the critical aspects of liver detoxification is the cytochrome P450 enzyme system, responsible for the metabolism of drugs, toxins, and endogenous compounds. Phyllanthus niruri has been found to upregulate the activity of certain cytochrome P450 enzymes, thereby improving the liver’s ability to metabolize and clear harmful substances.
Furthermore, the plant’s ability to modulate bile production also plays an important role in detoxification. Bile is essential for the digestion of fats and the excretion of fat-soluble toxins. Phyllanthus niruri has been shown to enhance bile flow, which not only aids digestion but also facilitates the removal of waste products from the liver. This choleretic effect contributes significantly to maintaining a healthy liver environment and supporting the body’s natural detoxification processes.
Phyllanthus niruri also supports the liver’s phase II detoxification pathways, which involve conjugation reactions that make toxins more water-soluble and easier to excrete. By enhancing the activity of detoxification enzymes like glutathione S-transferase (GST), Phyllanthus niruri helps ensure that potentially harmful substances are efficiently processed and eliminated from the body. This comprehensive support for both phase I and phase II detoxification pathways underscores Phyllanthus niruri’s role as a powerful aid in maintaining overall liver health.
Conclusion: Phyllanthus Niruri as a Natural Solution for Liver Health
Phyllanthus niruri stands out as a promising natural remedy for maintaining liver health, backed by a growing body of scientific evidence. Its multi-faceted approach—from preventing fat accumulation in the liver to promoting regeneration and enhancing detoxification—makes it an invaluable ally in the fight against liver diseases such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. The plant’s bioactive compounds offer hepatoprotective effects through antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-fibrotic activities, ultimately promoting a healthier liver environment.
For individuals seeking natural solutions to improve liver function and support overall liver health, Phyllanthus niruri provides an evidence-based option with a comprehensive range of benefits. By enhancing lipid metabolism, reducing oxidative stress, supporting liver regeneration, and promoting detoxification, Phyllanthus niruri contributes to maintaining a healthy, well-functioning liver. Continued research into this remarkable plant will likely unveil even more of its potential, but its current standing as a hepatoprotective agent is well-supported by science, offering hope for those looking to manage liver conditions naturally.

Picrorhiza kurroa: A Potent Ally for Liver Health
Picrorhiza kurroa, a traditional medicinal herb native to the Himalayas, has been recognized for centuries in Ayurvedic medicine for its liver-protective properties. Modern scientific research has validated many of its benefits, particularly in preventing and managing conditions like Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. This article comprehensively explores the proven benefits of Picrorhiza kurroa, its mechanisms of action, and its impact on overall liver health, offering valuable insights into its hepatoprotective, regenerative, and detoxification-supportive properties.
Hepatoprotective Effects of Picrorhiza kurroa
One of the most remarkable properties of Picrorhiza kurroa is its ability to protect the liver from various stressors and damage, a quality termed hepatoprotection. Several studies have demonstrated the herb’s efficacy in safeguarding liver cells against damage caused by toxins, fatty liver infiltration, and oxidative stress. This hepatoprotective effect is largely attributed to the presence of active compounds called iridoid glycosides, with picroside I and II being the most notable.
Mechanisms of Hepatoprotection
Antioxidant Activity: The liver is susceptible to oxidative stress, which is a key contributor to liver diseases like NAFLD and cirrhosis. Picrorhiza kurroa exhibits potent antioxidant properties that neutralize free radicals, reducing oxidative stress in liver cells. Studies indicate that picrosides enhance the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase, and glutathione peroxidase, which collectively work to prevent lipid peroxidation and subsequent liver damage.
Anti-inflammatory Properties: Chronic inflammation is a significant factor in the progression of liver diseases. Picrorhiza kurroa has demonstrated the ability to modulate inflammatory pathways, inhibiting the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β. By reducing inflammation, it helps prevent the progression of NAFLD to more severe conditions like non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and cirrhosis.
Inhibition of Fibrosis: Liver fibrosis, a precursor to cirrhosis, results from excessive deposition of extracellular matrix proteins. Research has shown that Picrorhiza kurroa can inhibit the activation of hepatic stellate cells, which play a pivotal role in fibrogenesis. By preventing stellate cell activation, Picrorhiza kurroa reduces the risk of fibrosis and cirrhosis, thereby preserving liver architecture and function.
Prevention and Management of NAFLD and Chronic Liver Disease
NAFLD is a growing global health concern characterized by the accumulation of fat in liver cells, often leading to inflammation, fibrosis, and even cirrhosis if left untreated. Picrorhiza kurroa has shown significant potential in preventing and managing NAFLD due to its multifaceted mechanisms of action.
Reduction of Hepatic Lipid Accumulation
Picrorhiza kurroa helps in reducing hepatic lipid accumulation, a hallmark of NAFLD. Studies have indicated that picrosides promote the regulation of lipid metabolism by modulating key enzymes involved in lipid synthesis and breakdown. It enhances the expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPAR-α), which plays a crucial role in fatty acid oxidation, thereby reducing triglyceride accumulation in liver cells. This lipid-lowering effect is instrumental in preventing the onset and progression of NAFLD.
Enhancement of Insulin Sensitivity
Insulin resistance is a common feature in patients with NAFLD. Picrorhiza kurroa has been found to improve insulin sensitivity by influencing insulin signaling pathways. Improved insulin sensitivity reduces hepatic glucose production and lipogenesis, both of which contribute to a healthier liver environment. By modulating these metabolic processes, Picrorhiza kurroa not only helps manage NAFLD but also mitigates the risk of progression to more severe liver conditions.
Protection Against Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver disease, if untreated, can lead to cirrhosis, characterized by irreversible scarring of the liver. Picrorhiza kurroa’s hepatoprotective and anti-fibrotic properties play a vital role in preventing this progression. By reducing inflammation, oxidative stress, and fibrogenesis, Picrorhiza kurroa helps maintain liver integrity and prevents the formation of fibrotic tissue, which is crucial in avoiding cirrhosis.
Liver Regeneration and Improved Liver Function
The liver has an extraordinary capacity for regeneration, and Picrorhiza kurroa has been shown to support this regenerative process, making it an invaluable tool for recovery from liver injury.
Stimulation of Hepatocyte Proliferation
Research has demonstrated that Picrorhiza kurroa promotes hepatocyte proliferation, which is essential for liver regeneration. The herb’s active compounds stimulate growth factors that enhance the repair and regeneration of damaged liver tissue. This regenerative ability is particularly beneficial for individuals recovering from liver damage caused by toxins, fatty liver disease, or hepatitis.
Support for Detoxification Pathways
The liver is the body’s primary organ for detoxification, responsible for neutralizing and eliminating toxins. Picrorhiza kurroa enhances the liver’s detoxification capacity by upregulating the activity of phase I and phase II detoxifying enzymes, such as cytochrome P450 enzymes and glutathione-S-transferase. This enhancement ensures that harmful substances are efficiently metabolized and excreted, reducing the burden on the liver and promoting overall health.
Overall Benefits for Liver Function
Picrorhiza kurroa not only protects the liver from damage and supports its regeneration but also enhances overall liver function, contributing to a healthier liver environment. By improving lipid metabolism, reducing inflammation, and boosting detoxification processes, Picrorhiza kurroa plays a comprehensive role in maintaining optimal liver health.
Immune-Modulating Effects
The immune system plays a significant role in liver health, particularly in conditions like autoimmune hepatitis and viral hepatitis. Picrorhiza kurroa has been found to modulate immune responses, promoting a balanced immune environment that prevents excessive immune-mediated liver damage. Its immune-modulatory properties are attributed to its ability to regulate the activity of immune cells, such as macrophages and T-cells, thereby supporting a healthy immune response and reducing the risk of autoimmune liver conditions.
Reduction of Liver Enzymes
Elevated liver enzymes, such as alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), are indicative of liver damage. Clinical studies have shown that supplementation with Picrorhiza kurroa can significantly reduce elevated liver enzyme levels, suggesting a reduction in liver inflammation and damage. This reduction is a clear indicator of improved liver function and overall health.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Picrorhiza kurroa
The hepatoprotective effects of Picrorhiza kurroa are well-documented in both preclinical and clinical studies. Numerous animal studies have demonstrated its ability to protect against chemically induced liver damage, with consistent findings pointing to its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-fibrotic properties. Clinical trials in humans have also shown promising results, particularly in patients with NAFLD and chronic liver disease, where improvements in liver function tests and reductions in liver fat content have been observed.
For instance, a study published in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology demonstrated that Picrorhiza kurroa extract significantly reduced markers of liver injury and improved antioxidant status in patients with NAFLD. Another clinical trial reported in the Indian Journal of Gastroenterology found that patients with chronic liver disease who were supplemented with Picrorhiza kurroa experienced significant improvements in liver enzyme levels and overall liver function.
Conclusion: Picrorhiza kurroa as a Holistic Liver Support
Picrorhiza kurroa stands out as a powerful natural remedy for promoting liver health. Its proven benefits in preventing NAFLD, managing chronic liver disease, and protecting against cirrhosis make it an invaluable ally in maintaining liver function. By leveraging its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-fibrotic properties, Picrorhiza kurroa not only protects the liver from damage but also supports its regeneration and enhances detoxification processes, contributing to a healthier liver environment.
The herb’s ability to reduce hepatic lipid accumulation, improve insulin sensitivity, and stimulate hepatocyte proliferation underscores its comprehensive approach to liver health. As scientific research continues to validate its efficacy, Picrorhiza kurroa holds promise as a cornerstone in the management of liver conditions and the promotion of overall well-being.
For individuals seeking a natural approach to liver health, Picrorhiza kurroa offers a scientifically backed solution that addresses the root causes of liver dysfunction while supporting the liver’s remarkable regenerative abilities. As always, it is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional before beginning any new supplement regimen, particularly for those with pre-existing liver conditions or who are taking other medications.

Picroside and Its Role in Preventing and Managing Liver Diseases
Picroside, an active compound derived from the herb Picrorhiza kurroa, has gained attention in recent years for its potent hepatoprotective properties. Known for its ability to prevent and manage a range of liver-related conditions such as Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis, Picroside is making its mark in modern phytomedicine. This article offers an in-depth look at how Picroside contributes to liver health, supported by scientific evidence, and delves into the mechanisms by which it works.
Preventing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD is one of the most common liver disorders globally, driven by factors such as obesity, insulin resistance, and an unhealthy diet. It occurs when fat accumulates in liver cells without the involvement of alcohol consumption. Picroside has demonstrated significant efficacy in preventing the onset of NAFLD by modulating metabolic pathways and reducing oxidative stress.
Mechanism of Action: Picroside works through its powerful antioxidant properties, mitigating oxidative stress, which plays a critical role in the development of NAFLD. Oxidative stress is triggered by an imbalance between reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and the body’s antioxidant defenses. By scavenging free radicals, Picroside prevents lipid peroxidation and reduces fat accumulation in the liver. Furthermore, it has been shown to modulate lipid metabolism, promoting a favorable balance between lipid synthesis and breakdown.
Scientific Evidence: Multiple studies have highlighted Picroside’s role in preventing liver fat accumulation. In animal models, Picroside supplementation significantly reduced hepatic triglyceride levels, thereby lowering the risk of NAFLD development. These studies confirm its potential to regulate metabolic pathways involved in lipid synthesis and promote overall liver health.
Managing Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver disease and cirrhosis are progressive liver conditions characterized by inflammation, fibrosis, and impaired liver function. The role of Picroside in managing these conditions has been well documented in preclinical research, showcasing its anti-inflammatory, antifibrotic, and antioxidant activities.
Mechanism of Action: Picroside exhibits anti-inflammatory properties by inhibiting the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6. Chronic inflammation is a key driver of liver fibrosis, where excessive collagen deposition leads to scarring and eventual cirrhosis. By reducing inflammation, Picroside helps prevent fibrosis and mitigates further liver damage.
In addition, Picroside inhibits the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), which are responsible for collagen production during liver injury. By preventing HSC activation, Picroside effectively reduces fibrosis and helps in managing chronic liver disease.
Scientific Evidence: Preclinical studies have provided substantial evidence of Picroside’s antifibrotic effects. In experimental models of liver fibrosis, Picroside treatment led to a marked decrease in collagen deposition, reduced liver stiffness, and improved liver function. Moreover, it attenuated liver damage markers such as ALT and AST levels, indicating its protective effects against chronic liver injury.
Hepatoprotective Effects: Reducing Liver Damage
The liver is frequently exposed to toxins, medications, and other stressors that can cause significant damage. Picroside has been extensively studied for its hepatoprotective properties, which help shield the liver from various stressors, including a fatty liver, alcohol, and other toxic insults.
Mechanism of Action: Picroside enhances the liver’s natural antioxidant defenses by boosting the levels of key enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase, and glutathione peroxidase. These enzymes play an essential role in neutralizing ROS and reducing oxidative damage to liver cells. Additionally, Picroside helps maintain the integrity of liver cell membranes by preventing lipid peroxidation, which is a crucial factor in protecting the liver from damage.
Scientific Evidence: Several studies have shown that Picroside administration leads to a significant reduction in oxidative stress markers, ultimately reducing hepatocellular damage. In models of drug-induced liver injury, Picroside not only reduced liver enzyme levels but also showed histological improvements, such as decreased necrosis and inflammation, further supporting its hepatoprotective benefits.
Liver Regeneration and Enhanced Liver Function
One of the unique features of the liver is its remarkable ability to regenerate after injury. Picroside plays an important role in promoting liver regeneration, making it a valuable therapeutic agent for individuals recovering from liver damage or surgery.
Mechanism of Action: Picroside stimulates hepatocyte proliferation, which is crucial for liver regeneration. It activates growth factors and signaling pathways that are involved in the regeneration process, such as hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and epidermal growth factor (EGF). These factors help stimulate the growth of new liver cells, ensuring the restoration of normal liver structure and function.
Moreover, Picroside has been shown to improve mitochondrial function within liver cells. Healthy mitochondria are essential for energy production, which supports the high metabolic demand during liver regeneration. By enhancing mitochondrial efficiency, Picroside aids in maintaining optimal liver function during the recovery phase.
Scientific Evidence: Experimental studies have indicated that Picroside accelerates liver regeneration following partial hepatectomy (surgical removal of part of the liver). Animals treated with Picroside exhibited faster restoration of liver mass and improved liver enzyme profiles compared to controls, demonstrating its regenerative potential.
Improving Overall Liver Function and Detoxification
The liver plays a central role in detoxifying harmful substances and maintaining metabolic balance. Picroside contributes to improving overall liver function and enhancing the body’s natural detoxification processes, which is essential for maintaining good health.
Mechanism of Action: Picroside enhances bile production and flow, which is vital for the digestion and elimination of fats and fat-soluble toxins. Improved bile production also helps in the excretion of metabolic waste products and toxic substances from the body, promoting an overall healthier liver environment.
In addition, Picroside modulates key liver enzymes involved in phase I and phase II detoxification processes. Phase I involves the conversion of toxins into intermediate metabolites, while phase II involves conjugation, making these metabolites more water-soluble for excretion. By upregulating these detoxification enzymes, Picroside ensures efficient detoxification and reduces the burden on the liver.
Scientific Evidence: Studies have demonstrated that Picroside enhances the activity of liver enzymes such as cytochrome P450, glutathione-S-transferase (GST), and UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT), which are crucial for detoxification. This enhanced enzyme activity leads to more effective elimination of toxins, thereby improving overall liver health and function.
Conclusion: Picroside as a Potent Ally for Liver Health
Picroside has emerged as a powerful natural compound with significant benefits for liver health. Its ability to prevent NAFLD, manage chronic liver disease, and protect the liver from various stressors is well supported by scientific evidence. Through its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antifibrotic, and regenerative properties, Picroside not only shields the liver from damage but also enhances its ability to regenerate and function optimally.
The comprehensive hepatoprotective effects of Picroside make it a promising candidate for individuals seeking to improve their liver health or prevent liver-related disorders. However, while preclinical studies have demonstrated its efficacy, further clinical trials are needed to establish standardized dosages and validate its use in humans. As research continues, Picroside holds great potential as a natural, effective approach to supporting liver health and ensuring the body’s natural detoxification processes are functioning at their best.
Key Takeaways
Prevention of NAFLD: Picroside’s antioxidant properties reduce oxidative stress and prevent fat accumulation in the liver, helping to mitigate the risk of NAFLD.
Managing Chronic Liver Disease: Its anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic actions prevent the progression of liver fibrosis and reduce liver inflammation.
Hepatoprotective Effects: Picroside enhances the liver’s natural defenses by boosting antioxidant enzymes, thus reducing damage from various stressors.
Liver Regeneration: It promotes hepatocyte proliferation and improves mitochondrial function, aiding in liver regeneration and recovery.
Enhanced Detoxification: By improving bile production and upregulating detoxification enzymes, Picroside supports the liver’s role in detoxifying harmful substances.
Picroside stands out as a comprehensive solution for enhancing liver health, offering a natural approach to prevent and manage liver diseases while promoting overall detoxification and regeneration. Its multifaceted benefits underscore its potential as an essential component of liver health supplements, though its use should be guided by future clinical research.

Pleurotus Eryngii: A Comprehensive Review of Hepatoprotective Benefits for NAFLD, Chronic Liver Disease, and Cirrhosis
Pleurotus eryngii, commonly known as king oyster mushroom, has gained significant attention for its therapeutic properties in the context of liver health. As non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis become increasingly common due to modern lifestyle factors, natural interventions such as Pleurotus eryngii are being explored for their potential to prevent and manage these conditions. This article presents a comprehensive scientific synopsis of Pleurotus eryngii’s proven hepatoprotective benefits, focusing on its effects in preventing liver damage, promoting regeneration, and enhancing overall liver function. All findings discussed here are grounded in peer-reviewed research, presenting only what is scientifically certain and evidence-based.
Prevention of NAFLD and Hepatoprotective Effects
Pleurotus eryngii has been studied extensively for its effects on preventing NAFLD, a condition characterized by the excessive accumulation of fat in liver cells without significant alcohol consumption. Studies indicate that Pleurotus eryngii possesses multiple bioactive compounds, including polysaccharides, phenolic acids, and ergothioneine, which contribute to its hepatoprotective properties.
Mechanisms of Action in NAFLD Prevention
The primary mechanism by which Pleurotus eryngii prevents the development of NAFLD is through its powerful antioxidant activity. The mushroom contains high levels of ergothioneine, a unique antioxidant that reduces oxidative stress—a key factor in the progression of fatty liver disease. Oxidative stress leads to lipid peroxidation and inflammation, which ultimately result in liver damage. By reducing oxidative damage, Pleurotus eryngii helps prevent the formation of fat deposits in the liver.
Moreover, the polysaccharides found in Pleurotus eryngii play a crucial role in modulating lipid metabolism. These polysaccharides have been shown to reduce serum levels of triglycerides and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol while enhancing high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol. By improving lipid metabolism, Pleurotus eryngii reduces the likelihood of hepatic fat accumulation, thereby preventing the onset of NAFLD.
Additionally, Pleurotus eryngii has anti-inflammatory effects that are vital for preventing NAFLD progression. Chronic inflammation is a significant driver of NAFLD, and studies have shown that Pleurotus eryngii reduces the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6. This anti-inflammatory action not only prevents liver fat accumulation but also reduces the risk of liver fibrosis, which can lead to cirrhosis if left unchecked.
Managing Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver disease and cirrhosis are conditions characterized by prolonged liver inflammation, fibrosis, and loss of liver function. Pleurotus eryngii has shown promise in managing these conditions due to its antifibrotic and hepatoprotective properties.
Antifibrotic Effects
One of the major challenges in managing chronic liver disease and cirrhosis is the prevention of liver fibrosis—the excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix proteins that leads to scarring of the liver tissue. Pleurotus eryngii contains bioactive compounds that inhibit hepatic stellate cell activation, a key process in liver fibrosis development. Studies have demonstrated that ergothioneine and polysaccharides from Pleurotus eryngii can downregulate the expression of fibrogenic genes, reducing collagen deposition in the liver.
By reducing fibrosis, Pleurotus eryngii helps maintain liver architecture and function, which is critical in the management of chronic liver disease and the prevention of cirrhosis progression. Additionally, the mushroom’s anti-inflammatory properties further mitigate the risk of fibrosis by reducing chronic inflammation in the liver.
Reducing Liver Damage from Fatty Liver and Other Stressors
In cases of fatty liver and other liver stressors, Pleurotus eryngii exerts a protective effect by reducing hepatic lipid accumulation and oxidative stress. The mushroom’s ability to modulate lipid metabolism helps prevent further fat buildup in the liver, while its antioxidant compounds protect hepatocytes from oxidative damage. This dual action is crucial for mitigating liver injury and preventing the progression of fatty liver disease to more severe conditions such as cirrhosis.
Pleurotus eryngii has also been found to enhance the activity of key liver enzymes involved in detoxification, such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx). These enzymes play a vital role in neutralizing free radicals and reducing oxidative damage, thereby protecting liver cells from injury caused by various stressors, including fatty liver, alcohol, and toxins.
Liver Regeneration and Enhanced Liver Function
Beyond its protective effects, Pleurotus eryngii also contributes to liver regeneration and overall liver function. Liver regeneration is a critical process for maintaining liver health, especially after injury or in the presence of chronic liver disease. Studies suggest that Pleurotus eryngii stimulates hepatocyte proliferation, aiding in the repair and regeneration of damaged liver tissue.
Mechanisms Promoting Liver Regeneration
The regenerative effects of Pleurotus eryngii are attributed to its ability to modulate growth factors and signaling pathways involved in cell proliferation. Research has shown that Pleurotus eryngii increases the expression of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), a key regulator of liver regeneration. By promoting HGF activity, Pleurotus eryngii facilitates the repair of damaged liver tissue and helps restore normal liver architecture and function.
In addition to promoting hepatocyte proliferation, Pleurotus eryngii enhances mitochondrial function in liver cells, which is essential for energy production and overall cellular health. Improved mitochondrial function supports the energy demands of regenerating liver tissue, thereby contributing to faster and more efficient liver recovery.
Improving Overall Liver Function and Detoxification
The liver is the body’s primary organ for detoxification, and maintaining optimal liver function is essential for overall health. Pleurotus eryngii has been shown to enhance liver function by improving the liver’s ability to detoxify harmful substances and by supporting bile production—a critical component of the digestive process and fat metabolism.
Enhanced Detoxification
Pleurotus eryngii improves the liver’s detoxification capacity by upregulating the activity of phase I and phase II detoxification enzymes. These enzymes are involved in the metabolism and elimination of toxins from the body. By enhancing the activity of these enzymes, Pleurotus eryngii supports the liver’s ability to process and eliminate harmful substances, reducing the toxic burden on the body.
Furthermore, the mushroom’s high antioxidant content plays a crucial role in protecting the liver during the detoxification process. Detoxification generates reactive oxygen species (ROS), which can cause oxidative damage if not neutralized. The antioxidants present in Pleurotus eryngii, such as ergothioneine and phenolic compounds, help neutralize these ROS, ensuring that the detoxification process does not harm liver cells.
Bile Production and Fat Metabolism
Bile production is another critical aspect of liver function, as bile is necessary for the digestion and absorption of dietary fats. Pleurotus eryngii has been found to support bile production, thereby enhancing fat metabolism and reducing the risk of fat accumulation in the liver. By improving bile production, Pleurotus eryngii not only aids in digestion but also helps prevent conditions such as NAFLD, which are linked to impaired fat metabolism.
Conclusion: Pleurotus Eryngii as a Natural Ally for Liver Health
Pleurotus eryngii, or king oyster mushroom, offers a range of scientifically-proven benefits for liver health, making it a promising natural intervention for the prevention and management of NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Its hepatoprotective effects are attributed to its potent antioxidant properties, anti-inflammatory activity, modulation of lipid metabolism, and ability to reduce fibrosis. Additionally, Pleurotus eryngii supports liver regeneration and enhances overall liver function, including detoxification and bile production.
The unique combination of bioactive compounds found in Pleurotus eryngii—such as ergothioneine, polysaccharides, and phenolic acids—contributes to its effectiveness in protecting the liver from damage, promoting regeneration, and maintaining optimal liver function. As research continues to explore the potential of natural compounds for liver health, Pleurotus eryngii stands out as a valuable ally in the fight against liver disease.
For individuals looking to support their liver health, incorporating Pleurotus eryngii into the diet may provide a natural and effective way to enhance liver function, prevent liver damage, and promote overall well-being. However, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before making any significant changes to the diet, especially for those with existing liver conditions or those taking medications that may interact with the bioactive compounds in Pleurotus eryngii.
In summary, Pleurotus eryngii’s hepatoprotective, antifibrotic, and regenerative properties make it a powerful natural supplement for supporting liver health. Its ability to prevent NAFLD, manage chronic liver disease, reduce liver damage, and promote liver regeneration is backed by scientific evidence, making it a promising addition to a comprehensive approach to liver care.

Pleurotus Florida: A Natural Solution for Liver Health and Disease Prevention
Pleurotus Florida, also known as the oyster mushroom, is emerging as a natural powerhouse for liver health, with substantial scientific evidence supporting its hepatoprotective benefits. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis are increasing public health concerns, linked to poor dietary habits, obesity, and environmental toxins. Leveraging Pleurotus Florida as a dietary supplement can offer a preventive and therapeutic edge for these liver conditions. This scientific synopsis breaks down the benefits, mechanisms of action, and liver-supporting properties of Pleurotus Florida.
Hepatoprotective Effects of Pleurotus Florida
Pleurotus Florida has been scientifically validated for its hepatoprotective effects, which are essential in mitigating liver damage caused by fatty liver disease, alcohol consumption, medications, and other liver stressors. The active compounds in Pleurotus Florida, including polysaccharides, ergothioneine, and phenolic antioxidants, play pivotal roles in reducing liver inflammation and oxidative stress.
Reduction of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation
Oxidative stress is a key contributor to liver damage, particularly in conditions like NAFLD and cirrhosis. Pleurotus Florida contains high levels of antioxidants, such as ergothioneine and phenolic compounds, that scavenge free radicals, thereby reducing oxidative stress. Scientific studies have shown that the antioxidant activity in Pleurotus Florida significantly lowers malondialdehyde (MDA) levels—a marker of oxidative damage—while boosting antioxidant enzyme activity, such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase.
Moreover, Pleurotus Florida’s anti-inflammatory properties have been demonstrated through its ability to modulate inflammatory pathways. The mushroom’s polysaccharides inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α and IL-6, which are implicated in liver inflammation and fibrosis. By reducing the inflammatory response, Pleurotus Florida helps in limiting liver injury and preventing the progression of chronic liver diseases.
Mitigation of Fatty Liver Disease
NAFLD is characterized by the accumulation of fat in liver cells, leading to inflammation and potentially progressing to cirrhosis if untreated. Pleurotus Florida has been shown to have lipid-lowering properties, making it effective in managing NAFLD. Studies involving animal models with induced fatty liver have demonstrated that Pleurotus Florida supplementation reduces hepatic lipid accumulation by regulating lipid metabolism pathways.
The mushroom’s bioactive compounds influence key enzymes involved in lipid synthesis and breakdown, such as AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPAR-α). Activation of these enzymes promotes fatty acid oxidation and reduces lipogenesis, thereby preventing fat build-up in the liver. This mechanism is crucial for reversing early-stage NAFLD and improving overall liver function.
Protection Against Liver Fibrosis and Cirrhosis
Liver fibrosis, a precursor to cirrhosis, involves excessive deposition of extracellular matrix proteins, leading to scarring and impaired liver function. Pleurotus Florida has demonstrated antifibrotic properties through its ability to inhibit hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation—a key driver of fibrosis. Research has highlighted that the polysaccharides in Pleurotus Florida reduce the expression of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β), a major fibrogenic cytokine that stimulates collagen production in the liver.
By modulating TGF-β and other fibrogenic markers, Pleurotus Florida helps to prevent the progression of liver fibrosis to cirrhosis, thus preserving liver architecture and function. This antifibrotic action not only halts the progression of liver damage but also provides an opportunity for the liver to regenerate and recover.
Promotion of Liver Regeneration and Detoxification
The liver’s ability to regenerate is vital for maintaining its function, especially after injury. Pleurotus Florida supports liver regeneration by enhancing cellular proliferation and tissue repair mechanisms. The mushroom’s polysaccharides have been found to stimulate hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), which plays a crucial role in liver regeneration. Increased HGF activity promotes the proliferation of healthy liver cells, replacing damaged ones and restoring normal liver function.
Additionally, Pleurotus Florida aids in detoxification—one of the liver’s primary roles. The mushroom enhances phase I and phase II detoxification enzyme activities, which are involved in metabolizing and excreting harmful substances from the body. By boosting these detoxification pathways, Pleurotus Florida helps to reduce the toxic burden on the liver, promoting a healthier internal environment and improving overall liver resilience.
Mechanisms of Action for Liver Health
The hepatoprotective effects of Pleurotus Florida are attributed to several mechanisms:
Antioxidant Defense: The high levels of ergothioneine and other antioxidants in Pleurotus Florida neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS), preventing oxidative damage to liver cells. This is particularly important in preventing the progression of NAFLD and other liver diseases where oxidative stress plays a central role.
Anti-Inflammatory Pathways: Pleurotus Florida modulates the NF-κB pathway, a critical regulator of inflammation. By inhibiting NF-κB activation, the mushroom reduces the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, thereby minimizing liver inflammation and damage.
Lipid Metabolism Regulation: The activation of AMPK and PPAR-α pathways by Pleurotus Florida promotes fatty acid oxidation and decreases lipogenesis. This dual action helps in reducing hepatic fat accumulation, which is crucial for managing and reversing NAFLD.
Antifibrotic Effects: Pleurotus Florida inhibits the activation of hepatic stellate cells and reduces TGF-β expression, thereby preventing excessive collagen deposition and fibrosis. This helps in maintaining the structural integrity of the liver and preventing cirrhosis.
Promotion of Hepatocyte Proliferation: By enhancing HGF levels, Pleurotus Florida supports the proliferation of healthy liver cells, aiding in the regeneration of liver tissue and the recovery of liver function after damage.
Enhanced Detoxification: The mushroom boosts the activity of detoxification enzymes, supporting the liver’s role in metabolizing and excreting toxins. This reduces the overall toxic load on the liver, promoting a healthier liver environment.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Pleurotus Florida’s Hepatoprotective Role
Several peer-reviewed studies have investigated the hepatoprotective effects of Pleurotus Florida, providing robust evidence for its use in liver health management:
Animal Studies on NAFLD: Research involving rodent models with diet-induced NAFLD has demonstrated that supplementation with Pleurotus Florida extract significantly reduces hepatic lipid accumulation and improves liver enzyme profiles, such as ALT and AST levels. These findings indicate the mushroom’s potential in reversing fatty liver conditions and enhancing liver function.
Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Studies have shown that Pleurotus Florida extracts enhance antioxidant enzyme activities, such as SOD and glutathione peroxidase, while reducing MDA levels. This indicates a reduction in oxidative damage, which is crucial for preventing liver injury and supporting recovery.
Antifibrotic Activity: In vitro studies have highlighted the ability of Pleurotus Florida polysaccharides to inhibit HSC activation and reduce TGF-β expression. This antifibrotic effect is instrumental in preventing the progression of fibrosis to cirrhosis, making Pleurotus Florida a valuable dietary intervention for individuals at risk of chronic liver disease.
Human Relevance: While most studies have been conducted in animal models or in vitro, the mechanisms elucidated provide a strong foundation for the potential benefits of Pleurotus Florida in humans. The bioactive compounds present in the mushroom have been shown to exert similar antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and lipid-lowering effects in human cells, suggesting a promising role for Pleurotus Florida in liver health management.
Conclusion: Pleurotus Florida for Optimal Liver Health
Pleurotus Florida offers a scientifically backed, natural approach to liver health, with proven benefits in preventing and managing conditions like NAFLD, liver fibrosis, and cirrhosis. Its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antifibrotic, and regenerative properties make it a comprehensive solution for supporting liver function and enhancing the body’s natural detoxification processes.
By incorporating Pleurotus Florida into the diet, individuals can potentially reduce liver fat accumulation, minimize inflammation, prevent fibrosis, and promote liver regeneration. These benefits contribute to maintaining a healthier liver environment, ultimately enhancing overall well-being. As the burden of liver diseases continues to rise globally, Pleurotus Florida stands out as a valuable ally in liver disease prevention and management, offering a natural, effective, and scientifically validated solution.
For those seeking to improve liver health, Pleurotus Florida presents a promising supplement that aligns with both traditional wisdom and modern scientific evidence. Its multifaceted approach to liver protection and regeneration highlights its importance as part of a balanced diet, particularly for individuals at risk of liver-related conditions. With continued research, the therapeutic potential of Pleurotus Florida in liver health will undoubtedly become even more apparent, solidifying its role in natural health interventions.

Pleurotus Ostreatus Mycelium: A Comprehensive Review on Liver Health and Disease Prevention
Introduction
Pleurotus ostreatus, commonly known as oyster mushroom, is a species of medicinal mushroom that has gained attention for its extensive health benefits, particularly regarding liver health. Its mycelium, the root-like structure of the mushroom, has been studied for its hepatoprotective properties and its role in managing conditions such as Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. This article provides an in-depth analysis of the scientifically-proven benefits of Pleurotus ostreatus mycelium, with a focus on its mechanisms of action, effects on liver regeneration, detoxification processes, and overall liver function.
Preventing NAFLD and Chronic Liver Disease
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is a growing global health concern, characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver in the absence of excessive alcohol consumption. This condition can progress to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), cirrhosis, or even hepatocellular carcinoma. Studies on Pleurotus ostreatus mycelium have highlighted its potential in preventing and managing NAFLD due to its ability to reduce hepatic fat accumulation, modulate inflammation, and improve insulin sensitivity.
One of the key mechanisms by which Pleurotus ostreatus mycelium combats NAFLD is through its potent antioxidant properties. The mycelium is rich in bioactive compounds such as polysaccharides, phenolic acids, and ergothioneine, which have been shown to reduce oxidative stress in the liver. Oxidative stress plays a critical role in the development of NAFLD, and by neutralizing reactive oxygen species (ROS), Pleurotus ostreatus mycelium helps to protect hepatocytes from damage.
Additionally, studies have demonstrated that Pleurotus ostreatus mycelium can regulate lipid metabolism. It activates AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), a key enzyme that promotes fatty acid oxidation and inhibits lipogenesis. By enhancing the breakdown of fatty acids and reducing the synthesis of new fat molecules, Pleurotus ostreatus mycelium effectively reduces hepatic steatosis, a hallmark of NAFLD. Its role in improving insulin sensitivity further aids in controlling the metabolic dysfunctions associated with NAFLD, thus providing a multifaceted approach to managing this condition.
Hepatoprotective Effects Against Liver Stressors
Chronic liver diseases, including those caused by alcohol, toxins, or viral infections, lead to persistent inflammation and fibrosis, eventually resulting in cirrhosis. Pleurotus ostreatus mycelium exhibits significant hepatoprotective effects, which can help mitigate liver damage caused by these stressors. Its anti-inflammatory properties are crucial in reducing hepatic inflammation, thereby preventing the progression of chronic liver diseases.
The anti-inflammatory activity of Pleurotus ostreatus mycelium is primarily attributed to its ability to modulate key inflammatory pathways, including the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) pathway. By inhibiting NF-κB activation, the mycelium reduces the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β. This modulation helps in reducing hepatic inflammation and fibrosis, ultimately protecting the liver from chronic damage.
Moreover, Pleurotus ostreatus mycelium contains beta-glucans, which have been shown to enhance the immune system’s response to harmful pathogens and toxins. These polysaccharides activate macrophages and natural killer (NK) cells, which play a vital role in clearing damaged cells and promoting tissue repair. This immunomodulatory effect not only protects the liver from ongoing damage but also supports the overall healing process.
Reducing Damage from Fatty Liver and Enhancing Regeneration
In addition to its preventive and protective roles, Pleurotus ostreatus mycelium has been found to aid in the reduction of existing liver damage, particularly in cases of fatty liver. Its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects work synergistically to create a favorable environment for liver healing and regeneration. The presence of ergothioneine, a powerful antioxidant unique to fungi, has been shown to reduce lipid peroxidation and protect cellular membranes from oxidative damage, thereby preserving the structural integrity of hepatocytes.
Pleurotus ostreatus mycelium also promotes liver regeneration by stimulating the production of growth factors that are essential for hepatocyte proliferation. Studies have indicated that the mycelium enhances the expression of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β), both of which are critical for liver regeneration. By supporting the regeneration of healthy liver tissue, Pleurotus ostreatus mycelium helps restore normal liver function and improve overall liver health.
Improving Overall Liver Function and Detoxification
A healthy liver is essential for the body’s natural detoxification processes. Pleurotus ostreatus mycelium contributes to improved liver function by enhancing the liver’s ability to detoxify harmful substances and by promoting bile production. Bile plays a critical role in the digestion and absorption of fats, as well as the excretion of toxins and metabolic waste products. By stimulating bile flow, Pleurotus ostreatus mycelium helps to ensure efficient detoxification and optimal liver function.
Furthermore, Pleurotus ostreatus mycelium has been shown to upregulate the expression of various detoxification enzymes, including glutathione S-transferase (GST) and cytochrome P450 enzymes. These enzymes are involved in the phase II detoxification process, where toxic substances are converted into less harmful forms that can be easily excreted from the body. The mycelium’s ability to enhance the activity of these enzymes supports the liver’s role in maintaining a clean internal environment, thereby promoting overall health and well-being.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Pleurotus Ostreatus Mycelium for Liver Health
The hepatoprotective effects of Pleurotus ostreatus mycelium are supported by numerous peer-reviewed studies. Research conducted on animal models of NAFLD and liver injury has consistently demonstrated the mycelium’s ability to reduce hepatic fat accumulation, lower liver enzyme levels (such as ALT and AST), and improve liver histology. These findings suggest that Pleurotus ostreatus mycelium can effectively prevent and manage liver diseases by targeting multiple pathways involved in liver damage and repair.
In a study published in the journal Food & Function, researchers found that supplementation with Pleurotus ostreatus mycelium significantly reduced markers of liver injury and oxidative stress in rats with induced NAFLD. The study concluded that the mycelium’s antioxidant and lipid-lowering effects played a key role in mitigating liver damage. Another study published in International Journal of Medicinal Mushrooms demonstrated that Pleurotus ostreatus mycelium reduced fibrosis and inflammation in a model of chronic liver injury, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic agent for chronic liver diseases.
Clinical evidence, though limited, also supports the use of Pleurotus ostreatus mycelium for liver health. Preliminary human trials have shown promising results in improving liver enzyme profiles and reducing symptoms of liver dysfunction in individuals with fatty liver disease. However, more extensive clinical studies are needed to fully establish the efficacy of Pleurotus ostreatus mycelium in human populations.
Conclusion
Pleurotus ostreatus mycelium offers a multifaceted approach to liver health, with proven benefits in preventing and managing conditions such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Its hepatoprotective effects are mediated through antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory mechanisms, which help reduce liver damage, promote regeneration, and enhance overall liver function. By supporting the liver’s natural detoxification processes and improving lipid metabolism, Pleurotus ostreatus mycelium contributes to a healthier liver environment and optimal well-being.
While further research is needed to fully understand its potential in clinical settings, the existing body of evidence suggests that Pleurotus ostreatus mycelium is a valuable natural supplement for promoting liver health. Its ability to target multiple pathways involved in liver disease makes it a promising candidate for inclusion in comprehensive liver health strategies. As interest in natural and holistic approaches to health continues to grow, Pleurotus ostreatus mycelium stands out as a potent ally in the fight against liver disease.

Plumbagin and Its Proven Benefits in Managing Liver Health: A Comprehensive Scientific Synopsis
Introduction to Plumbagin’s Role in Liver Health
Plumbagin, a natural naphthoquinone found primarily in plants of the Plumbago genus, has attracted significant scientific attention due to its numerous health benefits, particularly for liver health. It has been extensively studied for its potential in preventing and managing liver-related disorders, including Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, cirrhosis, and other liver stressors. Plumbagin’s hepatoprotective effects are increasingly supported by scientific research, highlighting its potential to protect against liver damage, enhance liver regeneration, and promote overall liver function. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the current evidence-based health effects of plumbagin, emphasizing its mechanisms of action, proven benefits, and role in maintaining liver health.
1. Preventing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is a common liver condition characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver in the absence of significant alcohol consumption. Scientific studies have indicated that plumbagin may be effective in preventing the progression of NAFLD through multiple mechanisms. Its anti-inflammatory properties play a crucial role in mitigating hepatic inflammation, which is one of the primary drivers of NAFLD progression.
Research shows that plumbagin modulates key signaling pathways, including the NF-κB pathway, which is known to regulate inflammation and immune responses. By inhibiting the activation of NF-κB, plumbagin reduces the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, thereby minimizing liver inflammation and oxidative stress—two major contributors to NAFLD. Additionally, plumbagin’s ability to activate AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) helps regulate lipid metabolism, promoting the breakdown of fatty acids and reducing hepatic fat accumulation.
2. Mitigating Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver disease and cirrhosis are conditions characterized by prolonged liver injury, often leading to fibrosis and scarring of the liver tissue. The antifibrotic properties of plumbagin are central to its effectiveness in managing chronic liver disease. Studies have demonstrated that plumbagin inhibits hepatic stellate cell activation—a critical process in liver fibrosis—thus reducing the risk of progression to cirrhosis.
The antioxidant capabilities of plumbagin further contribute to its hepatoprotective effects. By scavenging free radicals and enhancing the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes, such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx), plumbagin helps reduce oxidative damage to liver cells. This mechanism is particularly beneficial in chronic liver disease, where oxidative stress is a major factor in the progression of fibrosis and liver injury.
3. Hepatoprotective Effects Against Liver Stressors
Plumbagin’s hepatoprotective properties extend to its ability to protect the liver from various stressors, including alcohol, drugs, and environmental toxins. Experimental studies have shown that plumbagin effectively mitigates hepatotoxicity induced by these stressors by enhancing the liver’s natural defense mechanisms.
One of the primary ways plumbagin exerts its hepatoprotective effects is through the upregulation of detoxifying enzymes. Plumbagin activates the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) pathway, which is responsible for regulating the expression of detoxifying and antioxidant enzymes. This activation leads to an increase in the production of phase II detoxification enzymes, such as glutathione S-transferase (GST), which aid in neutralizing toxic substances and protecting liver cells from damage.
4. Reducing Damage Caused by Fatty Liver
Fatty liver disease, whether alcoholic or non-alcoholic, can lead to significant liver damage if left untreated. Plumbagin has been shown to effectively reduce liver damage associated with fatty liver conditions by improving lipid metabolism and reducing inflammation. The activation of AMPK by plumbagin not only aids in lipid breakdown but also improves insulin sensitivity, which is crucial for preventing fat accumulation in the liver.
Furthermore, plumbagin’s ability to inhibit lipogenesis—the process of fat synthesis—contributes to its protective role in fatty liver disease. By downregulating the expression of key lipogenic enzymes, such as fatty acid synthase (FAS) and acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC), plumbagin helps limit the synthesis of new fatty acids in the liver, thereby reducing the overall fat burden.
5. Promoting Liver Regeneration and Repair
One of the remarkable benefits of plumbagin is its potential to promote liver regeneration and repair. The liver has a unique ability to regenerate following injury, and plumbagin appears to enhance this regenerative capacity by modulating various growth factors and signaling pathways involved in liver regeneration.
Studies have shown that plumbagin increases the expression of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), a key player in liver regeneration. HGF stimulates the proliferation of hepatocytes, the main functional cells of the liver, thereby facilitating the repair of damaged tissue. In addition, plumbagin has been found to inhibit the overproduction of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β), a cytokine that can impede liver regeneration by promoting fibrosis. By balancing these growth factors, plumbagin supports a favorable environment for liver repair and regeneration.
6. Enhancing Overall Liver Function and Detoxification
The overall health of the liver is crucial for the body’s detoxification processes, as the liver is responsible for metabolizing and eliminating toxins. Plumbagin has been shown to enhance liver function by improving the liver’s enzymatic activity and supporting its natural detoxification pathways. The activation of the Nrf2 pathway by plumbagin not only increases antioxidant enzyme levels but also enhances the liver’s capacity to detoxify harmful substances.
Moreover, plumbagin has been reported to improve bile flow, which is essential for the excretion of waste products and the digestion of fats. By stimulating bile production and flow, plumbagin helps ensure that toxins are efficiently removed from the body, thereby reducing the overall toxic load on the liver and promoting a healthier internal environment.
7. Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Mechanisms
The anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties of plumbagin are central to its role in maintaining liver health. Chronic inflammation and oxidative stress are key drivers of liver damage in various liver conditions, including NAFLD, alcoholic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Plumbagin’s ability to inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α and IL-6, helps reduce inflammation in the liver, preventing further damage and promoting healing.
Additionally, the antioxidant effects of plumbagin are mediated through its ability to enhance the activity of key antioxidant enzymes and reduce the levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS). By minimizing oxidative stress, plumbagin helps protect liver cells from damage, supports their normal function, and prevents the progression of liver disease.
8. Scientific Evidence Supporting Plumbagin’s Benefits
The health benefits of plumbagin for liver health are supported by a growing body of scientific literature. Multiple in vitro and in vivo studies have demonstrated its hepatoprotective effects, anti-inflammatory properties, and ability to modulate key signaling pathways involved in liver health. For instance, a study published in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology found that plumbagin significantly reduced liver inflammation and fibrosis in an animal model of chronic liver disease, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic agent for liver disorders.
Another study published in Phytomedicine demonstrated that plumbagin effectively activated the Nrf2 pathway, leading to increased expression of detoxifying enzymes and enhanced protection against liver toxicity induced by chemical stressors. These findings provide strong evidence for the role of plumbagin in supporting liver detoxification and overall liver function.
Conclusion: Plumbagin as a Promising Natural Compound for Liver Health
Plumbagin is emerging as a powerful natural compound with significant potential for improving liver health. Its ability to prevent NAFLD, mitigate chronic liver disease, reduce liver damage caused by fatty liver, and promote liver regeneration makes it a promising candidate for managing various liver conditions. The hepatoprotective effects of plumbagin are largely attributed to its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antifibrotic properties, as well as its ability to enhance the liver’s natural detoxification processes.
While the current scientific evidence is promising, further clinical studies are needed to fully establish the efficacy and safety of plumbagin for human use in liver health. Nonetheless, the existing research provides a strong foundation for considering plumbagin as a valuable natural supplement for supporting liver function and promoting a healthier liver environment. As our understanding of plumbagin continues to grow, it may become an important tool in the prevention and management of liver-related disorders, offering a natural and effective approach to maintaining optimal liver health.

Polydatin: A Comprehensive Look at Its Benefits for Liver Health, NAFLD, and Cirrhosis Prevention
Polydatin, a natural polyphenolic compound found in various plants, especially in the roots of Polygonum cuspidatum, is a derivative of resveratrol. Emerging as a powerful nutraceutical, polydatin has gained attention in scientific research for its hepatoprotective properties. Specifically, its role in managing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, cirrhosis, and its ability to protect and regenerate liver cells has been extensively explored in recent years. This article provides an in-depth exploration of polydatin’s role in liver health, presenting only the most robust, peer-reviewed findings and highlighting the mechanisms that make it effective.
Understanding Polydatin and Its Mechanisms in Liver Health
Polydatin is known for its strong antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-fibrotic properties, which are key in mitigating liver damage. The liver, a vital organ responsible for detoxification and various metabolic processes, is vulnerable to numerous stressors that can lead to NAFLD, fibrosis, and eventually cirrhosis. Polydatin plays an essential role in preventing these conditions, primarily through its ability to reduce oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis (cell death).
1. Preventing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is a prevalent condition characterized by excess fat accumulation in the liver. NAFLD can progress to more severe forms, such as Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH), which can lead to fibrosis, cirrhosis, and even liver cancer. Polydatin has shown substantial efficacy in combating NAFLD through multiple mechanisms:
Reducing Lipid Accumulation: Polydatin has been found to modulate lipid metabolism by activating the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) pathway. Activation of AMPK helps decrease lipid synthesis while increasing fatty acid oxidation, ultimately reducing lipid accumulation within hepatocytes (liver cells). Scientific studies have shown that polydatin significantly lowers hepatic triglyceride levels, thereby preventing fat buildup, which is a hallmark of NAFLD.
Modulating Inflammatory Responses: Inflammation plays a critical role in the progression of NAFLD. Polydatin inhibits the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β, which are known to exacerbate liver inflammation. By reducing inflammation, polydatin helps prevent the transition of simple steatosis to more severe forms of liver damage like NASH.
Attenuating Oxidative Stress: Oxidative stress is a key player in the development of NAFLD. Polydatin, due to its potent antioxidant properties, neutralizes reactive oxygen species (ROS), thereby protecting liver cells from oxidative damage. This reduction in oxidative stress helps maintain liver function and prevents cellular injury, which is pivotal in managing NAFLD.
2. Protecting Against Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver disease often results from prolonged inflammation and damage, eventually leading to fibrosis and cirrhosis. Cirrhosis is characterized by the formation of scar tissue that disrupts normal liver architecture and function. Polydatin offers hepatoprotective effects that help combat chronic liver disease through the following mechanisms:
Anti-Fibrotic Effects: Liver fibrosis is the process of excess connective tissue buildup, which can progress to cirrhosis if left unchecked. Polydatin exerts anti-fibrotic effects by inhibiting hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation, a crucial step in the fibrotic process. Studies indicate that polydatin downregulates the expression of transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1), a major pro-fibrotic cytokine, thus preventing the activation of HSCs and reducing collagen deposition in the liver.
Inhibition of Apoptosis: Chronic liver conditions often lead to increased hepatocyte apoptosis, contributing to liver dysfunction. Polydatin has demonstrated the ability to inhibit apoptosis by modulating the Bcl-2/Bax ratio and reducing caspase-3 activity, which are key factors in the apoptosis pathway. By preserving hepatocyte viability, polydatin helps maintain overall liver function.
Mitigating Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Stress: ER stress has been implicated in the pathogenesis of chronic liver disease. Polydatin alleviates ER stress by modulating the unfolded protein response (UPR) and reducing the accumulation of misfolded proteins, which are associated with liver damage and fibrosis progression.
3. Hepatoprotective Effects Against Liver Damage
The liver is constantly exposed to a variety of stressors, including alcohol, toxins, and metabolic imbalances. Polydatin has been found to protect the liver from various forms of damage by exerting its hepatoprotective effects:
Antioxidant Defense Mechanism: The antioxidant properties of polydatin are primarily mediated through the upregulation of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2). Nrf2 is a key regulator of antioxidant defense, promoting the expression of enzymes such as glutathione peroxidase (GPx), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and catalase. These enzymes play a critical role in detoxifying harmful substances and reducing oxidative damage in the liver.
Protection Against Alcohol-Induced Damage: Alcohol consumption is a major risk factor for liver injury. Studies have shown that polydatin can mitigate alcohol-induced liver damage by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation. It also enhances the activity of alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) and aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH), enzymes involved in the metabolism of alcohol, thus facilitating the detoxification process and minimizing liver injury.
Reducing Liver Enzyme Levels: Elevated liver enzymes, such as alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), are markers of liver damage. Research has demonstrated that polydatin administration can significantly reduce ALT and AST levels, indicating its role in protecting liver tissue and reducing hepatocellular injury.
4. Promoting Liver Regeneration and Enhancing Detoxification
The liver has a remarkable ability to regenerate, which is crucial for recovering from injury or surgery. Polydatin plays a supportive role in enhancing liver regeneration and overall liver function:
Stimulating Hepatocyte Proliferation: Polydatin has been shown to promote hepatocyte proliferation by activating pathways such as the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, which is involved in cell growth and regeneration. This ability to stimulate hepatocyte proliferation aids in liver regeneration, especially after injury or partial hepatectomy.
Improving Mitochondrial Function: Mitochondria are essential for energy production and overall cellular health. Polydatin enhances mitochondrial function by improving mitochondrial membrane potential and reducing mitochondrial ROS production. Improved mitochondrial health is critical for liver regeneration and maintaining the liver’s metabolic functions.
Supporting Detoxification Pathways: The liver is the body’s primary detoxification organ, responsible for metabolizing drugs, toxins, and endogenous waste products. Polydatin enhances detoxification by upregulating phase II detoxification enzymes, such as glutathione S-transferase (GST) and UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT). These enzymes facilitate the conjugation and excretion of toxins, promoting a healthier liver environment and enhancing the body’s natural detoxification processes.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Polydatin’s Efficacy
Multiple peer-reviewed studies have validated the hepatoprotective properties of polydatin, providing substantial evidence for its use in liver health management:
A study published in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology demonstrated that polydatin effectively reduced hepatic lipid accumulation and inflammation in a mouse model of NAFLD by activating the AMPK pathway and reducing pro-inflammatory cytokine levels.
Research featured in Phytomedicine showed that polydatin exerted anti-fibrotic effects by inhibiting TGF-β1 expression and hepatic stellate cell activation, thereby reducing liver fibrosis in a rat model.
Another study in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences highlighted polydatin’s ability to alleviate oxidative stress and apoptosis in alcohol-induced liver injury by modulating Nrf2 and the Bcl-2/Bax pathway, confirming its protective role against alcohol-related liver damage.
Clinical trials have also indicated that polydatin supplementation can lower serum ALT and AST levels in patients with elevated liver enzymes, further supporting its hepatoprotective benefits.
Conclusion: Polydatin as a Promising Agent for Liver Health
Polydatin’s multi-faceted approach to liver protection makes it a promising natural compound for the prevention and management of liver diseases such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Its ability to reduce lipid accumulation, inhibit inflammation, combat oxidative stress, prevent fibrosis, and promote liver regeneration highlights its potential as a powerful hepatoprotective agent.
By modulating key signaling pathways and enhancing the liver’s natural detoxification and regenerative capabilities, polydatin not only helps prevent liver damage but also supports overall liver function and health. Given the increasing prevalence of liver diseases worldwide, polydatin presents a compelling, evidence-backed option for those seeking to maintain liver health and prevent disease progression.
As research into polydatin continues, its role in liver health is likely to expand, offering new insights into its therapeutic potential. However, while the existing evidence is robust, it is essential for individuals to consult healthcare professionals before incorporating polydatin into their regimen, especially those with pre-existing liver conditions or those taking other medications.
Key Takeaways
Polydatin is a potent natural compound with significant hepatoprotective effects, including preventing NAFLD, reducing inflammation, combating oxidative stress, and inhibiting fibrosis.
It supports liver regeneration by stimulating hepatocyte proliferation and improving mitochondrial function, thus enhancing overall liver health and detoxification.
Scientific evidence supports its role in reducing liver enzyme levels, preventing lipid accumulation, and protecting against chronic liver disease and cirrhosis.
Incorporating polydatin into a liver health regimen could be a valuable strategy for those seeking to protect their liver from damage and enhance its natural regenerative and detoxification processes. Its broad-spectrum benefits and scientifically backed mechanisms of action make it a noteworthy addition to the landscape of liver health management.

The Science Behind Polyene Phosphatidylcholine: Protecting and Enhancing Liver Health
Polyene Phosphatidylcholine (PPC) has emerged as a scientifically validated supplement for protecting the liver and promoting its overall health. It plays a key role in preventing conditions like Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. This comprehensive synopsis highlights the proven benefits of PPC, focusing on its mechanisms, evidence-backed hepatoprotective effects, liver regeneration properties, and how it promotes a healthier liver environment, thereby enhancing natural detoxification processes.
What is Polyene Phosphatidylcholine (PPC)?
Polyene Phosphatidylcholine is a phospholipid derived mainly from soy lecithin. It is rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids, which are essential for cellular membrane integrity and health. PPC serves as a primary component of the liver cell membrane, which provides it with unique attributes that make it an effective hepatoprotective agent. Its efficacy is supported by clinical trials and peer-reviewed studies that demonstrate its therapeutic potential in liver health management.
Mechanisms of Action: How PPC Benefits Liver Health
PPC works through several mechanisms to support and protect liver health. Understanding these mechanisms offers insights into how PPC is effective in both treatment and prevention of liver diseases:
Membrane Stabilization and Repair: PPC incorporates into damaged liver cell membranes, helping to stabilize and repair these cells. By providing phospholipid components identical to those found in liver cells, PPC restores the structural integrity of cell membranes. This membrane repair mechanism is crucial for sustaining normal liver function and promoting liver regeneration.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Chronic liver inflammation is a hallmark of liver diseases like NAFLD and cirrhosis. PPC has demonstrated significant anti-inflammatory effects, reducing the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines. This helps decrease the extent of liver inflammation, preventing the progression of liver damage.
Antioxidant Protection: PPC protects the liver from oxidative stress by enhancing antioxidant defenses. It has been shown to increase glutathione levels, which is one of the most important antioxidants in the liver. By combating oxidative stress, PPC helps minimize cellular damage, a critical factor in preventing chronic liver disease.
Reduction in Fat Accumulation: PPC has been shown to inhibit the accumulation of fat within liver cells, a process central to the development of NAFLD. PPC enhances lipid metabolism, which helps reduce triglyceride levels within the liver. By reducing hepatic fat deposition, PPC significantly mitigates the risk of liver inflammation and fibrosis.
Improvement of Bile Flow: PPC contributes to improving bile fluidity, which is essential for the liver’s detoxification role. Enhanced bile flow aids in the elimination of toxins and excess cholesterol, thereby supporting overall liver health and function.
Preventing and Managing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD is a condition characterized by excessive fat build-up in the liver in individuals who consume little or no alcohol. It is a growing global health concern linked to obesity and metabolic syndrome. PPC has emerged as a powerful intervention for preventing and managing NAFLD, as evidenced by numerous studies:
Reduction in Hepatic Steatosis: PPC reduces hepatic steatosis, which is the primary feature of NAFLD. Clinical studies have demonstrated that regular supplementation with PPC results in reduced liver fat content, improved liver enzymes (such as ALT and AST), and decreased levels of circulating triglycerides.
Enhanced Insulin Sensitivity: Insulin resistance is often associated with NAFLD. PPC has been found to improve insulin sensitivity, thereby reducing the risk factors associated with NAFLD development. By modulating lipid and glucose metabolism, PPC directly impacts the metabolic processes underlying fatty liver disease.
Hepatoprotective Effects and Liver Regeneration
The liver has an incredible capacity for regeneration, and PPC enhances this ability by providing the phospholipids necessary for membrane repair and regeneration. The following outlines the hepatoprotective effects of PPC and how it contributes to liver regeneration:
Prevention of Liver Fibrosis: Liver fibrosis occurs as a result of chronic injury, leading to the excessive deposition of extracellular matrix proteins. PPC has demonstrated efficacy in reducing collagen accumulation and fibrogenesis. By preventing fibrosis, PPC halts the progression towards cirrhosis, which is a more severe, irreversible form of liver damage.
Protection Against Hepatotoxins: Exposure to hepatotoxins, such as alcohol, certain medications, and industrial chemicals, can lead to liver damage. PPC has shown a protective effect against such hepatotoxins by stabilizing liver cell membranes and reducing lipid peroxidation. This protective effect is beneficial for individuals exposed to environmental liver stressors or those on medications that could potentially cause liver damage.
Promotion of Liver Cell Regeneration: Studies have found that PPC enhances liver cell regeneration by providing essential phospholipids that are integrated into new cell membranes. This not only helps repair damaged liver tissues but also promotes the formation of new, healthy liver cells, thereby supporting liver regeneration after injury or illness.
PPC and Cirrhosis Prevention
Cirrhosis is the result of long-term, continuous damage to the liver, characterized by scarring and impaired liver function. PPC has been shown to be effective in slowing or even halting the progression of cirrhosis, particularly in individuals with alcohol-induced liver damage or chronic viral hepatitis.
Reduction in Scar Tissue Formation: PPC reduces the production of collagen and other fibrotic tissue that contribute to scarring. By modulating the activation of hepatic stellate cells, which are responsible for fibrosis, PPC significantly reduces scar tissue formation and preserves healthy liver architecture.
Improvement in Liver Function Tests: Patients with cirrhosis often show abnormal liver function tests, indicating impaired liver function. Supplementation with PPC has been associated with improvements in liver enzyme levels, indicating a beneficial effect on overall liver function and reduced hepatic stress.
Enhancing the Body’s Natural Detoxification Process
One of the liver’s primary roles is detoxification—removing harmful substances from the bloodstream. PPC enhances this natural detoxification process through several mechanisms:
Bile Production and Toxin Elimination: PPC increases bile production and improves its flow, which is crucial for the excretion of fat-soluble toxins. Effective bile flow ensures that waste products and toxins are efficiently eliminated from the body, reducing the toxic load on the liver.
Strengthening Antioxidant Defenses: PPC supplementation has been shown to enhance the levels of hepatic antioxidants, such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione. These antioxidants are vital in neutralizing free radicals produced during detoxification, thereby minimizing oxidative damage to liver cells.
Evidence Supporting PPC’s Role in Liver Health
The hepatoprotective effects of PPC are supported by a substantial body of scientific evidence, including animal studies, clinical trials, and meta-analyses. Key findings include:
Clinical Trials: Randomized controlled trials have demonstrated that PPC supplementation leads to significant reductions in liver enzymes, improved liver histology, and decreased symptoms in patients with NAFLD and chronic hepatitis. PPC has also been shown to improve the quality of life in patients with liver cirrhosis by reducing liver-related symptoms and complications.
Meta-Analyses: Meta-analyses of multiple clinical studies indicate that PPC is effective in reducing hepatic fat content, improving liver function, and preventing fibrosis progression. These findings support the use of PPC as a therapeutic agent for a range of liver diseases.
Animal Studies: Preclinical studies in animal models have demonstrated PPC’s ability to prevent liver damage caused by alcohol, drugs, and other hepatotoxins. These studies have provided insight into the mechanisms through which PPC exerts its protective effects, including membrane stabilization, reduced inflammation, and enhanced lipid metabolism.
Conclusion: Polyene Phosphatidylcholine for a Healthier Liver
Polyene Phosphatidylcholine is a well-researched, scientifically validated supplement that offers significant hepatoprotective benefits. Its ability to stabilize liver cell membranes, reduce inflammation, combat oxidative stress, and promote liver regeneration makes it an effective intervention for preventing and managing liver conditions such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis.
The evidence supporting PPC’s role in liver health is compelling. Through its unique mechanisms of action, PPC not only protects the liver from damage but also enhances its regenerative capacity, promotes detoxification, and supports overall liver function. For individuals looking to maintain a healthy liver or manage existing liver conditions, PPC represents a promising therapeutic option that is backed by solid scientific research.
By understanding the multifaceted benefits of PPC and incorporating it into a liver health regimen, individuals can take proactive steps towards achieving and maintaining optimal liver function. As research continues, PPC’s role in liver health is likely to become even more prominent, offering hope for those affected by liver disease and seeking effective, science-backed solutions.

The Proven Benefits of Polygonum cuspidatum Extract for Liver Health: Preventing NAFLD, Chronic Liver Disease, and Enhancing Liver Function
Polygonum cuspidatum, also known as Japanese Knotweed or Hu Zhang, has gained considerable attention in the medical community for its wide-ranging health benefits. Among its many uses, the extract of Polygonum cuspidatum is particularly recognized for its hepatoprotective properties, making it a promising natural remedy for supporting liver health. This scientific synopsis provides a comprehensive breakdown of the proven effects of Polygonum cuspidatum in preventing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, cirrhosis, and its contribution to overall liver function. Focusing on evidence-based research, this article aims to reveal the exact mechanisms behind its ability to protect, rejuvenate, and detoxify the liver.
1. Hepatoprotective Effects of Polygonum cuspidatum Extract
The hepatoprotective effects of Polygonum cuspidatum are well-supported by scientific research, largely attributed to its high concentration of resveratrol. Resveratrol is a natural polyphenol that has potent antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-fibrotic properties, which play a key role in mitigating liver damage and improving liver function.
Research has shown that resveratrol inhibits lipid peroxidation in the liver, a process that causes cellular damage due to the accumulation of free radicals. By reducing oxidative stress, Polygonum cuspidatum helps prevent injury to hepatocytes, the primary cells responsible for maintaining liver function. Additionally, resveratrol helps modulate inflammatory pathways, reducing cytokine production and thereby mitigating chronic inflammation—a major contributor to liver damage and fibrosis.
2. Prevention and Management of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD is a common liver disorder characterized by the accumulation of excess fat in liver cells, often linked to obesity, metabolic syndrome, and insulin resistance. Polygonum cuspidatum extract has shown significant promise in preventing and managing NAFLD due to its ability to reduce hepatic lipid accumulation and improve insulin sensitivity.
Several studies have demonstrated that resveratrol, the primary bioactive compound in Polygonum cuspidatum, can activate AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) in liver cells. AMPK plays a crucial role in regulating energy homeostasis and lipid metabolism. Activation of AMPK leads to a decrease in fatty acid synthesis and an increase in fatty acid oxidation, effectively reducing hepatic steatosis. Furthermore, resveratrol enhances the expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPAR-α), which facilitates lipid breakdown and reduces triglyceride accumulation in the liver.
By addressing insulin resistance and promoting lipid metabolism, Polygonum cuspidatum helps prevent the progression of NAFLD to more severe conditions, such as non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), fibrosis, and cirrhosis.
3. Protection Against Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver disease, including cirrhosis, often results from prolonged inflammation and fibrosis, leading to irreversible liver damage. Polygonum cuspidatum extract exerts anti-fibrotic effects that help prevent the progression of chronic liver disease to cirrhosis. The anti-fibrotic properties of resveratrol are primarily attributed to its ability to inhibit the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), which are responsible for the production of collagen and other extracellular matrix components that contribute to liver fibrosis.
Research has shown that resveratrol suppresses the expression of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β), a key cytokine involved in HSC activation and fibrosis development. By downregulating TGF-β signaling, Polygonum cuspidatum reduces collagen deposition in the liver, thereby limiting fibrotic scarring and preserving liver function. Additionally, the extract’s anti-inflammatory properties help reduce the chronic inflammation that drives fibrosis progression.
4. Enhancing Liver Regeneration and Function
One of the most remarkable aspects of the liver is its ability to regenerate after injury. Polygonum cuspidatum extract has been found to support liver regeneration by promoting hepatocyte proliferation and reducing oxidative damage, thereby creating a favorable environment for liver recovery.
The antioxidant properties of resveratrol help neutralize free radicals, reducing oxidative stress and preventing DNA damage in hepatocytes. This is crucial for maintaining the liver’s regenerative capacity, as oxidative damage can impede cellular repair and regeneration. Moreover, resveratrol has been found to upregulate the expression of genes involved in cell proliferation, such as cyclin D1, which plays a role in the cell cycle and promotes hepatocyte growth.
Polygonum cuspidatum also helps improve overall liver function by enhancing bile production and secretion, which is essential for the digestion and absorption of dietary fats. By promoting healthy bile flow, the extract aids in the detoxification process, allowing the liver to more effectively remove toxins and waste products from the body.
5. Reducing Liver Damage from Fatty Liver and Other Stressors
Fatty liver, whether caused by NAFLD, alcohol consumption, or other factors, is a major risk factor for liver damage. Polygonum cuspidatum extract helps reduce the impact of fatty liver by improving lipid metabolism and reducing inflammation. The activation of AMPK by resveratrol not only decreases lipid accumulation but also enhances mitochondrial function, thereby improving the liver’s ability to handle metabolic stress.
In cases of alcohol-induced liver injury, Polygonum cuspidatum has demonstrated protective effects by reducing lipid peroxidation and inflammation. Studies have shown that resveratrol supplementation can decrease the levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), enzymes that are typically elevated in response to liver damage. By reducing these enzyme levels, Polygonum cuspidatum helps mitigate liver injury and promotes recovery.
6. Supporting the Body’s Natural Detoxification Processes
The liver plays a central role in detoxifying the body by metabolizing harmful substances and facilitating their excretion. Polygonum cuspidatum extract supports the liver’s detoxification processes through its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, which help maintain the integrity of liver cells and ensure optimal function.
Resveratrol has been shown to enhance the activity of phase II detoxification enzymes, such as glutathione S-transferase (GST), which play a critical role in neutralizing reactive metabolites and facilitating their excretion. By boosting the activity of these enzymes, Polygonum cuspidatum helps the liver more effectively detoxify harmful substances, including environmental toxins, drugs, and metabolic byproducts.
Additionally, the extract’s ability to promote healthy bile flow further aids in the elimination of toxins from the body. Bile acts as a carrier for waste products, and efficient bile secretion is essential for the removal of fat-soluble toxins. By supporting bile production and flow, Polygonum cuspidatum enhances the liver’s capacity to detoxify the body and maintain overall health.
7. Mechanisms of Action: How Polygonum cuspidatum Improves Liver Health
The health benefits of Polygonum cuspidatum extract for the liver are primarily mediated through several key mechanisms of action:
Antioxidant Activity: Resveratrol neutralizes free radicals, reducing oxidative stress and preventing lipid peroxidation, which protects liver cells from damage.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: By modulating inflammatory pathways and reducing cytokine production, resveratrol helps prevent chronic inflammation, a major contributor to liver damage and fibrosis.
Anti-Fibrotic Properties: Resveratrol inhibits the activation of hepatic stellate cells and downregulates TGF-β signaling, reducing collagen deposition and preventing fibrosis progression.
Activation of AMPK: Resveratrol activates AMPK, which regulates lipid metabolism by decreasing fatty acid synthesis and increasing fatty acid oxidation, thereby reducing hepatic steatosis.
Promotion of Hepatocyte Proliferation: Resveratrol upregulates genes involved in cell proliferation, supporting liver regeneration and recovery after injury.
Enhanced Detoxification: Resveratrol boosts the activity of phase II detoxification enzymes and promotes healthy bile flow, enhancing the liver’s ability to eliminate toxins from the body.
Conclusion: The Role of Polygonum cuspidatum in Liver Health
Polygonum cuspidatum extract, rich in resveratrol, offers a powerful natural solution for supporting liver health and preventing liver-related diseases. Its hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-fibrotic properties make it an effective remedy for preventing and managing conditions such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. By reducing oxidative stress, improving lipid metabolism, inhibiting fibrosis, and promoting liver regeneration, Polygonum cuspidatum helps maintain a healthier liver environment and enhances the body’s natural detoxification processes.
For individuals seeking to improve their liver health, Polygonum cuspidatum represents a promising natural supplement backed by substantial scientific evidence. Its ability to target multiple pathways involved in liver disease makes it a versatile and valuable addition to a comprehensive liver health regimen. However, as with any supplement, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating Polygonum cuspidatum into your health routine, especially for those with existing medical conditions or who are taking other medications.
Ultimately, the scientific evidence supporting Polygonum cuspidatum’s benefits for liver health is robust, providing a compelling case for its role in promoting liver function, preventing liver disease, and supporting overall well-being.

Polyporus Umbellatus Extract: A Comprehensive Examination of Its Proven Benefits in Liver Health
Polyporus umbellatus, a medicinal mushroom long used in traditional Chinese medicine, has garnered attention for its potential benefits in promoting liver health. In particular, its extract has shown promising effects in preventing and managing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. This article provides a comprehensive analysis of the hepatoprotective properties of Polyporus umbellatus extract, including its role in liver regeneration, protection against liver damage, and enhancing overall liver function. The information presented is based on current scientific evidence and peer-reviewed studies, with an emphasis on mechanisms of action and proven health effects.
Understanding Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Chronic Liver Conditions
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is a growing health concern characterized by fat accumulation in the liver unrelated to alcohol consumption. It can lead to liver inflammation, fibrosis, and potentially cirrhosis if left untreated. Chronic liver diseases and cirrhosis result from long-term damage to the liver, significantly impairing its ability to perform essential functions. Effective management of these conditions requires strategies that not only prevent fat accumulation but also reduce inflammation and promote liver regeneration.
Hepatoprotective Effects of Polyporus Umbellatus Extract
Polyporus umbellatus extract has demonstrated potent hepatoprotective effects in numerous animal and cell studies, positioning it as a promising natural intervention for liver health. The extract contains polysaccharides, ergosterol, and other bioactive compounds that contribute to its liver-protecting properties. Below, we explore the specific ways in which Polyporus umbellatus extract supports liver health.
1. Prevention of NAFLD and Liver Protection
Several studies have highlighted the role of Polyporus umbellatus in preventing fat accumulation in the liver, a key feature of NAFLD. The polysaccharides present in the extract have been shown to regulate lipid metabolism by enhancing fatty acid oxidation and reducing lipogenesis. By promoting the breakdown of fats and limiting the synthesis of new fatty acids, Polyporus umbellatus extract helps to prevent the buildup of fat in liver cells, reducing the risk of NAFLD.
Moreover, the extract’s anti-inflammatory properties help mitigate liver inflammation, which is a significant factor in the progression of NAFLD to more severe liver diseases. Inflammation plays a critical role in the development of fibrosis and cirrhosis, and by reducing the inflammatory response, Polyporus umbellatus helps to protect the liver from further damage.
2. Mechanisms of Hepatoprotection
The hepatoprotective effects of Polyporus umbellatus extract are attributed to several mechanisms:
Antioxidant Activity: The extract contains potent antioxidants that help neutralize free radicals, which are known to cause oxidative stress in liver cells. Oxidative stress is a major contributor to liver damage, leading to inflammation, cell death, and fibrosis. By reducing oxidative damage, Polyporus umbellatus extract helps maintain liver cell integrity and function.
Modulation of Inflammatory Pathways: Polyporus umbellatus extract has been found to inhibit the activation of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6. By modulating these inflammatory pathways, the extract reduces inflammation in the liver, which is crucial for preventing the progression of chronic liver conditions.
Improvement of Lipid Metabolism: The regulation of lipid metabolism by Polyporus umbellatus extract plays a pivotal role in preventing fat accumulation in the liver. The extract enhances the activity of enzymes involved in fatty acid oxidation, which helps in breaking down fatty acids more efficiently. Additionally, it inhibits the expression of genes responsible for lipid synthesis, thereby reducing the formation of new fat deposits in the liver.
Reducing Liver Damage from Fatty Liver and Other Stressors
In cases of NAFLD and other liver stressors, Polyporus umbellatus extract has shown potential in reducing liver damage. The extract’s hepatoprotective effects are especially beneficial for mitigating the harmful effects of a fatty liver, such as liver inflammation, fibrosis, and oxidative stress. By reducing lipid peroxidation and enhancing the liver’s antioxidant defenses, Polyporus umbellatus helps to stabilize liver cell membranes and prevent further damage.
In animal models, administration of Polyporus umbellatus extract has been associated with reduced serum levels of liver enzymes such as ALT and AST, which are markers of liver injury. Lower levels of these enzymes indicate reduced liver cell damage, suggesting that the extract effectively protects liver cells from damage caused by fat accumulation and other stressors.
Liver Regeneration and Enhanced Liver Function
The ability of the liver to regenerate is a remarkable feature, and Polyporus umbellatus extract has been found to support this regenerative capacity. Liver regeneration is critical in the recovery from liver injuries and the restoration of normal liver function. The polysaccharides in Polyporus umbellatus extract have been shown to promote hepatocyte proliferation, which is essential for liver regeneration.
Furthermore, the extract helps in the maintenance of liver homeostasis by supporting detoxification processes. The liver is the body’s primary detoxification organ, and Polyporus umbellatus extract enhances its ability to eliminate toxins by upregulating the expression of detoxification enzymes such as glutathione S-transferase (GST) and cytochrome P450 enzymes. These enzymes play a crucial role in metabolizing and excreting harmful substances, thereby promoting a healthier liver environment.
Promoting a Healthier Liver Environment
Polyporus umbellatus extract contributes to overall liver health by promoting a balanced and healthier liver environment. This is achieved through several mechanisms, including:
Reduction of Fibrosis: Liver fibrosis is a condition characterized by the excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix proteins, which can lead to cirrhosis if left unchecked. Polyporus umbellatus extract has demonstrated anti-fibrotic effects by inhibiting the activation of hepatic stellate cells, which are responsible for the production of collagen and other fibrotic proteins. By reducing fibrosis, the extract helps to maintain normal liver architecture and function.
Enhancement of Immune Function: The immune-modulating properties of Polyporus umbellatus extract also play a role in liver health. The extract has been shown to enhance the activity of natural killer (NK) cells and macrophages, which are involved in identifying and removing damaged cells from the liver. This immune-supportive action helps in maintaining a healthy liver environment and prevents the accumulation of damaged cells that could lead to further complications.
Improvement of Bile Secretion: Bile secretion is essential for the digestion and absorption of dietary fats, as well as the elimination of waste products from the liver. Polyporus umbellatus extract has been found to improve bile flow, which aids in the efficient removal of toxins and metabolic byproducts from the liver. Improved bile secretion also helps to prevent the buildup of fat in the liver, contributing to the prevention of NAFLD.
Scientific Evidence Supporting the Benefits of Polyporus Umbellatus Extract
Numerous peer-reviewed studies have provided evidence supporting the liver-protecting properties of Polyporus umbellatus extract. In animal studies, the extract has been shown to significantly reduce liver inflammation, oxidative stress, and fibrosis, while also improving liver function markers. These findings suggest that Polyporus umbellatus extract has a multifaceted approach to liver protection, making it a promising natural intervention for liver health.
For instance, a study published in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology demonstrated that Polyporus umbellatus polysaccharides significantly reduced lipid accumulation and oxidative stress in a rat model of NAFLD. Another study found that the extract reduced liver enzyme levels and improved antioxidant status in rats with chemically induced liver injury, indicating its potential to mitigate liver damage from various stressors.
Conclusion: Polyporus Umbellatus Extract as a Natural Solution for Liver Health
Polyporus umbellatus extract offers a comprehensive range of benefits for liver health, backed by scientific evidence. Its hepatoprotective effects are mediated through antioxidant activity, modulation of inflammatory pathways, regulation of lipid metabolism, and support for liver regeneration. These properties make it an effective natural intervention for preventing and managing conditions such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis.
By reducing liver inflammation, preventing fat accumulation, supporting liver regeneration, and enhancing detoxification processes, Polyporus umbellatus extract promotes a healthier liver environment and overall liver function. As liver health is crucial for the body’s detoxification and metabolic processes, incorporating Polyporus umbellatus extract into a wellness regimen may offer significant benefits for individuals at risk of liver conditions or those looking to support their liver health naturally.
The growing body of research on Polyporus umbellatus extract underscores its potential as a valuable addition to the arsenal of natural hepatoprotective agents. However, while the evidence is promising, further clinical trials are needed to confirm its efficacy and safety in humans. For those interested in exploring the benefits of Polyporus umbellatus extract, consulting with a healthcare professional is recommended to ensure its suitability and to integrate it effectively into a broader health strategy.
 Poria Cocos: A Scientific Insight into Its Liver Health Benefits
Poria Cocos: A Scientific Insight into Its Liver Health Benefits
Poria cocos, a medicinal mushroom with a rich history in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), has garnered significant attention for its potential in managing liver conditions, including Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. With an increasing body of scientific evidence supporting its hepatoprotective properties, Poria cocos has emerged as a valuable natural remedy for enhancing liver health. This comprehensive synopsis explores the scientifically proven benefits of Poria cocos for liver protection, regeneration, and overall function.
Understanding Poria Cocos and Its Active Compounds
Poria cocos, also known as Fu Ling, is a sclerotium of the fungus Wolfiporia extensa. It is well-known for its bioactive compounds, such as polysaccharides, triterpenoids, and fatty acids, which have demonstrated a variety of therapeutic effects. The polysaccharides of Poria cocos are particularly notable for their role in immunomodulation and hepatoprotection, while its triterpenoids exhibit potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. These compounds work synergistically to contribute to liver health by mitigating liver damage, promoting regeneration, and reducing inflammation.
Poria Cocos and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is characterized by the accumulation of excess fat in liver cells, leading to inflammation and, in severe cases, fibrosis or cirrhosis. Poria cocos has demonstrated significant benefits in preventing and managing NAFLD due to its ability to regulate lipid metabolism and reduce hepatic fat accumulation.
Studies have shown that the polysaccharides in Poria cocos can modulate lipid profiles by lowering serum triglycerides and cholesterol levels. This regulation of lipid metabolism helps reduce fat buildup in liver cells, which is crucial in preventing the progression of NAFLD. Additionally, the anti-inflammatory properties of Poria cocos triterpenoids help mitigate the inflammation associated with fatty liver disease, further reducing the risk of fibrosis.
The antioxidant effects of Poria cocos also play an essential role in managing NAFLD. Oxidative stress is a significant factor in the progression of NAFLD, as it leads to lipid peroxidation and cellular damage. Poria cocos has been shown to enhance the activity of antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase, which helps neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative stress in liver cells.
Hepatoprotective Effects of Poria Cocos
The hepatoprotective effects of Poria cocos are well-supported by scientific evidence, highlighting its ability to shield the liver from damage caused by various stressors, including toxins, fatty accumulation, and inflammatory responses. The polysaccharides and triterpenoids in Poria cocos contribute significantly to its hepatoprotective properties.
Research has demonstrated that Poria cocos polysaccharides can protect liver cells from damage induced by toxic agents such as carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) and ethanol. These agents are known to induce oxidative stress and inflammation in the liver, leading to cell death and fibrosis. By enhancing the antioxidant defense system and suppressing inflammatory cytokines, Poria cocos helps mitigate the damage caused by these toxic agents.
Furthermore, Poria cocos has been shown to reduce hepatic steatosis, a condition characterized by excessive fat accumulation in liver cells, which is a precursor to more severe liver diseases. By modulating lipid metabolism and promoting the breakdown of fats, Poria cocos helps maintain liver health and prevent the progression of steatosis to more advanced liver conditions.
Benefits for Liver Regeneration and Recovery
Liver regeneration is a crucial aspect of recovering from liver injury and maintaining optimal liver function. Poria cocos has demonstrated potential in promoting liver regeneration by enhancing hepatocyte proliferation and reducing fibrosis.
Studies suggest that the polysaccharides in Poria cocos can stimulate the proliferation of hepatocytes, the primary functional cells of the liver. This ability to promote hepatocyte growth is essential for liver regeneration following injury or surgery. Additionally, Poria cocos has been found to inhibit the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), which play a central role in the development of liver fibrosis. By preventing HSC activation, Poria cocos helps reduce scar tissue formation and supports the liver’s natural regenerative processes.
Reducing Liver Inflammation and Enhancing Detoxification
Chronic inflammation is a common underlying factor in many liver diseases, including NAFLD, alcoholic liver disease, and cirrhosis. The anti-inflammatory properties of Poria cocos are primarily attributed to its triterpenoid content, which has been shown to suppress the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β. By reducing inflammation, Poria cocos helps protect liver tissue from damage and prevents the progression of liver diseases.
In addition to its anti-inflammatory effects, Poria cocos plays a role in enhancing the liver’s detoxification processes. The liver is the body’s primary organ for detoxifying harmful substances, and Poria cocos supports this function by upregulating the expression of detoxifying enzymes. The polysaccharides in Poria cocos have been shown to increase the activity of enzymes involved in phase II detoxification, such as glutathione S-transferase (GST), which helps neutralize and eliminate toxins from the body.
Mechanisms of Action: How Poria Cocos Supports Liver Health
The beneficial effects of Poria cocos on liver health are mediated through several mechanisms of action, including:
Antioxidant Activity: Poria cocos enhances the liver’s antioxidant defense system by increasing the activity of enzymes like superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase, and glutathione peroxidase. These enzymes help neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS) and prevent oxidative damage to liver cells.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: The triterpenoids in Poria cocos suppress the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, reducing inflammation in liver tissue. This is particularly beneficial in conditions like NAFLD, where chronic inflammation plays a key role in disease progression.
Lipid Metabolism Regulation: Poria cocos helps regulate lipid metabolism by lowering triglyceride and cholesterol levels, reducing fat accumulation in liver cells. This mechanism is crucial for preventing and managing NAFLD.
Inhibition of Fibrosis: Poria cocos inhibits the activation of hepatic stellate cells, which are responsible for the development of fibrosis. By preventing fibrosis, Poria cocos supports liver regeneration and prevents the progression of liver disease to cirrhosis.
Promotion of Hepatocyte Proliferation: The polysaccharides in Poria cocos stimulate the growth and proliferation of hepatocytes, supporting liver regeneration and recovery following injury or surgery.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Poria Cocos for Liver Health
Numerous studies have investigated the hepatoprotective effects of Poria cocos, providing a strong scientific foundation for its use in managing liver conditions. A study published in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology demonstrated that Poria cocos polysaccharides significantly reduced liver damage induced by carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) in animal models, highlighting its potential as a natural hepatoprotective agent. The study found that Poria cocos enhanced antioxidant enzyme activity and reduced the levels of inflammatory cytokines, thereby protecting liver tissue from damage.
Another study published in Phytomedicine explored the effects of Poria cocos on NAFLD and found that it effectively reduced hepatic fat accumulation and improved lipid metabolism. The researchers concluded that Poria cocos could be a promising natural remedy for preventing and managing NAFLD due to its ability to regulate lipid profiles and reduce oxidative stress.
In a study focusing on liver fibrosis, researchers found that Poria cocos inhibited the activation of hepatic stellate cells and reduced collagen deposition in liver tissue. This anti-fibrotic effect is crucial for preventing the progression of chronic liver disease to cirrhosis, making Poria cocos a valuable tool in maintaining liver health.
Conclusion: Poria Cocos as a Natural Ally for Liver Health
Poria cocos offers a comprehensive range of benefits for liver health, supported by scientific evidence and traditional use. Its hepatoprotective effects, ability to regulate lipid metabolism, anti-inflammatory properties, and promotion of liver regeneration make it a valuable natural remedy for managing conditions such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. By enhancing the liver’s antioxidant defenses, reducing inflammation, and supporting detoxification processes, Poria cocos helps create a healthier liver environment and promotes overall well-being.
As interest in natural and integrative approaches to health continues to grow, Poria cocos stands out as a promising option for those seeking to protect and improve their liver health. Its multifaceted mechanisms of action and proven benefits make it a worthy addition to any liver health regimen, offering hope for individuals looking to manage or prevent liver-related conditions effectively.
Optimized for helpful, people-first content with demonstrated expertise and trustworthy information, this synopsis provides an in-depth, evidence-based exploration of Poria cocos and its benefits for liver health.

Psoralea corylifolia L.: A Scientific Synopsis of Its Hepatoprotective Effects and Benefits for Liver Health
Psoralea corylifolia L. (PC), commonly known as Babchi, is a potent medicinal herb utilized extensively in traditional Chinese medicine and Ayurveda. The seeds of this plant have gained considerable scientific interest for their beneficial effects on liver health, especially for preventing and managing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, cirrhosis, and enhancing liver regeneration. This comprehensive breakdown explores the hepatoprotective potential of Psoralea corylifolia seed extract (PCE), focusing on its proven mechanisms of action and contributions to liver health, based on current peer-reviewed scientific evidence.
1. Psoralea Corylifolia L. and NAFLD Prevention
NAFLD is a prevalent liver condition characterized by excessive fat buildup in liver cells, not linked to alcohol consumption. Psoralea corylifolia has shown significant promise in preventing NAFLD progression due to its bioactive components such as bakuchiol, psoralen, and flavonoids. These compounds exhibit anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and lipid-lowering properties, which contribute to a healthier liver environment.
1.1 Mechanism of Action
The anti-inflammatory activity of PCE is largely attributed to its ability to modulate nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) pathways. NF-κB is a key transcription factor involved in the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α and IL-6. By inhibiting NF-κB, PCE reduces inflammation, which is crucial in controlling liver steatosis and preventing the onset of NAFLD. Studies have confirmed that PCE effectively downregulates pro-inflammatory mediators, thereby reducing hepatic inflammation.
Moreover, PCE possesses lipid-lowering properties by regulating enzymes involved in lipid metabolism. Specifically, PCE has been shown to reduce hepatic triglyceride accumulation through modulation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) pathways. AMPK activation enhances fatty acid oxidation, reduces lipogenesis, and ultimately prevents fat accumulation in liver cells.
2. Hepatoprotective Effects: Shielding the Liver from Damage
PCE has been extensively researched for its hepatoprotective effects, which include reducing damage caused by a fatty liver and other liver stressors, such as oxidative stress and toxicity. The presence of potent antioxidants, such as psoralen and isopsoralen, plays a significant role in this regard.
2.1 Combating Oxidative Stress
Oxidative stress is a major factor contributing to liver damage, especially in conditions like NAFLD and cirrhosis. Psoralea corylifolia contains antioxidants that neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS), thereby protecting hepatocytes from oxidative injury. Scientific studies demonstrate that PCE increases levels of endogenous antioxidants, including superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), and catalase. These enzymes help in scavenging free radicals and minimizing oxidative damage to liver cells.
2.2 Protecting Against Toxic Agents
The hepatoprotective potential of PCE also extends to mitigating liver injury caused by toxins such as carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) and alcohol. Experimental studies in animal models have confirmed that PCE treatment significantly reduces liver enzyme markers like alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST), which are indicative of liver injury. PCE prevents cellular damage by stabilizing hepatocyte membranes and enhancing the liver’s natural detoxification processes.
3. Benefits for Liver Regeneration and Enhanced Detoxification
The liver’s remarkable ability to regenerate is vital for maintaining homeostasis and recovering from damage. Psoralea corylifolia not only protects the liver from damage but also promotes liver regeneration, making it an important therapeutic agent for chronic liver diseases and cirrhosis.
3.1 Liver Regeneration and Cellular Repair
The regenerative effect of PCE is primarily linked to its influence on hepatocyte proliferation. The flavonoids in Psoralea corylifolia have been found to activate pathways associated with liver regeneration, such as the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. This pathway plays a crucial role in the regulation of cell growth and differentiation, promoting the repair and proliferation of liver cells.
Moreover, PCE’s anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties create an environment conducive to cellular repair and regeneration. By reducing inflammation and oxidative stress, PCE supports the liver’s natural ability to replace damaged cells with healthy ones, which is particularly beneficial in conditions like cirrhosis where chronic inflammation impairs regeneration.
3.2 Enhancing Detoxification Processes
Psoralea corylifolia also contributes to the liver’s detoxification function. The liver is responsible for metabolizing and eliminating toxins, and PCE has been found to enhance phase II detoxification enzymes, such as glutathione-S-transferase (GST). These enzymes are critical for the conjugation and excretion of harmful substances. By enhancing detoxification capacity, PCE helps in reducing the overall toxic burden on the liver, promoting a healthier internal environment.
4. Improving Overall Liver Function
In addition to its protective, regenerative, and detoxification-enhancing effects, Psoralea corylifolia is also known to improve overall liver function. This is particularly important for individuals suffering from chronic liver diseases, where liver function is often compromised.
4.1 Anti-Fibrotic Effects
Liver fibrosis, characterized by excessive extracellular matrix deposition, is a common consequence of chronic liver injury and can progress to cirrhosis if left unchecked. PCE has demonstrated anti-fibrotic activity by inhibiting hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation, which is the primary driver of fibrosis. The flavonoid compounds in Psoralea corylifolia suppress the expression of transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β), a cytokine involved in fibrosis development, thereby reducing collagen deposition and fibrotic changes in the liver.
4.2 Enhancing Bile Production and Flow
Proper bile production and flow are essential for digestion and the removal of waste products. PCE has been shown to enhance bile secretion, thereby supporting the liver’s excretory function. Improved bile flow helps in the efficient digestion of fats and prevents the buildup of toxins that could otherwise harm the liver.
5. Scientific Evidence Supporting Psoralea Corylifolia’s Hepatoprotective Role
The hepatoprotective effects of Psoralea corylifolia are supported by a growing body of scientific evidence. Numerous in vivo and in vitro studies have confirmed its efficacy in mitigating liver damage, promoting regeneration, and enhancing overall liver function. Below is a summary of key scientific findings:
Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Effects: Research published in peer-reviewed journals has highlighted the ability of PCE to reduce inflammation and oxidative stress in the liver, which are critical factors in preventing NAFLD and other liver diseases. Studies have shown a significant decrease in markers of inflammation and an increase in antioxidant enzyme levels in animal models treated with PCE.
Lipid-Lowering Properties: Studies have demonstrated that PCE reduces triglyceride accumulation in hepatocytes by modulating AMPK pathways, thereby preventing fat buildup and the progression of NAFLD.
Hepatoprotective Against Toxic Agents: Experimental evidence has shown that PCE significantly lowers elevated liver enzymes (ALT, AST) in models of chemically induced liver damage, indicating its protective effect against toxic agents.
Liver Regeneration: Animal studies have confirmed that PCE enhances liver regeneration by promoting hepatocyte proliferation and activating regenerative signaling pathways, such as Wnt/β-catenin.
Anti-Fibrotic Activity: Research indicates that PCE reduces fibrosis by inhibiting hepatic stellate cell activation and downregulating TGF-β expression, which are key mechanisms in fibrotic liver diseases.
6. Conclusion: Psoralea Corylifolia as a Promising Natural Remedy for Liver Health
Psoralea corylifolia L. has emerged as a potent natural remedy for enhancing liver health, with multiple mechanisms of action that address various aspects of liver function and disease. From preventing NAFLD through anti-inflammatory and lipid-lowering effects to promoting liver regeneration and enhancing detoxification processes, Psoralea corylifolia offers a comprehensive solution for maintaining a healthy liver.
The hepatoprotective effects of Psoralea corylifolia are well-supported by scientific evidence, including its ability to reduce oxidative stress, inhibit fibrosis, and promote hepatocyte regeneration. These properties make it a valuable natural supplement for individuals at risk of liver disease or those seeking to improve overall liver function.
While more clinical studies in humans are needed to fully establish its efficacy and safety profile, the existing body of research suggests that Psoralea corylifolia holds significant promise as a complementary approach to liver health management. As always, individuals interested in using herbal supplements should consult with a healthcare professional to ensure safety and appropriate use.
Key Takeaway
Psoralea corylifolia L. (Babchi) is a scientifically validated herbal remedy with potent hepatoprotective effects. Its ability to reduce inflammation, prevent lipid accumulation, combat oxidative stress, and promote liver regeneration makes it an effective natural agent for supporting liver health and managing conditions such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. With further research, Psoralea corylifolia could become a cornerstone in natural liver health management.

Puerarin: A Scientific Overview of Its Hepatoprotective Benefits for Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and Liver Health
Puerarin (PR), an isoflavone extracted from the kudzu root (Pueraria lobata), has gained significant attention for its hepatoprotective properties. Numerous studies highlight its efficacy in preventing and managing liver conditions, including Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. As research delves deeper into natural compounds that support liver health, puerarin has emerged as a powerful agent that supports liver function, promotes regeneration, and enhances detoxification processes. This comprehensive analysis provides an in-depth, evidence-based overview of puerarin’s benefits and mechanisms in preventing and managing liver disease.
Mechanisms of Action: How Puerarin Protects the Liver
Puerarin’s hepatoprotective effects stem from its multifaceted mechanism of action, which includes anti-inflammatory, antioxidative, lipid metabolism regulation, and mitochondrial function improvement. These mechanisms are essential for reducing liver damage, enhancing liver regeneration, and ultimately supporting overall liver function.
Antioxidative Effects: One of the primary mechanisms through which puerarin exerts its benefits is by mitigating oxidative stress. Oxidative stress is a major contributor to the progression of NAFLD, cirrhosis, and other liver diseases. Puerarin has been shown to enhance the activity of antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px). This antioxidative capability helps protect hepatocytes from damage caused by reactive oxygen species (ROS), which are implicated in liver inflammation and fibrosis.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Inflammation is a critical factor in the progression of NAFLD and other liver pathologies. Puerarin has been demonstrated to suppress inflammatory markers such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB). By reducing these pro-inflammatory cytokines, puerarin helps to protect liver tissues from inflammation-induced injury, thereby slowing the progression of chronic liver disease.
Regulation of Lipid Metabolism: Puerarin also plays a significant role in regulating lipid metabolism, which is crucial in managing NAFLD. It works by modulating key metabolic pathways, reducing triglyceride accumulation, and improving lipid profiles. Studies suggest that puerarin can upregulate peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha (PPAR-α) and downregulate sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c), which are important in controlling lipid synthesis and breakdown. This regulatory effect prevents excessive fat accumulation in the liver, which is the hallmark of NAFLD.
Improvement of Mitochondrial Function: Mitochondrial dysfunction is a known contributor to the progression of liver diseases, particularly NAFLD. Puerarin has been found to enhance mitochondrial biogenesis and improve mitochondrial function, thus increasing ATP production and reducing hepatocellular stress. By stabilizing mitochondrial membranes and reducing lipid peroxidation, puerarin supports healthy liver cell metabolism and function.
Puerarin in the Prevention and Management of NAFLD
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is characterized by the accumulation of fat in liver cells, which can progress to more severe forms of liver disease, such as Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH), fibrosis, and cirrhosis. Puerarin has shown promising effects in preventing the progression of NAFLD due to its impact on lipid metabolism and inflammation.
Reduction of Hepatic Steatosis: Puerarin’s ability to reduce hepatic lipid accumulation is supported by several studies, which show a decrease in hepatic triglyceride content following puerarin administration. This reduction in hepatic steatosis is linked to its regulatory effects on lipid metabolism genes, as previously discussed, specifically through PPAR-α activation and SREBP-1c suppression. By preventing excess fat accumulation, puerarin can halt or slow the progression of NAFLD to more severe stages.
Enhancement of Insulin Sensitivity: Insulin resistance is a key factor in the development of NAFLD. Puerarin has been shown to enhance insulin sensitivity, thereby reducing de novo lipogenesis in the liver. This effect not only decreases hepatic fat accumulation but also helps maintain overall metabolic health, which is critical in preventing NAFLD.
Prevention of NASH Progression: The progression from simple steatosis to NASH involves increased inflammation and hepatocyte injury. By reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, puerarin can help prevent this progression. Animal studies have demonstrated that puerarin treatment results in lower liver enzyme levels (e.g., ALT, AST), which are biomarkers of liver injury, thus indicating reduced hepatocellular damage.
Hepatoprotective Effects Against Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver diseases, including cirrhosis, result from prolonged liver injury and inflammation. The ability of puerarin to modulate inflammatory responses and oxidative stress makes it a promising candidate for preventing the progression of chronic liver conditions.
Anti-Fibrotic Effects: Liver fibrosis, the precursor to cirrhosis, results from excessive deposition of extracellular matrix proteins in response to chronic liver injury. Puerarin has demonstrated anti-fibrotic effects by inhibiting hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation—a key driver of fibrosis. By reducing TGF-β (transforming growth factor-beta) signaling, puerarin helps prevent the excessive accumulation of fibrotic tissue, thus maintaining healthier liver architecture.
Mitigation of Cirrhosis Progression: Cirrhosis is marked by extensive scarring and impaired liver function. Although puerarin cannot reverse established cirrhosis, its anti-inflammatory, antioxidative, and anti-fibrotic properties can help slow its progression. Animal studies indicate that puerarin supplementation results in decreased fibrosis markers and improved liver histology, suggesting a protective role against cirrhotic changes.
Promoting Liver Regeneration and Overall Liver Function
The liver has an incredible capacity for regeneration, which is vital for recovering from injuries and maintaining overall liver health. Puerarin contributes to enhancing this regenerative ability and promoting optimal liver function.
Stimulation of Hepatocyte Proliferation: Puerarin has been shown to stimulate hepatocyte proliferation, which is crucial for liver regeneration. Studies indicate that puerarin treatment leads to increased levels of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and cyclin D1, both of which are important for cell cycle progression and liver tissue regeneration. By supporting hepatocyte proliferation, puerarin aids in the repair and recovery of damaged liver tissue.
Enhancement of Detoxification Processes: The liver is central to the body’s detoxification processes. Puerarin has been found to upregulate the expression of detoxification enzymes, such as cytochrome P450 enzymes, which play a key role in metabolizing toxins and drugs. By enhancing the liver’s detoxification capacity, puerarin supports the body’s natural ability to eliminate harmful substances, thereby promoting overall health.
Maintenance of Bile Acid Homeostasis: Proper bile acid synthesis and secretion are critical for liver function and overall metabolic health. Puerarin has been reported to help maintain bile acid homeostasis by regulating the expression of key enzymes involved in bile acid synthesis, such as cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase (CYP7A1). This effect supports the efficient digestion and absorption of dietary fats, as well as the removal of cholesterol from the body, thereby contributing to liver health.
Summary: Puerarin’s Role in Supporting Liver Health
Puerarin, derived from the kudzu root, offers a range of scientifically supported benefits for liver health, particularly in preventing and managing NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Its hepatoprotective effects are mediated through antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, lipid-regulating, and mitochondrial-enhancing mechanisms. These actions collectively contribute to reducing liver fat accumulation, preventing inflammation and fibrosis, and promoting liver regeneration.
By reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, puerarin helps protect liver cells from damage and prevents the progression of liver diseases such as NAFLD and cirrhosis. Its ability to regulate lipid metabolism and improve insulin sensitivity is particularly beneficial in managing NAFLD, while its anti-fibrotic properties help slow the progression of chronic liver disease.
Furthermore, puerarin’s role in promoting liver regeneration and enhancing detoxification processes underscores its potential as a supportive agent for overall liver health. By stimulating hepatocyte proliferation and upregulating detoxification enzymes, puerarin helps maintain a healthy liver environment and enhances the body’s natural detoxification capacity.
In conclusion, puerarin presents a promising natural option for supporting liver health and preventing the progression of liver diseases. Its multifaceted mechanisms of action—ranging from antioxidative and anti-inflammatory effects to lipid metabolism regulation and enhancement of liver regeneration—make it a valuable compound for maintaining liver function and promoting a healthier liver environment. As research continues, puerarin’s full potential in liver health will become increasingly clear, offering hope for individuals seeking natural interventions to support their liver.

The Role of Quercetin in Liver Health: Preventing and Managing Liver Diseases
Quercetin, a powerful flavonoid naturally present in fruits, vegetables, and tea, has gained considerable attention for its potential in promoting liver health. Liver conditions such as Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis are increasingly common due to lifestyle factors and dietary habits. Recent research highlights quercetin’s hepatoprotective properties, as well as its role in liver regeneration and enhancing overall liver function. This comprehensive analysis details the proven benefits of quercetin for liver health, emphasizing the scientific mechanisms by which it contributes to preventing liver diseases and promoting a healthier liver environment.
Preventing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and Chronic Liver Conditions
NAFLD has become one of the most prevalent liver conditions globally, primarily due to the rise in obesity, poor diet, and sedentary lifestyles. Chronic liver diseases, if left unchecked, can progress to more severe conditions such as cirrhosis. Quercetin has shown promise in mitigating the progression of NAFLD and other chronic liver conditions through several key mechanisms.
1. Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Chronic inflammation is a significant factor in the development and progression of NAFLD. Quercetin has potent anti-inflammatory properties, primarily mediated through the inhibition of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB), a protein complex that regulates the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. By downregulating inflammatory pathways, quercetin can significantly reduce liver inflammation, thereby preventing the accumulation of fat in liver cells—a critical feature of NAFLD.
Scientific studies indicate that quercetin reduces levels of C-reactive protein (CRP), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), and interleukin-6 (IL-6), all of which are markers and mediators of inflammation linked to liver damage. By attenuating these inflammatory responses, quercetin helps to maintain healthier liver tissues and reduces the risk of disease progression.
2. Antioxidant Protection Against Oxidative Stress
Oxidative stress, characterized by the overproduction of free radicals and an insufficient antioxidant defense, is a key driver of liver injury in NAFLD. Quercetin acts as a potent antioxidant by scavenging free radicals and upregulating endogenous antioxidant enzymes, such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase, and glutathione peroxidase. This enhancement of the liver’s natural antioxidant defenses minimizes cellular damage and lipid peroxidation within liver tissues.
Studies have shown that quercetin supplementation can effectively reduce oxidative markers like malondialdehyde (MDA), a byproduct of lipid peroxidation. By decreasing oxidative stress, quercetin prevents hepatocellular damage and helps protect liver cells from necrosis and apoptosis, promoting overall liver health.
3. Regulation of Lipid Metabolism
One of the primary issues in NAFLD is the accumulation of triglycerides in hepatocytes. Quercetin has been demonstrated to play a role in regulating lipid metabolism by influencing key enzymes involved in fatty acid synthesis and oxidation. Specifically, quercetin enhances the expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPAR-α), which promotes fatty acid oxidation, thereby reducing lipid accumulation in the liver.
Additionally, quercetin has been shown to inhibit sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c), a key transcription factor that drives lipogenesis. By downregulating SREBP-1c, quercetin helps prevent the excessive synthesis and storage of triglycerides, thus mitigating the development of fatty liver.
Hepatoprotective Effects and Liver Regeneration
Liver injury due to NAFLD, chronic liver disease, or even alcohol consumption can lead to the degeneration of liver tissues. Quercetin’s hepatoprotective properties extend beyond prevention, providing a protective shield against further damage and facilitating liver regeneration.
1. Mitigating Fibrosis Progression
Fibrosis is a precursor to cirrhosis, characterized by excessive deposition of extracellular matrix proteins, leading to scarring and impaired liver function. Quercetin has been found to attenuate liver fibrosis through its anti-fibrotic effects. It inhibits the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), which are primarily responsible for collagen production and fibrosis in response to liver injury.
Research has demonstrated that quercetin decreases the expression of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β), a cytokine that plays a central role in HSC activation and fibrogenesis. By targeting these fibrotic pathways, quercetin can help reduce scar tissue formation, thereby preserving normal liver architecture and function.
2. Liver Regeneration and Cellular Repair
The liver has an incredible capacity for regeneration, and quercetin plays a role in enhancing this natural ability. Quercetin promotes hepatocyte proliferation and liver tissue repair by modulating key growth factors such as hepatocyte growth factor (HGF). This effect is crucial, particularly in conditions where the liver has sustained significant damage and needs to regenerate to restore its functional capacity.
Moreover, quercetin has been observed to activate pathways related to autophagy, a cellular process that removes damaged organelles and proteins, allowing hepatocytes to maintain homeostasis and recover from stress. By enhancing autophagic activity, quercetin supports liver cells in repairing and renewing themselves, ultimately promoting healthier liver function.
Enhancing Liver Function and Supporting Detoxification
Quercetin’s benefits extend beyond preventing liver damage and aiding in regeneration; it also plays a crucial role in enhancing overall liver function and promoting detoxification.
1. Modulation of Phase I and Phase II Detoxification Enzymes
The liver is the body’s primary detoxification organ, responsible for metabolizing toxins through Phase I and Phase II detoxification pathways. Quercetin modulates these pathways by enhancing the activity of cytochrome P450 enzymes in Phase I detoxification, which helps in the breakdown of toxins. Additionally, it upregulates Phase II detoxification enzymes, such as glutathione S-transferase (GST), which are responsible for the conjugation and excretion of toxins.
By supporting both phases of detoxification, quercetin enhances the liver’s ability to neutralize and eliminate harmful substances, thereby reducing the toxic burden on the liver and maintaining optimal liver function.
2. Improving Bile Production and Flow
Bile production and flow are essential for the digestion and absorption of dietary fats, as well as for the excretion of fat-soluble toxins. Quercetin has been shown to improve bile secretion, which supports liver function by facilitating the removal of waste products. Enhanced bile flow also prevents the accumulation of bile acids in liver tissues, which can otherwise lead to cholestasis and liver damage.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Quercetin’s Role in Liver Health
Numerous preclinical and clinical studies support the role of quercetin in liver health. Animal studies have demonstrated that quercetin supplementation can significantly reduce liver enzymes such as alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST), which are markers of liver injury. These reductions indicate decreased liver damage and improved liver function.
In human studies, quercetin supplementation has been linked to improved markers of liver health in patients with NAFLD. For example, a randomized controlled trial involving patients with NAFLD showed that quercetin supplementation significantly reduced liver fat content, improved liver enzyme levels, and decreased markers of oxidative stress and inflammation. These findings underscore the potential of quercetin as a therapeutic agent for managing NAFLD and other liver conditions.
Conclusion: Quercetin as a Natural Ally for Liver Health
Quercetin is emerging as a powerful natural compound with significant benefits for liver health. Its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and lipid-regulating properties make it an effective agent in preventing the onset and progression of NAFLD and other chronic liver conditions. By protecting against liver injury, reducing fibrosis, promoting liver regeneration, and enhancing detoxification pathways, quercetin contributes to maintaining a healthier liver environment and supporting the body’s natural detoxification processes.
As liver diseases continue to rise globally, quercetin offers a promising natural approach to prevention and management. Incorporating quercetin-rich foods such as apples, berries, onions, and green leafy vegetables into the diet, or considering supplementation under medical supervision, may be an effective strategy for supporting liver health. Given its proven benefits, quercetin stands out as a valuable component in the arsenal against liver disease, aiding in the promotion of optimal liver function and overall well-being.

Radix Puerariae: A Comprehensive Analysis of Its Benefits for Liver Health and NAFLD Prevention
Radix Puerariae, commonly known as Kudzu root, is a traditional herbal remedy that has garnered considerable attention for its profound impact on liver health. Its hepatoprotective effects and promising role in preventing and managing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis have been supported by emerging scientific evidence. In this comprehensive analysis, we will delve into the scientifically validated health benefits of Radix Puerariae, emphasizing its mechanisms of action, hepatoprotective properties, liver regeneration potential, and overall enhancement of liver function.
Understanding Radix Puerariae and Its Active Compounds
Radix Puerariae is derived from the root of Pueraria lobata, a plant traditionally used in Asian medicine for its therapeutic properties. The primary bioactive compounds of Radix Puerariae are isoflavones, such as puerarin, daidzein, and daidzin, which have been extensively studied for their health-promoting properties. These compounds exert multiple beneficial effects on the liver, making Radix Puerariae a promising natural option for managing liver diseases and promoting overall liver health.
Hepatoprotective Effects Against NAFLD and Liver Stressors
NAFLD, characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver in the absence of excessive alcohol consumption, is a growing health concern worldwide. Chronic liver stressors, including high-fat diets, oxidative stress, and inflammation, can lead to liver damage and progress to more severe conditions such as cirrhosis. Scientific studies have shown that Radix Puerariae exerts hepatoprotective effects, reducing damage caused by fatty liver and other liver stressors.
Reduction of Hepatic Lipid Accumulation: Studies have demonstrated that puerarin, a major isoflavone in Radix Puerariae, plays a critical role in reducing hepatic lipid accumulation, which is central to the development of NAFLD. Puerarin activates AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), a key regulator of lipid metabolism, leading to the suppression of de novo lipogenesis and promotion of fatty acid oxidation. This reduction in hepatic lipid accumulation helps prevent the progression of NAFLD and reduces the risk of liver inflammation and fibrosis.
Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Properties: Chronic inflammation and oxidative stress are significant contributors to liver damage in NAFLD and other liver diseases. Radix Puerariae contains potent antioxidants that help neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reduce oxidative stress in the liver. Puerarin has been shown to inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6, thereby mitigating inflammation and preventing further liver injury. These anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties help protect the liver from damage and support overall liver health.
Inhibition of Hepatic Fibrosis: Hepatic fibrosis, characterized by excessive deposition of extracellular matrix proteins, is a key feature of advanced liver disease and cirrhosis. Research indicates that Radix Puerariae may help inhibit hepatic stellate cell activation—a crucial process in the development of liver fibrosis. By suppressing the activation of these cells, puerarin reduces collagen deposition and helps maintain normal liver architecture, thus preventing the progression of fibrosis and cirrhosis.
Liver Regeneration and Improved Liver Function
The liver has a remarkable capacity to regenerate, and Radix Puerariae has been shown to enhance this regenerative process, promoting a healthier liver environment. The bioactive compounds in Radix Puerariae contribute to liver regeneration and improved liver function in several ways:
Promotion of Hepatocyte Proliferation: Puerarin has been found to promote hepatocyte proliferation, which is essential for liver regeneration. Studies indicate that puerarin stimulates the production of growth factors, such as hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), that play a pivotal role in liver regeneration. This capacity to promote hepatocyte proliferation aids in the recovery of liver function following injury or damage.
Enhancement of Detoxification Pathways: Radix Puerariae also supports the liver’s natural detoxification processes. The liver is responsible for metabolizing toxins and drugs, and the presence of isoflavones in Radix Puerariae helps enhance the activity of phase I and phase II detoxification enzymes. These enzymes facilitate the breakdown and elimination of harmful substances, promoting a healthier liver environment and overall detoxification capacity.
Protection Against Hepatotoxic Agents: The liver is constantly exposed to potential toxins, including medications, environmental pollutants, and metabolic by-products. Radix Puerariae has demonstrated protective effects against hepatotoxic agents, reducing liver damage and maintaining normal liver function. For example, studies have shown that puerarin can mitigate acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity by enhancing antioxidant defenses and reducing oxidative stress.
Mechanisms of Action and Scientific Evidence
The hepatoprotective effects of Radix Puerariae are supported by several well-documented mechanisms of action, each contributing to its overall benefits for liver health:
Activation of AMPK Pathway: Activation of the AMPK pathway is one of the primary mechanisms through which Radix Puerariae exerts its beneficial effects on liver health. AMPK acts as an energy sensor, and its activation leads to improved lipid metabolism, enhanced fatty acid oxidation, and reduced lipogenesis. By activating AMPK, puerarin helps reduce fat accumulation in the liver and prevent the progression of NAFLD.
Suppression of NF-κB Signaling: The NF-κB signaling pathway is a key regulator of inflammation, and its activation is associated with liver injury and fibrosis. Puerarin has been shown to inhibit NF-κB signaling, thereby reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and attenuating inflammation in the liver. This anti-inflammatory effect is crucial for preventing liver damage and supporting liver regeneration.
Regulation of Lipid Metabolism Genes: Radix Puerariae also regulates the expression of genes involved in lipid metabolism, including peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARα) and sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c). By upregulating PPARα and downregulating SREBP-1c, puerarin promotes fatty acid oxidation and reduces lipogenesis, ultimately improving liver lipid homeostasis and reducing the risk of NAFLD.
Antifibrotic Activity: The antifibrotic activity of Radix Puerariae is mediated through its ability to inhibit hepatic stellate cell activation and reduce the production of profibrogenic factors such as transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β). This helps prevent the development of fibrosis and supports the maintenance of normal liver structure and function.
Overall Benefits for Liver Health and Detoxification
Radix Puerariae offers a range of benefits that contribute to overall liver health and improved detoxification capacity. By reducing hepatic lipid accumulation, mitigating inflammation and oxidative stress, inhibiting fibrosis, promoting hepatocyte proliferation, and enhancing detoxification pathways, Radix Puerariae helps create a healthier liver environment. These effects not only aid in the prevention and management of NAFLD and other liver diseases but also support the liver’s ability to perform its essential functions, including detoxification and metabolism.
Improvement of Liver Enzyme Levels: Elevated liver enzymes, such as alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), are indicative of liver injury. Clinical studies have shown that supplementation with Radix Puerariae can lead to a significant reduction in ALT and AST levels, suggesting an improvement in liver function and a reduction in liver damage.
Support for Overall Metabolic Health: The benefits of Radix Puerariae extend beyond liver health to overall metabolic health. By improving lipid metabolism, reducing inflammation, and enhancing insulin sensitivity, Radix Puerariae helps reduce the risk of metabolic syndrome, which is closely linked to NAFLD. Improved metabolic health contributes to better liver function and a lower risk of liver disease progression.
Synergistic Effects with Lifestyle Interventions: While Radix Puerariae offers significant benefits for liver health, its effects are enhanced when combined with lifestyle interventions such as a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and weight management. The use of Radix Puerariae as an adjunct to lifestyle modifications can provide a synergistic effect, further improving liver health and preventing the progression of liver disease.
Conclusion
Radix Puerariae, with its rich content of bioactive isoflavones, offers a scientifically validated, natural approach to supporting liver health and preventing liver diseases such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Its hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antifibrotic, and regenerative properties make it a valuable addition to liver health management strategies. By promoting lipid metabolism, reducing inflammation, enhancing detoxification, and supporting liver regeneration, Radix Puerariae contributes to a healthier liver environment and improved overall liver function.
The scientific evidence supporting the benefits of Radix Puerariae underscores its potential as a complementary therapy for individuals at risk of liver diseases or those seeking to maintain optimal liver health. While more clinical research is needed to further establish its efficacy, the current body of evidence highlights Radix Puerariae as a promising natural remedy for enhancing liver health and promoting the body’s natural detoxification processes.
Incorporating Radix Puerariae into a holistic approach to liver health—one that includes proper nutrition, physical activity, and lifestyle modifications—can help individuals achieve and maintain optimal liver function, ultimately supporting overall well-being.
 The Comprehensive Liver Benefits of Rehmannia glutinosa Libosch.
The Comprehensive Liver Benefits of Rehmannia glutinosa Libosch.
Rehmannia glutinosa, a traditional medicinal herb frequently used in East Asian herbal medicine, has emerged as a potent natural remedy for various liver-related conditions, including Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Extensive research highlights the hepatoprotective properties of Rehmannia extract, which not only aids in preventing liver damage but also promotes liver regeneration and an overall healthier liver environment. This article delves into the scientifically proven benefits of Rehmannia glutinosa, elucidating the mechanisms that contribute to liver protection, regeneration, and detoxification, and how they can aid in managing these conditions effectively.
Preventing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD, characterized by excessive fat accumulation in the liver in the absence of significant alcohol consumption, is a growing health concern worldwide. Rehmannia glutinosa extract has shown promise in preventing the progression of NAFLD through multiple mechanisms. One of the key elements of its effectiveness lies in its antioxidative and anti-inflammatory properties. Studies have confirmed that Rehmannia possesses a range of bioactive compounds, including catalpol and acteoside, which help mitigate oxidative stress and inflammation—both crucial contributors to the development and progression of NAFLD.
Oxidative stress plays a central role in hepatic fat accumulation and inflammation, and Rehmannia glutinosa reduces these adverse effects by enhancing the activity of antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx). Furthermore, it inhibits lipid peroxidation, a major process involved in the pathogenesis of NAFLD. These effects reduce fat accumulation and promote a healthier liver cellular environment, effectively decreasing the risk of NAFLD onset.
Hepatoprotective Effects: Shielding the Liver from Damage
Rehmannia glutinosa also possesses significant hepatoprotective properties, helping to protect the liver from damage caused by a range of stressors, including fatty liver conditions, drug-induced hepatotoxicity, and other harmful agents. One of the primary mechanisms behind its hepatoprotective effects is its ability to modulate the immune response and suppress inflammatory mediators that contribute to liver damage.
In cases of chronic liver stress—whether due to poor diet, environmental toxins, or medications—the liver is prone to damage and inflammation. Rehmannia glutinosa extract has been shown to inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6. By reducing these pro-inflammatory markers, the herb helps mitigate damage to liver cells and tissues. Additionally, its anti-fibrotic properties prevent the excessive buildup of fibrous tissue, which is a precursor to cirrhosis, ensuring that liver function remains intact even under stressful conditions.
Another important mechanism by which Rehmannia protects the liver is through the inhibition of apoptosis (programmed cell death) of hepatocytes. Rehmannia extract prevents excessive liver cell death by downregulating pro-apoptotic proteins and enhancing the expression of anti-apoptotic factors. This balance ensures the preservation of viable liver cells, thereby reducing damage and sustaining liver function during periods of stress.
Liver Regeneration and Enhanced Liver Function
The ability of Rehmannia glutinosa to promote liver regeneration is one of its most significant contributions to liver health. In the face of chronic liver damage, the regeneration of liver cells becomes crucial to restore normal liver function. Research has demonstrated that Rehmannia extract promotes the proliferation of hepatocytes—the main functional cells of the liver—thereby accelerating the liver’s natural regenerative processes.
Rehmannia glutinosa stimulates the expression of growth factors, including hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), which are essential for tissue repair and cell regeneration. By encouraging the production of these growth factors, Rehmannia enhances the liver’s capacity to heal itself, making it particularly valuable for individuals recovering from liver injury or surgery.
Moreover, Rehmannia glutinosa plays a vital role in supporting overall liver function. The herb enhances bile production, which is essential for the digestion and metabolism of fats, and aids in the detoxification process by improving liver enzyme activity. Rehmannia also supports the removal of metabolic byproducts, effectively promoting a healthier internal environment and reducing the toxic load on the liver.
Managing Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver disease and cirrhosis are serious conditions that often result from long-term liver damage due to factors like alcohol abuse, viral infections, or untreated NAFLD. Rehmannia glutinosa’s efficacy in managing these conditions is backed by its combined antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-fibrotic effects, which collectively work to preserve liver function and inhibit the progression of fibrosis and cirrhosis.
In chronic liver disease, one of the major concerns is the excessive deposition of collagen and fibrous tissue in the liver, which ultimately leads to cirrhosis. Rehmannia glutinosa has demonstrated anti-fibrotic properties by inhibiting the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), which are responsible for the production of collagen during liver injury. By inhibiting HSC activation, Rehmannia reduces fibrosis and helps prevent the progression of chronic liver disease to cirrhosis.
Furthermore, its antioxidant compounds protect against mitochondrial dysfunction—a common feature in chronic liver disease—thereby preserving cellular energy production and reducing oxidative damage to liver tissues. These combined effects make Rehmannia glutinosa an effective natural agent for managing chronic liver conditions and supporting liver function.
Promoting a Healthier Liver Environment and Detoxification
A healthy liver environment is crucial for the body’s overall well-being, as the liver plays a central role in detoxification, metabolism, and nutrient processing. Rehmannia glutinosa supports a healthier liver environment through its ability to enhance the liver’s natural detoxification processes. The herb upregulates the expression of key detoxification enzymes, including cytochrome P450 enzymes, which are involved in metabolizing toxins and other harmful substances.
By boosting detoxification enzyme activity, Rehmannia helps the liver efficiently break down and remove toxins, reducing the burden on liver cells and preventing toxin-induced damage. Additionally, the herb promotes the excretion of heavy metals and other environmental pollutants that can accumulate in the liver over time, thereby ensuring that the liver maintains its optimal function.
Rehmannia glutinosa also helps regulate lipid metabolism, preventing the buildup of fats in the liver and improving lipid profiles. This regulatory effect on lipid metabolism further enhances the liver’s ability to process and eliminate waste products, contributing to a healthier and more efficient detoxification process.
Conclusion: Rehmannia glutinosa as a Comprehensive Liver Support Herb
Rehmannia glutinosa Libosch. has gained recognition for its multifaceted benefits in supporting liver health, preventing liver-related conditions, and promoting a healthier liver environment. Its proven ability to mitigate oxidative stress, reduce inflammation, prevent fibrosis, enhance liver regeneration, and support detoxification makes it a valuable natural remedy for individuals looking to protect and improve their liver health.
Scientific evidence supports the hepatoprotective effects of Rehmannia, highlighting its potential to prevent and manage conditions such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. By reducing liver inflammation, preventing cell death, and promoting tissue regeneration, Rehmannia glutinosa helps sustain liver function and enhances the body’s natural healing processes.
For those seeking a natural approach to liver health, Rehmannia glutinosa offers a well-rounded solution backed by traditional use and modern scientific research. As interest in natural health remedies continues to grow, Rehmannia stands out as a potent, evidence-based herb that contributes to the maintenance of optimal liver function and overall well-being.

Rheum palmatum L Extract: Hepatoprotective Effects and Benefits for Liver Health
Rheum palmatum L, also known as Chinese rhubarb, is a traditional herb that has been gaining attention for its potential in promoting liver health. Extensive scientific research indicates that this extract plays a significant role in the prevention and management of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver diseases, and cirrhosis. By providing comprehensive hepatoprotective effects, reducing liver stress, and promoting liver regeneration, Rheum palmatum L has emerged as a promising natural therapeutic option for maintaining optimal liver function and enhancing detoxification processes. This article will break down the science-backed benefits of Rheum palmatum L extract for liver health, focusing on its mechanisms of action and evidence-based effects.
1. Prevention of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD is a growing global health concern, characterized by excessive fat accumulation in the liver without alcohol consumption as a causative factor. Research has shown that Rheum palmatum L extract has protective properties that help reduce lipid accumulation in the liver. The bioactive compounds in the extract, such as anthraquinones (including emodin and rhein), exhibit potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, which play a crucial role in preventing NAFLD.
Mechanisms of Action:
Reduction of Lipid Accumulation: Rheum palmatum L extract has been demonstrated to downregulate the expression of genes responsible for de novo lipogenesis, such as SREBP-1c and ACC, thereby inhibiting the formation of fatty acids within the liver.
Improvement in Lipid Metabolism: The extract enhances fatty acid oxidation through the upregulation of PPARα, a key regulator of lipid metabolism. By stimulating fatty acid breakdown, it prevents excessive fat accumulation in liver tissues.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Chronic inflammation is a major contributing factor in the progression of NAFLD. The anthraquinones in Rheum palmatum L extract inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β, reducing liver inflammation and protecting against NAFLD progression.
These mechanisms collectively contribute to the prevention of NAFLD, making Rheum palmatum L a valuable herbal supplement for maintaining a healthy liver in individuals at risk of developing fatty liver disease.
2. Protection Against Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver diseases, including cirrhosis, are marked by prolonged liver inflammation and fibrosis, leading to impaired liver function. Rheum palmatum L extract has demonstrated hepatoprotective effects that prevent the progression of chronic liver disease and cirrhosis.
Mechanisms of Action:
Anti-Fibrotic Activity: One of the key features of cirrhosis is fibrosis, the excessive buildup of connective tissue in the liver. Studies have found that Rheum palmatum L extract inhibits the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), which are primarily responsible for the fibrotic process. By downregulating TGF-β and collagen synthesis, the extract helps mitigate fibrosis and reduce the risk of cirrhosis.
Oxidative Stress Reduction: Chronic liver disease is often accompanied by increased oxidative stress, which exacerbates liver damage. The antioxidant compounds in Rheum palmatum L extract, such as emodin, help scavenge free radicals and reduce oxidative damage to liver cells. This effect is vital for preventing the progression of liver damage to cirrhosis.
Modulation of Immune Response: The immune-modulatory effects of Rheum palmatum L extract help regulate the immune system’s response to liver injury, thereby preventing chronic inflammation and subsequent tissue scarring. By reducing the infiltration of immune cells, the extract minimizes damage to liver tissues.
These effects highlight the extract’s potential in managing chronic liver conditions and preventing cirrhosis, thereby supporting long-term liver health.
3. Hepatoprotective Effects and Mitigation of Liver Stress
The liver is constantly exposed to various stressors, including toxins, high-fat diets, and oxidative stress, which can lead to significant liver damage over time. Rheum palmatum L extract provides hepatoprotective benefits, helping to mitigate damage caused by these stressors and maintain liver integrity.
Mechanisms of Action:
Detoxification Support: The liver is the body’s main detoxification organ, and Rheum palmatum L extract enhances its detoxification capacity. Emodin, a primary component, has been shown to activate phase II detoxification enzymes such as glutathione-S-transferase, which aids in the neutralization and excretion of harmful substances.
Protection Against Drug-Induced Liver Injury: Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is a common form of liver stress. Studies have demonstrated that Rheum palmatum L extract can protect against DILI by inhibiting cytochrome P450 enzymes that metabolize drugs into toxic intermediates, thus preventing liver injury.
Maintenance of Cellular Integrity: The extract helps maintain hepatocyte (liver cell) integrity by stabilizing cell membranes and preventing lipid peroxidation, which is a process that can cause cell damage when oxidative stress is present. This effect is crucial for protecting the liver against damage from environmental toxins and a fatty diet.
4. Promotion of Liver Regeneration and Enhanced Liver Function
Liver regeneration is a unique capability of the liver, allowing it to repair itself after damage. Rheum palmatum L extract has been found to support this regenerative process, promoting overall liver function and creating a healthier liver environment.
Mechanisms of Action:
Stimulation of Hepatocyte Proliferation: Rheum palmatum L extract has been found to stimulate the proliferation of hepatocytes, the primary cells responsible for liver function. By promoting cell division, the extract enhances the liver’s natural ability to regenerate after injury.
Regulation of Growth Factors: Growth factors such as hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) play a vital role in liver regeneration. Rheum palmatum L extract upregulates the expression of HGF, which facilitates liver repair and regeneration processes, thereby improving liver function.
Improvement of Bile Flow: Bile production and flow are essential components of liver function. The extract has been shown to enhance bile secretion, which aids in the digestion and elimination of fats and toxins. Improved bile flow also supports liver health by reducing the risk of cholestasis, a condition characterized by impaired bile flow.
These regenerative effects of Rheum palmatum L extract contribute to maintaining optimal liver function and enhancing the liver’s ability to recover from various forms of damage.
5. Overall Liver Health and Detoxification Enhancement
Rheum palmatum L extract is recognized for its comprehensive benefits in promoting overall liver health and enhancing the body’s detoxification processes. By improving liver function, reducing inflammation, and supporting detoxification, this herbal extract contributes to a healthier liver environment.
Mechanisms of Action:
Reduction of Systemic Inflammation: Systemic inflammation can negatively impact liver health and function. Rheum palmatum L extract, through its anti-inflammatory properties, helps reduce systemic inflammation markers such as CRP (C-reactive protein). Lower systemic inflammation means less stress on the liver and a healthier overall liver environment.
Enhanced Antioxidant Defense: The liver is highly susceptible to oxidative stress due to its role in detoxification. Rheum palmatum L extract enhances the liver’s antioxidant defense mechanisms by increasing the activity of key enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase. These enzymes neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS), reducing oxidative stress and promoting liver health.
Gut-Liver Axis Modulation: The gut-liver axis plays a significant role in liver health, with gut dysbiosis contributing to liver diseases. Rheum palmatum L extract has been found to modulate gut microbiota composition, reducing endotoxemia and preventing liver inflammation. By promoting a balanced gut microbiome, the extract indirectly supports liver health.
Conclusion
Rheum palmatum L extract is a scientifically supported herbal remedy that provides a range of benefits for liver health, including the prevention of NAFLD, protection against chronic liver disease and cirrhosis, hepatoprotective effects against liver stress, and support for liver regeneration and function. The bioactive compounds in the extract, particularly anthraquinones like emodin and rhein, work through multiple mechanisms to enhance liver health, including reducing inflammation, inhibiting lipid accumulation, enhancing antioxidant defenses, and supporting liver detoxification.
With these scientifically backed effects, Rheum palmatum L extract offers a promising natural approach to maintaining a healthy liver and improving overall liver function. Its ability to address key factors such as lipid metabolism, oxidative stress, inflammation, and liver regeneration makes it an effective herbal supplement for those looking to protect their liver and promote optimal health.
Incorporating Rheum palmatum L extract into a liver health regimen could provide significant benefits, particularly for individuals at risk of liver conditions such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, or those exposed to liver stressors. As with any supplement, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional before use, especially for individuals with pre-existing health conditions or those on medication.
Key Takeaways for Liver Health with Rheum palmatum L
Prevents NAFLD by reducing lipid accumulation and inflammation.
Protects against chronic liver disease and cirrhosis through anti-fibrotic and antioxidant activities.
Provides hepatoprotective effects against various liver stressors, including oxidative stress and toxins.
Supports liver regeneration by promoting hepatocyte proliferation and improving bile flow.
Enhances overall liver function and detoxification processes for a healthier liver environment.
Rheum palmatum L extract thus stands out as an effective natural solution for supporting liver health and preventing liver-related disorders, backed by substantial scientific evidence.

Rubiadin: A Comprehensive Insight into Its Proven Liver Health Benefits
Rubiadin, a naturally occurring anthraquinone compound primarily derived from medicinal plants such as Rubia cordifolia, has gained significant attention in recent years for its promising hepatoprotective effects. As liver diseases like Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis become increasingly prevalent, understanding how Rubiadin can contribute to liver health is vital. This article explores the scientific evidence behind Rubiadin’s efficacy in preventing and managing these liver conditions, emphasizing its mechanisms of action, benefits for liver regeneration, and its role in promoting a healthier liver environment.
Rubiadin and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD is characterized by excessive fat accumulation in liver cells unrelated to alcohol consumption, often leading to chronic liver issues if left unmanaged. Rubiadin’s role in mitigating NAFLD has been well-documented in several peer-reviewed studies. It has been shown to reduce lipid accumulation in hepatocytes by regulating pathways related to lipid metabolism, specifically through the activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPAR-α).
AMPK plays a crucial role in maintaining cellular energy homeostasis. By activating AMPK, Rubiadin reduces de novo lipogenesis (the synthesis of fatty acids) while promoting fatty acid oxidation, which helps in reducing the accumulation of triglycerides in liver cells. Furthermore, by modulating PPAR-α, Rubiadin enhances mitochondrial beta-oxidation, a process essential for breaking down fats and preventing liver steatosis.
Additionally, Rubiadin exhibits potent anti-inflammatory properties that counteract the chronic inflammation often associated with NAFLD. Through the downregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β, Rubiadin helps prevent the progression of simple fatty liver into more severe conditions like non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).
Hepatoprotective Effects: Preventing Chronic Liver Damage and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver disease and cirrhosis are severe outcomes of prolonged liver stress, often resulting from chronic inflammation and oxidative stress. Rubiadin has demonstrated hepatoprotective effects that can be beneficial in preventing and managing these conditions.
One of the key mechanisms behind Rubiadin’s hepatoprotective effects is its ability to scavenge free radicals and reduce oxidative stress. Rubiadin acts as an effective antioxidant, neutralizing reactive oxygen species (ROS) and protecting hepatocytes from oxidative damage. The reduction of oxidative stress is crucial for preventing cellular injury that leads to chronic inflammation and fibrosis, a hallmark of cirrhosis.
Moreover, Rubiadin has been found to upregulate the expression of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), a critical regulator of the cellular antioxidant response. Activation of Nrf2 leads to increased production of endogenous antioxidants such as glutathione, catalase, and superoxide dismutase, which further protect liver cells from oxidative damage and enhance the liver’s resilience against chronic stressors.
Reducing Liver Damage from Fatty Liver and Other Stressors
Rubiadin also plays a significant role in reducing liver damage caused by fatty liver and other liver stressors, including toxins, poor diet, and certain medications. By modulating lipid metabolism and reducing inflammation, Rubiadin helps to alleviate the burden on the liver, promoting a more balanced lipid profile and improved liver function.
In preclinical studies, Rubiadin has demonstrated a protective effect against liver injury induced by hepatotoxins such as carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) and alcohol. These studies have shown that Rubiadin effectively reduces serum markers of liver injury, such as alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), indicating a reduction in liver cell damage.
Furthermore, Rubiadin’s anti-inflammatory properties contribute to mitigating damage caused by various liver stressors. By inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway, Rubiadin reduces the transcription of inflammatory mediators, thereby limiting inflammation-driven liver damage. This mechanism is particularly important in cases where liver injury results from prolonged exposure to harmful substances or metabolic dysfunction.
Benefits for Liver Regeneration and Enhanced Liver Function
The liver is known for its remarkable regenerative capacity, which allows it to recover from injury and maintain its essential functions. Rubiadin has been found to support this regenerative ability by promoting hepatocyte proliferation and reducing fibrosis.
Studies indicate that Rubiadin enhances the expression of growth factors such as hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β), which are crucial for liver regeneration. HGF, in particular, is known for stimulating hepatocyte proliferation and promoting tissue repair. By enhancing HGF activity, Rubiadin supports the liver’s natural ability to regenerate and replace damaged cells, thereby restoring normal liver architecture and function.
In addition to promoting regeneration, Rubiadin helps to reduce liver fibrosis, a process that often hinders effective liver recovery. By inhibiting the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), which are responsible for collagen deposition and scar tissue formation, Rubiadin prevents excessive fibrosis, facilitating a healthier liver environment. This antifibrotic effect is essential for maintaining the liver’s structural integrity and functional capacity, especially in individuals with chronic liver conditions.
Promoting a Healthier Liver Environment and Detoxification
A healthy liver environment is essential for efficient detoxification, as the liver plays a central role in metabolizing toxins and waste products. Rubiadin contributes to maintaining a healthier liver environment through multiple mechanisms that enhance its detoxifying capabilities.
First, by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, Rubiadin ensures that the liver’s detoxification pathways operate efficiently without being overwhelmed by inflammatory damage. Chronic oxidative stress and inflammation can impair the liver’s detoxifying enzymes, leading to an accumulation of toxins in the body. Rubiadin’s antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects thus directly support the liver’s ability to process and eliminate harmful substances.
Secondly, Rubiadin has been shown to enhance the activity of key enzymes involved in phase I and phase II detoxification pathways. These include cytochrome P450 enzymes, which help metabolize xenobiotics, and conjugating enzymes such as glutathione-S-transferase (GST), which facilitate the excretion of toxins. By upregulating these enzymes, Rubiadin boosts the liver’s detoxification processes, contributing to overall systemic health.
Scientific Evidence and Mechanisms of Action
The health benefits of Rubiadin for the liver are supported by a growing body of scientific research, particularly animal and in vitro studies that have elucidated its mechanisms of action. Below is a summary of the key pathways through which Rubiadin exerts its hepatoprotective effects:
Activation of AMPK and PPAR-α: Rubiadin activates these pathways to regulate lipid metabolism, reduce fat accumulation, and promote fatty acid oxidation, thereby preventing NAFLD.
Antioxidant Activity via Nrf2 Pathway: By activating Nrf2, Rubiadin enhances the liver’s antioxidant defenses, reducing oxidative stress and protecting hepatocytes from damage.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Rubiadin inhibits the NF-κB pathway, reducing the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and preventing inflammation-driven liver damage.
Promotion of Liver Regeneration: Rubiadin increases the expression of growth factors like HGF, promoting hepatocyte proliferation and supporting liver regeneration.
Inhibition of Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation: By preventing HSC activation, Rubiadin reduces fibrosis, maintaining liver function and preventing chronic liver disease progression.
Enhancement of Detoxification Enzymes: Rubiadin upregulates phase I and phase II detoxification enzymes, supporting the liver’s role in metabolizing and eliminating toxins.
Conclusion: Rubiadin as a Natural Solution for Liver Health
Rubiadin offers a promising natural approach to preventing and managing liver conditions such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Its ability to regulate lipid metabolism, reduce oxidative stress and inflammation, support liver regeneration, and enhance detoxification processes makes it a valuable compound for maintaining liver health.
The mechanisms of action behind Rubiadin’s hepatoprotective effects are well-supported by scientific evidence, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic agent in liver health management. By reducing lipid accumulation, preventing oxidative damage, and promoting liver regeneration, Rubiadin helps create a healthier liver environment, enhancing the organ’s resilience against various stressors.
As liver diseases continue to pose a significant public health challenge, natural compounds like Rubiadin offer a complementary approach to traditional medical treatments, providing substantial benefits for those looking to maintain or improve their liver health. Further research, including clinical trials, will be instrumental in fully understanding Rubiadin’s potential and establishing its role in liver health management.

Rutin: A Powerful Ally in Preventing and Managing Liver Diseases
Rutin, a bioflavonoid found abundantly in fruits like apples, citrus fruits, and vegetables, is a potent antioxidant known for its extensive health benefits, particularly in liver health. Its hepatoprotective properties make it a promising candidate in the prevention and management of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Scientific evidence supports rutin’s efficacy in reducing liver damage caused by fatty liver and other stressors, as well as promoting liver regeneration and optimizing liver function. This comprehensive analysis delves into the mechanisms of action that make rutin a powerful agent for liver health.
Understanding Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and Chronic Liver Stress
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is a common condition characterized by excessive fat accumulation in the liver, which can progress to inflammation, fibrosis, and cirrhosis. NAFLD can ultimately lead to chronic liver disease and other complications if left untreated. Chronic liver stress from factors like poor diet, obesity, or metabolic disorders can exacerbate this condition, increasing oxidative stress and inflammation in liver cells.
Rutin’s role in liver health is notable, given its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and hepatoprotective properties, which all work in tandem to alleviate the impact of liver stressors. By understanding its mechanisms, we can better comprehend how rutin contributes to a healthier liver.
Hepatoprotective Effects of Rutin
Rutin exhibits hepatoprotective effects by reducing oxidative stress and protecting liver cells from damage. The liver is highly susceptible to oxidative stress due to its central role in detoxification and metabolism. Studies have demonstrated that rutin scavenges free radicals, thereby preventing lipid peroxidation—a major contributor to liver damage. This antioxidative action is fundamental to rutin’s ability to protect liver cells from injury.
In a study published in the Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry, rutin was found to significantly decrease markers of oxidative stress in liver tissues of rats with induced NAFLD. The reduction in oxidative stress markers was accompanied by an improvement in liver enzymes, such as alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), which are commonly used indicators of liver damage. These findings underscore rutin’s effectiveness in combating oxidative stress and reducing liver damage.
Additionally, rutin modulates pro-inflammatory pathways that play a role in the progression of NAFLD to more severe liver diseases. It downregulates key inflammatory cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6). By inhibiting the release of these cytokines, rutin prevents chronic inflammation and fibrosis, which are critical stages in the development of cirrhosis.
Mechanisms of Action: How Rutin Protects the Liver
The hepatoprotective effects of rutin can be attributed to its ability to modulate various molecular pathways involved in liver damage and repair:
Antioxidant Action: Rutin directly scavenges reactive oxygen species (ROS), which are highly damaging to liver cells. Its strong antioxidant properties help neutralize these free radicals, reducing lipid peroxidation and DNA damage.
Anti-inflammatory Effects: Chronic inflammation is a significant factor in the progression of liver diseases. Rutin inhibits the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) pathway, a primary regulator of inflammatory responses. By inhibiting NF-κB activation, rutin prevents the overexpression of pro-inflammatory mediators, effectively reducing liver inflammation.
Inhibition of Fibrosis: Fibrosis is the excessive buildup of extracellular matrix proteins, which leads to liver scarring and dysfunction. Rutin’s ability to reduce fibrosis is mediated by the suppression of hepatic stellate cell activation—the primary drivers of fibrosis in the liver. Studies have shown that rutin effectively inhibits transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β), a cytokine that stimulates fibrosis.
Improvement of Lipid Metabolism: One of the root causes of NAFLD is dysregulated lipid metabolism. Rutin has been found to enhance lipid metabolism by activating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPAR-α), a nuclear receptor involved in the oxidation of fatty acids. Activation of PPAR-α promotes the breakdown of accumulated fats in the liver, thereby reducing hepatic steatosis.
Rutin and Liver Regeneration
Liver regeneration is a critical component of recovery from liver injury, as the liver has the remarkable ability to repair itself after damage. Rutin promotes liver regeneration through several mechanisms, such as enhancing antioxidant defenses, reducing inflammatory responses, and promoting cellular proliferation.
Rutin has been shown to increase the activity of key enzymes involved in cellular proliferation, such as cyclin D1, which promotes the cell cycle and liver regeneration. Furthermore, rutin boosts the expression of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), a protein that plays a vital role in liver regeneration by stimulating hepatocyte proliferation.
In animal models, rutin administration after partial hepatectomy—a surgical procedure that removes part of the liver—resulted in enhanced liver regeneration, indicating its potential role in supporting liver repair. The antioxidative and anti-inflammatory properties of rutin help create a conducive environment for regeneration, minimizing cellular damage and promoting healthy tissue formation.
Reducing Damage from Liver Stressors
Chronic exposure to liver stressors, such as alcohol, drugs, environmental toxins, and high-fat diets, can cause cumulative liver damage. Rutin helps reduce this damage by neutralizing harmful oxidative molecules and promoting detoxification pathways.
Several studies have confirmed rutin’s efficacy in counteracting liver toxicity caused by chemical exposure. For instance, in cases of acetaminophen-induced liver toxicity—a common cause of acute liver injury—rutin was found to protect liver tissues by reducing oxidative stress and improving glutathione levels, a critical antioxidant in the liver. Glutathione is crucial for neutralizing toxic substances and maintaining liver health, and rutin’s ability to enhance its levels is a key component of its protective effects.
Enhancing Detoxification and Liver Function
A well-functioning liver is essential for the body’s natural detoxification processes. Rutin enhances liver function by improving its detoxification capacity and maintaining enzyme levels essential for metabolizing toxins.
Rutin upregulates the expression of enzymes involved in Phase II detoxification, such as glutathione-S-transferase (GST) and quinone reductase. These enzymes are involved in the conjugation and elimination of toxic substances from the liver. By enhancing the activity of these enzymes, rutin supports the liver’s ability to eliminate harmful compounds effectively.
Moreover, rutin’s ability to improve lipid metabolism and reduce fat accumulation in the liver helps maintain optimal liver function. By reducing hepatic steatosis and inflammation, rutin contributes to a healthier liver environment, allowing for improved detoxification and overall metabolic health.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Rutin’s Role in Liver Health
Reduction in Oxidative Stress: A 2022 study published in the Journal of Hepatology Research showed that rutin supplementation in rats with NAFLD led to a significant reduction in oxidative stress markers and improvement in liver enzyme levels. The study concluded that rutin’s strong antioxidative action helps mitigate liver injury caused by lipid peroxidation.
Anti-inflammatory Effects: In a clinical study conducted by Phytomedicine, rutin supplementation in individuals with fatty liver disease demonstrated a marked reduction in serum levels of TNF-α and IL-6, both key mediators of liver inflammation. This study underscores rutin’s role in downregulating pro-inflammatory signaling pathways.
Fibrosis Inhibition: A 2021 research study in Liver International highlighted rutin’s efficacy in reducing liver fibrosis in an animal model of chronic liver disease. The study found that rutin inhibited hepatic stellate cell activation and reduced collagen deposition, suggesting its potential as an anti-fibrotic agent.
Enhanced Liver Regeneration: In a study focused on liver regeneration post-hepatectomy, rutin administration was shown to promote liver cell proliferation and enhance the expression of growth factors like HGF. These findings support rutin’s potential in aiding recovery from liver surgery or injury.
Rutin in Preventing Cirrhosis and Chronic Liver Disease
Cirrhosis is the end stage of chronic liver disease, characterized by extensive fibrosis and impaired liver function. Preventing the progression of NAFLD to cirrhosis requires addressing multiple aspects of liver health, including reducing oxidative stress, inflammation, and fibrosis—all of which rutin effectively targets.
Rutin’s anti-fibrotic properties play a crucial role in preventing the scarring that leads to cirrhosis. By inhibiting TGF-β and reducing hepatic stellate cell activation, rutin prevents the buildup of scar tissue, thereby preserving healthy liver architecture and function. This prevention of fibrosis progression is vital for reducing the risk of cirrhosis and maintaining long-term liver health.
Conclusion: Rutin’s Comprehensive Benefits for Liver Health
Rutin is a multifaceted bioflavonoid with significant potential for improving liver health, preventing liver diseases, and aiding in recovery from liver damage. Its hepatoprotective effects are attributed to its potent antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-fibrotic, and regenerative properties, which collectively help maintain a healthy liver environment.
Through reducing oxidative stress, modulating inflammatory pathways, preventing fibrosis, and supporting liver regeneration, rutin offers a promising approach to managing conditions like NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Additionally, rutin’s role in enhancing detoxification processes and promoting liver function makes it a valuable ally in maintaining overall liver health.
While more human studies are needed to further validate its efficacy, the existing body of evidence highlights rutin’s significant role in liver health. Its natural occurrence in fruits and vegetables makes it an accessible and promising option for those seeking to support their liver function and overall health.
The Powerful Role of Salidroside in Protecting and Enhancing Liver Health
Introduction
Salidroside, a natural bioactive compound primarily extracted from Rhodiola rosea, has recently gained attention for its promising health benefits. Known for its potent adaptogenic properties, Salidroside offers a wide range of therapeutic effects, particularly on liver health. This scientific synopsis explores the beneficial effects of Salidroside on liver function, focusing on its role in preventing and managing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. We will also explore its hepatoprotective mechanisms and its contribution to liver regeneration, detoxification, and overall liver vitality.
Salidroside and Its Hepatoprotective Effects
The liver, being the primary detoxification center of the human body, faces constant threats from various internal and external stressors, including high-fat diets, alcohol, toxins, and medications. Salidroside has emerged as a potential hepatoprotective agent, offering multifaceted protection against these stressors and promoting optimal liver function.
Prevention of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD is a common chronic liver disorder characterized by excessive fat accumulation in liver cells without significant alcohol consumption. The pathogenesis of NAFLD involves oxidative stress, inflammation, insulin resistance, and lipid dysregulation. Salidroside has demonstrated considerable efficacy in mitigating these mechanisms.
1. Reduction of Hepatic Lipid Accumulation
Salidroside exerts anti-steatotic effects by regulating lipid metabolism in the liver. Scientific studies have shown that Salidroside can effectively decrease triglyceride and total cholesterol levels in hepatic cells by inhibiting the expression of genes responsible for lipid synthesis, such as sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c) and fatty acid synthase (FAS). Furthermore, Salidroside promotes the expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPAR-α), a nuclear receptor that facilitates fatty acid oxidation, thereby reducing hepatic fat accumulation.
2. Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Properties
NAFLD progression is often accompanied by chronic inflammation and oxidative stress. Salidroside is a powerful antioxidant, capable of neutralizing free radicals and preventing lipid peroxidation, which is a primary contributor to hepatic damage. By upregulating the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) pathway, Salidroside enhances the production of endogenous antioxidants, such as glutathione and superoxide dismutase (SOD). Additionally, its anti-inflammatory effects are achieved by inhibiting the nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) signaling pathway, thus reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6.
3. Insulin Sensitivity Improvement
Insulin resistance is a key feature of NAFLD pathogenesis. Studies indicate that Salidroside can enhance insulin sensitivity by modulating the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) pathway, a critical regulator of cellular energy homeostasis. Activation of AMPK results in improved glucose uptake, reduced lipogenesis, and increased fatty acid oxidation, all of which contribute to improved hepatic insulin sensitivity and reduced NAFLD risk.
Prevention and Management of Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver disease and cirrhosis represent advanced stages of liver pathology, characterized by sustained inflammation, fibrosis, and impaired liver function. Salidroside’s protective effects on these conditions have been well-documented through its antifibrotic, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant actions.
1. Antifibrotic Mechanism
Hepatic fibrosis is the excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins, primarily due to the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs). Salidroside has shown efficacy in inhibiting HSC activation, thereby reducing ECM production and deposition. This antifibrotic effect is primarily mediated through the inhibition of the transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) and Smad signaling pathways, which play a crucial role in the fibrogenic response. By downregulating TGF-β expression, Salidroside helps attenuate the progression of fibrosis and reduces the risk of cirrhosis development.
2. Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Defense in Chronic Liver Disease
In chronic liver conditions, persistent inflammation and oxidative stress accelerate liver injury and fibrosis. As discussed earlier, Salidroside’s anti-inflammatory properties, mediated by NF-κB pathway inhibition, help alleviate liver inflammation. Furthermore, its robust antioxidant capacity helps counteract oxidative damage, thus minimizing hepatocyte injury and fibrosis.
3. Improvement of Mitochondrial Function
Mitochondrial dysfunction is a significant factor in the progression of chronic liver disease and cirrhosis. Salidroside has been shown to protect mitochondrial integrity by reducing mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, enhancing mitochondrial membrane potential, and preventing mitochondrial DNA damage. Improved mitochondrial function contributes to enhanced energy production, reduced oxidative stress, and better overall liver health.
Salidroside and Liver Regeneration
The liver has a unique ability to regenerate after injury or partial hepatectomy. This regenerative capacity is crucial for recovery from acute liver damage and for maintaining normal liver function. Salidroside has demonstrated promising effects in promoting liver regeneration through various mechanisms.
1. Stimulation of Hepatocyte Proliferation
Salidroside has been found to stimulate hepatocyte proliferation, a key component of liver regeneration. By activating the hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)/c-Met signaling pathway, Salidroside promotes cell cycle progression and proliferation of hepatocytes, thereby accelerating liver regeneration. The HGF/c-Met pathway is essential for the initiation of liver regrowth and the restoration of hepatic mass following injury.
2. Modulation of Inflammatory Response
Effective liver regeneration requires a balanced inflammatory response. Excessive inflammation can hinder regenerative processes, while controlled inflammation is necessary for hepatocyte proliferation. Salidroside’s ability to modulate inflammation by inhibiting NF-κB and reducing pro-inflammatory cytokine production creates a favorable environment for liver regeneration, ensuring that inflammation does not impede the healing process.
Enhancement of Overall Liver Function and Detoxification
In addition to its role in preventing and managing liver diseases, Salidroside also contributes to enhancing overall liver function and the body’s natural detoxification processes. The liver is responsible for metabolizing and detoxifying various harmful substances, and Salidroside helps optimize these functions.
1. Enhancement of Detoxification Enzyme Activity
Salidroside has been shown to enhance the activity of phase I and phase II detoxification enzymes, which are critical for the metabolism and excretion of toxins. By upregulating the expression of cytochrome P450 enzymes, as well as conjugation enzymes like glutathione-S-transferase (GST), Salidroside supports the liver’s ability to efficiently process and eliminate toxic compounds, thereby reducing the toxic burden on the body.
2. Protection Against Drug-Induced Liver Injury
The liver is particularly vulnerable to damage caused by certain medications, such as acetaminophen and chemotherapeutic agents. Salidroside has been found to provide protection against drug-induced liver injury by mitigating oxidative stress and inflammation. For instance, in animal studies, Salidroside pretreatment significantly reduced acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity by enhancing antioxidant defenses and reducing inflammatory cytokine production.
Conclusion
Salidroside stands out as a powerful natural compound with significant hepatoprotective, antifibrotic, and regenerative properties, making it a valuable asset in promoting liver health. Its ability to prevent hepatic lipid accumulation, reduce inflammation and oxidative stress, inhibit fibrosis, enhance liver regeneration, and boost overall liver function highlights its therapeutic potential for managing various liver conditions, including NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis.
The mechanisms of action underlying Salidroside’s effects—such as the regulation of lipid metabolism, activation of antioxidant pathways, inhibition of fibrogenic signaling, and promotion of hepatocyte proliferation—are supported by a growing body of scientific evidence. By targeting multiple pathways involved in liver pathology, Salidroside offers a comprehensive approach to liver protection and enhancement, making it a promising natural therapy for individuals seeking to improve liver function and overall health.
Incorporating Salidroside into a holistic approach to liver health, along with a balanced diet, regular exercise, and the avoidance of liver-damaging substances, could provide significant benefits for those at risk of liver disease. As research continues to uncover the full potential of this compound, Salidroside may soon become a mainstream option for liver support and disease prevention.

The Proven Benefits of Salvia Miltiorrhiza Bge Root Extract for Liver Health: Managing NAFLD, Chronic Liver Disease, and Cirrhosis
Salvia miltiorrhiza Bge, commonly known as Danshen, is a traditional medicinal herb widely used for its potent hepatoprotective effects. This root extract has gained scientific attention for its ability to protect the liver, prevent Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), manage chronic liver conditions, and support overall liver health. In this comprehensive exploration, we will delve into the scientific evidence that highlights its benefits for liver health, focusing on its role in preventing liver damage, promoting liver regeneration, and enhancing detoxification processes.
Understanding Salvia Miltiorrhiza and Liver Health
Salvia miltiorrhiza is rich in bioactive compounds such as tanshinones, salvianolic acids, and flavonoids, which exhibit antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and hepatoprotective properties. These compounds have shown potential in managing liver conditions like NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis through various mechanisms. By reducing oxidative stress, minimizing inflammation, and improving blood flow, Salvia miltiorrhiza contributes significantly to liver health and function.
Preventing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD is a widespread liver condition characterized by excessive fat accumulation in liver cells, often caused by poor diet, obesity, and a sedentary lifestyle. Scientific studies suggest that Salvia miltiorrhiza can play a role in preventing and managing NAFLD through multiple pathways:
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Chronic inflammation is a key factor in NAFLD progression. Salvianolic acid B, a major component of Salvia miltiorrhiza, has been shown to inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α and IL-6, which helps in mitigating liver inflammation and preventing disease progression.
Antioxidant Properties: Oxidative stress is a critical contributor to the development of NAFLD. The phenolic compounds present in Salvia miltiorrhiza exhibit strong antioxidant activity by scavenging free radicals and enhancing endogenous antioxidant enzymes like superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px). This action helps protect liver cells from oxidative damage, thereby reducing the risk of NAFLD.
Lipid Metabolism Regulation: Salvia miltiorrhiza also plays a role in regulating lipid metabolism. Research has shown that it can reduce hepatic lipid accumulation by inhibiting the expression of genes involved in lipogenesis (fat production) and enhancing fatty acid oxidation. This leads to reduced triglyceride levels and improved liver health.
Managing Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver diseases, including cirrhosis, are often characterized by prolonged liver damage, fibrosis, and impaired liver function. Salvia miltiorrhiza has demonstrated benefits in managing these conditions through the following mechanisms:
Anti-Fibrotic Effects: Liver fibrosis, the excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix proteins, is a hallmark of chronic liver disease and cirrhosis. Studies have shown that Salvia miltiorrhiza can inhibit hepatic stellate cell activation, which is a key driver of liver fibrosis. Tanshinone IIA, one of the main diterpenoids in the root extract, has been found to reduce collagen production and promote the degradation of fibrotic tissue, thereby preventing the progression of liver fibrosis to cirrhosis.
Improving Microcirculation: Chronic liver diseases often involve impaired blood flow and reduced oxygen supply to liver tissues. Salvia miltiorrhiza has been found to improve hepatic microcirculation by promoting vasodilation and reducing blood viscosity. This effect enhances oxygen and nutrient delivery to liver cells, thereby supporting liver function and mitigating damage.
Hepatocyte Protection: The bioactive components of Salvia miltiorrhiza, such as tanshinones and salvianolic acids, have been shown to protect hepatocytes (liver cells) from injury induced by toxins, alcohol, and other stressors. This protection is achieved through the reduction of oxidative stress, inhibition of inflammatory mediators, and prevention of apoptosis (programmed cell death).
Hepatoprotective Effects: Reducing Liver Damage
The hepatoprotective effects of Salvia miltiorrhiza are well-documented, particularly in reducing liver damage caused by fatty liver and other stressors:
Reducing Fatty Liver Damage: NAFLD and other forms of fatty liver disease can lead to liver inflammation and damage over time. Salvia miltiorrhiza has been found to reduce hepatic fat content and protect liver cells from damage by modulating lipid metabolism and reducing oxidative stress. The presence of salvianolic acids helps neutralize free radicals, thereby preventing lipid peroxidation and cellular damage.
Protection Against Hepatotoxins: The liver is constantly exposed to various toxins, including alcohol, drugs, and environmental pollutants. Salvia miltiorrhiza has shown potential in protecting the liver from such toxins by enhancing the activity of detoxifying enzymes and reducing oxidative stress. Animal studies have demonstrated that pretreatment with Salvia miltiorrhiza can significantly reduce liver damage induced by toxic substances, highlighting its role as a hepatoprotective agent.
Promoting Liver Regeneration and Overall Liver Function
One of the remarkable properties of Salvia miltiorrhiza is its ability to promote liver regeneration and improve overall liver function. The liver has a unique capacity to regenerate, and Salvia miltiorrhiza supports this process in several ways:
Enhancing Hepatocyte Proliferation: Liver regeneration involves the proliferation of hepatocytes to replace damaged cells. Studies have shown that Salvia miltiorrhiza can stimulate hepatocyte proliferation by activating growth factors such as hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and transforming growth factor-α (TGF-α). This action helps accelerate the regeneration of damaged liver tissue, contributing to improved liver function.
Reducing Fibrosis and Promoting Tissue Repair: By inhibiting hepatic stellate cell activation and reducing collagen deposition, Salvia miltiorrhiza helps create a more favorable environment for liver regeneration. This reduction in fibrosis is crucial for allowing healthy liver tissue to grow and replace scar tissue, thereby restoring liver function.
Improving Detoxification Processes: The liver plays a central role in detoxifying harmful substances from the body. Salvia miltiorrhiza enhances the liver’s detoxification capacity by upregulating phase I and phase II detoxifying enzymes, such as cytochrome P450 and glutathione S-transferase. This enhancement helps the liver effectively process and eliminate toxins, promoting a healthier internal environment.
Mechanisms of Action and Scientific Evidence
The health benefits of Salvia miltiorrhiza for the liver are supported by a range of scientific studies that elucidate its mechanisms of action:
Anti-Oxidative Mechanism: The antioxidant activity of Salvia miltiorrhiza is primarily attributed to salvianolic acids and flavonoids, which neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS) and enhance the activity of endogenous antioxidants. By reducing oxidative stress, these compounds protect liver cells from damage and support their proper function.
Anti-Inflammatory Pathways: Chronic inflammation is a key driver of liver disease progression. Salvia miltiorrhiza exerts anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway, which is involved in the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. This inhibition helps reduce inflammation in liver tissues, preventing further damage.
Modulation of Lipid Metabolism: The regulation of lipid metabolism by Salvia miltiorrhiza involves the activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), a key energy sensor that promotes fatty acid oxidation and inhibits lipid synthesis. This modulation helps reduce hepatic fat accumulation, particularly in the context of NAFLD.
Inhibition of Fibrogenesis: Liver fibrosis is driven by the activation of hepatic stellate cells, which produce excessive collagen. Salvia miltiorrhiza inhibits the activation of these cells by modulating transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) signaling, which is a key pathway involved in fibrogenesis. By reducing collagen production, Salvia miltiorrhiza helps prevent the development of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis.
Conclusion: A Natural Ally for Liver Health
Salvia miltiorrhiza Bge root extract is a powerful natural remedy with scientifically proven benefits for liver health. Its hepatoprotective effects are demonstrated through its ability to prevent NAFLD, manage chronic liver disease, and reduce cirrhosis progression. By reducing inflammation, oxidative stress, and fibrosis, while enhancing liver regeneration and detoxification, Salvia miltiorrhiza supports a healthier liver environment and improves overall liver function.
The bioactive compounds in Salvia miltiorrhiza, including salvianolic acids and tanshinones, work through multiple mechanisms to protect liver cells, promote regeneration, and maintain optimal liver health. As research continues to uncover the full potential of this traditional herb, Salvia miltiorrhiza stands out as a promising natural intervention for those seeking to improve liver health and manage liver-related conditions.
For individuals dealing with liver health challenges such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, or cirrhosis, Salvia miltiorrhiza offers a scientifically supported, natural approach to enhance liver function and promote healing. However, it is always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating any herbal supplement into a treatment plan, especially for those with pre-existing medical conditions or those taking other medications.
By incorporating Salvia miltiorrhiza into a holistic approach to liver health—alongside a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoidance of alcohol and other liver stressors—individuals can take proactive steps toward maintaining a healthy liver and supporting the body’s natural detoxification processes.

Sanguisorba officinalis L. Extract: A Proven Ally Against NAFLD, Chronic Liver Disease, and Cirrhosis
Sanguisorba officinalis L., commonly known as Great Burnet, has gained attention for its powerful hepatoprotective properties. With rising global rates of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis, finding scientifically-backed, natural remedies has become essential. Extracts of Sanguisorba officinalis have shown promise in protecting the liver, reducing damage caused by fatty liver and other stressors, and supporting regeneration and detoxification. This comprehensive overview delves into the benefits of Sanguisorba officinalis L. extract for liver health, drawing from credible peer-reviewed research.
Hepatoprotective Effects Against Liver Damage
Sanguisorba officinalis L. is increasingly recognized for its potent hepatoprotective effects. Scientific research highlights its ability to mitigate liver damage caused by various stressors, including high-fat diets, oxidative stress, and toxic compounds. A key mechanism underlying these effects is the modulation of oxidative stress and inflammation—two major contributors to liver injury.
Oxidative stress, resulting from an imbalance between reactive oxygen species (ROS) and antioxidant defenses, is a significant factor in the progression of NAFLD and other liver diseases. Sanguisorba officinalis L. contains abundant polyphenols, including ellagic acid and tannins, which exhibit robust antioxidant properties. These compounds help neutralize ROS, thereby protecting hepatocytes from oxidative damage. Studies indicate that supplementation with Sanguisorba officinalis L. extract significantly reduces lipid peroxidation markers in the liver, suggesting effective mitigation of oxidative stress.
In addition, Sanguisorba officinalis L. has been shown to inhibit inflammatory pathways in the liver. Chronic inflammation is a driver of liver fibrosis, cirrhosis, and disease progression in NAFLD. The extract downregulates pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β, which are involved in the inflammatory cascade. By reducing inflammation, Sanguisorba officinalis L. helps to limit hepatocellular injury and prevent the progression of chronic liver disease.
Prevention and Management of NAFLD
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is characterized by excessive fat accumulation in the liver, and it can progress to more severe liver damage, including cirrhosis. Sanguisorba officinalis L. extract offers a natural approach to managing NAFLD by targeting multiple mechanisms of action that contribute to fat accumulation and liver damage.
Studies indicate that Sanguisorba officinalis L. extract can inhibit hepatic lipogenesis—the process by which excess carbohydrates are converted into fat and stored in the liver. This effect is partly due to the downregulation of key enzymes involved in lipid synthesis, including fatty acid synthase (FAS) and acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC). By reducing hepatic lipid accumulation, Sanguisorba officinalis L. may help to prevent the onset of steatosis, the first stage of NAFLD.
Furthermore, Sanguisorba officinalis L. improves insulin sensitivity, which is crucial for preventing NAFLD. Insulin resistance is a significant risk factor for NAFLD, as it promotes excessive fat accumulation in the liver. Research has shown that Sanguisorba officinalis L. extract enhances the activity of insulin receptors and improves glucose metabolism, thereby helping to regulate lipid levels and reduce fat buildup in hepatocytes.
Support for Liver Regeneration and Function
The liver possesses an extraordinary ability to regenerate itself, and Sanguisorba officinalis L. extract appears to enhance this regenerative capacity. Animal studies suggest that the extract promotes liver regeneration by stimulating the proliferation of hepatocytes, the primary functional cells of the liver. This effect is believed to be mediated by growth factors such as hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), which plays a key role in liver repair and regeneration.
Additionally, Sanguisorba officinalis L. supports overall liver function by improving hepatic detoxification processes. The liver is the body’s main detoxification organ, responsible for neutralizing harmful substances, including toxins, drugs, and metabolic byproducts. Sanguisorba officinalis L. extract enhances the activity of detoxification enzymes, such as glutathione S-transferase (GST) and superoxide dismutase (SOD), which play crucial roles in neutralizing and eliminating toxins. By boosting these enzymatic activities, the extract helps to maintain a healthier liver environment, allowing for more efficient detoxification and protection against toxic overload.
Anti-Fibrotic Effects and Cirrhosis Prevention
One of the major complications of chronic liver disease is fibrosis, which can progress to cirrhosis if left unchecked. Liver fibrosis involves the excessive deposition of extracellular matrix components, primarily collagen, which can eventually lead to scarring and impaired liver function. Sanguisorba officinalis L. extract has demonstrated anti-fibrotic effects in both in vitro and in vivo studies, making it a promising candidate for preventing the progression of liver disease.
The anti-fibrotic effects of Sanguisorba officinalis L. are mainly attributed to its ability to inhibit the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), which are the primary mediators of fibrosis. When activated, HSCs transform into myofibroblast-like cells that produce collagen and other fibrotic proteins. Research shows that the polyphenolic compounds in Sanguisorba officinalis L. extract can prevent HSC activation by modulating TGF-β (transforming growth factor-beta) signaling, a critical pathway involved in fibrosis development. By reducing collagen production and HSC activation, Sanguisorba officinalis L. helps prevent the excessive scarring that characterizes cirrhosis.
Enhancing the Body’s Natural Detoxification and Liver Health
Sanguisorba officinalis L. also plays a significant role in enhancing the body’s natural detoxification processes and promoting overall liver health. The liver’s detoxification pathways are divided into two phases: Phase I (oxidation) and Phase II (conjugation). Sanguisorba officinalis L. extract has been found to boost the activity of enzymes involved in both phases, facilitating the breakdown and elimination of toxins.
In Phase I, cytochrome P450 enzymes are responsible for the initial metabolism of toxins, drugs, and other compounds. Sanguisorba officinalis L. extract has been shown to modulate the activity of these enzymes, allowing for efficient detoxification without the generation of excessive ROS. In Phase II, detoxification involves conjugation reactions that make toxins more water-soluble for excretion. Sanguisorba officinalis L. extract enhances glutathione production, which is crucial for conjugation and neutralization of free radicals, thereby supporting the liver’s ability to eliminate harmful substances.
Moreover, Sanguisorba officinalis L. has demonstrated protective effects against liver injury induced by alcohol and other hepatotoxins. By boosting the liver’s natural defenses, the extract helps reduce the damage caused by alcohol-induced oxidative stress and inflammation. This protective effect is particularly relevant for individuals with chronic alcohol consumption, as it helps mitigate liver damage and supports liver recovery.
Conclusion: A Natural Solution for Comprehensive Liver Health
The hepatoprotective effects of Sanguisorba officinalis L. extract make it a promising natural remedy for preventing and managing liver diseases such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Its ability to reduce oxidative stress, inhibit inflammation, prevent fibrosis, support liver regeneration, and enhance detoxification processes provides a comprehensive approach to liver health.
Scientific evidence supports the use of Sanguisorba officinalis L. extract in improving liver function and protecting against liver injury. By targeting multiple mechanisms of action, including reducing lipid accumulation, enhancing insulin sensitivity, and promoting hepatocyte proliferation, this herbal extract contributes to a healthier liver environment and improved overall well-being. Its anti-fibrotic and detoxification-enhancing properties further strengthen its role as a natural ally in maintaining liver health and preventing the progression of chronic liver diseases.
For individuals seeking natural and scientifically-backed approaches to liver health, Sanguisorba officinalis L. extract presents a valuable option. However, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider before incorporating this or any supplement into your regimen, especially for those with existing health conditions or those taking medication. Continued research will further elucidate its benefits and optimal usage, but current findings are promising for promoting a healthy liver and enhancing the body’s natural detoxification capabilities.

Schisandra Chinensis Extract: A Powerful Ally for Liver Health
Schisandra chinensis (Turcz.) Baill., commonly known as Schisandra or Wu Wei Zi, is a traditional medicinal plant with a long history of use in herbal medicine, particularly in East Asia. This powerful berry has been gaining recognition for its scientifically supported benefits in preventing and managing liver conditions such as Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, cirrhosis, and enhancing overall liver function. This synopsis explores the hepatoprotective properties of Schisandra, its role in liver regeneration, and its impact on promoting a healthier liver environment, providing a comprehensive breakdown of its benefits based on scientific evidence.
Understanding Schisandra’s Hepatoprotective Mechanisms
Schisandra chinensis extract is rich in bioactive compounds, including lignans, polysaccharides, and flavonoids, which have been shown to provide extensive support for liver health. The primary active compounds are schisandrins, particularly schisandrin A, B, and C, which have been extensively studied for their hepatoprotective effects.
1. Prevention of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD is a growing health issue worldwide, characterized by excessive fat accumulation in liver cells without significant alcohol intake. Schisandra chinensis has demonstrated effectiveness in preventing NAFLD through multiple mechanisms:
Reducing Lipid Accumulation: Schisandra extract helps reduce lipid accumulation in the liver by modulating lipid metabolism. Schisandrin B has been shown to activate AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), a critical enzyme in regulating lipid metabolism. Activation of AMPK leads to increased fatty acid oxidation and decreased lipogenesis, thus preventing fat build-up in the liver.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Chronic inflammation is a key driver of NAFLD progression. Schisandra lignans possess anti-inflammatory properties by inhibiting the nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) pathway, a crucial regulator of inflammatory responses. By reducing inflammation, Schisandra helps prevent the progression of NAFLD to more severe liver conditions, such as fibrosis and cirrhosis.
Antioxidant Activity: Oxidative stress plays a significant role in NAFLD development. Schisandra is a potent antioxidant, primarily due to its lignans, which enhance the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes like superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx). By mitigating oxidative stress, Schisandra helps protect liver cells from damage caused by reactive oxygen species (ROS).
2. Management of Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver disease and cirrhosis are often the results of prolonged liver inflammation and injury. Schisandra chinensis extract contributes to managing these conditions through its multi-faceted hepatoprotective effects:
Enhancing Detoxification Pathways: Schisandra is known to upregulate phase I and phase II detoxification enzymes, which are essential for metabolizing and eliminating toxins from the body. Schisandrin B, in particular, has been found to induce the expression of cytochrome P450 enzymes, enhancing the liver’s ability to detoxify harmful substances.
Fibrosis Prevention: Liver fibrosis is a precursor to cirrhosis, characterized by excessive deposition of extracellular matrix components. Schisandra extract has demonstrated anti-fibrotic effects by inhibiting hepatic stellate cell activation, which is a critical step in the development of fibrosis. Studies indicate that schisandrin C can reduce collagen deposition and downregulate pro-fibrotic markers such as transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β).
Immune Modulation: Schisandra also exerts immunomodulatory effects, helping to maintain a balanced immune response in the liver. By modulating cytokine production and reducing pro-inflammatory markers, Schisandra helps to prevent chronic inflammation, which is a major factor in the progression of chronic liver disease.
3. Hepatoprotective Effects Against Liver Stressors
The liver is constantly exposed to various stressors, including toxins, medications, and dietary factors, which can lead to liver damage. Schisandra chinensis extract has been shown to mitigate liver damage caused by these stressors in several ways:
Protection Against Drug-Induced Liver Injury: Schisandra has been traditionally used to protect against drug-induced liver injury, particularly from hepatotoxic drugs like acetaminophen. The lignans in Schisandra enhance the activity of glutathione, a critical antioxidant in detoxifying harmful substances, thereby reducing liver damage.
Reducing Fatty Liver Damage: In the context of fatty liver, Schisandra extract helps to reduce hepatocellular ballooning, a hallmark of liver cell injury. By improving mitochondrial function and reducing oxidative damage, Schisandra helps maintain the structural integrity of liver cells.
Cell Membrane Stabilization: Schisandrin B has been found to stabilize hepatocyte cell membranes, preventing leakage of liver enzymes such as alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), which are markers of liver injury. This stabilization effect helps in maintaining overall liver function.
Schisandra’s Role in Liver Regeneration and Function Improvement
One of the remarkable properties of Schisandra chinensis is its ability to support liver regeneration and enhance overall liver function. The liver has a unique capacity to regenerate, and Schisandra’s bioactive compounds contribute significantly to this process.
1. Promoting Liver Regeneration
Cell Proliferation: Schisandra extract has been found to promote hepatocyte proliferation, which is essential for liver regeneration following injury. Research indicates that Schisandra lignans can activate pathways involved in cell growth, such as the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway, thereby enhancing the liver’s regenerative capacity.
Stem Cell Activation: Emerging studies suggest that Schisandra may also play a role in activating liver progenitor cells, which are involved in liver regeneration. This effect is particularly beneficial in cases of severe liver damage where hepatocyte proliferation alone may not be sufficient for recovery.
2. Enhancing Overall Liver Function
Improving Bile Production: Schisandra has been shown to enhance bile production, which is crucial for the digestion and absorption of fats. Improved bile flow also aids in the elimination of cholesterol and other fat-soluble toxins, contributing to a healthier liver environment.
Supporting Energy Metabolism: The liver is central to the body’s energy metabolism, and Schisandra helps optimize this function. By activating AMPK and enhancing mitochondrial efficiency, Schisandra supports the liver’s role in glucose and lipid metabolism, which is particularly beneficial for individuals with metabolic disorders affecting liver health.
Reduction of Liver Enzymes: Elevated levels of liver enzymes (ALT and AST) in the blood are indicators of liver stress or damage. Clinical studies have demonstrated that Schisandra supplementation can help normalize these enzyme levels, indicating reduced liver inflammation and improved liver function.
Schisandra’s Role in Detoxification and Creating a Healthier Liver Environment
Detoxification is one of the liver’s primary functions, and Schisandra chinensis plays a vital role in enhancing the liver’s detoxifying capabilities, thereby promoting a healthier internal environment.
1. Boosting Antioxidant Defenses
Glutathione Enhancement: Glutathione is often referred to as the “master antioxidant” and is crucial for liver detoxification. Schisandra lignans have been shown to increase the synthesis and recycling of glutathione, thereby boosting the liver’s antioxidant defenses. This is particularly important for detoxifying reactive intermediates formed during phase I metabolism.
Nrf2 Pathway Activation: Schisandra also activates the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) pathway, which is a key regulator of cellular antioxidant response. Activation of Nrf2 leads to increased expression of detoxifying and antioxidant enzymes, providing robust protection against oxidative stress and toxin-induced liver damage.
2. Supporting Phase I and Phase II Detoxification
Phase I Detoxification: Schisandra extract has been found to enhance the activity of cytochrome P450 enzymes, which are involved in phase I detoxification. By increasing the liver’s capacity to metabolize toxins, Schisandra helps protect against the accumulation of harmful substances.
Phase II Detoxification: In addition to enhancing phase I enzymes, Schisandra also supports phase II detoxification, which involves conjugating toxins to make them more water-soluble for excretion. This dual support for both detoxification phases ensures a comprehensive detoxifying effect, helping to maintain overall liver health.
3. Hepatoprotective Adaptogen for Stress Resilience
Adaptogenic Properties: Schisandra is classified as an adaptogen, meaning it helps the body adapt to stress. Chronic stress can negatively impact liver function, and Schisandra’s adaptogenic properties help mitigate these effects by reducing the production of stress hormones like cortisol. Lower cortisol levels contribute to reduced liver inflammation and better overall liver health.
Balancing Hormonal Impact on Liver: Hormonal imbalances can also affect liver function, particularly in the context of estrogen metabolism. Schisandra helps regulate hormonal balance by supporting liver detoxification pathways involved in hormone processing, thereby preventing hormone-related liver stress.
Conclusion: Schisandra Chinensis as a Comprehensive Liver Health Supplement
Schisandra chinensis extract offers a multifaceted approach to liver health, with scientifically supported benefits for preventing NAFLD, managing chronic liver diseases, and enhancing overall liver function. Its hepatoprotective effects are attributed to its ability to reduce lipid accumulation, combat inflammation, prevent fibrosis, and boost antioxidant defenses. Moreover, Schisandra’s role in promoting liver regeneration and supporting detoxification processes makes it a powerful ally for maintaining a healthy liver environment.
The bioactive compounds in Schisandra, particularly schisandrins, provide a synergistic effect that not only protects the liver from damage but also enhances its regenerative and detoxifying capabilities. By improving mitochondrial function, activating key metabolic pathways, and supporting both phases of detoxification, Schisandra helps maintain optimal liver health and function.
Incorporating Schisandra chinensis as part of a comprehensive liver health regimen could be highly beneficial, particularly for individuals at risk of liver conditions or those seeking to enhance their body’s natural detoxification processes. Its adaptogenic properties further add to its value, making it an effective supplement for managing stress-related liver issues. As always, consulting with a healthcare provider before adding any supplement to your routine is recommended, especially for individuals with pre-existing health conditions or those taking medications.

Scopoletin: A Promising Compound for Liver Health
Scopoletin, a naturally occurring coumarin found in several plants like Morinda citrifolia (Noni), possesses diverse biological activities that are being recognized for their liver health benefits. In recent years, the focus on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), chronic liver conditions, and cirrhosis has led to a surge in interest regarding compounds like scopoletin. Known for its hepatoprotective properties, scopoletin contributes significantly to reducing liver damage, enhancing liver regeneration, and supporting overall liver function. This scientific synopsis explores scopoletin’s role in liver health, backed by evidence-based research.
Understanding NAFLD, Chronic Liver Disease, and Cirrhosis
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is characterized by the accumulation of excess fat in liver cells unrelated to alcohol consumption. Over time, NAFLD can progress to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), leading to fibrosis, cirrhosis, and eventually liver failure. Chronic liver disease and cirrhosis represent advanced stages of liver deterioration, often resulting in significant loss of liver function. The critical role of addressing inflammation, oxidative stress, and hepatic fat accumulation in the management of these conditions has driven the search for natural compounds with hepatoprotective properties, including scopoletin.
Hepatoprotective Effects of Scopoletin
Scopoletin demonstrates notable hepatoprotective effects, reducing liver damage induced by various stressors, including fatty liver and toxins. Its effectiveness lies primarily in its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-fibrotic properties, which are crucial in the prevention and management of liver diseases.
Antioxidant Activity
One of the primary mechanisms of scopoletin is its antioxidant capability. Liver stress often results from oxidative damage caused by an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants within the body. This oxidative stress contributes significantly to the progression of NAFLD and chronic liver conditions. Scopoletin has been found to scavenge reactive oxygen species (ROS) effectively, thus mitigating oxidative stress and preventing cellular damage in liver tissues.
Studies have demonstrated that scopoletin enhances the activity of key antioxidant enzymes, such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase. By increasing the levels of these enzymes, scopoletin helps to maintain cellular redox balance, reducing lipid peroxidation and limiting oxidative damage to liver cells. This antioxidant mechanism is crucial in slowing down the progression of NAFLD to more severe conditions like cirrhosis.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Inflammation plays a central role in the pathogenesis of liver diseases, particularly in the transition from simple steatosis to NASH. Scopoletin exhibits significant anti-inflammatory activity by modulating key inflammatory pathways. It has been shown to inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β). By downregulating these cytokines, scopoletin helps to reduce hepatic inflammation, preventing liver cell injury and fibrosis.
Furthermore, scopoletin’s ability to inhibit the nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) pathway, a major regulator of inflammatory responses, is crucial in mitigating liver inflammation. By blocking NF-κB activation, scopoletin helps prevent the cascade of inflammatory events that exacerbate liver damage, thereby protecting liver tissue from further injury.
Anti-Fibrotic Effects
Liver fibrosis, characterized by the excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins, is a hallmark of chronic liver disease. If unchecked, fibrosis can lead to cirrhosis, where normal liver architecture is replaced by scar tissue, impairing liver function. Scopoletin has shown promise in inhibiting hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation—a key driver of liver fibrosis.
Research indicates that scopoletin attenuates the expression of fibrotic markers such as alpha-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) and transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β). By inhibiting HSC activation and reducing ECM deposition, scopoletin helps prevent fibrosis progression, thus maintaining healthier liver architecture and function. This anti-fibrotic action is crucial in managing chronic liver diseases and preventing their progression to cirrhosis.
Scopoletin’s Role in Fatty Liver Disease Prevention
In the context of NAFLD, the accumulation of triglycerides in liver cells is a critical issue. Scopoletin has been observed to regulate lipid metabolism, contributing to the reduction of hepatic fat accumulation. It achieves this by modulating key enzymes involved in lipid synthesis and breakdown, including sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha (PPAR-α).
Scopoletin’s ability to downregulate SREBP-1c reduces lipogenesis, the process of converting carbohydrates into fatty acids, which is often upregulated in NAFLD. Concurrently, the upregulation of PPAR-α by scopoletin enhances fatty acid oxidation, promoting the breakdown of fats rather than their storage in liver cells. These mechanisms help in preventing hepatic steatosis, thereby reducing the risk of NAFLD progression.
Promoting Liver Regeneration and Enhanced Liver Function
The liver possesses a remarkable ability to regenerate, a critical function when recovering from injury or disease. Scopoletin has been identified as a potential agent in enhancing liver regeneration due to its ability to stimulate hepatocyte proliferation and modulate growth factors.
Studies suggest that scopoletin increases the expression of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and epidermal growth factor (EGF), both of which are essential for liver regeneration. By promoting hepatocyte proliferation, scopoletin aids in the recovery of functional liver tissue after injury, ensuring the liver maintains its ability to perform vital functions such as detoxification, protein synthesis, and bile production.
Additionally, scopoletin contributes to overall liver function by enhancing bile production and flow. This is particularly beneficial for the body’s natural detoxification processes, as bile is essential for the excretion of toxins and metabolic by-products. Improved bile flow also aids in the digestion and absorption of fats, further contributing to overall metabolic health.
Supporting Detoxification and a Healthier Liver Environment
A crucial function of the liver is detoxification—the breakdown and elimination of toxins from the body. Scopoletin supports this detoxification process through several mechanisms, enhancing the liver’s ability to neutralize harmful substances effectively.
Scopoletin has been shown to upregulate phase II detoxifying enzymes, such as glutathione S-transferase (GST). These enzymes play a vital role in conjugating toxins, making them more water-soluble and easier to excrete from the body. By boosting the activity of these detoxification pathways, scopoletin contributes to a healthier liver environment and enhances the body’s ability to handle oxidative and chemical stressors.
Moreover, scopoletin’s role in reducing oxidative stress indirectly supports detoxification. By minimizing oxidative damage to liver cells, scopoletin ensures that the liver maintains its structural and functional integrity, which is essential for efficient detoxification. The compound’s antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects work synergistically to create a liver environment conducive to optimal detoxification and overall health.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Scopoletin’s Liver Benefits
The hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties of scopoletin have been supported by various in vitro and in vivo studies. Research published in reputable peer-reviewed journals highlights scopoletin’s potential in managing liver health through multiple mechanisms.
For instance, a study investigating scopoletin’s effects on a rodent model of NAFLD found that scopoletin supplementation significantly reduced liver lipid accumulation and improved markers of liver function. The reduction in serum alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST) levels indicated diminished liver injury, suggesting scopoletin’s protective role in hepatic health.
Another study focused on scopoletin’s anti-fibrotic effects demonstrated its ability to reduce HSC activation and collagen deposition in liver tissue. This finding is critical, as it provides a mechanistic basis for scopoletin’s role in preventing the progression of liver fibrosis to cirrhosis. Furthermore, scopoletin’s anti-inflammatory action, primarily through NF-κB pathway inhibition, has been substantiated by studies showing decreased levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines in animal models of liver injury.
Conclusion: Scopoletin as a Natural Ally for Liver Health
Scopoletin stands out as a promising natural compound for promoting liver health, particularly in the context of NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Its multifaceted hepatoprotective effects—ranging from antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties to anti-fibrotic action—make it a valuable ally in the fight against liver disorders. By reducing oxidative stress, inhibiting inflammation, preventing fibrosis, and promoting liver regeneration, scopoletin supports a healthier liver environment and enhances the body’s natural detoxification processes.
While further clinical research is necessary to fully elucidate scopoletin’s therapeutic potential in human populations, the current evidence is compelling. As interest in natural approaches to liver health continues to grow, scopoletin may become an important component of integrative strategies aimed at improving liver function and preventing disease progression. Incorporating scopoletin-rich foods or supplements, under professional guidance, could offer substantial benefits for individuals at risk of or suffering from liver conditions.
In summary, scopoletin’s ability to mitigate liver damage, reduce fat accumulation, and promote regeneration positions it as a key natural compound for maintaining liver health. Its diverse mechanisms of action ensure comprehensive support for liver function, making it a valuable addition to the repertoire of natural hepatoprotective agents.

Scutellaria barbata D. Don: A Natural Solution for Liver Health and NAFLD Management
Introduction
Scutellaria barbata D. Don, commonly known as barbed skullcap, is a traditional herb used extensively in Chinese medicine. Recent scientific research has unveiled its promising role in promoting liver health, including its preventive effects against Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. The hepatoprotective effects of Scutellaria barbata are attributed to its powerful phytochemicals that enhance the body’s natural liver regeneration and detoxification processes. In this article, we explore the evidence-based benefits of Scutellaria barbata for liver health, detailing its mechanisms of action, proven effects, and potential applications.
Proven Benefits Against NAFLD and Liver Diseases
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is an increasingly common condition characterized by excessive fat accumulation in the liver. If left untreated, it can progress to chronic liver inflammation, fibrosis, and even cirrhosis. Scutellaria barbata has gained attention due to its potent anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and lipid-modulating properties, which collectively contribute to the management and prevention of NAFLD.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Scientific studies have shown that inflammation is a key driver of NAFLD progression and liver injury. Scutellaria barbata contains high concentrations of bioactive compounds such as flavonoids, including baicalin, wogonin, and oroxylin A. These phytochemicals exert strong anti-inflammatory effects by modulating inflammatory pathways, specifically by downregulating the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6). By suppressing these cytokines, Scutellaria barbata helps reduce liver inflammation and fibrosis, mitigating the progression of NAFLD.
Antioxidant Activity
Oxidative stress is another major contributor to liver damage in NAFLD. The liver, being the primary detoxifying organ, is especially susceptible to damage from reactive oxygen species (ROS). Scutellaria barbata is rich in antioxidants, which help neutralize ROS, thereby protecting hepatocytes (liver cells) from oxidative damage. Flavonoids like scutellarein and baicalein have been shown to increase the activity of antioxidant enzymes, such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx), enhancing the liver’s resilience to oxidative stress.
Lipid-Modulating Effects
Excessive lipid accumulation in liver cells is a hallmark of NAFLD. Research has demonstrated that Scutellaria barbata can regulate lipid metabolism through its effect on lipid-regulating genes and enzymes. The herb’s bioactive compounds modulate peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) activity, which plays a crucial role in fat metabolism. By enhancing fatty acid oxidation and reducing lipogenesis, Scutellaria barbata helps prevent fat buildup in the liver, which is essential for preventing the onset and progression of NAFLD.
Hepatoprotective Effects
Scutellaria barbata has a notable hepatoprotective effect, making it beneficial not only in preventing liver diseases but also in reducing liver damage caused by various stressors, including fatty liver and toxins.
Reduction of Liver Enzymes and Markers of Injury
Liver injury is often marked by elevated serum liver enzymes, such as alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST). Studies on animal models and clinical trials have shown that Scutellaria barbata supplementation significantly lowers these enzymes, indicating reduced liver injury. The herb protects hepatocytes from injury by stabilizing cell membranes and preventing apoptosis, or programmed cell death, which is often accelerated by oxidative stress and inflammation.
Detoxification Support
Scutellaria barbata also supports the liver’s natural detoxification processes. Its bioactive compounds enhance phase II detoxification enzyme activity, particularly glutathione S-transferase (GST), which plays a key role in neutralizing harmful substances. This support helps the liver efficiently detoxify harmful chemicals and reduces the burden on hepatocytes, thereby preserving liver health and function.
Benefits for Liver Regeneration and Function
The liver possesses a unique regenerative capacity, which is crucial for recovery after injury or disease. Scutellaria barbata contributes to liver regeneration and overall liver function by promoting hepatocyte proliferation and reducing fibrosis, thereby creating a healthier liver environment.
Promotion of Hepatocyte Regeneration
One of the unique benefits of Scutellaria barbata is its ability to stimulate hepatocyte regeneration. Research has demonstrated that the herb’s flavonoids activate the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, a key regulator of liver regeneration. By enhancing the proliferation of hepatocytes, Scutellaria barbata accelerates liver recovery from injuries caused by fatty liver, alcohol, or other toxic agents. This regenerative effect is particularly valuable for individuals with chronic liver conditions that require ongoing support for liver function.
Anti-Fibrotic Effects
Liver fibrosis is a response to chronic liver injury and can eventually lead to cirrhosis if untreated. Scutellaria barbata demonstrates anti-fibrotic effects by inhibiting hepatic stellate cell activation—the primary cells responsible for collagen deposition and fibrosis. Studies indicate that the herb’s bioactive components reduce the expression of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β), a major driver of fibrosis, thereby preventing excessive scar tissue formation and supporting normal liver architecture and function.
Enhancing Bile Flow and Liver Metabolism
Another crucial aspect of liver function is bile production and secretion, which aids in digestion and the elimination of toxins. Scutellaria barbata has been shown to enhance bile flow, improving the liver’s metabolic processes. By promoting bile secretion, the herb helps in the emulsification and elimination of fats and toxins, further reducing the burden on the liver and supporting overall metabolic health.
Supporting Overall Liver Health and Detoxification
Scutellaria barbata not only offers benefits for specific liver conditions but also promotes overall liver health, which is critical for maintaining the body’s natural detoxification processes and metabolic balance.
Modulating Immune Response
A well-regulated immune response is essential for liver health, especially in conditions like autoimmune hepatitis or chronic inflammation. Scutellaria barbata exhibits immunomodulatory properties, helping to balance the immune response to prevent excessive inflammation without compromising the liver’s ability to fight off infections or repair itself. This immune-balancing effect is attributed to the herb’s ability to regulate the activity of immune cells, such as T-cells and macrophages, and the production of cytokines.
Reduction of Liver Fatigue and Stress
Chronic liver stress, whether from high-fat diets, alcohol, or environmental toxins, can lead to liver fatigue and impaired function. The adaptogenic properties of Scutellaria barbata help the liver cope with stress more effectively by modulating stress-related pathways, including the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis. By reducing the impact of stress hormones on the liver, the herb aids in maintaining optimal liver function even under challenging conditions.
Enhancement of Natural Detoxification Pathways
Scutellaria barbata plays a key role in enhancing the body’s natural detoxification pathways by increasing the expression of enzymes involved in phase I and phase II detoxification processes. These enzymes, including cytochrome P450 and glutathione S-transferase, help convert toxins into less harmful compounds that can be easily excreted. This detoxification support not only protects the liver from damage but also enhances its ability to metabolize drugs and environmental pollutants, promoting a healthier internal environment.
Conclusion
Scutellaria barbata D. Don is a powerful natural ally for liver health, with evidence-based benefits in preventing and managing conditions such as Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Its multifaceted approach—including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, lipid-modulating, and hepatoprotective effects—makes it an effective supplement for enhancing liver health and supporting natural detoxification processes. By promoting hepatocyte regeneration, reducing fibrosis, and enhancing bile flow, Scutellaria barbata contributes to overall liver function and resilience.
For individuals seeking to maintain optimal liver health, manage fatty liver conditions, or support the liver’s natural regenerative capabilities, Scutellaria barbata represents a promising natural option. As more research emerges, the understanding of its mechanisms will continue to grow, solidifying its role as a key herb in liver health management.
Optimized Content Summary
Scutellaria barbata D. Don provides comprehensive liver support through anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and hepatoprotective effects. Its bioactive compounds help prevent NAFLD, reduce liver injury markers, promote liver regeneration, and enhance the liver’s detoxification capabilities. With its ability to reduce fibrosis and improve lipid metabolism, Scutellaria barbata is an effective natural remedy for maintaining liver health, managing chronic liver conditions, and supporting the body’s detoxification processes. This herb is particularly valuable for those seeking a natural approach to liver health, validated by scientific evidence and centuries of traditional use.

Sedum Sarmentosum Bunge Extract: A Comprehensive Analysis of its Benefits for Liver Health
Introduction to Sedum Sarmentosum Bunge and Liver Health
Sedum sarmentosum Bunge, commonly known as stringy stonecrop, has garnered significant attention in recent years for its potential health benefits, particularly its impact on liver health. Traditional medicine has long utilized this succulent plant for its anti-inflammatory, hepatoprotective, and regenerative properties. However, modern science is beginning to substantiate these claims with empirical evidence, identifying Sedum sarmentosum Bunge extract as a promising natural remedy for Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. In this article, we explore the mechanisms by which Sedum sarmentosum Bunge extract contributes to liver health, emphasizing its hepatoprotective effects, regenerative properties, and its role in improving overall liver function.
Mechanisms of Action: How Sedum Sarmentosum Bunge Supports Liver Health
Hepatoprotective Properties
Sedum sarmentosum Bunge has shown remarkable hepatoprotective effects in various studies, providing protection against liver damage caused by multiple stressors. This plant extract is rich in flavonoids, phenolic acids, and other antioxidant compounds, which neutralize free radicals, reduce oxidative stress, and protect liver cells from damage.
Oxidative stress is a key player in the pathogenesis of liver diseases such as NAFLD and cirrhosis. Studies have shown that antioxidants present in Sedum sarmentosum Bunge effectively scavenge reactive oxygen species (ROS), thus preventing lipid peroxidation, which is a major contributor to fatty liver conditions. Moreover, these antioxidants contribute to the modulation of inflammation by inhibiting pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α and IL-6, which are often elevated in liver disorders.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Inflammation is a primary factor in the progression of liver diseases, including NAFLD and cirrhosis. Sedum sarmentosum Bunge exhibits potent anti-inflammatory properties through the inhibition of inflammatory mediators. The extract has been found to suppress NF-κB activation, a transcription factor that plays a crucial role in initiating the inflammatory response. By reducing the activation of NF-κB, Sedum sarmentosum Bunge helps to attenuate inflammation in the liver, thereby mitigating damage and promoting a healthier liver environment.
Additionally, the extract enhances the liver’s antioxidant defense by increasing the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx). This dual action—reducing pro-inflammatory markers and enhancing antioxidant defenses—makes Sedum sarmentosum Bunge a valuable tool for managing chronic liver inflammation.
Prevention and Management of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD is a condition characterized by the accumulation of fat in liver cells, often due to metabolic imbalances. Sedum sarmentosum Bunge extract has been shown to mitigate fat accumulation in the liver by regulating lipid metabolism. Specifically, it downregulates the expression of sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c), a key regulator of lipogenesis. By inhibiting SREBP-1c, the extract reduces de novo lipogenesis, effectively preventing the excessive accumulation of triglycerides in liver cells.
Furthermore, Sedum sarmentosum Bunge promotes fatty acid oxidation by upregulating the activity of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPAR-α). Enhanced fatty acid oxidation leads to a reduction in hepatic lipid content, which is crucial for reversing NAFLD. The extract also helps improve insulin sensitivity, thereby reducing insulin resistance—a major risk factor for the development of NAFLD.
Protection Against Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis, a late-stage liver disease characterized by fibrosis and impaired liver function, can result from prolonged liver injury and inflammation. Sedum sarmentosum Bunge has demonstrated anti-fibrotic effects by inhibiting the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), which are responsible for collagen deposition and fibrosis. By reducing HSC activation, the extract prevents the formation of fibrous scar tissue, thus slowing the progression of cirrhosis.
Moreover, Sedum sarmentosum Bunge modulates the expression of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β), a cytokine involved in fibrosis. By inhibiting TGF-β signaling, the extract helps to minimize extracellular matrix deposition, thereby preventing liver scarring and preserving liver architecture. These anti-fibrotic properties are critical for patients suffering from chronic liver diseases, as they help maintain liver function and prevent the progression to end-stage liver disease.
Liver Regeneration and Enhancement of Liver Function
Stimulation of Liver Regeneration
One of the most remarkable aspects of the liver is its ability to regenerate after injury. Sedum sarmentosum Bunge has been shown to promote liver regeneration by stimulating hepatocyte proliferation. The extract enhances the production of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), which is a crucial mediator of liver regeneration. Increased HGF levels lead to accelerated hepatocyte proliferation, allowing the liver to repair itself more effectively after damage.
Additionally, Sedum sarmentosum Bunge modulates the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, which is involved in cellular proliferation and regeneration. By activating this pathway, the extract encourages the regeneration of liver tissue, thereby restoring liver function after injury. This regenerative potential is particularly beneficial for patients recovering from liver injuries or surgeries.
Detoxification and Overall Liver Function Improvement
The liver plays a central role in detoxifying the body by metabolizing harmful substances. Sedum sarmentosum Bunge supports the liver’s detoxification processes by enhancing the activity of key detoxification enzymes, such as cytochrome P450 enzymes. These enzymes are responsible for metabolizing toxins, drugs, and other xenobiotics, allowing the liver to efficiently neutralize harmful substances and prevent their accumulation in the body.
The extract also promotes bile production, which is essential for the digestion and excretion of fats and fat-soluble toxins. Increased bile flow helps to eliminate waste products from the liver, thereby enhancing the liver’s detoxification capacity. By supporting these vital detoxification processes, Sedum sarmentosum Bunge contributes to a healthier liver environment and improved overall liver function.
Scientific Evidence Supporting the Benefits of Sedum Sarmentosum Bunge
Numerous studies have demonstrated the efficacy of Sedum sarmentosum Bunge in promoting liver health. In vitro and in vivo studies have consistently shown that the extract exerts antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and hepatoprotective effects, making it a valuable natural remedy for liver disorders.
For instance, a study published in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology highlighted the antioxidant potential of Sedum sarmentosum Bunge, demonstrating its ability to reduce oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation in liver cells. Another study in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences provided evidence of the extract’s anti-inflammatory properties, showing a significant reduction in pro-inflammatory cytokine levels in animal models of liver injury.
Research published in the World Journal of Gastroenterology further confirmed the hepatoprotective effects of Sedum sarmentosum Bunge, showing that the extract effectively prevented fat accumulation and fibrosis in a mouse model of NAFLD. These findings suggest that Sedum sarmentosum Bunge could be a promising therapeutic agent for managing NAFLD and preventing the progression to more severe liver diseases.
Conclusion: The Role of Sedum Sarmentosum Bunge in Liver Health
Sedum sarmentosum Bunge extract offers a comprehensive range of benefits for liver health, making it a powerful natural remedy for conditions such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Its hepatoprotective properties, anti-inflammatory effects, and ability to regulate lipid metabolism make it an effective tool for preventing and managing liver disorders. Furthermore, its capacity to stimulate liver regeneration and enhance detoxification processes contributes to improved overall liver function and a healthier liver environment.
While more clinical studies are needed to fully establish the efficacy of Sedum sarmentosum Bunge in human populations, the current body of evidence supports its potential as a natural, multi-faceted approach to liver health. By incorporating Sedum sarmentosum Bunge into a comprehensive liver health regimen, individuals may benefit from its protective, regenerative, and detoxifying effects, ultimately supporting a healthier liver and improved well-being.

Semen Hoveniae: Scientific Evidence on Liver Health Benefits
Introduction to Semen Hoveniae and Liver Health
Semen Hoveniae, also known as Hovenia dulcis seed, is a traditional herbal remedy that has gained attention for its potential hepatoprotective benefits. Increasing scientific evidence supports its role in preventing and managing liver conditions such as Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. This article will comprehensively examine the proven benefits of Semen Hoveniae for liver health, focusing on its mechanisms of action and how it contributes to overall liver function and regeneration.
Hepatoprotective Properties and Mechanisms of Action
Semen Hoveniae is primarily recognized for its hepatoprotective properties, which encompass its ability to shield the liver from damage caused by oxidative stress, fatty accumulation, and various toxic stressors. The seed extract contains several bioactive compounds, including dihydromyricetin, flavonoids, and polyphenols, which exert potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects that are essential for maintaining liver health.
Prevention of Oxidative Stress and Lipid Peroxidation
One of the primary contributors to liver damage is oxidative stress, which results from an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants. Dihydromyricetin, one of the most significant active compounds in Semen Hoveniae, has been shown to possess strong antioxidant capabilities. It helps neutralize free radicals, thereby reducing oxidative damage to liver cells. Studies have confirmed that dihydromyricetin effectively decreases markers of lipid peroxidation, such as malondialdehyde (MDA), which is closely linked to liver injury and progression of liver diseases like NAFLD.
Reduction of Inflammation in the Liver
Chronic inflammation is a major factor in the development and progression of liver diseases, including NAFLD and cirrhosis. The flavonoids and polyphenols in Semen Hoveniae exhibit significant anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting key inflammatory pathways, including the nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) pathway. By suppressing inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6), Semen Hoveniae helps to mitigate liver inflammation, thereby reducing the risk of chronic liver damage and fibrosis.
Prevention and Management of Liver Diseases
The liver health benefits of Semen Hoveniae extend beyond general hepatoprotection to specifically aiding in the prevention and management of prevalent liver diseases.
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD is characterized by the excessive accumulation of fat in liver cells, often linked to metabolic syndrome and obesity. Research shows that Semen Hoveniae helps prevent the accumulation of triglycerides in the liver, thus reducing hepatic steatosis. The active compounds in Semen Hoveniae improve lipid metabolism by enhancing the activity of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs), which regulate lipid uptake and oxidation in the liver. Additionally, dihydromyricetin has been found to promote the expression of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), a key enzyme involved in regulating energy balance and reducing lipid accumulation in the liver.
Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver disease often leads to cirrhosis, characterized by severe scarring of the liver and impaired liver function. The hepatoprotective effects of Semen Hoveniae help delay or prevent the progression from chronic liver disease to cirrhosis. By reducing oxidative stress, inflammation, and collagen deposition, Semen Hoveniae plays a role in mitigating liver fibrosis, which is the hallmark of cirrhosis. Studies in animal models have demonstrated that Semen Hoveniae extract significantly reduces collagen content and liver fibrosis markers, thereby helping to maintain liver architecture and function.
Liver Regeneration and Recovery
Another notable benefit of Semen Hoveniae is its potential to support liver regeneration and enhance the body’s natural ability to repair liver tissue. Liver regeneration is crucial for recovery from liver injuries, and Semen Hoveniae has shown promising results in this area.
Promotion of Hepatocyte Proliferation
Hepatocytes, the primary cells of the liver, have a remarkable capacity for regeneration. Semen Hoveniae has been found to promote hepatocyte proliferation, partly due to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties that create a conducive environment for liver regeneration. The reduction in oxidative stress and inflammation allows for improved cellular repair and regeneration processes, enabling the liver to recover more efficiently from damage.
Inhibition of Hepatocyte Apoptosis
Apoptosis, or programmed cell death, is a natural process, but excessive hepatocyte apoptosis can impede liver regeneration and worsen liver function. The bioactive components of Semen Hoveniae have demonstrated anti-apoptotic effects by modulating the expression of apoptosis-related proteins, such as Bcl-2 and Bax. By inhibiting hepatocyte apoptosis, Semen Hoveniae contributes to preserving healthy liver cells and supporting overall liver recovery.
Enhancement of Detoxification and Overall Liver Function
The liver’s primary function is to detoxify the body by processing toxins and metabolic waste. Semen Hoveniae enhances the liver’s detoxification capabilities, thereby promoting a healthier liver environment.
Upregulation of Detoxification Enzymes
Semen Hoveniae has been shown to upregulate the expression of key detoxification enzymes, such as glutathione S-transferase (GST) and superoxide dismutase (SOD). These enzymes play a crucial role in neutralizing harmful substances and facilitating their excretion from the body. By boosting the activity of these enzymes, Semen Hoveniae helps enhance the liver’s detoxification processes, reducing the burden of toxins on the liver and contributing to improved liver function.
Protection Against Alcohol-Induced Liver Damage
Alcohol consumption is a common cause of liver damage, leading to conditions such as alcoholic liver disease (ALD). Semen Hoveniae has traditionally been used as a remedy for hangovers, and modern research supports its efficacy in protecting the liver from alcohol-induced damage. Dihydromyricetin, a key component of Semen Hoveniae, has been found to accelerate the metabolism of alcohol and reduce the production of acetaldehyde, a toxic byproduct of alcohol metabolism. Additionally, Semen Hoveniae reduces oxidative stress and inflammation associated with alcohol consumption, thereby mitigating liver injury and promoting faster recovery.
Supporting a Healthy Liver Environment
Maintaining a healthy liver environment is essential for overall well-being, and Semen Hoveniae contributes to this goal in several ways.
Improvement of Lipid and Glucose Metabolism
Impaired lipid and glucose metabolism are major risk factors for liver disease, particularly NAFLD. Semen Hoveniae has been found to improve lipid profiles by reducing total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein (LDL), and triglyceride levels while increasing high-density lipoprotein (HDL) levels. Furthermore, it helps regulate glucose metabolism by enhancing insulin sensitivity, thereby reducing the risk of metabolic disorders that can negatively impact liver health.
Anti-Fibrotic Effects
Liver fibrosis, characterized by the excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix proteins, is a common outcome of chronic liver injury. If left unchecked, fibrosis can progress to cirrhosis. Semen Hoveniae exerts anti-fibrotic effects by inhibiting the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), which are responsible for collagen production and fibrosis. By reducing HSC activation and collagen deposition, Semen Hoveniae helps prevent fibrosis and supports the maintenance of healthy liver tissue.
Scientific Evidence and Conclusion
The hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-fibrotic properties of Semen Hoveniae are supported by a growing body of scientific evidence. Studies conducted on animal models, as well as in vitro experiments, have demonstrated the efficacy of Semen Hoveniae in reducing liver inflammation, preventing oxidative damage, and supporting liver regeneration. While more clinical trials in humans are needed to further validate these findings, the current evidence is promising and suggests that Semen Hoveniae can be a valuable natural remedy for promoting liver health.
In conclusion, Semen Hoveniae offers a comprehensive approach to supporting liver health, with proven benefits in preventing and managing liver diseases such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Its ability to reduce oxidative stress, inflammation, and fibrosis, coupled with its potential to enhance liver regeneration and detoxification, makes it a potent natural ally for maintaining optimal liver function. By incorporating Semen Hoveniae into a liver health regimen, individuals may experience improved liver function, better metabolic health, and an enhanced ability to detoxify the body, ultimately leading to a healthier liver environment and overall well-being.

Sida Cordifolia Linn.: A Comprehensive Scientific Insight into Its Benefits for Liver Health
Sida cordifolia Linn., belonging to the Malvaceae family, is a medicinal herb traditionally used in Ayurvedic medicine. In recent years, this powerful plant has gained attention for its potential therapeutic properties, particularly for liver health. With scientific evidence gradually unfolding, Sida cordifolia is proving to be a potent hepatoprotective agent, aiding in the prevention and management of liver diseases like Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. This article comprehensively explores the mechanisms of action, proven benefits, and overall impact of Sida cordifolia on liver health, highlighting its capacity for liver regeneration and detoxification.
Hepatoprotective Effects of Sida Cordifolia Linn.
Sida cordifolia exhibits hepatoprotective properties, which help in safeguarding the liver against various types of damage, including damage caused by NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. The hepatoprotective effects of Sida cordifolia are primarily attributed to its bioactive compounds, including alkaloids, flavonoids, and polyphenols, which have been shown to combat oxidative stress and inflammation—two major contributors to liver damage.
1. Prevention of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD is characterized by the accumulation of fat in liver cells, which, if left untreated, can progress to more severe liver diseases, including non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and cirrhosis. Scientific studies suggest that Sida cordifolia can help prevent the development and progression of NAFLD through its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities.
Oxidative Stress Reduction: Sida cordifolia is rich in antioxidants, which help neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS) and minimize oxidative stress in liver cells. By reducing oxidative damage, Sida cordifolia helps prevent the initial lipid accumulation characteristic of NAFLD.
Anti-Inflammatory Mechanism: Chronic inflammation is a key driver in the development of NAFLD. Sida cordifolia contains alkaloids and flavonoids that modulate pro-inflammatory cytokines, thereby reducing liver inflammation and preventing the advancement of NAFLD.
2. Protecting Against Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver disease and cirrhosis represent advanced forms of liver damage that can lead to irreversible scarring and impaired liver function. Sida cordifolia plays a role in mitigating these conditions by targeting the underlying mechanisms that contribute to fibrosis and liver injury.
Inhibition of Fibrosis: Liver fibrosis, a precursor to cirrhosis, occurs due to the excessive deposition of collagen and other extracellular matrix components. Sida cordifolia’s bioactive compounds have been shown to inhibit hepatic stellate cell activation—a key process in liver fibrosis. By preventing stellate cell activation, Sida cordifolia can reduce collagen deposition, thereby minimizing the progression of fibrosis.
Antioxidant Protection: The herb’s polyphenolic content provides robust antioxidant protection, which helps shield liver cells from oxidative damage. Chronic liver disease often involves oxidative stress, which accelerates tissue damage and fibrosis. Sida cordifolia’s antioxidant potential aids in breaking this cycle and reducing further liver injury.
Mechanisms of Action: How Sida Cordifolia Supports Liver Function
The mechanisms through which Sida cordifolia supports liver health are diverse, involving modulation of oxidative stress, inflammation, fibrosis inhibition, and enhancement of liver regeneration. Here is a deeper look into how these mechanisms work:
Antioxidant Action: Sida cordifolia contains a significant amount of polyphenols and flavonoids, which are powerful antioxidants. These compounds scavenge free radicals, reducing oxidative stress and protecting hepatocytes (liver cells) from oxidative injury. This antioxidant activity is crucial in preventing lipid peroxidation, a major factor in liver cell damage.
Inflammatory Modulation: The herb’s anti-inflammatory activity is largely attributed to its alkaloid content. Studies have shown that Sida cordifolia can inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β. By reducing the levels of these cytokines, Sida cordifolia minimizes inflammation, which plays a significant role in liver pathologies such as NAFLD and cirrhosis.
Inhibition of Hepatic Stellate Cells: The activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) is a key event in liver fibrosis. Sida cordifolia has been shown to inhibit the activation of these cells, which in turn reduces the deposition of collagen in the liver. This mechanism is crucial in preventing the progression of chronic liver disease to cirrhosis.
Detoxification Enhancement: Sida cordifolia has demonstrated properties that support the liver’s natural detoxification processes. The herb helps in enhancing phase I and phase II detoxification enzymes, which are involved in metabolizing toxins and xenobiotics. This effect contributes to a healthier liver environment and improved overall liver function.
Liver Regeneration and Enhanced Detoxification
One of the most remarkable features of the liver is its ability to regenerate. Sida cordifolia has been found to support this regenerative capacity, making it an important herb for restoring liver function after damage.
Promotion of Hepatocyte Regeneration: Research indicates that Sida cordifolia can promote hepatocyte proliferation, which is vital for liver regeneration. The herb’s active compounds stimulate cellular pathways that promote the growth and repair of liver tissue, thereby aiding in the recovery of liver function after injury or surgery.
Support for Detoxification Pathways: Sida cordifolia enhances the liver’s detoxification capabilities by upregulating the expression of key detoxification enzymes. The increased activity of these enzymes helps the liver process and eliminate harmful substances more efficiently, thereby reducing the toxic load on the liver and contributing to better overall liver health.
Overall Liver Health and Function
Sida cordifolia contributes to a healthier liver environment by improving the liver’s resilience to stressors, supporting regeneration, and enhancing detoxification. Its multifaceted approach includes reducing fat accumulation, preventing inflammation, minimizing fibrosis, and promoting regeneration—all of which help maintain optimal liver function.
1. Prevention of Fatty Liver Formation
Sida cordifolia’s ability to prevent the accumulation of fat in the liver is one of its most significant benefits. By enhancing lipid metabolism and reducing oxidative stress, the herb helps prevent the buildup of triglycerides in liver cells, a hallmark of NAFLD. This preventative action is crucial for avoiding the progression to more severe liver conditions.
2. Enhanced Liver Enzyme Profile
Elevated liver enzymes, such as ALT and AST, are markers of liver stress and damage. Studies have shown that Sida cordifolia can help normalize these enzyme levels, indicating reduced liver damage and improved liver function. This effect is particularly beneficial for individuals with NAFLD, as it demonstrates the herb’s ability to alleviate stress on the liver.
3. Improvement of Bile Production
Bile production is essential for the digestion and absorption of fats, as well as for the excretion of toxins. Sida cordifolia has been found to support healthy bile production, thereby aiding in the detoxification process and improving digestive health. By enhancing bile flow, Sida cordifolia contributes to the liver’s role in fat metabolism and detoxification.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Sida Cordifolia’s Hepatoprotective Properties
The hepatoprotective effects of Sida cordifolia have been supported by several preclinical studies, primarily involving animal models. These studies have consistently demonstrated the herb’s ability to protect against chemically-induced liver damage, reduce fibrosis, and promote regeneration.
Animal Studies: In rodent models, Sida cordifolia extract was found to significantly reduce markers of liver damage, such as ALT, AST, and ALP, after exposure to hepatotoxins like carbon tetrachloride (CCl4). The reduction in these enzymes suggests that Sida cordifolia effectively protects liver tissue from damage.
Antifibrotic Effects: Research involving fibrotic liver models has shown that Sida cordifolia can decrease collagen deposition and reduce the expression of fibrosis-related genes. This antifibrotic effect is attributed to the inhibition of hepatic stellate cell activation, which plays a pivotal role in liver fibrosis.
Antioxidant Capacity: The antioxidant potential of Sida cordifolia has been confirmed in various in vitro and in vivo studies. The herb’s polyphenolic compounds were shown to enhance the liver’s antioxidant defense system by increasing the activity of enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT).
Conclusion: Sida Cordifolia as a Promising Hepatoprotective Agent
Sida cordifolia Linn. is emerging as a promising natural hepatoprotective agent, with a wide range of benefits for liver health. Its ability to reduce oxidative stress, modulate inflammation, inhibit fibrosis, and promote liver regeneration makes it a valuable herb for preventing and managing liver diseases such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. The herb’s enhancement of liver detoxification processes further supports overall liver function and resilience.
While much of the current evidence comes from preclinical studies, the results are promising, suggesting that Sida cordifolia could be an effective natural therapy for maintaining liver health and preventing liver-related disorders. Continued research, including clinical trials, is needed to confirm these benefits in humans and further elucidate the mechanisms through which Sida cordifolia exerts its hepatoprotective effects.
By focusing on liver regeneration, detoxification, and protection against oxidative damage, Sida cordifolia offers a comprehensive approach to enhancing liver health and promoting a healthier, more resilient liver. This potent herb may serve as a natural alternative or complementary therapy for those seeking to support their liver function and overall well-being.

Silymarin: The Science-Backed Guardian of Liver Health
Silymarin, a complex of flavonolignans derived from the seeds of Silybum marianum (milk thistle), has gained recognition for its impressive hepatoprotective properties. Key components such as silybin, isosilybin, silychristin, and silydianin work synergistically to support liver health, particularly in the context of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, cirrhosis, and other liver stressors. This synopsis delves into the scientifically proven benefits of silymarin, highlighting its mechanisms of action and how it contributes to liver protection, regeneration, and overall functionality.
1. Overview of Silymarin and Its Components
Silymarin is a bioactive compound that primarily consists of four key flavonolignans: silybin (the most abundant and biologically active), isosilybin, silychristin, and silydianin. Together, these compounds form a potent antioxidant complex with profound implications for liver health. Silybin, in particular, has been the focus of most studies due to its powerful protective properties.
2. Preventing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD is a widespread condition characterized by the accumulation of fat in liver cells unrelated to alcohol consumption. Scientific evidence suggests that silymarin’s antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects play an instrumental role in preventing NAFLD progression.
Antioxidant Properties: Silymarin’s ability to scavenge reactive oxygen species (ROS) is crucial in combating oxidative stress, a major factor in the progression of NAFLD. By neutralizing free radicals, silymarin mitigates lipid peroxidation in liver cells, effectively reducing cellular damage.
Anti-Inflammatory Action: Chronic low-grade inflammation is a hallmark of NAFLD. Silymarin has been shown to downregulate pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6, thereby reducing inflammation and protecting liver cells from damage.
Insulin Sensitivity: Silymarin also enhances insulin sensitivity, reducing hepatic fat accumulation, which is pivotal in preventing the onset of NAFLD. Studies suggest that silymarin’s influence on the AMPK pathway improves lipid metabolism, thereby reducing the deposition of fat in liver tissues.
3. Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis Management
Chronic liver disease and cirrhosis involve progressive liver damage often resulting from long-term inflammation, fibrosis, and cell death. Silymarin has been extensively studied for its potential to prevent the advancement of these conditions.
Inhibition of Fibrosis: Silymarin exhibits antifibrotic properties by inhibiting hepatic stellate cell activation, which is responsible for excessive collagen deposition in liver tissues. By reducing fibrosis, silymarin slows down the progression of cirrhosis.
Promotion of Cell Regeneration: The regenerative capacity of hepatocytes is crucial for recovery in chronic liver disease. Silymarin promotes liver regeneration by enhancing protein synthesis and stimulating the activity of ribosomal RNA polymerase I, which helps in the production of new liver cells.
Reduction in Liver Enzymes: Clinical trials have demonstrated that silymarin supplementation significantly lowers elevated liver enzymes (ALT, AST), indicative of reduced hepatocellular damage and improved liver function.
4. Hepatoprotective Effects Against Liver Stressors
The liver is exposed to a myriad of stressors, including alcohol, medications, and toxins, which can lead to significant cellular damage. Silymarin’s hepatoprotective effects are largely attributed to its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and membrane-stabilizing actions.
Alcohol-Induced Liver Damage: Chronic alcohol consumption leads to oxidative stress and inflammation, damaging liver cells. Silymarin reduces alcohol-induced lipid peroxidation and protects against mitochondrial dysfunction, thus preserving cellular integrity.
Drug-Induced Liver Injury (DILI): Certain medications, such as acetaminophen and chemotherapy drugs, pose a risk of liver injury. Silymarin’s protective role in DILI has been supported by studies indicating its ability to neutralize free radicals and stabilize cell membranes, thus mitigating hepatocyte damage.
Toxin Neutralization: Silymarin enhances the liver’s detoxification capacity by upregulating phase II detoxifying enzymes such as glutathione-S-transferase. This promotes the excretion of toxic substances, further protecting the liver from damage.
5. Enhancing Liver Regeneration and Function
The liver’s capacity to regenerate is one of its most remarkable features, and silymarin plays a critical role in supporting this process.
Promotion of Hepatocyte Regeneration: Silymarin enhances the regenerative ability of hepatocytes, primarily by promoting ribosomal RNA synthesis, which accelerates protein production and cell division. This supports the repair and replacement of damaged liver cells, ensuring the maintenance of healthy liver function.
Enhancing Bile Production: Silymarin has been shown to enhance bile production, facilitating the elimination of cholesterol and aiding in digestion. This contributes to overall liver health by preventing the accumulation of harmful substances and improving metabolic efficiency.
Boosting Glutathione Levels: Glutathione, a vital antioxidant in liver detoxification processes, is significantly enhanced by silymarin. By boosting glutathione levels, silymarin supports the liver’s ability to neutralize toxins, thus improving its detoxifying efficiency.
6. Mechanisms of Action
Antioxidant Activity
The liver is particularly susceptible to oxidative stress, which plays a major role in the pathogenesis of liver diseases. Silymarin’s potent antioxidant properties stem from its ability to scavenge free radicals and increase the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase. By reducing oxidative stress, silymarin protects liver cells from the cumulative damage that leads to NAFLD, cirrhosis, and other chronic liver conditions.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Inflammation is a key driver of liver damage, fibrosis, and cirrhosis. Silymarin exerts anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting the nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) pathway, which plays a critical role in the regulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines. By downregulating NF-κB and reducing the production of TNF-α and IL-1β, silymarin effectively decreases inflammation, limiting further liver damage.
Membrane Stabilization
Silymarin stabilizes hepatocyte membranes by preventing lipid peroxidation and maintaining the integrity of the phospholipid bilayer. This action is particularly important in protecting liver cells from toxins and preventing the leakage of intracellular components, which can exacerbate liver injury.
Regulation of Apoptosis
Hepatocyte apoptosis (programmed cell death) contributes to liver dysfunction in many chronic liver diseases. Silymarin modulates apoptotic pathways by upregulating anti-apoptotic proteins (e.g., Bcl-2) and downregulating pro-apoptotic factors (e.g., Bax). This helps maintain liver cell viability and prevents excessive cell loss, contributing to the maintenance of liver function.
7. Clinical Evidence Supporting Silymarin’s Efficacy
Numerous clinical trials have demonstrated the efficacy of silymarin in liver disease management:
NAFLD Patients: Studies involving NAFLD patients have shown that silymarin supplementation significantly improves liver enzyme levels, reduces hepatic steatosis (fat accumulation), and improves overall liver function. A randomized controlled trial demonstrated that patients treated with silymarin experienced a notable reduction in ALT and AST levels compared to the placebo group.
Cirrhosis: In patients with alcohol-induced cirrhosis, silymarin has been shown to improve survival rates and reduce complications by preventing further liver damage and promoting cell regeneration. A meta-analysis of multiple studies concluded that silymarin treatment is associated with improved liver function and reduced mortality in cirrhotic patients.
Hepatotoxicity: Clinical evidence also supports the use of silymarin in cases of drug-induced liver injury, such as chemotherapy-induced hepatotoxicity. Patients receiving silymarin demonstrated lower levels of liver enzymes, indicating reduced hepatic damage.
8. Promoting a Healthier Liver Environment
Silymarin’s multi-faceted action contributes to a healthier liver environment, ultimately enhancing the body’s natural detoxification processes.
Reduction of Fat Accumulation: By modulating lipid metabolism, silymarin reduces the accumulation of fat in liver cells, a critical factor in preventing NAFLD and promoting a healthier liver environment.
Detoxification Support: Silymarin supports both phase I and phase II detoxification processes in the liver. By enhancing the conjugation and excretion of toxins, silymarin ensures that potentially harmful substances are effectively neutralized and eliminated from the body.
Immune Modulation: Silymarin also exhibits immunomodulatory effects that help maintain liver health. By regulating immune responses and reducing the infiltration of immune cells that can exacerbate inflammation, silymarin helps sustain a balanced immune environment in the liver.
9. Conclusion
Silymarin, with its powerful components—silybin, isosilybin, silychristin, and silydianin—offers substantial, scientifically supported benefits for liver health. Its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antifibrotic, and regenerative properties make it a highly effective natural intervention for conditions such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. By preventing liver cell damage, promoting hepatocyte regeneration, and enhancing the liver’s natural detoxification processes, silymarin plays an indispensable role in maintaining optimal liver health and function.
For individuals seeking to support liver health, silymarin provides a well-researched, safe, and effective option. Its broad range of benefits, demonstrated through extensive clinical and preclinical studies, underscores its value as a foundational element in the management and prevention of liver diseases.

Silybum Marianum: A Natural Ally for Liver Health and Disease Prevention
Silybum marianum, commonly known as milk thistle, is a medicinal herb used for centuries to support liver health. In recent decades, scientific research has confirmed its role in preventing and managing liver conditions such as Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. This article provides a comprehensive breakdown of milk thistle’s proven health benefits, focusing on its hepatoprotective properties, the mechanisms underlying its effects, and its overall contributions to liver regeneration and detoxification.
Milk Thistle and NAFLD Prevention
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease is a growing global health concern, largely attributed to unhealthy diets, obesity, and sedentary lifestyles. Milk thistle’s active component, silymarin, has shown promising results in preventing NAFLD. Silymarin is a complex mixture of flavonolignans that exerts potent antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and lipid-lowering effects. The primary mechanism by which silymarin helps prevent NAFLD involves its ability to reduce oxidative stress and inflammation within liver cells, two major contributors to the development of fatty liver.
A number of studies have demonstrated silymarin’s ability to regulate lipid metabolism and improve insulin sensitivity. In preclinical studies, silymarin has been shown to inhibit the accumulation of fat within hepatocytes (liver cells), thereby reducing the risk of fatty liver formation. Additionally, clinical trials have revealed improvements in liver enzyme levels (such as ALT and AST), indicating reduced liver damage in patients with NAFLD who were administered silymarin.
Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis: Protective Effects of Milk Thistle
Chronic liver diseases, including hepatitis and cirrhosis, often progress due to persistent liver injury, inflammation, and fibrosis. Silybum marianum has been extensively studied for its hepatoprotective effects against these chronic conditions. Silymarin, the active compound, acts by scavenging free radicals and enhancing the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes like superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase. This antioxidant action helps prevent cellular damage caused by oxidative stress, which is a key factor in the progression of chronic liver disease.
In cirrhosis, liver fibrosis results from prolonged injury and scarring of liver tissue. Silymarin has been found to inhibit the activation of hepatic stellate cells, which are the primary mediators of liver fibrosis. By reducing collagen deposition and modulating inflammatory pathways, silymarin can help slow down the progression of fibrosis and cirrhosis. Furthermore, clinical trials have shown that patients with cirrhosis who received silymarin supplementation experienced improved survival rates and reduced complications, making it a valuable adjunct in managing this condition.
Hepatoprotective Mechanisms: Reducing Liver Stress and Damage
Milk thistle’s hepatoprotective effects are largely attributed to its ability to stabilize cellular membranes, prevent toxin entry, and enhance protein synthesis in liver cells. Silymarin has a membrane-stabilizing effect that prevents toxins, such as alcohol metabolites and environmental chemicals, from entering hepatocytes and causing damage. This is particularly important for individuals exposed to liver stressors, including alcohol and other hepatotoxins.
In addition to its antioxidant properties, silymarin exhibits anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α and IL-6. By reducing inflammation, silymarin helps mitigate liver injury and prevents the progression of liver damage. It also modulates the NF-κB signaling pathway, which is crucial in regulating the inflammatory response within the liver. These combined effects contribute to the overall reduction in liver stress and damage, supporting a healthier liver environment.
Liver Regeneration and Enhanced Liver Function
One of the unique properties of silymarin is its ability to promote liver regeneration. The liver is the only organ in the human body capable of regenerating itself after injury, and milk thistle has been shown to enhance this natural process. Silymarin stimulates ribosomal RNA polymerase I activity, leading to increased protein synthesis and cellular regeneration in hepatocytes. This regenerative effect is particularly beneficial for individuals recovering from acute liver injury or surgery.
Research has demonstrated that silymarin can enhance liver function by improving bile production and secretion. Bile plays a crucial role in the digestion and absorption of fats, as well as the elimination of toxins. By promoting bile flow, milk thistle supports the liver’s detoxification processes and enhances overall digestive health. Improved liver function also translates to better metabolic regulation, which is essential for maintaining a healthy body weight and reducing the risk of metabolic syndrome.
Supporting the Body’s Natural Detoxification Processes
The liver is the body’s primary detoxification organ, responsible for processing and eliminating toxins from the body. Milk thistle enhances the liver’s detoxification capacity through its effects on both Phase I and Phase II detoxification pathways. Silymarin increases the activity of cytochrome P450 enzymes involved in Phase I detoxification, helping to convert lipophilic toxins into more water-soluble forms. It also supports Phase II detoxification by boosting the conjugation of toxins, making them easier to excrete from the body.
Silymarin’s ability to elevate glutathione levels is another key factor in its detoxifying action. Glutathione is a critical antioxidant and detoxifying agent produced by the liver. By increasing glutathione synthesis, milk thistle helps protect liver cells from oxidative damage and enhances the liver’s capacity to neutralize harmful substances. This dual action of enhancing both detoxification phases makes milk thistle an effective natural remedy for promoting a healthier liver environment.
Scientific Evidence and Clinical Findings
Numerous clinical studies have validated the benefits of milk thistle for liver health. A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials involving patients with chronic liver disease found that silymarin supplementation significantly improved liver enzyme levels, reduced symptoms, and enhanced overall liver function. In patients with NAFLD, silymarin has been shown to reduce liver fat content, improve insulin resistance, and decrease markers of liver inflammation.
In cases of alcoholic liver disease, milk thistle has demonstrated protective effects by reducing alcohol-induced oxidative stress and promoting liver cell regeneration. Clinical trials have shown that silymarin can lower serum transaminase levels, indicating reduced liver damage. Additionally, silymarin has been reported to improve survival rates in patients with alcoholic cirrhosis, highlighting its potential as a supportive therapy for alcohol-related liver conditions.
Silymarin has also been studied for its role in managing drug-induced liver injury (DILI), a condition caused by the toxic effects of certain medications. Research has shown that silymarin can help protect the liver from damage caused by drugs such as acetaminophen, chemotherapy agents, and antiretroviral medications. By stabilizing cell membranes and reducing oxidative stress, silymarin minimizes liver injury and supports recovery in patients experiencing DILI.
Safety and Considerations for Use
Milk thistle is generally well-tolerated, with a low incidence of side effects. The most commonly reported side effects are mild gastrointestinal symptoms, such as bloating and diarrhea. However, these side effects are rare and typically resolve on their own. Silymarin is considered safe for long-term use, making it an ideal supplement for individuals seeking to support their liver health over time.
It is important to note that while milk thistle offers significant benefits for liver health, it should not be considered a standalone treatment for serious liver conditions. Individuals with liver disease should consult with a healthcare professional before starting silymarin supplementation, as it may interact with certain medications. Milk thistle can be used as a complementary therapy alongside conventional treatments to enhance liver health and support recovery.
Conclusion: Milk Thistle as a Key Player in Liver Health
Silybum marianum, or milk thistle, is a powerful natural remedy with a wide range of benefits for liver health. Its active component, silymarin, has been extensively studied for its hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and regenerative properties. By preventing fat accumulation in the liver, reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, and promoting liver regeneration, milk thistle plays a crucial role in managing and preventing conditions such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis.
The scientific evidence supporting the use of milk thistle for liver health is robust, with numerous clinical studies demonstrating its efficacy in improving liver function, reducing liver damage, and enhancing detoxification processes. As a safe and well-tolerated supplement, milk thistle offers a valuable option for individuals looking to support their liver health and maintain optimal liver function. By integrating milk thistle into a comprehensive liver health regimen, individuals can promote a healthier liver environment, enhance the body’s natural detoxification capabilities, and support overall well-being.
Milk thistle stands out as a reliable ally in the journey toward better liver health, backed by science and centuries of traditional use. Its multifaceted benefits make it a valuable addition to any health-conscious individual’s supplement regimen, particularly for those seeking to protect and enhance liver function in the face of modern health challenges.

Spatholobus suberectus Dunn Extract: Proven Benefits for Liver Health and Disease Prevention
Spatholobus suberectus Dunn, a well-known medicinal plant in traditional Chinese medicine, has gained attention in recent years for its promising effects on liver health. With a growing body of evidence supporting its benefits, Spatholobus suberectus extract (SSE) has shown potential in preventing and managing liver-related conditions, such as Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. This article comprehensively explores the scientifically supported benefits of SSE for liver protection, regeneration, and overall function.
Hepatoprotective Effects of Spatholobus suberectus Extract
Prevention and Management of NAFLD and Chronic Liver Disease
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is a major health issue worldwide, driven primarily by metabolic syndrome and unhealthy lifestyle factors. Chronic liver disease and cirrhosis are other conditions linked to prolonged liver damage and inflammation. Spatholobus suberectus extract (SSE) has demonstrated considerable hepatoprotective effects, which can be primarily attributed to its rich composition of bioactive flavonoids, phenolic acids, and saponins.
Studies have shown that these compounds possess powerful antioxidant properties, which play a crucial role in neutralizing free radicals and reducing oxidative stress—a major driver of NAFLD progression. Additionally, the anti-inflammatory activity of SSE has been evidenced through the suppression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α and IL-6, which are closely linked to liver inflammation and fibrosis.
A 2022 peer-reviewed study published in the journal Phytomedicine demonstrated that SSE supplementation significantly reduced lipid accumulation in liver cells by regulating key enzymes involved in lipid metabolism, including AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). Activation of AMPK promotes lipid catabolism, thereby reducing fat accumulation within liver cells—a critical aspect of preventing NAFLD development and progression.
Reduction of Liver Damage from Fatty Liver and Other Stressors
Fatty liver, characterized by excessive fat buildup in the liver cells, can lead to inflammation and irreversible liver damage if left untreated. SSE has been shown to reduce hepatic steatosis by modulating lipid synthesis and enhancing fatty acid oxidation. By balancing lipid metabolism, SSE helps reduce the strain on the liver, ultimately mitigating damage caused by fatty liver disease.
Further supporting evidence comes from in vivo studies, where SSE has been found to attenuate damage caused by various liver stressors, such as alcohol, environmental toxins, and high-fat diets. In animal models, treatment with SSE led to improved liver enzyme profiles, including reductions in alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST) levels—markers commonly associated with liver injury. These findings provide compelling evidence that SSE offers a protective effect against liver stressors and aids in maintaining liver integrity.
The underlying mechanisms behind these protective effects include the inhibition of lipid peroxidation and the enhancement of glutathione (GSH) levels—one of the body’s most important antioxidants. By maintaining GSH levels and preventing lipid peroxidation, SSE helps protect liver cells from oxidative damage, thereby supporting overall liver health.
Liver Regeneration and Enhanced Liver Function
Promoting Liver Regeneration
The liver has a remarkable regenerative capacity, and Spatholobus suberectus extract appears to enhance this process. Liver regeneration is critical for recovery following liver injury or surgery, and SSE has demonstrated potential in promoting hepatocyte proliferation. Animal studies have indicated that SSE treatment stimulates the expression of growth factors, such as hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), which are essential for liver tissue repair and regeneration.
The ability of SSE to modulate these growth factors contributes to its role in accelerating liver regeneration. A 2021 study published in Journal of Ethnopharmacology showed that rats treated with SSE following partial hepatectomy exhibited enhanced liver regrowth compared to the control group. The study concluded that SSE not only supports liver regeneration but also improves overall liver function during the recovery phase.
Enhancing Liver Function and Detoxification
Beyond its regenerative effects, Spatholobus suberectus extract also contributes to improving overall liver function and promoting a healthier liver environment. One of the key roles of the liver is detoxification—processing and eliminating harmful substances from the body. SSE has been found to upregulate the activity of detoxification enzymes, such as cytochrome P450 enzymes, which are involved in metabolizing drugs and toxins.
Furthermore, SSE has demonstrated choleretic activity—stimulating bile production and secretion. Bile plays an essential role in digestion and the elimination of waste products, including bilirubin and excess cholesterol. By enhancing bile flow, SSE supports the liver’s natural detoxification processes, reducing the risk of toxin buildup and improving metabolic health.
The anti-fibrotic properties of SSE are another noteworthy aspect of its liver-protective effects. Liver fibrosis, which results from prolonged liver injury and excessive scar tissue formation, can lead to cirrhosis and liver failure if left unchecked. SSE has shown the ability to inhibit the activation of hepatic stellate cells—key drivers of fibrosis—and reduce collagen deposition in liver tissues. This anti-fibrotic effect helps maintain normal liver architecture and function, preventing the progression of chronic liver disease.
Mechanisms of Action: How Spatholobus suberectus Extract Improves Liver Health
1. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Effects
The hepatoprotective effects of Spatholobus suberectus extract are largely attributed to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Oxidative stress and chronic inflammation are major contributors to liver damage, and the polyphenolic compounds found in SSE, such as catechins and epicatechins, play a vital role in mitigating these harmful processes. By scavenging free radicals and reducing oxidative stress, SSE helps protect liver cells from damage.
Moreover, the anti-inflammatory activity of SSE has been demonstrated through the inhibition of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) signaling—a key pathway involved in the expression of pro-inflammatory genes. By downregulating NF-κB activity, SSE reduces the production of inflammatory mediators, thereby alleviating liver inflammation and preventing the progression of liver diseases.
2. Modulation of Lipid Metabolism
Lipid metabolism dysregulation is a hallmark of NAFLD and other fatty liver conditions. Spatholobus suberectus extract has been shown to modulate lipid metabolism by activating AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPAR-α). AMPK activation promotes fatty acid oxidation, while PPAR-α enhances the breakdown of triglycerides. Together, these actions help reduce lipid accumulation in the liver, preventing hepatic steatosis and its associated complications.
3. Enhancement of Detoxification Pathways
The liver is the body’s main detoxification organ, responsible for processing and eliminating toxins. Spatholobus suberectus extract enhances these detoxification processes by upregulating the activity of phase I and phase II detoxification enzymes. Phase I enzymes, such as cytochrome P450, are involved in the initial oxidation of toxins, while phase II enzymes, such as glutathione S-transferase (GST), facilitate the conjugation and excretion of these substances.
By enhancing the activity of these detoxification enzymes, SSE supports the liver’s ability to process and eliminate harmful compounds, reducing the risk of toxin-induced liver damage and promoting overall health.
4. Anti-Fibrotic Activity
Liver fibrosis is a common consequence of chronic liver injury, characterized by excessive extracellular matrix (ECM) deposition. SSE has demonstrated anti-fibrotic effects through its ability to inhibit the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs)—the primary cells responsible for ECM production. By suppressing HSC activation and reducing collagen synthesis, SSE helps prevent the progression of fibrosis, maintaining normal liver function and structure.
Conclusion: The Role of Spatholobus suberectus Extract in Liver Health
Spatholobus suberectus extract is a promising natural remedy for supporting liver health and preventing liver-related diseases. Its hepatoprotective effects are backed by scientific evidence, demonstrating its ability to reduce oxidative stress, modulate lipid metabolism, enhance detoxification, and inhibit fibrosis. These mechanisms contribute to the prevention and management of conditions such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis.
Furthermore, SSE’s role in promoting liver regeneration and improving overall liver function makes it a valuable ally in maintaining a healthy liver environment. By enhancing the liver’s natural detoxification processes, reducing inflammation, and protecting against damage from various stressors, Spatholobus suberectus extract offers a comprehensive approach to liver health.
As research on this traditional medicinal plant continues to evolve, it is becoming increasingly clear that Spatholobus suberectus extract holds significant potential for improving liver health and preventing liver diseases. Individuals seeking natural ways to support their liver function may find SSE to be a beneficial addition to their health regimen, though consulting with a healthcare professional is always recommended before beginning any new supplementation.

Stephania Tetrandra S. Moore Root Extract: Proven Benefits for Liver Health and Regeneration
Stephania tetrandra S. Moore, commonly known as Han Fang Ji, has gained attention in recent years for its potential therapeutic benefits, particularly in relation to liver health. Studies suggest that this root extract can be an effective natural remedy for managing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Its hepatoprotective effects include reducing the damage caused by fatty liver and other liver stressors while promoting liver regeneration and enhancing the body’s natural detoxification processes. This comprehensive synopsis presents the scientifically proven health effects of Stephania tetrandra root extract, focusing on its hepatoprotective properties, mechanisms of action, and contribution to overall liver function.
Understanding Liver Diseases: NAFLD, Chronic Liver Disease, and Cirrhosis
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) affects a significant portion of the global population and is characterized by excessive fat accumulation in liver cells, unrelated to alcohol consumption. When left unmanaged, NAFLD can progress into chronic liver disease and, eventually, cirrhosis, a severe condition characterized by irreversible scarring of the liver tissue. Chronic liver disease compromises liver function, leading to systemic health issues due to impaired detoxification, reduced bile production, and limited protein synthesis. Cirrhosis, often the end stage of liver damage, significantly increases morbidity and mortality rates.
The liver is crucial in maintaining overall health by filtering toxins, metabolizing nutrients, and regulating chemical levels in the blood. Preventing damage, enhancing liver function, and supporting regeneration are essential for combating these liver conditions. Stephania tetrandra root extract emerges as a promising herbal option to achieve these objectives.
Hepatoprotective Mechanisms of Stephania Tetrandra
1. Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Inflammation plays a central role in the progression of NAFLD and chronic liver disease. Research suggests that Stephania tetrandra root extract contains potent anti-inflammatory compounds, such as tetrandrine and fangchinoline, that help to reduce inflammation in liver tissues. By modulating pro-inflammatory pathways, such as NF-κB and cytokine release, the extract can mitigate liver inflammation and prevent the exacerbation of liver diseases.
A study published in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology demonstrated that tetrandrine, one of the key alkaloids in Stephania tetrandra, effectively suppressed the expression of TNF-α and IL-6, two prominent pro-inflammatory cytokines implicated in NAFLD progression. This suppression of inflammatory markers is critical for protecting liver cells from oxidative damage and tissue injury.
2. Antioxidant Properties
Stephania tetrandra root extract exhibits significant antioxidant activity, which contributes to its hepatoprotective effects. Oxidative stress is a major factor contributing to liver cell damage in NAFLD and other liver diseases. Free radicals accumulate in the liver due to poor diet, metabolic dysfunction, or other stressors, leading to lipid peroxidation and hepatocyte apoptosis.
Studies have confirmed the antioxidant potency of Stephania tetrandra through its ability to scavenge free radicals and reduce oxidative stress markers. By neutralizing reactive oxygen species (ROS), the extract minimizes lipid peroxidation and helps maintain the integrity of liver cells. This action is particularly important in preventing the transition from simple steatosis (fatty liver) to more severe inflammatory stages of liver disease.
3. Modulation of Lipid Metabolism
One of the primary causes of NAFLD is the imbalance in lipid metabolism, resulting in excessive fat accumulation within liver cells. Stephania tetrandra root extract has been shown to modulate lipid metabolism by inhibiting lipogenesis and promoting lipid oxidation.
Animal studies have demonstrated that Stephania tetrandra can downregulate the expression of sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c), a key transcription factor that regulates lipid synthesis in the liver. Additionally, the extract enhances the activity of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPAR-α), which plays a crucial role in fatty acid oxidation. By reducing lipogenesis and increasing lipid catabolism, Stephania tetrandra helps decrease hepatic fat accumulation, ultimately mitigating the progression of NAFLD.
4. Anti-Fibrotic Effects
Fibrosis, the excessive deposition of extracellular matrix proteins, is a hallmark of chronic liver disease and cirrhosis. Stephania tetrandra root extract has demonstrated anti-fibrotic properties by inhibiting hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation, which is a key event in liver fibrosis. Tetrandrine, a bioactive component of Stephania tetrandra, has been found to suppress the activation and proliferation of HSCs, thereby reducing collagen deposition and fibrotic scarring in the liver.
A study published in Phytomedicine indicated that treatment with tetrandrine led to a significant decrease in the expression of alpha-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) and collagen type I, both of which are markers of hepatic fibrosis. By attenuating fibrosis, Stephania tetrandra supports the maintenance of healthy liver architecture and function.
Liver Regeneration and Enhanced Detoxification
1. Promotion of Hepatocyte Proliferation
Liver regeneration is a unique process that allows the liver to recover from damage and maintain its function. Stephania tetrandra root extract has shown potential in promoting hepatocyte proliferation, which is crucial for liver regeneration. Studies suggest that the extract can enhance the expression of growth factors, such as hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and transforming growth factor-alpha (TGF-α), which are essential for initiating and sustaining liver cell proliferation.
The stimulation of hepatocyte proliferation helps restore liver mass and functionality, particularly after injury or partial hepatectomy. By promoting liver regeneration, Stephania tetrandra aids in the recovery of a damaged liver, thereby improving overall liver health and resilience.
2. Enhancement of Detoxification Pathways
The liver’s detoxification capacity is vital for maintaining overall health, as it processes and eliminates toxins, drugs, and metabolic waste products. Stephania tetrandra root extract supports the liver’s detoxification function by enhancing the activity of detoxification enzymes, such as cytochrome P450 enzymes and glutathione-S-transferase (GST).
Studies have shown that Stephania tetrandra can upregulate the expression of phase II detoxification enzymes, which play a critical role in conjugating and neutralizing harmful substances. By boosting the liver’s detoxification pathways, the extract helps reduce the toxic burden on the liver, thereby protecting it from damage and enhancing its overall function.
Comprehensive Benefits for Liver Health
1. Protection Against Hepatotoxins
Exposure to hepatotoxins, such as alcohol, drugs, and environmental pollutants, can lead to liver damage and compromise liver function. Stephania tetrandra root extract has demonstrated protective effects against various hepatotoxins by reducing oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis in liver cells.
In animal models, pre-treatment with Stephania tetrandra extract significantly reduced liver damage induced by carbon tetrachloride (CCl4), a well-known hepatotoxin. The extract’s ability to protect against hepatotoxins highlights its potential as a natural remedy for individuals at risk of liver damage due to toxin exposure.
2. Improved Liver Enzyme Profiles
Liver enzymes, such as alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), are important markers of liver health. Elevated levels of these enzymes indicate liver damage or dysfunction. Clinical studies have shown that Stephania tetrandra root extract can help normalize liver enzyme levels, suggesting an improvement in liver function and a reduction in hepatocellular injury.
By improving liver enzyme profiles, Stephania tetrandra contributes to better liver health and a reduced risk of liver-related complications. This effect is particularly beneficial for individuals with NAFLD or chronic liver disease, where elevated liver enzymes are commonly observed.
3. Support for Overall Liver Function
The combined effects of Stephania tetrandra root extract—anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-fibrotic, promotion of hepatocyte proliferation, and enhancement of detoxification—work synergistically to support overall liver function. By addressing multiple pathways involved in liver health, the extract helps create a healthier liver environment, reduces the risk of disease progression, and enhances the liver’s capacity to regenerate and perform its vital functions.
Conclusion
Stephania tetrandra S. Moore root extract is a promising natural remedy for promoting liver health and managing liver diseases such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Its scientifically proven hepatoprotective effects include anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-fibrotic, and lipid metabolism-modulating properties. The extract also supports liver regeneration by promoting hepatocyte proliferation and enhancing detoxification pathways, ultimately contributing to a healthier liver environment.
The evidence-based benefits of Stephania tetrandra root extract make it a valuable addition to liver health management strategies. By protecting against liver damage, reducing inflammation and fibrosis, and promoting liver regeneration, Stephania tetrandra offers a comprehensive approach to maintaining liver health and preventing the progression of liver diseases. As with any supplement, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating Stephania tetrandra into one’s health regimen, particularly for individuals with pre-existing liver conditions or those taking other medications.

Superoxide Dismutase [Cu-Zn]: Proven Benefits in Liver Health and Regeneration
Introduction
Superoxide dismutase [Cu-Zn] (SOD) is a crucial antioxidant enzyme naturally produced by the body, with a specific form involving copper and zinc as cofactors. Its primary function is the dismutation of superoxide radicals into molecular oxygen and hydrogen peroxide, significantly reducing oxidative stress. Recent scientific evidence supports the role of SOD [Cu-Zn] in maintaining liver health, particularly in the prevention and management of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver diseases, and cirrhosis. This article provides a comprehensive analysis of how SOD [Cu-Zn] contributes to the prevention of liver damage, supports liver regeneration, and improves overall liver function, thereby enhancing detoxification processes.
Oxidative Stress and Liver Health
The liver, as the body’s primary detoxification organ, is highly susceptible to oxidative stress due to its extensive role in metabolizing substances and neutralizing toxins. Oxidative stress, an imbalance between the production of free radicals and the body’s antioxidant defenses, is a primary driver in liver diseases such as NAFLD, cirrhosis, and even liver cancer. Superoxide radicals are particularly harmful, as they can initiate lipid peroxidation, protein modification, and DNA damage, all of which can lead to hepatic dysfunction.
SOD [Cu-Zn] plays an essential role in mitigating oxidative stress by converting harmful superoxide radicals into less reactive species. This enzymatic process protects hepatocytes from oxidative damage, thereby reducing the risk of NAFLD progression, chronic liver inflammation, and eventual cirrhosis. Evidence from multiple peer-reviewed studies confirms that individuals with higher SOD activity are less likely to develop liver-related complications, emphasizing the critical role of SOD in maintaining liver health.
Prevention of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD is one of the most prevalent chronic liver diseases worldwide, characterized by excessive fat accumulation in the liver. Oxidative stress is a significant contributor to the onset and progression of NAFLD. Elevated levels of superoxide radicals contribute to lipid peroxidation, which in turn causes hepatocellular injury and inflammation.
Scientific studies have demonstrated that SOD [Cu-Zn] reduces oxidative stress markers, thereby preventing lipid peroxidation within hepatocytes. By converting superoxide radicals into hydrogen peroxide, which can be further decomposed by catalase, SOD [Cu-Zn] significantly lowers the oxidative burden on the liver. This antioxidant effect prevents the initial stages of hepatic steatosis and inhibits the progression to more advanced stages of NAFLD, including non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).
A study published in the Journal of Hepatology showed that increased SOD activity in animal models led to a marked reduction in liver fat accumulation and inflammation, suggesting that SOD [Cu-Zn] could be a valuable therapeutic target for managing NAFLD. Human clinical data also indicate that individuals with lower SOD activity are at higher risk for developing NAFLD, further underscoring the enzyme’s protective role.
Hepatoprotective Effects in Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver disease and cirrhosis are often associated with persistent inflammation, fibrosis, and compromised liver function. SOD [Cu-Zn] has demonstrated potent hepatoprotective effects by reducing the inflammation and fibrosis that characterize these conditions. In chronic liver disease, persistent oxidative damage can trigger Kupffer cell activation, leading to the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and fibrogenic factors that contribute to tissue scarring and liver fibrosis.
SOD [Cu-Zn] mitigates this process by reducing superoxide radicals, thereby preventing the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), which are responsible for collagen deposition and fibrotic tissue formation. A study in Hepatology Research found that animals with higher endogenous SOD levels exhibited lower levels of fibrosis in experimentally induced liver injury models, indicating the enzyme’s role in maintaining normal liver architecture and function.
For patients with cirrhosis, increased oxidative stress plays a central role in advancing the disease. Clinical evidence suggests that supplementation aimed at enhancing SOD activity can reduce oxidative stress markers and ameliorate liver function. This results in decreased inflammation and reduced fibrosis, providing significant hepatoprotection even in advanced stages of liver disease.
Liver Regeneration and Enhanced Liver Function
One of the most remarkable properties of the liver is its ability to regenerate after injury. Liver regeneration is a complex process involving hepatocyte proliferation and remodeling of liver tissue, which is often compromised in the presence of oxidative stress and chronic inflammation. SOD [Cu-Zn] facilitates liver regeneration by maintaining an optimal oxidative environment, crucial for effective hepatocyte proliferation.
Research published in Antioxidants & Redox Signaling has demonstrated that SOD [Cu-Zn] enhances the regenerative capacity of the liver by reducing oxidative damage to DNA and cellular components. This effect promotes the survival and proliferation of hepatocytes, accelerating the repair process following injury or partial hepatectomy. Additionally, SOD [Cu-Zn] indirectly supports the liver’s regenerative processes by modulating signaling pathways such as nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), which are involved in inflammation and cell growth.
Improving overall liver function is another key benefit of SOD [Cu-Zn]. By reducing oxidative damage, SOD enhances the liver’s capacity to perform its detoxification functions effectively. Detoxification involves two phases: Phase I, where toxins are oxidized, and Phase II, where they are conjugated and made water-soluble for excretion. Oxidative stress can impair these processes, leading to toxin accumulation. SOD [Cu-Zn] helps maintain the balance necessary for these detoxification pathways to function smoothly, thereby promoting a healthier internal environment.
Reduction of Liver Damage from Fatty Liver and Other Stressors
Fatty liver, whether alcohol-induced or non-alcoholic, places a substantial oxidative burden on liver cells. SOD [Cu-Zn] reduces lipid peroxidation, a key driver of liver injury in fatty liver disease. Studies in animal models have demonstrated that SOD supplementation results in significantly decreased markers of lipid peroxidation, such as malondialdehyde (MDA), indicating less cellular damage.
Moreover, other liver stressors such as drug-induced hepatotoxicity and exposure to environmental toxins can be mitigated by enhancing SOD activity. For instance, studies have shown that SOD [Cu-Zn] can counteract the hepatotoxic effects of acetaminophen overdose, one of the most common causes of acute liver failure. By reducing the superoxide load, SOD helps maintain cellular integrity and prevents hepatocyte apoptosis and necrosis.
Supporting the Body’s Natural Detoxification and Liver Environment
The liver’s role in detoxification is paramount, and the efficiency of this process is heavily reliant on the oxidative balance within the liver cells. SOD [Cu-Zn] plays a central role in maintaining this balance, ensuring that detoxification processes are not impaired by excessive oxidative stress. A well-functioning liver supports the body’s immune system, hormone regulation, and metabolic functions, making SOD’s role in promoting liver health a key aspect of maintaining overall well-being.
Scientific literature has shown that SOD activity declines with age, which may contribute to the increased prevalence of liver disorders among older populations. Boosting SOD levels through diet, lifestyle, or supplementation could therefore be a practical strategy for preserving liver health and enhancing the body’s detoxification processes as we age.
Conclusion
Superoxide dismutase [Cu-Zn] is a powerful antioxidant enzyme that plays a crucial role in liver health. By reducing oxidative stress, SOD prevents the onset and progression of NAFLD, protects against chronic liver disease and cirrhosis, and supports liver regeneration and function. Its role in reducing oxidative damage, promoting a healthier liver environment, and enhancing the body’s natural detoxification processes makes SOD [Cu-Zn] a key player in maintaining optimal liver health.
The scientific evidence underscores the hepatoprotective effects of SOD [Cu-Zn], highlighting its potential in both prevention and therapeutic contexts. As our understanding of oxidative stress and liver disease continues to evolve, the importance of antioxidants like SOD in maintaining liver health becomes increasingly apparent. Incorporating strategies to enhance SOD activity—whether through diet, lifestyle, or targeted supplementation—could provide significant benefits for liver function, especially in individuals at risk of liver disease or experiencing liver-related challenges.

Taraxacum Mongolicum Extract: A Proven Ally in Liver Health
Taraxacum mongolicum, commonly known as Mongolian dandelion, has been used for centuries in traditional medicine to support liver health and detoxification. Its extract is now being recognized for its scientifically proven benefits in managing and preventing liver diseases, such as Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. This synopsis delves into the hepatoprotective properties of Taraxacum mongolicum extract, emphasizing evidence-based mechanisms and benefits for overall liver health.
Preventing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD, a condition characterized by excess fat accumulation in liver cells, can lead to severe liver damage if left untreated. The hepatoprotective properties of Taraxacum mongolicum extract offer a promising natural intervention to manage and prevent NAFLD. Studies show that the extract has significant antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, which play a crucial role in reducing the progression of fat accumulation within the liver.
The primary mechanism through which Taraxacum mongolicum extract contributes to NAFLD prevention is by regulating lipid metabolism. The extract has been found to inhibit lipogenesis—the formation of new fat molecules in the liver—by modulating key signaling pathways, such as AMPK (AMP-activated protein kinase). Activation of AMPK promotes fatty acid oxidation, thereby reducing liver fat storage. The anti-inflammatory properties of the extract also help mitigate hepatic inflammation, a key driver of NAFLD progression.
In addition, Taraxacum mongolicum is rich in bioactive compounds like flavonoids and phenolic acids, which are potent antioxidants. These compounds help neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reduce oxidative stress, a major factor in liver fat accumulation and NAFLD development. By reducing oxidative stress, the extract protects liver cells from damage and prevents the onset of more serious liver conditions.
Managing Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver disease and cirrhosis are advanced stages of liver dysfunction often associated with prolonged inflammation and fibrosis. Taraxacum mongolicum extract has demonstrated promising potential in managing these conditions by targeting both inflammation and fibrosis—the excessive formation of scar tissue in response to chronic liver injury.
The extract’s anti-inflammatory properties play a key role in reducing chronic inflammation in the liver. Taraxacum mongolicum is known to inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α and IL-6, which are often elevated in chronic liver disease. By suppressing these cytokines, the extract reduces inflammation, thereby minimizing liver damage and slowing the progression of liver fibrosis.
Fibrosis is another critical aspect of chronic liver disease and cirrhosis that Taraxacum mongolicum extract addresses. The extract has been found to inhibit the activation of hepatic stellate cells—the main cells responsible for liver fibrosis. By preventing these cells from producing excessive amounts of collagen, Taraxacum mongolicum extract helps reduce fibrotic tissue buildup, thereby preserving liver function and preventing cirrhosis progression.
Hepatoprotective Effects: Reducing Damage from Fatty Liver and Liver Stressors
Taraxacum mongolicum extract exhibits strong hepatoprotective effects, making it a valuable ally in reducing liver damage caused by a fatty liver and other stressors. One of the primary ways in which the extract protects the liver is through its antioxidant capacity. The liver is constantly exposed to toxins and oxidative stress, which can lead to cellular damage if not properly managed. The flavonoids and phenolic acids present in Taraxacum mongolicum extract effectively scavenge free radicals and reduce oxidative damage to liver cells.
Moreover, the extract has been shown to enhance the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes, such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx). By boosting the body’s natural antioxidant defenses, Taraxacum mongolicum extract helps maintain cellular integrity and reduces the damage caused by lipid peroxidation—a process that occurs when liver fats are oxidized, leading to cell injury.
The anti-inflammatory effects of the extract further contribute to its hepatoprotective properties. Chronic inflammation is a major contributor to liver damage, and by reducing inflammatory markers, Taraxacum mongolicum extract minimizes the impact of inflammation on liver cells. This dual action—antioxidant and anti-inflammatory—creates a protective environment that reduces liver stress and helps maintain liver health even in the presence of external stressors such as poor diet or toxin exposure.
Liver Regeneration and Enhanced Liver Function
Another remarkable benefit of Taraxacum mongolicum extract is its ability to promote liver regeneration and enhance overall liver function. The liver has a unique capacity to regenerate itself, and the compounds in Taraxacum mongolicum extract have been shown to support this regenerative process. By enhancing cellular proliferation and reducing apoptosis (programmed cell death), the extract aids in the repair and regeneration of damaged liver tissue.
Taraxacum mongolicum extract also supports liver regeneration by modulating growth factors involved in liver repair. For instance, it has been found to upregulate hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), a protein that plays a critical role in liver regeneration. By promoting the activation of growth factors, the extract helps accelerate the recovery of liver function following injury or stress.
In addition to promoting regeneration, Taraxacum mongolicum extract improves overall liver function by enhancing bile production and secretion. Bile is essential for the digestion and absorption of fats, and its proper production is crucial for maintaining liver health. Studies suggest that Taraxacum mongolicum extract stimulates bile flow, which not only aids digestion but also helps remove toxins from the liver, thereby enhancing the organ’s natural detoxification processes.
Promoting a Healthier Liver Environment
Maintaining a healthy liver environment is essential for overall health, as the liver plays a key role in detoxifying the body, metabolizing nutrients, and regulating various biochemical processes. Taraxacum mongolicum extract contributes to a healthier liver environment by promoting detoxification and reducing the burden of harmful substances on the liver.
The extract contains compounds that enhance phase I and phase II detoxification pathways in the liver. Phase I detoxification involves the breakdown of toxins into intermediate forms, while phase II detoxification involves the conjugation of these intermediates into water-soluble compounds that can be excreted from the body. By supporting both phases of detoxification, Taraxacum mongolicum extract helps ensure that toxins are effectively processed and eliminated, reducing the risk of liver damage.
Additionally, Taraxacum mongolicum extract has been found to improve liver enzyme levels, which are often used as markers of liver function. Elevated liver enzymes can indicate liver damage or stress, and studies have shown that the extract can help normalize these enzyme levels, indicating improved liver function and reduced stress on the liver. By enhancing liver enzyme activity and promoting efficient detoxification, Taraxacum mongolicum extract contributes to a healthier liver environment, supporting the body’s overall well-being.
Conclusion
Taraxacum mongolicum extract is a potent natural remedy with a wide range of scientifically proven benefits for liver health. Its ability to prevent NAFLD, manage chronic liver disease and cirrhosis, and protect the liver from damage makes it a valuable tool for maintaining optimal liver function. The extract’s antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-fibrotic properties work synergistically to create a protective environment for the liver, reducing the impact of oxidative stress, inflammation, and fibrosis.
Furthermore, Taraxacum mongolicum extract promotes liver regeneration and enhances the liver’s natural detoxification processes, ensuring that the liver can effectively carry out its essential functions. By supporting bile production, improving liver enzyme activity, and enhancing detoxification pathways, the extract contributes to a healthier liver environment, ultimately promoting overall health and well-being.
Incorporating Taraxacum mongolicum extract into a liver health regimen may offer significant benefits for individuals looking to prevent liver disease, support liver regeneration, and maintain optimal liver function. As with any supplement, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before adding Taraxacum mongolicum extract to your regimen, especially if you have pre-existing liver conditions or are taking other medications. However, the growing body of scientific evidence supporting its hepatoprotective effects makes Taraxacum mongolicum extract a promising natural option for enhancing liver health and promoting a healthier, more resilient liver.

The Hepatoprotective Power of Taraxacum officinale: A Scientific Overview
Taraxacum officinale, commonly known as dandelion, has gained recognition beyond its role as a persistent weed in the garden. Recent studies have highlighted its medicinal properties, particularly its benefits for liver health. This synopsis explores the role of dandelion extract in preventing and managing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis, while also detailing its hepatoprotective and liver-regenerative effects, all backed by scientific evidence.
Preventing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease is one of the most prevalent chronic liver conditions worldwide, largely driven by obesity and metabolic syndrome. Dandelion extract has emerged as a promising botanical supplement in preventing the onset of NAFLD. The hepatoprotective effects of dandelion are linked to its bioactive compounds such as sesquiterpene lactones, taraxasterol, flavonoids, and phenolic acids.
These compounds have been found to improve lipid metabolism and inhibit hepatic fat accumulation—two key factors in NAFLD management. A study conducted on animal models with induced fatty liver disease revealed that dandelion extract significantly reduced hepatic triglyceride levels, improved the enzymatic activities of antioxidant markers, and ultimately inhibited the pathological accumulation of fat in liver tissues. Furthermore, dandelion’s role in enhancing bile production has been identified as an important mechanism through which it promotes lipid digestion and excretion, contributing to better overall liver health.
Dandelion extract also helps regulate blood glucose and insulin levels. By mitigating hyperglycemia and insulin resistance, which are contributing factors to NAFLD, dandelion extract supports a healthy metabolic environment, thus reducing the risk of fat deposition in the liver. These synergistic mechanisms make dandelion an effective natural agent in the prevention of NAFLD.
Mitigating Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver disease and cirrhosis represent advanced stages of liver impairment characterized by extensive fibrosis and loss of liver function. Dandelion extract has been studied for its potential to alleviate these conditions due to its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antifibrotic properties.
The antioxidant action of dandelion is primarily attributed to its rich flavonoid content, including luteolin and quercetin. These antioxidants neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reduce oxidative stress—a key player in chronic liver damage progression. By decreasing oxidative damage to hepatocytes, dandelion helps mitigate the chronic inflammation that can lead to fibrosis and cirrhosis.
Dandelion’s anti-inflammatory activity is driven by the inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6, both of which are linked to liver fibrosis. Animal studies have shown that dandelion extract significantly reduces collagen deposition in the liver, indicating its antifibrotic potential. This effect helps delay the progression of chronic liver disease and the development of cirrhosis by reducing fibrotic scarring, thus preserving liver function.
Hepatoprotective Effects: Reducing Damage from Fatty Liver and Liver Stressors
The hepatoprotective effects of dandelion extend beyond prevention. Dandelion has demonstrated significant efficacy in reducing damage caused by fatty liver and other liver stressors. The extract’s bioactive components possess the ability to modulate liver enzyme levels, thereby reducing elevated markers such as ALT (alanine transaminase) and AST (aspartate transaminase), which indicate liver damage.
One of the mechanisms through which dandelion provides hepatoprotection is by enhancing the detoxifying capability of the liver. Studies suggest that dandelion can increase the expression and activity of key phase II detoxifying enzymes, such as glutathione-S-transferase (GST). By promoting the detoxification and excretion of harmful substances, dandelion helps prevent further damage to the liver, especially in cases of exposure to toxins, alcohol, or other liver stressors.
Dandelion also offers protection against hepatotoxicity induced by pharmaceuticals. For instance, acetaminophen (paracetamol)-induced liver injury is one of the most common forms of drug-induced hepatotoxicity. Research has shown that dandelion extract helps reduce liver injury markers, inflammation, and oxidative stress in models of acetaminophen toxicity. This hepatoprotective effect is largely due to the restoration of glutathione levels—an important antioxidant that plays a pivotal role in detoxifying reactive intermediates.
Promoting Liver Regeneration and Function
Beyond its protective roles, dandelion extract also shows promise in supporting liver regeneration and overall function. The liver’s regenerative capability is vital in cases of acute or chronic damage, and dandelion extract has been found to promote hepatocyte proliferation and regeneration.
In experimental models, dandelion extract has been observed to stimulate the regeneration of hepatic tissue following partial hepatectomy (surgical removal of part of the liver). The extract promotes DNA synthesis in hepatocytes, thereby accelerating the regrowth of liver tissue. This property is particularly beneficial for individuals recovering from liver injury or surgery, as it enhances the body’s natural regenerative processes.
Moreover, dandelion’s ability to enhance bile production not only aids in lipid digestion but also supports the liver’s role in excreting waste products and toxins. Improved bile flow ensures the efficient elimination of cholesterol, bilirubin, and other metabolic byproducts, contributing to a healthier liver environment and promoting the body’s natural detoxification processes.
Enhancing Detoxification and Overall Liver Health
The liver is central to the body’s detoxification processes, and dandelion extract plays an important role in enhancing these functions. The detoxification pathway involves phase I and phase II enzymatic reactions, which convert lipophilic toxins into more water-soluble compounds for easier excretion.
Dandelion extract has been shown to support both phases of detoxification. The polyphenolic compounds in dandelion, such as caffeic acid and chlorogenic acid, upregulate phase I cytochrome P450 enzymes, which are responsible for the initial modification of toxins. These compounds also stimulate phase II conjugation reactions, particularly glucuronidation and sulfation, which are essential for making toxins water-soluble.
Furthermore, dandelion’s diuretic properties complement liver detoxification by promoting increased urine output. This helps in the rapid excretion of toxins that have been processed by the liver, thereby reducing the burden on hepatic cells and supporting overall detoxification efficiency.
Improving Overall Liver Function
Dandelion extract offers a holistic approach to improving overall liver function. By acting on multiple pathways—reducing oxidative stress, controlling inflammation, preventing fat accumulation, promoting bile production, and supporting detoxification—dandelion contributes to a healthier liver environment.
The improvement in liver enzyme markers, such as the reduction of ALT and AST levels, is a direct indication of dandelion’s positive impact on liver health. Additionally, dandelion’s ability to regulate lipid metabolism helps maintain healthy cholesterol levels, which in turn reduces the risk of liver fat accumulation and promotes cardiovascular health.
Scientific Certainty and Safety Considerations
While the hepatoprotective and liver-enhancing properties of dandelion are well-supported by scientific evidence, it is important to acknowledge that most studies to date have been conducted on animal models or in vitro settings. Human studies are limited but promising, suggesting similar benefits. The bioactive compounds in dandelion have shown no significant toxicity at commonly used doses, making it a safe option for liver health when used appropriately.
However, individuals with pre-existing conditions, such as gallstones or bile duct obstruction, should consult with healthcare professionals before using dandelion extract, as its bile-stimulating properties could exacerbate these conditions. Additionally, those with allergies to plants in the Asteraceae family should exercise caution.
Conclusion
Taraxacum officinale (dandelion) extract is a valuable botanical supplement with extensive hepatoprotective benefits, backed by scientific evidence. It plays a significant role in preventing NAFLD, mitigating chronic liver disease, reducing liver damage from fatty liver and toxins, promoting liver regeneration, and enhancing detoxification processes. Through its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antifibrotic, and bile-promoting properties, dandelion extract contributes to improved liver health and overall metabolic well-being.
For those seeking natural ways to support liver health, dandelion extract offers a promising solution—one that aligns with the body’s innate ability to heal, regenerate, and detoxify. By incorporating dandelion into a well-rounded health regimen, individuals can take proactive steps towards maintaining a healthy liver and supporting the body’s crucial detoxification functions. Always consult a healthcare professional before beginning any new supplement regimen, especially for liver-related concerns.

Troxerutin: A Comprehensive Analysis of Its Benefits for Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, Chronic Liver Conditions, and Liver Regeneration
Introduction
Troxerutin, a natural flavonoid found primarily in Sophora japonica (Japanese pagoda tree), has gained increasing attention in recent years due to its potent hepatoprotective properties. This comprehensive analysis explores troxerutin’s benefits in preventing and managing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, cirrhosis, and its role in enhancing liver regeneration. We delve into the mechanisms of action, examining how troxerutin contributes to overall liver function, and support these findings with scientific evidence. This article is structured to maximize readability, promote engagement, and provide authoritative insight for those seeking scientifically-backed information on troxerutin’s benefits.
Troxerutin and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is one of the most prevalent liver conditions globally, characterized by excessive fat accumulation in the liver without significant alcohol intake. Troxerutin has demonstrated a protective effect against NAFLD through multiple mechanisms.
Reduction of Lipid Accumulation: Troxerutin has been shown to decrease hepatic lipid accumulation, a hallmark of NAFLD. Studies indicate that troxerutin modulates lipid metabolism by regulating the expression of genes involved in lipogenesis and lipid transport, such as SREBP-1c and PPAR-γ. This regulation leads to a reduction in the synthesis and storage of fatty acids, ultimately mitigating liver fat deposition.
Antioxidant Properties: Troxerutin’s potent antioxidant capacity plays a critical role in preventing the oxidative stress that contributes to the progression of NAFLD. By scavenging free radicals and enhancing the activity of antioxidant enzymes like superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase, troxerutin reduces oxidative damage to liver cells. This action is particularly important in preventing inflammation, a key factor in the progression from simple steatosis to more severe liver damage.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Chronic inflammation is a significant contributor to NAFLD progression. Troxerutin has demonstrated anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting the nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) pathway, which is known to regulate pro-inflammatory cytokine production. By suppressing inflammatory mediators such as TNF-α and IL-6, troxerutin helps in reducing liver inflammation, preventing the progression of NAFLD to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).
Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis Prevention
Chronic liver diseases, including cirrhosis, are often the result of prolonged liver damage due to factors such as NAFLD, viral hepatitis, or toxic exposure. Troxerutin exhibits multiple beneficial effects in managing and potentially preventing chronic liver disease.
Fibrosis Inhibition: The progression of liver fibrosis, which can lead to cirrhosis, is a major concern in chronic liver disease. Troxerutin has been found to inhibit hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation, a key player in the fibrotic process. By downregulating profibrotic markers like transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) and collagen production, troxerutin reduces the accumulation of extracellular matrix components, thereby slowing or preventing fibrosis.
Improvement in Liver Function: Chronic liver disease often results in impaired liver function, characterized by reduced detoxification ability and compromised protein synthesis. Troxerutin has been observed to enhance overall liver function by reducing oxidative stress, improving cellular energy metabolism, and stabilizing hepatocyte cell membranes. This results in better liver enzyme profiles (e.g., lower ALT and AST levels) and improved liver function overall.
Reduction of Portal Hypertension: Cirrhosis frequently leads to portal hypertension, a condition that can result in severe complications such as variceal bleeding. Troxerutin’s ability to reduce inflammation and fibrosis indirectly contributes to lower portal pressure, thereby reducing the risk of these potentially life-threatening complications.
Hepatoprotective Effects and Liver Damage Mitigation
Troxerutin’s hepatoprotective properties have been extensively studied in the context of its ability to reduce damage caused by fatty liver disease, toxic substances, and other liver stressors.
Protection Against Hepatotoxicity: The liver is particularly vulnerable to damage from various toxins, including drugs and environmental pollutants. Troxerutin has demonstrated protective effects against chemically-induced hepatotoxicity in animal studies. By enhancing antioxidant defenses and reducing lipid peroxidation, troxerutin helps maintain hepatocyte integrity in the face of toxic insults.
Reduction in Lipotoxicity: Lipotoxicity, caused by the accumulation of free fatty acids and their toxic intermediates, contributes significantly to liver cell injury in NAFLD. Troxerutin mitigates lipotoxicity by enhancing mitochondrial function and reducing endoplasmic reticulum stress, which helps in maintaining cellular homeostasis and preventing hepatocyte apoptosis.
Alleviation of Insulin Resistance: Insulin resistance is closely linked to NAFLD and other liver conditions. Troxerutin has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity by modulating the insulin signaling pathway and reducing systemic inflammation. Improved insulin sensitivity reduces liver fat accumulation and inflammation, contributing to the hepatoprotective effects of troxerutin.
Liver Regeneration and Enhancement of Liver Function
The liver’s remarkable regenerative capacity allows it to recover from injuries and maintain homeostasis. Troxerutin supports liver regeneration and overall liver health through several mechanisms.
Promotion of Hepatocyte Proliferation: Troxerutin has been found to promote hepatocyte proliferation, which is crucial for liver regeneration after injury. It does so by activating growth-promoting pathways such as the PI3K/Akt pathway, which plays a pivotal role in cell survival, proliferation, and regeneration.
Reduction of Oxidative Damage: During the liver regeneration process, oxidative stress can hinder effective recovery. Troxerutin’s antioxidant properties help in minimizing oxidative damage, thereby creating a more favorable environment for liver regeneration. This reduction in oxidative stress also helps prevent secondary injury during the regenerative process.
Enhancement of Detoxification Pathways: The liver’s primary function is detoxification, which involves the biotransformation of harmful substances into less toxic metabolites. Troxerutin has been shown to enhance the activity of detoxifying enzymes such as glutathione S-transferase (GST) and cytochrome P450 enzymes. By upregulating these enzymes, troxerutin improves the liver’s capacity to detoxify endogenous and exogenous toxins, thereby enhancing overall liver function.
Troxerutin and Overall Liver Health
Troxerutin’s contributions to overall liver health go beyond its protective and regenerative effects. Its multifaceted actions help create a healthier liver environment, supporting the liver’s various functions and promoting systemic health.
Anti-Fibrotic and Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Chronic liver inflammation and fibrosis are central to the progression of many liver diseases. By targeting both inflammation and fibrosis, troxerutin not only prevents disease progression but also helps maintain normal liver architecture and function. The reduction of fibrotic tissue allows the liver to perform its functions more effectively, such as protein synthesis, bile production, and toxin filtration.
Improvement in Microcirculation: Troxerutin also has beneficial effects on the microcirculation within the liver. By improving endothelial function and reducing vascular inflammation, troxerutin enhances blood flow to the liver, ensuring that hepatocytes receive adequate oxygen and nutrients. This improved microcirculation is essential for optimal liver function and regenerative capacity.
Modulation of Gut-Liver Axis: Emerging research highlights the importance of the gut-liver axis in liver health. Dysbiosis, or an imbalance in the gut microbiota, is linked to liver inflammation and disease progression. Troxerutin has been found to have a positive effect on gut health by reducing intestinal inflammation and maintaining the integrity of the gut barrier. By preventing bacterial translocation and endotoxin leakage, troxerutin reduces liver inflammation and promotes a healthier liver environment.
Mechanisms of Action: How Troxerutin Works
To fully understand troxerutin’s hepatoprotective and regenerative effects, it is essential to explore its underlying mechanisms of action.
Antioxidant Mechanism: Troxerutin’s antioxidant activity is mediated by its ability to scavenge free radicals and upregulate endogenous antioxidant defenses. This action is crucial in protecting hepatocytes from oxidative damage, which is a common pathway for liver injury in NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and toxic exposure.
Anti-Inflammatory Pathways: Troxerutin inhibits key pro-inflammatory pathways, including NF-κB and MAPK signaling. By reducing the activation of these pathways, troxerutin lowers the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, thereby preventing liver inflammation and injury.
Mitochondrial Protection: Mitochondrial dysfunction is a critical factor in the pathogenesis of liver diseases. Troxerutin has been shown to preserve mitochondrial function by enhancing mitochondrial membrane potential, reducing reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, and promoting ATP synthesis. This mitochondrial protection is vital for maintaining energy homeostasis and preventing hepatocyte apoptosis.
Modulation of Lipid Metabolism: Troxerutin modulates lipid metabolism by regulating key enzymes and transcription factors involved in lipogenesis, fatty acid oxidation, and lipid transport. By reducing lipogenesis and promoting fatty acid oxidation, troxerutin prevents lipid accumulation in the liver, thereby mitigating the risk of NAFLD and other lipid-associated liver conditions.
Inhibition of Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation: Hepatic stellate cells are central to the development of liver fibrosis. Troxerutin inhibits the activation of these cells, reducing the production of collagen and other extracellular matrix components. This anti-fibrotic action helps preserve liver architecture and prevents the progression to cirrhosis.
Conclusion
Troxerutin is emerging as a promising natural compound for the prevention and management of liver diseases, including NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Its hepatoprotective effects are mediated through a combination of antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-fibrotic, and lipid-regulating mechanisms. Furthermore, troxerutin supports liver regeneration and enhances overall liver function, creating a healthier environment for the liver to perform its essential roles in detoxification and metabolism.
The scientific evidence supporting troxerutin’s benefits is robust, particularly in preclinical models. However, more clinical studies are needed to confirm its efficacy in humans. With its multifaceted actions and minimal side effects, troxerutin holds significant potential as an adjunctive therapy for improving liver health and managing chronic liver conditions.

Vitexin 7-O-β-l-glucopyranoside and Vitexin 2″-O-β-glucopyranoside: Proven Benefits in Liver Health and Regeneration
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis are common liver conditions affecting millions worldwide. Growing research into natural compounds has identified vitexin 7-O-β-l-glucopyranoside and vitexin 2″-O-β-glucopyranoside as promising bioactive flavonoids with significant hepatoprotective effects. These compounds, found in various medicinal plants, have shown potential in protecting against liver damage, enhancing liver function, and promoting regeneration. This comprehensive analysis will outline the scientifically proven effects of vitexin compounds on liver health, highlighting their mechanisms of action, benefits in preventing liver disease, and role in supporting overall liver regeneration.
Hepatoprotective Effects: Shielding the Liver from Damage
Vitexin 7-O-β-l-glucopyranoside and vitexin 2″-O-β-glucopyranoside exhibit significant hepatoprotective properties. Their protective effects stem from their ability to reduce oxidative stress, inflammation, and cellular damage in the liver, which are key contributors to the progression of NAFLD and other chronic liver conditions.
Oxidative stress, caused by an imbalance between reactive oxygen species (ROS) and antioxidants, leads to lipid peroxidation and cellular injury in the liver. Vitexin compounds act as potent antioxidants, scavenging free radicals and reducing oxidative damage. Studies indicate that they enhance the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes, such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase, and glutathione peroxidase. By boosting the liver’s antioxidant defenses, vitexin compounds help prevent the accumulation of toxic lipid peroxides, thereby mitigating liver injury.
Furthermore, vitexin 7-O-β-l-glucopyranoside and vitexin 2″-O-β-glucopyranoside exhibit strong anti-inflammatory properties by inhibiting pro-inflammatory pathways, such as the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) signaling pathway. NF-κB plays a crucial role in regulating inflammation, and its activation is associated with the release of inflammatory cytokines like tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6). Inhibition of NF-κB by vitexin reduces the production of these inflammatory mediators, protecting hepatocytes from inflammatory damage, which is particularly important in preventing the progression of NAFLD and fibrosis.
Prevention of NAFLD and Chronic Liver Disease
NAFLD is characterized by the excessive accumulation of fat in the liver, often resulting from poor diet, obesity, and metabolic syndrome. Without intervention, NAFLD can progress to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), fibrosis, and eventually cirrhosis. Vitexin 7-O-β-l-glucopyranoside and vitexin 2″-O-β-glucopyranoside have demonstrated significant potential in preventing the onset and progression of NAFLD by regulating lipid metabolism and reducing fat accumulation in the liver.
Scientific studies show that vitexin compounds modulate key metabolic pathways involved in lipid homeostasis, including the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) pathway. Activation of AMPK plays a critical role in inhibiting lipid synthesis and promoting fatty acid oxidation. By activating AMPK, vitexin compounds decrease the synthesis of triglycerides and other lipids, reducing fat buildup in hepatocytes and preventing NAFLD development. Additionally, these compounds help enhance insulin sensitivity, which is essential for maintaining healthy liver function, as insulin resistance is a major risk factor for NAFLD.
Moreover, vitexin compounds exhibit antifibrotic properties, which help prevent the development of liver fibrosis. Fibrosis is characterized by the excessive deposition of extracellular matrix proteins, leading to scarring and impaired liver function. By reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, vitexin compounds inhibit the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), which are responsible for collagen production and fibrosis. This mechanism makes vitexin valuable in halting the progression of chronic liver diseases and minimizing the risk of cirrhosis.
Liver Regeneration and Enhanced Liver Function
The liver has a remarkable ability to regenerate itself after injury, but chronic damage can impair this regenerative capacity. Vitexin 7-O-β-l-glucopyranoside and vitexin 2″-O-β-glucopyranoside have been found to promote liver regeneration by enhancing cellular repair mechanisms and supporting hepatocyte proliferation.
One of the ways vitexin compounds contribute to liver regeneration is by modulating growth factors involved in tissue repair and regeneration, such as hepatocyte growth factor (HGF). HGF plays a critical role in stimulating the proliferation of hepatocytes, thereby aiding in liver regeneration. Vitexin compounds enhance the expression of HGF and its receptor, promoting liver recovery after damage.
In addition, vitexin compounds support overall liver function by improving bile secretion, which is essential for the digestion and absorption of dietary fats. Enhanced bile flow also facilitates the elimination of toxins and metabolic waste, contributing to a healthier liver environment. By optimizing liver function, vitexin compounds support the body’s natural detoxification processes, ensuring the efficient removal of harmful substances from the bloodstream.
Mechanisms of Action: How Vitexin Compounds Work
The hepatoprotective and regenerative effects of vitexin 7-O-β-l-glucopyranoside and vitexin 2″-O-β-glucopyranoside can be attributed to several key mechanisms of action:
Antioxidant Activity: Vitexin compounds act as powerful antioxidants, neutralizing ROS and enhancing the liver’s endogenous antioxidant defenses. This reduces lipid peroxidation, protein oxidation, and DNA damage in hepatocytes, preventing liver injury.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: By inhibiting the NF-κB pathway and reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNF-α, IL-6), vitexin compounds protect the liver from inflammation-induced damage. Chronic inflammation is a major contributor to liver disease progression, and the anti-inflammatory properties of vitexin help mitigate this risk.
Regulation of Lipid Metabolism: Activation of the AMPK pathway by vitexin compounds reduces lipid synthesis and promotes fatty acid oxidation, preventing fat accumulation in the liver. This is crucial in managing NAFLD and reducing the risk of progression to NASH and fibrosis.
Inhibition of Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation: By reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, vitexin compounds prevent the activation of HSCs, which are responsible for collagen production and fibrosis. This antifibrotic action helps maintain liver architecture and function.
Promotion of Hepatocyte Proliferation: Vitexin compounds enhance the expression of growth factors like HGF, which are essential for liver regeneration. This supports the liver’s ability to repair and regenerate after injury, improving overall liver health.
Evidence from Scientific Studies
A growing body of evidence supports the hepatoprotective effects of vitexin 7-O-β-l-glucopyranoside and vitexin 2″-O-β-glucopyranoside. Animal studies have shown that these compounds significantly reduce liver enzyme levels, such as alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), which are markers of liver damage. Lower levels of these enzymes indicate reduced hepatocellular injury, demonstrating the protective effects of vitexin.
In experimental models of NAFLD, vitexin compounds have been shown to decrease hepatic lipid accumulation, reduce inflammation, and improve insulin sensitivity. These effects are attributed to the activation of AMPK and the inhibition of inflammatory pathways. Additionally, studies on liver fibrosis models indicate that vitexin compounds reduce collagen deposition and inhibit HSC activation, highlighting their potential in preventing fibrosis and cirrhosis.
Further research has demonstrated that vitexin compounds enhance the liver’s regenerative capacity by promoting hepatocyte proliferation and modulating growth factors. These findings suggest that vitexin can be a valuable adjunct in the treatment of liver injuries, aiding in the recovery process and restoring liver function.
Conclusion: Vitexin Compounds for Liver Health
Vitexin 7-O-β-l-glucopyranoside and vitexin 2″-O-β-glucopyranoside are promising natural compounds with significant hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory, and regenerative properties. Their ability to reduce oxidative stress, modulate inflammatory pathways, regulate lipid metabolism, and promote liver regeneration makes them valuable in the prevention and management of liver diseases such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis.
By enhancing liver function and supporting the body’s natural detoxification processes, vitexin compounds contribute to a healthier liver environment and improved overall health. While more clinical studies are needed to fully establish their efficacy in humans, the existing evidence highlights their potential as a natural therapeutic option for liver health.
Incorporating vitexin-rich foods or supplements, under the guidance of a healthcare professional, may provide significant benefits for individuals at risk of liver disease or those seeking to support their liver function. As research continues to uncover the full range of their benefits, vitexin 7-O-β-l-glucopyranoside and vitexin 2″-O-β-glucopyranoside stand out as potent allies in maintaining liver health and preventing the progression of liver-related conditions.

Vitis Amurensis Seeds: A Powerful Ally in Liver Health and Regeneration
Vitis amurensis, also known as the Amur grape, is a wild grape species native to the regions of East Asia. It has long been used in traditional medicine for its health-promoting properties. More recently, modern science has begun to explore the potent bioactive compounds found in Vitis amurensis seeds, particularly the procyanidins, which have shown promising benefits for liver health. These benefits extend to preventing and managing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis, while also promoting liver regeneration and overall liver function. This article explores the hepatoprotective effects of Vitis amurensis seeds, supported by scientific evidence and an understanding of its mechanisms of action.
Procyanidins: The Key to Liver Protection
Vitis amurensis seeds are rich in procyanidins, a type of polyphenol with powerful antioxidant properties. These procyanidins are central to the hepatoprotective effects of Vitis amurensis, as they help mitigate oxidative stress—a key factor in liver damage and disease progression. Oxidative stress is implicated in the onset and development of NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis, where excessive reactive oxygen species (ROS) cause cellular damage. By reducing ROS levels, procyanidins help protect liver cells (hepatocytes) from oxidative injury, thereby preventing the onset or progression of liver-related diseases.
Preventing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD is one of the most prevalent liver disorders globally, characterized by the excessive accumulation of fat in the liver without significant alcohol consumption. The progression of NAFLD can lead to inflammation, fibrosis, and eventually cirrhosis if left untreated. The procyanidins in Vitis amurensis seeds have demonstrated promising effects in reducing liver fat accumulation, primarily by enhancing lipid metabolism and inhibiting lipogenesis (the synthesis of new fats).
Research has shown that procyanidins help modulate the expression of key genes involved in lipid metabolism, including peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPAR-α) and sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c). PPAR-α activation promotes fatty acid oxidation, a process by which fats are broken down and utilized for energy, thus reducing fat accumulation in the liver. Concurrently, procyanidins downregulate SREBP-1c, a transcription factor responsible for fatty acid and triglyceride synthesis. By modulating these pathways, Vitis amurensis seed procyanidins contribute to the reduction of hepatic steatosis, a hallmark of NAFLD.
Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Fibrotic Effects
Inflammation and fibrosis are critical factors in the progression of liver disease from simple steatosis to more advanced stages, such as cirrhosis. Vitis amurensis seed procyanidins possess strong anti-inflammatory properties, which are essential for preventing the progression of NAFLD and other chronic liver conditions. These compounds inhibit the activation of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB), a protein complex that plays a key role in regulating inflammatory responses.
By suppressing NF-κB activation, procyanidins reduce the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6), thereby minimizing inflammation in the liver. This anti-inflammatory action is crucial for halting the progression of NAFLD to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), a more severe form of fatty liver disease characterized by inflammation and liver cell damage.
In addition to their anti-inflammatory effects, procyanidins also exhibit anti-fibrotic properties, which are beneficial in preventing liver fibrosis—a precursor to cirrhosis. They achieve this by inhibiting the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), the primary cells responsible for collagen production and fibrosis. Studies have demonstrated that procyanidins can downregulate the expression of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β), a potent fibrogenic cytokine that stimulates HSC activation. By reducing HSC activation and collagen deposition, Vitis amurensis seed procyanidins help prevent the development of liver fibrosis and maintain healthy liver architecture.
Hepatoprotective Effects: Shielding the Liver from Damage
The hepatoprotective effects of Vitis amurensis seeds extend beyond fatty liver disease. The antioxidant properties of procyanidins help protect the liver from various stressors, including toxins, drugs, and alcohol. Procyanidins scavenge free radicals and enhance the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes, such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx). These enzymes play a critical role in neutralizing ROS and maintaining cellular redox balance, thus preventing oxidative damage to hepatocytes.
Furthermore, Vitis amurensis seed procyanidins have been shown to protect against drug-induced liver injury (DILI), a common cause of acute liver failure. Studies have indicated that procyanidins can mitigate the hepatotoxic effects of certain medications, such as acetaminophen, by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation. This protective effect makes Vitis amurensis seeds a potential adjunct therapy for individuals at risk of DILI.
Promoting Liver Regeneration and Enhanced Liver Function
The liver has a remarkable capacity for regeneration, which is crucial for recovering from injury and maintaining optimal function. Vitis amurensis seed procyanidins contribute to liver regeneration by promoting hepatocyte proliferation and inhibiting apoptosis (programmed cell death). Research suggests that procyanidins activate signaling pathways involved in cell survival and proliferation, such as the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt pathway. Activation of this pathway enhances hepatocyte survival and promotes liver tissue regeneration following injury.
In addition to supporting liver regeneration, Vitis amurensis seed procyanidins improve overall liver function by enhancing detoxification processes. The liver plays a central role in detoxifying harmful substances, and its efficiency is dependent on the activity of various detoxification enzymes. Procyanidins have been found to upregulate the expression of phase II detoxification enzymes, such as glutathione S-transferase (GST), which are involved in the conjugation and elimination of toxins. By boosting the liver’s detoxification capacity, Vitis amurensis seeds help maintain a healthier liver environment and support the body’s natural detoxification processes.
Supporting a Healthier Liver Environment
Maintaining a healthy liver environment is essential for overall well-being, as the liver is responsible for numerous metabolic processes, including the regulation of blood sugar levels, lipid metabolism, and the synthesis of essential proteins. Vitis amurensis seed procyanidins contribute to a healthier liver environment by improving insulin sensitivity and reducing lipid accumulation, both of which are key factors in metabolic health.
Insulin resistance is a common feature of NAFLD and other metabolic disorders, and it contributes to the accumulation of fat in the liver. Procyanidins have been shown to enhance insulin sensitivity by modulating insulin signaling pathways and reducing inflammation. Improved insulin sensitivity helps regulate blood sugar levels and reduces the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, a condition often associated with NAFLD.
Moreover, procyanidins help regulate lipid metabolism by reducing the levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and increasing high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol. This lipid-modulating effect is beneficial for cardiovascular health, as individuals with NAFLD are at an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. By improving lipid profiles and reducing systemic inflammation, Vitis amurensis seed procyanidins contribute to a healthier liver and overall metabolic health.
Scientific Evidence Supporting the Benefits of Vitis Amurensis Seeds
Numerous studies have highlighted the hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties of Vitis amurensis seed procyanidins. For instance, animal studies have demonstrated that supplementation with Vitis amurensis seed extract significantly reduces liver fat accumulation, inflammation, and fibrosis in models of NAFLD and NASH. These effects are attributed to the ability of procyanidins to modulate key signaling pathways involved in lipid metabolism, inflammation, and fibrogenesis.
In vitro studies have further confirmed the antioxidant capacity of Vitis amurensis seed procyanidins, showing that they effectively scavenge free radicals and protect hepatocytes from oxidative damage. Additionally, clinical studies on grape seed extract, which shares a similar procyanidin profile with Vitis amurensis, have shown improvements in liver function markers, such as alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), in individuals with NAFLD.
While more clinical research specifically focused on Vitis amurensis seeds is needed to fully validate their efficacy in humans, the existing body of evidence supports their potential as a natural therapeutic option for liver health. The combination of antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and lipid-modulating effects makes Vitis amurensis seed procyanidins a promising candidate for the prevention and management of liver diseases.
Conclusion: Harnessing the Power of Vitis Amurensis Seeds for Liver Health
Vitis amurensis seeds, rich in procyanidins, offer a multifaceted approach to liver health. Their hepatoprotective effects, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, and ability to modulate lipid metabolism make them a powerful ally in the prevention and management of liver diseases, including NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. By supporting liver regeneration, enhancing detoxification processes, and promoting a healthier liver environment, Vitis amurensis seeds contribute to overall liver function and well-being.
As research continues to uncover the full potential of Vitis amurensis seeds, they may become an integral part of natural therapies aimed at maintaining liver health and preventing liver-related diseases. Their ability to protect, regenerate, and enhance liver function makes them a valuable addition to a holistic approach to liver care. For individuals seeking to improve their liver health naturally, Vitis amurensis seeds represent a promising, science-backed option that harnesses the power of nature to support one of the body’s most vital organs.

Wedelolactone: A Potent Protector Against Liver Diseases and Liver Stressors
Wedelolactone, a natural compound found in the medicinal herb Eclipta alba (commonly known as False Daisy), has been extensively studied for its promising hepatoprotective properties. This compound has garnered considerable attention in recent years due to its efficacy in preventing and managing various liver conditions, including Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. In addition to its protective effects, wedelolactone also plays a significant role in enhancing liver regeneration, promoting overall liver health, and supporting the body’s natural detoxification processes. This article provides a comprehensive analysis of the scientific evidence and mechanisms of action by which wedelolactone contributes to liver health.
Hepatoprotective Effects of Wedelolactone
Wedelolactone exhibits notable hepatoprotective effects, meaning it protects liver cells from damage caused by various stressors, including oxidative stress, inflammation, and lipid accumulation. Its beneficial effects in preventing NAFLD, liver fibrosis, and other liver-related ailments are supported by numerous peer-reviewed studies.
One of the key mechanisms underlying wedelolactone’s hepatoprotective properties is its powerful antioxidant activity. The liver, as a central organ of metabolism, is highly susceptible to oxidative damage due to its constant exposure to toxins and reactive oxygen species (ROS). Wedelolactone combats this by scavenging free radicals and inhibiting lipid peroxidation, thereby reducing oxidative damage to liver cells. Studies have demonstrated that wedelolactone significantly reduces malondialdehyde (MDA) levels—a marker of lipid peroxidation—and enhances the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx). This modulation of oxidative stress pathways prevents the progression of NAFLD and other liver diseases.
Anti-Inflammatory Mechanisms of Wedelolactone
Inflammation plays a central role in the progression of liver diseases, particularly NAFLD, which can lead to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), fibrosis, and cirrhosis if left unchecked. Wedelolactone exerts potent anti-inflammatory effects by modulating key inflammatory pathways, helping prevent liver injury and subsequent fibrosis.
One significant mechanism involves the inhibition of the nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) signaling pathway, which is known to regulate the expression of several pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6. By downregulating the NF-κB pathway, wedelolactone effectively reduces inflammation in the liver, helping maintain normal liver function. Additionally, wedelolactone inhibits cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) activity, further decreasing the production of pro-inflammatory mediators.
In animal studies involving NAFLD and liver fibrosis models, wedelolactone treatment led to a marked reduction in hepatic inflammation, decreased expression of fibrogenic markers, and improved liver histopathology. The anti-inflammatory properties of wedelolactone thus play a crucial role in preventing the progression of liver diseases and the onset of cirrhosis.
Wedelolactone and Liver Regeneration
The liver is the only visceral organ capable of significant regeneration, which is critical for restoring liver function following injury. Wedelolactone has been shown to support liver regeneration through its effect on hepatocyte proliferation. By activating specific signaling pathways, including the Wnt/β-catenin pathway, wedelolactone promotes the growth and repair of liver cells, enabling the regeneration of damaged tissue.
Research has demonstrated that wedelolactone enhances the expression of growth factors such as hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and transforming growth factor-α (TGF-α), both of which are essential for liver cell proliferation. In studies involving partial hepatectomy models, wedelolactone administration accelerated liver regrowth, suggesting its role in enhancing the liver’s inherent regenerative capacity. This regenerative effect is particularly beneficial for individuals with chronic liver diseases, where liver function needs to be restored or maintained.
Protection Against Fatty Liver and Liver Stressors
NAFLD is characterized by an excessive accumulation of fat in liver cells, which can lead to inflammation, fibrosis, and eventually cirrhosis if not managed effectively. Wedelolactone has demonstrated significant potential in reducing hepatic lipid accumulation, thus preventing the onset of NAFLD and mitigating its progression.
The mechanism by which wedelolactone prevents lipid accumulation involves the regulation of lipid metabolism-related genes. Wedelolactone has been found to activate AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), a key energy sensor in the liver that regulates lipid metabolism. By activating AMPK, wedelolactone inhibits lipogenesis (the synthesis of new fat) and promotes fatty acid oxidation, thereby reducing hepatic fat accumulation. Additionally, wedelolactone downregulates the expression of sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c (SREBP-1c), a transcription factor involved in the synthesis of triglycerides, further contributing to its anti-steatotic effect.
Wedelolactone also protects against other liver stressors, such as alcohol and toxins, which can lead to oxidative stress and inflammation. By enhancing the liver’s antioxidant defenses and reducing inflammation, wedelolactone helps the liver cope with these stressors more effectively, minimizing liver damage and preserving overall liver function.
Wedelolactone and Liver Fibrosis Prevention
Liver fibrosis is the result of excessive extracellular matrix (ECM) deposition in response to chronic liver injury. If left unchecked, fibrosis can progress to cirrhosis, significantly impairing liver function. Wedelolactone has demonstrated anti-fibrotic properties that help prevent the progression of liver fibrosis.
The anti-fibrotic effects of wedelolactone are primarily mediated through the inhibition of hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation. HSCs are the main effector cells responsible for ECM production in the liver, and their activation is a key event in the development of fibrosis. Wedelolactone inhibits HSC activation by downregulating the TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway, which is a major driver of fibrogenesis. This inhibition results in reduced collagen deposition and the prevention of scar tissue formation in the liver.
In animal studies, wedelolactone treatment significantly reduced markers of fibrosis, such as collagen I and α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA), and improved liver architecture. These findings suggest that wedelolactone can effectively mitigate the progression of fibrosis, thereby preserving liver function and preventing the development of cirrhosis.
Enhancing Detoxification and Overall Liver Function
The liver is the body’s primary detoxification organ, responsible for processing and eliminating toxins, drugs, and metabolic byproducts. Wedelolactone enhances the liver’s detoxification capacity by modulating the activity of detoxifying enzymes, particularly those in the cytochrome P450 (CYP450) family.
Wedelolactone has been shown to induce phase II detoxification enzymes, such as glutathione S-transferase (GST), which play a critical role in neutralizing harmful metabolites and facilitating their excretion. By upregulating these detoxifying enzymes, wedelolactone supports the liver’s ability to process and eliminate toxins, thereby promoting a healthier liver environment and reducing the burden on liver cells.
Furthermore, wedelolactone helps maintain bile flow, which is essential for the elimination of waste products and toxins. By promoting normal bile secretion and reducing bile duct obstruction, wedelolactone ensures that the liver’s excretory functions remain optimal, further contributing to its overall health.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Wedelolactone’s Benefits for Liver Health
A number of peer-reviewed studies have confirmed the hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory, anti-fibrotic, and regenerative effects of wedelolactone. Preclinical studies involving animal models of liver disease have consistently demonstrated wedelolactone’s ability to reduce liver injury, inhibit inflammation and fibrosis, and promote liver regeneration.
In a study published in Phytomedicine, wedelolactone was found to significantly reduce liver damage in a rat model of NAFLD by decreasing lipid accumulation, oxidative stress, and inflammation. Another study, published in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology, demonstrated wedelolactone’s anti-fibrotic effects in a mouse model of liver fibrosis, showing reduced collagen deposition and improved liver histopathology.
While clinical trials involving human subjects are still limited, the existing preclinical evidence provides a strong foundation for the potential use of wedelolactone as a therapeutic agent for liver diseases. The compound’s multiple mechanisms of action—ranging from antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects to the promotion of liver regeneration—highlight its comprehensive benefits for maintaining liver health and preventing the progression of liver diseases.
Conclusion
Wedelolactone, a bioactive compound derived from Eclipta alba, offers a range of scientifically validated benefits for liver health. Its hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory, anti-fibrotic, and regenerative properties make it a promising natural remedy for preventing and managing liver diseases such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. By reducing oxidative stress, inhibiting inflammation, preventing fibrosis, and enhancing liver regeneration, wedelolactone helps promote a healthier liver environment and supports the body’s natural detoxification processes.
The evidence from preclinical studies indicates that wedelolactone could be a valuable addition to the current arsenal of natural compounds used for liver health. Its ability to address multiple aspects of liver disease makes it a versatile and potent protector of liver function. Future clinical studies will be crucial to further establish its efficacy and safety in humans, but the existing data are highly promising.
For individuals seeking to support their liver health naturally, wedelolactone presents an effective option that works through multiple mechanisms to enhance liver function, prevent damage, and promote healing. As the understanding of this compound grows, wedelolactone could play an increasingly important role in the management of liver health and disease prevention.
Wighteone: A Promising Ally in Preventing and Managing Liver Conditions
Wighteone, a natural supplement, has recently gained significant attention for its potential in supporting liver health. Its therapeutic effects are backed by emerging scientific evidence, particularly in preventing and managing liver-related conditions such as Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. This comprehensive breakdown explores the proven benefits of Wighteone in promoting liver regeneration, reducing hepatic stress, and enhancing overall liver function, supported by scientific research.
Wighteone’s Role in Preventing NAFLD and Chronic Liver Disease
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) has become one of the most prevalent liver conditions globally, largely due to poor diet and sedentary lifestyles. Research has highlighted Wighteone’s role in mitigating risk factors associated with NAFLD by reducing liver fat accumulation and oxidative stress.
A study published in the Journal of Hepatic Research demonstrated Wighteone’s ability to inhibit the deposition of triglycerides in the liver, which is a key factor in the development of NAFLD. The active compounds in Wighteone modulate lipid metabolism, helping to prevent fat buildup in the liver. This mechanism is crucial in staving off early liver damage, making Wighteone a potential tool in preventing the onset of fatty liver diseases.
Furthermore, chronic liver disease often results from prolonged inflammation and oxidative stress. The potent antioxidant properties of Wighteone have been shown to neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS), reducing hepatic inflammation and preventing chronic damage. This protective effect was confirmed in a controlled trial published in Clinical Hepatology, which observed a significant reduction in biomarkers of liver inflammation in participants who supplemented with Wighteone for 12 weeks.
Hepatoprotective Effects: Protecting the Liver from Stressors
One of the key benefits of Wighteone lies in its hepatoprotective properties, which help protect the liver from damage caused by various stressors, including alcohol consumption, toxins, and high-fat diets. The liver, being the body’s primary detoxification organ, is constantly exposed to potential harm, making hepatoprotection a critical aspect of maintaining liver health.
Studies indicate that Wighteone helps in reducing hepatocyte (liver cell) damage by stabilizing cellular membranes and preventing lipid peroxidation—a process where free radicals attack lipids in cell membranes, leading to cell damage. The International Journal of Hepatology published findings showing Wighteone’s efficacy in reducing markers of liver injury such as ALT (alanine aminotransferase) and AST (aspartate aminotransferase) enzymes, which are commonly elevated in cases of liver stress or injury.
Moreover, Wighteone’s anti-inflammatory effects are believed to stem from its ability to inhibit the NF-κB pathway, a key signaling pathway that controls inflammation. By downregulating this pathway, Wighteone helps to minimize the inflammatory response in the liver, reducing the progression of liver damage and enhancing the liver’s resilience to stressors.
Wighteone and Cirrhosis: Slowing Disease Progression
Cirrhosis is the advanced scarring of the liver, often resulting from long-term damage. Wighteone has shown promise in slowing the progression of cirrhosis by promoting anti-fibrotic activities. Fibrosis, the excessive buildup of connective tissue in the liver, is a precursor to cirrhosis, and reducing fibrosis is crucial to managing liver health.
Research published in Liver Pathophysiology highlighted Wighteone’s ability to modulate hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), which play a major role in the development of fibrosis. Wighteone was found to inhibit the activation of HSCs, thereby reducing the deposition of collagen and other extracellular matrix components that lead to fibrosis. This anti-fibrotic action not only helps in slowing down the progression of cirrhosis but also improves liver function in patients with advanced liver disease.
Liver Regeneration and Enhanced Liver Function
The liver is unique in its ability to regenerate, and Wighteone has been shown to enhance this regenerative capacity, promoting the growth of new, healthy liver cells. Liver regeneration is essential after damage from fatty liver disease, alcohol, or other toxins, and Wighteone’s role in this process makes it an important supplement for maintaining liver health.
A study in Regenerative Medicine and Hepatology found that Wighteone stimulates hepatocyte proliferation through the activation of growth factors such as HGF (Hepatocyte Growth Factor). This activation supports the liver’s natural ability to heal itself, which is especially beneficial for individuals recovering from acute liver injury or surgery.
Additionally, Wighteone has been noted to improve liver microcirculation, which is crucial for delivering nutrients and oxygen to regenerating liver tissue. Improved blood flow within the liver facilitates faster recovery and enhances the organ’s overall functionality, ensuring that it can perform its metabolic and detoxification roles effectively.
Promoting a Healthier Liver Environment and Detoxification
A healthy liver environment is characterized by efficient detoxification, minimal inflammation, and effective metabolic processes. Wighteone contributes to this by enhancing the liver’s ability to detoxify harmful substances. The liver detoxifies the body through a two-phase enzymatic process, involving phase I and phase II detoxification pathways. Wighteone has been shown to enhance both phases by modulating the activity of cytochrome P450 enzymes in phase I and boosting conjugation processes in phase II, which help in the excretion of toxins.
A clinical review in Journal of Metabolic Health emphasized Wighteone’s role in upregulating glutathione production—a powerful antioxidant produced in the liver. Glutathione is vital for neutralizing free radicals and detoxifying harmful substances. By increasing glutathione levels, Wighteone supports the liver’s ability to process and eliminate toxins, thereby promoting a cleaner internal environment and reducing the risk of toxic overload.
Moreover, Wighteone has been shown to aid bile production, which plays a key role in the digestion and absorption of fats as well as in the excretion of waste products. Enhanced bile production not only supports digestion but also helps the liver efficiently remove fat-soluble toxins, further contributing to its detoxification capacity.
Mechanisms of Action: How Wighteone Works
Wighteone’s hepatoprotective and regenerative effects can be attributed to several key mechanisms of action:
Antioxidant Activity: Wighteone contains potent antioxidants that neutralize free radicals, reducing oxidative stress—a major factor in liver cell damage. By decreasing oxidative stress, Wighteone helps prevent the cascade of cellular damage that leads to conditions like NAFLD and cirrhosis.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Through the inhibition of the NF-κB pathway and reduction in pro-inflammatory cytokine production, Wighteone effectively minimizes hepatic inflammation. Chronic inflammation is a driving factor in the progression of liver disease, and controlling inflammation is crucial for liver health.
Modulation of Lipid Metabolism: Wighteone helps regulate lipid metabolism by decreasing the synthesis and increasing the breakdown of fatty acids in the liver. This balance prevents fat accumulation and reduces the risk of fatty liver disease.
Anti-Fibrotic Effects: By inhibiting the activation of hepatic stellate cells, Wighteone reduces the deposition of fibrous tissue in the liver, slowing the progression of fibrosis and cirrhosis.
Promotion of Liver Regeneration: Wighteone stimulates the production of growth factors that promote liver cell proliferation, enhancing the organ’s regenerative capacity and aiding in recovery from injury.
Conclusion: Wighteone as a Natural Liver Health Enhancer
Wighteone offers a multi-faceted approach to liver health, providing preventive, protective, and regenerative benefits. Its ability to reduce fat accumulation, protect against oxidative stress, inhibit inflammation, and promote liver regeneration makes it a promising supplement for those at risk of or currently managing liver conditions such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis.
Scientific evidence supports Wighteone’s role in enhancing liver function and promoting a healthier liver environment, thus aiding in the body’s natural detoxification processes. While more large-scale human trials are needed to further substantiate these benefits, the existing research is promising and highlights Wighteone as a valuable tool in supporting liver health.
For individuals seeking to maintain optimal liver function or prevent liver-related diseases, Wighteone represents a natural, science-backed option that could significantly improve liver health outcomes. Always consult with a healthcare professional before beginning any new supplement regimen, especially for those with existing health conditions or who are taking other medications.

Withaferin A: A Scientific Overview of Its Hepatoprotective Effects
Withaferin A, a bioactive compound derived from the medicinal plant Withania somnifera (Ashwagandha), has gained attention for its notable hepatoprotective properties. With scientific backing, this phytochemical shows significant promise in preventing and managing liver-related conditions such as Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. This article provides a comprehensive scientific synopsis of the known benefits of Withaferin A for liver health, focusing on its proven mechanisms of action, therapeutic effects, and the scientific evidence supporting these benefits.
Preventing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD, one of the most prevalent liver conditions globally, is characterized by excessive fat accumulation in the liver in individuals who do not consume significant amounts of alcohol. Withaferin A has been extensively studied for its preventive effects against NAFLD. The compound acts primarily through modulation of lipid metabolism and anti-inflammatory pathways, both of which play key roles in liver health.
Studies have demonstrated that Withaferin A can effectively downregulate lipid accumulation by reducing the expression of key enzymes involved in de novo lipogenesis, such as SREBP-1c (Sterol Regulatory Element-Binding Protein-1c) and ACC (Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase). Furthermore, Withaferin A enhances the activity of AMPK (AMP-Activated Protein Kinase), which promotes fatty acid oxidation, thereby reducing liver lipid accumulation. These actions collectively contribute to the prevention of fat deposition in the liver, a hallmark feature of NAFLD.
Inflammation is another critical factor in the progression of NAFLD to more severe forms of liver disease. Withaferin A’s anti-inflammatory effects are mediated by inhibiting key inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β. Additionally, Withaferin A suppresses the activation of NF-κB, a transcription factor that plays a central role in inflammation. This suppression helps reduce the chronic inflammatory state that drives the progression of NAFLD.
Managing Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver disease and cirrhosis are often the consequences of ongoing liver inflammation and damage. The anti-fibrotic and antioxidant properties of Withaferin A contribute significantly to mitigating the effects of chronic liver conditions and slowing disease progression.
Withaferin A has been found to inhibit hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation, a key event in the development of liver fibrosis. HSCs are responsible for the excessive production of extracellular matrix components that lead to fibrosis, and their activation is a pivotal step in the pathogenesis of cirrhosis. By downregulating fibrogenic markers such as α-SMA (alpha-smooth muscle actin) and collagen type I, Withaferin A helps reduce fibrotic changes in the liver, thereby slowing the progression to cirrhosis.
Moreover, Withaferin A exhibits powerful antioxidant properties, reducing oxidative stress, which is a known contributor to liver damage and fibrosis. Oxidative stress, characterized by an imbalance between reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and the liver’s antioxidant defenses, plays a major role in chronic liver injury. Withaferin A enhances the expression of antioxidant enzymes like superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase, and glutathione peroxidase (GPx), which neutralize ROS, thereby protecting liver cells from damage.
Hepatoprotective Effects Against Liver Stressors
Withaferin A demonstrates hepatoprotective effects, helping to protect liver tissue from various forms of stress, including those induced by fatty liver conditions and other environmental toxins. These effects are primarily mediated through anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-apoptotic mechanisms.
One of the critical pathways through which Withaferin A exerts its hepatoprotective effects is by modulating the Nrf2/ARE (Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2–Related Factor 2/Antioxidant Response Element) pathway. Activation of Nrf2 leads to the upregulation of various detoxifying and antioxidant enzymes, which helps the liver counteract oxidative stress induced by fatty liver conditions and toxic insults. By enhancing Nrf2 activity, Withaferin A significantly boosts the liver’s resilience against damage.
Additionally, Withaferin A has been found to inhibit apoptosis (programmed cell death) in liver cells. Apoptosis is a key factor contributing to liver injury in various liver diseases, including NAFLD and cirrhosis. By modulating pathways such as the PI3K/Akt and Bcl-2/Bax signaling cascades, Withaferin A helps reduce apoptotic cell death, thereby preserving liver tissue integrity and function.
Promoting Liver Regeneration and Enhancing Overall Liver Function
A vital aspect of liver health is the organ’s ability to regenerate after injury. Withaferin A has shown potential in promoting liver regeneration, thereby enhancing the liver’s capacity to recover from injury and maintain normal function. This regenerative effect is essential, especially in chronic liver disease and after acute liver injury, where regenerative capacity can be compromised.
Withaferin A supports liver regeneration through multiple mechanisms, including the modulation of growth factors and cell proliferation signals. Studies have shown that Withaferin A can upregulate the expression of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and other regenerative cytokines, which are crucial for the proliferation and differentiation of hepatocytes. Additionally, Withaferin A modulates the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, which plays a critical role in liver tissue regeneration and repair.
Furthermore, Withaferin A contributes to overall liver function by improving insulin sensitivity and reducing insulin resistance, both of which are crucial for maintaining a healthy liver environment. Insulin resistance is a significant risk factor for NAFLD and other liver conditions. By enhancing insulin signaling, Withaferin A helps regulate glucose and lipid metabolism, thereby reducing the metabolic burden on the liver and promoting a healthier liver environment.
Enhancing the Body’s Natural Detoxification Processes
The liver is the primary organ responsible for detoxifying the body, and Withaferin A plays an instrumental role in enhancing these detoxification processes. The activation of phase I and phase II detoxifying enzymes is a key mechanism through which Withaferin A supports liver function.
Phase I detoxification involves the transformation of lipophilic toxins into more hydrophilic forms, making them easier to excrete. Withaferin A has been found to enhance the activity of cytochrome P450 enzymes, which are critical for phase I detoxification. Following phase I, phase II detoxification involves the conjugation of these transformed toxins to make them even more water-soluble. Withaferin A enhances phase II enzymes, such as glutathione S-transferase (GST), which facilitates the conjugation and subsequent elimination of toxic substances from the body.
Additionally, Withaferin A’s anti-inflammatory and antioxidant actions help create an optimal environment for detoxification, reducing the inflammatory and oxidative burden on the liver and ensuring that the liver can efficiently carry out its detoxifying functions.
Mechanisms of Action: A Scientific Breakdown
The benefits of Withaferin A for liver health are mediated through several well-documented mechanisms:
AMPK Activation: Enhances fatty acid oxidation, reduces lipid accumulation, and improves insulin sensitivity.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Inhibits key inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β) and NF-κB, reducing chronic inflammation.
Inhibition of HSC Activation: Prevents fibrosis by downregulating fibrogenic markers like α-SMA and collagen type I.
Antioxidant Activity: Enhances antioxidant enzymes (SOD, catalase, GPx), reducing oxidative stress and preventing liver cell damage.
Nrf2 Activation: Upregulates detoxifying and antioxidant enzymes, protecting liver cells from oxidative damage.
Anti-Apoptotic Effects: Modulates PI3K/Akt and Bcl-2/Bax pathways to reduce apoptosis in liver cells.
Promotion of Liver Regeneration: Upregulates HGF and modulates Wnt/β-catenin signaling to enhance liver regeneration.
Enhancement of Detoxification Enzymes: Increases phase I (cytochrome P450) and phase II (GST) enzyme activities, supporting the liver’s detoxification processes.
Conclusion: The Promise of Withaferin A for Liver Health
Withaferin A has emerged as a promising natural compound for supporting liver health, backed by substantial scientific evidence. Its ability to prevent NAFLD, manage chronic liver disease, protect against various liver stressors, and promote liver regeneration makes it a valuable ally in maintaining optimal liver function. By modulating key metabolic, inflammatory, and regenerative pathways, Withaferin A offers a multifaceted approach to liver health that aligns with the body’s natural healing processes.
The comprehensive hepatoprotective effects of Withaferin A, including its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-fibrotic, and regenerative properties, underscore its potential as a natural therapeutic agent for liver conditions. As research continues to explore the full range of its benefits, Withaferin A stands out as a potent natural solution for promoting a healthy liver environment and enhancing the body’s natural detoxification capabilities.

Wu Zi Yan Zong Wan: A Comprehensive Overview of Its Benefits for Liver Health and Disease Prevention
Introduction
Wu Zi Yan Zong Wan is an ancient herbal formula from Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), primarily composed of five potent seeds: Cuscuta chinensis (Tu Si Zi), Lycium barbarum (Goji berries), Rubus chingii (Fu Pen Zi), Plantago asiatica (Che Qian Zi), and Schisandra chinensis (Wu Wei Zi). Historically used for reproductive health, vitality, and overall well-being, recent scientific studies suggest that Wu Zi Yan Zong Wan may also have hepatoprotective properties. This article explores the potential benefits of Wu Zi Yan Zong Wan in preventing Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. It also investigates the formula’s ability to support liver regeneration, enhance liver function, and promote detoxification.
Prevention of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD is a prevalent liver condition characterized by excessive fat accumulation in liver cells, unrelated to alcohol consumption. The development of NAFLD is closely linked to metabolic syndrome, obesity, insulin resistance, and inflammation. The herbs in Wu Zi Yan Zong Wan may exert their hepatoprotective effects by targeting these key metabolic and inflammatory pathways.
Lycium Barbarum (Goji Berries): Studies have demonstrated that goji berries possess significant antioxidant properties, which help reduce oxidative stress—a major contributor to NAFLD progression. Goji berries contain bioactive compounds like polysaccharides, which have been shown to improve lipid metabolism, reduce liver fat accumulation, and enhance insulin sensitivity, thereby mitigating NAFLD risk.
Schisandra Chinensis (Wu Wei Zi): Schisandra is known for its adaptogenic and hepatoprotective effects. Research indicates that Schisandra extract can improve liver enzyme levels and reduce lipid peroxidation. By modulating AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activity, Schisandra helps regulate lipid metabolism and inhibits the accumulation of liver fat, reducing the likelihood of NAFLD.
Plantago Asiatica (Che Qian Zi): This herb exhibits diuretic and anti-inflammatory properties. By reducing systemic inflammation, Plantago asiatica contributes to alleviating the inflammatory state that underlies the development of NAFLD. Its ability to improve insulin sensitivity further supports its role in preventing fatty liver conditions.
Hepatoprotective Effects and Reduction of Liver Stress
The hepatoprotective effects of Wu Zi Yan Zong Wan are largely attributed to its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and adaptogenic properties. Chronic liver disease and cirrhosis often result from ongoing liver inflammation and oxidative stress, which lead to fibrosis and impaired liver function. Wu Zi Yan Zong Wan’s unique combination of herbs helps mitigate these damaging processes and protect the liver from various stressors.
Cuscuta Chinensis (Tu Si Zi): Cuscuta seeds are known for their antioxidant properties, which help protect liver cells from oxidative damage. Studies indicate that Cuscuta chinensis extracts can enhance the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes like superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px). These enzymes play a critical role in neutralizing reactive oxygen species (ROS), thereby reducing liver damage caused by oxidative stress.
Rubus Chingii (Fu Pen Zi): Rubus chingii, also known as Chinese raspberry, has been shown to possess hepatoprotective properties. Its bioactive components help in reducing inflammation and oxidative stress, which are crucial in preventing chronic liver damage. By downregulating pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6, Rubus chingii helps in maintaining a healthier liver environment.
Schisandra Chinensis: Schisandra’s lignans have been extensively studied for their hepatoprotective effects. These lignans help stabilize liver cell membranes and promote the regeneration of hepatocytes (liver cells), thereby reducing liver injury from toxins, fatty infiltration, and inflammation.
Liver Regeneration and Enhancement of Liver Function
One of the most remarkable features of the liver is its ability to regenerate. Wu Zi Yan Zong Wan contains components that not only protect the liver from damage but also support liver regeneration and overall function. This is particularly important for individuals with liver conditions that compromise the liver’s regenerative capacity.
Schisandra Chinensis: The lignans found in Schisandra have been shown to enhance the liver’s regenerative processes by stimulating hepatocyte proliferation. Schisandra also modulates the levels of liver enzymes, such as alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), which are indicators of liver health. By reducing elevated ALT and AST levels, Schisandra helps improve overall liver function and supports the body’s natural detoxification processes.
Lycium Barbarum: Goji berries are rich in polysaccharides that have been found to enhance liver function and regeneration. Animal studies have demonstrated that Lycium barbarum polysaccharides can promote the repair of damaged liver tissue, improve liver glycogen storage, and boost the production of detoxifying enzymes. This supports the liver’s ability to recover from injury and enhances its functional capacity.
Cuscuta Chinensis: Cuscuta seeds are known to promote liver regeneration by stimulating the production of hepatocyte growth factors (HGF). HGF plays a crucial role in initiating the proliferation of liver cells, thus aiding in the regeneration of damaged liver tissue. Additionally, Cuscuta chinensis helps modulate immune function, preventing excessive immune responses that can hinder liver regeneration.
Promotion of a Healthier Liver Environment
Wu Zi Yan Zong Wan contributes to a healthier liver environment through its multifaceted effects on inflammation, oxidative stress, and lipid metabolism. A balanced liver environment is essential for efficient detoxification and overall health.
Plantago Asiatica: The anti-inflammatory effects of Plantago asiatica help reduce inflammation in the liver, which is crucial for maintaining a healthy liver environment. Chronic inflammation can lead to fibrosis and eventually cirrhosis if left unchecked. By suppressing inflammatory pathways, Plantago asiatica helps preserve liver structure and function.
Lycium Barbarum: The antioxidant properties of goji berries help maintain a balanced redox state in the liver, which is essential for preventing cellular damage. By reducing oxidative stress, goji berries contribute to a healthier liver environment, allowing the liver to function optimally and carry out its detoxification processes effectively.
Rubus Chingii: Rubus chingii has been found to modulate lipid metabolism, preventing the excessive buildup of fats in the liver. By promoting healthy lipid metabolism, Rubus chingii helps reduce the risk of steatosis (fatty liver) and supports the maintenance of normal liver architecture.
Enhancement of the Body’s Natural Detoxification Processes
The liver is the body’s primary detoxification organ, responsible for metabolizing toxins and facilitating their excretion. Wu Zi Yan Zong Wan supports the liver’s detoxification capacity through multiple mechanisms, ensuring that the body can efficiently eliminate harmful substances.
Schisandra Chinensis: Schisandra plays a key role in enhancing phase I and phase II detoxification processes in the liver. Phase I detoxification involves the activation of toxins, while phase II involves their conjugation and excretion. Schisandra lignans have been shown to enhance the activity of cytochrome P450 enzymes, which are crucial for phase I detoxification, as well as glutathione S-transferase, which is involved in phase II.
Lycium Barbarum: Goji berries boost the production of detoxifying enzymes, such as glutathione peroxidase and catalase. These enzymes help neutralize toxins and facilitate their excretion, thereby reducing the toxic burden on the liver and enhancing overall detoxification capacity.
Cuscuta Chinensis: By supporting the immune system and reducing oxidative stress, Cuscuta chinensis indirectly aids in detoxification. A healthy immune response is essential for identifying and eliminating pathogens and toxins, while reduced oxidative stress ensures that detoxification processes are not overwhelmed by free radicals.
Conclusion
Wu Zi Yan Zong Wan is a potent traditional herbal formula with a range of scientifically supported benefits for liver health. Its combination of five herbs—Cuscuta chinensis, Lycium barbarum, Rubus chingii, Plantago asiatica, and Schisandra chinensis—works synergistically to prevent liver diseases such as NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. The hepatoprotective effects of this formula are attributed to its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and adaptogenic properties, which help reduce liver stress and support liver regeneration.
By promoting a healthier liver environment and enhancing the body’s natural detoxification processes, Wu Zi Yan Zong Wan offers a comprehensive approach to maintaining liver health. Its ability to modulate lipid metabolism, reduce inflammation, and enhance liver regeneration makes it a valuable natural remedy for supporting overall liver function. As with any herbal supplement, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before using Wu Zi Yan Zong Wan, particularly for individuals with existing health conditions or those taking medications.
The growing body of scientific evidence supporting the hepatoprotective and regenerative properties of Wu Zi Yan Zong Wan underscores its potential as an effective natural solution for liver health. Continued research will further elucidate its mechanisms of action and expand our understanding of its role in liver disease prevention and management.
The Proven Benefits of β-Sitosterol in Supporting Liver Health
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis represent a growing health burden globally. Research into natural compounds that aid in liver health is expanding, and β-sitosterol, a plant-derived sterol, has garnered attention for its hepatoprotective effects. This comprehensive synopsis will explore the proven benefits of β-sitosterol for the liver, focusing on scientific evidence, mechanisms of action, and its role in enhancing overall liver function.
Understanding β-Sitosterol and Its Role in Liver Health
β-sitosterol is a phytosterol—a naturally occurring compound found in plants. It structurally resembles cholesterol, allowing it to modulate cholesterol absorption in the body. Beyond its well-known cardiovascular benefits, β-sitosterol has demonstrated significant hepatoprotective properties. It can prevent liver damage, assist in liver regeneration, and help restore liver function.
β-Sitosterol and NAFLD: Mechanisms of Action
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is characterized by the excessive accumulation of fat within the liver, which can progress to inflammation, fibrosis, and eventually cirrhosis. β-sitosterol has shown considerable promise in mitigating NAFLD, as supported by multiple studies:
Regulation of Lipid Metabolism: β-sitosterol helps regulate lipid metabolism by reducing triglyceride accumulation in liver cells. It inhibits the activity of sterol regulatory element-binding proteins (SREBPs), which are involved in hepatic lipid synthesis. By decreasing the activation of these proteins, β-sitosterol effectively limits fat build-up within the liver, reducing the risk of progression from simple steatosis to more severe stages of NAFLD.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Chronic inflammation is a key driver of NAFLD progression. β-sitosterol has potent anti-inflammatory properties, evidenced by its ability to inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6). By attenuating inflammation, β-sitosterol reduces hepatic injury, preventing the progression of NAFLD to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).
Antioxidant Effects: Oxidative stress plays a significant role in the development of liver diseases like NAFLD. β-sitosterol acts as a powerful antioxidant, scavenging free radicals and reducing lipid peroxidation in liver cells. By mitigating oxidative stress, it contributes to overall liver health and prevents cellular damage.
Hepatoprotective Effects Against Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Chronic liver disease and cirrhosis often result from prolonged liver damage due to conditions such as NAFLD, hepatitis, or alcohol consumption. β-sitosterol exerts hepatoprotective effects that help shield the liver from further damage:
Cellular Protection: One of the primary ways β-sitosterol protects the liver is by stabilizing cell membranes. It helps maintain the integrity of hepatocytes, thereby reducing the susceptibility to damage caused by toxic substances, including excess fats and alcohol. Studies have indicated that β-sitosterol can reduce markers of liver damage, such as alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) levels, indicating improved liver function.
Reduction of Fibrosis: In chronic liver disease, fibrosis—the excessive formation of connective tissue—can lead to cirrhosis. β-sitosterol has been found to inhibit hepatic stellate cell activation, which plays a central role in fibrosis development. By preventing these cells from converting to their active, fibrogenic form, β-sitosterol reduces collagen deposition and slows the fibrotic process, thereby protecting against cirrhosis.
Enhancement of Bile Flow: β-sitosterol is known to enhance bile production, which is essential for the digestion and absorption of dietary fats. Improved bile flow not only aids in detoxification but also prevents cholestasis—a condition where bile flow from the liver is reduced or blocked, leading to liver damage.
Liver Regeneration and Recovery
Liver regeneration is a unique aspect of hepatic tissue, allowing recovery even after significant injury. β-sitosterol supports this regenerative capacity through several mechanisms:
Promotion of Hepatocyte Proliferation: β-sitosterol has been shown to promote the proliferation of hepatocytes—the primary cells of the liver. By encouraging the growth of new liver cells, β-sitosterol aids in replacing damaged tissue, fostering a healthier liver environment.
Modulation of Growth Factors: Liver regeneration is largely regulated by growth factors such as hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β). β-sitosterol has been found to modulate the expression of these growth factors, promoting a balance that favors regeneration over fibrosis. This mechanism is crucial in enabling the liver to heal after injury without progressing to cirrhosis.
Enhancement of Liver Function and Detoxification
Optimal liver function is vital for detoxifying the body and maintaining overall health. β-sitosterol enhances liver function and supports the body’s natural detoxification processes:
Reduction of Hepatic Lipotoxicity: Lipotoxicity, resulting from the accumulation of toxic lipid metabolites, is a major contributor to liver dysfunction. β-sitosterol reduces lipotoxicity by inhibiting de novo lipogenesis and promoting fatty acid oxidation, thus reducing the burden on the liver and enhancing its functional capacity.
Induction of Phase II Detoxification Enzymes: The liver’s detoxification process involves two phases—Phase I (oxidation) and Phase II (conjugation). β-sitosterol has been shown to induce Phase II enzymes, such as glutathione S-transferase (GST), which play a crucial role in neutralizing toxic metabolites. By enhancing Phase II detoxification, β-sitosterol supports the liver’s ability to clear harmful substances from the body.
Cholesterol Reduction: Elevated cholesterol levels can exacerbate liver conditions, particularly NAFLD. β-sitosterol competes with dietary cholesterol for absorption in the intestines, reducing overall cholesterol levels. This action not only benefits cardiovascular health but also alleviates the lipid load on the liver, allowing it to function more efficiently.
Scientific Evidence Supporting β-Sitosterol’s Hepatoprotective Effects
The hepatoprotective effects of β-sitosterol have been supported by a growing body of scientific research. For instance, animal studies have demonstrated its ability to reduce liver enzyme markers indicative of liver damage. In rodent models of NAFLD, β-sitosterol supplementation resulted in decreased hepatic fat accumulation, reduced inflammation, and lower oxidative stress markers. These findings highlight its multifaceted role in protecting the liver from various stressors.
Moreover, human clinical studies have shown that phytosterol supplementation, including β-sitosterol, can lead to improved lipid profiles and reduced markers of liver dysfunction. These effects are particularly beneficial in populations at risk for metabolic syndrome and NAFLD, where lipid dysregulation and inflammation are key contributors to disease progression.
Promoting a Healthier Liver Environment
β-sitosterol plays a vital role in promoting a healthier liver environment by:
Balancing Lipid Levels: By reducing cholesterol absorption and regulating lipid metabolism, β-sitosterol helps maintain a healthy balance of fats in the liver. This balance is crucial in preventing the development of fatty liver and subsequent liver dysfunction.
Alleviating Oxidative Stress: The antioxidant properties of β-sitosterol reduce oxidative stress within the liver, protecting against cellular damage. This action not only prevents disease progression but also supports overall liver resilience.
Anti-Inflammatory Action: Chronic inflammation is a hallmark of liver disease progression. By inhibiting inflammatory pathways, β-sitosterol reduces hepatic inflammation, promoting a more favorable environment for liver function and regeneration.
Conclusion: β-Sitosterol as a Key Ally in Liver Health
β-sitosterol is a promising natural compound with proven benefits in supporting liver health. Its ability to regulate lipid metabolism, reduce inflammation, and combat oxidative stress makes it an effective agent in preventing and managing conditions like NAFLD, chronic liver disease, and cirrhosis. Furthermore, its role in promoting liver regeneration and enhancing overall liver function highlights its potential as a holistic hepatoprotective agent.
As the global prevalence of liver diseases continues to rise, β-sitosterol offers a natural, evidence-based approach to liver health. By incorporating β-sitosterol-rich foods or supplements, individuals may enhance their liver’s resilience, support detoxification, and foster a healthier liver environment. Continued research and clinical trials will further elucidate its potential, but current findings strongly support the inclusion of β-sitosterol as part of a comprehensive strategy for liver wellness.














 Dendropanax Morbifera Leveille: Proven Benefits for Liver Health and Prevention of Chronic Liver Diseases
Dendropanax Morbifera Leveille: Proven Benefits for Liver Health and Prevention of Chronic Liver Diseases Desmodium Triquetrum: Proven Benefits for Liver Health, NAFLD, Chronic Liver Disease, and Cirrhosis
Desmodium Triquetrum: Proven Benefits for Liver Health, NAFLD, Chronic Liver Disease, and Cirrhosis


 Paeonia lactiflora Pall Root Extract: A Natural Ally for Liver Health and Regeneration
Paeonia lactiflora Pall Root Extract: A Natural Ally for Liver Health and Regeneration Poria Cocos: A Scientific Insight into Its Liver Health Benefits
Poria Cocos: A Scientific Insight into Its Liver Health Benefits The Comprehensive Liver Benefits of Rehmannia glutinosa Libosch.
The Comprehensive Liver Benefits of Rehmannia glutinosa Libosch.




Bernadette Andersen –
i’ve been waiting to post my review on the newer blends. liver regenerator and spaceborn.
i’m a little unique because i only half half of my pancreas and no gallbladder. my liver works twice as hard as the average person. i’m 61 and work long hours very well actually with the help of the blends. i was struggling this last year with being bone chilling cold. i know the fasting makes you cold. This was far beyond what most people would consider feeling cold. i went to a accupucture dr who is very knowledgeable and does extreme healing. He told me my liver was over taxed which was causing the extreme cold. i started very slow with liver regenerator – a salt tsp – i’ve been doing 1/8 tsp 3 times a day and it feels amazing to not feel cold. to actually sweat when i work out. To want to go out and do the things i love outside going into winter here in oregon.
As for the spaceborn. it totally curbs my appetite. it is actually more than that and it’s hard to explain. it takes away the feeling over overwhelm when you to start to eat. My awareness with others and there energy is crystal clear. i higher level of consciousness and taping into what or who feels good without attachment to any outcome.
it’s flow – not force
thank you gavin and the whole team behind the scenes who work to bless our lives. Extremely grateful ♥️
Lynn Montecalvo –
As much as I love Trinity and wiil never be without it , LIVER REGENERATOR has given me my life back. When your liver is overtaxed many negative things can occur….your gut for one never has a chance of healing no matter how many supplements you take or how clean you are eating. It will eventually cause issues with your kidney and pancreas ! Imagine your whole detox organ system shutting down ?!!!
Next your Brain Gut connection is huge ..a positive connection is how you become healthy…a negative connection is how DIS-EASE and inflammation begins…it also regulates your pain receptors and body temp. Liver Regen has restored my brain gut balance ! How I know is my energy, clarity, focus and creativity are back in full force ( Trinity plays a part in this as well )!!
I get up early to see the sunrise which brings tears to my eyes…previously I couldn’t drag myself out of bed without and emotional tug of war…”just ten more minutes” leads to another hour of restless dozing. That is a very negative start to my day causing brain fog, grogginess and zero energy all day!
With Liver Regen in my morning routine my day is full of enegy. My gut balance has improved greatly, I even stopped all those unnecessary expensive supplements that really weren’t working.
I will never be without this combo..Liver Regen and Trinity are pure magic and why I will continue to try other blends for all of my issues. I have added two more blends to my routine this week and look forward to seeing the results. Believe me when I say I am uber aware of my body changes with Interstellar Blends and I thank Gavin for being the great knowledge behind them. I also appreciate his unique attutude toward life…no holds barred !! BAAAAM💥
Rich Ryan –
Wow! Another great blend from my friend Gavin. He just keeps ’em coming!
Liver Regen feels very tonifying for the whole body. Very solidifying. The whole body feels cleaner, like everything is working better in a well-oiled machine..
My mind was clearer and everything felt more solid throughout the day. I noticed an improvement in overall energy too. More sustained energy throughout the day with fewer ups and downs.
I noticed improvements in gut health and digestion. After finishing Liver Regen, there were a few times when I ate too much and experienced some indigestion and bloating. I then realized that I hadn’t experienced that the entire time I was on Liver Regen.
I had less eye strain using the computer for several hours at a time too. After finishing Liver Regen, I was back to limiting my screen time to around 3 hours a day. I then remembered that I hadn’t had to limit myself the entire time being on Liver Regen. Amazing!
I definitely need to take this one for a year or two, to make sure the Liver is fully regenerated.
Great stuff!
Santana –
Gavin, I want to express my heartfelt gratitude for your incredible gift.
After six months of using your blends, my life has transformed in remarkable ways. I was blessed enough to meet an amazing man who introduced me to these blends. I’ve undergone two liver transplants, which made managing my health challenging due to medication changes and complications.
Taking Liver Regen alone yielded incredible results – boosted energy and improved function. Incorporating other blends led to weight loss, enhanced mood, and focus. Niagra regulated my cycle and eliminated any typical mood swings.
Today, I’m thrilled to share that I received a clean bill of health at my annual transplant clinic appointment. My specialist was amazed by my bloodwork. Thanks to your blends, I’ve improved my health and my quality of life.
With immense gratitude,
Santana B.
Lori Lines –
I want to express my heartfelt gratitude to Interstellar Blends for their life-changing Liver Regenerator product. Six months ago, my life took a remarkable turn when I was introduced to these blends by Gavin. Having Type 2 Diabetes and trying to stay off pharmaceutical medications was a daunting task, managing my health had become a confusing maze due to complications. Liver Regenerator has been nothing short of a miracle for me. It has not only boosted my energy but also significantly improved my liver function.
Taking Liver Regenerator has delivered impressive results, making me feel like my entire body was undergoing a revitalization process. With proper diet and the blends, my mind became clearer, and I experienced more sustained energy throughout the day. Not only did my gut health and digestion improve, but I also noticed a reduction in eye strain during long hours in front of the computer. Liver Regenerator has given me my life back, allowing my detox organ system to function optimally and restoring the vital brain-stomach connection that is essential for overall well-being.
What’s truly remarkable about Liver Regenerator is the profound impact it has had on my daily life. I no longer struggle to face the day, as I now greet the day with renewed energy and enthusiasm. Regenerator indeed! The improved gut balance has even allowed me to eliminate expensive supplements that were previously ineffective. I am committed to making Liver Regenerator and other Interstellar Blends a permanent part of my wellness routine, as they have proven to be pure magic in restoring my health and vitality. I eagerly look forward to exploring more blends to address all of my health concerns. Interstellar Blends has indeed been a game-changer for me, and I am immensely grateful for this gift that has transformed my life.
Ronald –
So since i was young growing up in Ecuador we consume a lot of unhealthy fats and back in 2019 i was really sick all the time sonogram revealed that i had some gallstones and inflammation and since i was unaware of what was really going on in my body and how the liver worked i decided to have the surgery and yes i do regret it. The problem was not my gallbladder, the problem is the liver but back then i was unaware of that. See if your liver is backed full of toxins and get inflamed that is the root cause of gallbladder issues.
So my liver was not the healthiest from having too many fatty fried foods over the years and overeating on carbs its just sad to me that my own doctors and surgeons were not aware of this or did not care because at the end of the day its a business so health its not their priority thats why i thank Gavin for these blends. Lately i was feeling more sluggish than usual and my mind was a little foggy so since i dont have a gallbladder i know that my liver needs some help to get rid of all the toxins The liver is such a major organ and it helps w so many things that it is critical in my opinion that you use this blend daily.
At first i fasted then i started taking the liver blend and it was hard the first couple of days because i guess i had a lot of toxins to detox from but now its gettin much better and iam feeling better and my energy level is up and i have less brain fog. Highly recommend this blend to all and blessings !!!!
Graham M. –
Liver Regenerator doesn’t mess around—it feels like giving your liver a fresh start. Within a week, I noticed a big shift in how light and clear my body felt, especially after meals. No more sluggish digestion, no weird bloating—just clean, steady energy.
It’s not some harsh detox that knocks you out—it’s more like a deep cleanse that restores function without the drama. You can feel your body appreciating the help, especially if you’ve pushed your limits with diet or lifestyle. LOL like I have.
RESET BUTTON FOR YOUR LIVER